Submitted:
04 June 2023
Posted:
06 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Cytotoxicity of the Extractsn
| Sample | LC50 (µg/mL) |
|---|---|
| Pan cyanescens cold-water (PC) | 66.1 ± 1.8 |
| Pan cyanescens hot-water (PH) | >100 |
| Pan cyanescens 70% ethanol (PE) | > 100 |
| P. cubensis cold-water (GC) | >100 |
| P. cubensis hot-water (GH) | >100 |
| P. cubensis 70% ethanol (GE) | >100 |
| P. A+ strain cold-water (AC) | >100 |
| P. A+ strain hot-water (AH) | >100 |
| P. A+ strain 70% ethanol (AE) | >100 |
| P. natalensis cold-water (NC) | >100 |
| P. natalensis hot-water (NH) | >100 |
| P. natalensis 70% ethanol (NE) | >100 |
| Doxorubicin | 0.2169 ± 0.037 |
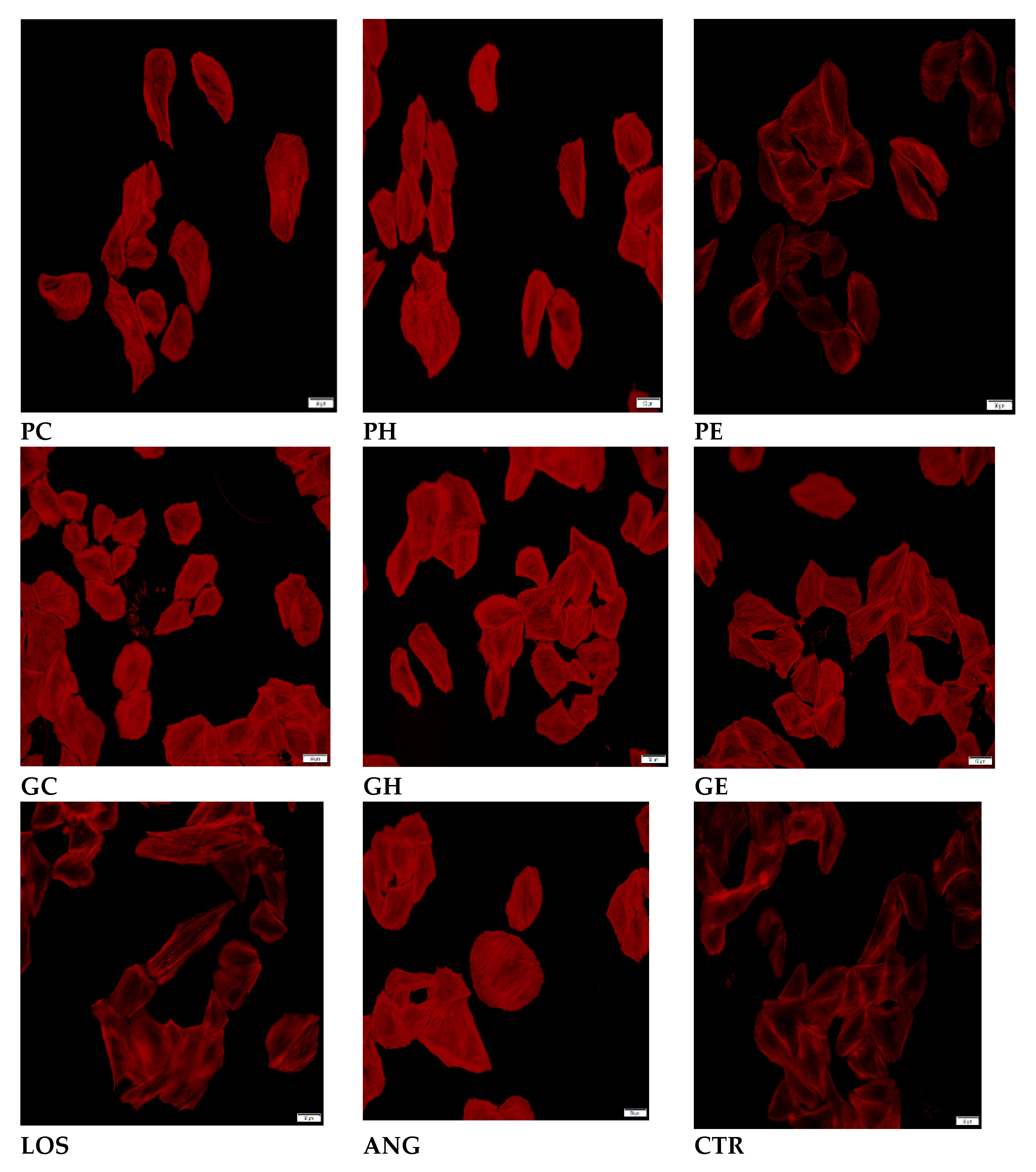
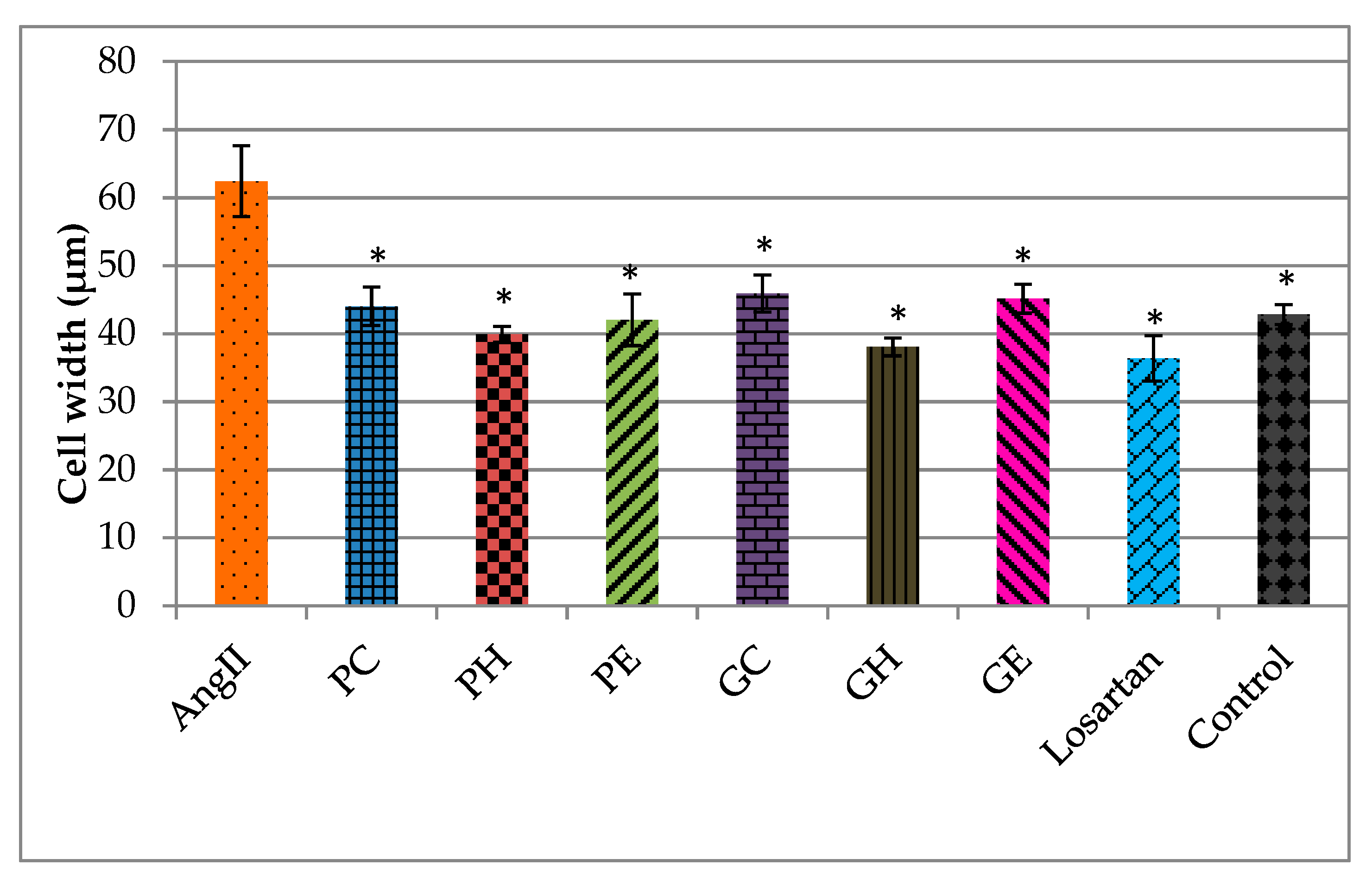
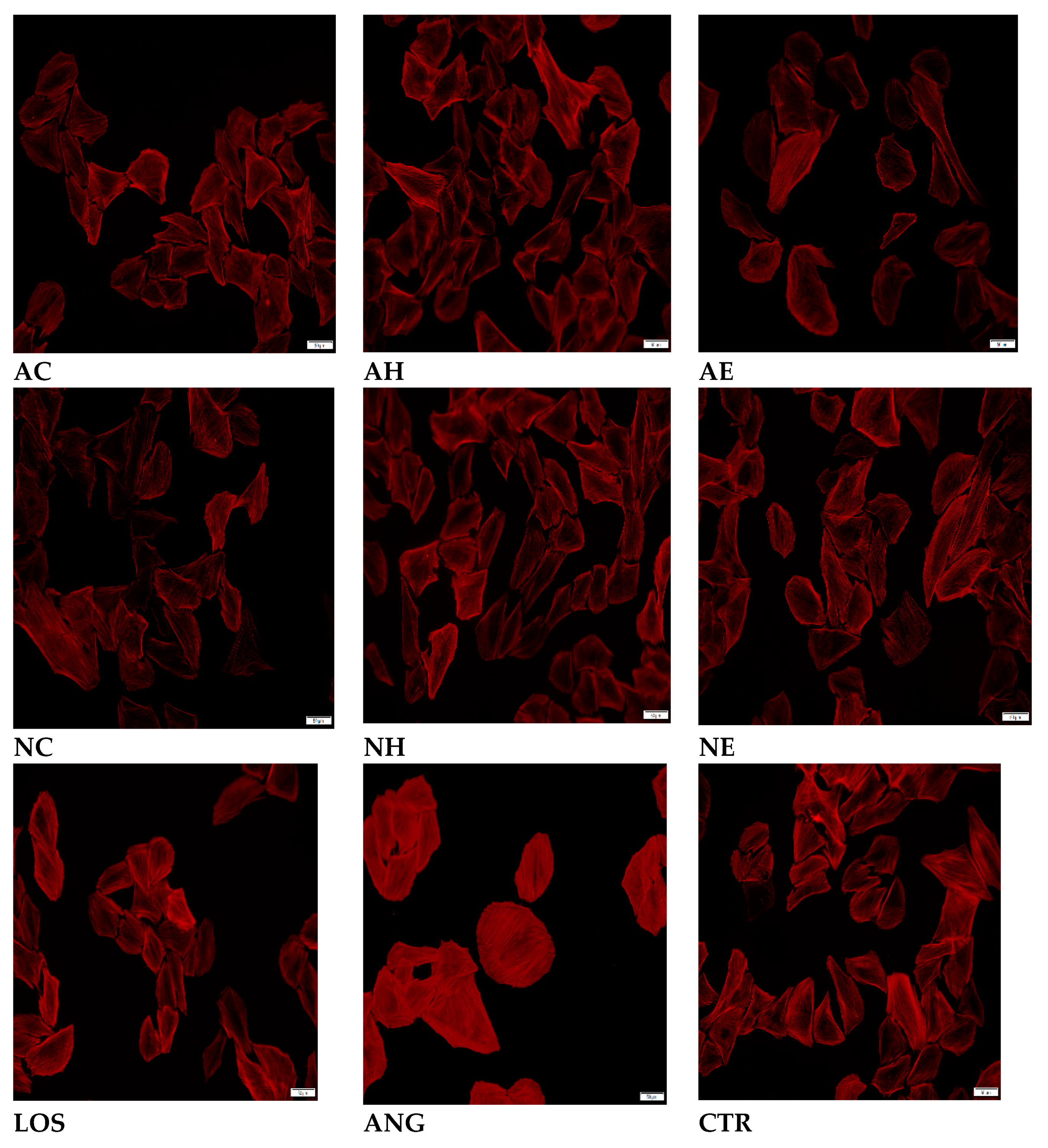
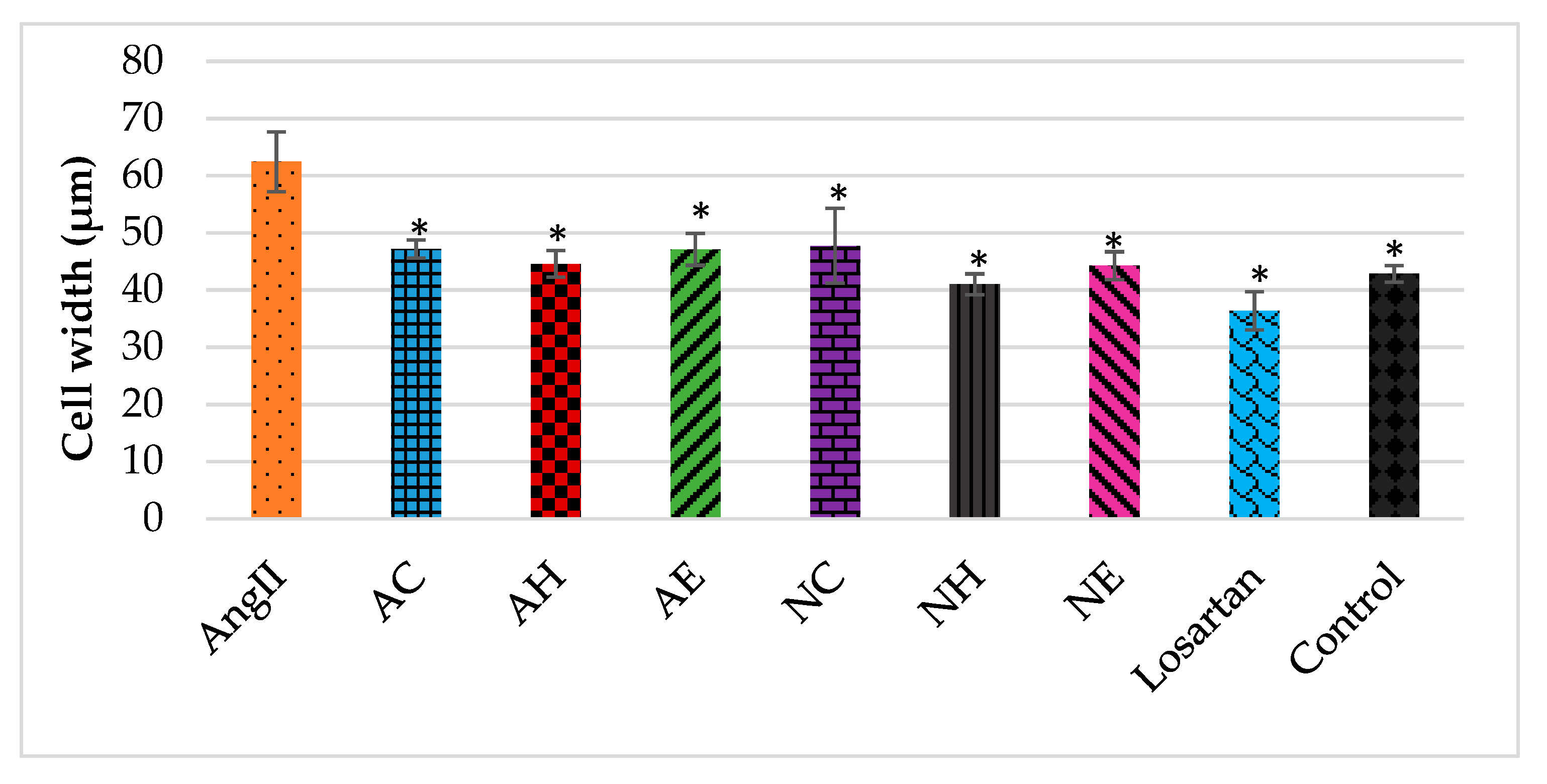
2.2. Effects of the Extracts on AngII-Induced Hypertrophy in H9C2 Cardiomyocytes
2.3. Effects of the Extracts on ANP Levels in AngII-Induced Cardiomyocytes
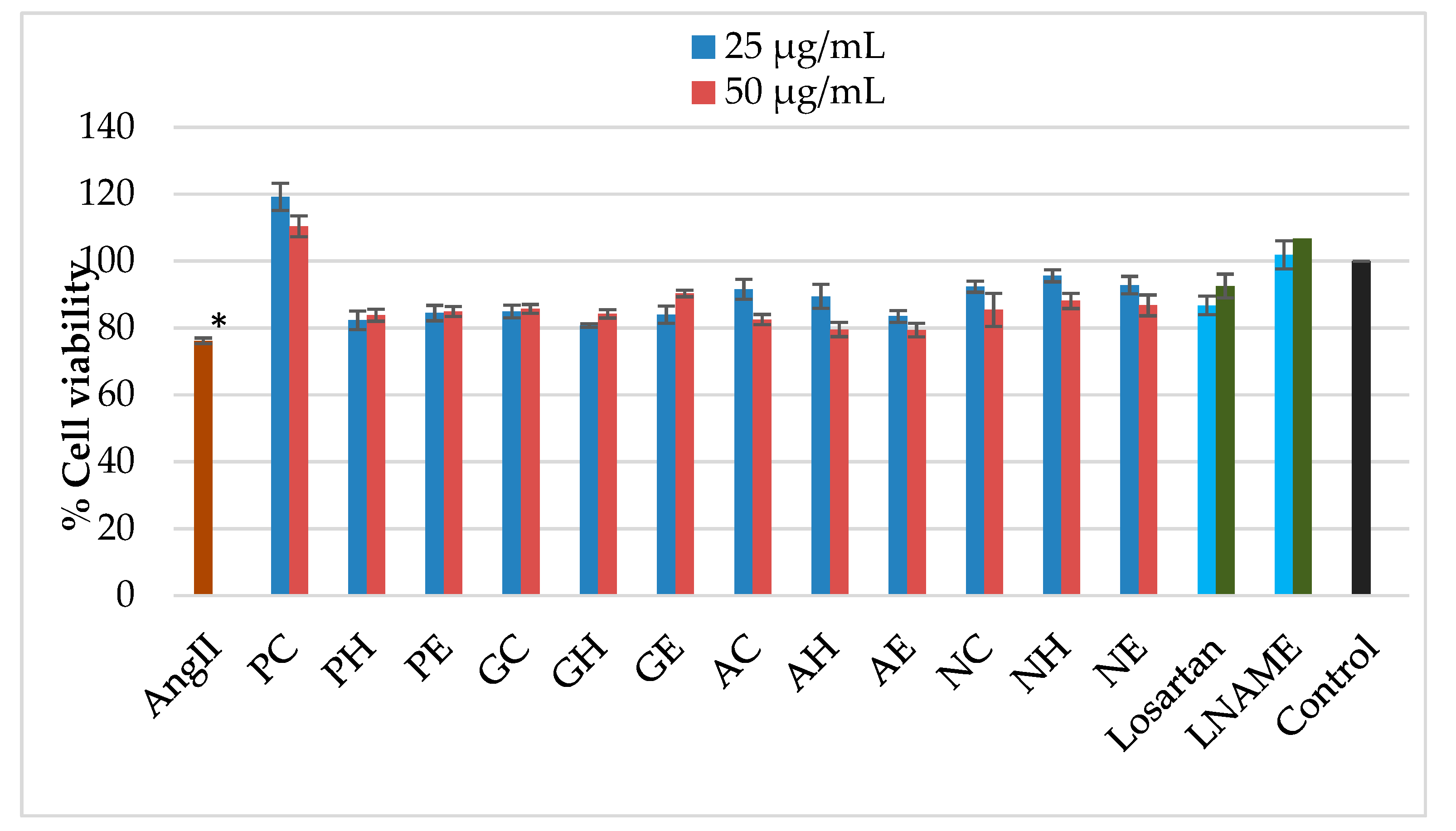
2.4. Effects of the Extracts on Mitochondrial Activity of AngII-Induced Cells
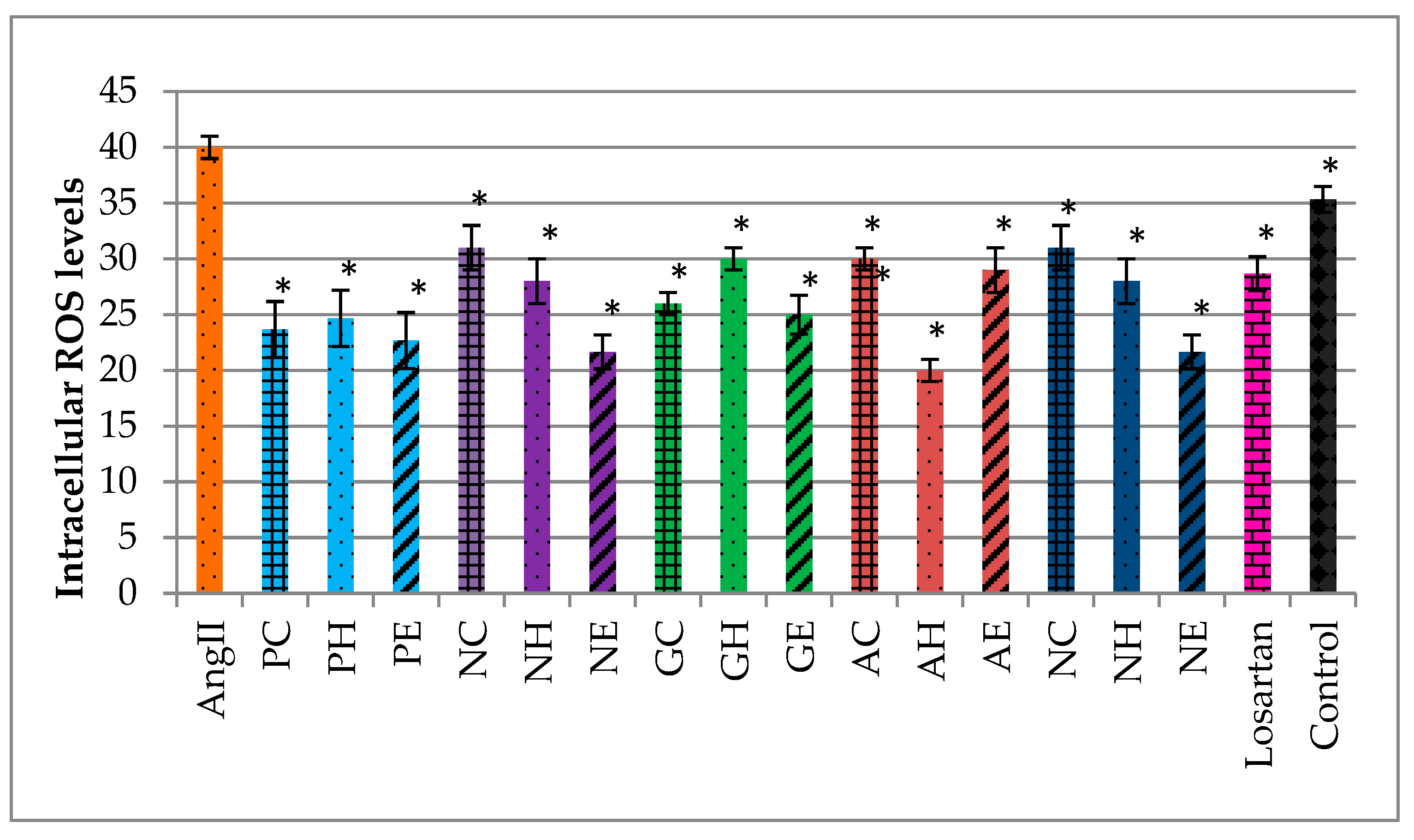
2.5. Effects of the Extracts on Intracellular ROS Levels in AngII-Induced Cardiomyocytes
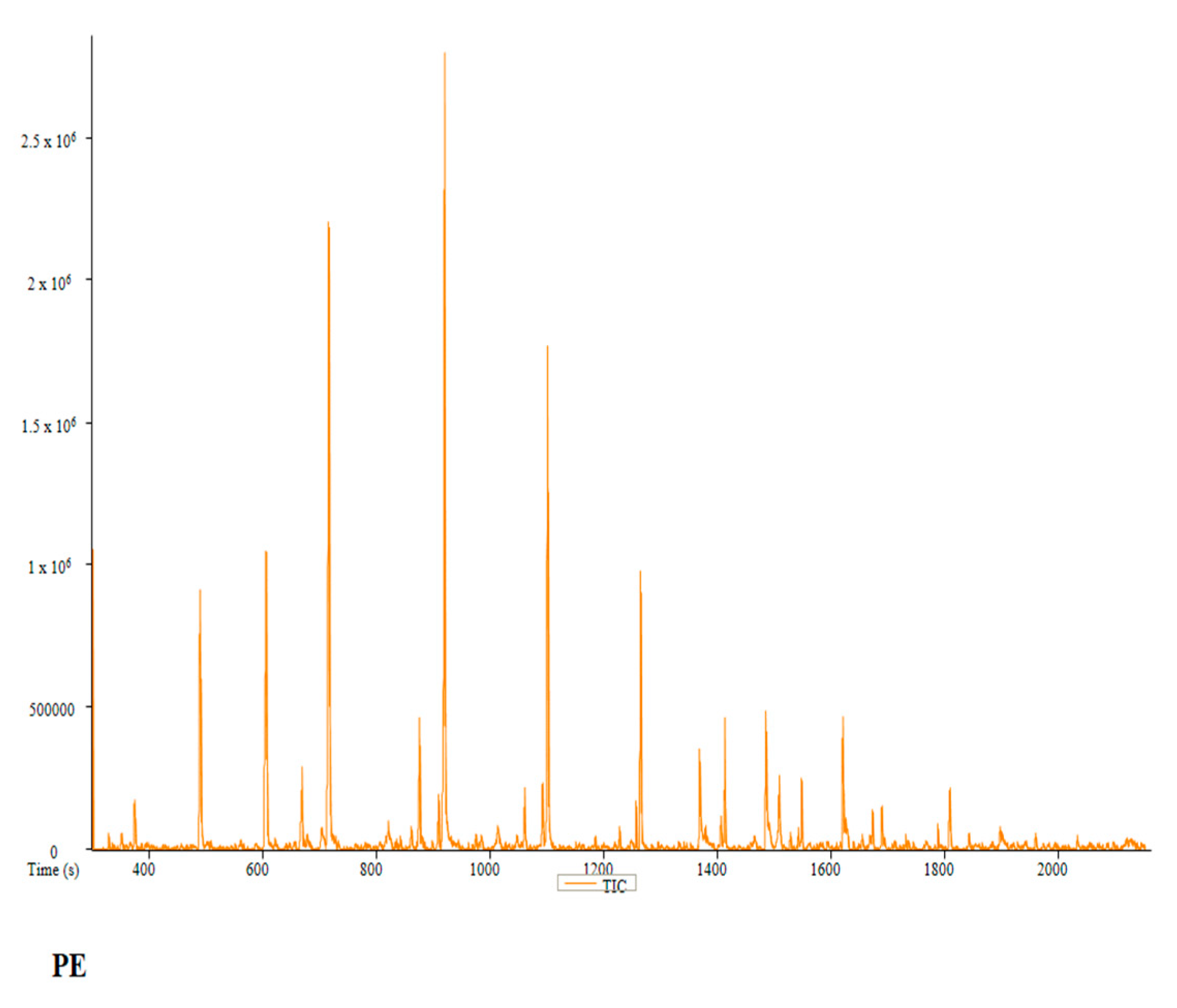
2.6. Phytochemistry Analysis of the Water and Ethanol Extracts of Pan cyanescens, P. cubensis and A+ Strain Mushrooms
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethical Clearances
4.2. Growing Mushrooms and Making Extracts
4.3. Culturing of Cells
4.3.1. Cytotoxicity Determination of the Mushroom
4.3.2. Cell Culture for Treatment
Mitochondrial Activity
Actin Filament Labelling and Surface Area Measurements
ANP Concentration Measurements
Intracellular ROS Measurements
4.3.3. Phytochemical Determination of the Ethanol and Water Extracts
4.3.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Depression and Other Common Mental Disorders: Global Health Estimates; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Guzman, G.; Allen, J.W.; Gartz, J. A worldwide geographical distribution of the neurotropica fungi, an analysis and discussion. Ann. Mus. Civ. Stor. Nat. Giacomo Doria 1998, 14, 189–280. [Google Scholar]
- Kraehenmann, R.; Preller, K.H.; Scheidegger, M.; Pokomy, T.; Bosch, O.G.; Seifritz, E.; Vollenweider, F.X. Psilocybin-induced decrease in amygdala reactivity correlates with enhanced positive mood in healthy volunteers. Biol. Psychiatry 2015, 78, 572–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasler, F.; Grimberg, U.; Benz, M.A.; Huber, T.; Vollenweider, F.X. Acute psychological and physiological effects of psilocybin in healthy humans: A double-blind, placebo-controlled dose-effect study. Psychopharmacology 2004, 172, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Amsterdam, J.G.C.; Opperhuizen, A.; van den Brink, W. Harm potential of magic mushroom: A review. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2011, 59, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GBD 2017 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators. 2018 Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 392, 1789–1858.
- Groenewegen, A.; Rutten, F.H.; Mosterd, A.; Hoes, A.W. Epidemiology of heart failure. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2020, 22, 1342–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curl, C.L.; Danes, V.R.; Bell, J.R.; Raaijmakers, A.J.A.; Ip, W.T.K.; Chandramouli, C.; Harding, T.W.; Porrello, E.R.; Erickson, J.R.E.; Charchar, F.J.; et al. Cardiomyocyte functional etiology in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction is distinctive; A new preclinical model. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2018, 7, e007451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, A.K.; Bhullar, S.K.; Elimban, V.; Dhalla, N.S. Oxidative stress as a mechanism for functional alterations in cardiac hypertrophy and heart failure. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohini, A.; Agrawal, N.; Koyani, C.N.; Singh, R. Molecular targets and regulators of cardiac hypertrophy. Pharmacol. Res. 2010, 61, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molkentin, J.D.; Dorn, G.W. Cytoplasmic signaling pathways that regulate cardiac hypertrophy. Annual Rev. Physiol. 2001, 63, 391–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sil, P.; Sen, S. Angiotensin II and myocyte growth role of fibroblasts. Hypertension 1997, 30, 209–216. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, H.; Gwathmey, J.K.; Xie, L.-H. Oxidative Stress-mediated effects of angiotensin II in the cardiovascular system. World J. Hypertens. 2012, 2, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, G.; Zhou, G.; Zhou, G.; Tan, Y.; Wang, X.; Wei, W.; Liu, L.; Xue, W.; Feng, W.; et al. Angiotensin II-induced p53-dependent cardiac apoptotic cell death: Its prevention by metallothionein. Toxicol. Lett. 2009, 191, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.-X.; Lu, X.-M.; Kimura, S.; Nishiyama, A. Role of mitochondria in angiotensin II-induced reactive oxygen species and mitogenactivated protein kinase activation. Cardiovasc. Res. 2007, 79, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, M.; Yasue, H.; Ogawa, H. Pathophysiological significance and clinical application of ANP and BNP in patients with heart failure. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2001, 79, 730–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Sharma, R.; McElhanon, K.; Allen, C.D.; Megyesi, J.K.; Beneš, H.; Singh, S.P. Sulforaphane protects the heart from doxorubicin-induced toxicity. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 86, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkadimeng, S.M.; Nabatanzi, A.; Steinmann, C.M.L.; Eloff, J.N. Phytochemical, cytotoxicity, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of Psilocybe natalensis magic mushroom. Plants. 9, 127.Author 1, A.B. (University, City, State, Country); Author 2, C. (Institute, City, State, Country). Personal communication, 2020, 2012.
- Sholeb, M.S.; El-Kadi, A.O.S. Resveratrol protects against angiotensin II-induced cellular hypertrophy through inhibition of CYP1B1/Mid-Chain hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid mechanism. FASEB J. 2019, 2019, 33. [Google Scholar]
- Nkadimeng, S.M.; Steinmann, C.M.L.; Eloff, J.N. Effects and safety of Psilocybe cubensis and Panaeolus cyanescens magic mushroom extracts on endothelin-1-induced hypertrophy and cell injury in cardiomyocytes. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 22314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nkadimeng, S.M.; Steinmann, C.M.L.; Eloff, J.N. Anti-inflammatory effects of four psilocybin-containing magic mushroom water extracts in vitro on 15-lipoxygenase activity and on lipopolysaccharide-induced cyclooxygenase-2 and inflammatory cytokines in human U937 macrophages. J. Inflamm. Res. 2021, 14, 3729–3738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aparna, V.; Dileep, K.V.; Mandal, P.K.; Karthe, P.; Sadasivan, C.; Haridas, M. Anti-inflammatory property of n-Hexadecanoic acid: Structural evidence and kinetic assessment. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2012, 80, 434–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.P.; Kumaravel, S.; Latlitha, C. Screening of antioxidant activity, total phenolics and GC-MS study of Vitex negundo. Afr. J. Biochem. Res. 2010, 4, 191–195. [Google Scholar]
- Korbecki, J.; Bajdak-Rusinek, K. The effect of palmitic acid on inflammatory response in macrophages: An overview of molecular mechanisms. Inflamm. Res. 2019, 68, 915–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumaresan, S.; Senthilkumar, V.; Stephen, A.; Balakumar, B.S. GC-MS analysis and pass-assisted predictions of biological activity spectra of extract of Phomopsis SP. Isolated from Andrographis paniculate. World J. Pharm. Res. 2015, 4, 1035–1053. [Google Scholar]
- Gurudeeban, S.; Sathyavani, K.; Ramanathan, T. Bitter apple (Citrulus colocynthis): An overview of chemical composition and biomedical potentials. Asian J. Plant Sci. 2010, 2010, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmoodreza, M.; Forough, K.; Hossein, T.; Younes, G. Composition of the essential oil of Rosa damascene mill from South of Iran. Iran. J. Psychiatry Behav. Sci. 2010, 6, 59–62. [Google Scholar]
- Ombito, O.J.; Matasyoh, C.J.; Vulule, M.J. Chemical composition and larvicidal activity of Zantoxylem gilletii essential oil against Anopheles gambie. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2014, 13, 2175–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horiuchi, T.; Tsukamoto, H. Complement-targeted therapy: Development of C5- and C5a-targeted inhibition. Inflamm. Regen. 2016, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hema, R.; Kumaravel, S.; Alagusundaram, K. GC/MS Determination of Bioactive Components of Murraya koenigii. J. Am. Sci. 2011, 2011, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Palariya, D.; Singh, A.; Dhami, A.; Pant, A.K.; Kumar, R.; Prakash, O. Phytochemical analysis and screening of antioxidant, antibacterial and anti-inflammatory activity of essential oil of Premna mucronata Roxb. leaves. Trends Phytochem. Res. 2019, 3, 275–286. [Google Scholar]
- Asong, J.A.; Amoo, S.O.; McGaw, L.J.; Nkadimeng, S.M.; Aremu, A.O.; Otang-Mbeng, W. Antimicrobial Activity, Antioxidant Potential, Cytotoxicity and Phytochemical Profiling of Four Plants Locally Used against Skin Diseases. Plants 2019, 8, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gideon, V.A. GC-MS analysis of phytochemical components of Pseudoglochidion anamalayanum Gamble: An endangered medicinal tree. Asian J. Plant Sci. 2015, 5, 36–4. [Google Scholar]
- Choulis, N.H. Chapter 49-Miscellaneous Drugs, Materials, Medical Devices, and Techniques. In Side Effects of Drugs Annual; Aronson, J.K., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; Volume 33, pp. 1009–1029. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández, M.L.; Sicardo, M.; Dolores, B.A.; Martínez-Rivas, J.M. The oleic/linoleic Acid ratio in olive (Olea europaea L.) fruit Mesocarp is mainly controlled by OeFAD2–2 and OeFAD2–5 genes together with the different specificity of extraplastidial acyltransferase enzymes. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Hafidi, M.; Pérez, I.; Zamora, J.; Soto, V.; Carvajal-Sandoval, G.; Baños, G. Glycine intake decreases plasma free fatty acids, adipose cell size, and blood pressure in sucrose-fed rats. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2004, 287, R1387–R1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senol, H.; Ozgun-Acar, O.; Dağ, A.; Eken, A.; Guner, H.; Aykut, Z.G.; Topcu, G.; Sen, A. Synthesis and Comprehensive in Vivo Activity Profiling of Olean-12-en-28-ol, 3β-Pentacosanoate in Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis: A Natural Remyelinating and Anti-Inflammatory Agent. J. Nat. Prod. 2023, 86, 103–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
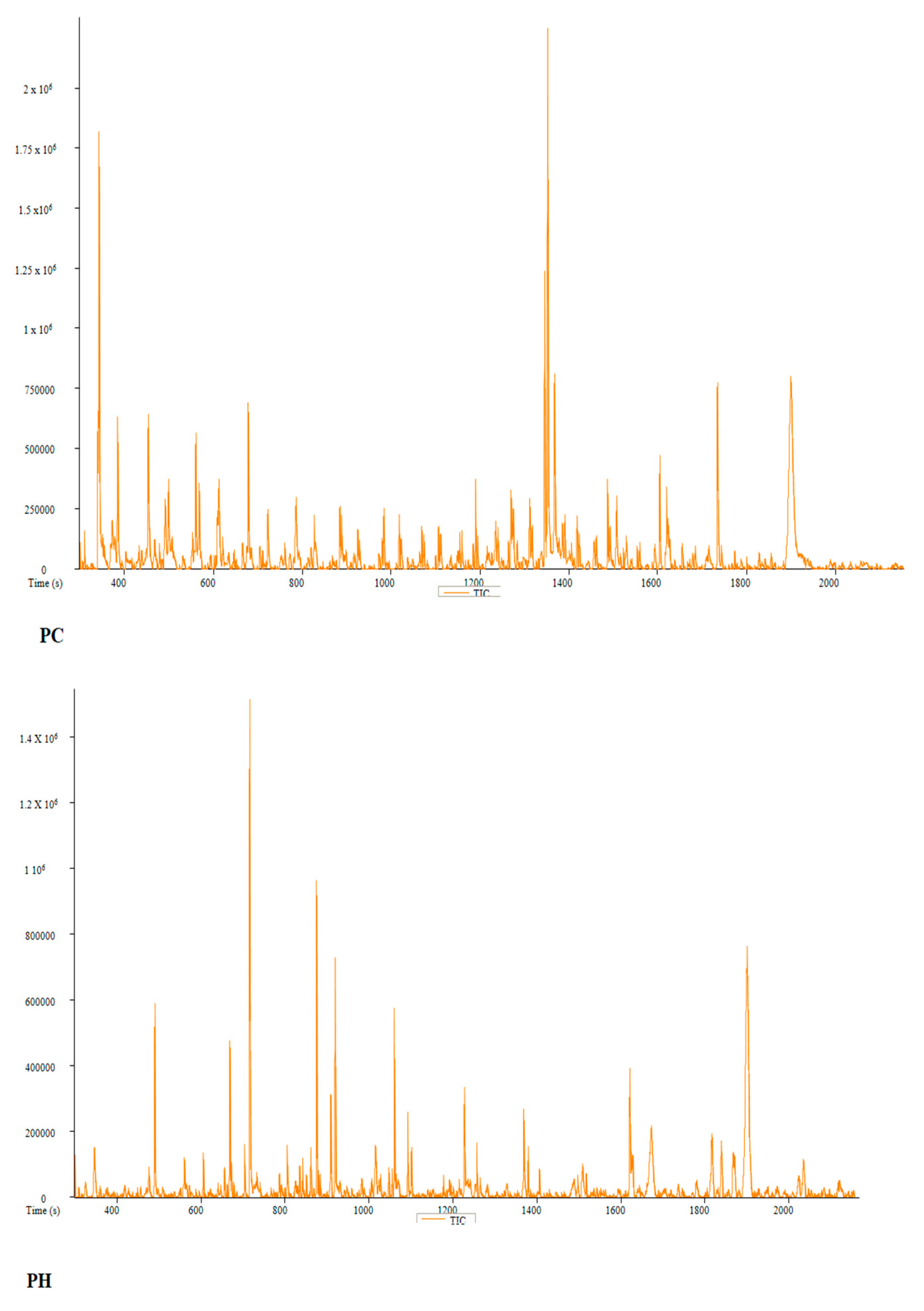
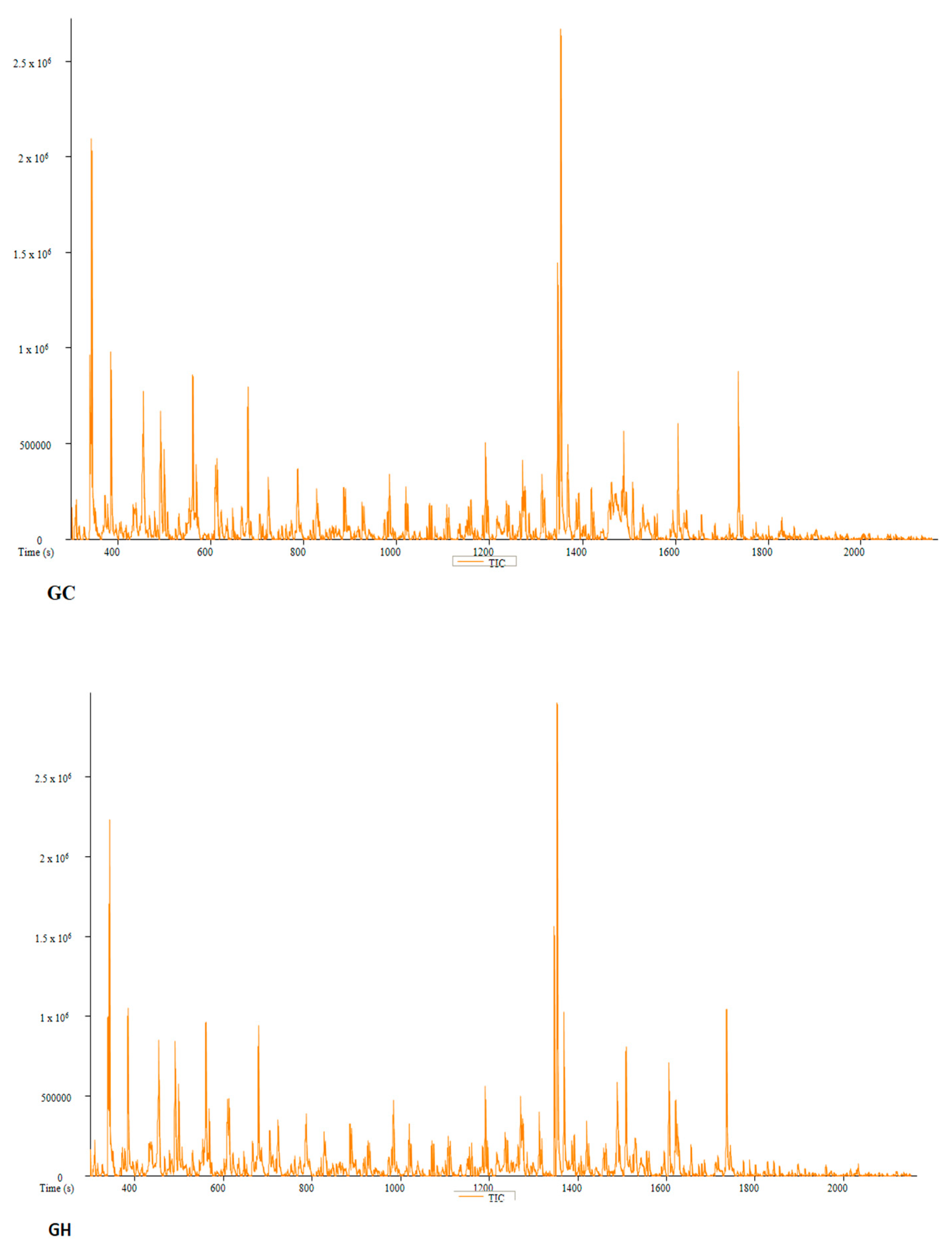
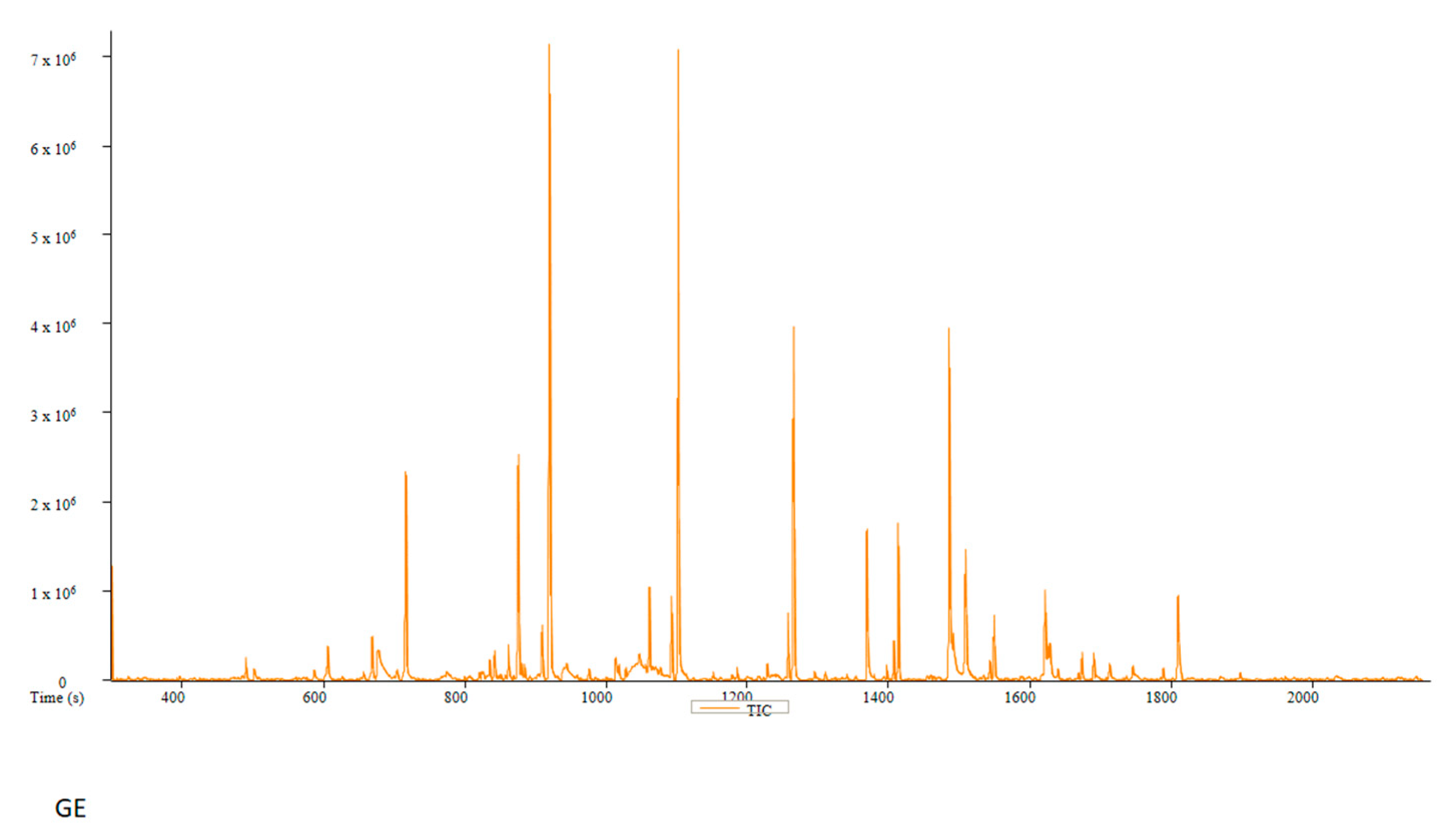
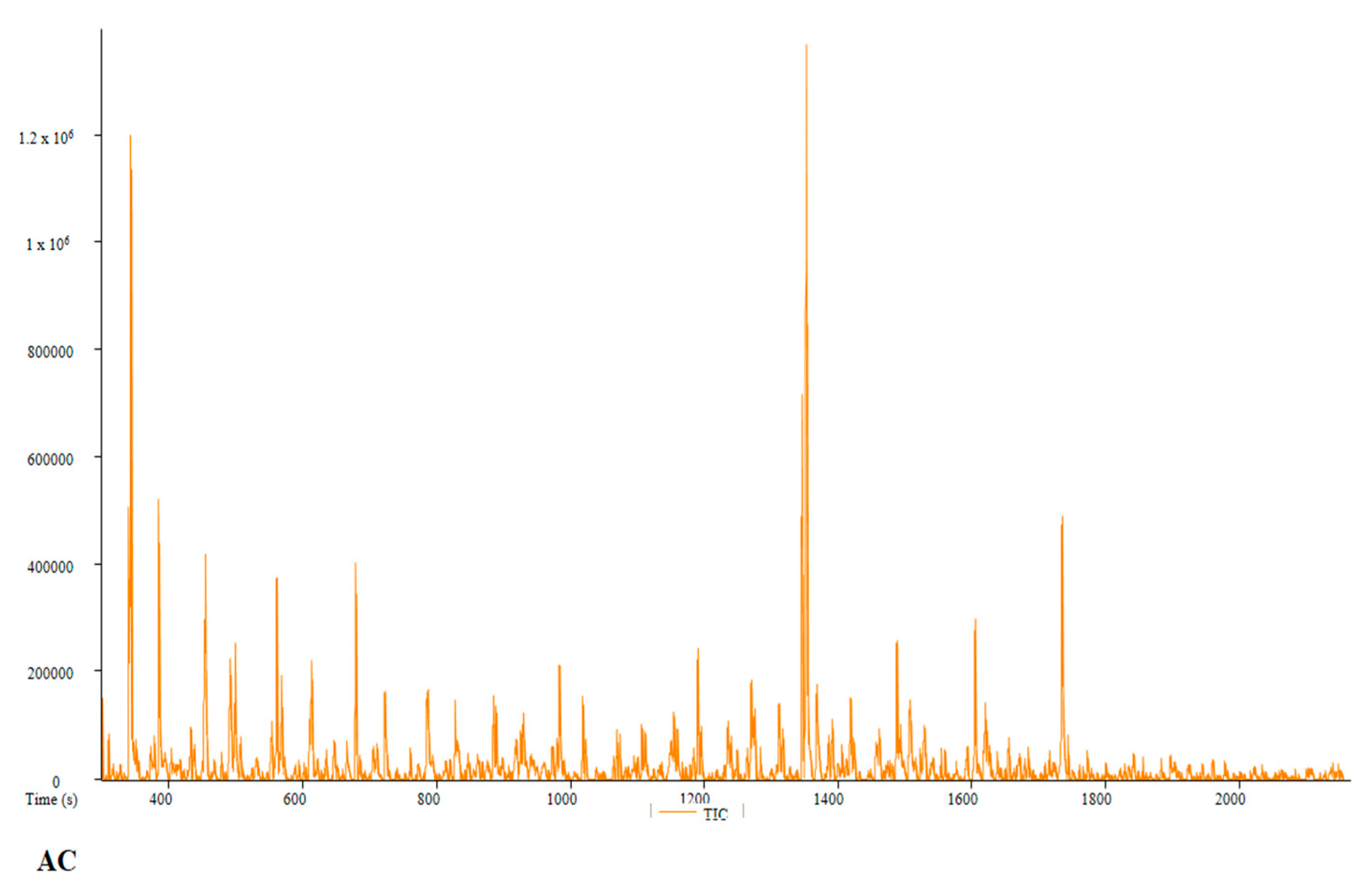
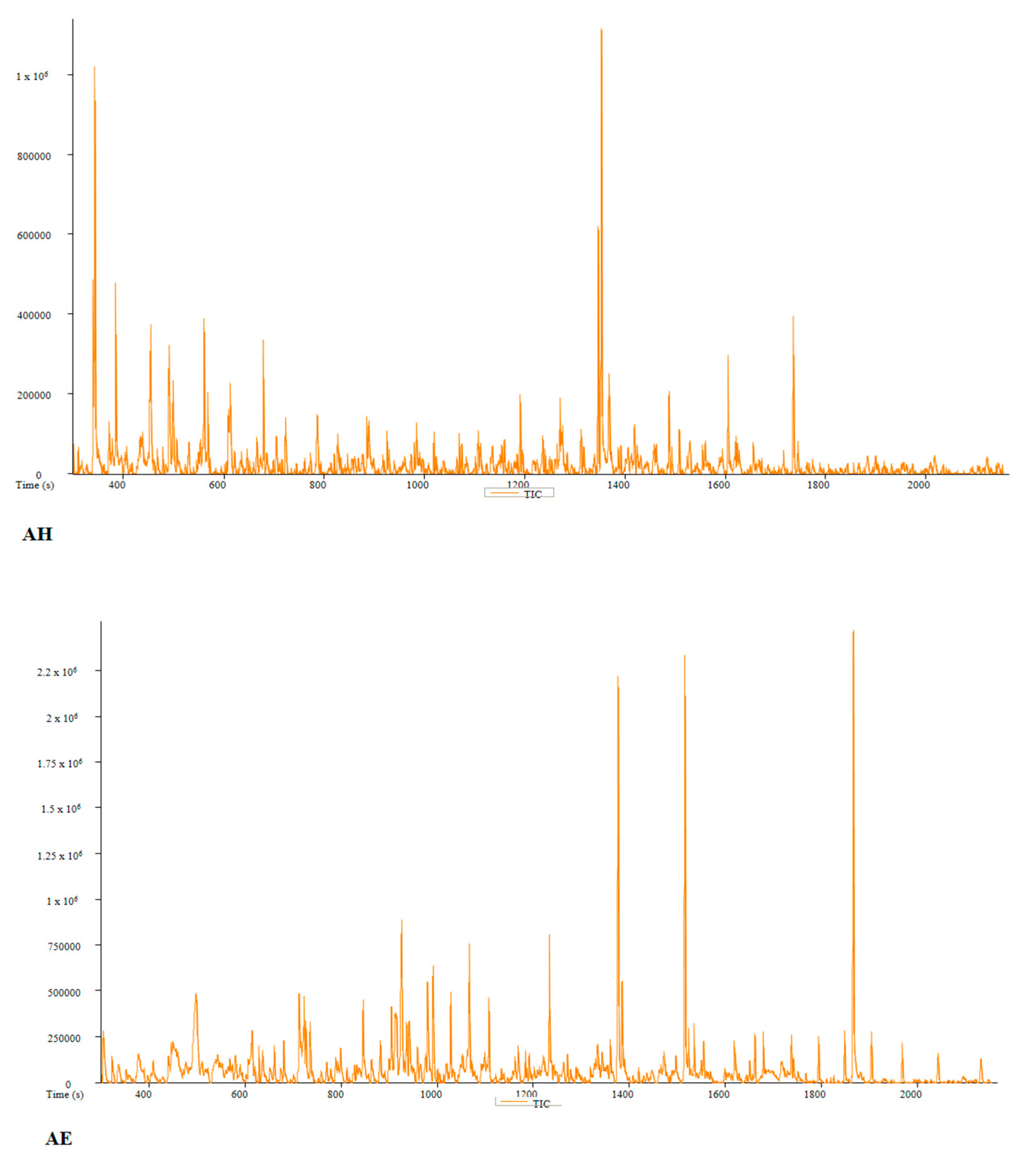
| PC | Peak # | Name | Weight | Formula | CAS | Similarity | Area % | 1st Dimension Time (s) | Height |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | Hexanoic acid, methyl ester | 130 | C7H14O2 | 106-70-7 | 927 | 2,0459 | 385,6 | 614562 | |
| 6 | 3-Octanone | 128 | C8H16O | 106-68-3 | 794 | 2,9534 | 453,6 | 647828 | |
| 7 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 705 | 2,8617 | 455 | 639963 | |
| 22 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 778 | 0,66502 | 785,8 | 265590 | |
| 26 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 816 | 0,79635 | 886 | 265712 | |
| 30 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 820 | 0,36008 | 980,6 | 132773 | |
| 35 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 843 | 0,4545 | 1070,3 | 185705 | |
| 38 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 815 | 0,46437 | 1155,4 | 155284 | |
| 42 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 794 | 0,93345 | 1236,3 | 196900 | |
| 43 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 800 | 0,56178 | 1241,5 | 176011 | |
| 47 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 781 | 1,0495 | 1313,4 | 297088 | |
| 51 | n-Hexadecanoic acid | 256 | C16H32O2 | 57-10-3 | 899 | 2,891 | 1369 | 754734 | |
| 52 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 840 | 0,65301 | 1386,9 | 155364 | |
| 53 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 774 | 0,66727 | 1392,4 | 200963 | |
| 58 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 798 | 0,22375 | 1524,4 | 90547 | |
| 62 | 9-Octadecenamide, (Z)- | 281 | C18H35NO | 301-02-0 | 908 | 1,1739 | 1621,3 | 345374 | |
| 63 | 9-Octadecenamide, (Z)- | 281 | C18H35NO | 301-02-0 | 816 | 0,81034 | 1624,9 | 215839 | |
| 64 | 9-Octadecenamide, (Z)- | 281 | C18H35NO | 301-02-0 | 733 | 0,51097 | 1628,1 | 131186 | |
| 66 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 770 | 0,35671 | 1716,6 | 102006 | |
| 68 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 791 | 0,20132 | 1774,1 | 81447 | |
| PH | Peak # | Name | Weight | Formula | CAS | Similarity | Area % | 1st Dimension Time (s) | Height |
| 13 | Tetradecane | 198 | C14H30 | 629-59-4 | 884 | 4,0398 | 920,1 | 731151 | |
| 19 | n-Hexadecanoic acid | 256 | C16H32O2 | 57-10-3 | 868 | 1,9932 | 1369,2 | 270343 | |
| 22 | 9-Octadecenamide, (Z)- | 281 | C18H35NO | 301-02-0 | 921 | 2,6151 | 1621,3 | 395816 | |
| 23 | 9-Octadecenamide, (Z)- | 281 | C18H35NO | 301-02-0 | 829 | 0,98533 | 1625 | 141739 | |
| 24 | 9-Octadecenamide, (Z)- | 281 | C18H35NO | 301-02-0 | 877 | 1,1489 | 1628,4 | 130670 | |
| 26 | Dotriacontane | 450 | C32H66 | 544-85-4 | 885 | 5,8278 | 1673,2 | 221028 | |
| 32 | Olean-12-ene-3,28-diol, (3á)- | 442 | C30H50O2 | 545-48-2 | 613 | 19,938 | 1900,8 | 766581 | |
| PE | Peak # | Name | Weight | Formula | CAS | Similarity | Area % | 1st Dimension Time (s) | Height |
| 5 | Decane | 142 | C10H22 | 124-18-5 | 846 | 8,8254 | 605,8 | 1051849 | |
| 10 | Tetradecane | 198 | C14H30 | 629-59-4 | 880 | 18,263 | 919,9 | 2801754 | |
| 14 | Nonadecane | 268 | C19H40 | 629-92-5 | 893 | 10,729 | 1101,5 | 1772907 | |
| 15 | Nonadecane | 268 | C19H40 | 629-92-5 | 904 | 5,3724 | 1265 | 980759 | |
| 17 | n-Hexadecanoic acid | 256 | C16H32O2 | 57-10-3 | 880 | 2,671 | 1369,1 | 353542 | |
| 19 | 9,12-Octadecadienoic acid (Z,Z)- | 280 | C18H32O2 | 60-33-3 | 910 | 3,4485 | 1485,3 | 489829 | |
| 22 | Heneicosane | 296 | C21H44 | 629-94-7 | 899 | 1,3394 | 1548,6 | 251573 | |
| 23 | 9-Octadecenamide, (Z)- | 281 | C18H35NO | 301-02-0 | 924 | 2,509 | 1621,2 | 466852 |
| GC | Peak # | Name | Weight | Formula | CAS | Similarity | Area % | 1st Dimension Time (s) | Height |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 739 | 6,3304 | 343,2 | 2096696 | |
| 6 | Hexanoic acid, methyl ester | 130 | C7H14O2 | 106-70-7 | 928 | 2,8062 | 385,1 | 955717 | |
| 9 | 3-Octanone | 128 | C8H16O | 106-68-3 | 830 | 2,7283 | 452,8 | 762082 | |
| 27 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 779 | 0,71327 | 785,7 | 314589 | |
| 31 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 813 | 0,69149 | 885,8 | 276576 | |
| 35 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 855 | 0,35927 | 980,5 | 151860 | |
| 38 | Dodecanoic acid, methyl ester | 214 | C13H26O2 | 111-82-0 | 900 | 0,70445 | 1019,3 | 279675 | |
| 41 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 807 | 0,44597 | 1070,2 | 197083 | |
| 48 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 809 | 0,78095 | 1236,2 | 194599 | |
| 53 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 736 | 1,2754 | 1313,2 | 346174 | |
| 55 | Hexadecanoic acid, methyl ester | 270 | C17H34O2 | 112-39-0 | 910 | 3,7206 | 1346,9 | 1438966 | |
| 57 | n-Hexadecanoic acid | 256 | C16H32O2 | 57-10-3 | 876 | 1,7469 | 1368,7 | 479084 | |
| 58 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 837 | 0,81401 | 1386,7 | 214202 | |
| 59 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 761 | 0,89417 | 1392,1 | 245098 | |
| 65 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 851 | 0,21253 | 1524,3 | 93108 | |
| 71 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 729 | 0,20497 | 1716,4 | 85138 | |
| GH | Peak # | Name | Weight | Formula | CAS | Similarity | Area % | 1st Dimension Time (s) | Height |
| 3 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 718 | 5,7808 | 343,8 | 2236529 | |
| 11 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 739 | 3,5171 | 454,8 | 833100 | |
| 20 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 745 | 0,93596 | 569 | 403943 | |
| 28 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 759 | 0,65184 | 785,8 | 327037 | |
| 32 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 827 | 0,73365 | 885,8 | 331466 | |
| 37 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 833 | 0,44286 | 980,5 | 180459 | |
| 40 | Dodecanoic acid, methyl ester | 214 | C13H26O2 | 111-82-0 | 862 | 0,76451 | 1019,3 | 332902 | |
| 46 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 813 | 0,47338 | 1155,3 | 187669 | |
| 48 | Hexadecanoic acid, methyl ester | 270 | C17H34O2 | 112-39-0 | 829 | 1,4125 | 1191,3 | 568445 | |
| 50 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 802 | 0,88819 | 1236,2 | 252623 | |
| 55 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 784 | 1,2221 | 1313,2 | 405746 | |
| 56 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 789 | 0,80275 | 1318,5 | 238850 | |
| 59 | n-Hexadecanoic acid | 256 | C16H32O2 | 57-10-3 | 891 | 3,1125 | 1368,8 | 1020178 | |
| 60 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 827 | 0,72977 | 1386,7 | 208562 | |
| 61 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 772 | 0,67475 | 1392,2 | 260361 | |
| 69 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 845 | 0,23403 | 1524,2 | 119865 | |
| 74 | 9-Octadecenamide, (Z)- | 281 | C18H35NO | 301-02-0 | 901 | 1,5525 | 1620,9 | 476077 | |
| 75 | 9-Octadecenamide, (Z)- | 281 | C18H35NO | 301-02-0 | 828 | 0,94615 | 1624,4 | 327188 | |
| 76 | 9-Octadecenamide, (Z)- | 281 | C18H35NO | 301-02-0 | 768 | 0,71306 | 1627,7 | 212987 | |
| 78 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 839 | 0,41231 | 1716,3 | 134307 | |
| 80 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 772 | 0,22056 | 1773,7 | 103514 | |
| 81 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 735 | 0,27314 | 1829,2 | 96189 | |
| GE | Peak # | Name | Weight | Formula | CAS | Similarity | Area % | 1st Dimension Time (s) | Height |
| 1 | Decane | 142 | C10H22 | 124-18-5 | 897 | 0,44944 | 490,3 | 252016 | |
| 3 | Decane | 142 | C10H22 | 124-18-5 | 842 | 0,98073 | 605,7 | 379188 | |
| 8 | Tetradecane | 198 | C14H30 | 629-59-4 | 864 | 4,5504 | 716,3 | 2342975 | |
| 14 | Tetradecane | 198 | C14H30 | 629-59-4 | 873 | 12,505 | 919,9 | 7151813 | |
| 20 | Hexadecane | 226 | C16H34 | 544-76-3 | 914 | 11,926 | 1101,7 | 7087174 | |
| 24 | Nonadecane | 268 | C19H40 | 629-92-5 | 919 | 6,5048 | 1265 | 3973633 | |
| 26 | n-Hexadecanoic acid | 256 | C16H32O2 | 57-10-3 | 916 | 3,2652 | 1368,9 | 1698554 | |
| 29 | Heneicosane | 296 | C21H44 | 629-94-7 | 901 | 2,7681 | 1413,3 | 1765288 | |
| 30 | 9,12-Octadecadienoic acid (Z,Z)- | 280 | C18H32O2 | 60-33-3 | 920 | 7,7412 | 1485,4 | 3942406 | |
| 31 | Oleic Acid | 282 | C18H34O2 | 112-80-1 | 901 | 1,7768 | 1490,7 | 498823 | |
| 32 | Dodecanamide | 199 | C12H25NO | 1120-16-7 | 822 | 0,1794 | 1506,4 | 175567 | |
| 36 | 9-Octadecenamide, (Z)- | 281 | C18H35NO | 301-02-0 | 920 | 2,013 | 1620,9 | 1001169 | |
| 37 | 9-Octadecenamide, (Z)- | 281 | C18H35NO | 301-02-0 | 875 | 1,1399 | 1627,8 | 415638 | |
| 42 | 9-Octadecenamide, (Z)- | 281 | C18H35NO | 301-02-0 | 827 | 0,33757 | 1745 | 161336 |
| AC | Peak # | Name | Weight | Formula | CAS | Similarity | Area % | 1st Dimension Time (s) | Height |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 732 | 7,2746 | 343,1 | 1201850 | |
| 5 | Hexanoic acid, methyl ester | 130 | C7H14O2 | 106-70-7 | 928 | 3,7608 | 385 | 524718 | |
| 7 | 3-Octanone | 128 | C8H16O | 106-68-3 | 852 | 3,7989 | 452,8 | 422676 | |
| 8 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 725 | 3,7989 | 454,5 | 422676 | |
| 24 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 742 | 0,77714 | 785,7 | 152661 | |
| 27 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 805 | 1,1092 | 885,8 | 160107 | |
| 30 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 841 | 0,47523 | 980,5 | 80179 | |
| 35 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 850 | 0,5429 | 1070,1 | 98825 | |
| 38 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 810 | 1,0146 | 1155,1 | 128129 | |
| 39 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 748 | 0,71579 | 1160,2 | 83648 | |
| 41 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 829 | 1,066 | 1236,1 | 112539 | |
| 45 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 754 | 1,2357 | 1313,2 | 144052 | |
| 46 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 732 | 0,83455 | 1318,6 | 97752 | |
| 47 | Hexadecanoic acid, methyl ester | 270 | C17H34O2 | 112-39-0 | 910 | 4,4828 | 1347 | 720709 | |
| 49 | n-Hexadecanoic acid | 256 | C16H32O2 | 57-10-3 | 884 | 2,0361 | 1369,1 | 181013 | |
| 50 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 802 | 0,68996 | 1386,7 | 85828 | |
| 60 | 9-Octadecenamide, (Z)- | 281 | C18H35NO | 301-02-0 | 895 | 1,3478 | 1621 | 146411 | |
| 61 | 9-Octadecenamide, (Z)- | 281 | C18H35NO | 301-02-0 | 764 | 0,62809 | 1624,5 | 93200 | |
| 63 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 859 | 0,36481 | 1716,4 | 56531 | |
| AH | Peak # | Name | Weight | Formula | CAS | Similarity | Area % | 1st Dimension Time (s) | Height |
| 3 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 729 | 7,5091 | 343,1 | 1023514 | |
| 6 | Hexanoic acid, methyl ester | 130 | C7H14O2 | 106-70-7 | 942 | 3,4369 | 384,8 | 481718 | |
| 8 | 3-Octanone | 128 | C8H16O | 106-68-3 | 822 | 0,94495 | 452,6 | ||
| 9 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 711 | 4,0912 | 454,3 | 366395 | |
| 26 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 783 | 0,82861 | 785,6 | 133376 | |
| 30 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 817 | 1,059 | 885,7 | 146601 | |
| 33 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 854 | 0,51922 | 980,3 | 80840 | |
| 38 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 827 | 0,58444 | 1070,1 | 106177 | |
| 41 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 817 | 0,60789 | 1155,2 | 76344 | |
| 43 | Hexadecanoic acid, methyl ester | 270 | C17H34O2 | 112-39-0 | 851 | 1,3131 | 1191,4 | 202951 | |
| 44 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 828 | 1,0656 | 1236,1 | 99142 | |
| 45 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 779 | 0,30158 | 1241,2 | 66062 | |
| 48 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 773 | 1,0275 | 1313,2 | 116536 | |
| 50 | Hexadecanoic acid, methyl ester | 270 | C17H34O2 | 112-39-0 | 910 | 3,9708 | 1347,1 | 619698 | |
| 52 | n-Hexadecanoic acid | 256 | C16H32O2 | 57-10-3 | 894 | 2,3541 | 1368,8 | 236893 | |
| 53 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 831 | 0,54835 | 1386,7 | 69077 | |
| 54 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 740 | 0,54021 | 1392,2 | 75964 | |
| 59 | Glycine | 75 | C2H5NO2 | 56-40-6 | 754 | 1,0692 | 1530,1 | 87122 | |
| 63 | 9-Octadecenamide, (Z)- | 281 | C18H35NO | 301-02-0 | 864 | 0,62408 | 1621,2 | 97425 | |
| 65 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 808 | 0,58739 | 1716,4 | 61884 | |
| AE | Peak # | Name | Weight | Formula | CAS | Similarity | Area % | 1st Dimension Time (s) | Height |
| 10 | Decane | 142 | C10H22 | 124-18-5 | 933 | 20,924 | 497,5 | 783673 | |
| 31 | Tetradecane | 198 | C14H30 | 629-59-4 | 888 | 3,381 | 925,5 | 289073 | |
| 39 | n-Hexadecanoic acid | 256 | C16H32O2 | 57-10-3 | 911 | 3,0487 | 1375,1 | 418335 | |
| 37 | Hexadecanoic acid, methyl ester | 270 | C17H34O2 | 112-39-0 | 851 | 0,54568 | 1353 | 74443 | |
| 42 | 9,12-Octadecadienoic acid (Z,Z)- | 280 | C18H32O2 | 60-33-3 | 914 | 2,1293 | 1491,4 | 204219 | |
| 35 | Eicosane | 282 | C20H42 | 112-95-8 | 896 | 1,4654 | 1107,3 | 168172 |
| NH | Peak # | Name | Weight | Formula | CAS | Similarity | Area % | 1st Dimension Time (s) | Height |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 715 | 3,2977 | 454,6 | 567775 | |
| 23 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 817 | 1,1041 | 885,9 | 210887 | |
| 26 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 830 | 0,42934 | 980,6 | 105250 | |
| 28 | Dodecanoic acid, methyl ester | 214 | C13H26O2 | 111-82-0 | 907 | 1,1472 | 1019,6 | 224678 | |
| 30 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 843 | 0,63486 | 1070,3 | 134265 | |
| 33 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 810 | 0,86841 | 1155,4 | 139945 | |
| 36 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 806 | 0,92241 | 1236,2 | 152342 | |
| 37 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 821 | 0,4793 | 1241,4 | 120478 | |
| 40 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 750 | 1,677 | 1313,3 | 251622 | |
| 45 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 809 | 1,1774 | 1386,7 | 152379 | |
| 46 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 777 | 0,97402 | 1392,3 | 175193 | |
| 50 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 795 | 0,26298 | 1524,4 | 67498 | |
| 55 | 9-Octadecenamide, (Z)- | 281 | C18H35NO | 301-02-0 | 860 | 1,1976 | 1621,4 | 205738 | |
| 57 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 771 | 0,27229 | 1716,4 | 72493 | |
| 59 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 731 | 0,47328 | 1773,9 | 89699 | |
| NC | Peak # | Name | Weight | Formula | CAS | Similarity | Area % | 1st Dimension Time (s) | Height |
| 13 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 733 | 3,6742 | 454,9 | 751534 | |
| 31 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 779 | 0,68667 | 785,7 | 315435 | |
| 33 | Decanoic acid, methyl ester | 186 | C11H22O2 | 110-42-9 | 890 | 0,63556 | 827,8 | 263610 | |
| 35 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 831 | 0,74448 | 885,8 | 274267 | |
| 40 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 837 | 0,43806 | 980,5 | 161533 | |
| 43 | Dodecanoic acid, methyl ester | 214 | C13H26O2 | 111-82-0 | 913 | 0,67789 | 1019,4 | 277970 | |
| 46 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 797 | 0,44929 | 1070,1 | 184949 | |
| 49 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 789 | 0,58295 | 1155,3 | 183945 | |
| 53 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 783 | 0,87504 | 1236,2 | 203315 | |
| 58 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 751 | 0,94274 | 1313,2 | 320486 | |
| 59 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 809 | 0,79948 | 1318,7 | 210365 | |
| 63 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 820 | 0,75158 | 1386,7 | 170332 | |
| 64 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 759 | 0,71847 | 1392,2 | 224832 | |
| 65 | Hexadecanoic acid, methyl ester | 270 | C17H34O2 | 112-39-0 | 844 | 0,87915 | 1419,5 | 273632 | |
| 70 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 836 | 0,24407 | 1524,3 | 103354 | |
| 73 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 758 | 0,50675 | 1594,8 | 141017 | |
| 75 | 9-Octadecenamide, (Z)- | 281 | C18H35NO | 301-02-0 | 889 | 0,73559 | 1621,2 | 243511 | |
| 76 | 9-Octadecenamide, (Z)- | 281 | C18H35NO | 301-02-0 | 713 | 0,68859 | 1624,7 | 202379 | |
| 78 | Dodecane, 1,1-dimethoxy- | 230 | C14H30O2 | 14620-52-1 | 776 | 0,52186 | 1656,7 | 149748 | |
| NE | Peak # | Name | Weight | Formula | CAS | Similarity | Area % | 1st Dimension Time (s) | Height |
| 2 | Decane | 142 | C10H22 | 124-18-5 | 874 | 1,1285 | 490 | 365956 | |
| 17 | 5-Eicosene, (E)- | 280 | C20H40 | 74685-30-6 | 904 | 1,1568 | 1257,2 | 551903 | |
| 23 | 5-Eicosene, (E)- | 280 | C20H40 | 74685-30-6 | 904 | 0,76517 | 1406,5 | 329793 | |
| 24 | Heneicosane | 296 | C21H44 | 629-94-7 | 901 | 3,1921 | 1413,2 | 1359751 | |
| 25 | 9,12-Octadecadienoic acid (Z,Z)- | 280 | C18H32O2 | 60-33-3 | 884 | 1,6761 | 1485,1 | 574310 | |
| 27 | Oleic Acid | 282 | C18H34O2 | 112-80-1 | 828 | 1,6454 | 1508,6 | 534460 | |
| 28 | Dotriacontane | 450 | C32H66 | 544-85-4 | 921 | 1,3086 | 1548,6 | 624893 | |
| 29 | 9-Octadecenamide, (Z)- | 281 | C18H35NO | 301-02-0 | 927 | 2,1573 | 1621 | 787743 | |
| 30 | 9-Octadecenamide, (Z)- | 281 | C18H35NO | 301-02-0 | 857 | 0,99448 | 1624,7 | 316129 | |
| 31 | 9-Octadecenamide, (Z)- | 281 | C18H35NO | 301-02-0 | 847 | 1,0811 | 1627,8 | 304295 | |
| 35 | 9-Octadecenamide, (Z)- | 281 | C18H35NO | 301-02-0 | 827 | 0,26441 | 1745 | 100584 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





