Introduction
Heart failure is a frequent long-term complication of diabetes mellitus type 2. Otherwise, coexisting diabetes mellitus significantly deteriorates the prognosis of patients with heart failure (1). Recently, randomized trials demonstrated beneficial effects of sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT-2) inhibitors in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (2-4). These favourable effects have been also demonstrated in non-diabetic patients with heart failure and reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) (5-7).
The beneficial effects of SGLT-2 inhibitors on heart failure are still under discussion. SGLT2-inhibitors act as diuretics and in the proximal tubule and thereby reduce states of hypervolemia. Moreover, they modify intrarenal hemodynamics, induce a slight decrease of blood pressure and induce a metabolic shift to mild ketonemia. The majority of these effects may be elicited by other diuretics as well, noteworthy without yielding those outstanding benefits observed in SGLT2-inhibitor trials. Thus, it has to be hypothesized that there are undetected additional mechanims, e. g. antiinflammatory effects (8-10). However, data on the immunological and inflammatory responses to SGLT-2 inhibitors in patients with HFrEF are sparse. Therefore, the aim of this prospective controlled proof-of-concept study is to investigate, whether the SGLT-2-inhibitor empagliflozin elicits an immunomodulatory effect in patients with HFrEF. For this aim, we assessed a broad profile of soluble immunological mediators before and three months after initiation of SGLT2-inhibition and compared the results to a control group without a SGLT2-inhibitor.
Methods
Study population
From June 2020 to September 2021, we enrolled hospitalized patients treated for heart failure in the Department of Cardiology/Rhythmology at St. Josef Hospital (Hospital of the Ruhr-University Bochum). Thus, the study was designed, when SGLT2-inhibitors were approved for diabetes mellitus type 2 with heart failure with reduced but not for preserved ejection fraction.
Inclusion criteria were: symptomatic left heart failure (NYHA stage II-IV), left ventricular ejection fraction ≤ 40%, Diabetes mellitus type II, life expectancy > 1-year, informed consent, and age ≥ 18 years. Exclusion criteria were: any immunosuppressive therapy, fever and clinical signs of an on-going infectious disease, ongoing or former therapy with an SGLT2 inhibitor, diabetes mellitus type I, renal insufficiency (GFR < 45 ml/min/1.73 m²), hypotension or systolic blood pressure < 90 mmHg, myocardial infarction in the 30 days prior to study inclusion, known peripheral arterial disease and insufficient compliance that makes regular use of medication unlikely.
Patients were clinically in a stable condition at the time of study inclusion and were willing to participate in this prospective non-interventional proof-of-concept study. Written informed consent was obtained from all participants. The study was approved by the local ethics committee of the Ruhr University Bochum (reg. number 20-6944).
Study protocol
We performed a prospective, controlled but non-randomized study. Study investigations particularly included quality of life, functional status, left ventricular ejection fraction, and immunological factors.
The Minnesota Living with Heart Failure Questionnaire (MLHFQ) was designed to measure the impact of heart failure and heart failure treatment on the physical, emotional, social, and mental dimensions of quality of life. The sum of the responses to each item yields the total MLHFQ score for each patient. The test score ranges from 0 to 110, with a higher score indicating poorer quality of life (11). An adaptation of the MLHFQ for German-speaking patients was used.
The 6-minute walk test was performed according to American Thoracic Society guidelines for a functional test. Patients were instructed to walk rapidly for 6 minutes or until the onset of dyspnea or muscle fatigue. The walking distance was 30 m. The total walking distance was recorded (12).
Echocardiographic imaging was performed on the same day as the clinical examinations. Transthoracic echocardiography was obtained according to the guidelines of the American Society of Echocardiography and European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging (13) using a digital ultrasound machine (Vivid 9, General Electrics, Horton, Norway). Left ventricular ejection fraction was measured by the Simpson method in the 4- and 2-chamber views. The echocardiographic examination was performed by a single observer.
Blood samples were taken on the day of the study investigations. The estimated glomerular filtration rate was calculated using the abbreviated Modification of Diet in Renal Disease Study equation. Kidney disease was defined as a glomerular filtration rate of 60 ml/min/1.73 m².
Soluble factors were analyzed as previously described by Stervbo et al (14). Briefly, soluble mediators including human IFN-α2, IFN-γ, TNF-α, MCP-1, IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, IL-12p70, IL-17A, IL-18, and IL-23 were assessed using the LEGENDplex custom panel (BioLegend, San Diego, CA, USA). The samples were processed following the manufacturer’s instructions. The analyte concentration was extracted using LEGENDplex Data Analysis Software.The analysis of the immunological factors was blinded to the clinical parameters.
SGLT-2 inhibitor and follow-up
Prescription of empagliflozin was done at the advice of the attending physicians not involved in this study. Usually, the indication for empagliflozin was optimizing the glucose control. The results of the examinations for quality of life, functional status, and immunological factors were not known to the treating physicians.
The examinations (MLHFQ, 6-minute walk test, laboratory tests of immunological parameters, and echocardiographic determination of left ventricular ejection fraction) were repeated on an outpatient visit after 3 months.
Statistics
Results are presented as mean ± standard deviation (SD). Continuous variables were compared between groups (with and without SGLT-2 inhibitors) using an unpaired t test (for normally distributed variables) or Mann-Whitney U test (for non-normally distributed variables). χ2 analysis was used to compare categoric variables.
The continuous variables were compared at baseline and after 3 months using the paired Student t test for normally distributed variables or the Wilcoxon test for nonnormally distributed variables. Post-hoc multiple comparisons tests are performed testing using the Benjamini-Hochberg adjustment. A P value < 0.05 was considered significant. All probability values reported are 2-sided.
Results
In this study, we enrolled a total of 50 hospitalised patients (11 women, 39 men) with HFrEF and diabetes mellitus type II. The mean age of the patients was 71 ± 11 years, the mean left ventricular ejection fraction was 30.7 ± 8.7%, and the mean HbA1c was 7.8 ± 1.8%. Coronary artery disease was present in 30 patients. Drug therapy included beta-blockers (n = 44), angiotensin-converting enzymes, angiotensin II receptor blockers, or sacubitril/valsartan (n = 46), aldosterone antagonists (n = 16), insulin (n = 12), and metformin (n = 23).
The six-minute walk test could only be performed in 43 of the 50 study patients due to orthopaedic problems or walking disabilities. All other examinations were performed in all patients at baseline and 3 months later.
After enrolment, 25 patients received the SGLT-2 inhibitor empagliflozin (dose 10 mg daily) in addition to their previous therapy at the decision of the treating physician. In the remaining 25 patients, considered the control group, no SGLT-2 inhibitor was prescribed.
The clinical characteristics, medication, MLHFQ results, distance of the 6-minute walk test, and echocardiographic parameters are given in
Table 1 and
Table 2. The results of the immunological tests are listed in
Table 3. Although the present study was not a randomized trial, the patients with and without SGLT-2 inhibitor demonstrated no significant differences at baseline (
Table 1-3).
The results of the study-specific tests (MLHFQ, 6-minute walk test, left ventricular ejection fraction, and immunologic factors) at baseline and after 3 months are presented in
Table 4.
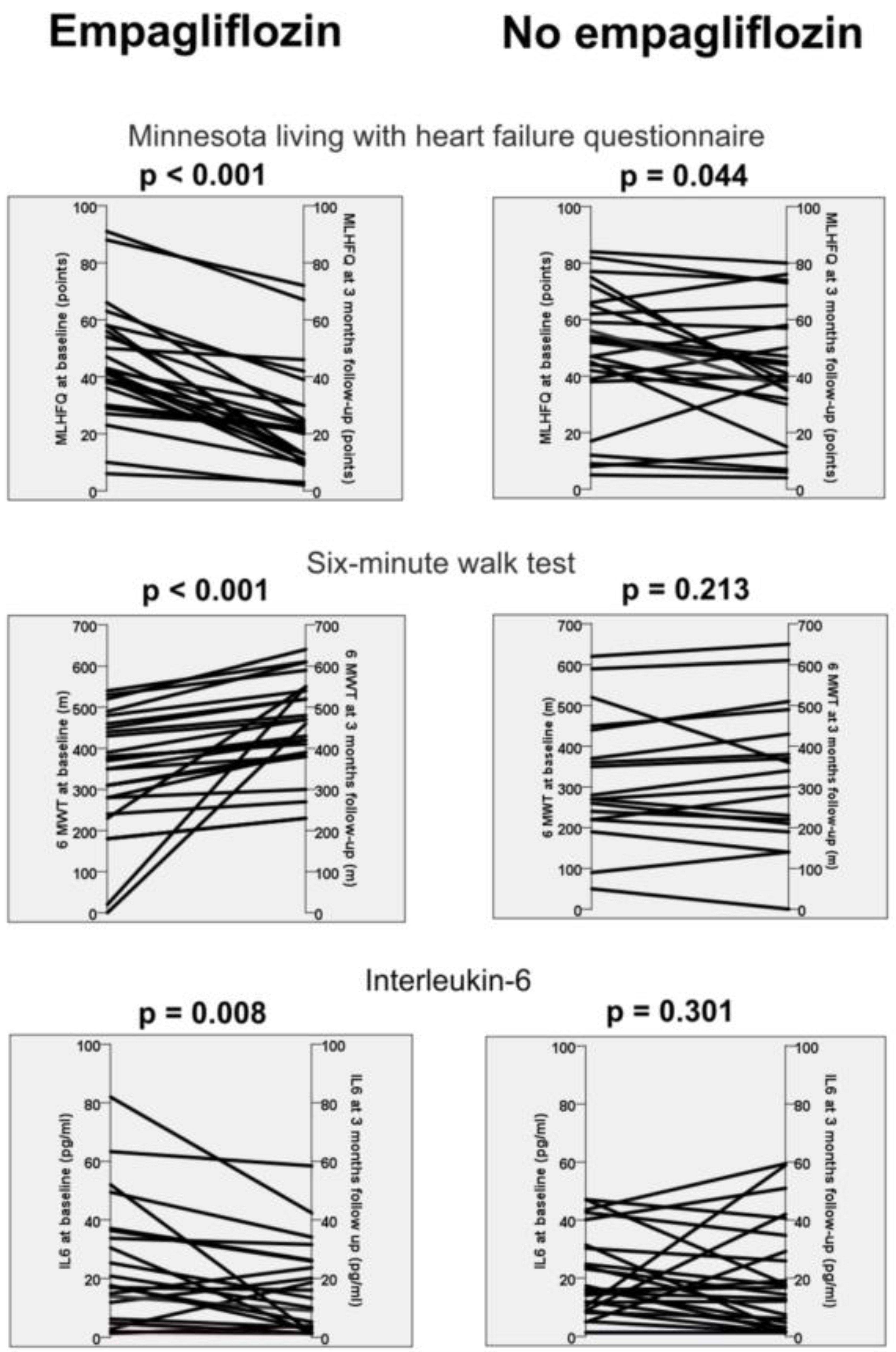
Patients receiving empagliflozin presented better quality of life, increased walking distance in the 6-minute walk test, improved left ventricular ejection fraction, reduced C-reactive protein and reduced interleukin-6 levels at 3 months compared with baseline (
Table 4). In comparison, the control group (patients without empagliflozin) demonstrated only an improvement in quality of life, left ventricular ejection fraction and reduced C-reactive protein levels. Notably, the other immunological factors revealed no difference in these patients (
Table 4).
Discussion
The main finding of this prospective proof-of-concept study is that three months of empagliflozin in patients with HFrEF and diabetes mellitus type II is associated with a reduction in soluble interleukin-6 levels. In contrast, patients without therapy with empagliflozin revealed no change in their soluble immune mediators (
Table 4). In addition, the use of an SGLT-2 inhibitor was also associated with an improvement in quality of life, functional capacity, and left ventricular ejection fraction (
Figure 1). Our study therefore supports the hypothesis that part of the effects of SGLT-2 inhibitors may be due to positive immunological effects.
In recent years, a number of studies have demonstrated beneficial effects of SGLT-2 inhibitors on diabetes mellitus but also on renal function and cardiovascular disease (2-6). The exact mechanism of these relatively new agents remains elusive. Various hemodynamic, metabolic, and immunologic effects have been described in the past (8-10).
For example, increased ketone body concentrations have been suggested to be responsible for any anti-inflammatory effect (15). On the other hand, there is evidence for an interaction between cytokines and the glucose transporter SGLT-2 (16,17). Recently, using lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages (in vitro), empagliflozin was shown to reduce COX-2 and iNOS gene expression. Empagliflozin also attenuated the secretion and mRNA expression of proinflammatory cytokines, such as Tumor necrosis factor-α, Interleukin-1β, Interleukin-6, and Interferon-γ, and proinflammatory chemokines (18). Kim et al. also investigated the effect of SGLT-2 inhibitors on macrophages. The authors concluded that SGLT-2 inhibitor attenuates pyrin domain-containing 3 inflammasome activation, which may explain its cardioprotective effects (19). A different approach was taken by Kolijn et al. in their in vitro study in human and murine cardiac myocytes with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. In this study, empagliflozin significantly suppressed elevated levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines and attenuated pathological oxidative parameters in both cardiomyocyte cytosol and mitochondria (20). In a secondary analysis of EMPA-TROPISM [ATRU-4] 6 months of empagliflozin significantly improved body mass index, interstitial myocardial fibrosis, aortic stiffness, and inflammatory markers. In proteomic analysis, 92 proteins were studied. The empagliflozin group showed significant changes in the expression of 17 proteins (proteins mostly involved in inflammatory processes) compared with the placebo group (21).
These previous (mainly in vitro) studies provide evidence that immunological parameters are affected by the use of SGLT-2 inhibitors and, in particular, empagliflozin. This effect seems to be consistent in different types of heart failure with preserved (20) and reduced ejection fraction (21) and in diabetic (19) and non-diabetic patients (21). However, there have been no studies investigating the changes in immunological parameters in vivo in patients with heart failure.
At the beginning of our study, SGLT-2 inhibitors were approved only for the treatment of HFrEF and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Accordingly, we included only patients with these diseases. Consistent with previous studies, our study demonstrated an effect of therapy with empagliflozin on immunological parameters. However, in contrast to previous studies, we were able to demonstrate for the first time this effect in vivo by determining the soluble immune mediators in serum (
Table 4).
As a limitation, it should be noted, that of the 18 factors analyzed, only C-reactive protein and soluble interleukin-6 showed a significant change. Interestingly, the level of C-reactive protein decreased both in the group of patients with and without empagliflozin. However, the change in C-reactive protein was no longer significant in both groups after adjustment for multiple testing (
Table 4). The fact that other immunological parameters did not exhibit a change could be due to the relatively small number of patients and the relatively short duration of therapy with empagliflozin. Nevertheless, our study confirms observations made in previous studies. A reduction in mRNA expression of interleukin-6 in empagliflozin-treated macrophages (18) and intracellular levels in human and murine myocardium (20) had already been described.
Interleukin-6 has a key role in innate immunity. The action of this cytokine is particularly related to host defense, regulation, proliferation and differentiation of immune cells (22). Interleukin-6, which is detectable in blood, originates from various sources, mainly mononuclear macrophages, but also T-helper cells, B-cells, vascular endothelial cells, smooth muscle cells, and fibroblasts (23).
For several years, it has been known that the expression of interleukin-6 is increased in the circulation and myocardium of patients with heart failure. Similarly, interleukin-6 is known to be associated with the progression of heart failure. Inflammation-induced remodeling of the myocardium (including an increase in apoptosis of myocytes and a decrease in contractility) is thought to be responsible (24,25). Elevated blood interleukin-6 concentrations have also been associated with increased heart failure-related mortality (26).
As pointed out, previous experimental analyses suggest that SGLT-2 inhibitors have an immunomodulatory effect (18-21). Nevertheless, it remains conceivable that the reduction in soluble interleukin-6 that we observed is mediated by other beneficial effects of empaglifozin. Of importance in this context is the observation of Ghezzi et al. whose study mapped the distribution of functional SGLT2 proteins in rodents using positron emission tomography with 4-[18F]fluorodapagliflozin (F-Dapa). Microscopic ex vitro autoradiography of the kidney revealed binding of F-Dapa to the proximal tubules. Of note, in vivo imaging demonstrated no measurable specific binding of F-Dapa in heart, muscle, salivary glands, liver, or brain. The high renal specificity of SGLT2 inhibitors may indicate that there is primarily a renal mechanism of these drugs (27).
In our study population with 3 months of therapy with empagliflozin, there was a clear, clinically relevant difference in quality of life and distance in the 6-minute walk test. This difference was only partially reproducible in the control group (
Table 4). Thus, it may be that interleukin-6 is merely a marker of heart failure severity. However, this information would also be of interest because soluble interleukin-6 is easy to determine and could be a suitable marker for further studies on therapy monitoring when taking SGLT-2 inhibitors.
Limitations
In this study, only the SGLT-2 inhibitor empagliflozin was used. It is therefore not clear whether other SGLT-2 inhibitors have a similar effect. Another limitation is the fact that this is not a randomized, double-blinded study. Even if there was no randomisation, however, the control group did not show any changes in quality of life, physical capacity or inflammatory parameters and thereby make a false-positive result unlikely. Moreover, the analysis of the immunological factors was performed without knowledge of the clinical parameters.
The main limitation of the study is the small number of patients. However, this study is a proof-of-concept study to determine whether the use of SGLT-2 inhibitors leads to a significant effect of different soluble immune mediators. Further studies should confirm the effects on soluble interleukin-6 and other immunological factors.
Conclusion
Three months of empagliflozin significantly improves quality of life and functional capacity in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Simultaneously, there is a reduction in soluble interleukin-6 levels, an effect that cannot be demonstrated in a corresponding control group. Hence, our study provides first in-vivo evidence for a potential antiinflammatory effect of SGLT2-inhibition in patients with heart failure. Thereby, our study confirms preliminary in-vitro data on immunomodulatory effects of SGLT-2 inhibitors. Whether the reduction of interleukin-6 levels is a mechanism for clinical improvement in patients or a marker of heart failure severity should be the subject of further research.
Conflict of interest disclosure
MG was a speaker for Abbott, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Novartis, Pfizer, and an advisor for Boehringer Ingelheim. TW received research grants and/or speakers’ honoraria from Akcea, Amgen, Astellas, Astra Zeneca, Bayer, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Daiichi-Sankyo, Hexal, MSD, Novartis, Otsuka, Pfizer, Sanofi Aventis, Vifor.
Ethics approval statement
The study was approved by the local ethics committee of the Ruhr University Bochum (Number 20-6944).
Appendix A
The appendix is an optional section that can contain details and data supplemental to the main text—for example, explanations of experimental details that would disrupt the flow of the main text but nonetheless remain crucial to understanding and reproducing the research shown; figures of replicates for experiments of which representative data is shown in the main text can be added here if brief, or as Supplementary data. Mathematical proofs of results not central to the paper can be added as an appendix.
Appendix B
All appendix sections must be cited in the main text. In the appendices, Figures, Tables, etc. should be labeled starting with “A”—e.g., Figure A1, Figure A2, etc.
References
- McDonagh TA, Metra M, Adamo M, Gardner RS, Baumbach A, Böhm M, Burri H, Butler J, Čelutkienė J, Chioncel O, Cleland JGF, Coats AJS, Crespo-Leiro MG, Farmakis D, Gilard M, Heymans S, Hoes AW, Jaarsma T, Jankowska EA, Lainscak M, Lam CSP, Lyon AR, McMurray JJV, Mebazaa A, Mindham R, Muneretto C, Francesco Piepoli M, Price S, Rosano GMC, Ruschitzka F, Kathrine Skibelund A; ESC Scientific Document Group. (2021) 2021 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure. Eur Heart J. 42(36):3599-3726. [CrossRef]
- Zinman B, Wanner C, Lachin JM, Fitchett D, Bluhmki E, Hantel S, Mattheus M, Devins T, Johansen OE, Woerle HJ, Broedl UC, Inzucchi SE; EMPA-REG OUTCOME Investigators (2015). Empagliflozin, cardiovascular outcomes, and mortality in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 373(22):2117-2128.
- Neal B, Perkovic V, Mahaffey KW, de Zeeuw D, Fulcher G, Erondu N, Shaw W, Law G, Desai M, Matthews DR; CANVAS Program Collaborative Group. (2017) Canagliflozin and cardiovascular and renal events in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 377(7):644-657.
- Wiviott SD, Raz I, Bonaca MP, Mosenzon O, Kato ET, Cahn A, Silverman MG, Zelniker TA, Kuder JF, Murphy SA, Bhatt DL, Leiter LA, McGuire DK, Wilding JP, Ruff CT, Gause-Nilsson IA, Fredriksson M, Johansson PA, Langkilde AM, Sabatine MS; DECLARE–TIMI 58 Investigators. (2019) Dapagliflozin and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 380(4):347-357. [CrossRef]
- McMurray JJV, Solomon SD, Inzucchi SE, Køber L, Kosiborod MN, Martinez FA, Ponikowski P, Sabatine MS, Anand IS, Bělohlávek J, Böhm M, Chiang CE, Chopra VK, de Boer RA, Desai AS, Diez M, Drozdz J, Dukát A, Ge J, Howlett JG, Katova T, Kitakaze M, Ljungman CEA, Merkely B, Nicolau JC, O'Meara E, Petrie MC, Vinh PN, Schou M, Tereshchenko S, Verma S, Held C, DeMets DL, Docherty KF, Jhund PS, Bengtsson O, Sjöstrand M, Langkilde AM; DAPA-HF Trial Committees and Investigators. (2019) Dapagliflozin in Patients with Heart Failure and Reduced Ejection Fraction. N Engl J Med. 381(21):1995-2008.
- Packer M, Anker SD, Butler J, Filippatos G, Pocock SJ, Carson P, Januzzi J, Verma S, Tsutsui H, Brueckmann M, Jamal W, Kimura K, Schnee J, Zeller C, Cotton D, Bocchi E, Böhm M, Choi DJ, Chopra V, Chuquiure E, Giannetti N, Janssens S, Zhang J, Gonzalez Juanatey JR, Kaul S, Brunner-La Rocca HP, Merkely B, Nicholls SJ, Perrone S, Pina I, Ponikowski P, Sattar N, Senni M, Seronde MF, Spinar J, Squire I, Taddei S, Wanner C, Zannad F; EMPEROR-Reduced Trial Investigators. (2020) Cardiovascular and Renal Outcomes with Empagliflozin in Heart Failure. N Engl J Med. 383 (15):1413-1424. [CrossRef]
- Anker SD, Butler J, Filippatos G, Ferreira JP, Bocchi E, Böhm M, Brunner-La Rocca HP, Choi DJ, Chopra V, Chuquiure-Valenzuela E, Giannetti N, Gomez-Mesa JE, Janssens S, Januzzi JL, Gonzalez-Juanatey JR, Merkely B, Nicholls SJ, Perrone SV, Piña IL, Ponikowski P, Senni M, Sim D, Spinar J, Squire I, Taddei S, Tsutsui H, Verma S, Vinereanu D, Zhang J, Carson P, Lam CSP, Marx N, Zeller C, Sattar N, Jamal W, Schnaidt S, Schnee JM, Brueckmann M, Pocock SJ, Zannad F, Packer M; EMPEROR-Preserved Trial Investigators. (2021) Empagliflozin in Heart Failure with a Preserved Ejection Fraction. N Engl J Med. 385 (16):1451-1461. [CrossRef]
- Fonseca-Correa JI, Correa-Rotter R. (2021) Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors Mechanisms of Action: A Review. Front Med (Lausanne). 8:777861. [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim NE, Januzzi JL. (2021) Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter 2 Inhibitors and Insights from Biomarker Measurement in Heart Failure Patients. Clin Chem. 67 (1):79-86. [CrossRef]
- Dutka M, Bobiński R, Ulman-Włodarz I, Hajduga M, Bujok J, Pająk C, Ćwiertnia M. (2021) Sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors: mechanisms of action in heart failure. Heart Fail Rev. 26 (3):603-622.
- Guyatt GH. (1993) Measurement of health-related quality of life in heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol. 22(4 Suppl A):185A-191A. [CrossRef]
- ATS Committee on Proficiency Standards for Clinical Pulmonary Function Laboratories. (2002) ATS statement: guidelines for the six-minute walk test. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 166 (1):111-117. Erratum in: Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 193 (10):1185.
- Lang RM, Badano LP, Mor-Avi V, Afilalo J, Armstrong A, Ernande L, Flachskampf FA, Foster E, Goldstein SA, Kuznetsova T, Lancellotti P, Muraru D, Picard MH, Rietzschel ER, Rudski L, Spencer KT, Tsang W, Voigt JU. (2015) Recommendations for cardiac chamber quantification by echocardiography in adults: an update from the American Society of Echocardiography and the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 16 (3):233-270. Erratum in: Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 17(4):412. Erratum in: Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 17 (9):969. [CrossRef]
- Stervbo U, Roch T, Westhoff TH, Gayova L, Kurchenko A, Seibert FS, Babel N. (2019) Repeated Changes to the Gravitational Field Negatively Affect the Serum Concentration of Select Growth Factors and Cytokines. Front Physiol. 10:402. [CrossRef]
- Prattichizzo F, De Nigris V, Micheloni S, La Sala L, Ceriello A. (2018) Increases in circulating levels of ketone bodies and cardiovascular protection with SGLT2 inhibitors: Is low-grade inflammation the neglected component? Diabetes Obes Metab. 20 (11):2515-2522.
- Maldonado-Cervantes MI, Galicia OG, Moreno-Jaime B, Zapata-Morales JR, Montoya-Contreras A, Bautista-Perez R, Martinez-Morales F. (2012) Autocrine modulation of glucose transporter SGLT2 by IL-6 and TNF-α in LLC-PK(1) cells. J Physiol Biochem. 68(3):411-420. [CrossRef]
- Mohamed HE, Asker ME, Keshawy MM, Hasan RA, Mahmoud YK. (2020) Inhibition of tumor necrosis factor-α enhanced the antifibrotic effect of empagliflozin in an animal model with renal insulin resistance. Mol Cell Biochem. 466 (1-2):45–54. [CrossRef]
- Lee N, Heo YJ, Choi SE, Jeon JY, Han SJ, Kim DJ, Kang Y, Lee KW, Kim HJ. (2021) Anti-inflammatory Effects of Empagliflozin and Gemigliptin on LPS-Stimulated Macrophage via the IKK/NF-κB, MKK7/JNK, and JAK2/STAT1 Signalling Pathways. J Immunol Res. 2021:9944880.
- Kim SR, Lee SG, Kim SH, Kim JH, Choi E, Cho W, Rim JH, Hwang I, Lee CJ, Lee M, Oh CM, Jeon JY, Gee HY, Kim JH, Lee BW, Kang ES, Cha BS, Lee MS, Yu JW, Cho JW, Kim JS, Lee YH. (2020) SGLT2 inhibition modulates NLRP3 inflammasome activity via ketones and insulin in diabetes with cardiovascular disease. Nat Commun. 11 (1):2127. [CrossRef]
- Kolijn D, Pabel S, Tian Y, Lódi M, Herwig M, Carrizzo A, Zhazykbayeva S, Kovács Á, Fülöp GÁ, Falcão-Pires I, Reusch PH, Linthout SV, Papp Z, van Heerebeek L, Vecchione C, Maier LS, Ciccarelli M, Tschöpe C, Mügge A, Bagi Z, Sossalla S, Hamdani N. (2021) Empagliflozin improves endothelial and cardiomyocyte function in human heart failure with preserved ejection fraction via reduced pro-inflammatory-oxidative pathways and protein kinase Gα oxidation. Cardiovasc Res. 117 (2):495-507. [CrossRef]
- Requena-Ibáñez JA, Santos-Gallego CG, Rodriguez-Cordero A, Vargas-Delgado AP, Mancini D, Sartori S, Atallah-Lajam F, Giannarelli C, Macaluso F, Lala A, Sanz J, Fuster V, Badimon JJ. (2021) Mechanistic Insights of Empagliflozin in Nondiabetic Patients With HFrEF: From the EMPA-TROPISM Study. JACC Heart Fail. 9 (8):578-589.
- Ridker PM, Rane M. (2021) Interleukin-6 Signaling and Anti-Interleukin-6 Therapeutics in Cardiovascular Disease. Circ Res. 128 (11):1728-1746. [CrossRef]
- Su JH, Luo MY, Liang N, Gong SX, Chen W, Huang WQ, Tian Y, Wang AP. (2021) Interleukin-6: A Novel Target for Cardio-Cerebrovascular Diseases. Front Pharmacol. 12:745061. [CrossRef]
- Mann DL. (2002) Inflammatory mediators and the failing heart: past, present, and the foreseeable future. Circ Res. 91(11):988-998.
- Gullestad L, Ueland T, Vinge LE, Finsen A, Yndestad A, Aukrust P. (2012) Inflammatory cytokines in heart failure: mediators and markers. Cardiology. 122 (1):23-35. [CrossRef]
- Maeda K, Tsutamoto T, Wada A, Mabuchi N, Hayashi M, Tsutsui T, Ohnishi M, Sawaki M, Fujii M, Matsumoto T, Kinoshita M. (2000) High levels of plasma brain natriuretic peptide and interleukin-6 after optimized treatment for heart failure are independent risk factors for morbidity and mortality in patients with congestive heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol. 36 (5):1587-1593. [CrossRef]
- Ghezzi C, Yu AS, Hirayama BA, Kepe V, Liu J, Scafoglio C, Powell DR, Huang SC, Satyamurthy N, Barrio JR, Wright EM. (2017) Dapagliflozin Binds Specifically to Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 in the Proximal Renal Tubule. J Am Soc Nephrol. 28 (3):802-810. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).