Submitted:
05 June 2023
Posted:
05 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
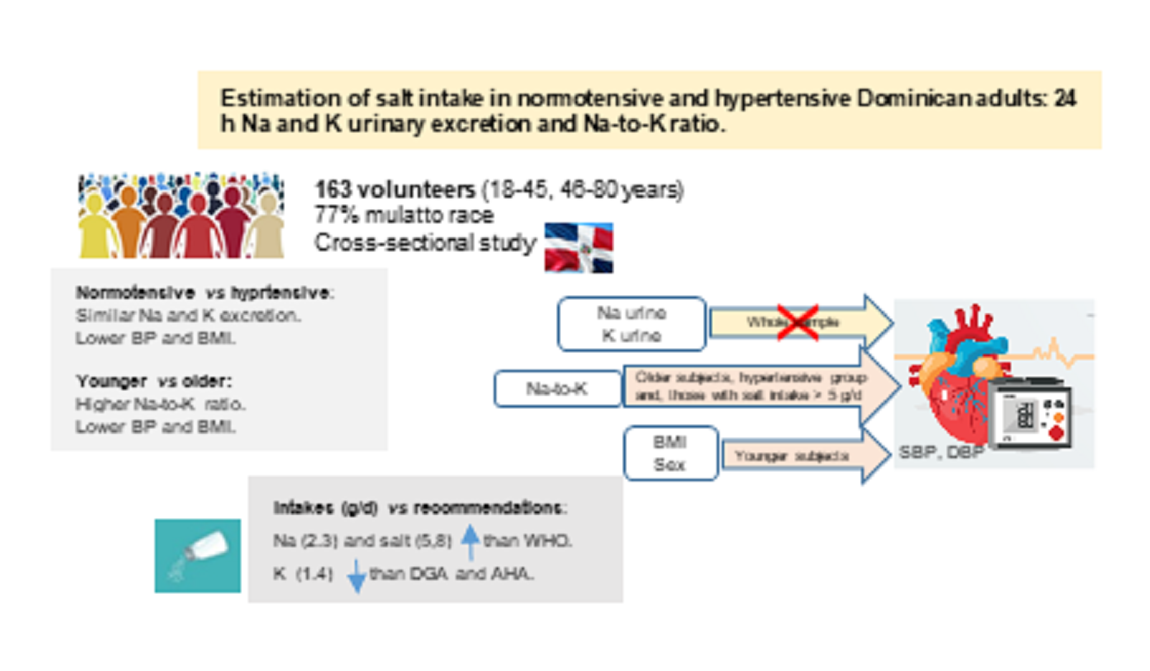
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Materials and Methods
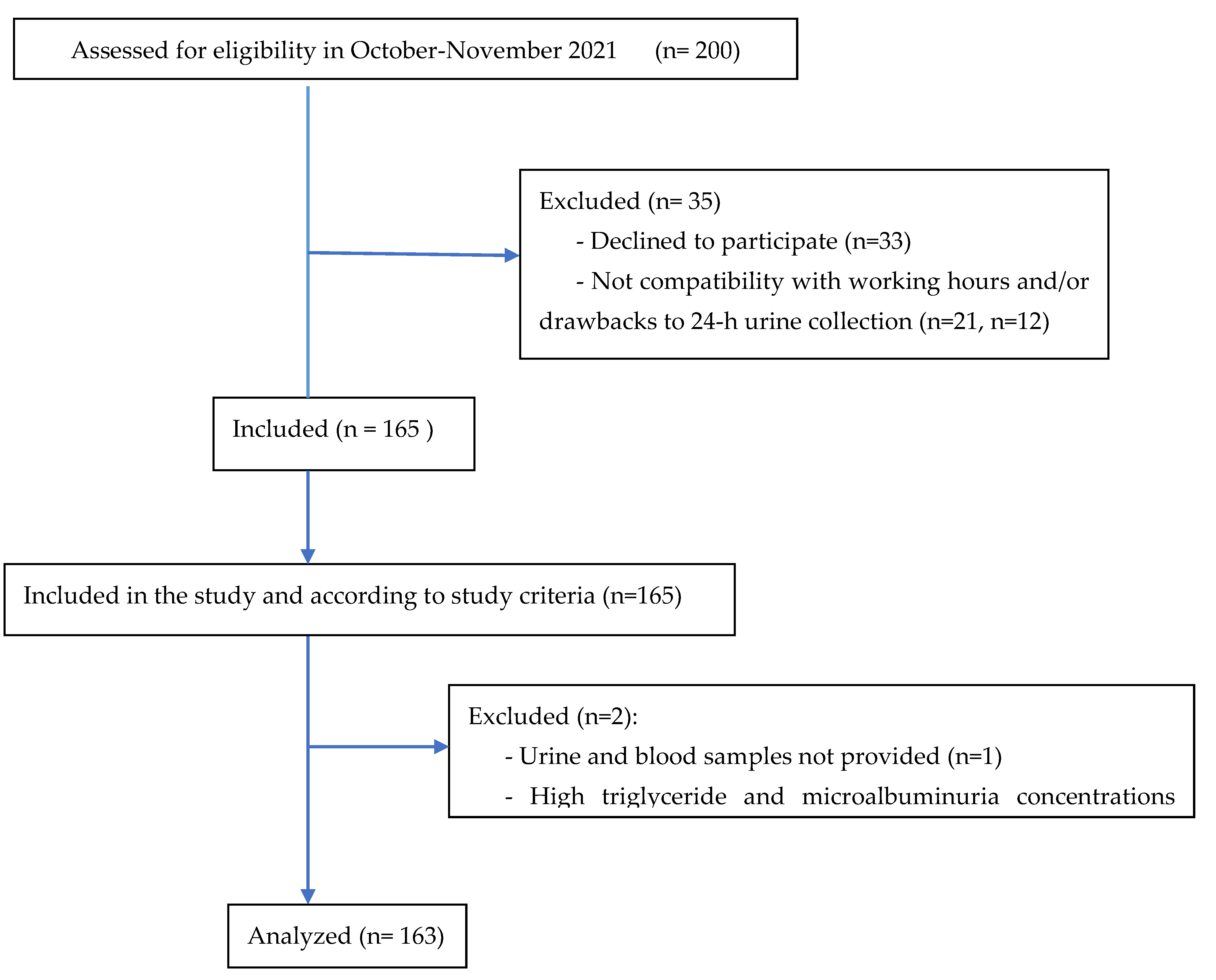
Subjects and Study Design
Anthropometric and Blood Pressure Measurements
Urine and Blood Samples
Statistical Analysis
Results
Discussion
Urinary Sodium and Potassium Excretion
Estimated Sodium, Salt and Potassium Intake: Comparison with Recommended Intake
Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McGuire: S. Institute of Medicine. 2013. Sodium intake in populations: Assessment of evidence. Adv Nutr 2014, 5, 19–20. [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.W.; Baqar, S.; Jerums, F.; Ekinci, E.I. Sodium and its role in cardiovascular disease - the debate continues. Front Endocrinol 2016, 7, 164. [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; He, F.J.; Sun, Q.I.; Changzheng, Y.; Kieneker, L.M.; Curhan, G.C.; et al. Urinary sodium and potassium excretion and cardiovascular risk. N Engl J Med 2022, 386, 252–263. [CrossRef]
- He, F.J.; Li, J.; Macgregor, G.A. Effect of longer term modest salt reduction on blood pressure: Cochrane systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised trials. Brit Med J 2013; 3: 346, 1325. [CrossRef]
- Morrissey, E.; Giltinan, M.; Kehoe, L.; Nugent, A.P.; McNulty, B.A.; Flynn, A.; et al. Sodium and potassium intakes and their ratio in adults (18-90 y): Findings from the Irish National Adult Nutrition Survey. Nutrients 2020, 12, 938. [CrossRef]
- Langford, H.G. Dietary potassium and hypertension: epidemiologic data. Ann Intern Med 1983, 98, 770–772. [CrossRef]
- Sacks, F.M.; Svetkey, L.P.; Vollmer, W.M.; Appel, L.J.; Bray, G.A.; Harsha, D.; et al. Effects on blood pressure of reduced dietary sodium and the Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet. DASH-Sodium collaborative Research Group. N Engl J Med 2001, 34, 3–10. [CrossRef]
- Mente, A.; Martin, J.; O’Donnell, M.J.; Rangarajan, S.; McQueen, M.J.; Poirier, P.; et al. for the PURE investigators. Association of urinary sodium and potassium excretion with blood pressure. N Engl J Med 2014, 371, 601–611. [CrossRef]
- Perez, V.; Chang, E.T. Sodium-to-potassium ratio and blood pressure, hypertension, and related factors. Adv Nutr 2014, 5, 712–741. [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kwock, C.K.; Yan, Y.J. The effect of the sodium to potassium ratio on hypertension prevalence: A propensity score matching approach. Nutrients 2016, 8, 482. [CrossRef]
- Iwahori, T.; Miura, K.; Ueshima, H. Time to consider use of the sodium-to-potassium ratio for practical sodium reduction and potassium increase. Nutrients 2017, 8, 700. [CrossRef]
- Athanasatou, A.; Kandyliari, A.; Malisova, O.; Pepa, A.; Kapsokefalou, M. Sodium and Potassium Intake from Food Diaries and 24-h Urine Collections from 7 Days in a Sample of Healthy Greek Adults. Front Nutr 2018, 5, 13. [CrossRef]
- Nohara-Shitama, Y.; Adachi, H.; Enomoto, M.; Fukami, A.; Kumagai, E.; Nakamura, S.; et al. Twenty-four-hour urinary potassium excretion, but not sodium excretion, is associated with all-cause mortality in a general population. J Am Heart Assoc 2018, 7, e007369. [CrossRef]
- Bhagavathula, A.S.; Refaat, S.A.; Bentley, B.L.; Rahmani, J. Association between intake of sodium, potassium, sodium-to-potassium ratio, and blood pressure among US adults. Int J Vitam Nutr Res 2021, 1-9. [CrossRef]
- Willey, J.; Gardener, H.; Cespedes, S.; Cheung, Y.K.; Sacco, R.L.; Elkind, M.S.V. Dietary sodium to potassium ratio and risk of stroke in a multiethnic urban population. The Northern Manhattan Study. Stroke 2017, 48, 2979–2983. [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Huang, X.; Liu, X.; Wang, L.; Chen, Z.; Ortega, D.; et al. Urinary sodium and potassium excretion and cerebrovascular health: a multimodal imaging study. Eur J Nutr 2021, 60, 4555–4563. [CrossRef]
- WHO. World Health Organization. Hypertension. 2021. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hypertension (accessed on 20 February 2023.
- American Diabetes Association, Bantle, J.P.; Wylic-Rosett, J.; Albright, A.L.; Apovian, C.M.; Clark, N.G.; Franz, M.J.; et al. Nutrition recommendations and interventions for diabetes: a position statement of the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care 2008, 31, S61–S78. [CrossRef]
- Lloyd-Jones, D.M.; Hong, Y.; Labarthe, D.; Mozaffarian, D.; Appel, L.J.; Van Horn, L.; et al. Defining and setting national goals for cardiovascular health promotion and disease reduction: the American Heart Association’s strategic Impact Goal through 2020 and beyond. Circulation 2010, 121, 586–613. [CrossRef]
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO). CKD Work Group, KDIGO 2012 clinical practice guideline for the evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int Suppl 2013, 3, 1–150.
- WHO. Sodium intake for adults and children. Geneve: WHO, 2012. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/77985/9789241504836_eng.pdf (accessed on 20 February 2023).
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services and U.S. Department of Agriculture. 2015 – 2020 Dietary Guidelines for Americans. 8th Edition. December 2015. Available online: https://health.gov/our-work/food-nutrition/previous-dietary-guidelines/2015 (accessed on 20 February 2023).
- EFSA NDA Panel (EFSA Panel on Nutrition, Novel Foods and Food Allergens), Turck, D.; Castenmiller, J.; de Henauw, S.; Hirsch-Ernst, H.; Kearney, J.; Maciuk, A.; et al. Scientific Opinion on the dietary reference values for sodium. EFSA J 2019, 17, 5778.
- 24. AHA, American Heart Association. Available online: https://www.heart.org/en/healthy-living/healthy-eating/eat-smart/sodium/how-much-sodium-should-i-eat-per-day (accessed on 20 February 2023).
- Aparicio, A.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, E.; Cuadrado-Soto, E.; Navia, B.; López-Sobaler, A.M.; Ortega, R.M. Estimation of salt intake assessed by urinary excretion of sodium over 24 h in Spanish subjects aged 7-11 years. Eur J Nutr 2017, 56, 171–178. [CrossRef]
- Ortega, R.M.; López-Sobaler, A.M.; Ballesteros, J.M.; Pérez-Farinós, N.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, E.; Aparicio, A.; et al. Estimation of salt intake by 24 h urinary sodium excretion in a representative sample of Spanish adults. Brit J Nutr 2011, 105, 787–794. [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Reducing Salt Intake in Populations: Report of a WHO Forum and Technical Meeting, 5–7 October 2006, Paris, France. Geneva: WHO, 2007.
- WHO/PAHO regional expert group for cardiovascular disease prevention through population-wide dietary salt reduction. Protocol for population level sodium determination in 24-hour urine samples. May, 2010. Available online: https://www.paho.org/hq/dmdocuments/2013/24h-urine-Protocol-eng.pdf (accessed on 20 February 2023).
- PAHO. Mapping Dietary Salt/Sodium Reduction Policies and Initiatives in the Region of the Americas. Washington, D.C.: Pan American Health Organization; 2021.
- MISPAS. Ministerio de Salud Pública y Asistencia Social, Gobierno de la República Dominicana. 1era Jornada Nacional de Hipertensión Arterial: Prevención de diabetes y obesidad. Informe de resultados. Santo Domingo D.N. Octubre, 2021.
- PAHO (PanAmerican Health Organization). Plan of Action for the Prevention and Control of Noncommunicable Diseases in the Americas 2013-2019. Washington, DC: OPS, 2014. Available online: https://www.paho.org/hq/dmdocuments/2014/NCD-SP-low.pdf (accessed on 20 February 2023).
- 32. Williams, B.; Mancia, G.; Spiering, W.; Rosei, E.Z.; Azizi, M.; Burnier, M.; et al. Guía ESC/ESH 2018 sobre el diagnóstico y tratamiento de la hipertensión arterial. Rev Esp Cardiol 2019, 72, 160e1–e78.
- PAHO. Hypertension. Available online: https://www.paho.org/en/topics/hypertension (accessed on 20 February 2023).
- Whelton, P.K.; Caarey, R.M.; Mancia, G.; Kreutz, R.; Bundy, J.D.; Williams, B. Harmonization of the American College of Cardiology/ American Heart Association and European Society of Cardiology / European Society of Hypertension Blood Pressure /Hypertension Guidelines. Eur Heart J 2022, 43, 3302–3311. [CrossRef]
- PAHO. Consumers International. Cuestionario sobre conocimiento, actitud, comportamiento acerca de la sal dietética y la salud. Available at: https://www.paho.org/hq/dmdocuments/2013/Knowledge-behaviour-questionaire-salt-Spa.pdf Accessed: 2 March 2023.
- Mosteller, R.D. Simplified calculation of body-surface area. N Engl J Med 1987, 317, 1098. [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, T.; Itoh, K.; Uezono, K.; Sasaki, H. A simple method for estimating 24 h urinary sodium and potassium excretion from second morning voiding urine specimen in adults. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol, 1993,20,7-14. [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.; Lee, J.; Koo, H.S.; Kim, S.; Chin, H.J. Estimated 24-hour urine sodium excretion is correlated with blood pressure in korean population: 2009-2011 Korean National Health and Nutritional Examination Survey. J Korean Med Sci 2014, 29, S109–S116. [CrossRef]
- Pichardo, R.; González, A.R.; Ramírez, W.; et al. Estudio de los factores de riesgo cardiovascular y síndrome metabólico en la República Dominicana. EFRICARD II. Rev Domin Cardiol 2012, 1, 36–55. Available online: https://static.elsevier.es/cardio/static/premio_cardio/revista-dominicana-cardiologia.pdf (accessed on 20 February 2023).
- Paulino-Ramirez, R.; Oakley, E.; Vega, B.; Vilar, M.G.; Mencía-Ripley, A.; Tapia, L.; et al. Diversidad genética en ADN mitocondrial en la República Dominicana: Implicaciones para la historia y demografía de La Española. CLÍO 2019, 88, 193–206.
- Consejo de Ministros de Salud de Centroamérica y República Dominicana (COMISCA), INCAP / OPS-OMS. Instituto de Nutrición de Centro América y Panamá / organización Panamericana de la salud / organización mundial de la salud / consejo de Ministros de Salud de Centroamérica y República dominicana. Estrategia regional para la reducción del consumo de sal y sodio en Centroamérica y República Dominicana. Enero 2019. Available online: http://www.incap.int/index.php/es/noticias/145-estrategia-regional-para-la-reduccion-del-consumo-de-sal-y-sodio-en-centroamerica-y-republica-dominicana (Accessed on 20 February 2023).
- Vasara, E.; Marakis, G.; Breda, J.; Skepastianos, P.; Hassapidou, M.; Kafatos, A.; Rodopaios, N.; Koulouri, A.A.; Cappucio, F.P. Sodium and Potassium Intake in Healthy Adults in Thessaloniki Greater Metropolitan Area—The Salt Intake in Northern Greece (SING) Study, Nutrients, 2017; 9:417. [CrossRef]
- Meyer, H.E.; Johansson, L.; Eggen, A.E.; Johansen, H.; Holvik, K. Sodium and potassium intake assessed by spot and 24-h urine in the population-based TromsØ study 201-2016. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1619. [CrossRef]
- Cogswell, M.W.; Loria, C.M.; Terry, A.L.; Zhao, L.; Wang, C.-Y.; Chen, T-C.; et al. Estimated 24-hour urinary sodium and potassium excretion in US adults. JAMA 2018, 319, 1209–1220. [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, P.; Li, Y.; He, F.J.; Wu, J.; Xu, J.; et al. Association of sodium, potassium and sodium-to-potassium ratio with urine albumin excretion among the general Chinese population. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3456. [CrossRef]
- Trieu, K.; Ospanova, F.; Tazhibayev, S.; Jewell, J.; Breda, J.; Santos, J.A.; et al. Sodium and potassium intakes in the Kazakhstan population estimated using 24-h urinary excretion: evidence for national action. Eur J Nutr 2021, 60, 1537–1546. [CrossRef]
- Moliterno, P.; Álvarez-Vaz, R.; Pécora, M.; Luzardo, L.; Borgarello, K.; Olascoaga, A.; et al. Blood pressure in relation to 23-hour urinary sodium and potassium excretion in a Uruguayan population sample. Int J Hypertens 2018, 6956078. [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Yu, P.; Yuan, Y.; Li, Q.; Lin, F.; Gao, Z.; et al. The relationship between sodium excretion and blood pressure, urine albumin, central retinal arteriolar equivalent. BMC Cardiovasc Disord 2016, 16, 194. [CrossRef]
- Durán-Cabral, M.; Fernández-Jalao, I.; Estévez-Santiago, R.; Olmedilla-Alonso, B. Assessment of individual carotenoid and vitamin A dietary intake in overweight and obese Dominican subjects. Nutr Hosp 2017, 34, 407–415. [CrossRef]
- Del Rosario, P. El consumo de alimentos en República Dominicana. Instituto Dominicano de Investigaciones Agropecuarias y Forestales (IDIAF). Santo Domingo, DO. 2021.
- Johnson, C.; Mohan, S.; Rogers, K.; Shivashankar, R.; Thout, S.R.; Gupta, P.; et al. Mean dietary salt intake in urban andrural areas in India: A population survey of 1395 persons. J Am Heart Assoc 2017, 6, e004547.
- McLean, R.M. Measuring population sodium intake: A review of methods. Nutrients 2014, 6: 4651-4662. [CrossRef]
- Mannheimer, B.; Sterea-Grossu, A.; Falhammar, H.; Calissendorff, J.; Skov, J.; Lindh, J.D. Current and future burdens of heat-related hyponatremia: A nationwide register-based study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2022, 107, e2388–e2393. [CrossRef]
- EFSA NDA Panel (EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies), Turck, D.; Bresson, J-L.; Burlingame, B.; Dean, T.; Fairweather-Tait, S.; Heinonen, M.; et al. Scientific opinion on dietary reference values for potassium. EFSA J. 2016, 14, 459.
- Huang. L.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Ding, G. Associations of dietary sodium, potassium, and sodium to potassium ratio with blood pressure – regional disparities in China. Nutrients 2020, 12, 366.
- López, P.; Pérez, W. Situación del consumo de sal y sodio en Centroamérica y República Dominicana. INCAP. Notas Técnicas PP/NT/079. 2018. Available online: http://www.incap.int/index.php/es/publicaciones-destacadas/218-situacion-consumo-sal-sodio-2018 (accessed on 20 February 2023).
- EFSA NDA Panel (EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies), Bresson, J.L.; Burlingame, B.; Dean, T.; Fairweather-Tait, S.; Heinonen, M.; Hirsch-Ernst, K.I.; et al. Scientific opinion on dietary reference values for potassium. EFSA J 2016, 14, 4592.
- WHO, 2020. Salt reduction. Key facts (29 April 2020). Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/salt-reduction (accessed on 20 February 2023).
- AHA, American Heart Association. How potassium can help control high blood pressure. Available online: https://www.heart.org/en/health-topics/high-blood-pressure/changes-you-can-make-to-manage-high-blood-pressure/how-potassium-can-help-control-high-blood-pressure (accessed on 20 February 2023).
| Age (years) | 44.5 ± 14.6 (18 – 80) |
| Sex | Men 78 / women 85 |
| Race | Mix-race (mulatto) 125 / Black 21 / White 15 / Asian 2 |
| Diabetes | No 143 (87.7%) / yes 20 (12.3%) |
| Normotensive / Hypertensive | 88 / 75 |
| Total sample (n=163) | Normotensive (n=88) |
Hypertensive (n=75) |
P value | 18–45 years (n=84) (normotensive=64, hypertensive=20) |
46–80 years (n=79) (normotensive=24, hypertensive=55) |
P value |
||
| Systolic blood pressure (mm Hg) | 126.2 ± 21.1 [123.3] | 116.3 ± 11.8 [115.8] | 138.0 ± 23.4 [135] |
0.000 | 119.3 ± 15.5 [120.2] |
133.7 ± 23.6 [128.6] |
<0.001 | |
| Diastolic blood pressure (mm Hg) | 81.2 ± 11.2 [81.0] |
76.6 ± 7.3 [76.6] |
86.7 ± 12.5 [87.3] |
<0.001 | 78.7 ± 10.6 [77.6] |
84.0 ± 11.2 [83.6] |
0.001 | |
| Heart rate (bpm) | 71.3 ± 10.2 [71.6] |
71.0 ± 9.8 [70.8] |
71.5 ± 10.8 [72.0] |
0.826 | 72.2 ±10.7 [73.0] |
70.2 ± 9.7 [69.3] |
0.077 | |
| Anthropometric measurementes | ||||||||
| Height (cm) | 166.3 ± 10.0 [165.5] | 167.8 ± 10.6 [166.2] | 164.6 ± 9.1 [164.1] | 0.072 | 169.2 ± 10.3 [169.0] |
163.2 ± 8.8 [162.0] |
<0.001 | |
| Weight (kg) | 80.6 ± 16.0 [79.7] |
79.0 ± 17.6 [77.8] |
82.4 ± 13.9 [83.1] |
0.054 | 81.8 ± 18.1 [79.1] |
79.4 ± 13.4 [80.0] |
0.717 | |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 29.1 ± 4.8 [28.6] |
27.9 ± 4.7 [27.1] |
30.5 ± 4.6 [30.4] |
<0.001 | 28.4 ± 4.8 [27.4] |
29.9 ± 4.7 [29.6] |
0.031 | |
| Waist (cm) | 95.9 ± 12.3 [95.0] |
92.7 ± 12.0 [92.8] |
99.5 ± 11.7 [99.0] |
<0.001 | 93.0 ± 12.2 [92.8] |
98.9 ± 11.8 [98.0] |
<0.001 | |
| Hip (cm) | 107.5 ± 9.0 [107.0] | 106.3 ± 9.4 [104.0] | 108.9 ± 8.5 [109.0] | 0.015 | 106.5 ± 9.2 [104.2] |
108.4 ± 8.8 [108.5] |
0.081 | |
| Waist - hip ratio | 0.89 ± 0.08 [0.89] |
0.87 ± 0.07 [0.87] |
0.91 ± 0.07 [0.92] |
<0.001 | 0.87 ± 0.07 [0.88] |
0.91 ± 0.08 [0.91] |
0.002 | |
| Body fat (%) | 36.3 ± 9.8 [35.4] |
34.8 ± 9.6 [33.3] |
38.1 ± 9.8 [40.3] |
0.019 | 34.1 ± 9.7 [31.5] |
38.7 ± 9.4 [40.0] |
0.002 | |
| Visceral fat (%) | 10.6 ± 4.2 [10.0] |
9.2 ± 3.8 [9.0] |
12.1 ± 4.0 [11.5] |
<0.001 | 9.3 ± 4.0 [9.0] |
11.8 ± 3.9 [11.0] |
<0.001 | |
| Muscle mass (%) | 28.5 ± 5.9 [28.0] |
29.4 ± 6.4 [28.8] |
27.4 ± 5.1 [27.6] |
0.038 | 30.0 ± 6.2 [30.9] |
26.9 ± 5.3 [25.9] |
<0.001 | |
| Urine (24-h) | ||||||||
| Volume (mL) | 1775.2 ± 819.1 [1740.0] | 1709.4 ± 842.7 [1680] | 1833.4 ± 777.2 [1780] | 0.257 | 1732.0 ± 839.2 [1575.0] | 1821.0 ± 800.0 [1850] | 0.367 | |
| Creatinine (mmol) | 12.4 ± 5.3 [11.5] |
13.3 ± 5.3 [11.5] |
11.5 ± 3.5 [11.5] |
0.493 | 14.8 ± 8.3 [14.1] |
12.0 ± 3.6 [11.2] |
<0.001 | |
| Endogenus creatinine clearance (ECC) (mL/min) | 108.7 ±35.7 [105.3] | 113.5 ± 37.1 [115.3] | 103.4 ± 33.4 [101.9] | 0.089 | 118.0 ±35.8 [120.7] |
98.8 ± 33.0 [97.1] |
<0.001 | |
| ECC corrected by surface area (ECC-c) (mL/min) | 100.9 ± 30.6 [102.3] | 105.4 ± 30.1 [105.6] | 96.3 ± 30.3 [96.9] | 0.041 | 107.7 ± 30.5 [109.3] |
93.6 ± 29.2 [93.1] |
<0.001 | |
| Sodium (mmol) | 99.4 ± 46.5 [89.0] |
100.8 ± 47.3 [96.5] | 97.9 ± 46.1 [84.5] | 0.670 | 105.4 ± 46.8 [98.5] |
92.9 ± 45.5 [81.0] |
0.058 | |
| Potassium (mmol) | 35.0 ± 17.5 [31.0] |
37.8 ± 20.2 [33.2] |
31.8 ± 13.1 [29.0] | 0.123 | 35.2 ± 17.6 [31.0] |
34.8 ± 17.5 [31.2] |
0.976 | |
| Sodium : potassium ratio 1 | 3.1 ± 1.3 [2.9] |
3.0 ± 1.3 [2.9] |
3.2 ± 1.3 [3.0] |
0.255 | 3.3 ± 1.3 [3.1] |
2.9 ± 1.1 [2.9] |
0.040 | |
| Na : creatinine ratio | 9.1 ± 6.1 [7.4] |
9.4 ± 7.0 [6.8] |
8.8 ± 4.8 [7.8] |
0.562 | 9.1 ± 6.7 [6.4] |
9.1 ± 5.4 [8.0] |
0.273 | |
| K : creatinine ratio | 3.2 ± 2.3 [2.7] |
3.5 ± 2.8 [2.7] |
2.9 ± 1.5 [2.6] |
0.067 | 3.0 ±2.3 [2.4] |
3.5 ± 2.4 [3.0] |
0.013 | |
| Microalbumin (mg) | 10.4 ± 27.9 [4.8] |
7.0 ± 16.2 [4.3] |
14.4 ± 37.0 [5.5] |
0.005 | 11.0 ±33.8 [4.5] |
9.7 ± 20.0 [5.2] |
0.616 | |
| Blood | ||||||||
| Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 193.0 ± 47.4 [189.7] | 194.8 ± 48.0 [190.5] | 190.6 ± 47.3 [189.6] | 0.687 | 188.4 ± 44.5 [185.2] |
198.3 ± 50.3 [198.7] |
0.258 | |
| HDL-cholesterol (mg/dL) | 48.8 ± 14.6 [46.5] |
51.4 ± 13.3 [49.1] |
45.9 ± 15.7 [42.8] | 0.002 | 50.6 ± 12.7 [48.7] |
47.2 ± 16.5 [44.6] |
0.051 | |
| LDL-chol.(mg/dL) | 122.2 ± 42.6 [42.6] | 123.4 ± 43.9 [122.5] | 120.7 ± 41.3 [125.5] | 0.844 | 118.3 ± 42.8 [121.0] |
126.7 ± 42.3 [127.0] |
0.338 | |
| VLDL-cholesterol (mg/dL) | 21.9 ± 11.1 [19.5] |
20.2 ± 10.8 [17.9] |
24.0 ± 11.2 [20.6] | 0.006 | 19.6 ± 11.2 [14.6] |
24.5 ± 10.5 [22.3] |
<0.001 | |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 111.6 ± 60.6 [97.3] |
101.0 ± 54.2 [89.3] | 120.1 ± 55.8 [103.0] | 0.004 | 98.0 ± 56.2 [73.2] |
122.5 ± 52.7 [111.3] |
<0.001 | |
| Total cholesterol / HDL-chol. | 4.3 ± 2.2 [4.1] |
4.0 ± 1.2 [3.8] |
4.7 ± 3.0 [4.3] |
0.032 | 3.9 ± 1.3 [3.8] |
4.8 ± 2.9 [4.5] |
0.008 | |
| LDL-chol / HDL-chol. | 2.8 ± 2.0 [2.6] |
2.6 ± 1.0 [2.4] |
3.1 ± 2.6 [2.8] |
0.140 | 2.5 ± 1.1 [2.3] |
3.1 ± 2.5 [2.8] |
0.030 | |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.92 ± 0.28 [0.87] |
0.88 ± 0.22 [0.85] |
0.96 ± 0.34 [0.92] | 0.137 | 0.94 ± 0.29 [0.93] |
0.90 ± 0.28 [0.85] |
0.267 | |
| Glucaemia (mg/dL) | 103.5 ± 31.1 [97.1] | 97.5 ± 25.1 [95.8] |
110.5 ± 35.9 [99.4] | 0.010 | 95.1 ± 14.5 [93.3] |
112.4 ± 40.4 [100.4] |
0.001 | |
| Total group (n=163) | 18 - 45 years (n=84) 46-80 years (n= 79) | Normotensive Hypertensive | |||||||
| SBP | DBP | SBP | DBP | SBP | DBP | SBP DBP | |||
| Waist – hip index | 0.432 (<0.001) | 0.259 (<0.001) | 0.508 (<0.001) | 0.316 (0.003) | 0.249 (0.027) | ||||
| BMI | 0.367 (<0.001) | 0.261 (<0.001) | 0.374 (<0.001) | 0.326 (0.002) | 0.264 (0.019) | ||||
| Body fat | 0.196 (0.013) | ||||||||
| Muscle mass | 0.333 (0.002) | ||||||||
| Visceral fat | 0.492 (<0.001) | 0.293 (<0.001) | 0.559 (<0.001) | 0.318 (0.003) | 0.294 (0.009) | ||||
| Sodium | |||||||||
| Potassium | 0.249 (0.019) | ||||||||
| Soldium /Potassium 1 | 0.153 (0.052) | 0.350 (0.002) | 0.373 (<0.001) | 0.395 (<0.001) | |||||
| Sodium/ creatinine | 0.241 (0.032) | ||||||||
| Potassium / creatinine | |||||||||
| Creatinine 24h-urine | 0.429 (<0.001) | ||||||||
| Microalbumin | 0.219 (0.005) | 0.187 (0.017) | 0.262 (0.016) | 0.269 (0.013) | |||||
| HDL-cholesterol | -0.230 (0.003) | - 0.357 (<0.001) | |||||||
| LDL-cholesterol | 0.155 (0.049) | ||||||||
| VLDL | 0.269 (<0.001) | 0.203 (0.010) | 0.216 (0.049) | ||||||
| TG | 0.282 (<0.001) | 0.217 (0.005 ) | 0.226 (0.038) | 0.243 (0.026) | |||||
| Chol. (total) /HDL | 0.303 (<0.001) | 0.373 (<0.001) | |||||||
| LDL / HDL | 0.259 (<0.001) | 0.333 (0.002) | |||||||
| Creatinine (serum) | 0.326 (<0.001) | 0.507 (<0.001) | 0.239 (0.034) | ||||||
| CCE-c | - 0.195 (0.013) | - 0.185 (0.018) | |||||||
| Systolic blood pressure | ||||||
| beta | S.E. | p | 95% CI | |||
| 18-45 years | Constant | 114.4 | 4.8 | 0.000 | 105.0 , 123.8 | |
| Sex (man) | 14.02 | 2.87 | < 0.001 | 8.40 , 19.64 | ||
| Sex (woman) | 0 | |||||
| BMI -normoweight | -12.07 | 3.72 | 0.001 | -19.35 , -4.79 | ||
| BMI - overweight | - 10.7 | 3.2 | <0.001 | -16.95 , -4.49 | ||
| BMI- obese | 0 | |||||
| 46- 80 years | Constant | 118.6 | 7.7 | 0.000 | 103.6 , 133.6 | |
| Sodium-to-potassium ratio | 6.7 | 2.4 | 0.005 | 2.07 , 11.34 |
||
| Diastolic blood pressure | ||||||
| beta | S.E. | P | 95% IC | |||
| 18-45 years | Constant | 78.3 | 3.7 | 0.000 | 71.1 , 85.5 | |
| BMI-normoweight | -9.44 | 2.87 | 0.001 | - 3.8 , 10.8 | ||
| BMI-overweight | -5.1 | 2.5 | 0.039 | -9.9 , -0.26 | ||
| BMI- obese | 0 | |||||
| 46- 80 years | Constant | 73.4 | 3.6 | 0.000 | 66.4 , 80.4 | |
| Sodium-to-potassium ratio | 3.8 | 1.1 | < 0.001 | 1.6 , 5.9 | ||
| Sodium intake (g/day) | Salt intake (g/day) | Potassium intake (g/day) | Dietary Na : K (g) | |
| Total sample (n=163) Normotensive (n=88) Hypertensive (n=75) |
2.29 ± 1.07 [2.05] 2.32 ± 1.09 [2.22] 2.25 ± 1.06 [1.94] |
5.8 ± 2.7 [5.2] 5.9 ± 2.8 [5.6] 5.7 ± 2.7 [4.9] |
1.37 ± 0.68 [1.21] 1.47 ± 0.79 [1.30] a 1.24 ± 0.51 [1.17] |
1.7 1.6 1.82 |
| Aged 18-45 years Normotensive (n=64) Hypertensive (n=20) |
2.45 ± 1.12 [2.36] 2.32 ± 0.94 [2.16] |
6.2 ± 2.9 [6.0] 5.9 ± 2.4 [5.5] |
1.43 ± 0.73 [1.24] 1.19 ± 0.52 [1.03] |
1.7 2 |
| Aged 46- 80 years Normotensive (n= 24) Hypertensive (n= 55) |
1.95 ± 0.92 [1.85] 2.22 ± 1.10 [1.91] |
5.0 ± 2.3 [4.7] 5.6 ± 2.8 [4.8] |
1.60 ± 0.94 [1.36] b 1.26 ± 0.52 [1.20] |
1.22 1.76 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





