1. Introduction
The incidence of infections caused by antibiotic-resistant bacteria has increased over the last decades and it is more and more recognized as a global health problem, to an extent that the name “silent pandemic” has been used [
1,
2]. Especially, hospital-acquired infections represent a pressure on the health care system, due to the increased mortality, hospitalization time, and healthcare costs [
3,
4]. Surgical site infections (SSI) occur in about 2% of all surgeries and make up at least 20% of all nosocomial infections [
5]. On the other side, infections can cause considerable complications in the treatment of chronic wounds leading to prolonged and cost-intensive treatments [6-8]. The prevalence of all chronic wounds is estimated to be of 2.21 per 1000 population while the prevalence of chronic leg ulcers is of 1.51 per 1000 population [
9]. Notably, these numbers are going to increase dramatically due to the demographic growth of the elderly population [
10]. The annual costs estimation for acute and chronic wound treatments in the USA made by Medicare in 2014 ranged from
$28.1 billion to
$96.8 billion [
11].
Consequently, new prevention strategies and more affordable treatments against wound infections are urgently needed. Topically applied antiseptics would be of advantage due to the rapid onset of the treatment and high local drug concentrations avoiding systemic toxicity. Importantly, in order to prevent the formation of antibiotic resistant strains and to reach biofilm-associated bacteria, a sufficiently high concentration of antibiotic should be ensured [
12]. Difficulties often lie in the form of application, with liquid formulations drying out and ointments being poorly distributed. The modern treatment of chronic wounds includes wound dressings as a therapeutic principle. Conventional, occlusive wound dressings (e.g., made of gauze) can create an anaerobic wound environment and promote the spread of pathogens. In comparison, hydroactive wound dressings ensure a moist wound environment and an exchange of water and oxygen, which contributes to accelerate the wound healing process. Currently, there are only few examples of wound dressings with antimicrobial properties. Silver-based materials are the most used local treatments of wound infections. Such dressings can efficiently prevent infections; however, they are expensive and not free from safety and environment related concerns. In addition, reports on silver-resistant bacteria are increasing [13-15]. Novel biomaterials like nanofibers, hydrogels, films made of alginate, chitosan, collagen etc., can also be combined with antimicrobial agents or other substances relevant to wound healing and thus ensure the treatment and closure of infected wounds within one application [
16,
17]. Such dressings may represent very attractive alternative options to oral antibiotic therapies. . Among the several wound dressings presented in the literature, dressings based on pol-yvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) showed promising results in the management of infected and unhealed wounds [
18]. This polymer can ensure a high level of bio- and hemo- com-patibility, adhesion properties comparable to commercial patches, excellent water absorption, and controllable release of drugs when combined with other polymers [
19].
In general, to test the antimicrobial efficacy of newly developed dressing materials,
in vivo rodent models are used. However, beside the fact that for ethical reasons animal experiments should be kept to a minimum, the translation of such results to humans is limited due to large anatomical and physiological differences between human and rodent skin. Further models consist of three-dimensional reconstructed skin made of differentiated keratinocytes and fibroblasts. These
in vitro models cannot reflect the complex reaction of the skin as an immune organ because of the lack of cell populations like mast cells, dendritic cells, skin-resident T and B cells. In order to circumvent these differences and limitations, a wound infection model was developed based on human skin explants where superficial wounds were created and inoculated with Pseudomonas
aeruginosa [
20]. Such a model was intended to simulate poorly perfused wounds characterized by prolonged or increased inflammatory phase and associated with bacterial infections and biofilm formation.
P. aeruginosa bacteria could proliferate in the
ex vivo wounds and form biofilm-like structures. It was also observed that the PAO1 strain had strong proteolytic effects and that the cutaneous immune response was significantly reduced with respect to untreated controls. In this study, we used an improved protocol, in which after infection, skin was cultured at the air-liquid interface. Furthermore, because methicillin resistant Staphylococcus
aureus (MRSA) represents another pathogen commonly isolated from chronic wounds [
21] that is particularly threatening in the hospital context, an
ex vivo wound model infected with an MRSA strain was also developed and compared to the existing PAO1 wound model. The strains used in this study, PAO1 (ATCC 15692) and MRSA (ATCC 43300), originated from clinical isolates [
22,
23]. Both strains form biofilms, which lend the bacteria extremely increased resistance to external influences, including disinfectants and antibiotics, and even the ability to withstand the host immune response [
24,
25].
The two models were used to test foils made of PVP loaded with the antibiotic drug ciprofloxacin (Cipro). Cipro has a low water solubility. The corresponding salt is water soluble but has a different biodistribution. Therefore, Cipro was solubilized using 5% acetic acid and incorporated in the PVP foil. Interestingly, the residual acetic acid conferred to the foil special elasticity properties [
26]. The Cipro-foils showed very promising antimicrobial and anti-biofilm properties when tested on the
ex vivo PAO1 wound infection model using the old incubation protocol. In this study, we used the new culture protocol and tested the antimicrobial properties of Cipro-foils also with the MRSA infection model. To characterize and compare the two infection models, the distribution of bacteria in the wound tissue was analysed microscopically using
in situ fluorescence hybridization (FISH). The growth of the bacteria and the success of the Cipro-foils treatment was determined by quantifying the living bacteria extracted from wounds. The immunological reaction to the bacteria with and without treatment was analysed by monitoring the most common inflammatory cytokines.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of PVP Foils loaded with Ciprofloxacin (Cipro-foils)
PVP transparent foils were prepared by a solvent casting method starting from aqueous solutions of PVP (3% w/v) with a molecular weight (MW) of 360,000 g/mol (Sigma-Aldrich, Milan, Italy), monohydrochloride monohydrate free ciprofloxacin (≥ Sigma-Aldrich, Milan, Italy, 98.0% HPLC tested purity) and acetic acid (≥ 99.7%, Sigma-Aldrich, Milan, Italy). The detailed preparation protocol is described elsewhere [
26]. An amount of 60 mg of ciprofloxacin was dissolved in acetic acid 30% (v/v) and added to the PVP solution to reach a final volume of 30 mL and a final drug concentration of 88 mmol. These solutions were poured on Petri dishes (diameter 8.75 cm) and placed under an aspiration hood at room temperature (20 °C and 40–50% relative humidity) for 3 days and successively in a vacuum desiccator for further 3 days.
2.2. Ex vivo wound infection model and treatment with Cipro-foils
The skin material was obtained, after signed consent, from healthy individuals who underwent a plastic surgical procedure. The investigations were carried out with the approval of the ethics committee Charité –Universitätsmedizin Berlin (application no. EA1/135/06, renewed in January 2018) of the Charité University Medicine Berlin, in accordance with the ethical principles and guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki. The excised human skin was collected from the clinic on the day of the surgery and processed within 2-4 h. Skin samples were first roughly cleaned of blood residues and other impurities using phosphate-buffered saline solution (PBS) and then cut into pieces of about 1.5 x 1.5 cm². Excess subcutaneous fat was removed using scissors. Skin pieces were stretched slightly and fixed with cannulas to Styrofoam blocks wrapped in aluminum foil and covered with parafilm (Bemis Company, Neenah, WI, USA). A further cleaning step with PBS and ethanol (70%) followed. To create the wounds, a spherical ball-shaped milling cutter, 6 mm in size (No. 28725, Proxxon, Föhren, Germany), rotating at 16,000 rpm, and mounted on a micro motor handpiece (Marathon N7, TPC Advanced Technology, Inc. Diamond Bar, CA, USA) was used. In this way, reproducible superficial wounds with a diameter of approximately 5 mm were created. For the infection, PAO1 (ATCC 15692) and MRSA (ATCC 43300) strains were used. The pathogens were thawed from the cryo-stock and cultured overnight in tryptic soy broth (TSB, Corning, Kaiserslautern, Germany) at 37 °C and 150 rpm. The steady-state bacterial suspension had at a final concentration of approximately 1 x 109 colony forming units (CFU)/mL. Starting from this concentration, two dilutions (1:10) with TSB resulted in a suspension of 1 x 107 CFU/mL. Using a 10 μL syringe (26 gauge) with tapered tip (#002000, SGE Analytical Science, Ringwood Victoria, Australia), 10 µL of the bacterial suspension were taken and injected in the dermis from the wound edge toward the wound center at an angle of about 10° resulting in an inoculum of ~ 1 x 105 bacteria per wound. The skin samples were placed in a humid chamber (a box with wet towels and closed with a lid) and incubated at 37 °C, 5% CO2, and 95% humidity. In each experiment, skin samples with uninfected wounds were used as a control. After 20 h, skin samples were transferred to 6-well plates each containing 2 mL 1640 RPMI medium with 10% fetal calf serum (FCS). Medium with streptomycin (100 μg/mL, Gibco, Darmstadt, Germany) and penicillin (100 I.E./mL, Sigma-Aldrich, Hamburg, Germany) was used for the uninfected controls. For the treatment groups, discs with a diameter of 8 mm were cut from the Cipro-foils using a biopsy punch device and placed on the top of each wound. This resulted in a final concentration of approximately 500 µg antibiotic per wound. The incubation was carried out for a further 20 hours in a humidified box placed in an incubator (37°C, 5% CO2, 95% relative humidity). After the incubation, culture media were collected and the treated wound tissue was removed using a biopsy punch (8 mm). Skin was processed for bacterial count and cytokine measurements. Skin samples were also prepared for cryosections and in situ hybridization to visualize the microorganisms in the wounds.
2.3. Fluorescence In-Situ Hybridization (FISH)
FISH was used to visualize the pathogens inoculated in the skin samples. This is a molecular-biological method for the direct and specific detection of nucleic acids. Oligonucleotides (probes) marked with fluorescent dyes are used, which bind to specific ribosomal RNA target sequences. The EUB 338 probe (Integrated DNA Technologies, Coralville, IA), Sequence: 5'-GCT GCC TCC CGT AGG AGT-3', was used to identify the Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain PAO1. This is a cross-strain eubacteria probe, which, in this case is labeled at the 5' end with the fluorescent dye cyanine-3 (Cy3). The detection of the MRSA strain was carried out with a staphylococcus aureus-specific probe (5'-GAA GCA AGC TTC TCG TCC G-3'), which is marked with the dye DY549P1. Both probes bind to the 16S rRNA as a target sequence for detecting the bacteria. Cryosections with a thickness of 10 µm were prepared using a Microm HM 560 Leica microtome (Leica Microsystems, Wetzlar, Germany). The slides were stored at -20 °C until further processing. For the staining, slides were thawed at room temperature and the chosen sections were delimited with a DAKO pen. Sections were fixed for 10 min at room temperature with 20 µL PFA (4%, Sigma-Aldrich, Sigma-Aldrich Chemie, Steinheim, Germany.). For the samples inoculated with the gram-positive MRSA a permeabilization step with Tween-20 (0.02%) for 30 minutes at room temperature was carried out. For the hybridization, the probes (500 µg/mL) were diluted to a working concentration of 5 ng/mL using a hybridization buffer (5M NaCl, 1M Tris pH = 8, 10% SDS and 30% formamide in ddH2O). Hybridization was carried out in an oven at 48 °C for 90 minutes. Two washing steps followed. Skin sections were observed with a confocal laser scanning microscope (LSM-700, Zeiss, Jena, Germany).
2.4. Wound extraction and quantification of bacteria
For the quantification of the bacteria, the individual 8 mm biopsies were transferred to a 1.5 mL tube with 0.2 mL of phosphate buffer (Dulbecco PBS, pH7.4). Tissue was homogenized for 3 minutes using a sterile steel pistil at 150 rpm mounted on a digital overhead stirrer (DSL, VELP Scientifica Srl, Usmate, MB, Italy). Thereafter, samples were sonicated for 10 minutes at 40 kHz and 200 Weff using an ultrasonic bath (BactoSonic1, Bandelin, Berlin, Germany). For the quantification of the bacteria number, 80 µL of the wound tissue homogenate were taken and transferred to a 96-well plate. Dilution series with a dilution factor of 10 (1:10 dilution with PBS) were prepared. The remaining sample extracts were stored at -20 °C for protein extraction and subsequent IL-8 analysis using an ELISA assay. Using a multichannel pipette, 5 µL of the individual sample dilutions were taken from each well, applied to a square tryptic soy agar plate (Axon Lab, Reichenbach, Germany) and incubated at 37 °C overnight. The number of bacteria per wound was then calculated taking in account the number of dilutions.
2.5. Protein Extraction and measurement
For the protein extraction, samples were thawed on ice, mixed with 200 µL of ice-cold extraction buffer (100 mM Tris-HCl, 150 mM NaCl, 1 mM EDTA, 1 g Triton-X-100 in dH2O) and mixed well. Incubation was carried out with constant shaking (700 rpm) for 30 minutes at 4 °C. The individual samples were then sonicated (70 Hz, 240 Weff, 10 min) and centrifuged for 10 minutes at 450 x g. The supernatant was stored at -20 °C and used for total protein and cytokine determination by ELISA assay. The total amount of protein was determined by the Pierce 660 nm Protein Assay (Thermo Scientific Inc., Rockford, USA) following the manufacturer's instructions. Absorbance values were measured with the EnSpire Multimode plate reader (Perkin Elmer, Akron, OH, USA). Bovine serum albumin was used as the standard.
2.6. ELISA and multi-analyte ELISA
The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) was used to detect IL-8 in the tissue extracts as well as in the culture medium (Human IL-8 CytoSet, Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Rockford, USA). The assay was run according to the manufacturer's instructions. For the determination of other inflammatory cytokines (IFN-ᵧ, TNF-α, GM-CFS, IL-1α, IL-1ß, IL-2, IL-4, IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, IL-12 and IL-17A), the protein extracts from three donors were pooled, diluted 2-fold and analysed using a Human Inflammatory Cytokines Multi-Analyte ELISArray Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany).
2.7. Data Analysis and Statistics
In total, skin from 12 donors was used. Each experiment was repeated at least three times using skin from different donors. Data of CFU and IL-8 measurements are reported as dot plots with arithmetic means and standard error of the mean (SEM) of at least three experiments run in triplicate. Data of the multi-analyte ELISA are reported as bar diagrams of averages and standard errors of duplicates resulted from wound extracts pooled from three donors (three independent experiments). Calculations and statistical analysis were done with Excel 2007 (Microsoft, Redmond, WA, USA). One way ANOVA and two-tailed unpaired student-T tests were used. p values were reported in figures as follows: p > 0.05, **p > 0.01, *** p < 0.001. Only p ≤ 0.05 was regarded as a significant difference. Graphics were created with Prism GraphPad (GraphPad Software, CA, USA).
3. Results
3.1. Visualizatoin of bacteria in the wound model (FISH)
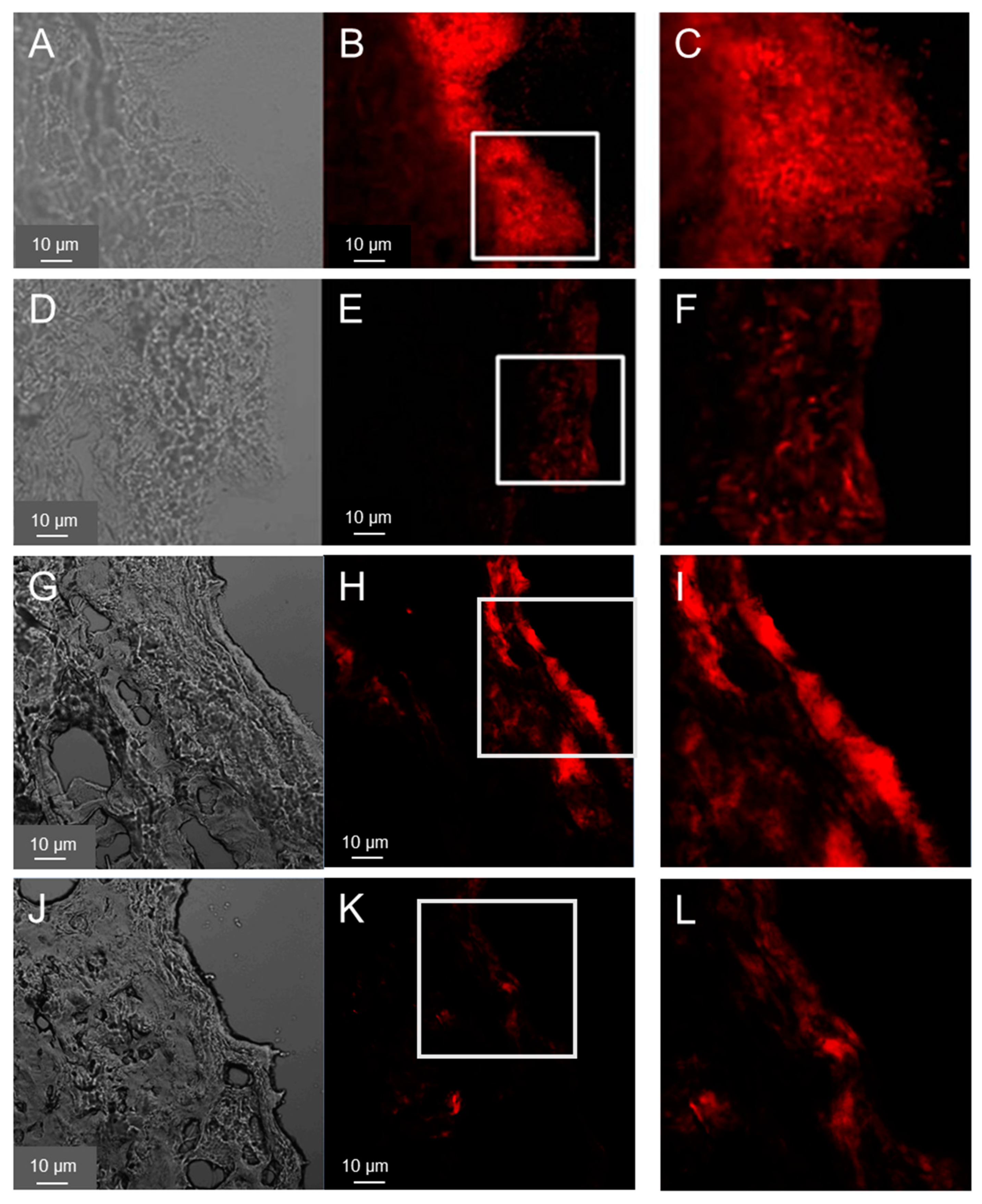
FISH was used to visualize pathogens introduced into the wound tissue. The results are shown in
Figure 1A–F for PAO1and
Figure 1G–L for MRSA. After 40 hours, sections of the wound infected with PAO1 showed clear biofilm-like structures, especially on the surface of the wound bed (
Figure 1A–C). PAO1 were also found in the deeper layers of the dermis, but far fewer. Similarly, biofilm-like structures could be detected in the samples treated with ciprofloxacin-loaded PVP film but with a weaker fluorescence signal, i.e. much less bacteria (
Figure 1D–F). These are likely dead bacteria and suggest that the treatment of the infection was successful as confirmed by the subsequent results of the CFU test (
Figure 2).
Cryosections of wounds 40 h after the infection with MRSA showed a distribution of the bacteria on the wound surface but predominantely at the wound edges (
Figure 1D–I) along with smaller agglomerations in the deeper layers of the wound. In general, the growth of the MRSA biofilm-like structures on the top of the wound was less pronounced. Also for the MRSA samples a reduction of fluorescence intensity (i.e. of the bacteria) was observed after the treatment with the Cipro-foils. These results were confirmed by those of the CFU assay (
Figure 2).
3.2. Antimicrobial Efficacy of Cipro-Foils
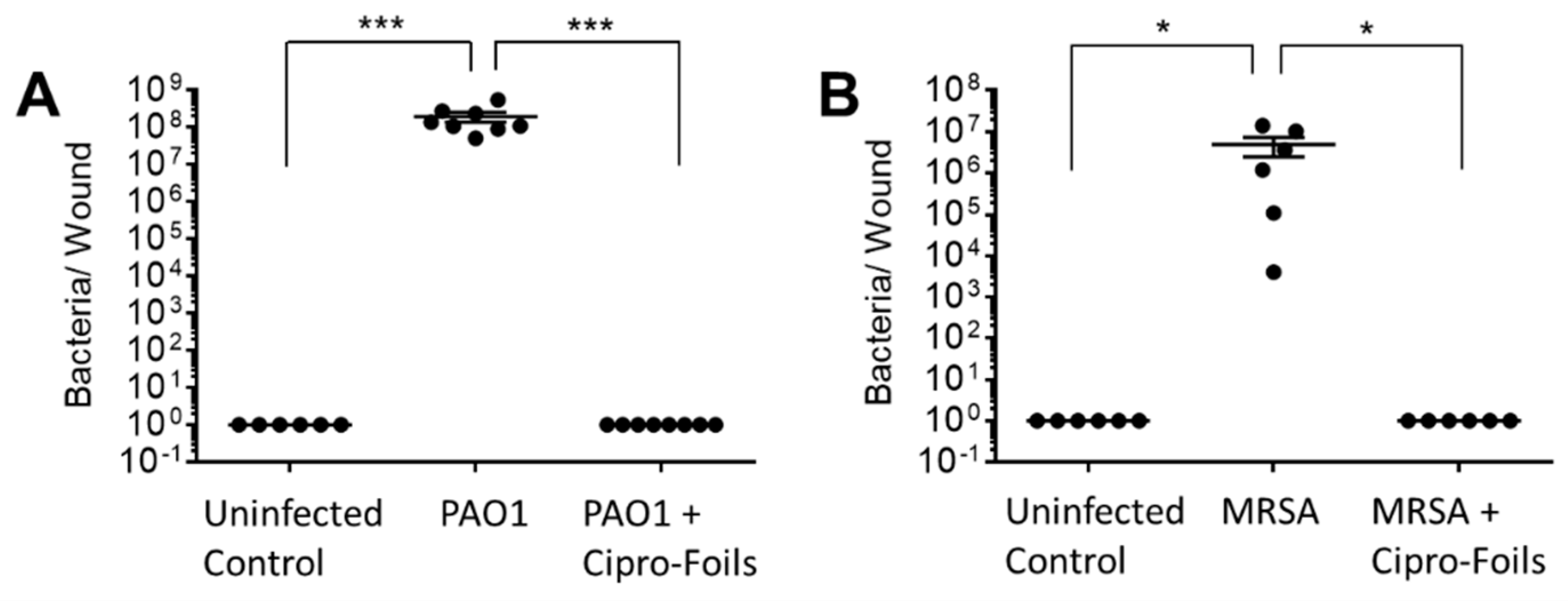
To test the antimicrobial efficacy of the Cipro-foils, tissue extracts were prepared, and the number of living bacteria was assessed using the CFU assay (
Figure 2). After 40h of inoculation without antibiotic treatment, an increase in the number of PAO1 bacteria from the injected 1 x 10
5 to the extracted 4 x 10
8 CFU was measured (
Figure 2A).
The CFU count from different samples was very reproducible with very low SEM. On the contrary, for the MRSA bacteria the CFU counted in the extracts differed strongly from sample to sample. In average 5 x 106 CFU were found after the inoculation of 1 x 105 bacteria. In both wound infection models, no bacteria were extracted from uninfected control wounds injected with saline only. The 20h-treatment with the Cipro-films (corresponding to about 500 µg antibiotic per wound) showed a complete eradication of both bacteria strains from the wound tissue.
3.2. Skin Immune Response
To test the immunological response of skin in the
ex vivo wound infection model with or without treatment with antimicrobial agents, the IL-8 released in wound tissue extracts as well as culture media was quantified using an ELISA assay (
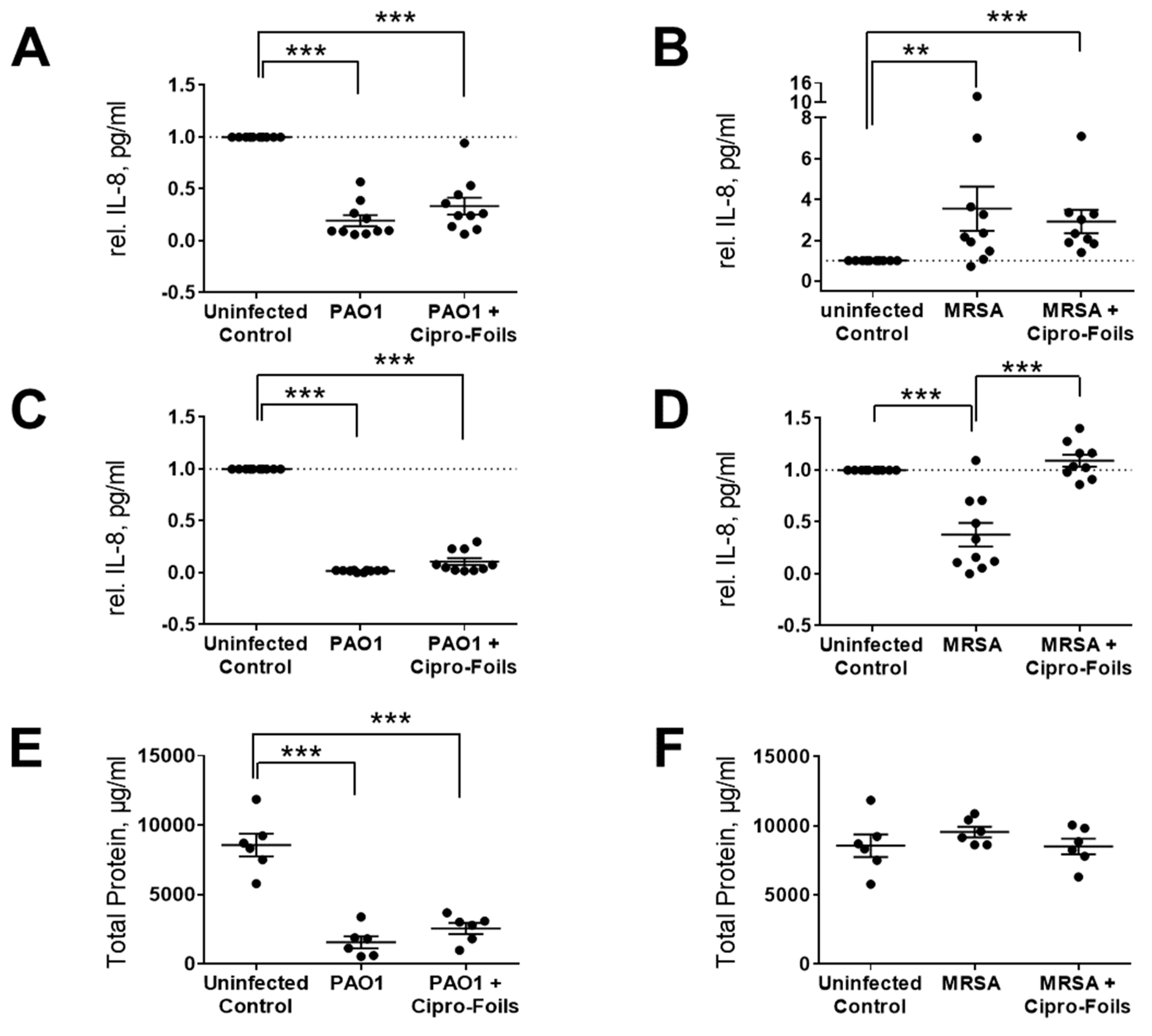
Figure 3).
The concentration of IL-8 in PAO1 infected wound samples was lower than in uninfected control wounds (
Figure 3A,C). Even the amount of total protein in tissue extracts of PAO1 infected wounds was strongly reduced (
Figure 3E). According to the manufacturer's information, only proteins and peptides with a size ≥ 2500 Da can be detected with the Pierce 660 nm Protein Assay. Thus, knowing that PAO1 has strong proteolytic effects, these results suggest that PAO1 was able to digest the proteins of the
ex vivo wound tissue, including IL-8. For this reason, the amounts of IL-8 were not normalized to the total extracted protein values but were normalized to the untreated controls. In general, IL-8 levels in PAO-1 infected wounds were always lower than those in the uninfected controls. Similarly, the IL-8 amounts in the culture media of infected wounds were always lower than that of the respective controls and always lower with respect to that of tissue extracts. Similar results were found also for infected wounds treated with the Cipro-foils.
Surprisingly, for the
ex vivo infection model with MRSA, a completely different picture was found in relation to the IL-8 secretion (
Figure 3B,D,F). The IL-8 levels detected in wound extracts after MRSA infection were in average 3.5 times higher than those of uninfected wounds. The average relative IL-8 value for the group treated with Cipro-foils was slightly lower than the infection group but three-times higher than that of the control group (
Figure 3B). Accordingly, the measured concentrations of total proteins in the extracts of MRSA infected samples were similar for all groups: uninfected, infected, and treated. The values of the single samples were relatively spread, probably due to differences in the donor-specific immune response (e.g., due to donor age or gender). This trend could not be confirmed by the analysis of IL-8 secretion in the culture medium. The presence of MRSA caused a reduction in the IL-8 released in the medium to an average value of 0.38 with respect to the control group. Nevertheless, this effect was counteracted by the treatment with the Cipro-foils, with an average value of IL-8 similar to that of the control group.
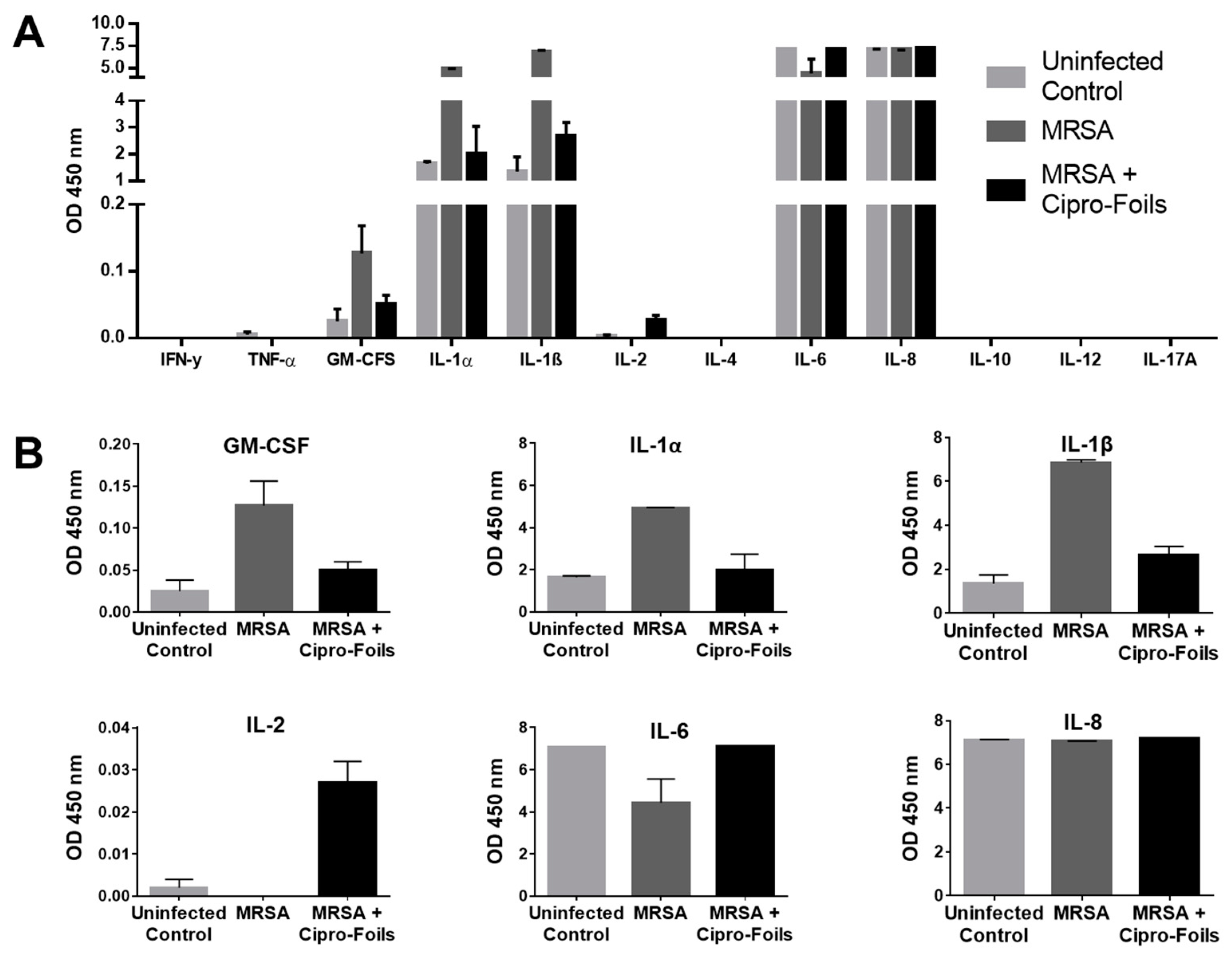
To detect further inflammatory cytokines stimulated by the infection with the MRSA strain and the possible effects of the antibiotic treatments, a multi-analyte ELISA was carried out (
Figure 4). Extracts from three MRSA infected samples and corresponding controls were pooled and analyzed.
No absorption, i.e., expression, of the cytokines IFN-γ, TNF-α, IL-4, IL-10, IL-12 and IL-17A could be detected. On the contrary, high levels of IL-6 and IL-8 were measured for both infected and non-infected wounds. In the case of IL-8, all samples reached the maximum OD value and thus, it was not possible to show any differences between the groups. For IL-6, both uninfected and Cipro-foil treated samples reached the highest OD value, while the MRSA infected wounds had a clearly lower OD, pointing to an inhibitory effect of the MRSA strain. IL-1α, IL-1-β were moderately expressed in uninfected wounds (OD ≅ 2) but their expression increased to higher levels (OD ≅ 5 and 7, respectively) in MRSA infected wounds. Interestingly, the effects of MRSA infection on these cytokines could be counteracted by the treatment with the Cipro-foils. A similar effect was observed for GM-CSF even if the levels of this analyte were extremely low (OD = 0.04-0.16). Finally, a very low but slightly increased level of IL-2 could be detected in infected samples treated with the Cipro-foils. In contrast, there was no IL-2 signal for skin samples inoculated with MRSA or uninfected controls.
4. Discussion
Bacterial infections play a causal role in the development of chronic wounds. Two of the most common isolated pathogens are
Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus
aureus. Both possess a variety of virulence factors that allow them to invade the injured tissue, proliferate and evade the human immune response, especially in immune suppressed patients [27-29]. The development of new topical preventive and therapeutic procedures is important for the containment of chronic and nosocomial wound infections. On the other side, the selection of proper models that reflect host-specific characteristics and interactions with pathogens is required to test the efficacy of new materials. In previous investigations, a wound infection model with
ex vivo human skin infected with PAO1 and incubated for 20 h in a humid chamber was characterized [
20]. A biofilm-like accumulation of the predominantly aerobic strain on the wound surface was detected by electron microscopy. In this work, FISH was used to visualize both bacteria strains after a longer incubation time. This method allowed the direct detection of bacteria ribosomal RNA using fluorescence-labelled oligonucleotide probes. After 40 hours of infection, biofilm-like structures were observed on the wound surface like those found in the previous study after 20 h of incubation (
Figure 1A–C). Fewer bacteria were found in the deeper dermis layers due to the lower oxygen content. MRSA bacteria were detected mainly in the wound edges but also in deeper dermis layers. Other than the PAO1 strain that formed a thicker biofilm covering almost the whole wound surface, the used MSRA strain formed less biofilm and with irregular clusters (
Figure 1G–I).
To test the antimicrobial efficacy of the antibiotic topical treatment, cryosection of wound infections treated with the Cipro-foils were also analyzed. The much lower fluorescent signal indicated that only a few, presumably dead, bacteria were present in the wound tissue. These results were confirmed by the CFU assay results (
Figure 2). Cipro-foils were able to eradicate both bacterial infections 20 h after one single application. In our previous work [
30], we demonstrated that the efficacy of Cipro was not only connected with its antibiotic properties, but also with the type of formulation. Indeed, Cipro loaded in foils and fibers resulted in having totally different capacity in eradicating or not the infection. The slow and sustained release of the drug from the foils had the best antimicrobial efficacy. The results of this study confirm the previous findings using gram negative bacteria and demonstrate once again, how a proper deliver and control of drug release can enhance its performances. In addition, they show that Cipro-foils are efficient also against a gram-positive penicillin-resistant strain and are particularly relevant because obtained using human-derived, three-dimensional infection models.
Furthermore, eventual effects of the infections and the topical antimicrobial treatment on skin inflammatory response, i.e., the expression of inflammatory markers, was investigated. The cytotoxic and proteolytic effects of PAO1 were evident. Compared to the previous study, the enzymatic effects towards IL-8 and skin proteins were even stronger. Whereas in the previous study, after 20 h of infection, the amount of IL-8 was similar to that of uninfected controls, in this study, after a 40 h the levels of IL-8 had diminished even more (
Figure 3A,C). Even though the treatment with Cipro-foils eliminated all living PAO1 bacteria (
Figure 2A), the proteolytic effects were not counteracted as shown by the low concentration of total protein in the extracts (
Figure 3E). These results show that bacterial proteases and toxins acted in the 20 h before the Cipro-foils were applied and that the effects of toxins continued despite the treatment. These findings are in accordance with previously reported data showing that cytokines are among the targets of bacterial proteases [
31]. PAO1 has many extracellular proteases that are able to break down small peptides but also collagen fibers [
32], which make up to 70% of the dermis components [
33]. Also
S. aureus strains possess collagen-degrading enzymes [
32,
34]. However, no extensive protein degradation was observed in the MRSA
ex-vivo model. The differences between PAO1 and MRSA infection models, may be due to the fact that MRSA is non-motile and forms local colonies with restricted local nutrient resource [
35]. This might limit the toxic effects of the
S. aureus infection. Accordingly, in the tissue extracts of MRSA infected samples, an increase of some inflammatory cytokines could be measured as reaction to the bacteria (
Figure 3 and
Figure 4). The amounts of IL-8, GM-CSF, IL-1α, and IL-1ß expression in infected samples were higher than in uninfected samples. IL-8 acts as chemokine and is released by several cell types during infections. GM-CSF is a growth factor released by fibroblasts, endothelial cells, macrophages and other immune system cells also in response to pathogen associated signals [
36]. IL-1α and IL-1ß are mainly expressed by epithelial cells, monocytes and macrophages and play a role in maintaining skin barrier function [
37]. In the case of acute barrier injuries, as during infections, there is an increase in the epidermal expression of these interleukins [
38].
Interestingly, with exemption for IL-8, the increase of these inflammatory cytokines could be reduced to the level of uninfected skin thanks to the treatment with Cipro-foils. In the case of IL-6 and IL-2, a rather opposite effect was measured: the infected untreated samples had lower cytokine levels than the infected treated samples. Surprisingly, also in the culture medium a lower amount of IL-8 was measured compared to uninfected and infected but treated wounds. These results may be explained by a selective inhibition of specific cell populations upon MRSA infection. In fact, it has already been reported that
S. aureus inhibited IL-8 expression in human neutrophils [
39]. Furthermore, Tajima et
al. reported that beta-hemolysin reduced IL-8 production without cytotoxicity to endothelial cells [
40]. Interestingly, this inhibitory or toxic effect was counteracted by Cipro-foils resulting in cytokine levels in medium comparable to those released by uninfected skin.
5. Conclusions
Infection of acute and chronic wounds is becoming a serious problem, especially in the nosocomial contest where patients are often immunosuppressed. The development of resistance and its spread is progressing rapidly. Therefore, the development of new delivery methods assuring a sustained and effective concentration of antimicrobials in the infected area is becoming urgent. This study shows that PVP foils loaded with the antibiotic drug ciprofloxacin using a co-solvent could achieve the complete eradication of biofilm-like colonies in the wound bet. Thus, we conclude that such transparent, easy to use, adhesive, adaptable foils are feasible and affordable dressings with both protection and antimicrobial functions for a wide range of applications.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.R., C.S., M.C. and I.S.B.; methodology, F.R., C.S., M.C.; formal analysis, F.R., J.J., C.S.; investigation, J.J.; resources, A.V. and U.B.-P.; data curation, J.J., S.H.; writing—original draft preparation, J.J., F.R.; writing—review and editing, C.S., M.C., A.V.; visualization, J.J., S.H.; supervision, F.R., C.S., I.S.B.; funding acquisition, F.R., C.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the German Federal Ministry of Economics (BMWi), grants: KF2928204MD4 and KF2088119MD4.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Ethics Committee of Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin (approval EA1/135/06, renewed in January 2018).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all skin donors.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Mahoney, A.R.; Safaee, M.M.; Wuest, W.M.; Furst, A.L. The silent pandemic: Emergent antibiotic resistances following the global response to SARS-CoV-2. IScience 2021, 24, 102304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sneka, P.; Mahalakshmi, K. Antimicrobial Resistance–A Silent Pandemic. National Journal of Community Medicine 2023, 14, 71–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, M.; Sartelli, M.; McKimm, J.; Bakar, M.A. Health care-associated infections–an overview. Infection and drug resistance 2018, 11, 2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimlichman, E.; Henderson, D.; Tamir, O.; Franz, C.; Song, P.; Yamin, C.K.; Keohane, C.; Denham, C.R.; Bates, D.W. Health care–associated infections: a meta-analysis of costs and financial impact on the US health care system. JAMA internal medicine 2013, 173, 2039–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Lissovoy, G.; Fraeman, K.; Hutchins, V.; Murphy, D.; Song, D.; Vaughn, B.B. Surgical site infection: incidence and impact on hospital utilization and treatment costs. American journal of infection control 2009, 37, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leaper, D.; Assadian, O.; Edmiston, C.E. Approach to chronic wound infections. British Journal of Dermatology 2015, 173, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjarnsholt, T.; Kirketerp-Møller, K.; Jensen, P.Ø.; Madsen, K.G.; Phipps, R.; Krogfelt, K.; Høiby, N.; Givskov, M. Why chronic wounds will not heal: a novel hypothesis. Wound repair and regeneration 2008, 16, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, M.; Järbrink, K.; Divakar, U.; Bajpai, R.; Upton, Z.; Schmidtchen, A.; Car, J. The humanistic and economic burden of chronic wounds: a systematic review. Wound Repair and Regeneration 2019, 27, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinengo, L.; Olsson, M.; Bajpai, R.; Soljak, M.; Upton, Z.; Schmidtchen, A.; Car, J.; Järbrink, K. Prevalence of chronic wounds in the general population: systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Annals of epidemiology 2019, 29, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, B.; Huang, S.; Gao, D.; Xie, J.; Liu, N.; Fu, X. Age-associated changes in regenerative capabilities of mesenchymal stem cell: impact on chronic wounds repair. International Wound Journal 2016, 13, 1252–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, C.K. Human wounds and its burden: an updated compendium of estimates. Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers 140 Huguenot Street, 3rd Floor New …:. 2019; 8, 39–48. [Google Scholar]
- Demidova-Rice, T.N.; Hamblin, M.R.; Herman, I.M. Acute and impaired wound healing: pathophysiology and current methods for drug delivery, part 1: normal and chronic wounds: biology, causes, and approaches to care. Advances in skin & wound care 2012, 25, 304. [Google Scholar]
- Silver, S. Bacterial silver resistance: molecular biology and uses and misuses of silver compounds. FEMS microbiology reviews 2003, 27, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddique, M.H.; Aslam, B.; Imran, M.; Ashraf, A.; Nadeem, H.; Hayat, S.; Khurshid, M.; Afzal, M.; Malik, I.R.; Shahzad, M. Research article effect of silver nanoparticles on biofilm formation and EPS production of multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumonia. Hindawi BioMed Res. Int 2020, 2020, 6398165. [Google Scholar]
- Panáček, A.; Kvítek, L.; Smékalová, M.; Večeřová, R.; Kolář, M.; Röderová, M.; Dyčka, F.; Šebela, M.; Prucek, R.; Tomanec, O. Bacterial resistance to silver nanoparticles and how to overcome it. Nature nanotechnology 2018, 13, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negut, I.; Grumezescu, V.; Grumezescu, A.M. Treatment strategies for infected wounds. Molecules 2018, 23, 2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boateng, J.S.; Matthews, K.H.; Stevens, H.N.; Eccleston, G.M. Wound healing dressings and drug delivery systems: a review. Journal of pharmaceutical sciences 2008, 97, 2892–2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contardi, M.; Russo, D.; Suarato, G.; Heredia-Guerrero, J.A.; Ceseracciu, L.; Penna, I.; Margaroli, N.; Summa, M.; Spanò, R.; Tassistro, G. Polyvinylpyrrolidone/hyaluronic acid-based bilayer constructs for sequential delivery of cutaneous antiseptic and antibiotic. Chemical Engineering Journal 2019, 358, 912–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contardi, M.; Summa, M.; Picone, P.; Brancato, O.R.; Di Carlo, M.; Bertorelli, R.; Athanassiou, A. Evaluation of a multifunctional polyvinylpyrrolidone/hyaluronic acid-based bilayer film patch with anti-inflammatory properties as an enhancer of the wound healing process. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaudinn, C.; Dittmann, C.; Jurisch, J.; Laue, M.; Günday-Türeli, N.; Blume-Peytavi, U.; Vogt, A.; Rancan, F. Development, standardization and testing of a bacterial wound infection model based on ex vivo human skin. PLoS One 2017, 12, e0186946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, R.; Grande, R.; Butrico, L.; Rossi, A.; Settimio, U.F.; Caroleo, B.; Amato, B.; Gallelli, L.; De Franciscis, S. Chronic wound infections: the role of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus. Expert review of anti-infective therapy 2015, 13, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holloway, B.; Krishnapillai, V.; Morgan, A. Chromosomal genetics of Pseudomonas. Microbiological reviews 1979, 43, 73–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDOUGAL, L.K.; Thornsberry, C. The role of beta-lactamase in staphylococcal resistance to penicillinase-resistant penicillins and cephalosporins. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 1986, 23, 832–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boles, B.R.; Thoendel, M.; Singh, P.K. Self-generated diversity produces “insurance effects” in biofilm communities. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2004, 101, 16630–16635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mah, T.-F.C.; O'Toole, G.A. Mechanisms of biofilm resistance to antimicrobial agents. Trends in microbiology 2001, 9, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contardi, M.; Heredia-Guerrero, J.A.; Perotto, G.; Valentini, P.; Pompa, P.P.; Spanò, R.; Goldoni, L.; Bertorelli, R.; Athanassiou, A.; Bayer, I.S. Transparent ciprofloxacin-povidone antibiotic films and nanofiber mats as potential skin and wound care dressings. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 2017, 104, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, S. Immune system and surgical site infection. Journal of Chemotherapy 2001, 13, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jong, N.W.; Van Kessel, K.P.; Van Strijp, J.A. Immune evasion by Staphylococcus aureus. Microbiology spectrum 2019, 7, 7–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.Y. Molecular pathogenesis of Staphylococcus aureus infection. Pediatric research 2009, 65, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rancan, F.; Contardi, M.; Jurisch, J.; Blume-Peytavi, U.; Vogt, A.; Bayer, I.S.; Schaudinn, C. Evaluation of drug delivery and efficacy of ciprofloxacin-loaded povidone foils and nanofiber mats in a wound-infection model based on ex vivo human skin. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potempa, J.; Pike, R.N. Corruption of innate immunity by bacterial proteases. Journal of innate immunity 2009, 1, 70–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsay, S.; Oates, A.; Bourdillon, K. The detrimental impact of extracellular bacterial proteases on wound healing. International wound journal 2017, 14, 1237–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitellaro-Zuccarello, L.; Cappelletti, S.; Rossi, V.D.P.; Sari-Gorla, M. Stereological analysis of collagen and elastic fibers in the normal human dermis: variability with age, sex, and body region. The Anatomical Record 1994, 238, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugioka, K.; Kodama-Takahshi, A.; Sato, T.; Okada, K.; Murakami, J.; Park, A.-M.; Mishima, H.; Shimomura, Y.; Kusaka, S.; Nishida, T. Plasminogen-dependent collagenolytic properties of Staphylococcus aureus in collagen gel cultures of human corneal fibroblasts. Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science 2018, 59, 5098–5107. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Y.-W.; Stratton, C.W. Staphylococcus aureus: an old pathogen with new weapons. Clinics in laboratory medicine 2010, 30, 179–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, X.; Liu, K.; Li, H.; Wang, F.-S.; Xu, R. Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor: an immunotarget for sepsis and COVID-19. Cellular & Molecular Immunology 2021, 18, 2057–2058. [Google Scholar]
- Macleod, T.; Berekmeri, A.; Bridgewood, C.; Stacey, M.; McGonagle, D.; Wittmann, M. The immunological impact of IL-1 family cytokines on the epidermal barrier. Frontiers in Immunology 2021, 12, 5563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, L.S.; Cho, J.S. Immunity against Staphylococcus aureus cutaneous infections. Nature Reviews Immunology 2011, 11, 505–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zurek, O.W.; Pallister, K.B.; Voyich, J.M. Staphylococcus aureus inhibits neutrophil-derived IL-8 to promote cell death. The Journal of infectious diseases 2015, 212, 934–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajima, A.; Iwase, T.; Shinji, H.; Seki, K.; Mizunoe, Y. Inhibition of endothelial interleukin-8 production and neutrophil transmigration by Staphylococcus aureus beta-hemolysin. Infection and immunity 2009, 77, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).