1. Introduction
Cheeses are dairy products with great acceptability by consumers, with a progressive increase in consumer demand [1-3]. Minas Frescal cheese is a fresh, soft, semi-fat cheese with a very high moisture content [
4]. These characteristics contribute to the proliferation of pathogens [
5]. Cheese contamination with bacterial pathogens can occur during cheese-making, ripening, and storage. It can be related to direct contamination or cross-contamination events during processing in retail and domestic environments [
6].
Among the bacterial contaminants,
Staphylococcus aureus and
Escherichia coli stand out. These microorganisms are involved in outbreaks of foodborne illnesses, causing mild headaches to more complex conditions such as hemolytic uremic syndrome, and constitute a common cause of diarrhea in developing countries [
7,
8].
One of the ways the food industry avoids or minimizes microbial contaminations and increases the shelf life of foods is by using chemical additives as preservatives. Although they are often necessary for food, the consumers’ quest for a healthier lifestyle affects their view of food, where preserving agents are included. Thus, using natural compounds with antimicrobial activity may be a more appropriate strategy in searching for healthier and safer foods [ 9, 10].
Adding essential oil can improve the sensory characteristics, besides its function as a preserving agent for the product [11, 12]. Essential oils from various spices have been used as an alternative to chemical preservatives in foods [13, 14].
The objective of this work was to verify the in vitro antibacterial activity of essential oils of oregano and rosemary on strains of E. coli and S. aureus, as well as to evaluate the inhibition potential of essential oil of oregano on microbial growth in samples of Minas fresh cheese experimentally inoculated with E. coli during ten days of refrigerated storage.
2. Results
The essential oil of oregano promoted growth inhibition only when used at a concentration of 16% in tests in solid medium on both tested microorganisms. In the case of rosemary oil, growth inhibition was also observed at a concentration of 16%, but only for
S. aureus (
Table 1).
The oregano essential oil formed an inhibition halo of 6.6 ± 0.10 mm for S aureus and 3.3 ± 0.06 mm for E. coli. On the other hand, the rosemary oil formed a halo of 0.6 ± 0.17 mm for S aureus, and did not display antagonistic effects on E. coli.
The Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) of oregano essential oil against
strains of S. aureus and E. coli displayed values of 0.5% and 0.25%, respectively. For rosemary essential oil, the
S. aureus strain showed sensitivity to rosemary oil at 8.0%, while
E. coli was not inhibited at the tested concentrations (
Table 2).
There was no bactericidal action of rosemary essential oil against
S. aureus and
E. coli at the studied concentrations. On the other hand, the oregano essential oil displayed a 1% MBC against
S. aureus and 0.25% against
E.coli (
Table 3).
Table 4 describes the average values of the results of the physicochemical analyzes of the cheeses of the treatments (T1, treatment 1; T2, treatment 2; T3, treatment 3, and T4, treatment 4) with and without
E. coli inoculation and the addition of essential oregano oil.
Considering the moisture of the cheeses, the mean values of the results obtained for all times for the treatments were: T1, 57.28% ± 0.32; T2, mean of 56.78 ± 0.73; T3, 55.94% ± 0.27; and T4, a mean value of 55.62% ± 0.34. There was no statistically significant difference between analysis times (p≥0.05), but there were differences between treatments. Fat contents ranged from 19.00% to 20.83% for all treatments, with an average of 19.49% ± 0.49 for T1, 20.08% ± 0.1 for T2, 20.28% ± 0.34 for T3 and 20.49% ± 0.23 for T4; the differences accompanied the variation in moisture content. Likewise, the fat content in the dry matter also varied statistically (p≤0.05) according to moisture, with an average of 45.65% ± 0.91 for T1, 46.48% ± 0.88, for T2; 46.06% ± 0.84, for T3; and, 46.19% ± 0.43 for T4.
For the average pH values, T1 presented a general average of 6.80 ± 0.11; T2 mean of 6.92 ± 0.10; T3, 6.75% ± 0.09 and, T4 mean value of 6.84 ± 0.09. These values showed detectable differences between analysis times and treatments (p≤0.05). Likewise, the average titratable acidity levels displayed the same trend, with detectable statistical differences between analysis times and treatments (p≤0.05). Thus, T1 presented an average of 0.50 g/mL ± 0.31; T2 averaged 0.53 g/mL ± 0.36; T3 had a mean of 0.86 g/mL ± 0.64; and T4 had a mean value of 0.69 g/mL ± 0.52.
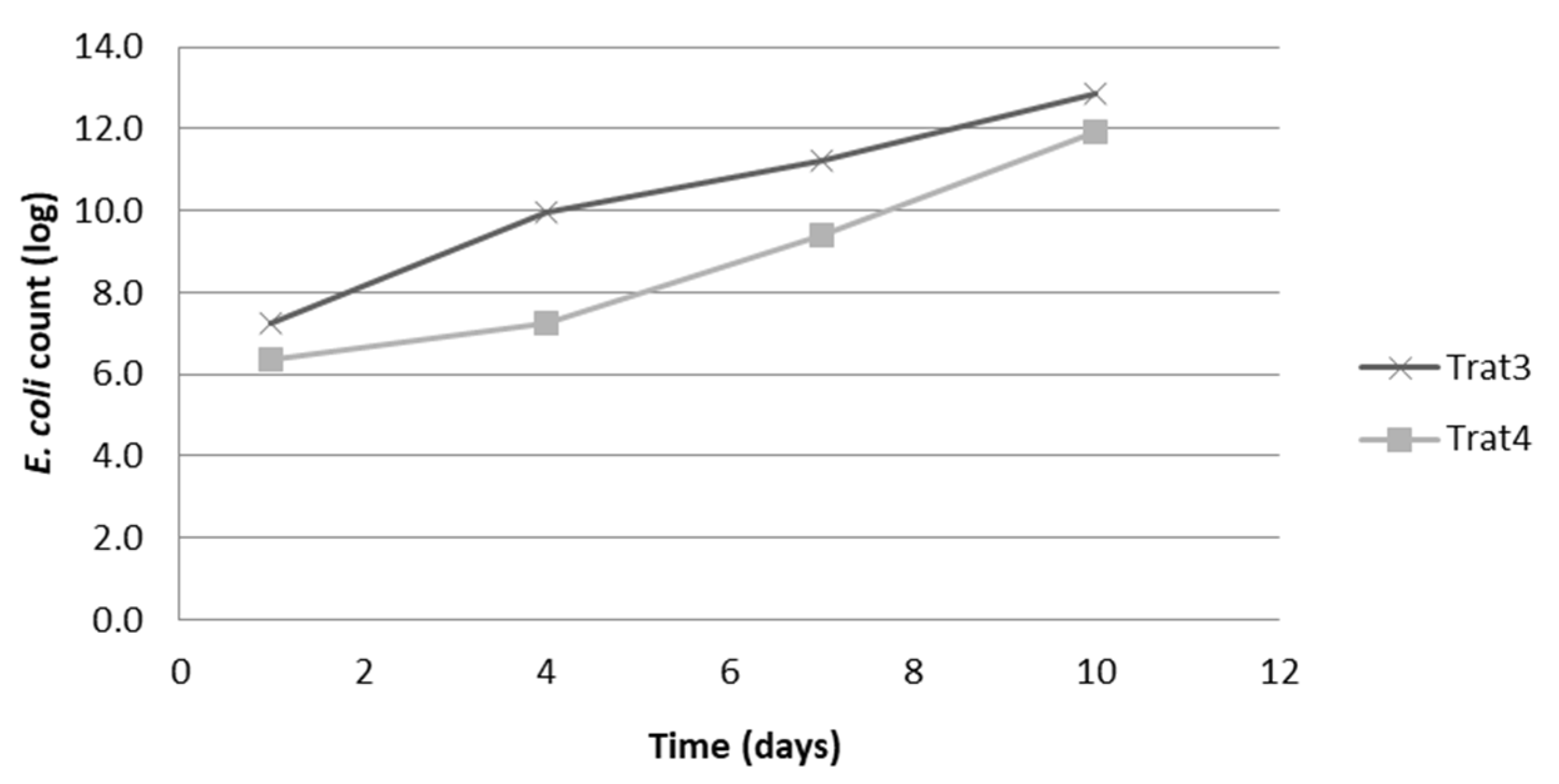
Regarding the behavior of
E. coli in the cheese samples, it was not possible to obtain
E. coli growth in the cheese samples that had not been previously inoculated (T1 and T2), with a more likely number count <1.1 CFU/mL with < 3.0 MPN/g of the analyzed sample. However, the cheeses from the treatments with the inoculation of the microorganism (T3 and T4) showed
E. coli persistence throughout the storage period (
Figure 1).
In the T3 treatment samples (added E. coli and without oregano essential oil), counts above 7 log were observed for all analyzed times, with a progressive increase over time, ranging from log 7.2, on the storage day 1, up to log 12.8 on day 10 of storage.
As for cheeses from treatment T4 (added E. coli and 0.25% essential oil), the counts at all storage times were one to two logs lower than those detected for Treatment 3. Treatment 4, counts ranged from 6.4 log on the first analysis day (storage day 1) to 11.9 log on the last (storage day 10).
3. Discussion
The essential oils inhibited the evaluated strains in all tests except for the rosemary essential oil on
E. coli. The oregano oil at the 16% concentration used promoted an inhibition zone both for S.
aureus and
E. coli, being more effective in inhibiting
S. aureus than
E. coli. Rosemary essential oil inhibited only
S. aureus, not showing antimicrobial activity for
E. coli. These data agree with the results obtained by Pereira et al. [
15], who reported an inhibitory effect of oregano essential oil against
E. coli, with the formation of a 0.9 cm halo and against
S. aureus, forming a 1.0 cm inhibition halo, using a concentration of 10% and 20% of essential oil, without displaying any variation in the inhibition halo diameter related to the essential oil concentration. The results obtained in the present study showed that the essential oil of oregano displayed a broader spectrum of action than that of rosemary and was more efficient against
S. aureus, as reported by Pombo et al. [
16], in a study carried out comparing essential oil of oregano and clove against
S. aureus and
E. coli at an amount of 20 μ L of essential oil. In this study, the inhibition zone was 23.67 ± 1.15 mm for
S. aureus and 15.00 ± 1.00 mm for
E. coli. Oregano essential oil has intense antimicrobial activity against foodborne pathogenic bacteria, with potential as a tool to achieve food safety [
17].
However, the results obtained in this experiment differ from those found in the study by Mathlouthi and collaborators [
18], which highlighted that rosemary essential oil had antibacterial activity in the disk diffusion method against three pathogenic bacteria (Escherichia coli,
Salmonella americana, and
Listeria innocua).
In the minimum inhibitory concentration evaluation, the essential oil of oregano was more effective, notably for E. coli,
with MIC values of 0.25% compared to 0.5% for
S. aureus. On the other hand, Rosemary essential oil required a higher concentration of oil to inhibit
S. aureus (8%) and did not show efficacy against
E. coli. These results agree with those found by Ribeiro-Santos and collaborators [
19], who performed a disk diffusion test to verify the activity of rosemary essential oil on
Escherichia coli,
Staphylococcus aureus,
Penicillium spp and found no antimicrobial activity.
When assessing the Minimum Bacterial Concentration, the rosemary essential oil did not display any antimicrobial action, neither against
S. aureus nor
E. coli at the concentrations studied, demonstrating the ineffectiveness of this essential oil against the studied microorganisms. The essential oil of oregano required a higher concentration to inhibit
S. aureus (1%) than
E. coli (0.25%). In this way, using 0.25% of oregano essential oil proved adequate to present a bactericidal effect on
E. coli. Another experiment with encapsulated rosemary oil [
14] observed no inhibitory action on
E. coli development due to the oil inclusion. Still, these researchers detected a reduction in the mesophilic bacteria counting that may also be related to food contamination.
The lack of standardized methods hampered the research on this activity, making it difficult to compare studies and impeding their reproducibility [
20]. In addition, there are still other factors related to the plants used, such as the age and maturation stage of the plant that originated the oil that can influence the amount of metabolites produced that are related to the bacterial growth antagonistic action [
21]. As the present experiment adopted commercial-origin essential oils, it was impossible to trace the process of obtaining them, so that this factor may explain the lack of appropriete inhibitory action of rosemary oil against pathogenic strains.
Concerning the cheese produced, the mean analysis results did not present modifications that could influence the expected outcomes of the applied treatments. Other experiments observed the same behavior [11, 14]. Moisture content, which is one of the factors that could most modify the behavior of microorganisms in cheese [2 2], remained statistically constant throughout storage time, with slight variations between treatments, without practical significance in cheese. Also, the variations found between the different treatments were not enough to influence the metabolism of the microorganisms. The fat content in the dry matter, a critical determination used to characterize and classify the cheeses, was constant for all treatments and during storage time. On the other hand, the pH and titratable acidity showed behaviors within the expected range, with a reduction in pH and an increase in titratable acidity, which are indicative of acidification during storage [
14]. This acidification tendency was found mainly for treatments with the inoculation of
E. coli (T3 and T4), demonstrating the ability of this microorganism to metabolize the cheese lactose and release organic acids, mainly lactic acid [4, 22].
The average moisture, fat, and fat values in the dry matter found for Minas Frescal cheese agree with those described by other researchers [1, 7, 14] and follow the Brazilian legislation requirements [
4]. The fat content in the dry matter in all samples was slightly above expected. The cheese produced for all treatments could be classified as very high moisture cheese (greater than 55%) and semi-fat (fat content in the dry matter between 25.0% and 44.9%) and fat (fat in the dry matter between 45.0 % and 59.9%). Most of the tested samples can be classified as full-fat cheeses according to the classification of fat in the dry matter, but with values very close to the minimum content of this classification (45.0%).
The cheeses not inoculated with E. coli (T1 and T2) did not display any contamination by this bacterium, indicating that the production process was hygienically performed and no cross-contamination occurred between the treatments. The cheeses samples inoculated with E. coli (T3 and T4) displayed increased E. coli concentration along with the storage period. However, at all observed times, E. coli counts were lower for cheeses with addition of oregano essential oil. The increase in the E. coli count during storage indicated that the microorganism inhibition induced by the essential oil at the concentration used in the cheese was not total. Despite this, adding essential oil can be considered a barrier to the microorganism’s development, making the pathogen’s growth slower compared to the non-added sample of essential oil.
Data on the initial inhibition of
E. coli are similar to those found in another study [
23], which evaluated the behavior of
Listeria innocua with a edible film incorporated with oregano essential oil in Minas Frescal Cheese, observing a reduction of 0.5 to 1.0 log in the microbial growth.
Another research [
11] also found inhibition of
E. coli inoculated in Minas Frescal cheese, adding essential oils of oregano and rosemary, acting in synergism, but found higher levels of inhibition over time when compared to the present study. Likewise, these researchers found in vitro inhibition in the minimum inhibitory concentration tests.
4. Materials and Methods
This experiment used ATCC strains of
Escherichia coli (ATCC 25922) and
Staphylococcus aureus (ATCC 25923). Microorganisms were activated in BHI broth (Brain Heart Infusion), incubated at 35-37°C for 24 hours, and later in tubes containing inclined BHI agar and incubated again at 35-37°C for 24 hours [
24]. After activation, the concentration of microorganisms was adjusted, constituting a bacterial suspension equivalent to a 0.5 MacFarland scale (approximately 1.5 x 10⁸ CFU/mL).
The essential oils of oregano (
Origanum vulgare ) and rosemary (
Rosmarinus officinalis ) (Ferquima®Ind. e Com. Ltda, São Paulo, Brazil) were previously evaluated for bacteriological quality using Standard Counting Agar, Baird Parker Agar and EMB (Eosin Methyl Blue) [
25]. The oils were diluted in sterile distilled water, or BHI broth with Tween 80 added, obtaining a concentration of 16%, considered the initial standard solution [
26]. This solution was filtered through a 0.22µm porosity membrane. The other solutions were carried out using the serial dilution method, obtaining the following concentrations: 8%, 4%, and 2%. This process was followed by storage in a flask in a dark environment, protected from sunlight, until the moment of the test [
27].
To perform the
in vitro antimicrobial action test, the
E. coli or
S. aureus cultures were spread on the surface of Mueller Hinton agar with the aid of a sterile
swab soaked in bacterial suspensions adjusted to the 0.5 MacFarland scale (approximately 1.5 x 10⁸ CFU/ mL). Subsequently, equidistant wells were made and inoculated with 15 µl of essential oil (16%, 8%, 4%, and 2%). The assay was performed in triplicate, and the plates were incubated at 35°C-37°C for 24 hours. After incubation, the halos of microbial growth inhibition were observed and measured with the aid of a ruler. Discs commercially available for the antibiotics Chloramphenicol (for tests with
E.coli ) and Vancomycin (for tests with
S. aureus ) were used as positive controls. The negative control was performed by inoculating sterile saline solution in the wells [
28].
The Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) was determined through the microdilution technique in wells using plates with 96 wells, evaluating decreasing concentrations of each essential oil (8%, 4%, 2%, 1%, 0.5%, 0.25%, 0.125%, 0.062%, and 0%). The Minimum Bactericidal Concentration (MBC) was obtained by seeding 10µl of the contents of the wells of the microdilution plates, in which there was complete inhibition of microbial growth on the surface of tryptone soybean agar (TSA). The bactericidal concentration was defined by the absence of bacterial growth [
26]. For both tests, three repetitions were performed, in duplicate for each concentration of essential oils.
Pasteurized milk was used to manufacture Minas Frescal cheese. The milk was within the physical-chemical quality standards (titratable acidity, cryoscopy, density, and fat) recommended by Brazilian legislation [
29]. The mesophilic aerobic heterotrophic bacteria counts, enumeration of lactic acid bacteria (LAB), and the most probable number of coliforms [
24] also indicated the initial quality of the raw material. The cheese was manufactured by enzymatic milk coagulation with the addition of 0.04% calcium chloride (CAP-LAB, São Paulo, Brazil) and 0.09% coagulating agent (HA-LA®, São Paulo, Brazil). After draining and before molding, the cheeses were salted at 0.75% to the mass obtained. For the cheeses added with essential oil, the incorporation occurred together with the salting step. During the same stage,
E. coli was inoculated as described by the experimental protocol.
E. coli was included following the precepts of laboratory hygiene and safety to avoid contamination of the environment and handlers. For the addition of the
E. coli culture to the cheeses, the pathogen inoculum had a concentration of 10⁸ CFU/mL. After draining, the inoculum was added to the dough to obtain an
E. coli concentration close to 10
6 CFU/g in the cheese samples.
Four different treatments were evaluated in cheese making: T1 (Cheese Minas Frescal control); T2 (Minas Frescal cheese with 0.25% oregano essential oil); T3 (Minas Frescal cheese added with E. coli); and T4 (Minas Frescal cheese added with E. coli and with 0.25% oregano essential oil). The cheeses were stored under refrigeration between + 4º C and +8º C, and samples were collected on days 1, 4, 7, and 10 of storage for physical-chemical and microbiological analyses.
Physicochemical (pH, acidity, moisture, fat, and fat in the dry matter) [2 9] and microbiological (lactic acid bacteria (LAB) enumeration and
Escherichia coli [
25] enumeration were performed in triplicates.
Analysis data were analyzed using Minitab 16 software (Minitab Inc., Brazil). The effect between treatments was evaluated daily, and the effect of storage for each treatment by Analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Tukey’s test for mean comparisons with a significance level of 95%. Microbiological data were statistically analyzed by Student’s t-test (Excel®, Microsoft Office).
5. Conclusions
Oregano essential oil showed better antimicrobial activity than rosemary essential oil, which showed promising results, but with lower intensity. The oregano essential oil can be used as a natural preservative since it shows action against pathogenic strains, mainly E. coli. Rosemary essential oil, in turn, did not display antimicrobial activity against E. coli and cannot be considered efficient for such use.
Oregano essential oil promoted bacterial inhibition in Minas Frescal Cheese inoculated with E. coli when compared to the same product without adding the essential oil. Although it did not completely inhibit the growth of E.coli, this inclusion can be considered more as a hurdle technology, slowing the pathogen development compared to the non-added sample of essential oil.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Marco Antonio Sloboda Cortez, Maria Carmela Kasnowski Holanda Duarte and Aline dos Santos Garcia-Gomes ; methodology, Marco Antonio Sloboda Cortez, Maria Carmela Kasnowski Holanda Duarte and Aline dos Santos Garcia-Gomes; formal analysis, Juliana de Carvalho Cruz and Evelyn Siqueira de Carvalho Vilela ; investigation, Juliana de Carvalho Cruz and Evelyn Siqueira de Carvalho Vilela ; resources, Marco Antonio Sloboda Cortez ; data curation, Marco Antonio Sloboda Cortez ; writing—original draft preparation, Marco Antonio Sloboda Cortez, Maria Carmela Kasnowski Holanda Duarte and Aline dos Santos Garcia-Gomes ; writing—review and editing, Marco Antonio Sloboda Cortez, Maria Carmela Kasnowski Holanda Duarte and Aline dos Santos Garcia-Gomes ; visualization, Marco Antonio Sloboda Cortez, Maria Carmela Kasnowski Holanda Duarte and Aline dos Santos Garcia-Gomes ; supervisor, Marco Antonio Sloboda Cortez, Maria Carmela Kasnowski Holanda Duarte and Aline dos Santos Garcia-Gomes ; project administration, Marco Antonio Sloboda Cortez ; funding acquisition, Marco Antonio Sloboda Cortez. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data resulting from this experiment are described in this article.
Acknowledgments
To Federal Fluminense University and Federal Institute of Rio de Janeiro.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Rocha, RS; Silva, R.; Guimarães, J. T; Balthazar, CF; Pimentel, TC; Neto, RPC; et al. Possibilities for using ohmic heating in Minas Frescal cheese production. Food Res. Int. 2020, 131:109027. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2020.109027. [CrossRef]
- OECD/FAO (2022), OECD-FAO Agricultural Outlook 2022-2031, OECD Publishing, Paris, https://doi.org/10.1787/f1b0b29c-en. [CrossRef]
- Silva, ACO; Cortez, MAS Technology of milk and dairy products. EDUFF: Niteroi, Brazil, 2021, 87p. [CrossRef]
- BRAZIL. MINISTRY OF LIVESTOCK AGRICULTURE AND SUPPLY. Normative Instruction No. 4 of March 1, 2004. Technical regulation for establishing the identity and quality of Minas fresh cheese. Brasília, DF, MAPA, 5 mar. 2004.
- Abreu, ACS; Crippa, BL; Souza, VVMA; Nuñez, KVM; Almeida, JM; Rodrigues, MX; Silva, NCC Assessment of sanitizer efficacy against Staphylococcus spp. isolated from Minas Frescal cheese producers in São Paulo, Brazil, Inter. Dairy J. 2021, Volume 123, 105171, ISSN 0958-6946, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.idairyj.2021.105171. [CrossRef]
- Paula, ACL; Medeiros, JD; Fernandes, GR; Silva, VL; Diniz, CG Microbiome of industrialized Minas Frescal Cheese reveals high prevalence of putative bacteria: A concern in the One Health context, 2021, LWT, Volume 139, 110791, ISSN 0023-6438, https://doi.org/10.1016/j. lwt.2020.110791. [CrossRef]
- Franco, RM Etiological Agents of Food Diseases. EDUFF: Niterói, Brazil, 2012.120p.
- Kousta, M.; Mataragas, M.; Skandamis, P.; Drosinos, EH Prevalence and sources of cheese contamination with pathogens at farm and processing levels. FoodControl, v. 21, no. 6, p. 805-815, 2010.
- Levison, W. Medical Microbiology and Immunology. 13th ed., AMGH Editora Ltda: São Paulo, Brazil, 2016, 800p.
- Diniz-Silva, HT; Brandao, LR; Galvão, MS; Madruga, MS; Maciel, JF; Souza, EL; Magnani, M. Survival of Lactobacillus acidophilus LA-5 and Escherichia coli O157:H7 in Minas Frescal cheese made with oregano and rosemary essential oils, 2020, Food Microbiology, V.86, 103348, ISSN 0740-0020, https://doi .org/10.1016/j.fm.2019.103348. [CrossRef]
- Taylor, TM Natural food antimicrobials: recent trends in their use, limitations, and opportunities for their applications in food preservation. In Natural and biobased antimicrobials for food applications. X. Fan, H. Ngo & C. Wu (Eds.). American Chemical Society: Washington. 2018, p.25-43.
- Santos, JR; Hafemann, SPG; Pieretti, GG; Old, JL; Pozza, MSS; Scapim, MRS; Madrona, GS Sensorial, microbiological, and physico-chemical analysis of Minas fresh cheese with oregano essential oil (Origanum vulgare) addition, 2014, Inter. J. of Food Sci. and Nut. Eng., v.4, n.3, pp.86-90. [CrossRef]
- Araujo, LS; Araújo, RS; Sierra, JL; Nascimento, AR Chemical composition and susceptibility of essential oil of oregano (ORIGANUM VULGARE) against strains of Escherichua coli, Staphylococcus aureus and Salmonella choleraesuis . 2015, B. CEPPA, v. 33, no. 1, p. 73-78.
- Fernandes, RVdB; Guimaraes, IC; Ferreira, CLR; Botrel, DA; Borges, SV and de Souza, AU (2017), Microencapsulated Rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis) Essential Oil as a Biopreservative in Minas Frescal Cheese. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation, 41: e12759. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfpp.12759. [CrossRef]
- Pereira, AA; Cardoso, MG; Abrey, LR; Morais, AR; Guimaraes, LGL; Salgado, APSP Chemical characterization and inhibitory effect of essential oils on the growth of Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli. 2008, Ciênc. and Agrotec., v. 32, no. 03, p. 887-893.
- Pigeon, JCP; Ribeiro, ER; Pinto, RL; Silva, BJM Antimicrobial and synergistic effect of essential oils on food contaminating bacteria. 2018, Insurance food Nutri.: Campinas, Brazil, v. 25, no. 2, p. 108-117.
- Preedy, VR Essential Oils in Food Preservation, Flavor and Safety, 1st edition, London: Academic Press Publisher – Elsevier, 2015, 930p.
- Mathlouthi, N.; Bouzaienne, T.; Oueslati, I.; Recoquillay, F.; Hamdi, M.; Urdaci, M.; Bergaoui, R. Use of rosemary, oregano, and a commercial blend of essential oils in broiler chickens: In vitro antimicrobial activities and effects on growth performance. 2012, Jour. Animal Scienc., n.90, p.813-823. [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro-Santos, R.; Andrade, M.; Melo, NR; Sanches-Silva, A. Essential oils: in vitro biological activity and its potential application to food packaging. 2016, National Institute of Health Doctor Ricardo Jorge, Brief Articles, n.7, p. 29-33.
- Nascimento, PFC; Nascimento, AC; Rodrigues, CS; Antoniolli, AR; Santos, PO; Junior, AMB; Trindade, RC Antimicrobial activity of essential oils: a multifactorial approach to methods.2007, Rev. Bra. of Pharmacognosy, v. 17, no. 1, p. 108-113.
- Morais, LAS INFLUENCE OF ABIOTICS FACTORS ON THE CHEMICAL COMPOSITION OF ESSENTIAL OILS. 2009, Horticultura Brasileira, v. 27, no. two.
- Boas, AF V; Belpiede, ELS; Silva, NRF; Silva, MF; Veiga, SMOM Microbiological quality of artisanal and industrialized fresh minas cheeses. 2020, Brazilian J. of Development, v. 6, no. 10, p. 83536-83552.
- Soares, NF; Santiago-Silva, P.; Silva, WA Development and evaluation of an active film incorporated with oregano essential oil (ORIGANUM VULGARE L.) in the growth of Listeria innocua in Minas fresh cheese. 2008, Rev. Inst. Latic. “Cândido Tostes”, Nov/Dec, nº 365, 63: 36-40.
- CARVALHO, RJ; SOUZA, GT; HONORIO, VG; SOUSA, JP; CONCEIÇÃO, ML; MAGANANI, M.; SOUZA, EL Comparative inhibitory effects of Thymus vulgaris L. essential oil against Staphylococcus aureus, Listeria monocytogenes and mesophilic starter co-culture in cheese-mimicking models. Food Microbiology, v. 52, p. 59-65, 2015. [CrossRef]
- American Public Health Association. APHA Committee on Microbiological Methods for Foods. Compendium of methods for the microbiological examination of foods. 5.ed. 2015, Washington, 676p.
- Freire, ICM; Perez, ALAL; Cardoso, AMR; Mariz, BALA; Almeida, LFD; Cavalcanti, YW; Padilha, WWN Antibacterial activity of essential oils against Streptococcus mutans and Staphylococcus aureus, 2014, Rev. Bras. Pl. Med., Campinas, v.16, n.2, p. 372-377.
- Aligianns, N.; Kalpoutzakis, E.; Mitaku, S.; Chinou, JB Composition and Antimicrobial Activity of the Essential Oils of Two Origanum Species. 2001, J. of Agric. and Food Chem., v. 49, n.9, p. 4168-67. [CrossRef]
- Guimaraes, CC; Ferreira, TC; Oliveira, RCF; Simoni, PU; Ugrinovich, LA In vitro antimicrobial activity of aqueous extract and essential oil of rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis L.) and clove (Caryophyllusaromaticus L.) against strains of Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli. 2017, Rev. Bras. of Biosciences, v. 15, no. two.
- BRAZIL. MINISTRY OF LIVESTOCK AGRICULTURE AND SUPPLY. Normative Instruction No. 30 of June 28, 2018. Establishes as official the methods contained in the Manual of Official Methods for the Analysis of Food of Animal Origin. Brasilia, DF, MAPA, 13 Jul. 2018, ed.134, section 1, p9.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).