Submitted:
31 May 2023
Posted:
01 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
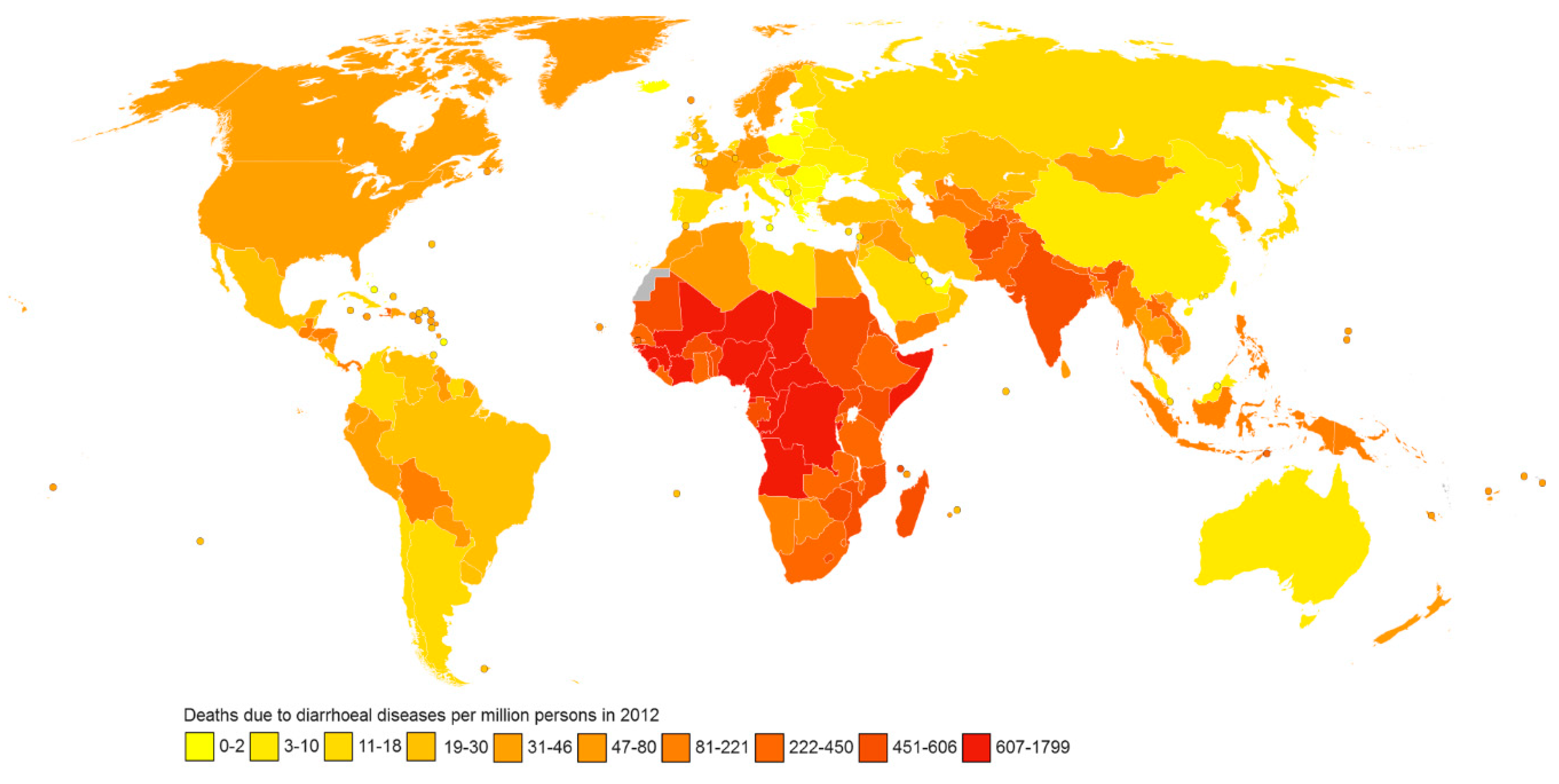
2. Current global status
| Name | Transmission mode/ agent characteristics | Health symptoms | Hosts | Disinfection resistance | Outbreaks/ Cases | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cryptosporidium spp. | Water (drinking and recreational), faecal-oral route, | Moderate/ diarrhoea | Humans, cattle, rodents | Very high | 239/65,540(2004 – 2014) | [2,3,6,7] |
| Oocyst, 3.5 – 6.5 µm (Ø) | Ozone (4 ppm/10 min); > 3% hypochlorite | |||||
| Giardia spp. | Water, faecal-oral route | Moderate/ diarrhoea, gas, bloating, anorexia | Human, animals | High | 142/1110(2007 – 2014) | [1,3,7,8] |
| Cyst (ovoid, 8 – 18 × 7 – 10 µm) | Fenbendazole (5 mg/kg); Ozone (0.3 ppm/ 3 min); 1% Na- hypochlorite | |||||
| Entamoeba spp. | Water, food, faecal-oral route | Severe/ Colitis, dysentery, diarrhoea, liver issues | Humans | High | 15/ 9.41 million (2000 - 2015) | [2,4,8,9] |
| Cyst (10 - 16µm Ø) | Chlorine (5 ppm, pH 7, 5 min), 1% sodium hypochlorite | |||||
| Cyst (40 - 60µm Ø), trophozoites (100 – 150 µm) | 1% sodium hypochlorite |
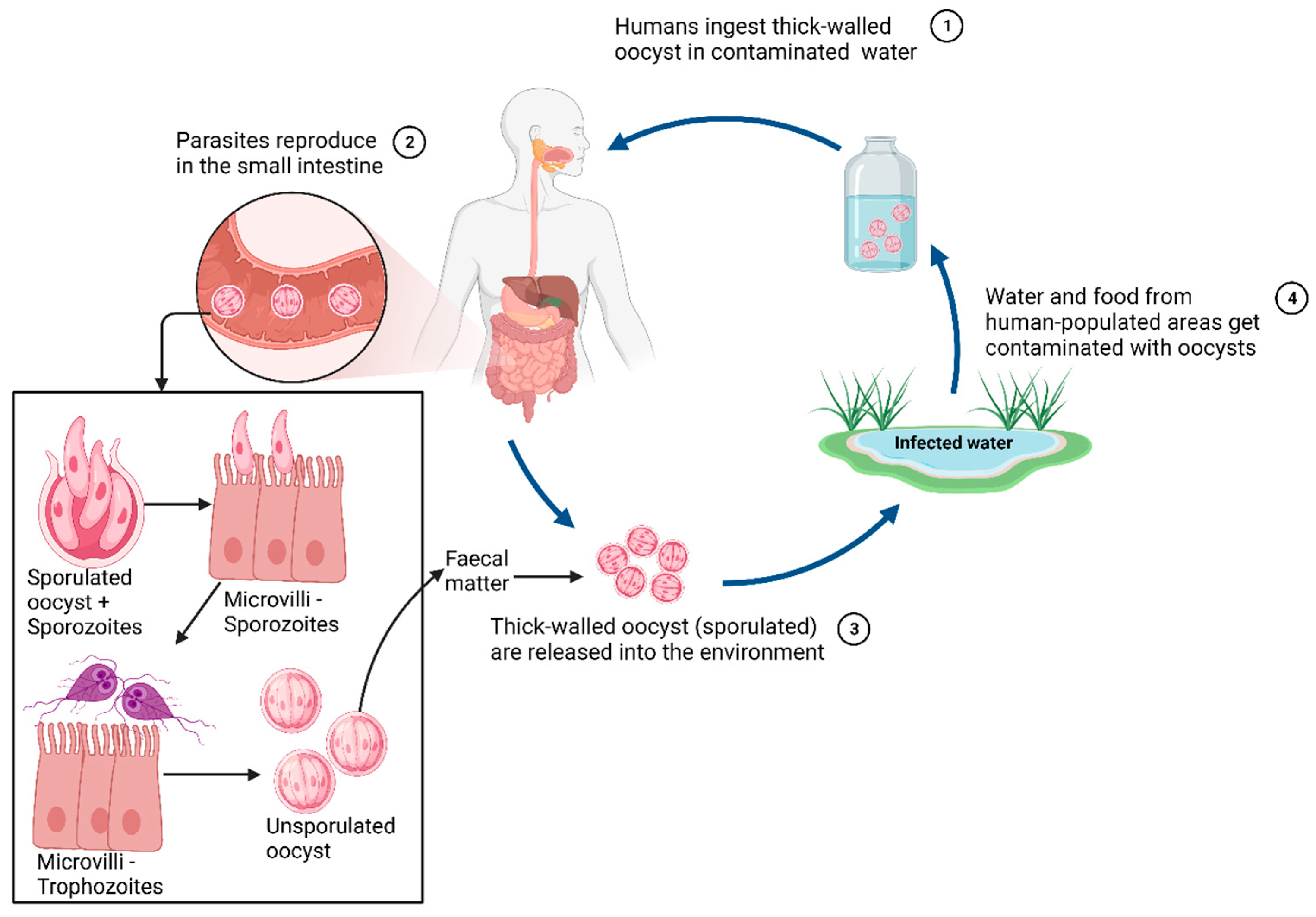
3. Life cycle and infection mechanism
3.1. Life cycle
3.2. Dysbiosis and target organs
3.2.1. Dysbiosis
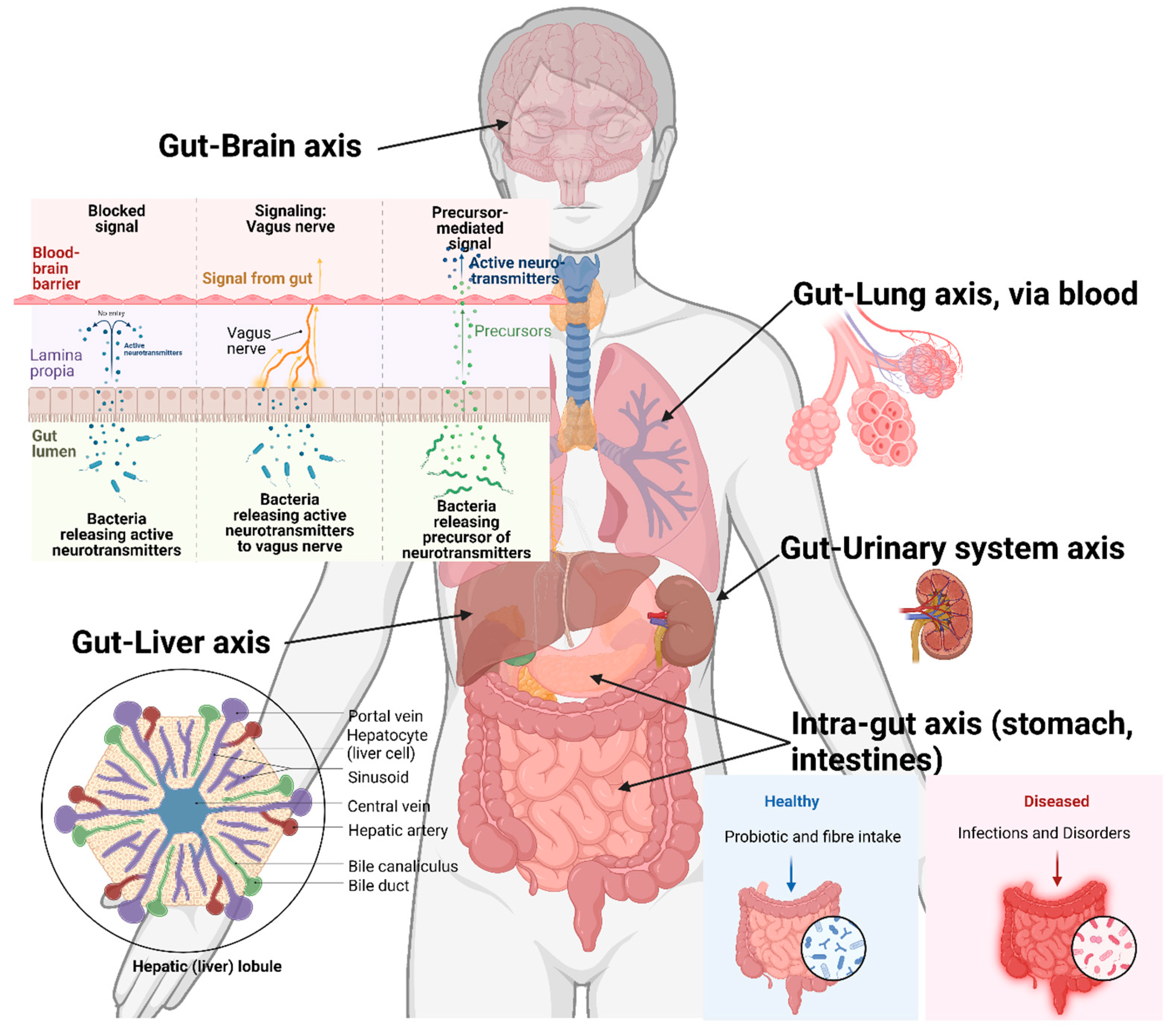
4. Cross-organ impacts
4.1. Gut-Liver axis
4.2. Gut-Lung axis
5. Nutritional interventions
5.1. Prebiotics, probiotics and synbiotics supplementation
5.2. Postbiotics and microbiome modulation to improve MDR resilience
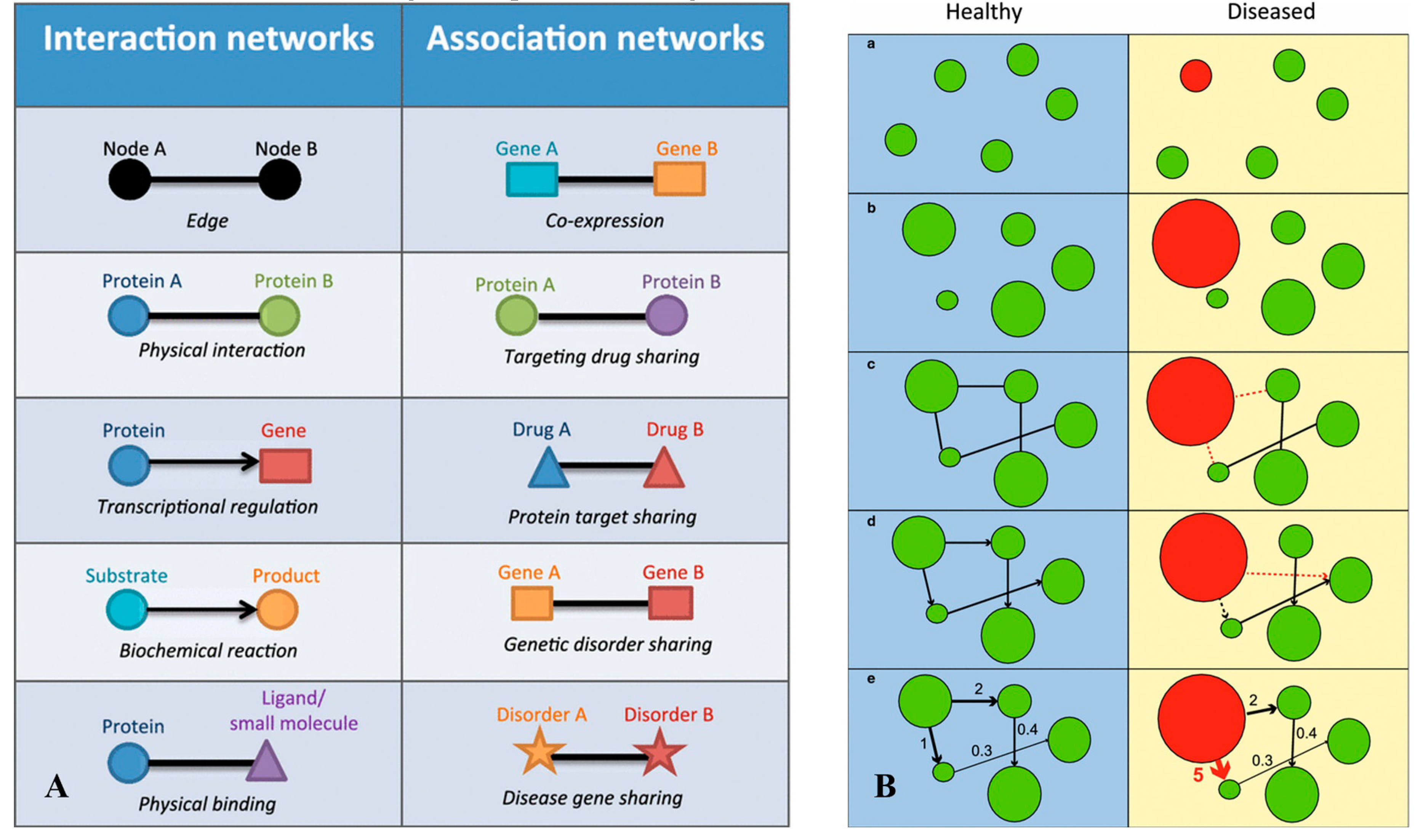
6. Application of multiomics in high-throughput analysis of gut microbiome health and inter-organ axes
6.1. Multiomics approaches
6.2. Application of Artificial intelligence and machine learning (AIML) and future aspects
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Petri, W.A.; Miller, M.; Binder, H.J.; Levine, M.M.; Dillingham, R.; Guerrant, R.L. Enteric infections, diarrhea, and their impact on function and development. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 1277–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Global Health Observatory Data Repository: Diarrhoeal Diseases. Available online: http://apps.who.int/gho/data/view.main.CM1002015WORLD-CH3?lang=enhttp://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs310/en/ (accessed on 17 January).
- Efstratiou, A.; Ongerth, J.E.; Karanis, P. Waterborne transmission of protozoan parasites: Review of worldwide outbreaks - An update 2011–2016. Water Res. 2017, 114, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, S. Amoebiasis: Global Status; GIDEON Informatics Inc: Los Angeles, CA, UNITED STATES, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Berger, S. Giardiasis: Global Status; GIDEON Informatics Inc: Los Angeles, CA, UNITED STATES, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Berger, S. Cryptosporidiosis: Global Status; GIDEON Informatics Inc: Los Angeles, CA, UNITED STATES, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Betancourt, W.Q.; Rose, J.B. Drinking water treatment processes for removal of Cryptosporidium and Giardia. Vet. Parasitol. 2004, 126, 219–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarroll, E.L.; Hoff, J.C. Effect of disinfectants on Giardia cysts. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1988, 18, 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Rubin, A.J.; Engel, J.P.; Sproul, O.J. Disinfection of amoebic cysts in water with free chlorine. J. (Water Pollut. Control Fed. ) 1983, 55, 1174–1182. [Google Scholar]
- Chalmers, R.M. Chapter Sixteen - Cryptosporidium. In Microbiology of Waterborne Diseases (Second Edition); Academic Press: London, 2014; pp. 287–326. [Google Scholar]
- Lane, S.; Lloyd, D. Current trends in research into the waterborne parasite Giardia. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2002, 28, 123–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalmers, R.M. Chapter Eighteen - Entamoeba histolytica. In Microbiology of Waterborne Diseases (Second Edition); Academic Press: London, UK, 2014; pp. 355–373. [Google Scholar]
- Duncan, H.E.; Edberg, S.C. Host-Microbe Interaction in the Gastrointestinal Tract. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 1995, 21, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macfarlane, S.; Dillon, J.F. Microbial biofilms in the human gastrointestinal tract. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 102, 1187–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swidsinski, A.; Ung, V.; Sydora, B.C.; Loening-Baucke, V.; Doerffel, Y.; Verstraelen, H.; Fedorak, R.N. Bacterial overgrowth and inflammation of small intestine after carboxymethylcellulose ingestion in genetically susceptible mice. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2009, 15, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, W.; Clode, P.L.; Monis, P.; Thompson, R.A. Multiplication of the waterborne pathogen Cryptosporidium parvum in an aquatic biofilm system. Parasites Vectors 2013, 6, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenney, E.A.; Greene, L.K.; Drea, C.M.; Yoder, A.D. Down for the count: Cryptosporidium infection depletes the gut microbiome in Coquerel’s sifakas. Microb. Ecol. Health Dis. 2017, 28, 1335165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Certad, G.; Viscogliosi, E.; Chabé, M.; Cacciò, S.M. Pathogenic Mechanisms of Cryptosporidium and Giardia. Trends Parasitol. 2017, 33, 561–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karpe, A.V.; Hutton, M.L.; Mileto, S.J.; James, M.L.; Evans, C.; Shah, R.M.; Ghodke, A.B.; Hillyer, K.E.; Metcalfe, S.S.; Liu, J.-W.; et al. Cryptosporidiosis Modulates the Gut Microbiome and Metabolism in a Murine Infection Model. Metabolites 2021, 11, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berrilli, F.; Di Cave, D.; Cavallero, S.; D'Amelio, S. Interactions between parasites and microbial communities in the human gut. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2012, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwyer, D.M.; Chang, K.P. Surface membrane carbohydrate alterations of a flagellated protozoan mediated by bacterial endosymbiotes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. United States Am. 1976, 73, 852–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, M.F.; Uetanabaro, A.P.T.; Costa, A.F.; Alves, C.A.; Farias, L.M.; Bambirra, E.A.; Penna, F.J.; Vieira, E.C.; Nicoli, J.R. Influence of bacteria from the duodenal microbiota of patients with symptomatic giardiasis on the pathogenicity of Giardia duodenalis in gnotoxenic mice. J. Med. Microbiol. 2000, 49, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirelman, D.; Feingold, C.; Wexler, A.; Bracha, R. Interactions between Entamoeba histolytica, bacteria and intestinal cells. In Cytopathology of Parasitic Disease. Pitman Books: London, UK, 1983; Volume 99, pp. 2–30. [Google Scholar]
- Galván-Moroyoqui, J.M.; Del Carmen Dominguez-Robles, M.; Franco, E.; Meza, I. The interplay between Entamoeba and enteropathogenic bacteria modulates epithelial cell damage. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2008, 2, e266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerbaba, T.K.; Gupta, P.; Rioux, K.; Hansen, D.; Buret, A.G. Giardia duodenalis-induced alterations of commensal bacteria kill Caenorhabditis elegans: a new model to study microbial-microbial interactions in the gut. Am. J. Physiol. -Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2015, 308, G550–G561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, J.L.; Blackler, R.W.; Chan, M.V.; Da Silva, G.J.; Elsheikh, W.; Flannigan, K.L.; Gamaniek, I.; Manko, A.; Wang, L.; Motta, J.-P. Anti-inflammatory and cytoprotective actions of hydrogen sulfide: Translation to therapeutics. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2015, 22, 398–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpe, A.V.; Hutton, M.L.; Mileto, S.J.; James, M.L.; Evans, C.; Ghodke, A.B.; Shah, R.M.; Metcalfe, S.S.; Liu, J.-W.; Walsh, T.; et al. Gut microbial perturbation and host response induce redox pathway upregulation along the Gut-Liver axis during giardiasis in C57BL/6J mouse model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kedia, S.; Rampal, R.; Paul, J.; Ahuja, V. Gut microbiome diversity in acute infective and chronic inflammatory gastrointestinal diseases in North India. J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 51, 660–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partida-Rodríguez, O.; Serrano-Vázquez, A.; Nieves-Ramírez, M.E.; Moran, P.; Rojas, L.; Portillo, T.; González, E.; Hernández, E.; Finlay, B.B.; Ximenez, C. Human intestinal microbiota: Interaction between parasites and the host immune response. Arch. Med. Res. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zermeño, V.; Ximénez, C.; Morán, P.; Valadez, A.; Valenzuela, O.; Rascón, E.; Diaz, D.; Cerritos, R. Worldwide genealogy of Entamoeba histolytica: An overview to understand haplotype distribution and infection outcome. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2013, 17, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzmán-Silva, M.A.; Santos, H.L.C.; Peralta, R.S.; Peralta, J.M.; de Macedo, H.W. Experimental amoebic liver abscess in hamsters caused by trophozoites of a Brazilian strain of Entamoeba dispar. Exp. Parasitol. 2013, 134, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolabella, S.S.; Serrano-Luna, J.; Navarro-García, F.; Cerritos, R.; Ximénez, C.; Galván-Moroyoqui, J.M.; Silva, E.F.; Tsutsumi, V.; Shibayama, M. A mo ebic liver abscess production by Entamoeba dispar. parasite 2012, 13, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Weber, C.; Koutero, M.; Dillies, M.-A.; Varet, H.; Lopez-Camarillo, C.; Coppée, J.Y.; Hon, C.-C.; Guillén, N. Extensive transcriptome analysis correlates the plasticity of Entamoeba histolytica pathogenesis to rapid phenotype changes depending on the environment. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigothier, M.-C.; Khun, H.; Tavares, P.; Cardona, A.; Huerre, M.; Guillén, N. Fate of Entamoeba histolytica during establishment of amoebic liver abscess analyzed by quantitative radioimaging and histology. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 3208–3215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanley, S.L. Pathophysiology of amoebiasis. Trends Parasitol. 2001, 17, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsutsumi, V.; Mena-Lopez, R.; Anaya-Velazquez, F.; Martinez-Palomo, A. Cellular bases of experimental amebic liver abscess formation. Am. J. Pathol. 1984, 117, 81. [Google Scholar]
- Ungar, B.L.; Burris, J.A.; Quinn, C.A.; Finkelman, F.D. New mouse models for chronic Cryptosporidium infection in immunodeficient hosts. Infect. Immun. 1990, 58, 961–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astiazaran-Garcia, H.; Lopez-Teros, V.; Valencia, M.E.; Vazquez-Ortiz, F.; Sotelo-Cruz, N.; Quihui-Cota, L. Giardia lamblia infection and its implications for vitamin a liver stores in school children. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2010, 57, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swann, J.; Jamshidi, N.; Lewis, N.E.; Winzeler, E.A. Systems analysis of host–parasite interactions. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. : Syst. Biol. Med. 2015, 7, 381–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakaria, A.; Al-Share, B.; Al Asad, K. Primary Pulmonary Amebiasis Complicated with Multicystic Empyema. Case Rep. Pulmonol. 2016, 2016, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, L.M.L.; Marrone, J.R. Entamoeba histolytica meningoencephalitis diagnosed by trophozoites in cerebrospinal fluid. New Microbes New Infect. 2013, 1, 16–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reina, F.T.R.; Ribeiro, C.A.; Araújo, R.S.D.; Matté, M.H.; Castanho, R.E.P.; Tanaka, I.I.; Viggiani, A.M.F.S.; Martins, L.P.A. INTESTINAL AND PULMONARY INFECTION BY Cryptosporidium parvum IN TWO PATIENTS WITH HIV/AIDS. Rev. Do Inst. De Med. Trop. De São Paulo 2016, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Vélez, R.; Tarazona, R.; Camacho, A.G.; Gomez-Mampaso, E.; Guerrero, A.; Moreira, V.; Villanueva, R. Intestinal and extraintestinal cryptosporidiosis in AIDS patients. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 1995, 14, 677–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clavel, A.; Arnal, A.C.; Sánchez, E.C.; Castillo, F.J.; Varea, M.; Gómez-Lus, R.; Cuesta, J.; Letona, S.; Amiguet, J.A. Respiratory cryptosporidiosis: Case series and review of the literature. Infection 1996, 24, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, S.L.; Lu, M.; Ma, J.Z.; Naylor, C.; Donowitz, J.R.; Kirkpatrick, B.D.; Haque, R.; Petri, W.A., Jr. Inflammatory markers predict episodes of wheezing during the first year of life in Bangladesh. Respir. Med. 2015, 110, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braamskamp, M.J.A.M.; Dolman, K.M.; Tabbers, M.M. Clinical practice. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2010, 169, 1179–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wypych, T.P.; Wickramasinghe, L.C.; Marsland, B.J. The influence of the microbiome on respiratory health. Nat. Immunol. 2019, 20, 1279–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trompette, A.; Gollwitzer, E.S.; Yadava, K.; Sichelstiel, A.K.; Sprenger, N.; Ngom-Bru, C.; Blanchard, C.; Junt, T.; Nicod, L.P.; Harris, N.L.; et al. Gut microbiota metabolism of dietary fiber influences allergic airway disease and hematopoiesis. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cait, A.; Hughes, M.R.; Antignano, F.; Cait, J.; Dimitriu, P.A.; Maas, K.R.; Reynolds, L.A.; Hacker, L.; Mohr, J.; Finlay, B.B.; et al. Microbiome-driven allergic lung inflammation is ameliorated by short-chain fatty acids. Mucosal Immunol. 2018, 11, 785–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorburn, A.N.; McKenzie, C.I.; Shen, S.; Stanley, D.; Macia, L.; Mason, L.J.; Roberts, L.K.; Wong, C.H.Y.; Shim, R.; Robert, R.; et al. Evidence that asthma is a developmental origin disease influenced by maternal diet and bacterial metabolites. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trompette, A.; Gollwitzer, E.S.; Pattaroni, C.; Lopez-Mejia, I.C.; Riva, E.; Pernot, J.; Ubags, N.; Fajas, L.; Nicod, L.P.; Marsland, B.J. Dietary Fiber Confers Protection against Flu by Shaping Ly6c<sup>−</sup> Patrolling Monocyte Hematopoiesis and CD8<sup>+</sup> T Cell Metabolism. Immunity 2018, 48, 992–1005.e1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, C.L.F.; Rudan, I.; Liu, L.; Nair, H.; Theodoratou, E.; Bhutta, Z.A.; O'Brien, K.L.; Campbell, H.; Black, R.E. Global burden of childhood pneumonia and diarrhoea. Lancet 2013, 381, 1405–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halliez, M.C.M.; Buret, A.G. Extra-intestinal and long term consequences of Giardia duodenalis infections. World J. Gastroenterol. : WJG 2013, 19, 8974–8985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buret, A.G.; Reti, K. Acute enteric infections alter commensal microbiota: new mechanisms in post-infectious intestinal inflammatory disorders. In Proceedings of the Old Herborn University Seminar Monograph: Persisting Consequences of Intestinal Infection; 2014; pp. 87–100. [Google Scholar]
- Hanevik, K. Long-Term Consequences of Cryptosporidium and Giardia Gastroenteritis. Curr. Trop. Med. Rep. 2016, 3, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbara, G.; Grover, M.; Bercik, P.; Corsetti, M.; Ghoshal, U.C.; Ohman, L.; Rajilić-Stojanović, M. Rome Foundation Working Team Report on Post-Infection Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 46–58.e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, S.J.; Martinez, E.G.; Gregorio, G.V.; Dans, L.F. Probiotics for treating acute infectious diarrhoea. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depoorter, L.; Vandenplas, Y. Chapter 21 - Probiotics in pediatrics. In Probiotics; Brandelli, A., Ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2022; pp. 425–450. [Google Scholar]
- Su, G.L.; Ko, C.W.; Bercik, P.; Falck-Ytter, Y.; Sultan, S.; Weizman, A.V.; Morgan, R.L. AGA Clinical Practice Guidelines on the Role of Probiotics in the Management of Gastrointestinal Disorders. Gastroenterology 2020, 159, 697–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Nardo, G.; Cremon, C.; Staiano, A.; Stanghellini, V.; Borrelli, O.; Strisciuglio, C.; Romano, C.; Mallardo, S.; Scarpato, E.; Marasco, G.; et al. Role of inflammation in pediatric irritable bowel syndrome. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2023, 35, e14365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nocerino, R.; Di Costanzo, M.; Bedogni, G.; Cosenza, L.; Maddalena, Y.; Di Scala, C.; Della Gatta, G.; Carucci, L.; Voto, L.; Coppola, S.; et al. Dietary Treatment with Extensively Hydrolyzed Casein Formula Containing the Probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG Prevents the Occurrence of Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders in Children with Cow's Milk Allergy. J Pediatr 2019, 213, 137–142.e132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, A.C.; Lacy, B.E.; Talley, N.J. Irritable Bowel Syndrome. N Engl J Med 2017, 376, 2566–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinde, T.; Perera, A.P.; Vemuri, R.; Gondalia, S.V.; Beale, D.J.; Karpe, A.V.; Shastri, S.; Basheer, W.; Southam, B.; Eri, R. Synbiotic supplementation with prebiotic green banana resistant starch and probiotic Bacillus coagulans spores ameliorates gut inflammation in mouse model of inflammatory bowel diseases. Eur. J. Nutr. 2020, 59, 3669–3689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitali, B.; Ndagijimana, M.; Cruciani, F.; Carnevali, P.; Candela, M.; Guerzoni, M.E.; Brigidi, P. Impact of a synbiotic food on the gut microbial ecology and metabolic profiles. BMC Microbiol. 2010, 10, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersson, J.; Karlsson, P.C.; ouml; ransson, U.; Rafter, J.J.; Bohlin, L. The Flavouring Phytochemical 2-Pentanone Reduces Prostaglandin Production and COX-2 Expression in Colon Cancer Cells. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2008, 31, 534–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.K.; Beckett, J.M.; Kalpurath, K.; Ishaq, M.; Ahmad, T.; Eri, R.D. Synbiotics as Supplemental Therapy for the Alleviation of Chemotherapy-Associated Symptoms in Patients with Solid Tumours. Nutrients 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boger, M.C.L.; Bueren, A.L.v.; Dijkhuizen, L. Cross-Feeding among Probiotic Bacterial Strains on Prebiotic Inulin Involves the Extracellular <i>exo</i>-Inulinase of Lactobacillus paracasei Strain W20. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84, e01539–01518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez Quintero, D.F.; Kok, C.R.; Hutkins, R. The Future of Synbiotics: Rational Formulation and Design. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, C.M.; Costa, V.M.; Gomes, M.I.F.V.; Golim, M.A.; Modolo, J.R.; Langoni, H. Effects of synbiotic-based Bifidobacterium animalis in female rats experimentally infected with Toxoplasma gondii. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2011, 34, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emery, S.J.; Baker, L.; Ansell, B.R.E.; Mirzaei, M.; Haynes, P.A.; McConville, M.J.; Svärd, S.G.; Jex, A.R. Differential protein expression and post-translational modifications in metronidazole-resistant Giardia duodenalis. GigaScience 2018, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharyya, S. Herbal, Nutritional, and Traditional Remedies for Giardiasis. In Neglected Tropical Diseases and Phytochemicals in Drug Discovery; 2021; pp. 135–169. [Google Scholar]
- Anthony, J.P.; Fyfe, L.; Stewart, D.; McDougall, G.J.; Smith, H.V. The effect of blueberry extracts on Giardia duodenalis viability and spontaneous excystation of Cryptosporidium parvum oocysts, in vitro. Methods 2007, 42, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoud, A.; Attia, R.; Said, S.; Ibraheim, Z. Ginger and cinnamon: can this household remedy treat giardiasis? Parasitological and histopathological studies. Iran J Parasitol 2014, 9, 530–540. [Google Scholar]
- de Almeida, C.R.; Bezagio, R.C.; Colli, C.M.; Romera, L.I.L.; Ferrari, A.; Gomes, M.L. Elimination of Giardia duodenalis BIV in vivo using natural extracts in microbiome and dietary supplements. Parasitol. Int. 2022, 86, 102484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaber, M.; Galal, L.A.A.; Farrag, H.M.M.; Badary, D.M.; Alkhalil, S.S.; Elossily, N. The Effects of Commercially Available Syzygium aromaticum, Anethum graveolens, Lactobacillus acidophilus LB, and Zinc as Alternatives Therapy in Experimental Mice Challenged with Cryptosporidium parvum. Infect. Drug Resist. 2022, 15, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popovic, A.; Bourdon, C.; Wang, P.W.; Guttman, D.S.; Soofi, S.; Bhutta, Z.A.; Bandsma, R.H.J.; Parkinson, J.; Pell, L.G. Micronutrient supplements can promote disruptive protozoan and fungal communities in the developing infant gut. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salminen, S.; Collado, M.C.; Endo, A.; Hill, C.; Lebeer, S.; Quigley, E.M.M.; Sanders, M.E.; Shamir, R.; Swann, J.R.; Szajewska, H.; et al. The International Scientific Association of Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on the definition and scope of postbiotics. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 649–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinde, T.; Vemuri, R.; Shastri, S.; Perera, A.P.; Gondalia, S.V.; Beale, D.J.; Karpe, A.V.; Eri, R.; Stanley, R. Modulating the microbiome and immune responses using whole plant fibre in synbiotic combination with fibre-digesting probiotic attenuates chronic colonic inflammation in spontaneous colitic mice model of IBD. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, J. D-amino acids and lactic acid bacteria. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasabe, J.; Miyoshi, Y.; Rakoff-Nahoum, S.; Zhang, T.; Mita, M.; Davis, B.M.; Hamase, K.; Waldor, M.K. Interplay between microbial d-amino acids and host d-amino acid oxidase modifies murine mucosal defence and gut microbiota. Nat. Microbiol. 2016, 1, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpe, A.V.; Hutton, M.L.; Mileto, S.J.; James, M.L.; Evans, C.; Ghodke, A.B.; Shah, R.M.; Metcalfe, S.S.; Liu, J.-W.; Walsh, T.; et al. Gut Microbial Perturbation and Host Response Induce Redox Pathway Upregulation along the Gut–Liver Axis during Giardiasis in C57BL/6J Mouse Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1636. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sencio, V.; Barthelemy, A.; Tavares, L.P.; Machado, M.G.; Soulard, D.; Cuinat, C.; Queiroz-Junior, C.M.; Noordine, M.-L.; Salomé-Desnoulez, S.; Deryuter, L.; et al. Gut Dysbiosis during Influenza Contributes to Pulmonary Pneumococcal Superinfection through Altered Short-Chain Fatty Acid Production. Cell Rep. 2020, 30, 2934–2947.e2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobson, A.; Lam, L.; Rajendram, M.; Tamburini, F.; Honeycutt, J.; Pham, T.; Van Treuren, W.; Pruss, K.; Stabler, S.R.; Lugo, K.; et al. A Gut Commensal-Produced Metabolite Mediates Colonization Resistance to Salmonella Infection. Cell Host Microbe 2018, 24, 296–307.e297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vemuri, R.; Gundamaraju, R.; Shinde, T.; Perera, A.P.; Basheer, W.; Southam, B.; Gondalia, S.V.; Karpe, A.V.; Beale, D.J.; Tristram, S.; et al. Lactobacillus acidophilus DDS-1 Modulates Intestinal-Specific Microbiota, Short-Chain Fatty Acid and Immunological Profiles in Aging Mice. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hochbaum, A.I.; Kolodkin-Gal, I.; Foulston, L.; Kolter, R.; Aizenberg, J.; Losick, R. Inhibitory effects of D-amino acids on Staphylococcus aureus biofilm development. J Bacteriol 2011, 193, 5616–5622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassone-Corsi, M.; Nuccio, S.-P.; Liu, H.; Hernandez, D.; Vu, C.T.; Takahashi, A.A.; Edwards, R.A.; Raffatellu, M. Microcins mediate competition among Enterobacteriaceae in the inflamed gut. Nature 2016, 540, 280–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upatissa, S.; Mitchell, R.J. The “Cins” of Our Fathers: Rejuvenated Interest in Colicins to Combat Drug Resistance. J. Microbiol. 2023, 61, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Said, L.; Emond-Rheault, J.-G.; Soltani, S.; Telhig, S.; Zirah, S.; Rebuffat, S.; Diarra, M.S.; Goodridge, L.; Levesque, R.C.; Fliss, I. Phenomic and genomic approaches to studying the inhibition of multiresistant Salmonella enterica by microcin J25. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 22, 2907–2920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Gómez, H.; Jorba, M.; Albericio, F.; Viñas, M.; Tulla-Puche, J. Chemical Modification of Microcin J25 Reveals New Insights on the Stereospecific Requirements for Antimicrobial Activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guesdon, W.; Pezier, T.; Menard, S.; Nicolosi, A.; Le Vern, Y.; Silvestre, A.; Diana, J.; Laurent, F.; Lacroix-Lamandé, S. Cryptosporidium parvum Subverts Antimicrobial Activity of CRAMP by Reducing Its Expression in Neonatal Mice. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabiá Júnior, E.F.; Menezes, L.F.S.; de Araújo, I.F.S.; Schwartz, E.F. Natural Occurrence in Venomous Arthropods of Antimicrobial Peptides Active against Protozoan Parasites. Toxins 2019, 11, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahdavi Abhari, F.; Pirestani, M.; Dalimi, A. Anti-amoebic activity of a cecropin-melittin hybrid peptide (CM11) against trophozoites of Entamoeba histolytica. Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. 2019, 131, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.-Y.; Kim, M.-S.; Kim, E.; Cheon, J.H.; Lee, Y.-S.; Kim, Y.; Lee, S.-H.; Seo, S.-U.; Shin, S.-H.; Choi, Sun S.; et al. Enteric Viruses Ameliorate Gut Inflammation via Toll-like Receptor 3 and Toll-like Receptor 7-Mediated Interferon-β Production. Immunity 2016, 44, 889–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsigalou, C.; Konstantinidis, T.; Stavropoulou, E.; Bezirtzoglou, E.E.; Tsakris, A. Potential elimination of human gut resistome by exploiting the benefits of functional foods. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, A.; Bhattacharjee, R.; Nandi, A.; Sinha, A.; Kar, S.; Manoharan, N.; Mitra, S.; Mojumdar, A.; Panda, P.K.; Patro, S.; et al. Phage delivered CRISPR-Cas system to combat multidrug-resistant pathogens in gut microbiome. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 151, 113122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Galgano, S.; Houdijk, J.; Xie, W.; Jin, Y.; Lin, J.; Song, W.; Fu, Y.; Li, X.; et al. Recent Progress in Phage Therapy to Modulate Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii, including in Human and Poultry. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, J.; Kim, J.-w.; Yong, D.; Lee, K.; Chong, Y. Complete Genome Sequence of the Podoviral Bacteriophage YMC/09/02/B1251 ABA BP, Which Causes the Lysis of an OXA-23-Producing Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Isolate from a Septic Patient. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 12437–12438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Hu, K.; Xie, Y.; Liu, Y.; Mu, D.; Guo, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Chang, D.; Shi, Y. A novel phage PD-6A3, and its endolysin Ply6A3, with extended lytic activity against Acinetobacter baumannii. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strati, F.; Lattanzi, G.; Amoroso, C.; Facciotti, F. Microbiota-targeted therapies in inflammation resolution. Semin. Immunol. 2022, 59, 101599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinu, F.R.; Beale, D.J.; Paten, A.M.; Kouremenos, K.; Swarup, S.; Schirra, H.J.; Wishart, D. Systems Biology and Multi-Omics Integration: Viewpoints from the Metabolomics Research Community. Metabolites 2019, 9, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balvočiūtė, M.; Huson, D.H. SILVA, RDP, Greengenes, NCBI and OTT — how do these taxonomies compare? BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagarajan, M. Metagenomics: Perspectives, methods, and applications. In Metagenomics; Academic Press: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Antoine, L.; Bruno, D. Advances in high-resolution accurate mass spectrometry application to targeted proteomics. PROTEOMICS 2015, 15, 880–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyer, R.; Schallert, K.; Zoun, R.; Becher, B.; Saake, G.; Benndorf, D. Challenges and perspectives of metaproteomic data analysis. J. Biotechnol. 2017, 261, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, H.; Krausz, K.; Manna, S.; Li, F.; Johnson, C.; Gonzalez, F. Optimization of harvesting, extraction, and analytical protocols for UPLC-ESI-MS-based metabolomic analysis of adherent mammalian cancer cells. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 5279–5289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcinowska, R.; Trygg, J.; Wolf-Watz, H.; Mortiz, T.; Surowiec, I. Optimization of a sample preparation method for the metabolomic analysis of clinically relevant bacteria. J. Microbiol. Meth. 2011, 87, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beale, D.; Barratt, R.; Marlow, D.; Dunn, M.; Palombo, E.; Morrison, P.; Key, C. Application of metabolomics to understanding biofilms in water distribution systems: a pilot study. Biofouling 2013, 29, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beale, D.; Karpe, A.; Ahmed, W.; Cook, S.; Morrison, P.; Staley, C.; Sadowsky, M.; Palombo, E. A community multi-omics approach towards the assessment of surface water quality in an urban river system. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beale, D.J.; Morrison, P.D.; Palombo, E.A. Detection of Listeria in milk using non-targeted metabolic profiling of Listeria monocytogenes: A proof-of-concept application. Food Control 2014, 42, 343–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijer, S.; Otero, J.; Olivares, R.; Andersen, M.R.; Olsson, L.; Nielsen, J. Overexpression of isocitrate lyase—glyoxylate bypass influence on metabolism in Aspergillus niger. Metab. Eng. 2009, 11, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, K.; Hofmann, U.; Bauer, A.; Niebel, A.; Vacun, G.; Reuss, M.; Mauch, K. Quantification of statin effects on hepatic cholesterol synthesis by transient 13C-flux analysis. Metab. Eng. 2009, 11, 292–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niklas, J.; Schneider, K.; Heinzle, E. Metabolic flux analysis in eukaryotes. Curr. Opin. Biotech. 2010, 21, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beale, D.J.; Morrison, P.D.; Karpe, A.V.; Dunn, M.S. Chemometric Analysis of Lavender Essential Oils Using Targeted and Untargeted GC-MS Acquired Data for the Rapid Identification and Characterization of Oil Quality. Molecules 2017, 22, 1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Driouch, H.; Melzer, G.; Wittmann, C. Integration of in vivo and in silico metabolic fluxes for improvement of recombinant protein production. Metab. Eng. 2012, 14, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, H.; Carlsen, M.; Nielsen, J. Identification of enzymes and quantification of metabolic fluxes in the wild type and in a recombinant Aspergillus oryzae strain. Appl. Environ. Microb. 1999, 65, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beale, D.J.; Kouremenos, K.A.; Palombo, E.A. Microbial metabolomics; Springer Int. Publ: Basel, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Jinawath, N.; Bunbanjerdsuk, S.; Chayanupatkul, M.; Ngamphaiboon, N.; Asavapanumas, N.; Svasti, J.; Charoensawan, V. Bridging the gap between clinicians and systems biologists: from network biology to translational biomedical research. J. Transl. Med. 2016, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, G.M.; Maffei, V.J.; Zaneveld, J.R.; Yurgel, S.N.; Brown, J.R.; Taylor, C.M.; Huttenhower, C.; Langille, M.G. PICRUSt2 for prediction of metagenome functions. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 685–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNally, C.P.; Eng, A.; Noecker, C.; Gagne-Maynard, W.C.; Borenstein, E. BURRITO: An interactive multi-omic tool for visualizing taxa–function relationships in microbiome data. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, J.; Soufan, O.; Li, C.; Caraus, I.; Li, S.; Bourque, G.; Wishart, D.S.; Xia, J. MetaboAnalyst 4.0: towards more transparent and integrative metabolomics analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W486–W494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpe, A.V.; Liu, J.-W.; Shah, A.; Koloski, N.; Holtmann, G.; Beale, D.J. Utilising lipid and, arginine and proline metabolism in blood plasma to differentiate the biochemical expression in functional dyspepsia (FD) and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). Metabolomics 2022, 18, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpe, A.V.; Nguyen, T.V.; Shah, R.M.; Au, G.G.; McAuley, A.J.; Marsh, G.A.; Riddell, S.; Vasan, S.S.; Beale, D.J. A Time-Series Metabolomic Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in a Ferret Model. Metabolites 2022, 12, 1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beale, D.J.; Shah, R.; Karpe, A.V.; Hillyer, K.E.; McAuley, A.J.; Au, G.G.; Marsh, G.A.; Vasan, S.S. Metabolic Profiling from an Asymptomatic Ferret Model of SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Metabolites 2021, 11, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attia, S.; Versloot, C.J.; Voskuijl, W.; van Vliet, S.J.; Di Giovanni, V.; Zhang, L.; Richardson, S.; Bourdon, C.; Netea, M.G.; Berkley, J.A.; et al. Mortality in children with complicated severe acute malnutrition is related to intestinal and systemic inflammation: an observational cohort study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 104, 1441–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calder, N.; Walsh, K.; Olupot-Olupot, P.; Ssenyondo, T.; Muhindo, R.; Mpoya, A.; Brignardello, J.; Wang, X.; McKay, E.; Morrison, D.; et al. Modifying gut integrity and microbiome in children with severe acute malnutrition using legume-based feeds (MIMBLE): A pilot trial. Cell Rep. Med. 2021, 2, 100280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller Bark, J.; Karpe, A.V.; Doecke, J.D.; Leo, P.; Jeffree, R.L.; Chua, B.; Day, B.W.; Beale, D.J.; Punyadeera, C. A pilot study: Metabolic profiling of plasma and saliva samples from newly diagnosed glioblastoma patients. Cancer Medicine n/a. [CrossRef]
- Durán, C.; Ciucci, S.; Palladini, A.; Ijaz, U.Z.; Zippo, A.G.; Sterbini, F.P.; Masucci, L.; Cammarota, G.; Ianiro, G.; Spuul, P.; et al. Nonlinear machine learning pattern recognition and bacteria-metabolite multilayer network analysis of perturbed gastric microbiome. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, B.F.; van der Laan, M.J.; Hubbard, A.E.; Steel, C.; Kubofcik, J.; Hamlin, K.L.; Moss, D.M.; Nutman, T.B.; Priest, J.W.; Lammie, P.J. Measuring changes in transmission of neglected tropical diseases, malaria, and enteric pathogens from quantitative antibody levels. PLOS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, H.A.; Agarwal, V.; Bansal, C.; Kumar, A.; Faheem; Mohammed, M.-U.-R.; Murugesan, S.; Simpson, M.M.; Karpe, A.V.; Chandra, R.; et al. CoviRx: A User-Friendly Interface for Systematic Down-Selection of Repurposed Drug Candidates for COVID-19. Data 2022, 7, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, M.; Azcarate-Peril, M.A.; Barnard, A.; Benoit, V.; Grimaldi, R.; Guyonnet, D.; Holscher, H.D.; Hunter, K.; Manurung, S.; Obis, D.; et al. Shaping the Future of Probiotics and Prebiotics. Trends Microbiol. 2021, 29, 667–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbons, S.M.; Gurry, T.; Lampe, J.W.; Chakrabarti, A.; Dam, V.; Everard, A.; Goas, A.; Gross, G.; Kleerebezem, M.; Lane, J.; et al. Perspective: Leveraging the Gut Microbiota to Predict Personalized Responses to Dietary, Prebiotic, and Probiotic Interventions. Adv. Nutr. 2022, 13, 1450–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Sood, U.; Kaur, J.; Anand, S.; Gupta, V.; Patil, K.S.; Lal, R. The rising dominance of microbiology: what to expect in the next 15 years? Microb. Biotechnol. 2022, 15, 110–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





