Submitted:
30 May 2023
Posted:
01 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Role of miRNAs in cancer
2.1. Humans:
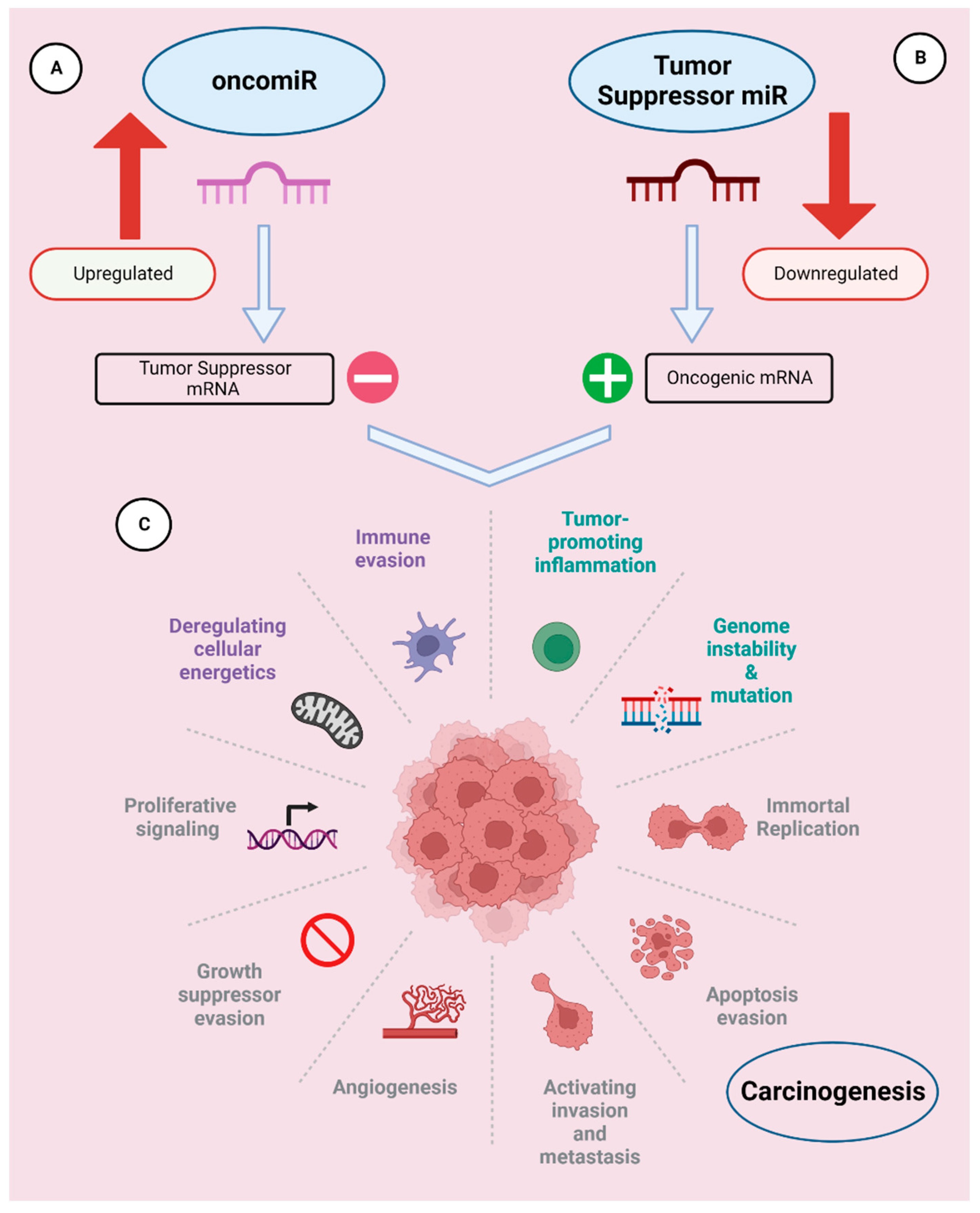
2.1.1. OncomiRs
2.1.1. Tumor suppressor miRNAs (TS-miRNAs)
2.2. Dogs
3. Role of miRNAs in cancer metastasis
3.1. Humans
3.2. Dogs
4.1. Humans
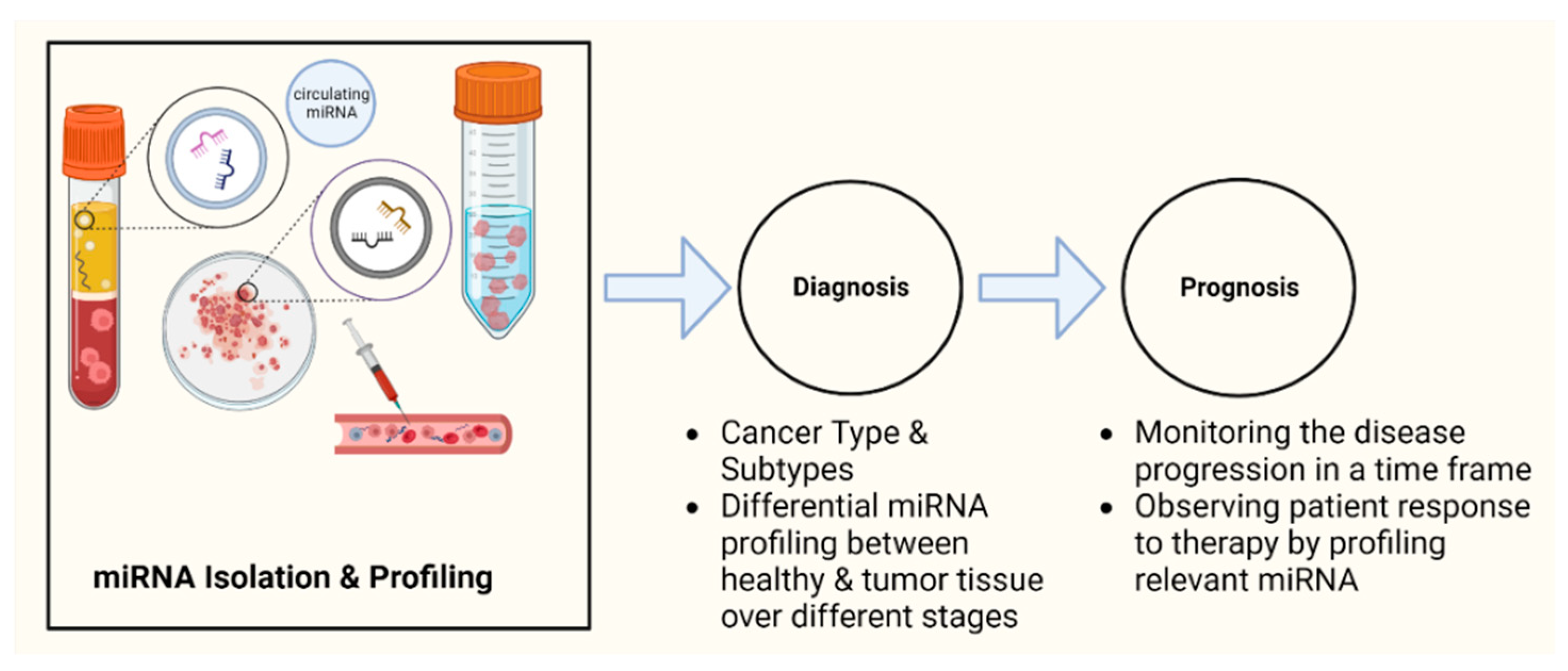
4.1.1. Diagnosis
4.1.2. Prognosis
4.1.3. Tumor staging
4.1.4. Treatment resistance
4.2. Dogs
5. Role of miRNAs in cancer treatment
5.1. Humans
5.2. Dogs
6. Future Perspective and Summary
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- www.miRBase.org. Available online: https://www.mirbase.org/cgi-bin/browse.pl.
- Fabian, M.R.; Sonenberg, N.; Filipowicz, W. Regulation of mRNA translation and stability by microRNAs. Annual review of biochemistry 2010, 79, 351–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broughton, J.P.; Lovci, M.T.; Huang, J.L.; Yeo, G.W.; Pasquinelli, A.E. Pairing beyond the Seed Supports MicroRNA Targeting Specificity. Mol Cell 2016, 64, 320–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarzenbach, H. The clinical relevance of circulating, exosomal miRNAs as biomarkers for cancer. Expert review of molecular diagnostics 2015, 15, 1159–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valadi, H.; Ekstrom, K.; Bossios, A.; Sjostrand, M.; Lee, J.J.; Lotvall, J.O. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nature cell biology 2007, 9, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, N.; Haider, S.; Jagannathan, S.; Anaissie, E.; Driscoll, J.J. MicroRNA theragnostics for the clinical management of multiple myeloma. Leukemia 2014, 28, 732–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svoronos, A.A.; Engelman, D.M.; Slack, F.J. OncomiR or Tumor Suppressor? The Duplicity of MicroRNAs in Cancer. Cancer Res 2016, 76, 3666–3670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogilyansky, E.; Rigoutsos, I. The miR-17/92 cluster: a comprehensive update on its genomics, genetics, functions and increasingly important and numerous roles in health and disease. Cell Death Differ 2013, 20, 1603–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Han, C.; Wu, T. MiR-17-92 cluster promotes hepatocarcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis 2015, 36, 1213–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchida, A.; Ohno, S.; Wu, W.; Borjigin, N.; Fujita, K.; Aoki, T.; Ueda, S.; Takanashi, M.; Kuroda, M. miR-92 is a key oncogenic component of the miR-17-92 cluster in colon cancer. Cancer Sci 2011, 102, 2264–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takakura, S.; Mitsutake, N.; Nakashima, M.; Namba, H.; Saenko, V.A.; Rogounovitch, T.I.; Nakazawa, Y.; Hayashi, T.; Ohtsuru, A.; Yamashita, S. Oncogenic role of miR-17-92 cluster in anaplastic thyroid cancer cells. Cancer Sci 2008, 99, 1147–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashita, Y.; Osada, H.; Tatematsu, Y.; Yamada, H.; Yanagisawa, K.; Tomida, S.; Yatabe, Y.; Kawahara, K.; Sekido, Y.; Takahashi, T. A polycistronic microRNA cluster, miR-17-92, is overexpressed in human lung cancers and enhances cell proliferation. Cancer Res 2005, 65, 9628–9632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martens-de Kemp, S.R.; Komor, M.A.; Hegi, R.; Bolijn, A.S.; Tijssen, M.; de Groen, F.L.M.; Depla, A.; van Leerdam, M.; Meijer, G.A.; Fijneman, R.J.A.; et al. Overexpression of the miR-17-92 cluster in colorectal adenoma organoids causes a carcinoma-like gene expression signature. Neoplasia 2022, 32, 100820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, F.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, Z.; Xiong, M.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; He, B.; Zhu, J. The diagnostic and prognostic value of the miR-17-92 cluster in hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis. Front Genet 2022, 13, 927079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menon, A.; Abd-Aziz, N.; Khalid, K.; Poh, C.L.; Naidu, R. miRNA: A Promising Therapeutic Target in Cancer. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozgun, A.; Karagoz, B.; Bilgi, O.; Tuncel, T.; Baloglu, H.; Kandemir, E.G. MicroRNA-21 as an indicator of aggressive phenotype in breast cancer. Onkologie 2013, 36, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echevarria-Vargas, I.M.; Valiyeva, F.; Vivas-Mejia, P.E. Upregulation of miR-21 in cisplatin resistant ovarian cancer via JNK-1/c-Jun pathway. PLoS One 2014, 9, e97094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, C.; Shan, S.; Liu, X.; Jiang, Z.; Ren, T. TLR4/ROS/miRNA-21 pathway underlies lipopolysaccharide instructed primary tumor outgrowth in lung cancer patients. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 42172–42182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, H.; Sun, X.; Chen, Y.; Cao, Y.; Chen, S.; Wang, H.; Hu, C. Circulating microRNA-92a and microRNA-21 as novel minimally invasive biomarkers for primary breast cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 2013, 139, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baez-Vega, P.M.; Echevarria Vargas, I.M.; Valiyeva, F.; Encarnacion-Rosado, J.; Roman, A.; Flores, J.; Marcos-Martinez, M.J.; Vivas-Mejia, P.E. Targeting miR-21-3p inhibits proliferation and invasion of ovarian cancer cells. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 36321–36337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, Z.; Gao, C.; Chen, P.; Chen, J.; Liu, W.; Xiao, S.; Lu, H. miR-21 plays a pivotal role in gastric cancer pathogenesis and progression. Lab Invest 2008, 88, 1358–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaman Agaoglu, F.; Kovancilar, M.; Dizdar, Y.; Darendeliler, E.; Holdenrieder, S.; Dalay, N.; Gezer, U. Investigation of miR-21, miR-141, and miR-221 in blood circulation of patients with prostate cancer. Tumour Biol 2011, 32, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toiyama, Y.; Takahashi, M.; Hur, K.; Nagasaka, T.; Tanaka, K.; Inoue, Y.; Kusunoki, M.; Boland, C.R.; Goel, A. Serum miR-21 as a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker in colorectal cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 2013, 105, 849–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonian, M.; Mosallayi, M.; Mirzaei, H. Circulating miR-21 as novel biomarker in gastric cancer: Diagnostic and prognostic biomarker. J Cancer Res Ther 2018, 14, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sicard, F.; Gayral, M.; Lulka, H.; Buscail, L.; Cordelier, P. Targeting miR-21 for the therapy of pancreatic cancer. Mol Ther 2013, 21, 986–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, M.L.; Zhu, S.; Wu, H.; Lu, Z.; Wu, F.; Mo, Y.Y. miR-21-mediated tumor growth. Oncogene 2007, 26, 2799–2803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, J.K.; Blansit, K.; Kiet, T.; Sherman, A.; Wong, G.; Earle, C.; Bourguignon, L.Y. The inhibition of miR-21 promotes apoptosis and chemosensitivity in ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol 2014, 132, 739–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, W.; Pang, X.; Luan, F. Diagnosis value of miR-181, miR-652, and CA72-4 for gastric cancer. J Clin Lab Anal 2022, 36, e24411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, J.; Shen, R.; Yan, Y.; Deng, L. miR-186 promotes tumor growth in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma by inhibiting apoptotic protease activating factor-1. Experimental and therapeutic medicine 2018, 16, 4010–4018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Z.; Mu, T.; Zhao, L.; Li, Y.; Zhu, D.; Pan, Y. MiR-181a-5p facilitates proliferation, invasion, and glycolysis of breast cancer through NDRG2-mediated activation of PTEN/AKT pathway. Bioengineered 2022, 13, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strotbek, M.; Schmid, S.; Sanchez-Gonzalez, I.; Boerries, M.; Busch, H.; Olayioye, M.A. miR-181 elevates Akt signaling by co-targeting PHLPP2 and INPP4B phosphatases in luminal breast cancer. Int J Cancer 2017, 140, 2310–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, S.J.; Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Qu, L.X. microRNA-181 promotes prostate cancer cell proliferation by regulating DAX-1 expression. Exp Ther Med 2014, 8, 1296–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbato, A.; Iuliano, A.; Volpe, M.; D'Alterio, R.; Brillante, S.; Massa, F.; De Cegli, R.; Carrella, S.; Salati, M.; Russo, A.; et al. Integrated Genomics Identifies miR-181/TFAM Pathway as a Critical Driver of Drug Resistance in Melanoma. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrahamsson, A.; Dabrosin, C. Tissue specific expression of extracellular microRNA in human breast cancers and normal human breast tissue in vivo. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 22959–22969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, K.; Yang, J.; Guo, Z.; Hu, Y.; Sheng, H.; Gao, H.; Yu, H. Prognostic value of miR-221-3p, miR-342-3p and miR-491-5p expression in colon cancer. Am J Transl Res 2014, 6, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pineau, P.; Volinia, S.; McJunkin, K.; Marchio, A.; Battiston, C.; Terris, B.; Mazzaferro, V.; Lowe, S.W.; Croce, C.M.; Dejean, A. miR-221 overexpression contributes to liver tumorigenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2010, 107, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.X.; Hu, Q.; Qiu, M.T.; Zhong, S.L.; Xu, J.J.; Tang, J.H.; Zhao, J.H. miR-221/222: promising biomarkers for breast cancer. Tumour Biol 2013, 34, 1361–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calin, G.A.; Sevignani, C.; Dumitru, C.D.; Hyslop, T.; Noch, E.; Yendamuri, S.; Shimizu, M.; Rattan, S.; Bullrich, F.; Negrini, M.; et al. Human microRNA genes are frequently located at fragile sites and genomic regions involved in cancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2004, 101, 2999–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macfarlane, L.A.; Murphy, P.R. MicroRNA: Biogenesis, Function and Role in Cancer. Curr Genomics 2010, 11, 537–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Lee, D.Y.; Ben-David, Y. The roles of microRNAs in tumorigenesis and angiogenesis. Int J Physiol Pathophysiol Pharmacol 2011, 3, 140–155. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, H.; Zheng, L.; Song, H.; Jiao, W.; Li, D.; Fang, E.; Wang, X.; Mei, H.; Pu, J.; Huang, K.; et al. microRNA-558 facilitates the expression of hypoxia-inducible factor 2 alpha through binding to 5'-untranslated region in neuroblastoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 40657–40673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baradaran, B.; Shahbazi, R.; Khordadmehr, M. Dysregulation of key microRNAs in pancreatic cancer development. Biomed Pharmacother 2019, 109, 1008–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Fu, J.; Zhang, W.; Guo, M. Genetic and epigenetic changes in lung carcinoma and their clinical implications. Mod Pathol 2011, 24, 932–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Duan, Y.T.; Lu, P.; Zhang, Z.J.; Zheng, X.K.; Wang, J.L.; Feng, W.S. Epigenetic Targets and their Inhibitors in Cancer Therapy. Curr Top Med Chem 2018, 18, 2395–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Link, S.; Grund, S.E.; Diederichs, S. Alternative splicing affects the subcellular localization of Drosha. Nucleic Acids Research 2016, 44, 5330–5343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Zhang, D.; Du, R.; Pan, Y.; Zhao, L.; Sun, S.; Hong, L.; Liu, J.; Fan, D. miR-15b and miR-16 modulate multidrug resistance by targeting BCL2 in human gastric cancer cells. Int J Cancer 2008, 123, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Wan, R.; Hu, G.; Yang, L.; Xiong, J.; Wang, F.; Shen, J.; He, S.; Guo, X.; Ni, J.; et al. miR-15b and miR-16 induce the apoptosis of rat activated pancreatic stellate cells by targeting Bcl-2 in vitro. Pancreatology 2012, 12, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musumeci, M.; Coppola, V.; Addario, A.; Patrizii, M.; Maugeri-Sacca, M.; Memeo, L.; Colarossi, C.; Francescangeli, F.; Biffoni, M.; Collura, D.; et al. Control of tumor and microenvironment cross-talk by miR-15a and miR-16 in prostate cancer. Oncogene 2011, 30, 4231–4242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimmino, A.; Calin, G.A.; Fabbri, M.; Iorio, M.V.; Ferracin, M.; Shimizu, M.; Wojcik, S.E.; Aqeilan, R.I.; Zupo, S.; Dono, M.; et al. miR-15 and miR-16 induce apoptosis by targeting BCL2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2005, 102, 13944–13949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calin, G.A.; Dumitru, C.D.; Shimizu, M.; Bichi, R.; Zupo, S.; Noch, E.; Aldler, H.; Rattan, S.; Keating, M.; Rai, K.; et al. Frequent deletions and down-regulation of micro- RNA genes miR15 and miR16 at 13q14 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2002, 99, 15524–15529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, S.M.; Grosshans, H.; Shingara, J.; Byrom, M.; Jarvis, R.; Cheng, A.; Labourier, E.; Reinert, K.L.; Brown, D.; Slack, F.J. RAS is regulated by the let-7 microRNA family. Cell 2005, 120, 635–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.S.; Erkeland, S.J.; Pester, R.E.; Chen, C.Y.; Ebert, M.S.; Sharp, P.A.; Jacks, T. Suppression of non-small cell lung tumor development by the let-7 microRNA family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2008, 105, 3903–3908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buechner, J.; Tomte, E.; Haug, B.H.; Henriksen, J.R.; Lokke, C.; Flaegstad, T.; Einvik, C. Tumour-suppressor microRNAs let-7 and mir-101 target the proto-oncogene MYCN and inhibit cell proliferation in MYCN-amplified neuroblastoma. Br J Cancer 2011, 105, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Qin, S.; Fan, C.; Xu, C.; Du, N.; Ren, H. Let-7: a regulator of the ERalpha signaling pathway in human breast tumors and breast cancer stem cells. Oncol Rep 2013, 29, 2079–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slusarz, A.; Pulakat, L. The two faces of miR-29. J Cardiovasc Med (Hagerstown) 2015, 16, 480–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Ma, C.; Zhu, W. LncRNA HOTAIR Promotes Chemoresistance by Facilitating Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition through miR-29b/PTEN/PI3K Signaling in Cervical Cancer. Cells Tissues Organs 2022, 211, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera, O.; Bok, I.; Jasani, N.; Nakamura, K.; Xu, X.; Mecozzi, N.; Angarita, A.; Wang, K.; Tsai, K.Y.; Karreth, F.A. A MAPK/miR-29 Axis Suppresses Melanoma by Targeting MAFG and MYBL2. Cancers (Basel) 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hozaka, Y.; Seki, N.; Tanaka, T.; Asai, S.; Moriya, S.; Idichi, T.; Wada, M.; Tanoue, K.; Kawasaki, Y.; Mataki, Y.; et al. Molecular Pathogenesis and Regulation of the miR-29-3p-Family: Involvement of ITGA6 and ITGB1 in Intra-Hepatic Cholangiocarcinoma. Cancers (Basel) 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassilli, S.; Bertagnolo, V.; Brugnoli, F. Mir-29b in Breast Cancer: A Promising Target for Therapeutic Approaches. Diagnostics (Basel) 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Qian, J.X.; Yi, H.L.; Yang, Z.D.; Wang, C.F.; Chen, J.Y.; Wei, X.Z.; Fu, Q.; Ma, H. The microRNA-29 plays a central role in osteosarcoma pathogenesis and progression. Mol Biol (Mosk) 2012, 46, 622–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.N.; Yan, M.D.; Lai, H.C.; Huang, R.L.; Chou, Y.C.; Lin, W.C.; Yeh, L.T.; Lin, Y.W. Downregulation of miR-29 contributes to cisplatin resistance of ovarian cancer cells. Int J Cancer 2014, 134, 542–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.H.; Wu, Z.Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, F.Z.; Liu, Y. Expression of miR-29 and STAT3 in osteosarcoma and its effect on proliferation regulation of osteosarcoma cells. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 2019, 23, 7275–7282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Q.; Hao, X.; Zhang, M.; Tang, W.; Yang, M.; Li, L.; Xiang, D.; Desano, J.T.; Bommer, G.T.; Fan, D.; et al. MicroRNA miR-34 inhibits human pancreatic cancer tumor-initiating cells. PLoS One 2009, 4, e6816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corney, D.C.; Hwang, C.I.; Matoso, A.; Vogt, M.; Flesken-Nikitin, A.; Godwin, A.K.; Kamat, A.A.; Sood, A.K.; Ellenson, L.H.; Hermeking, H.; et al. Frequent downregulation of miR-34 family in human ovarian cancers. Clin Cancer Res 2010, 16, 1119–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Cheng, Y.L.; Matthen, M.; Yoon, A.; Schwartz, G.K.; Bala, S.; Taylor, A.M.; Momen-Heravi, F. Down-regulation of the tumor suppressor miR-34a contributes to head and neck cancer by up-regulating the MET oncogene and modulating tumor immune evasion. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 2021, 40, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Han, Y.; Shen, J.; Zheng, W.; Wei, L.; Liu, Y.; Ren, L.; Gu, Z.; et al. Distinct roles of miR-34 family members on suppression of lung squamous cell carcinoma. Biomed Pharmacother 2021, 142, 111967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Fan, B.; Chen, D.; Guo, C.; Xiang, H.; Nie, Y.; Zhong, D.; Shi, X. Human cytomegalovirus protein UL136 activates the IL-6/STAT3 signal through MiR-138 and MiR-34c in gastric cancer cells. Int J Clin Oncol 2020, 25, 1936–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghan, R.; Najafi, R.; Azizi Jalilian, F.; Saidijam, M.; Radaei, Z.; Zamani, A.; Ezati, R.; Asna-Ashari, F.; Amini, R. A promising effect of zerumbone with improved anti-tumor-promoting inflammation activity of miR-34a in colorectal cancer cell lines. Mol Biol Rep 2021, 48, 203–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, L.L.; Tobiasen, H.; Holm, A.; Schepeler, T.; Ostenfeld, M.S.; Thorsen, K.; Rasmussen, M.H.; Birkenkamp-Demtroeder, K.; Sieber, O.M.; Gibbs, P.; et al. MiRNA-362-3p induces cell cycle arrest through targeting of E2F1, USF2 and PTPN1 and is associated with recurrence of colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer 2013, 133, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahdan-Alaswad, R.S.; Cochrane, D.R.; Spoelstra, N.S.; Howe, E.N.; Edgerton, S.M.; Anderson, S.M.; Thor, A.D.; Richer, J.K. Metformin-Induced Killing of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells Is Mediated by Reduction in Fatty Acid Synthase via miRNA-193b. Hormones and Cancer 2014, 5, 374–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Kong, F.; Wu, K.; Song, K.; He, J.; Sun, W. miR-193b directly targets STMN1 and uPA genes and suppresses tumor growth and metastasis in pancreatic cancer. Mol Med Rep 2014, 10, 2613–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, M.; Moradi, N.; Ziaee, S.A.; Narouie, B.; Soltani, M.H.; Rezaei, M.; Shahkar, G.; Taheri, M. Association between single nucleotide polymorphism in miR-499, miR-196a2, miR-146a and miR-149 and prostate cancer risk in a sample of Iranian population. J Adv Res 2016, 7, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Y.G.; Zhou, X.M.; Cui, Z.G.; Hou, G. Effects of common polymorphisms in miR-146a and miR-196a2 on lung cancer susceptibility: a meta-analysis. J Thorac Dis 2016, 8, 1297–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhu, G.; Di, H.; Li, H.; Liu, X.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, Y. Associations between genetic variants located in mature microRNAs and risk of lung cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 41715–41724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Q.; Wang, N.; Duan, G. Long non-coding RNA XIST regulates ovarian cancer progression via modulating miR-335/BCL2L2 axis. World J Surg Oncol 2021, 19, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckstein, S. Dogs and Cancer: Get the Facts. Availabe online: https://pets.webmd.
- Uhl, E.; Krimer, P.; Schliekelman, P.; Tompkins, S.M.; Suter, S. Identification of altered MicroRNA expression in canine lymphoid cell lines and cases of B- and T-Cell lymphomas. Genes, chromosomes & cancer 2011, 50, 950–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenger, J.M.; Bear, M.D.; Volinia, S.; Lin, T.Y.; Harrington, B.K.; London, C.A.; Kisseberth, W.C. Overexpression of miR-9 in mast cells is associated with invasive behavior and spontaneous metastasis. BMC cancer 2014, 14, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, S.; Mori, T.; Hoshino, Y.; Yamada, N.; Maruo, K.; Akao, Y. MicroRNAs as tumour suppressors in canine and human melanoma cells and as a prognostic factor in canine melanomas. Veterinary and comparative oncology 2013, 11, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, S.; Mori, T.; Hoshino, Y.; Yamada, N.; Nakagawa, T.; Sasaki, N.; Akao, Y.; Maruo, K. Comparative study of anti-oncogenic microRNA-145 in canine and human malignant melanoma. The Journal of veterinary medical science 2012, 74, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gioia, G.; Mortarino, M.; Gelain, M.E.; Albonico, F.; Ciusani, E.; Forno, I.; Marconato, L.; Martini, V.; Comazzi, S. Immunophenotype-related microRNA expression in canine chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Veterinary immunology and immunopathology 2011, 142, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimes, J.A.; Prasad, N.; Levy, S.; Cattley, R.; Lindley, S.; Boothe, H.W.; Henderson, R.A.; Smith, B.F. A comparison of microRNA expression profiles from splenic hemangiosarcoma, splenic nodular hyperplasia, and normal spleens of dogs. BMC veterinary research 2016, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heishima, K.; Mori, T.; Sakai, H.; Sugito, N.; Murakami, M.; Yamada, N.; Akao, Y.; Maruo, K. MicroRNA-214 Promotes Apoptosis in Canine Hemangiosarcoma by Targeting the COP1-p53 Axis. PloS one 2015, 10, e0137361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutful Kabir, F.M.; DeInnocentes, P.; Bird, R.C. Altered microRNA Expression Profiles and Regulation of INK4A/CDKN2A Tumor Suppressor Genes in Canine Breast Cancer Models. Journal of cellular biochemistry 2015, 116, 2956–2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boggs, R.M.; Wright, Z.M.; Stickney, M.J.; Porter, W.W.; Murphy, K.E. MicroRNA expression in canine mammary cancer. Mamm Genome 2008, 19, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Deetzen, M.C.; Schmeck, B.T.; Gruber, A.D.; Klopfleisch, R. Malignancy Associated MicroRNA Expression Changes in Canine Mammary Cancer of Different Malignancies. ISRN veterinary science 2014, 2014, 148597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negrini, M.; Calin, G.A. Breast cancer metastasis: a microRNA story. Breast Cancer Res 2008, 10, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Reinhardt, F.; Pan, E.; Soutschek, J.; Bhat, B.; Marcusson, E.G.; Teruya-Feldstein, J.; Bell, G.W.; Weinberg, R.A. Therapeutic silencing of miR-10b inhibits metastasis in a mouse mammary tumor model. Nature biotechnology 2010, 28, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, T.; Yang, L.; Zhang, J. MiRNA5423p downregulation promotes trastuzumab resistance in breast cancer cells via AKT activation. Oncol Rep 2015, 33, 1215–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhao, L.; Wei, X.; Wang, L.; Liu, S.; Yang, Y.; Wang, F.; Sun, G.; Zhang, J.; Ma, Y.; et al. MicroRNA-320a promotes 5-FU resistance in human pancreatic cancer cells. Sci Rep 2016, 6, 27641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teplyuk, N.M.; Uhlmann, E.J.; Gabriely, G.; Volfovsky, N.; Wang, Y.; Teng, J.; Karmali, P.; Marcusson, E.; Peter, M.; Mohan, A.; et al. Therapeutic potential of targeting microRNA-10b in established intracranial glioblastoma: first steps toward the clinic. EMBO Mol Med 2016, 8, 268–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Wang, J.G.; Zhang, L.; Yang, H.P.; Wang, L.; Ding, D.; Chen, Q.; Yang, W.L.; Ren, K.H.; Zhou, D.M.; et al. MicroRNA-320a inhibits breast cancer metastasis by targeting metadherin. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 38612–38625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, J.; Fay, J.; Meehan, M.; Bryan, K.; Watters, K.M.; Murphy, D.M.; Stallings, R.L. MiRNA-335 suppresses neuroblastoma cell invasiveness by direct targeting of multiple genes from the non-canonical TGF-beta signalling pathway. Carcinogenesis 2012, 33, 976–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulkowska, M.; Rybicka, A.; Senses, K.M.; Ulewicz, K.; Witt, K.; Szymanska, J.; Taciak, B.; Klopfleisch, R.; Hellmen, E.; Dolka, I.; et al. MicroRNA expression patterns in canine mammary cancer show significant differences between metastatic and non-metastatic tumours. BMC cancer 2017, 17, 728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Fan, Y.; Shi, D.; Xu, E.; Liu, Y. MicroRNA-124 inhibits canine mammary carcinoma cell proliferation, migration and invasion by targeting CDH2. Res Vet Sci 2022, 146, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hino, Y.; Rahman, M.M.; Lai, Y.C.; Husna, A.A.; Chen, H.W.; Hasan, M.N.; Nakagawa, T.; Miura, N. Hypoxic miRNAs expression are different between primary and metastatic melanoma cells. Gene 2021, 782, 145552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarver, A.L.; Thayanithy, V.; Scott, M.C.; Cleton-Jansen, A.M.; Hogendoorn, P.C.; Modiano, J.F.; Subramanian, S. MicroRNAs at the human 14q32 locus have prognostic significance in osteosarcoma. Orphanet journal of rare diseases 2013, 8, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonardo, L.; Laura, P.; Serena, B.M. miR-1 and miR-133b expression in canine osteosarcoma. Res Vet Sci 2018, 117, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, C.M.; Yu, P.Y.; Zhang, X.; Yilmaz, A.S.; London, C.A.; Fenger, J.M. MiR-34a regulates the invasive capacity of canine osteosarcoma cell lines. PloS one 2018, 13, e0190086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenger, J.M.; Roberts, R.D.; Iwenofu, O.H.; Bear, M.D.; Zhang, X.; Couto, J.I.; Modiano, J.F.; Kisseberth, W.C.; London, C.A. MiR-9 is overexpressed in spontaneous canine osteosarcoma and promotes a metastatic phenotype including invasion and migration in osteoblasts and osteosarcoma cell lines. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhu, Y.; Liang, Z.; Li, S.; Xu, X.; Wang, X.; Wu, J.; Hu, Z.; Meng, S.; Liu, B.; et al. c-Met and CREB1 are involved in miR-433-mediated inhibition of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition in bladder cancer by regulating Akt/GSK-3beta/Snail signaling. Cell death & disease 2016, 7, e2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takasaki, S. Roles of microRNAs in cancers and development. Methods Mol Biol 2015, 1218, 375–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, P.; Crepps, M.P.; Stahr, N.A.; Kretzschmar, W.P.; Harris, H.C.; Prasad, N.; Levy, S.E.; Smith, B.F. Identification of canine circulating miRNAs as tumor biospecific markers using Next-Generation Sequencing and Q-RT-PCR. Biochem Biophys Rep 2021, 28, 101106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, S.; Zhao, X.; Wang, L.; Chen, F.; Gong, H.; Chen, C.; Cai, C. pH-activated DNA nanomachine for miRNA-21 imaging to accurately identify cancer cell. Mikrochim Acta 2022, 189, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.G.; Calin, G.A.; Meloon, B.; Gamliel, N.; Sevignani, C.; Ferracin, M.; Dumitru, C.D.; Shimizu, M.; Zupo, S.; Dono, M.; et al. An oligonucleotide microchip for genome-wide microRNA profiling in human and mouse tissues. P Natl Acad Sci USA 2004, 101, 9740–9744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Getz, G.; Miska, E.A.; Alvarez-Saavedra, E.; Lamb, J.; Peck, D.; Sweet-Cordero, A.; Ebert, B.L.; Mak, R.H.; Ferrando, A.A.; et al. MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature 2005, 435, 834–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volinia, S.; Calin, G.A.; Liu, C.G.; Ambs, S.; Cimmino, A.; Petrocca, F.; Visone, R.; Iorio, M.; Roldo, C.; Ferracin, M.; et al. A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines cancer gene targets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2006, 103, 2257–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanaihara, N.; Caplen, N.; Bowman, E.; Seike, M.; Kumamoto, K.; Yi, M.; Stephens, R.M.; Okamoto, A.; Yokota, J.; Tanaka, T.; et al. Unique microRNA molecular profiles in lung cancer diagnosis and prognosis. Cancer Cell 2006, 9, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenfeld, N.; Aharonov, R.; Meiri, E.; Rosenwald, S.; Spector, Y.; Zepeniuk, M.; Benjamin, H.; Shabes, N.; Tabak, S.; Levy, A.; et al. MicroRNAs accurately identify cancer tissue origin. Nat Biotechnol 2008, 26, 462–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, H.; Shimura, T.; Kitagawa, M.; Yamada, T.; Nishigaki, R.; Fukusada, S.; Okuda, Y.; Katano, T.; Horike, S.I.; Kataoka, H. A Novel Urinary miRNA Biomarker for Early Detection of Colorectal Cancer. Cancers (Basel) 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidarra, D.; Constancio, V.; Barros-Silva, D.; Ramalho-Carvalho, J.; Moreira-Barbosa, C.; Antunes, L.; Mauricio, J.; Oliveira, J.; Henrique, R.; Jeronimo, C. Circulating MicroRNAs as Biomarkers for Prostate Cancer Detection and Metastasis Development Prediction. Front Oncol 2019, 9, 900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downs-Holmes, C.; Silverman, P. Breast cancer: overview & updates. Nurse Pract 2011, 36, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanacore, D.; Boccellino, M.; Rossetti, S.; Cavaliere, C.; D'Aniello, C.; Di Franco, R.; Romano, F.J.; Montanari, M.; La Mantia, E.; Piscitelli, R.; et al. Micrornas in prostate cancer: an overview. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 50240–50251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Han, T.; Hu, P.; Guo, X.; Zhu, C.; Wang, Y.; Chang, S. Five microRNAs in serum as potential biomarkers for prostate cancer risk assessment and therapeutic intervention. Int Urol Nephrol 2018, 50, 2193–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, B.L.; Grabowska, A.; Ratan, H.L. MicroRNA in prostate cancer: functional importance and potential as circulating biomarkers. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, J.; Zhao, L.; Wang, F.; Ji, J.; Cao, Z.; Xu, H.; Shi, X.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Guo, F.; et al. Discovery and Validation of Serum MicroRNAs as Early Diagnostic Biomarkers for Prostate Cancer in Chinese Population. Biomed Res Int 2019, 2019, 9306803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogata-Kawata, H.; Izumiya, M.; Kurioka, D.; Honma, Y.; Yamada, Y.; Furuta, K.; Gunji, T.; Ohta, H.; Okamoto, H.; Sonoda, H.; et al. Circulating exosomal microRNAs as biomarkers of colon cancer. PLoS One 2014, 9, e92921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogli, S.; Polini, B.; Carpi, S.; Pardini, B.; Naccarati, A.; Dubbini, N.; Lanza, M.; Breschi, M.C.; Romanini, A.; Nieri, P. Identification of plasma microRNAs as new potential biomarkers with high diagnostic power in human cutaneous melanoma. Tumour Biol 2017, 39, 1010428317701646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Chen, G.; Zhang, X.; Li, D.; Huang, J.; Yang, C.; Zhang, P.; Qin, Y.; Duan, Y.; Gong, B.; et al. Salivary microRNAs as promising biomarkers for detection of esophageal cancer. PLoS One 2013, 8, e57502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humeau, M.; Vignolle-Vidoni, A.; Sicard, F.; Martins, F.; Bournet, B.; Buscail, L.; Torrisani, J.; Cordelier, P. Salivary MicroRNA in Pancreatic Cancer Patients. PLoS One 2015, 10, e0130996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.L.; Chen, H.Y.; Chang, G.C.; Chen, C.Y.; Chen, H.W.; Singh, S.; Cheng, C.L.; Yu, C.J.; Lee, Y.C.; Chen, H.S.; et al. MicroRNA signature predicts survival and relapse in lung cancer. Cancer Cell 2008, 13, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schetter, A.J.; Leung, S.Y.; Sohn, J.J.; Zanetti, K.A.; Bowman, E.D.; Yanaihara, N.; Yuen, S.T.; Chan, T.L.; Kwong, D.L.; Au, G.K.; et al. MicroRNA expression profiles associated with prognosis and therapeutic outcome in colon adenocarcinoma. JAMA 2008, 299, 425–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gahlawat, A.W.; Witte, T.; Haarhuis, L.; Schott, S. A novel circulating miRNA panel for non-invasive ovarian cancer diagnosis and prognosis. Br J Cancer 2022, 127, 1550–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farran, B.; Dyson, G.; Craig, D.; Dombkowski, A.; Beebe-Dimmer, J.L.; Powell, I.J.; Podgorski, I.; Heilbrun, L.; Bolton, S.; Bock, C.H. A study of circulating microRNAs identifies a new potential biomarker panel to distinguish aggressive prostate cancer. Carcinogenesis 2018, 39, 556–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, K.K.; Misra, S.; Pareek, P.; Mishra, V.; Singhal, B.; Sharma, P. Recent scenario of microRNA as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers of prostate cancer. Urol Oncol 2017, 35, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maierthaler, M.; Benner, A.; Hoffmeister, M.; Surowy, H.; Jansen, L.; Knebel, P.; Chang-Claude, J.; Brenner, H.; Burwinkel, B. Plasma miR-122 and miR-200 family are prognostic markers in colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer 2017, 140, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monzo, M.; Santasusagna, S.; Moreno, I.; Martinez, F.; Hernandez, R.; Munoz, C.; Castellano, J.J.; Moreno, J.; Navarro, A. Exosomal microRNAs isolated from plasma of mesenteric veins linked to liver metastases in resected patients with colon cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 30859–30869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Hu, T. Predicting distant metastasis and chemoresistance using plasma miRNAs. Med Oncol 2014, 31, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatnagar, N.; Li, X.; Padi, S.K.; Zhang, Q.; Tang, M.S.; Guo, B. Downregulation of miR-205 and miR-31 confers resistance to chemotherapy-induced apoptosis in prostate cancer cells. Cell Death Dis 2010, 1, e105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Shi, X.B.; Nori, D.; Chao, C.K.; Chen, A.M.; Valicenti, R.; White Rde, V. Down-regulation of microRNA 106b is involved in p21-mediated cell cycle arrest in response to radiation in prostate cancer cells. Prostate 2011, 71, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, A.; Zhao, Q.; Zhou, X.; Sun, C.; Si, J.; Zhou, R.; Gan, L.; Zhang, H. MicroRNA-449a enhances radiosensitivity by downregulation of c-Myc in prostate cancer cells. Sci Rep 2016, 6, 27346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagesh, P.K.B.; Chowdhury, P.; Hatami, E.; Boya, V.K.N.; Kashyap, V.K.; Khan, S.; Hafeez, B.B.; Chauhan, S.C.; Jaggi, M.; Yallapu, M.M. miRNA-205 Nanoformulation Sensitizes Prostate Cancer Cells to Chemotherapy. Cancers (Basel) 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.; Bucci, J.; Chang, L.; Malouf, D.; Graham, P.; Li, Y. Targeting MicroRNAs in Prostate Cancer Radiotherapy. Theranostics 2017, 7, 3243–3259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thieu, W.; Tilki, D.; de Vere White, R.; Evans, C.P. The role of microRNA in castration-resistant prostate cancer. Urol Oncol 2014, 32, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lieberman, R.; Pan, J.; Zhang, Q.; Du, M.; Zhang, P.; Nevalainen, M.; Kohli, M.; Shenoy, N.K.; Meng, H.; et al. miR-375 induces docetaxel resistance in prostate cancer by targeting SEC23A and YAP1. Mol Cancer 2016, 15, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Gong, J.P.; Li, J.; Zhong, S.L.; Chen, W.X.; Zhang, J.Y.; Ma, T.F.; Ji, H.; Lv, M.M.; Zhao, J.H.; et al. Down-regulation of miRNA-452 is associated with adriamycin-resistance in breast cancer cells. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 2014, 15, 5137–5142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safaei, S.; Amini, M.; Najjary, S.; Mokhtarzadeh, A.; Bolandi, N.; Saeedi, H.; Alizadeh, N.; Javadrashid, D.; Baradaran, B. miR-200c increases the sensitivity of breast cancer cells to Doxorubicin through downregulating MDR1 gene. Exp Mol Pathol 2022, 125, 104753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Yagüe, E.; Ji, W.; Liu, J.; Zhang, J. miRNA-205 targets VEGFA and FGF2 and regulates resistance to chemotherapeutics in breast cancer. Cell Death & Disease 2016, 7, e2291–e2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.H.; Tao, Z.H.; Zhang, J.; Li, T.; Ni, C.; Xie, J.; Zhang, J.F.; Hu, X.C. MiRNA-21 induces epithelial to mesenchymal transition and gemcitabine resistance via the PTEN/AKT pathway in breast cancer. Tumour Biol 2016, 37, 7245–7254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, J.; Xue, A.; Chi, Y.; Xue, J.; Wang, W.; Zhao, Z.; Fan, M.; Yang, C.H.; Shao, Z.M.; Pfeffer, L.M.; et al. Induction of miRNA-181a by genotoxic treatments promotes chemotherapeutic resistance and metastasis in breast cancer. Oncogene 2016, 35, 1302–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.J.; Li, J.; Zheng, Y.Q.; Liu, M.; Song, X.; Li, X.R. Expression and regulatory function of miRNA-182 in triple-negative breast cancer cells through its targeting of profilin 1. Tumour Biol 2013, 34, 1713–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Chi, Y.; Chen, Y.; Huang, S.; Ye, X.; Niu, J.; Wang, W.; Pfeffer, L.M.; Shao, Z.M.; Wu, Z.H.; et al. MiRNA-621 sensitizes breast cancer to chemotherapy by suppressing FBXO11 and enhancing p53 activity. Oncogene 2016, 35, 448–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi Yeganeh, S.; Vasei, M.; Tavakoli, R.; Kia, V.; Paryan, M. The effect of miR-340 over-expression on cell-cycle-related genes in triple-negative breast cancer cells. Eur J Cancer Care (Engl) 2017, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordentoft, I.; Birkenkamp-Demtroder, K.; Agerbaek, M.; Theodorescu, D.; Ostenfeld, M.S.; Hartmann, A.; Borre, M.; Orntoft, T.F.; Dyrskjot, L. miRNAs associated with chemo-sensitivity in cell lines and in advanced bladder cancer. BMC Med Genomics 2012, 5, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heishima, K.; Ichikawa, Y.; Yoshida, K.; Iwasaki, R.; Sakai, H.; Nakagawa, T.; Tanaka, Y.; Hoshino, Y.; Okamura, Y.; Murakami, M.; et al. Circulating microRNA-214 and -126 as potential biomarkers for canine neoplastic disease. Sci Rep 2017, 7, 2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleveland, M.J.; Casale, S. Incidence of malignancy and outcomes for dogs undergoing splenectomy for incidentally detected nonruptured splenic nodules or masses: 105 cases (2009-2013). J Am Vet Med Assoc 2016, 248, 1267–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kent, M.S.; Zwingenberger, A.; Westropp, J.L.; Barrett, L.E.; Durbin-Johnson, B.P.; Ghosh, P.; Vinall, R.L. MicroRNA profiling of dogs with transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder using blood and urine samples. BMC veterinary research 2017, 13, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinall, R.L.; Kent, M.S.; deVere White, R.W. Expression of microRNAs in urinary bladder samples obtained from dogs with grossly normal bladders, inflammatory bladder disease, or transitional cell carcinoma. American journal of veterinary research 2012, 73, 1626–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamarian, V.; Ferrari, R.; Stefanello, D.; Ceciliani, F.; Grieco, V.; Minozzi, G.; Chiti, L.E.; Arigoni, M.; Calogero, R.; Lecchi, C. miRNA profiles of canine cutaneous mast cell tumours with early nodal metastasis and evaluation as potential biomarkers. Sci Rep 2020, 10, 18918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fish, E.J.; Martinez-Romero, E.G.; DeInnocentes, P.; Koehler, J.W.; Prasad, N.; Smith, A.N.; Bird, R.C. Circulating microRNA as biomarkers of canine mammary carcinoma in dogs. J Vet Intern Med 2020, 34, 1282–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnica, T.K.; Lesbon, J.C.C.; Avila, A.; Rochetti, A.L.; Matiz, O.R.S.; Ribeiro, R.C.S.; Zoppa, A.; Nishiya, A.T.; Costa, M.T.; de Nardi, A.B.; et al. Liquid biopsy based on small extracellular vesicles predicts chemotherapy response of canine multicentric lymphomas. Sci Rep 2020, 10, 20371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaumier, A.; Robinson, S.R.; Robinson, N.; Lopez, K.E.; Meola, D.M.; Barber, L.G.; Bulmer, B.J.; Calvalido, J.; Rush, J.E.; Yeri, A.; et al. Extracellular vesicular microRNAs as potential biomarker for early detection of doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. J Vet Intern Med 2020, 34, 1260–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husna, A.A.; Rahman, M.M.; Lai, Y.C.; Chen, H.W.; Hasan, M.N.; Nakagawa, T.; Miura, N. Identification of melanoma-specific exosomal miRNAs as the potential biomarker for canine oral melanoma. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res 2021, 34, 1062–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narita, M.; Nishida, H.; Asahina, R.; Nakata, K.; Yano, H.; Dickinson, P.J.; Tanaka, T.; Akiyoshi, H.; Maeda, S.; Kamishina, H. Expression of microRNAs in plasma and in extracellular vesicles derived from plasma for dogs with glioma and dogs with other brain diseases. Am J Vet Res 2020, 81, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starkey, M.P.; Compston-Garnett, L.; Malho, P.; Dunn, K.; Dubielzig, R. Metastasis-associated microRNA expression in canine uveal melanoma. Vet Comp Oncol 2018, 16, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonardi, L.; Scotlandi, K.; Pettinari, I.; Benassi, M.S.; Porcellato, I.; Pazzaglia, L. MiRNAs in Canine and Human Osteosarcoma: A Highlight Review on Comparative Biomolecular Aspects. Cells 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethi, S.; Ali, S.; Sethi, S.; Sarkar, F.H. MicroRNAs in personalized cancer therapy. Clin Genet 2014, 86, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, P.M.; Pedroso de Lima, M.C. MicroRNAs as Molecular Targets for Cancer Therapy: On the Modulation of MicroRNA Expression. Pharmaceuticals (Basel) 2013, 6, 1195–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zheng, M.; Jiao, M.; Yan, C.; Xu, S.; Du, Q.; Morsch, M.; Yin, J.; Shi, B. Polymeric nanoparticle mediated inhibition of miR-21 with enhanced miR-124 expression for combinatorial glioblastoma therapy. Biomaterials 2021, 276, 121036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Liu, G.; Pei, C.; Chen, W.; Li, P.; Wang, Q.; Jin, X.; Zhu, J.; Wang, M.; Liu, X. Inhibition of NADPH oxidase protects against metastasis of human lung cancer by decreasing microRNA-21. Anticancer Drugs 2015, 26, 388–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.G.; Wu, W.K.; Feng, S.Y.; Wang, X.J.; Shao, J.F.; Qiao, J. Co-inhibition of microRNA-10b and microRNA-21 exerts synergistic inhibition on the proliferation and invasion of human glioma cells. Int J Oncol 2012, 41, 1005–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.J.; Bahal, R.; Babar, I.A.; Pincus, Z.; Barrera, F.; Liu, C.; Svoronos, A.; Braddock, D.T.; Glazer, P.M.; Engelman, D.M.; et al. MicroRNA silencing for cancer therapy targeted to the tumour microenvironment. Nature 2015, 518, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Oh, B.; Choi, M.; Oh, J.; Lee, M. Delivery of anti-microRNA-21 antisense-oligodeoxynucleotide using amphiphilic peptides for glioblastoma gene therapy. J Drug Target 2015, 23, 360–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahreyni, A.; Liu, H.; Mohamud, Y.; Xue, Y.C.; Zhang, J.; Luo, H. A new miRNA-Modified coxsackievirus B3 inhibits triple negative breast cancer growth with improved safety profile in immunocompetent mice. Cancer Lett 2022, 548, 215849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Zhou, X.; Mei, M.; Yuan, X.B.; Han, L.; Wang, G.X.; Jia, Z.F.; Xu, P.; Pu, P.Y.; Kang, C.S. MicroRNA-21 inhibitor sensitizes human glioblastoma cells U251 (PTEN-mutant) and LN229 (PTEN-wild type) to taxol. BMC Cancer 2010, 10, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, R.; Maeda, A.; Ueno, Y.; Sakai, H.; Kimura, S.; Sawadaishi, T.; Kohgo, S.; Yamada, K.; Mori, T. Intraperitoneal administration of synthetic microRNA-214 elicits tumor suppression in an intraperitoneal dissemination mouse model of canine hemangiosarcoma. Vet Res Commun 2022, 46, 447–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, R.; Mori, T.; Noguchi, S.; Akao, Y.; Maruo, K.; Kitade, Y. Synthetic microRNA-205 exhibited tumour suppression in spontaneous canine malignant melanoma by intratumoral injection. Vet Comp Oncol 2019, 17, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alegre, F.; Ormonde, A.R.; Snider, K.M.; Woolard, K.; Yu, A.M.; Wittenburg, L.A. A genetically engineered microRNA-34a prodrug demonstrates anti-tumor activity in a canine model of osteosarcoma. PLoS One 2018, 13, e0209941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




