1. Introduction
Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma (EHE) is an extremely rare vascular sarcoma, with an estimated prevalence of less than one in a million people [
1]. It originates from precursor cells with endothelial properties and specific fusion genes [2-5]. EHE has a peak incidence in middle age, however the range is broad with children also being affected [
1,
6,
7]. The tumor can occur in any part of the body but commonly affects the lungs, liver, soft tissue and more rarely bone [
1,
5,
8,
9].
Diagnosis is made based on histologic, immunohistochemical and molecular characteristics. Histological features consist commonly of relatively monomorphic epithelioid cells arranged in cords and nests within a myxohyaline stroma. The cells typically show very subtle intracytoplasmic lumina presenting as vacuoles [
5,
9,
10]. Cellular atypia with pleomorphism is rarely seen and mitotic figures are sparse [
5]. Positive staining for endothelial markers such as ERG, CD31 and specific staining for CAMTA1 or TFE3 identifies EHE immunohistochemically [8,11-13]. The genetic hallmark is a WWTR1-CAMTA1 or YAP-TFE3 gene fusion, detected in nearly 90% and 10% of the cases, respectively [8,14-16].
Clinical behavior of EHE was initially considered as intermediate/borderline between hemangioma and conventional angiosarcoma [
9]. Later on, the World Health Organization (WHO) reclassified EHE as fully malignant hereby acknowledging the aggressive nature [
5]. The tumor rarity, broad age range of patients, variable clinical presentation with different anatomical sites and multifocality in visceral organs makes it hard to define consolidated risk factors. Clinical and pathological parameters associated with survival have only been described in a handful large studies [
1,
17,
18]. Other studies performed statistical analyses on smaller subgroups, reducing the reliability of the statistic outcome [
10,
19,
20].
In this retrospective study of a nationwide collected, molecularly/immunohistochemically confirmed cohort of 57 EHEs, prognostic factors based on clinicopathologic characteristics were determined.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Tissue collection and clinical data
By PALGA-search (Dutch nationwide network and registry of histo- and cytopathology), data and formaline-fixed paraffin (FFPE) embedded material from available EHE cases has been collected. In order to receive clinical information (sex, age at diagnosis, tumor site and -size, treatment details and follow-up) data were anonymously retracted from Netherlands Cancer Registry (NCR). Missing clinical information was requested anonymously from the participating hospitals. Additionally, more recent cases from the Radboud University Medical Centre have been included. Ethical approval for this study was obtained from the local certified Medical Ethics Committee of the Radboud University Medical Center, Nijmegen, The Netherlands (file number: 2018-4610). Fifteen cases were previously published [
4,
21].
Cases were histologically reviewed. Additional immunohistochemistry and/or molecular testing (see below) were performed to confirm the diagnosis.
Tumor histology was classified as typical and atypical, in keeping with the definition by Shibayama et al and Rosenbaum et al [17-18]. Atypical histology was determined by at least two of the following criteria: high mitotic activity (>1/2mm2), high nuclear grade and/or tumor necrosis. High nuclear grade was defined as the presence of enlarged, round and swollen nuclei with vesicular chromatin and prominent nucleoli. Manual mitotic counting was performed with a standard area of 2.37 mm2 (40x objective and 10x ocular with field number 22 millimeters). The number of mitoses was scored in 10 high power fields (HPFs). Cases with less than 10 HPF were excluded from counting.
Tumor size was determined based on either macroscopy, histological slides and/or radiology. Multifocality was defined as multiple tumor nodules limited to one (visceral) organ at time of diagnosis whereas metastatic disease, syn- or metachronous, included (regional) lymph node involvement and deposits in visceral organs and all other sites.
Follow-up end point was referred as time between initial diagnosis to the date of death or the time between diagnosis and last follow-up.
2.2. Molecular analysis
2.2.1. Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH)
Sections of 4 µm FFPE tissue sections were submitted to FISH. For the FISH process, 10 µL SPEC TFE3 probe (ZytoLight ® SPEC TFE3 Dual Color Break Apart Probe, z-2109, Zytovision) and CAMTA1 probe (CAMTA1 Split FISH probe, FS0035, Abnova) were applied to the pre-treated slides. Finally, the slides were mounted with a solution containing both DAPI and Vectashield (Vector, Brunschwig, Amsterdam, The Netherlands). TFE3 and CAMTA1 signals were scored using a Leica DMRBE (Leitz) fluorescence microscope. At least 50 nuclei per sample were counted and were scored as negative (<20%) or positive (≥20%).
2.2.2. Reverse transcriptase-Polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR)
Extracted RNA was submitted to RT-PCR as described previously by Flucke et al (2014). For detection of the t(1;3)(p26.3;q25) translocation a WWTR1 exon3 and exon4 forward primer and a CAMTA1 exon8 reverse primer were used. For detection of YAP1-TFE3, the YAP1 exon1 forward primer and TFE3 exon4, exon6, exon8 and exon10 reverse primer were used [
4].
2.2.3. Immunohistochemistry
CAMTA1 (NBP1—93620, Novusbio) and TFE3 (HPA023881, Sigma-Aldrich) immunohistochemistry staining was performed on 4 µm FFPE tissue sections when both RT-PCR and FISH could not be performed or were not interpretable.
2.3. Statistical analysis
SPSS software 25.0 was used for data analyses. Kaplan-Meier estimate was used to determine the overall cumulative survival. The statistical significance of different variables (sex, age at diagnosis, tumor size, histology, focality) in relation to survival and progression were determined using log-rank analyses. Statistical analyses were considered as significant for any value of P less than 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. Patient demographics
Patient characteristics are described in
Table 1. The tumor occurred in adults (93.0%, n=53) and children (7.0%, n=4) of both sexes with a slight female predominance (female 52.6%, n=30; male 47.4%, n=27). Age at diagnosis ranged from 9 to 87 years, with a median of 54 years.
3.2. Tumor features
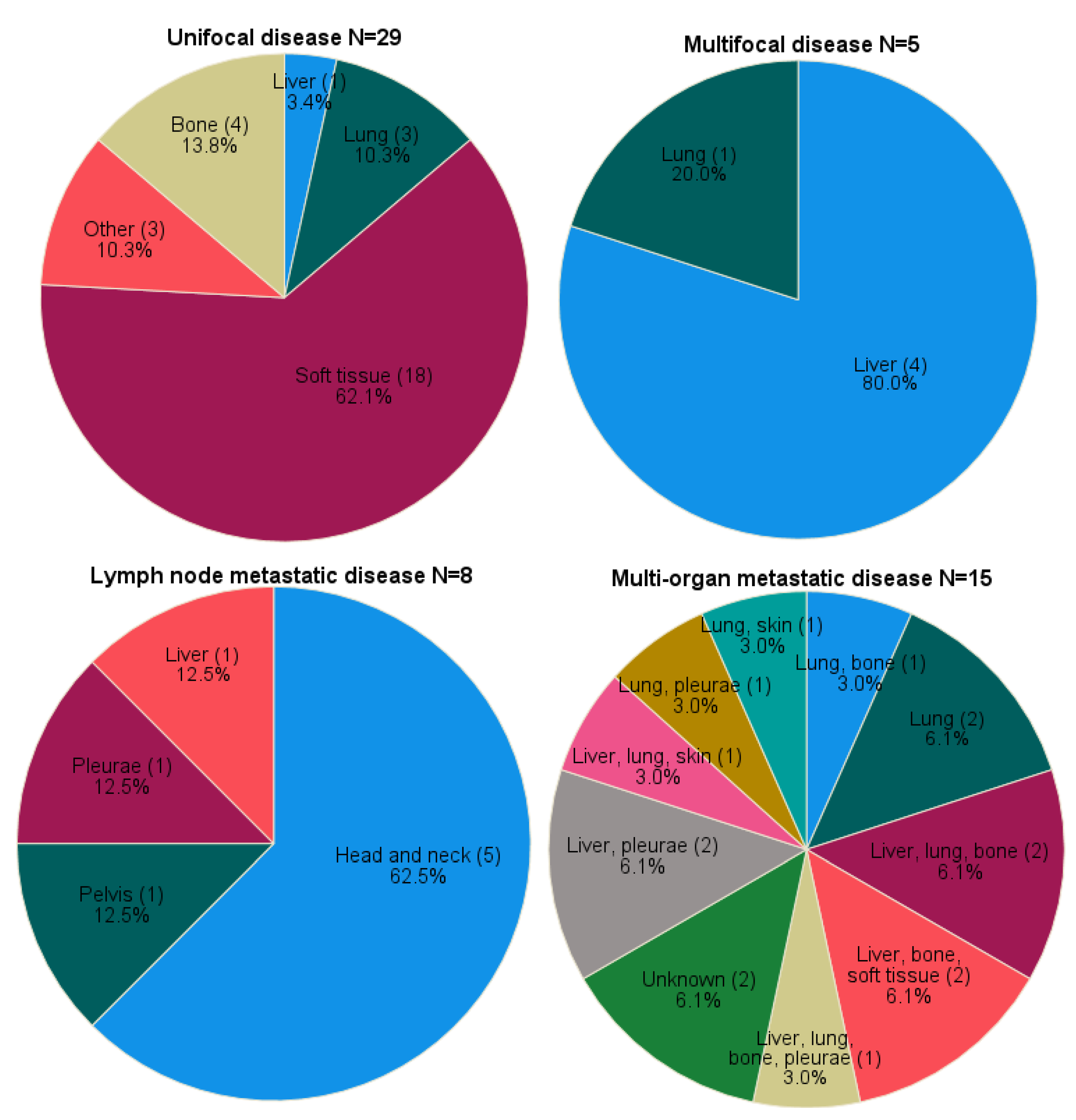
The majority of the cases had unifocal disease at time of diagnosis (50.9%, n=29). Multifocal and metastatic disease at time of diagnosis were seen in 5 (8.8%) and 23 (40.4%) cases, respectively. Metastatic disease included both lymph node (14.0%, n=8) and multi-organ (26.3%, n=15) involvement.
Unifocal soft tissue lesions (62.1%, n=18) arose in the lower extremities (20.7%, n=6), thorax (17.2%, n=5), upper extremities (10.3%, n=3), groin (6.9%, n=2) and soft tissue of the head and neck area (6.9%, n=2). Other unifocal localization was in the long bones (of the upper arm and lower leg) (13.8%, n=4), lung (10.3%, n=3), liver (3.4%, n=1), skin (of the thumb) (3.4%, n=1), ear (3.4%, n=1) and lymph node (3.4%, n=1) (
Figure 1). Median tumor size in unifocal disease was 3.5 centimeters (range 1.1-11.0, n=19). For seven cases tumor size was only defined as <3cm (n=2), >3cm (n=2),<5cm (n=2) or >5cm (n=1).
Multifocal disease originated in liver (80.0%, n=4) and lung (20.0%, n=1). Within the lymph node metastases group, primary localization comprised the clavicular region (37.5%, soft tissue n=2, bone n=1), mandibular bone (25.0%, n=2), liver (12.5%, n=1), pelvic soft tissue (12.5%, n=1) and pleura (12.5%, n=1).
The exact localization of distant metastases are shown in
Figure 1 with two cases (case 47 and 48) being unknown.
3.3. Treatment
For unifocal disease all but 3 cases were treated by surgery (86.2%, n=25). Additional radiotherapy was given in 6 (20.7%) tumors (adjuvant n=4, neo-adjuvant n=1, unknown n=1). The remaining patients received radiotherapy only (due to irresectable tumor or because of patient’s age) or followed an expectative policy. For one patient with unifocal disease primary treatment details were lacking.
Patients with multifocal localization underwent hemihepatectomy (40.0%, n=2), systemic therapy (40.0%, n=2) or had a wait and see approach (20.0%, n=1). All but one patient with lymph node metastases underwent surgery (87.5%, n=7), either as monotherapy (37.5%, n=3), with radiation (37.5%, adjuvant n=2, unknown n=1) or with systemic therapy (12.5%, n=1). Other treatment within the lymph node metastatic group comprised radiotherapy only (due to irresectable tumor, 12.5%, n=1).
For distant metastases treatment with systemic therapy was most common (66.7%, n=10) including 3 patients receiving additional surgical intervention (20.0%), followed by radiotherapy (20.0%, n=3), surgery only (6.7%, n=1) or expectative policy (6.7%, n=1).
3.4. Histopathological characteristics
Histological characteristics (n=53) including nuclear grade, mitotic count and necrosis are shown in
Table 2. Necrosis and high nuclear grade were seen in 18.9% (n=10) and 37.7% (n=20) of the cases, respectively. Mitotic count >1/10HPF was found in 37.7% (n=20) of the tumors. Atypical tumor histology, based on the classification of Shibayama et al and Rosenbaum et al, was observed in 30.2% (n=16) of the cases [17-18].
Of all cases, 24 (42.1%) were confirmed using RT-PCR resulting in 23 WWTR1-CAMTA1 and 1 YAP-TFE3 fusion-positive cases. 21 cases showed rearrangements for CAMTA1 (36.8%) and 1 for TFE3 (1.8%) using FISH. The remaining 11 cases (19.3%) were positive for CAMTA1 immunohistochemistry (
Table 2).
3.5. Survival
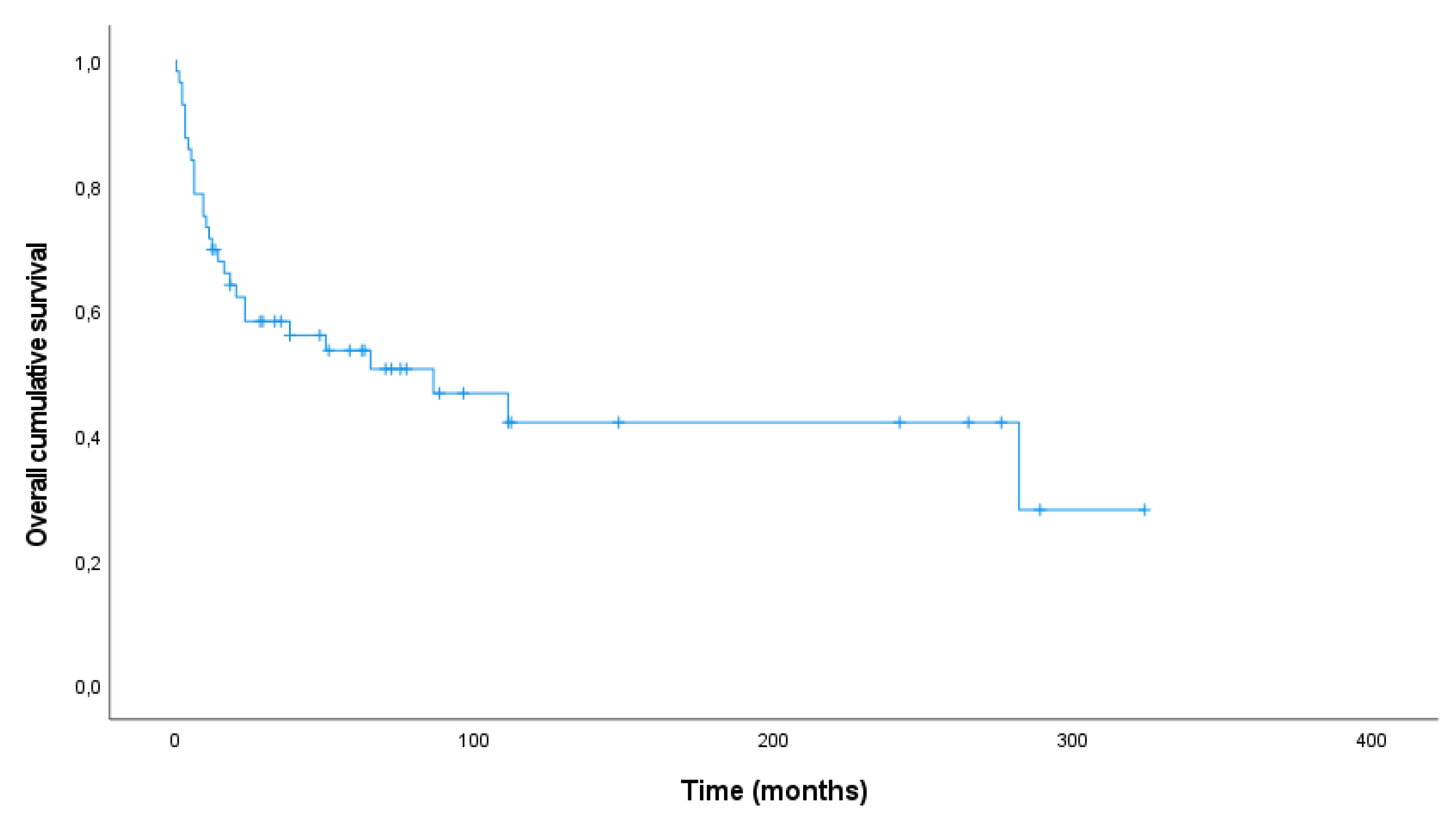
Follow-up was available for all cases. During a median follow-up time of 33 months (range 0-324 months), 27 patients were alive (no evidence of disease (NED) 35.1%, n=20; alive with disease (AWD) 12.3%, n=7) and 30 patients died (death of disease (DOD) 50.9%, n=29; dead due to other cause (DOC) 1.8%, n=1).
Median follow up time in the survivor group was 70.0 months (range 12-324 months) whereas patients died after a median period of 10.5 months (range 0-282 months). The overall 1- and 5-year survival rate was 69.6% and 50.5%, respectively. The Kaplan-Meier plot shows the overall survival for 56 patients (
Figure 2). One patient died as result of endometrial cancer and was therefore excluded from survival analyses.
Survival was unaffected by sex (P = 0.832), age at diagnosis (<55 or ≥55, P = 0.857), necrosis (P = 0.075), nuclear grade (P = 0.793), mitosis (≤1/10HPF or >1/10HPF, P =0.312) and atypical histology (P = 0.175). Unifocal disease showed better survival compared to lymph node (P = 0.019) and multi-organ (P =<0.001) metastatic disease. Patients with multifocal disease had the same prognosis compared to unifocal disease (P = 0.578), lymph node metastasis (P = 0.561) or multi-organ metastasis (P = 0.087). Concerning the multi-organ metastatic group, patients with pleura involvement had significant worse outcome (P = 0.012). Neither lung (P = 0.437) or bone involvement (P = 0.610) was correlated with outcome.
3.6. Progressive unifocal disease
Among the unifocal EHEs progressive clinical course was observed in 10 cases (41.7%) with progression of primary tumor (8.3%, n=2), residual disease (8.3%, n=2), metastatic disease (12.5%, n=3), and residual and metastatic disease (12.5%, n=3). Fourteen patients (58.3%) had no progressive disease. For 5 patients data about progression were lacking. The majority of the unifocal progression group was treated with surgery (either with or without radiotherapy, 90.0% n=9). In five of them (case 23, 36, 41, 44, 49) surgical margins were insufficient (defined as either positive margin or margin <5mm).
Parameters related to progressive clinical course in unifocal disease (n=22) were tumor size ≥3.0cm (P = 0.031) and mitotic number ≥1/10HPF (P = 0.031). Presence of necrosis (P = 0.928), nuclear grade (P = 0.689), atypical histology (P = 0.689) and soft tissue localization (P = 0.896) did not differentiate between both groups.
3.7. Risk stratification model of Shibayama et al.
To predict overall survival, patients with unifocal EHE localization were assigned for tumor size (≤3cm vs >3cm) and histology (atypical vs typical) stratifying 22 tumors into low-risk (18.2%, n=4), intermediate risk (68.2%, n=15) and high-risk (13.6%, n=3) groups, according to the classification of Shibayama et al [
18]. The other unifocal cases could not be implemented into the scoring system due to missing data (n=6) or because of another cause of death (n=1) (
Table 3). All patients conducted to the low-risk group were alive during follow-up (NED, n=3; AWD, n=1). The clinical course of the intermediate-risk category was variable (NED, n=9; AWD, n=1; DOD, n=5) and no disease-free patients were present within the high-risk group (AWD, n=1; DOD, n=2).
Survival differences were significant among the 3 risk groups (P = 0.029). However, tumor size (P = 0.072) and atypical histology (P = 0.224) as independent parameters were not associated with worse prognosis.
4. Discussion
In 1982 Weiss and Enzinger coined the term EHE to describe a low-grade malignant vascular tumor now considered as fully malignant [
5,
9]. Several reports reflected the remarkable heterogeneity of EHE. Therefore, identifying independent prognostic factors is challenging and often contradictory among the studies [1,10,17-19,22]. In the present investigation we searched for prognostic relevant clinical and histopathological parameters in a molecular or immunohistochemical confirmed cohort of 57 EHE.
Large data with regard to optimal treatment strategy is limited. However, if possible surgical resection with wide margin should be performed [
8,
23]. More than half of our unifocal cases lacking sufficient surgical margins consequently showed progressive disease course. Based on three cases we also confirmed the importance of surgical interventions for the management of multifocal hepatic EHE [
24].
Tumor size and mitotic count appeared to be important predictive values and were both included in the risk stratification models of Shibayama et al. and Deyrup et al. [
10,
18]. However, the model of Shibayama et al. includes the size of multifocal lesions, assuming that a multifocal equals unifocal disease. One could argue that multifocal EHE is rather early metastatic disease than simultaneous independent origin of multiple lesions [
25,
26]. This is supported by our finding that there is no significant difference in survival between the groups of multifocal and metastatic disease. Still we could not statistically distinguish unifocal from multifocal disease. It might be that primary treatment is a confounder influencing survival, thereby affecting the statistical difference between both groups (uni- versus multifocal). Also the multifocal cohort size needs to be larger to perform proper (statistical) analysis because of the heterogeneity.
However, when assuming that multifocal EHE represent early metastases, it seems reasonable to enter only unifocal tumor size into a prognostic model. We replicated the risk stratification from Shibayama et al. on the unifocal EHE group and confirmed the prognostic value of tumor size and atypical histology [
18]. Both parameters were not independently associated with shorter survival, highlighting the limitation of our findings (data not published). Also, when creating a reliable diagnostic model ideally the whole tumor should be histologically assessed instead of limited tissue (mostly provided by external laboratories, at least in our study).
Our population showed a lower 1- and 5 year overall survival rate (69.6% and 50.5%, respectively) compared to most previous studies reporting 1- and 5-year overall survival rates between 89.0%-96.2% and 68.0%-78.8%, respectively [
1,
10,
18,
20,
27]. We are aware of the fact that EHE populations are always very heterogeneous and therefore difficult to compare. Unlike other publications Rosenbaum et al demonstrated survival rates similar to ours, based on a molecular confirmed EHE population including 93 cases [
17]. In both ours and Rosenbaum’s study population metastatic disease (syn- or metachronous) was seen in half of the cases, whereas EHE was initially thought to metastasize in only 20-30% of the cases [
9,
10,
17]. This higher mortality number might be affected by several reasons. First, our cohort is too small when heterogeneity with variable behavior is taken into account. Also, it might be possible that previous especially older studies accidently excluded atypical morphological cases mimicking angiosarcoma or other neoplasms when specific immunohistochemical and molecular analyses were lacking, whereas we confirmed the diagnoses in all cases molecularly/immunohistochemically reflecting possibly in lower overall survival rates. Furthermore, the majority of the cases were treated within an academic center, probably causing some bias with more complex cases including unifocal tumors without complete resection and with progressive disease course.
Due to the heterogeneity of the study population of Rosenbaum et al. and ours, no overlying factors affecting survival could be observed. Within our cohort there is, besides the high metastatic number of cases, no clear explanation or causal relation between different parameters and survival. Previous described clinical parameters related to worse outcome such as pulmonary and/or pleura involvement did not predominate within this cohort, suggesting that the aggressiveness is probably due to the tumor biology. It might be that secondary (epi)genetic alterations enhance tumor progression, displayed by a lower survival rate within our study [
28,
29].
We classified cases with lymph node metastases as a separate group. Regarding the literature, lymph node metastatic disease is rarely described in larger subsets or as solitary category [
17]. Despite our small number of cases with lymph node metastases, it is striking that lymph node involvement mainly occurred in tumors originating in the head and neck region. This is probably due to the close relationship of anatomic structures including naturally lymphatic vessels. Since lymph node metastases show significant poorer survival compared to unifocal disease, preventing lymph node spread by locoregional lymph node dissection should be recommended especially in the head and neck area [
17,
30]. When looking at the group with distant metastases at time of diagnosis, all cases showed either lung or liver involvement. It is hypothesized that these organs provide a fertile soil for metastatic disease because of its good vascularization [
31].
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, we performed a nationwide multi-center study in a heterogenous population of 57 EHE. We showed a 1- and 5-year overall survival rate that is approximately 20% lower compared to the average based on previous articles demonstrating the aggressive behavior of a subset of EHE. Risk stratification by Shibayama et al is a good predictor for unifocal disease [
18]. As expected, multifocality and metastatic behavior have an similar worse prognosis. Tumors of the head and neck have a relatively high propensity for lymph node metastases which should have clinical implications. Given the rarity of EHE, this study enriches the scarce literature.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.T., U.F., and J.G.; methodology, M.W.; software, T.T. and M.W.; validation, T.T.; formal analysis, T.T. and Y.V-J.; investigation, T.T., Y.V.-J., M.H.-R., P.C., T.D., I.D., U.F. and J.G.; resources, T.T., Y.V.-J., M.H.-R., P.C., T.D., I.D., U.F. and J.G.; data curation, T.T.; writing—original draft preparation, T.T., U.F. and J.G.; writing—review and editing, T.T.; visualization, T.T.; supervision, U.F. and J.G.; project administration, T.T.; funding acquisition; not applicable. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Ethics Committee of the Radboud University Medical Centre, Nijmegen, The Netherlands (File number 2018-4610).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The authors will provide the data when requested.
Acknowledgments
We wish to acknowledge the help provided by the Netherlands Cancer Registry (NCR) for obtaining a large nationwide cohort of EHE. We are very grateful to the PALGA (Dutch nationwide network and registry of histo- and cytopathology) – contributors for their collaboration. We also would like to sincerely thank the nationwide pathology laboratories for kindly providing FFPE material.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Lau, K.; Massad, M.; Pollak, C.; Rubin, C.; Yeh, J.; Wang, J.; Edelman, G.; Yeh, J.; Prasad, S.; Weinberg, G. Clinical patterns and outcome in epithelioid hemangioendothelioma with or without pulmonary involvement: insights from an internet registry in the study of a rare cancer. Chest 2011, 140, 1312-1318. [CrossRef]
- Tanas, M.R.; Sboner, A.; Oliveira, A.M.; Erickson-Johnson, M.R.; Hespelt, J.; Hanwright, P.J.; Flanagan, J.; Luo, Y.; Fenwick, K.; Natrajan, R.; Mitsopoulos, C.; Zvelebil, M.; Hoch, B.L.; Weiss, S.W.; Debiec-Rychter, M.; Sciot, R.; West, R.B.; Lazar, A.J.; Ashworth, A.; Reis-Filho, J.S.; Lord, C.J.; Gerstein, M.B.; Rubin, M.A.; Rubin, B.P. Identification of a disease-defining gene fusion in epithelioid hemangioendothelioma. Sci Transl Med 2011, 3, 98ra82. [CrossRef]
- Errani, C.; Zhang, L.; Sung, Y.S.; Hajdu, M.; Singer, S.; Maki, R.G.; Healey, J.H.; Antonescu, C.R. A novel WWTR1-CAMTA1 gene fusion is a consistent abnormality in epithelioid hemangioendothelioma of different anatomic sites. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2011, 50, 644-53. [CrossRef]
- Flucke, U.; Vogels, R.J.C.; de Saint Aubain Somerhausen, N.; Creytens, D.H.; Riedl, R.G.; van Gorp, J.M.; Milne, A.N.; Huysentruyt, C.J.; Verdijk, M.A.J.; van Asseldonk, M.M.; Suurmeijer, A.J.H.; Bras, J.; Palmedo, G.; Groenen, P.J.T.A.; Mentzel, T. Epithelioid Hemangioendothelioma: clinicopathologic, immunhistochemical, and molecular genetic analysis of 39 cases. Diagn Pathol 2014, 9, 131. [CrossRef]
- W.H.O. Classification of Soft Tissue and Bone Tumours, 5th ed. Vol 3; International Agency for Research on Cancer; Lyon, France, 2020; pp. 172-175.
- Cournoyer, E.; Al-Ibraheemi, A.; Engel, E.; Chaudry, G.; Stapleton, S.; Adams, D.M. Clinical characterization and long-term outcomes in pediatric epithelioid hemangioendothelioma. Pediatr Blood Cancer 2020, 67, e28045. [CrossRef]
- Orbach, D.; Van Noesel, M.M.; Brennan, B.; Corradini, N.; Alaggio, R.; Ben Arush, M.; Schoot, R.A.; Berlanga, P.; Zanetti, I.; Hjalgrim, L.L.; Di Corti, F.; Ramirez, G.; Casanova, M.; Ferrari, A. Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma in children: The European Pediatric Soft Tissue Sarcoma Study Group experience. Pediatr Blood Cancer 2022, 69, e29882. [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, A.; Agulnik, M. Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma: update on diagnosis and treatment. Curr treat options oncol 2018, 19, 19. [CrossRef]
- Weiss, S.W.; Enzinger, F.M. Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma: a vascular tumor often mistaken for a carcinoma. Cancer 1982, 50, 970–81.
- Deyrup, A.T.; Tighiouart, M.; Montag, A.G.; Weiss, S.W. Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma of soft tissue: a proposal for risk stratification based on 49 cases. Am J Surg Pathol 2008, 32, 924-7. [CrossRef]
- Kuo, F.; Huang, H.; Chen, C.; Eng, H.; Huang, C. TFE3-rearranged hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma – a case report with immunohistochemical and molecular study. AMPIS 2017, 125, 849-853. [CrossRef]
- Sardaro, A.; Bardoscia, L.; Petruzzelli, M.F.; Portaluri, M. Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma: an overview and update on a rare vascular tumor. Oncol rev 2014, 8, 259. [CrossRef]
- Shibuya, R.; Matsuyama, A.; Shiba, E.; Harada, H.; Yabuki, K.; Hisaoka, M. CAMTA1 is a useful immunohistochemical marker for diagnosing epithelioid haemangioendothelioma. Histopathol 2015, 67, 827-835. [CrossRef]
- Antonescu, C.R.; Le Loarer, F.; Mosquera, J.M.; Sboner, A.; Zhang, L.; Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Pathan, N.; Krausz, T.; Dickson, B.C.; Weinreb, I.; Rubin, M.A.; Hameed, M.; Fletcher, C.D.M. Novel YAP1-TFE3 fusion defines a distinct subset of epithelioid hemangioendothelioma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2013, 52, 775–84. [CrossRef]
- Doyle, L.A.; Fletcher, C.D.; Hornick, J.L. Nuclear expression of CAMTA1 distinguishes epithelioid hemangioendothelioma from histologic mimics. Am J Surg Pathol 2016, 40, 94–102. [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.; Kim, H.N.; Jang, Y.; Park, C.K.; Ha, S.Y. CAMTA-1 Expression in 24 Cases of Hepatic Epithelioid Hemangioendothelioma in a Single Institute: Diagnostic Utility for Differential Diagnosis from Hepatic Angiosarcoma. In vivo 2019, 33, 2293-2297. [CrossRef]
- Rosenbaum, E.; Jadeja, B.; Xu, B.; Zhang, L.; Agaram, N.P.; Travis, W.; Singer, S.; Tap, W.D.; Antonescu, C.R. Prognostic stratification of clinical and molecular epithelioid hemangioendothelioma subsets. Mod Pathol 2020, 33, 591-602. [CrossRef]
- Shibayama, T.; Makise, N.; Motoi, T.; Mori, T.; Hiraoka, N.; Yonemori, K.; Watanabe, S.I.; Esaki, M.; Morizane, C.; Okuma, T.; Kawai, A.; Ushiku, T.; Yatabe, Y.; Yoshida, A. Clinicopathologic Characterization of Epithelioid Hemangioendothelioma in a Series of 62 Cases: A Proposal of Risk Stratification and Identification of a Synaptophysin-positive Aggressive Subset. Am j surg pathol 2021, 45, 616-626. [CrossRef]
- Shiba, S.; Imaoka, H.; Shioji, K.; Suzuki, E.; Horiguchi, S.; Terashima, T.; Kojima, Y.; Okuno, T.; Sukawa, Y.; Tsuji, K.; Umemoto, K.; Asagi, A.; Todaka, A.; Ueno, M.; Ikeda, M.; Morizane, C.; Furuse, J. Clinical characteristics of Japanese patients with epithelioid hemangioendothelioma: a multicenter retrospective study. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 993. [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Li, B.; Zheng, C.; Hong, T.; He, X. Clinical characteristics of epithelioid hemangioendothelioma: a single-center retrospective study. Eur J Med Res. 2019, 24, 16. [CrossRef]
- Witte, S.; Weidema, M.; Kaal, S.; Versleijen-Jonkers, Y.; Flucke, U.; van der Graaf, W.; Desar, I. The heterogeneity of Epithelioid Hemangioendothelioma (EHE): A case series and review of the literature with emphasis on treatment options. Semin Oncol. 2021, 48, 111-118. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; He, S. Epithelioid Hemangioendothelioma: Incidence, Mortality, Prognostic Factors, and Survival Analysis Using the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Database. J Oncol. 2022, 2022:2349991. [CrossRef]
- Angelini, A.; Mavrogenis, A.F.; Gambarotti, M.; Merlino, B.; Picci, P.; Ruggieri, P. Surgical treatment and results of 62 patients with epithelioid hemangioendothelioma of bone. J Surg Oncol. 2014, 109, 791-7. [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, R.; Liu, Y.; Min, Q.; Zeng, Q.; Liu, J. Hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma a case report and literature review. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2023, 104, 107926. [CrossRef]
- Errani, C.; Sung, Y.S.; Zhang, L.; Healey, J.H.; Antonescu, C.R. Monoclonality of multifocal epithelioid hemangioendothelioma of the liver by analysis of WWTR1-CAMTA1 breakpoints. Cancer Genet. 2012, 205, 12-7. [CrossRef]
- Ramkumar, S. Epithelioid Haemangioma of Bone: A Case Series and Comprehensive Literature Review Reappraising the Diagnostic Classification of All Epithelioid Vascular Neoplasms of Bone. Cureus. 2021, 13, e15371. [CrossRef]
- Yurkiewicz, I.R.; Zhou, M.; Ganjoo, K.N.; Charville, G.W.; Bolleddu, S.; Lohman, M.; Bui, N. Management Strategies for Patients With Epithelioid Hemangioendothelioma: Charting an Indolent Disease Course. Am J Clin Oncol. 2021, 44, 419-422. [CrossRef]
- Seavey, C.N.; Hallett, A.; Li, S.; Che, K.; Pobbati, A.V.; Ma, S.; Burtscher, A.; Kanai, R.; Lamar, J.M.; Rubin, B.P. Loss of CDKN2A cooperates with WWTR1(TAZ)-CAMTA1 gene fusion to promote tumor progression in epithelioid hemangioendothelioma. Clin Cancer Res. 2023 CCR-22-2497. [CrossRef]
- Stacchiotti, S.; Tap, W.; Leonard, H.; Zaffaroni, N.; Baldi GG. New Molecular Insights, and the Role of Systemic Therapies and Collaboration for Treatment of Epithelioid Hemangioendothelioma (EHE). Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2023, 24, 667-679. [CrossRef]
- Naqvi, J.; Ordonez, N.G.; Luna, M.A.; Williams, M.D; Weber, R.S.; El-Naggar, A.K. Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma of the head and neck: role of podoplanin in the differential diagnosis. Head Neck Pathol. 2008, 2, 25-30. [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, A.S.; Follain, G.; Patthabhiraman, S.; Harlepp, S.; Goetz, J.G. Metastasis of circulating tumor cells: favorable soil or suitable biomechanics, or both? Cell Adh Migr. 2015, 5, 345-56. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).