1. Introduction
Groundwater is referred to as water that is kept under the earth's surface in aquifers, which are soil and rock formations. The groundwater level, or the depth to which water penetrates underground aquifers, is a crucial factor in hydrological processes. Groundwater levels can fluctuate based on variables such as precipitation, evaporation, and anthropogenic factors like agriculture and potable water pumping (Sophocleous, 1992). Changes in groundwater levels can influence the hydrologic cycle (water flow between the atmosphere, land, and seas) (Famiglietti, 2014).
In most areas, groundwater provides a reliable source of drinkable water. These properties facilitate its extensive development, which may be extended and targeted according to demand, eliminating the need for extensive equipment. About 36% of all home water consumption, 42% of all irrigated agriculture consumption, and 27% of all commercial water usage are supplied by groundwater around the world (Döll et al., 2012). Although it has been known for a long time that the Basin's water needs must be met by extracting water from water sources, the amount of water that must be withdrawn to do so is still not well recorded, and its future availability is unknown. The level of groundwater is naturally renewed by phreatic and artesian aquifers, which supply water for all of agriculture and industry's requirements (Levin et al., 2016). A good grasp of groundwater table (GWL) past, present, and future conditions may help scientists and professionals in the water industry design techniques for water consumption and conservation that guarantee long-term social and economic growth (Wada et al., 2010).
In Colorado, the consumption of groundwater has been ongoing since long before the beginning of the 20th century, and the development of deep regenerative pumps has facilitated it. 19 of Colorado's 63 counties get all their drinking water and other household needs from this large water source. One-fifth to one-third of the population of the state is likely being supplied by groundwater extraction from private wells as well as public water distribution systems. Most groundwater extraction goes toward supplying agricultural irrigation demands, but it also supplies a significant portion of rural populations' household and commercial water requirements. Most of the state of Colorado's water is used for agriculture, households, and businesses, but there is a growing demand for water to support recreational activities and ecology.
Most of the state's potable water comes from surface water due to its easy availability and extensive recent and historical storage capacity. Groundwater has been under observation due to overexploitation, rising demand, and a dearth of good locations for future water aquifers. A local reservoir may have been enough for a small number of users, but as the population grows, the demand for water from wells in the area increases, and the aquifer's minimal storage capacity may be rapidly drained or contaminated. Excessive extraction of groundwater can result in its depletion, which in turn can have a variety of harmful effects, such as the sinking of land, saltwater intrusion, and a reduction in the amount of water that is available to meet the requirements of both humans and ecosystems (Scanlon et al., 2012).
It is possible to guarantee the accessibility and viability of groundwater for subsequent use through careful water management plans, preventative rules, and the protection of natural resources. The GWL can provide insightful data sets due to constant aquifer monitoring. To make the most effective use of GW resources, it is crucial to have an accurate assessment of both the existing and projected demand for GW, as well as the basin's overall groundwater resources.
This study addresses the limited availability of data by utilizing approaches for data augmentation and comparing the efficacy of different models for estimating groundwater levels in Cheyenne and Delta counties in the state of Colorado, United States. The dataset covers a time frame from 1980 to 2019 and contains observations from four locations across the state: two in Delta City and two in Cheyenne Wells. This research evaluates two models for predicting groundwater levels and draws comparisons between the Artificial Neural Network (ANN) and the Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average (ARIMA). Root Mean Squared Error, Mean Squared Error, and Mean Absolute Error are used as metrics to assess the performance of the models. Quantitative and qualitative evaluations of the models showed the ANN models provided more accurate forecasts of GWL than the ARIMA models at almost all of the monitoring wells. The small number of monitoring wells (4 total), the lack of easily accessible data, and the possibility of overfitting the ANN model due to data augmentation techniques all represent challenges and limitations to this study.
2. Literature review
Groundwater is an essential element of hydrological systems and a vital resource for many communities around the globe. Many variables, such as precipitation, land use changes, and abstraction rates, affect its levels (Sophocleous, 2002). The significance of groundwater highlights the importance of developing accurate methods for estimating and forecasting groundwater levels. Data-driven models, which can process large datasets and produce reliable forecasts, have recently seen a surge in adoption for use in estimating groundwater levels.
Several different conceptual and physical models have been used to evaluate different aspects of water. These models have certain advantages, but one of their drawbacks is that they require a substantial quantity of data in addition to an in-depth knowledge of the groundwater level. For this reason, time-series studies and data-driven methodologies are commonly employed for analyzing hydrological aspects. Estimating groundwater levels using data-driven models has been the subject of multiple research efforts. Groundwater levels in the North China Plain were predicted using machine learning models by (Xiao et al., 2018). According to the results, the SVM model has the highest accuracy and precision compared to the other models. (Zhang et al., 2023) analyzed the data to examine how accurate ARIMA models are at predicting groundwater levels in the Yellow River Basin in China. The findings demonstrated the ARIMA model's potential for short-term groundwater level forecasting. To better estimate groundwater levels in a karst region in China, (S. Wang et al., 2017) compared the accuracy of ARIMA, ANN, and support vector regression (SVR) models. The ANN model was determined to have the best performance out of the three models, according to the study's findings. (Maheshwari et al., 2017) utilized an artificial neural network model to predict groundwater levels in a semi-arid region of India. The research found that the ANN model provided high R2 values, indicating that it accurately predicted groundwater levels. A hybrid model created by (Hu et al., 2020) that combined ARIMA and ML models to predict the groundwater levels in a Chinese coastal aquifer. According to the findings, the hybrid model performed significantly better in terms of accuracy and precision than the individual models.
Predictions and estimates of GWL can be made with the help of a time-series statistical model that uses autoregressive integrated moving averages (ARIMA). Predicting dynamic water level variations using ARIMA and sequential Gaussian simulation (SGS) was the focus of (Takafuji et al., 2019). Groundwater fluctuation patterns in the Warangal district were assessed using the ARIMA and parametric Mann-Kendal (MK) methods (Satish Kumar & Venkata Rathnam, 2019) Multiple research (Birylo et al., 2018) (Gibrilla et al., 2018) used the ARIMA model to forecast yearly, monthly, and seasonal GWL. Forecasting GWL in a complex and uncertain environment can be made easier with the utilization of ANN algorithms. Since the 1970s, ANNs have been used to predict the GWL because they can figure out the complicated mathematical relationships between inputs and outputs. Potential advantages of utilizing ANN models include analyzing nonlinear interactions between predictive and targeted variables and evaluating unknown elements using simple training methods. Overfitting and the "black box" character of these models are just two problems that affect them. This (Daliakopoulos et al., 2005) study was the first to try predicting GWLs in the time-series domain using artificial neural networks. It has been shown in several research studies (Emamgholizadeh et al., 2014; Guzman et al., 2015; Taormina et al., 2012) that the ANN is effective in predicting GWL.
The precision and accuracy of data-driven models have been evaluated with the help of several measures. Root-mean-square error (RMSE) and mean square error (MSE) are typical metrics used to assess the dissimilarity between anticipated and observed values (Rahman et al., 2020). Model performance can also be measured by other metrics, such as the correlation coefficient or the coefficient of determination (S. Wang et al., 2018).
The quality and quantity of data utilized for training and validation are key components in performing data-driven models. Groundwater studies have relied on a wide range of data types, including hydrological and meteorological records, satellite imagery, and direct measurements of groundwater levels (Nikoo et al., 2018). Monitoring well data is the most common source of data for estimating groundwater levels and has been extensively used in several studies as the basis for data-driven forecasts of future predictions. (Singh et al., 2019) developed an ANN algorithm to estimate groundwater levels in India's hard rock terrain using groundwater level monitoring data. (Shafique et al., 2018) also used groundwater level monitoring data to create a support vector regression (SVR) model for forecasting groundwater levels in a coastal aquifer in Pakistan.
Recent research has focused on using satellite and remote sensing data to forecast groundwater levels. In this regard, (Li et al., 2019) study estimated groundwater storage changes in the North China Plain using time-series gravity data from the Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE) satellite mission. (Teferi et al., 2019) conducted another study that employed satellite data to estimate groundwater recharge in a semi-arid region of Ethiopia. The research concluded that satellite imaging data could be useful for calculating groundwater recharge in data-poor regions. Predictions of groundwater levels have also been made using a combination of satellite/remote sensing data and data from groundwater level monitors in different studies. For example, (Wu et al., 2018) developed an integrated hydrological model for estimating groundwater levels in the North China Plain by combining data from groundwater level monitoring with data on soil moisture collected from satellites.
The literature review highlights the importance of accurate groundwater level measurement and forecasts for efficiently managing groundwater resources. Several approaches have been used to predict groundwater levels, but data-driven models have shown the most potential. However, studies comparing the efficacy of alternative data-driven methods in estimating groundwater levels are still lacking. This research tries to fill the gap by comparing two data-driven techniques (ARIMA and ANN) for forcasting groundwater levels in Colorado, USA. This research adds to the literature by assessing the two models' precision and accuracy statistically and graphically. The relative performance of the models was evaluated using the mean square error (MSE), root-mean-square error (RMSE), and mean absolute error (MAE).
3. Study areas and dataset
The country seats of Cheyenne country in the east and the Delta country in the west of the state of Colorado, United States, were selected as the study region for this research. When compared to the other 64 counties in Colorado, Cheyenne County has the fourth-lowest population density. According to estimates from the year 2020, the population of the county was 1,748. Cheyenne Wells is a major city and the county seat. According to the statistics provided by the United States Census Bureau, the total land area of Cheyenne County is 1,781 square miles. Colorado's western area contains Delta County. Delta is located on the western side of Colorado, at the foot of Grand Mesa, the tallest flat-topped mountain on earth. This area is rich in history and agriculture and is home to a wide range of cultures. U.S. Census data shows that the Delta country covers 1,149 square miles (2,980 km2) and estimates put the delta country population at 31,196.
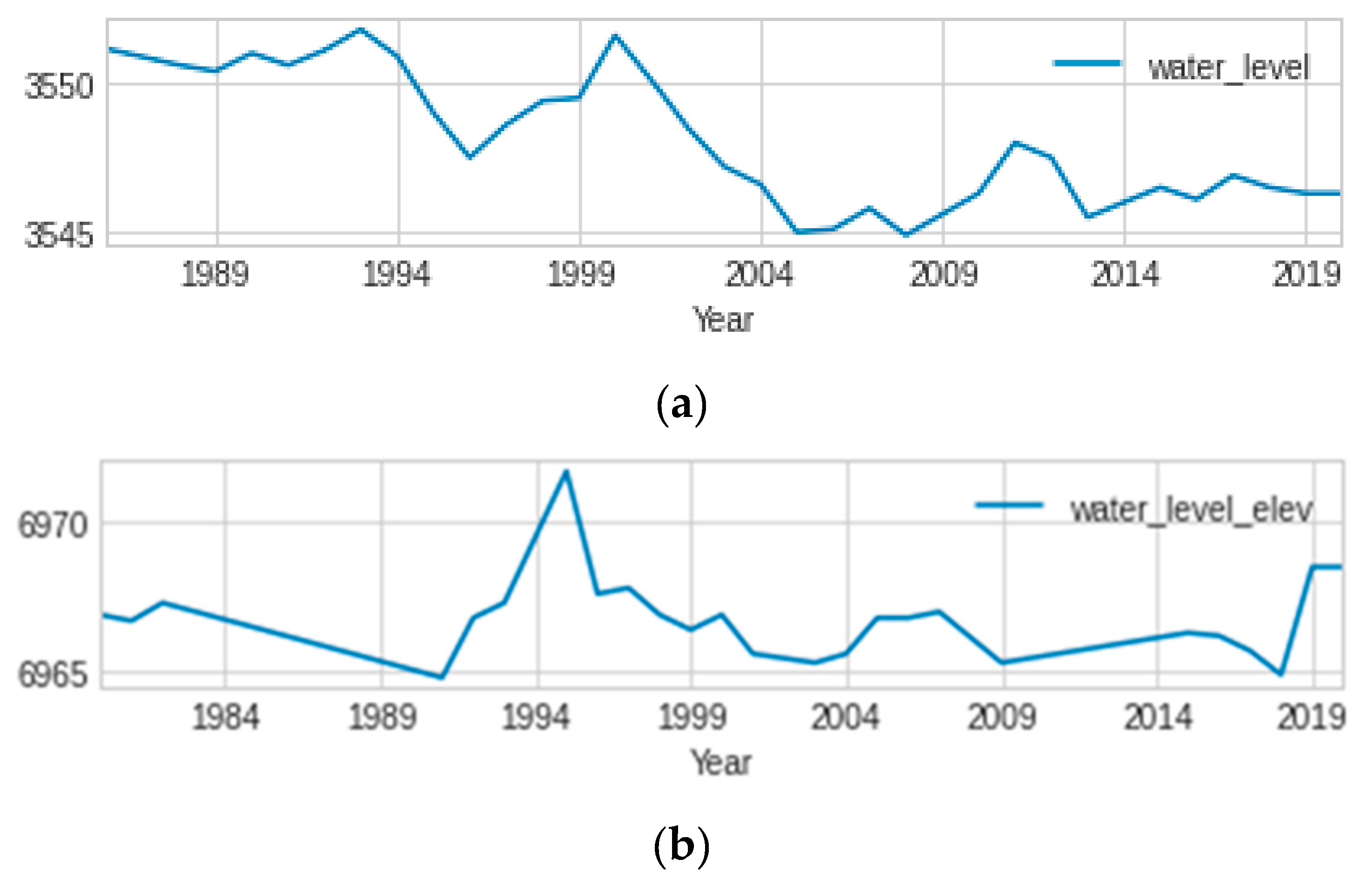
For this study, observations were taken from a total of four locations across the state of Colorado: two in Delta City, and two in Cheyenne Wells. The US Geological Survey (USGS) compiles and analyzes data from the National Ground Water Monitoring Network (NGWMN) to determine the current water level in Colorado. Kaggle, an open-source data repository, makes the information available to the public. The time frame covered by the dataset is from 1980 to 2019. Figure 9 displays the water-level trend across the selected sites of Cheyenne Wells and delta city. Figure 9 demonstrates that the selected sites exhibit irregular patterns of GWL.
Figure 1.
demonstrates the variability of GWL in the chosen Cheyenne and Delta wells from 1984 to 2019. (a) Fluctuation of GWL in the selected site of Cheyenne well. (b) Fluctuation of GWL at a selected site of delta city colorado.
Figure 1.
demonstrates the variability of GWL in the chosen Cheyenne and Delta wells from 1984 to 2019. (a) Fluctuation of GWL in the selected site of Cheyenne well. (b) Fluctuation of GWL at a selected site of delta city colorado.
4. Methodology
This study follows a quantitative research design, utilizing a data-driven approach to estimate groundwater levels. The forecasting of groundwater levels at four monitoring wells in Colorado State, USA, was made using two data-driven models: ARIMA and ANN. The study used one month's worth of information from each year from 1980 to 2019 to train and test the models.
The main objective of this study is to compare the performance of ARIMA and ANN models in predicting groundwater levels at four monitoring wells in Colorado State, USA. The study also aims to obtain the accuracy and precision of the proposed approach using different evaluation metrics.
The research questions are as follows:
How accurate are the ARIMA and ANN models in predicting groundwater levels at the monitoring wells in Colorado State, USA?
Which model provides the most reliable predictions of future groundwater levels?
The hypothesis of the study is that the ANN model will produce more accurate forecasts of groundwater levels than the ARIMA model. This hypothesis is based on the assumption that the ANN model, being a machine learning model, is better equipped to handle the non-linear and complex relationships between the groundwater levels and the various factors affecting them.
4.1. Data Preprocessing
In any data-driven modeling process, the step of "data preprocessing" plays a significant and important role. The data used in this investigation needed to be cleaned up, transformed, and supplemented to fulfill the needs of the data-driven models. In the first step of the process, we used the linear interpolation method to identify and handle any missing data points.
4.1.1. Data augmentation
Data augmentation is the process of creating new data components from existing data in order to artificially inflate the data set size. Due to the limited number of observations (30–40), the available data cannot be used for modeling. Consequently, data augmentation methods must be used to expand the number of observations. One way to resample a time series is to alter the interval between samples. The resample () function is provided in the Pandas library. This may be used for up-sampling to accommodate more observations and for down-sampling to cluster similar data.
This study makes use of up-sampling techniques to transform yearly data into monthly data. The resample () function is provided in the Pandas library. This may be used for up-sampling to accommodate more observations and for down-sampling to cluster similar data. The Pandas object has the interpolate () function and several other interpolation methods that can be used to fill in gaps. The linear interpolation method is used in this research. Observations at the preferred interval are derived by connecting the dots between the already available data.
4.2. Data-driven models
4.2.1. Artificial Neural Network
Neurons act as the brain's fundamental building blocks. In a neuron, information is relayed between its two terminals via electrical impulses (Han et al., 2018). Machine learning models called Artificial Neural Networks attempt to simulate the way the human brain operates. Many different types of neurons make up the ANN network, and they are all interconnected and responsible for different tasks. Similar to people, ANNs may acquire knowledge from their past experiences (Agatonovic-Kustrin & Beresford, 2000). They can use past data to make predictions of outcomes of time series that may be influenced by noise, or they can estimate functions that aren't well defined. A typical ANN consists of several neurons, which function as processing components, and the connections that link those neurons together. An artificial neural network (ANN) will typically consist of three separate layers: input, hidden, and output. In order to compute a result, each neuron in the hidden layer and each neuron in the output layer will use a different transfer (activation) function.
This study utilized an ANN with a single hidden layer in a multi-layer feed-forward architecture because of its widespread adoption in groundwater-level modelling and prediction. An output is computed by each layer's neuron using the transfer (activation) function in a manner that is robust to the weights and biases of the input. Rectified Linear Unit (ReLU) functions are employed as activation functions in the hidden layer, whereas linear functions are utilized in the output layer. The ANN model's forecast is expressed as the following phrase:
Where
After deciding on an ANN architecture, the next step is to train the model. The purpose of training an ANN network is to ensure that it can identify the most salient characteristics and patterns in the modeled data. During training, the ANN model's weights and biases are calibrated to optimal values. The network is "trained" using input and data resulting in a specified output; this is used to determine the appropriate weights to use. This ensures that the ANN's predictions are as near to the true predictions as acceptable. Back-propagation training is the most widely used approach for training feed-forward neural networks (Hagan & Menhaj, 1994). The procedure has two stages. An estimate of the outputs is calculated using the input signal, which is fed during the first step of the process. subsequently, in order to decrease the connection error, we modify the network parameters across the layers using back propagation techniques. There are several different approaches to optimizing weights that may be used to train models. The Adam optimizer technique was utilized in this study owing to its flexibility in accommodating non-stationary goals and the low frequency of its tuning requirements (Bank et al., 2020).
The activation (transfer) function of each node characterizes its response to the sum of its incoming signals. The most popular activation function, the Rectified Linear Unit (ReLU) (Fukushima, 1975) function, was employed during the training of the hidden layer in this research. However, for the output layer, the linear activation function (Rumelhart et al., 1995) was employed.
These two functions have the following mathematical expressions:
Where x represents the input to the neuron at the hidden layer in Eq (2), and in Eq (3), x is the input to the output layer.
ANN models can accurately represent the nonlinear and complicated interactions between inputs and outputs. ANNs can learn and generalize from the patterns that are present in the data without the need for prior knowledge of the correlations that are present. ANNs are better able to deal with noisy and non-linear data than outdated statistical models, and they are also more resistant to outliers. In hydrology and groundwater research, ANNs have seen widespread application, particularly in the forecasting of river flows, groundwater levels, and rainfall. ANNs have proven to have a significant amount of potential in the field of hydrology and groundwater research due to their capacity to recognize irregular patterns and their adaptability in dealing with a wide variety of data types.
4.2.2. Auto-Regressive Integrated Moving Average (ARIMA)
It is widely agreed that the autoregressive integrated moving average (ARIMA) model is among the most powerful models for evaluating time series. ARIMA and the Box-Jenkins technique are utilized in the modeling process for time series data. Using ARIMA, we can model the dynamics of time series and make accurate predictions. To infer relationships between variables that are not immediately apparent in the data, ARIMA modeling employs correlational methods (Geurts et al., 1977). It is made up of three distinct methods: moving average (MA), integration (I), and auto-regression (AR) (Young, 1977).
Auto Regressor: The term "auto-regression" refers to a type of model that takes into consideration the relationship between an input and a certain number of delayed variables.
Integrated: The process of normalizing a time series by computing the difference between two observations (or other data) at each time step is known as integration.
Moving average: A model that takes into account the interdependence of inputs and the ensuing error increase when applied to lagging inputs.
The following is a mathematical expression of the ARIMA model:
Where μ represents the constant value, φpYt-p is the lagging values of y and θqet-q is the representation of the lagging errors.
Stationarity detection: The input data series for an ARIMA model must be stationary, meaning that the time series should have a constant mean, standard deviation, and serial correlation (H. R. Wang et al., 2014). There are two main tests used to determine whether a time series is stationary or nonstationary: the Augmented Dickey-Fuller test and the Kwiatkowski-Phillips-Schmidt-Shin (KPSS) test. For stationarity testing, scatter plots and autocorrelation function diagrams are also used.
Model Selection: For accurate data analysis and forecasting, it is important to select an ARIMA model appropriate for the available data and to set its parameters to their lowest attainable values.
Prediction: Stationary time series may be used for forecasting after the ARIMA order is formed,
Allowing the model to make predictions.
It has been demonstrated that ARIMA models are capable of accurately estimating the levels of groundwater in a variety of places all over the world. When the data has a trend that is linear and can be considered normally distributed, ARIMA models are effective.
4.2.3. Model Evaluation
The following evaluation metrics have been used to evaluate predictive performance: Mean Absolute Error (MAE), Mean Absolute Percentage Error (MAPE), and Root Mean Square Error (RMSE). Where the symbols Qi represent the observed values, Pi represents the expected values, and n is the total number of samples.
4.2.4. Root Mean Square Error (RMSE)
Standard deviation of the differences between expected and actual values is measured by the root-mean-square error (RMSE).
4.2.5. Mean Absolute Error (MAE)
The MAE is a measure of the spread of errors over a set of forecasts that ignores the direction of individual errors. It's a simple estimate of how much the sample deviates from the mean of the predicted and actual values.
4.2.6. Mean Square Error (MSE)
The MSE measures the average squared divergence between actual and projected values and provides insight into how well a regression line fits a data set.
5. Results and Discussions
ARIMA and ANN models were utilized to make forecasts on the GWL for each of the study's selected locations in the state of Colorado, United States. The time series data from each of the 4 wells were independently analyzed using their respective site IDs. The Auto-ARIMA model was applied in this research to identify the appropriate ARIMA model ordering. By automatically determining the optimal p, d, and q values for a given data set, an Auto-ARIMA model improves the quality of predictions. The optimal ARIMA model ordering across all 4 locations is displayed in
Table 1.
The AIC values were used to calibrate the effectiveness of the predicted and actual GWL values. Table 7 shows the best model for each well, along with the AIC score. Multiple evaluation matrices, such as the MAE, the MSE, and the RMSE, were used to assess the model accuracy.
To study the variations in the selected sites of Colorado State groundwater level, an ANN with a multi-layer feed-forward architecture and a single hidden layer was employed. Groundwater level fluctuations are simulated using the ANN approach in the Keras open-source software library, and a prediction model is then created for all 4 wells utilized as monitoring sites in the research region. The steps of an ANN analysis involve gathering the necessary data, normalizing, and scaling it to a useful scale for the activation function, feeding the data to the model to be trained, and iterating until the desired results are achieved as measured by the chosen evaluation metrics.
5.1. Performance comparison between the ANN and ARIMA models
The mean absolute error MAE, RMSE, and MSE metrics were utilized to assess the precision of the ARIMA and ANN models of 4 sites for predicting groundwater levels.
Table 2 is a listing of the matrices that were obtained after evaluating all selected sites.
The findings show that the ANN models have much lower values of MAE, MSE, and RMSE at all 4 sites when compared ARIMA model.
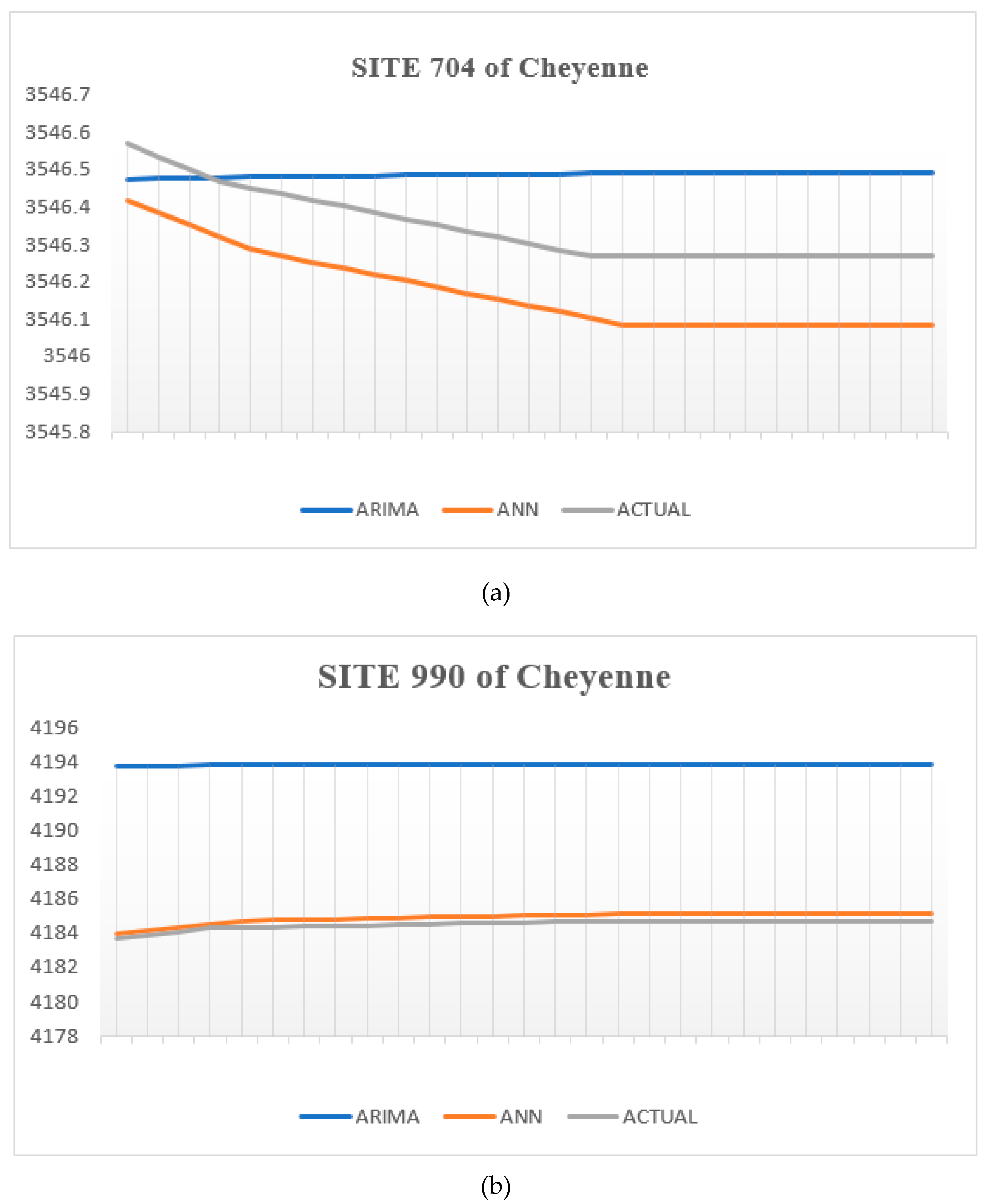
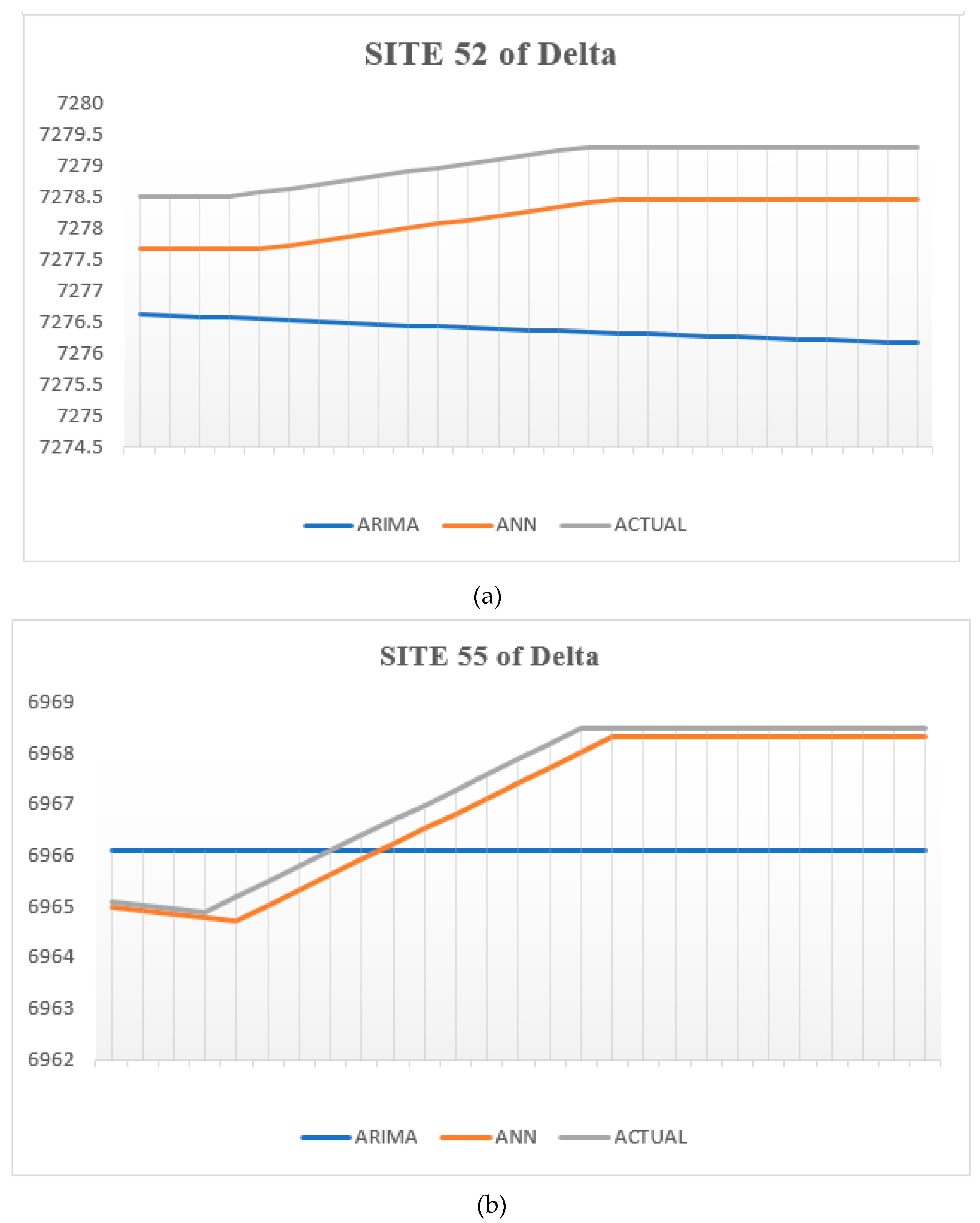
In terms of the findings of the visual indications, a comparison of actual and predicted GWL by the ARIMA and ANN models can be seen in Figures 10a, and 10b at sites 704, and 55. These graphs make it clear that the GWL predicted by ANN models more closely resembles the actual GWL than those predicted by the ARIMA model.
Figure 2.
ARIMA and ANN models predictions and actual GWL at site (a) site 704, (b) site 990 of Cheyenne wells.
Figure 2.
ARIMA and ANN models predictions and actual GWL at site (a) site 704, (b) site 990 of Cheyenne wells.
Figure 3.
ARIMA and ANN models predictions and actual GWL at (a) site 55, (b) site 52 of Delta.
Figure 3.
ARIMA and ANN models predictions and actual GWL at (a) site 55, (b) site 52 of Delta.
5.2. Discussion
This research aimed to use two distinct modeling approaches to estimate GWL fluctuations at 4 monitoring wells in two different countries (Cheyenne and Delta) of Colorado State. This study compares two different types of data-driven models: autoregressive integrated moving average (ARIMA), and artificial neural network (ANN) models. Quantitative and qualitative assessments of the ARIMA and ANN models designed for the 4 sites were performed using suitable statistics and visual indicators. The comparison of ARIMA, and ANN results showed the ANN algorithms produced more reliable predictions of GWL than the ARIMA model at nearly all 4 monitoring wells, with significantly lower values of MAE, MSE, and RMSE.
Artificial neural networks (ANNs) have been shown to be a resilient class of modelling algorithms, able to handle issues like outliers, noise, and non-Gaussian data distributions (Garg et al., 2016).
Figure 1 shows that there is no regular pattern or seasonality in the ground water fluctuations across all sites. As a result, unlike the ANN model, the ARIMA model could not deal with irregular data patterns and had poor performance. Furthermore, the dynamic nature of ANN, as well as their capacity to simulate non-linear connections and their adaptability to employ any set of available variables, makes them useful methods for use in scientific study and implementations (Shiri et al., 2013). ANNs are effective for predicting tasks due to their flexibility, non-linearity, and the capacity to map arbitrary functions, all of which are features that are unique to ANNs.
5.3. Challenges and Limitations
Limited Data: The standard of the data utilized in the analysis could have impacted on the reliability of the findings. The presence of missing data, outliers, or errors could affect the accuracy of the models employed in the study.
Model Interpretation: Although ANN models make reliable forecasts, they are sometimes referred to as "black box" models since their inner workings are not readily understandable. This can reduce their applicability in some scenarios.
Computational Complexity: The use of ANN models requires computational resources, which may be challenging in some situations, particularly when dealing with large datasets.
Generalization: Since the study was conducted on a specific region with a limited dataset, the generalization of the results may be challenging.
6. Conclusions
This research analyzed groundwater level data from four Colorado monitoring wells from 1980 to 2019 using both standard ARIMA and artificial neural network methods. For each of the four locations, to forecast GWL, we constructed an ARIMA and ANN model. Methods of Assessment Fitting well with the actual data series, the created ARIMA and ANN models were tested using the mean absolute error (MAE), root-mean-squared error (RMSE), and mean-squared error (MSE). When applied to GWL time-series data, both models produce reliable predictions. In addition, the present research work compares the ANN model's accuracy to that of the broadly used ARIMA model for predicting time series. The results showed that the ANN model performed better than the ARIMA model.
Author Contributions
H.G. and R.U.; conducted the research and wrote the manuscript, J.M., Z.R. and F. revised and convert it to the MDPI format. The final version of the work has been reviewed and approved by all authors. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Acknowledgments
sincerely thank the Balochistan University of Information Technology, Engineering, and Management Sciences for its assistance. We are thankful to Drs. Rahila Umer, Jan Muhammad, Zahid Rauf, and Naeem Shahwani for their essential assistance with this review. This endeavor is supported by the HEC LCF63 project.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest.
References
- Agatonovic-Kustrin, S., & Beresford, R. (2000). Basic concepts of artificial neural network (ANN) modeling and its application in pharmaceutical research. In Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis (Vol. 22, Issue 5). [CrossRef]
- Bank, D., Koenigstein, N., & Giryes, R. (2020). Autoencoders. ArXiv Preprint ArXiv:2003.05991.
- Birylo, M., Rzepecka, Z., Kuczynska-Siehien, J., & Nastula, J. (2018). Analysis of water budget prediction accuracy using ARIMA models. Water Science and Technology: Water Supply, 18(3), 819–830. [CrossRef]
- Daliakopoulos, I. N., Coulibaly, P., & Tsanis, I. K. (2005). Groundwater level forecasting using artificial neural networks. Journal of Hydrology, 309(1–4), Article 1–4. [CrossRef]
- Döll, P., Hoffmann-Dobrev, H., Portmann, F. T., Siebert, S., Eicker, A., Rodell, M., Strassberg, G., & Scanlon, B. (2012). Impact of water withdrawals from groundwater and surface water on continental water storage variations. Journal of Geodynamics, 59, 143–156. [CrossRef]
- Emamgholizadeh, S., Moslemi, K., & Karami, G. (2014). Prediction the groundwater level of bastam plain (Iran) by artificial neural network (ANN) and adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system (ANFIS). Water Resources Management, 28(15), 5433–5446. [CrossRef]
- Famiglietti, J. S. (2014). The global groundwater crisis. Nature Climate Change, 4(11), 945–948. [CrossRef]
- Fukushima, K. (1975). Cognitron: A self-organizing multilayered neural network. Biological Cybernetics, 20(3–4). [CrossRef]
- Garg, N., Sharma, M. K., Parmar, K. S., Soni, K., Singh, R. K., & Maji, S. (2016). Comparison of ARIMA and ANN approaches in time-series predictions of traffic noise. Noise Control Engineering Journal, 64(4). [CrossRef]
- Geurts, M., Box, G. E. P., & Jenkins, G. M. (1977). Time Series Analysis: Forecasting and Control. Journal of Marketing Research, 14(2). [CrossRef]
- Gibrilla, A., Anornu, G., & Adomako, D. (2018). Trend analysis and ARIMA modelling of recent groundwater levels in the White Volta River basin of Ghana. Groundwater for Sustainable Development, 6, 150–163. [CrossRef]
- Guzman, S. M., Paz, J. O., Tagert, M. L. M., & Mercer, A. (2015). Artificial Neural Networks and Support Vector Machines: Contrast Study for Groundwater Level Prediction. 2015 ASABE Annual International Meeting, 1.
- Hagan, M. T., & Menhaj, M. B. (1994). Training Feedforward Networks with the Marquardt Algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 5(6). [CrossRef]
- Han, S.-H., Kim, K. W., Kim, S., & Youn, Y. C. (2018). Artificial Neural Network: Understanding the Basic Concepts without Mathematics. Dementia and Neurocognitive Disorders, 17(3). [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q., Lu, Z., & Wang, S. (2020). A hybrid model combining ARIMA and machine learning techniques for forecasting groundwater levels in a coastal aquifer of China. Hydrological Sciences Journal, 65(5), 766–782.
- Levin, S., Krishnan, S., Rajkumar, S., Halery, N., & Balkunde, P. (2016). Monitoring of fluoride in water samples using a smartphone. Science of the Total Environment, 551, 101–107. [CrossRef]
- Li, J., Chen, C., Huang, Q., Zhang, J., Yang, L., & Zhao, C. (2019). Estimating groundwater storage changes in the North China Plain using GRACE data. Water Resources Research, 55(7), 5836–5852.
- Maheshwari, P., Singh, V., & Kumar, A. (2017). Artificial neural network modeling for groundwater level forecasting in a semi-arid region of India. Journal of Hydrology, 544, 622–633.
- Rahman, M. M., Jain, S. K., & Shamseldin, A. Y. (2020). Performance evaluation of data-driven models for groundwater level forecasting. Journal of Hydrology, 584, 124642.
- Rumelhart, D. E., Durbin, R., Golden, R., & Chauvin, Y. (1995). Backpropagation: The basic theory. In Backpropagation: Theory, architectures, and applications.
- Satish Kumar, K., & Venkata Rathnam, E. (2019). Analysis and prediction of groundwater level trends using four variations of Mann Kendall tests and ARIMA modelling. Journal of the Geological Society of India, 94, 281–289. [CrossRef]
- Scanlon, B. R., Faunt, C. C., Longuevergne, L., Reedy, R. C., Alley, W. M., McGuire, V. L., & McMahon, P. B. (2012). Groundwater depletion and sustainability of irrigation in the US High Plains and Central Valley. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 109(24), 9320–9325. [CrossRef]
- Shafique, M., Asghar, M. N., Abbas, Z., & Ashraf, M. (2018). Prediction of groundwater level using support vector regression in a coastal aquifer of Pakistan. Environmental Earth Sciences, 77(14), 518.
- Shiri, J., Kisi, O., Yoon, H., Lee, K. K., & Hossein Nazemi, A. (2013). Predicting groundwater level fluctuations with meteorological effect implications-A comparative study among soft computing techniques. Computers and Geosciences, 56. [CrossRef]
- Singh, R. P., Singh, A., & Gautam, R. (2019). Artificial neural network-based groundwater level prediction in a hard rock terrain of India. Modeling Earth Systems and Environment, 5(4), 1263–1272.
- Sophocleous, M. (1992). Groundwater recharge estimation and regionalization: The Great Bend Prairie of central Kansas and its recharge statistics. Journal of Hydrology, 137(1–4), 113–140. [CrossRef]
- Sophocleous, M. (2002). Interactions between groundwater and surface water: The state of the science. Hydrogeology Journal, 10, 52–67. [CrossRef]
- Takafuji, E. H. de M., Rocha, M. M. da, & Manzione, R. L. (2019). Groundwater level prediction/forecasting and assessment of uncertainty using SGS and ARIMA models: A case study in the Bauru Aquifer System (Brazil). Natural Resources Research, 28(2), 487–503. [CrossRef]
- Taormina, R., Chau, K., & Sethi, R. (2012). Artificial neural network simulation of hourly groundwater levels in a coastal aquifer system of the Venice lagoon. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 25(8), 1670–1676. [CrossRef]
- Teferi, E., Andargie, K., Gebrehiwot, K., & Legesse, D. (2019). Estimation of groundwater recharge using satellite imagery and GIS techniques: A case study in the Upper Awash Basin, Ethiopia. Environmental Earth Sciences, 78(2), 54.
- Wada, Y., Van Beek, L. P., Van Kempen, C. M., Reckman, J. W., Vasak, S., & Bierkens, M. F. (2010). Global depletion of groundwater resources. Geophysical Research Letters, 37(20). [CrossRef]
- Wang, H. R., Wang, C., Lin, X., & Kang, J. (2014). An improved ARIMA model for precipitation simulations. Nonlinear Processes in Geophysics, 21(6). [CrossRef]
- Wang, S., Zhang, Q., Wei, J., & Jiang, L. (2017). Comparison of ARIMA, ANN, and SVR models in forecasting groundwater levels in a coastal karst area of China. Water, 9(7), 490.
- Wang, S., Zhang, Q., Wei, J., & Jiang, L. (2018). Performance evaluation of machine learning models in groundwater level forecasting. Water Resources Management, 32(14), 4717–4734.
- Wu, Y., Guo, S., Jin, J., Li, X., & Liu, Z. (2018). Integration of groundwater level and satellite-derived soil moisture for improved estimation of groundwater variations in the North China Plain. Remote Sensing, 10(9), 1401.
- Xiao, Y., Shao, J., Frape, S. K., Cui, Y., Dang, X., Wang, S., & Ji, Y. (2018). Groundwater origin, flow regime and geochemical evolution in arid endorheic watersheds: A case study from the Qaidam Basin, northwestern China. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 22(8), 4381–4400. [CrossRef]
- Young, W. L. (1977). BOX-JENKINS APPROACH TO TIME SERIES ANALYSIS AND FORECASTING: PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATIONS. RAIRO Recherche Operationnelle, 11(2). [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M., Zhang, X., Qiao, W., Lu, Y., & Chen, H. (2023). Forecasting of runoff in the lower Yellow River based on the CEEMDAN–ARIMA model. Water Supply, 23(3), 1434–1450. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).