Submitted:
01 June 2023
Posted:
02 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
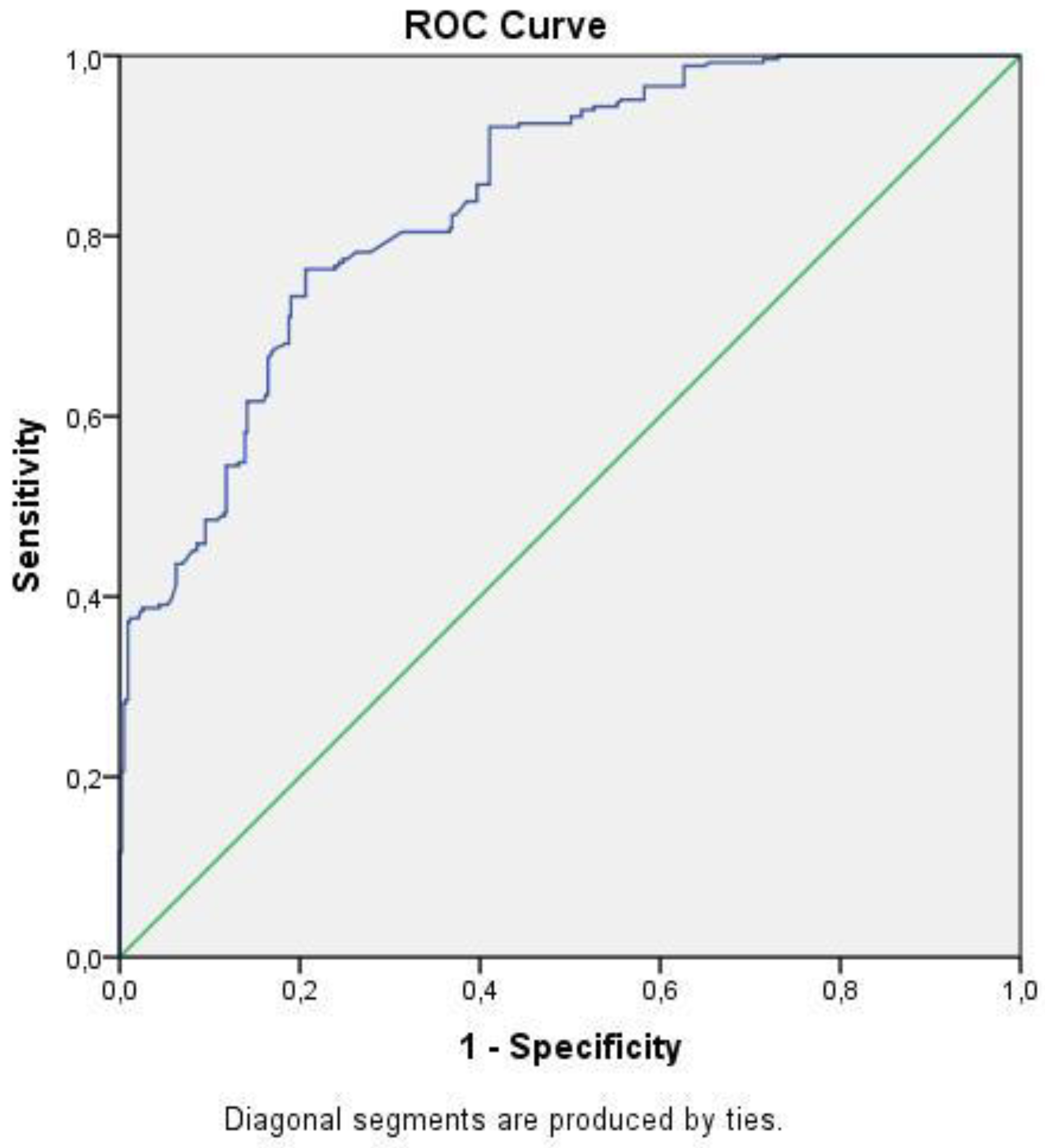
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tripathi, B.K.; Srivastava, A.K. Diabetes mellitus: complications and therapeutics. Med Sci Monit 2006, 12, Ra130–147. [Google Scholar]
- Pottie, K.; Jaramillo, A.; Lewin, G.; Dickinson, J.; Bell, N.; Brauer, P.; Dunfield, L.; Joffres, M.; Singh, H.; Tonelli, M. Recommendations on screening for type 2 diabetes in adults. CMAJ 2012, 184, 1687–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faselis, C.; Katsimardou, A.; Imprialos, K.; Deligkaris, P.; Kallistratos, M.; Dimitriadis, K. Microvascular Complications of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Curr Vasc Pharmacol 2020, 18, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Ley, S.H.; Hu, F.B. Global aetiology and epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications. Nat Rev Endocrinol 2018, 14, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolar, M. Glycemic control and complications in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Am J Med 2010, 123, S3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberti, K.G.; Eckel, R.H.; Grundy, S.M.; Zimmet, P.Z.; Cleeman, J.I.; Donato, K.A.; Fruchart, J.C.; James, W.P.; Loria, C.M.; Smith, S.C., Jr. Harmonizing the metabolic syndrome: a joint interim statement of the International Diabetes Federation Task Force on Epidemiology and Prevention; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; American Heart Association; World Heart Federation; International Atherosclerosis Society; and International Association for the Study of Obesity. Circulation 2009, 120, 1640–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galicia-Garcia, U.; Benito-Vicente, A.; Jebari, S.; Larrea-Sebal, A.; Siddiqi, H.; Uribe, K.B.; Ostolaza, H.; Martín, C. Pathophysiology of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandanmagsar, B.; Youm, Y.H.; Ravussin, A.; Galgani, J.E.; Stadler, K.; Mynatt, R.L.; Ravussin, E.; Stephens, J.M.; Dixit, V.D. The NLRP3 inflammasome instigates obesity-induced inflammation and insulin resistance. Nat Med 2011, 17, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pradhan, A.D.; Manson, J.E.; Rifai, N.; Buring, J.E.; Ridker, P.M. C-reactive protein, interleukin 6, and risk of developing type 2 diabetes mellitus. JAMA 2001, 286, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavey, C.; Lazennec, G.; Lagarrigue, S.; Clapé, C.; Iankova, I.; Teyssier, J.; Annicotte, J.S.; Schmidt, J.; Mataki, C.; Yamamoto, H.; et al. CXC ligand 5 is an adipose-tissue derived factor that links obesity to insulin resistance. Cell Metab 2009, 9, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vozarova, B.; Weyer, C.; Lindsay, R.S.; Pratley, R.E.; Bogardus, C.; Tataranni, P.A. High white blood cell count is associated with a worsening of insulin sensitivity and predicts the development of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 2002, 51, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaganathan, R.; Ravindran, R.; Dhanasekaran, S. Emerging Role of Adipocytokines in Type 2 Diabetes as Mediators of Insulin Resistance and Cardiovascular Disease. Can J Diabetes 2018, 42, 446–456.e441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haffner, S.; Temprosa, M.; Crandall, J.; Fowler, S.; Goldberg, R.; Horton, E.; Marcovina, S.; Mather, K.; Orchard, T.; Ratner, R.; et al. Intensive lifestyle intervention or metformin on inflammation and coagulation in participants with impaired glucose tolerance. Diabetes 2005, 54, 1566–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhlestein, J.B.; May, H.T.; Jensen, J.R.; Horne, B.D.; Lanman, R.B.; Lavasani, F.; Wolfert, R.L.; Pearson, R.R.; Yannicelli, H.D.; Anderson, J.L. The reduction of inflammatory biomarkers by statin, fibrate, and combination therapy among diabetic patients with mixed dyslipidemia: the DIACOR (Diabetes and Combined Lipid Therapy Regimen) study. J Am Coll Cardiol 2006, 48, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, D.H.; Massarotti, E.; Garg, R.; Liu, J.; Canning, C.; Schneeweiss, S. Association between disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs and diabetes risk in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and psoriasis. JAMA 2011, 305, 2525–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyck, P.J.; Kratz, K.M.; Karnes, J.L.; Litchy, W.J.; Klein, R.; Pach, J.M.; Wilson, D.M.; O’Brien, P.C.; Melton, L.J., 3rd; Service, F.J. The prevalence by staged severity of various types of diabetic neuropathy, retinopathy, and nephropathy in a population-based cohort: the Rochester Diabetic Neuropathy Study. Neurology 1993, 43, 817–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calcutt, N.A. Diabetic neuropathy and neuropathic pain: a (con)fusion of pathogenic mechanisms? Pain 2020, 161, S65–s86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeedi, P.; Petersohn, I.; Salpea, P.; Malanda, B.; Karuranga, S.; Unwin, N.; Colagiuri, S.; Guariguata, L.; Motala, A.A.; Ogurtsova, K.; et al. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9(th) edition. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2019, 157, 107843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demir, S.; Nawroth, P.P.; Herzig, S.; Ekim Üstünel, B. Emerging Targets in Type 2 Diabetes and Diabetic Complications. Adv Sci (Weinh) 2021, 8, e2100275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rendra, E.; Riabov, V.; Mossel, D.M.; Sevastyanova, T.; Harmsen, M.C.; Kzhyshkowska, J. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) in macrophage activation and function in diabetes. Immunobiology 2019, 224, 242–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamoto, K.; Martin, D.P.; Schmelzer, J.D.; Mitsui, Y.; Low, P.A. Pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokine gene expression in rat sciatic nerve chronic constriction injury model of neuropathic pain. Exp Neurol 2001, 169, 386–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braswell, K.; Dickey, C.A.; Jinwal, U.K. A commentary on: Modulating molecular chaperones improves sensory fiber recovery and mitochondrial function in diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Exp Neurol 2013, 241, 122–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Román-Pintos, L.M.; Villegas-Rivera, G.; Rodríguez-Carrizalez, A.D.; Miranda-Díaz, A.G.; Cardona-Muñoz, E.G. Diabetic Polyneuropathy in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Mitochondrial Function. J Diabetes Res 2016, 2016, 3425617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahrani, A.A.; Askwith, T.; Stevens, M.J. Emerging drugs for diabetic neuropathy. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs 2010, 15, 661–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakur, S.; Gupta, S.K.; Ali, V.; Singh, P.; Verma, M. Aldose Reductase: a cause and a potential target for the treatment of diabetic complications. Arch Pharm Res 2021, 44, 655–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloan, G.; Alam, U.; Selvarajah, D.; Tesfaye, S. The Treatment of Painful Diabetic Neuropathy. Curr Diabetes Rev 2022, 18, e070721194556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadosky, A.; Mardekian, J.; Parsons, B.; Hopps, M.; Bienen, E.J.; Markman, J. Healthcare utilization and costs in diabetes relative to the clinical spectrum of painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy. J Diabetes Complications 2015, 29, 212–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callaghan, B.C.; Little, A.A.; Feldman, E.L.; Hughes, R.A. Enhanced glucose control for preventing and treating diabetic neuropathy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2012, 6, Cd007543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khdour, M.R. Treatment of diabetic peripheral neuropathy: a review. J Pharm Pharmacol 2020, 72, 863–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilgin, S.; Kurtkulagi, O.; Atak Tel, B.M.; Duman, T.T.; Kahveci, G.; Khalid, A.; Aktas, G. Does C-reactive protein to serum Albumin Ratio correlate with diabEtic nephropathy in patients with Type 2 dIabetes MEllitus? The CARE TIME study. Prim Care Diabetes 2021, 15, 1071–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishizuka, M.; Nagata, H.; Takagi, K.; Iwasaki, Y.; Shibuya, N.; Kubota, K. Clinical Significance of the C-Reactive Protein to Albumin Ratio for Survival After Surgery for Colorectal Cancer. Ann Surg Oncol 2016, 23, 900–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haruki, K.; Shiba, H.; Shirai, Y.; Horiuchi, T.; Iwase, R.; Fujiwara, Y.; Furukawa, K.; Misawa, T.; Yanaga, K. The C-reactive Protein to Albumin Ratio Predicts Long-Term Outcomes in Patients with Pancreatic Cancer After Pancreatic Resection. World J Surg 2016, 40, 2254–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, T.B.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, Y.Z.; Li, W.M. The prognostic value of C-reactive protein to albumin ratio in patients with lung cancer. Medicine (Baltimore) 2018, 97, e13505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesfaye, S.; Boulton, A.J.; Dyck, P.J.; Freeman, R.; Horowitz, M.; Kempler, P.; Lauria, G.; Malik, R.A.; Spallone, V.; Vinik, A.; et al. Diabetic neuropathies: update on definitions, diagnostic criteria, estimation of severity, and treatments. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 2285–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.G.; Singleton, J.R. Obesity and hyperlipidemia are risk factors for early diabetic neuropathy. J Diabetes Complications 2013, 27, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callaghan, B.C.; Gallagher, G.; Fridman, V.; Feldman, E.L. Diabetic neuropathy: what does the future hold? Diabetologia 2020, 63, 891–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amour, A.A.; Chamba, N.; Kayandabila, J.; Lyaruu, I.A.; Marieke, D.; Shao, E.R.; Howlett, W. Prevalence, Patterns, and Factors Associated with Peripheral Neuropathies among Diabetic Patients at Tertiary Hospital in the Kilimanjaro Region: Descriptive Cross-Sectional Study from North-Eastern Tanzania. Int J Endocrinol 2019, 2019, 5404781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, T.J.; Lee, J.E.; Choi, S.H.; Jang, H.C. Association between Body Fat and Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy in Middle-Aged Adults with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Preliminary Report. J Obes Metab Syndr 2019, 28, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darivemula, S.; Nagoor, K.; Patan, S.K.; Reddy, N.B.; Deepthi, C.S.; Chittooru, C.S. Prevalence and Its Associated Determinants of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy (DPN) in Individuals Having Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus in Rural South India. Indian J Community Med 2019, 44, 88–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Xu, Y.; An, M.; Zeng, Q. The risk factors for diabetic peripheral neuropathy: A meta-analysis. PLoS One 2019, 14, e0212574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oyibo, S.O.; Prasad, Y.D.; Jackson, N.J.; Jude, E.B.; Boulton, A.J. The relationship between blood glucose excursions and painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy: a pilot study. Diabet Med 2002, 19, 870–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A.G.; Singleton, J.R. Impaired glucose tolerance and neuropathy. Neurologist 2008, 14, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A.G. Impaired glucose tolerance and metabolic syndrome in idiopathic neuropathy. J Peripher Nerv Syst 2012, 17 Suppl 2, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.B.; Zhao, L.H.; Zhang, X.L.; Cai, H.L.; Huang, H.Y.; Xu, F.; Chen, T.; Wang, X.Q. HbA1c variability and diabetic peripheral neuropathy in type 2 diabetic patients. Cardiovasc Diabetol 2018, 17, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, M.; Sarkar, M.; Mahbub, I.; Islam, S. A study on peripheral neuropathy and its related risk factors associated with hba1c levels. Journal of Bio-Science 2021, 29, 123-138.
- Ishibashi, F.; Taniguchi, M.; Kosaka, A.; Uetake, H.; Tavakoli, M. Improvement in Neuropathy Outcomes With Normalizing HbA(1c) in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casadei, G.; Filippini, M.; Brognara, L. Glycated Hemoglobin (HbA1c) as a Biomarker for Diabetic Foot Peripheral Neuropathy. Diseases 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocak, M.Z.; Aktas, G.; Atak, B.M.; Duman, T.T.; Yis, O.M.; Erkus, E.; Savli, H. Is Neuregulin-4 a predictive marker of microvascular complications in type 2 diabetes mellitus? Eur J Clin Invest 2020, 50, e13206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tesfaye, S.; Chaturvedi, N.; Eaton, S.E.; Ward, J.D.; Manes, C.; Ionescu-Tirgoviste, C.; Witte, D.R.; Fuller, J.H. Vascular risk factors and diabetic neuropathy. N Engl J Med 2005, 352, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, S.T.; Witte, D.R.; Dalsgaard, E.M.; Andersen, H.; Nawroth, P.; Fleming, T.; Jensen, T.M.; Finnerup, N.B.; Jensen, T.S.; Lauritzen, T.; et al. Risk Factors for Incident Diabetic Polyneuropathy in a Cohort With Screen-Detected Type 2 Diabetes Followed for 13 Years: ADDITION-Denmark. Diabetes Care 2018, 41, 1068–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, J. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the serum lipid profile in prediction of diabetic neuropathy. Sci Rep 2021, 11, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emanuelsson, F.; Nordestgaard, B.G.; Tybjærg-Hansen, A.; Benn, M. Impact of LDL Cholesterol on Microvascular Versus Macrovascular Disease: A Mendelian Randomization Study. J Am Coll Cardiol 2019, 74, 1465–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudou, K.; Hasuda, H.; Tsuda, Y.; Kusumoto, E.; Uehara, H.; Yoshida, R.; Koga, T.; Yamashita, Y.I.; Sakaguchi, Y.; Kusumoto, T. Prognostic significance of a novel index score based on the inflammation-based prognostic scores of patients with colorectal cancer. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.R.; Xu, J.Y.; Chen, G.C.; Yu, N.; Yang, J.; Zeng, D.X.; Gu, M.J.; Li, D.P.; Zhang, Y.S.; Qin, L.Q. Post-diagnostic C-reactive protein and albumin predict survival in Chinese patients with non-small cell lung cancer: a prospective cohort study. Sci Rep 2019, 9, 8143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, M.; Wu, W. Prognostic role of C-reactive protein to albumin ratio in cancer patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: a meta-analysis. Front Oncol 2023, 13, 1148786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shabrawy, M.; Alsadik, M.E.; El-Shafei, M.; Abdelmoaty, A.A.; Alazzouni, A.S.; Esawy, M.M.; Shabana, M.A. Interleukin-6 and C-reactive protein/albumin ratio as predictors of COVID-19 severity and mortality. Egyptian J Bronchol 2021, 15, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, K.; Choi, S.P.; Kim, S.H.; Oh, S.H. Prognostic value of ambulation ability with albumin and C-reactive protein to predict 28-day mortality in elderly sepsis patients: a retrospective multicentre registry-based study. BMC Geriatr 2022, 22, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seringec Akkececi, N.; Yildirim Cetin, G.; Gogebakan, H.; Acipayam, C. The C-Reactive Protein/Albumin Ratio and Complete Blood Count Parameters as Indicators of Disease Activity in Patients with Takayasu Arteritis. Med Sci Monit 2019, 25, 1401–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atas, D.B.; Sahin, G.K.; Şengül, Ş.; Kaya, B.; Paydaş, S.; Alibaz-Oner, F.; Direskeneli, H.; Tuglular, S.; Asicioglu, E. C-Reactive Protein to Albumin Ratio is Associated with Disease Activity in Anti-Neutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody Associated Vasculitis. Mediterr J Rheumatol 2023, 34, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koell, B.; Ludwig, S.; Weimann, J.; Waldschmidt, L.; Schirmer, J.; Reichenspurner, H.; Blankenberg, S.; Conradi, L.; Schofer, N.; Kalbacher, D. C-Reactive Protein to Albumin Ratio offers superior risk prediction in patients undergoing mitral valve edge-to-edge repair: a comparison to established surgical risk scores. Eur Heart J 2022, 43, ehac544.1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tharavath, V.; Rao, P.B.; Nayak, S.; Panda, A.; Bandyopadhyay, D.; Pati, S. Preoperative C-reactive protein - Albumin ratio as a predictor of requirement for postoperative mechanical ventilation after non-cardiac surgery under general anaesthesia: A prospective observational study (HICARV). Indian J Anaesth 2023, 67, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, M.; Mishra, D.; Sahu, M.; Nittala, R.; Singh, A.; Pati, G.; Agarwal, S.; Narayan, J. C-reactive protein/albumin and ferritin as predictive markers for severity and mortality in patients with acute pancreatitis. Gastroenterology Rev 2022, 17, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| DN group | Non-DN group | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Women (n, (%)) | 172 (65%) | 219 (56%) | 0.06 |
| Men (n, (%)) | 94 (35%) | 212 (44%) | ||
| Mean ± Standard Deviation | ||||
| Age (years) | 60 ± 10 | 56 ± 11 | 0.11 | |
| Median (min.-max.) | ||||
| Weight (kg) | 82 (48-120) | 83 (46-150) | 0.6 | |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 105 (75-132) | 105 (78-160) | 0.56 | |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 31,1 (17-46,3) | 30,8 (19-55,4) | 0.02 | |
| Diabetes duration (years) | 6 (1-24) | 3 (1-20) | <0.001 | |
| Systolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 128 (90-180) | 130 (90-200) | 0.17 | |
| Diastolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 75 (50-110) | 80 (50-110) | 0.07 | |
| DN group | Non-DN group | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± Standard Deviation | |||
| leukocyte count (k/mm3) | 6,9 ± 2 | 6,8 ± 2,3 | 0.33 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 13,1 ± 1,6 | 13,5 ± 1,7 | 0.16 |
| Hematocrit (%) | 39 ± 4 | 40 ± 5 | 0.27 |
| platelet count (k/mm3) | 262 ± 36 | 256 ± 34 | 0.35 |
| aspartate transaminase (U/L) | 24 ± 9 | 28 ± 10 | 0.68 |
| alanine transaminase (U/L) | 23 ± 11 | 22 ± 12 | 0.65 |
| Median (min.-max.) | |||
| C-reactive protein (mg/L) | 9,5 (1-250) | 2,2 (0,1-26,1) | <0.001 |
| Serum albumin (g/dL) | 4,3 (2,8-5,3) | 4,4 (2,9-5,6) | 0.01 |
| Fasting plasma glucose (mg/dL) | 8,3 (4,9-16,5) | 7,7 (5,1-17,2) | <0.001 |
| HbA1c (%) | 177 (66-565) | 147 (65-514) | 0.001 |
| Blood urea (mg/dL) | 34 (17-222) | 32 (13-258) | 0.14 |
| Serum creatinine (mg/dL) | 0,83 (0,59-3,41) | 0,8 (0,39-3,93) | 0.049 |
| eGFR (%) | 99,5 (15,3-185) | 99,8 (15,8-181) | 0.057 |
| Serum uric acid (mg/dL) | 5,6 (1,8-10,4) | 5,5 (2,4-13,6) | 0.07 |
| Triglyceride (mg/dL) | 153 (47-850) | 151 (50-856) | 0.36 |
| Total cholesteroö (mg/dL) | 187 (52-318) | 200 (50-378) | 0.14 |
| LDL-cholesterol (mg/dL) | 132 (21-200) | 114 (29-244) | 0.03 |
| HDL-cholesterol (mg/dL) | 46 (13-87) | 44 (17-92) | 0.1 |
| CAR (%) | 2,19 (0,2-49) | 0,56 (0,02-5,8) | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





