1. Introduction
In recent years, with the rapid development of technologies such as the Internet of Things, smart wearable and mobile computing, the exploration of human-oriented smart health situational awareness applications has attracted extensive attention from industry and academia. Among them, human motion perception (such as gait perception, gesture perception, and breathing perception) has attracted special attention from researchers because it is closely related to people's daily life and physical health. Traditional human motion sensing methods mainly sense human motion changes by attaching contact sensors or wearable devices with motion sensors to the surface of human skin to collect motion data [
1,
2,
3]. This type of method requires the user to wear or carry the sensing device always, which is not applicable to some special groups (such as infants, the elderly, and the disabled), because infants or the elderly wearing the sensing device for a long time is likely to cause physical discomfort, and some disabled people with limb disabilities cannot wear the sensory device. Due to the invasive nature of traditional contact sensing methods, researchers have studied and utilized computer vision technology to achieve non-contact human motion perception. In the early days of computer vision-based human motion perception research, image-based detection methods were mainly used [
4]. That is, a video stream of human activity is first recorded using a camera, then the video is segmented into frames, and finally uses the relevant image processing algorithm to detect the target human movement. In recent years, video-based human motion perception technology has become increasingly mature and widely used [
5,
6]. However, the perception method based on computer vision relies on lighting conditions and cannot work in non-line-of-sight environments, and there is also a risk of leaking personal privacy information such as face, height, weight.
In order to overcome the limitations of the above perception methods, such as intrusiveness, light dependence, and privacy leakage, researchers have focused on using wireless signals to implement non-contact human motion perception. As early as 2010, researchers proposed to use ultrasonic signals emitted by acoustic sensors to sense the user's gait, behavioral actions, and breathing rate [
7,
8,
9]. However, this method requires specialized acoustic equipment, which is expensive and difficult to deploy. Therefore, the researchers explored the direct use of acoustic sensing devices (speakers and microphones) built into smartphones to sense human movement [
10]. This method can overcome the limitations of light dependence and it has low hardware cost and is easily deployed, but acoustic signal-based sensing methods are susceptible to environmental noise and still have privacy leakage risks. With the innovation of wireless communication and intelligent computing technology, the research on human motion perception based on wireless radio frequency signal has become a research hotspot in the past five years. As early as 2015, researchers proposed to use frequency-modulated continuous wave radar and millimeter-wave radar technology to perceive human chest movement, gesture posture and even recognize human emotional changes [
11]. Although this method can not only achieve fine-grained human motion perception but also protect users' personal privacy, it also requires special radar equipment, which is costly and difficult to control. Then researchers proposed to use RFID readers/tags to sense human respiratory movement, sleep activity and fitness exercise [
12,
13]. Although the use of commercial RFID equipment can effectively reduce the cost of equipment, it is only deployed in specific applications (such as toll stations, parking lots, access control systems) now, and the popularity of equipment is not enough to achieve ubiquitous real-time human motion perception.
Recently, in order to achieve ubiquitous real-time human motion perception, WiFi signals have emerged. Specifically, researchers directly utilize the link-layer or physical-layer attributes of ubiquitous WiFi signals, such as the Received Signal Strength Indicator (RSSI) and the physical layer Channel State Information (CSI), to obtain perceptual information related to human movement. The link-layer or physical layer properties of WiFi signals can be extracted from commercial wireless cards such as Intel 5300 network card, Atheors 9580 network card [
14,
15]. Since the link-layer RSS measurement is susceptible to the time-varying and multipath fading of the wireless channel, the existing work mostly uses the physical layer CSI to implement non-contact human motion perception. That is, for a WiFi signal with a bandwidth of 20 MHz, the receiver can use the Intel 5300 network card to extract the Channel Frequency Response (CFR) estimate of 30 OFDM subcarriers, that is CSI, each CSI measurement contains the amplitude and phase information of any OFDM subcarrier, so CSI can provide wireless channel time-frequency domain change information to achieve fine-grained human motion perception. At present, the perception applications based on WiFi CSI mainly focus on human activity recognition, indoor positioning and respiratory monitoring [
16,
17,
18,
19,
20,
21,
22]. Medical studies have shown that frequent shaking of the head during sleep of children is often closely related to physiological diseases such as rickets and eczema, while frequent shaking of the head during sleep of adults is often closely related to mental diseases such as insomnia, anxiety and even depression. Therefore, monitoring people's head movement during sleep is an important research topic in the situational perception of smart health.
Therefore, this paper proposes Wi-Senser, a human head motion detection method based on WiFi signals. Wi-Senser directly utilizes the CSI amplitude information of ubiquitous WiFi signals to achieve contactless human head motion detection without revealing privacy of user. Specifically, Wi-Senser firstly uses an Intel 5300 network card to extract WiFi CSI data that records changes in human head movement. Then Wi-Senser uses a filter channel consisting of a Hampel filter, a wavelet filter, and an averaging filter to filter out outliers and strong noises in the original CSI signal and retain the rising/falling edges of the movement changes. Subsequently, Wi-Senser proposes a sensitivity metric combining standard deviation and kurtosis, and bases on this sensitivity metric, an optimal subcarrier is selected from 30 CSI subcarriers, which has the highest sensitivity to changes in head motion and is insensitive to irrelevant environmental changes. Finally, Wi-Senser uses the peak finding algorithm to capture the true set of peaks caused by head motion from the optimal subcarrier, so as to achieve accurate detection of human head motion.
Overall speaking, Wi-Senser has three main advantages: firstly, it utilizes WiFi signal to detect head movement during sleep, which can protect the privacy of user and is noninvasive to the human body; secondly, it directly utilizes existing WiFi routers as transmitters, which is cost-effective and easy to deploy; thirdly, WiFi signals have strong penetrability, enabling the detection of human movement in non-line-of-sight scenarios.
The main contributions of this paper are summarized as follows.
To the best of our knowledge, Wi-Senser is the first system enabling contactless human head movement detection during sleep by reusing the existing WiFi network.
We propose a new metric used to select an optimal subcarrier from candidate subcarriers and design algorithm that has the capability to track human head movements accurately from the extracted fine-grained CSI signals.
We implement Wi-Senser with COTS WiFi devices and evaluate the performance with extensive real-world experiments involving 6 volunteers (including 4 adults and 2 children). The results demonstrate that with WiFi signals alone, Wi-Senser is able to achieve higher than 98.5% accuracy in detecting human head movement during sleep.
2. Preliminaries
This section presents a theoretical model for utilizing WiFi signals to perceive changes of human body movement [
23]. Specifically, at time
t, if the WiFi signal reaches the receiver through N paths, the complex value of channel frequency response CFR of the
i-th subcarrier in the WiFi channel can be represented as
where
f is the carrier frequency,
△f is the carrier frequency offset between the transmitter and receiver,
λ is the wavelength, and
is the dynamic path set.
is the cumulative CFR of static paths, which has relatively stable energy attenuation and propagation delay due to near-constant propagation length. Therefore,
is usually regarded as a constant.
represents the energy attenuation of the
k-th dynamic path, and
represents the phase shift caused by the transmission delay along the
k-th dynamic path (with a length of
).
represents the phase shift caused by the carrier frequency offset
△f.
According to Equation 1, the CSI energy (
) can be derived as
Since
represents a unit vector rotating an angle of
in the complex plane, its influence on CSI energy (
) can be ignored. That is, under the condition of ignoring the effect of carrier frequency offset, Equation 1 can be rewritten as
where
is the rotation angle of the synthesized vector of static paths, and
is the initial phase of the
k-th dynamic path. Based on Euler's formula (
), Equation 3 can be further expanded as
Therefore, the sum of the squares of the real and imaginary parts in Equation 4 is the CSI energy:
Equation 5 can be expanded, organized and simplified based on trigonometric properties as
According to the literature [
23], by assuming that the
-th dynamic path has a relatively stable velocity change due to human movement in a short time, i.e.,
, substituting it into Equation 6, we can get:
where
,
and
represent the initial phase under static and dynamic paths respectively, which can be regarded as constants. In addition,
and
represent the initial phase shifts under different dynamic paths, which can also be regarded as constants. Therefore, we can get:
Substituting Equation 8 and Equation 9 into Equation 7, we can obtain:
Since
and
are approximately constants, the amplitude change of CSI caused by human movement (
) can be approximated as a sum of DC components and cosine signals whose frequencies change at a speed of
of dynamic paths and amplitudes change with the length
of dynamic paths.
In summary, human body movement causes changes of dynamic paths in WiFi signal multipath propagation, which in turn leads to changes in the CSI amplitude of the received signal.
3. System Design
3.1. System Overview
Wi-Senser aims to achieve non-device-based human head motion detection utilizing ubiquitous WiFi signals, without the need for users to wear any professional sensing devices.
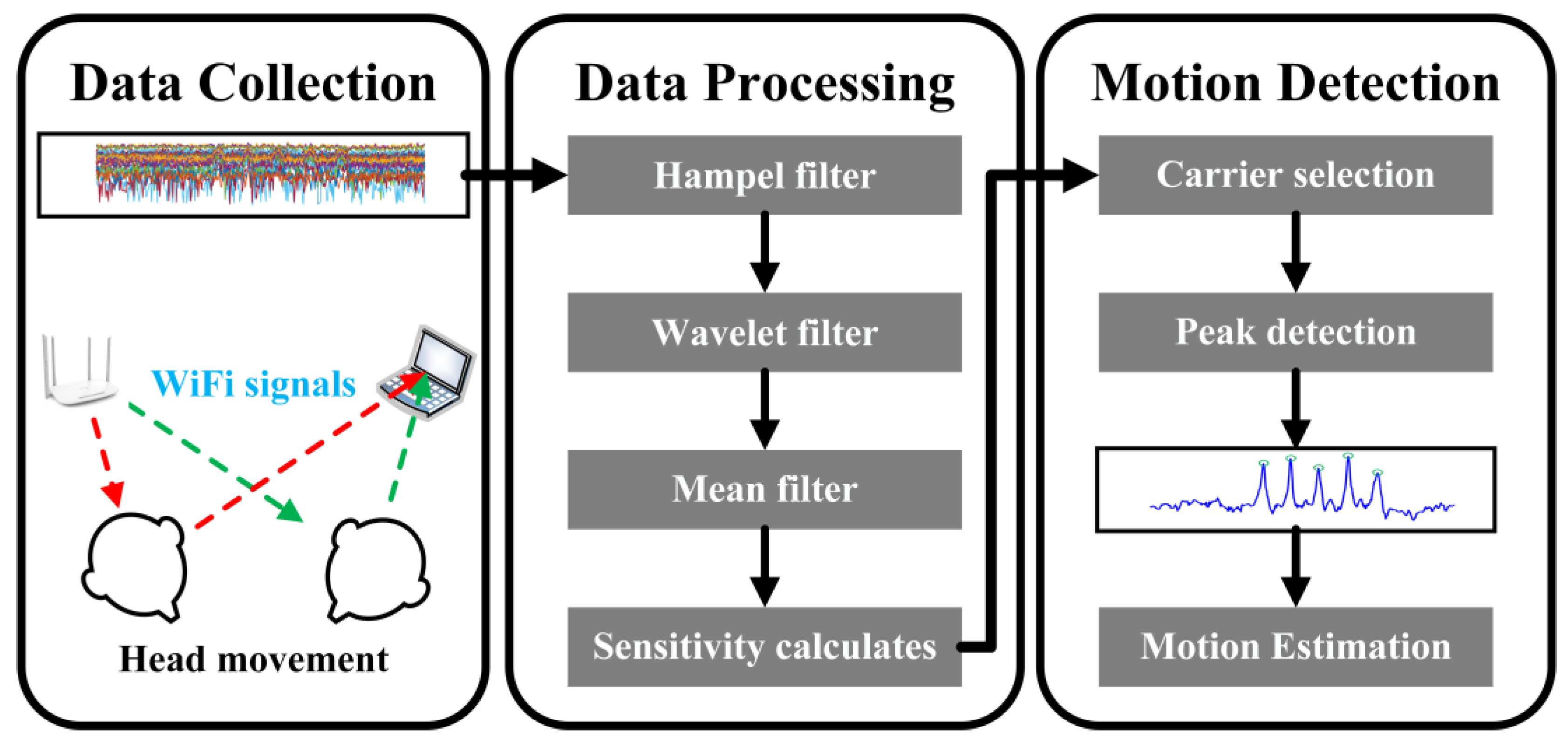
Figure 1 depicts the system architecture of Wi-Senser. Wi-Senser consists of three functional modules: data collection module, data processing module, and head motion detection module. In the data collection module, Wi-Senser directly uses a commercial WiFi router as a transmitter while using a laptop with an Intel 5300 network card to receive WiFi signals and extract CSI amplitude data. Since the original CSI amplitude data contains a large number of outliers and strong noise caused by the external environment and hardware equipment, Wi-Senser utilizes a filtering channel consisting of Hampel filter, wavelet filter, and mean filter in the data processing module to filter out outliers and strong noise, and then proposes a sensitivity measure to calculate the sensitivity of CSI amplitude fluctuations of each subcarrier to human head movement. As the CSI amplitude fluctuations of different subcarriers have different sensitivity to human head movement, Wi-Senser first selects the optimal subcarrier with the highest sensitivity from 30 subcarriers according to the calculated sensitivity in the head motion detection module, and then uses the peak-finding algorithm to capture the real peak set caused by human head movement from the optimal subcarrier to achieve human head motion estimation. The following sections will provide a detailed overview of each functional module of Wi-Senser for human head motion detection.
3.2. Data Collection
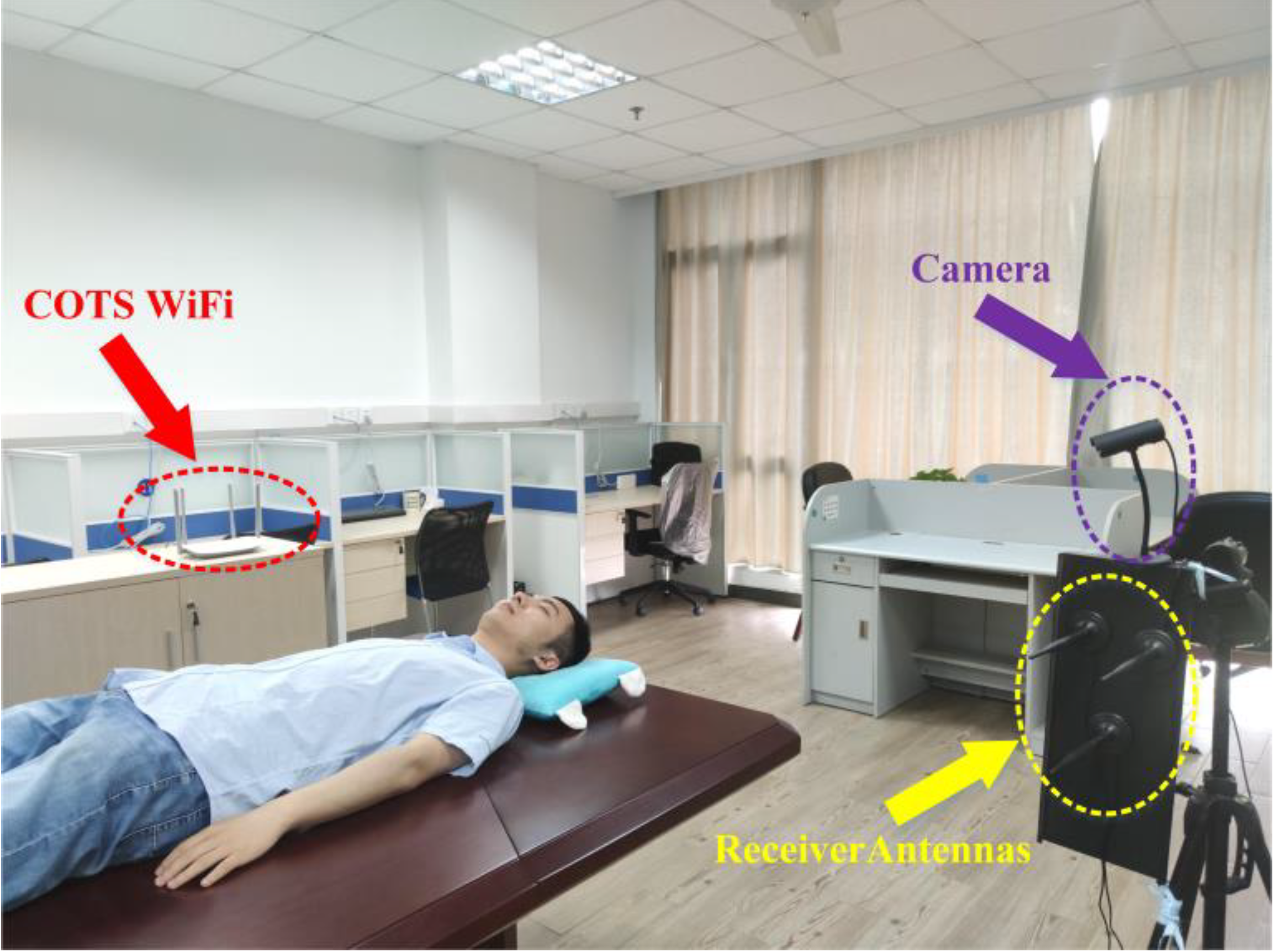
We conducted data collection experiment in the laboratory using an 802.11n WiFi network, with a commercial WiFi router (TP-Link WDR5620) set as the transmitter (TX) and a Lenovo laptop equipped with an Intel 5300 network card as the receiver (RX), as shown in
Figure 2. The network card has three antenna interfaces, and we connected external antennas to the receiver to enhance signal strength. The distance between the transmitter and receiver was set to 2.5 meters, and the packet transmission rate of the transmitter was set to 20 pkts/s. During the experiment, volunteers lay on a long table between the transmitter and receiver and freely rotated their heads (i.e., rolling their head in a supine position). We used the tool provided in literature [
14] to modify the firmware and driver of the receiver's network card to obtain CSI measurements of 30 subcarriers in the 2.4 GHz WiFi signal. Specifically, the received single CSI measurement is a complex matrix of size 30×
×
,
and
are the numbers of transmitting antennas and receiving antennas respectively.
3.3. Data Processing
Due to the strong noise in the original CSI measurements caused by environmental changes, wireless interference, etc., Wi-Senser needs to perform denoising processing on the original CSI measurements to extract fine-grained CSI amplitude information that records human head motion changes. Wi-Senser mainly considers three types of different noise: outliers (i.e., CSI measurements that deviate from the median by several times the standard deviation in a set of CSI measurements), high-frequency environmental noise, and low-frequency interfering noise, and uses a filtering channel consisting of a Hampel filter, wavelet filter, and mean filter to filter out the above noise.
3.3.1. Hampel Filter
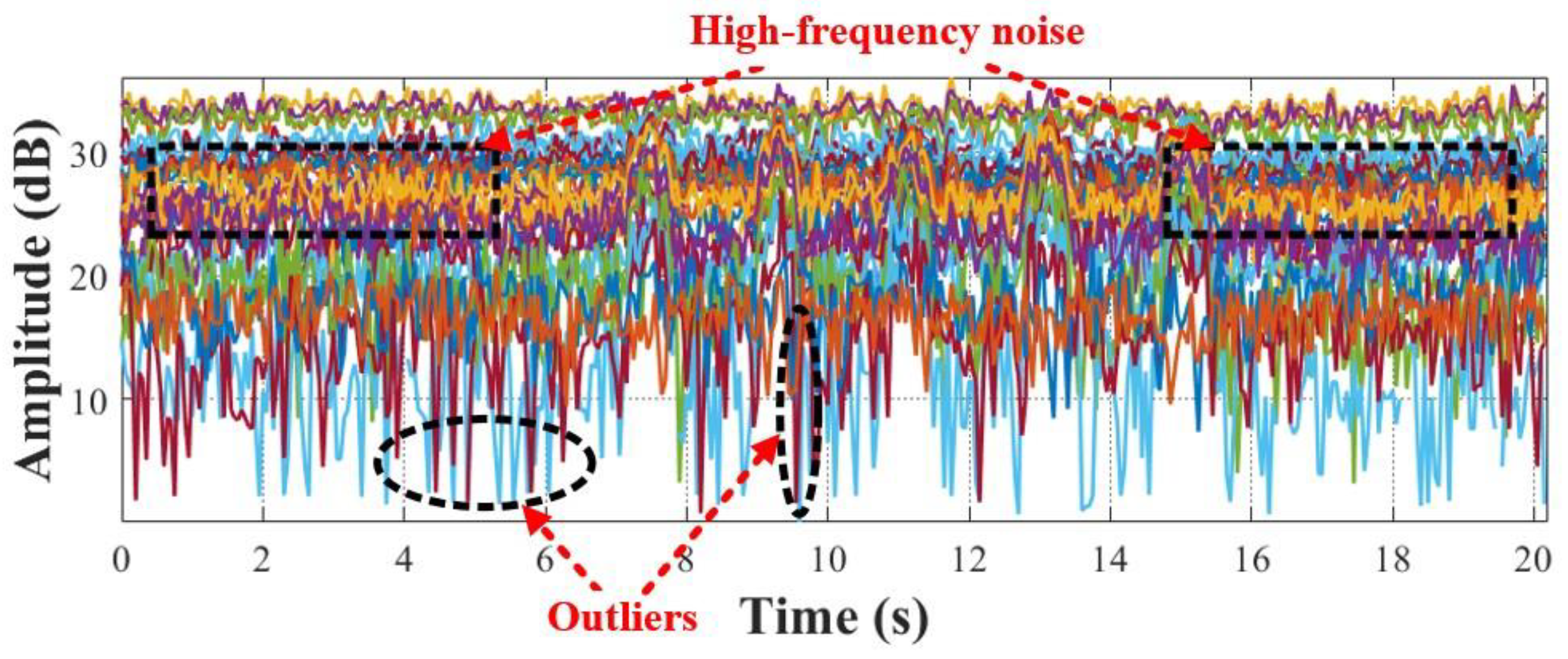
Figure 3 shows the raw CSI amplitude sequence (i.e., 30 CSI subcarriers) collected by the Intel 5300 network card, where it can be observed that there are generally many outliers in the raw CSI amplitude sequence. To address this issue, Wi-Senser utilizes a Hampel filter with a sliding window to remove the outlier CSI amplitudes. Specifically, given the n-length CSI amplitude sequence
in the
i-th subcarrier and the
j-th sliding window
with a length of
Φ, if any CSI amplitude
in the current sliding window satisfies the condition:
, where
and
represent the median and standard deviation of the CSI amplitudes in the current sliding window
, and γ represents an expandable factor (i.e., a constant), the Hampel filter considers it as an outlier. For any outlier
, the Hampel filter replaces it with the median
. In the experiments, we empirically set γ and Φ to 1.5 and 7 respectively.
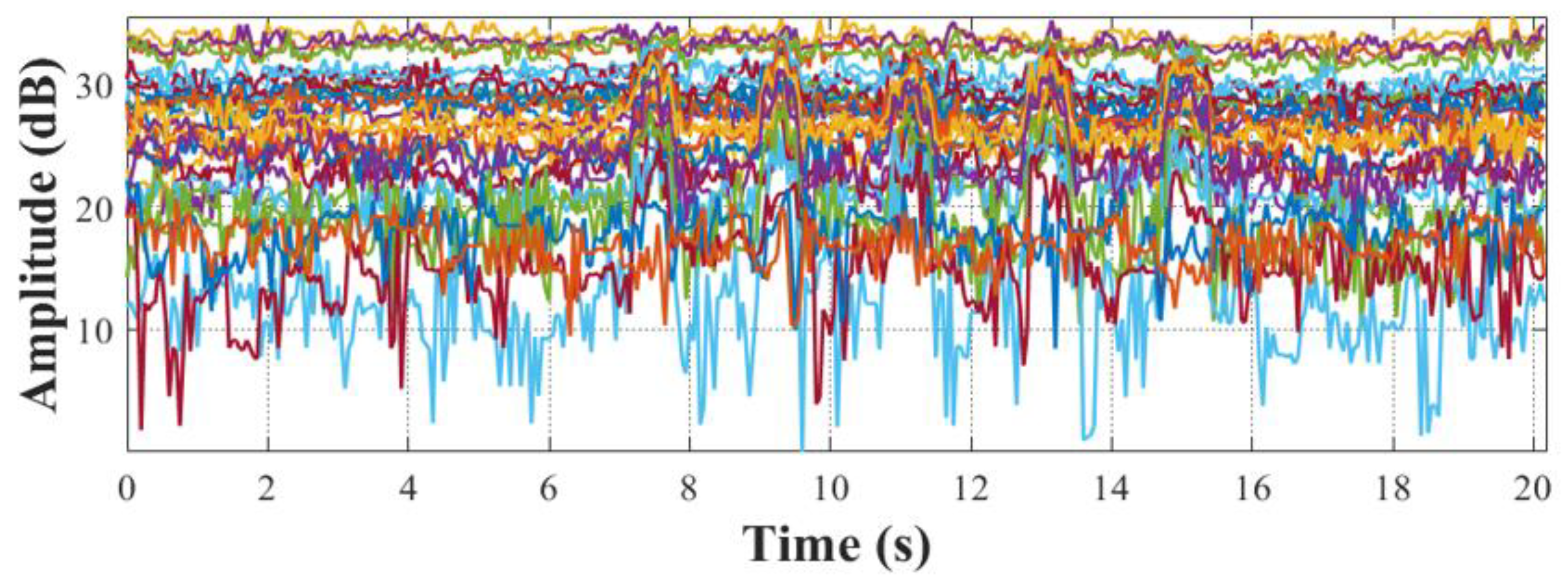
Figure 4 shows that the CSI subcarriers after being filtered by the Hampel filter, where it can be observed that the outliers identified in
Figure 3 can be effectively removed.
3.3.2. Wavelet Filter
Although the Hampel filter can remove outliers in the CSI amplitude sequence, high-frequency environmental noise still exists. Therefore, Wi-Senser needs to further filter out high-frequency environmental noise. Traditional low-pass filters such as Butterworth and Chebyshev filters suppress not only high-frequency noise but also the rising/falling edges in the CSI amplitude fluctuations, which are often caused by human motion events. Suppressing these edges may cause Wi-Senser to miss/detect false-positive head motion events. Compared with traditional low-pass filters, wavelet filters can better preserve transient changes in signals. Therefore, Wi-Senser utilizes a wavelet filter to suppress high-frequency environmental noise in the CSI amplitude sequence while preserving the rising/falling edges generated by head motion events. Specifically, Wi-Senser uses the Stein unbiased estimate as the threshold selection criterion and sets the threshold usage mode to soft thresholding in the wavelet filter. In each CSI subcarrier, Wi-Senser adopts 4-level db4 wavelet transform and retains the approximation coefficients (i.e., the useful low-frequency signal) to filter out high-frequency environmental noise.
Figure 5 shows the CSI subcarriers filtered by the wavelet, where it can be observed that high-frequency environmental noise is effectively suppressed, and the rising/falling edges in the CSI amplitude changes that record head motion are fully preserved. The experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of the low-pass filter (i.e., wavelet filter) selected by Wi-Senser to filter out high-frequency environmental noise.
3.3.3. Mean Filter
Although the wavelet filter can effectively remove high-frequency environmental noise from the CSI amplitude sequence, it cannot filter out low-frequency interfering noise with similar frequencies to human motion signals. Therefore, Wi-Senser further utilizes a mean filter to filter out low-frequency interfering noise and extract low-frequency CSI amplitude fluctuations that record head motion changes. Specifically, the mean filter treats consecutive sample data as a data queue with a length of
L. For each new measurement data, it removes the first sample data in the previous queue and adds a new sample data to the end of the queue to form a new data queue with a length of
L. Then, it performs arithmetic operations on the new data queue and uses the operation result as the final result of the new measurement task. That is, assuming the input is
X and the output is
Y, its calculation formula is as follows:
In the experiments, Wi-Senser empirically set
L to 20 to perform filtering tasks.
Figure 6 shows the CSI subcarriers further filtered by the mean filter, where it can be observed that compared with
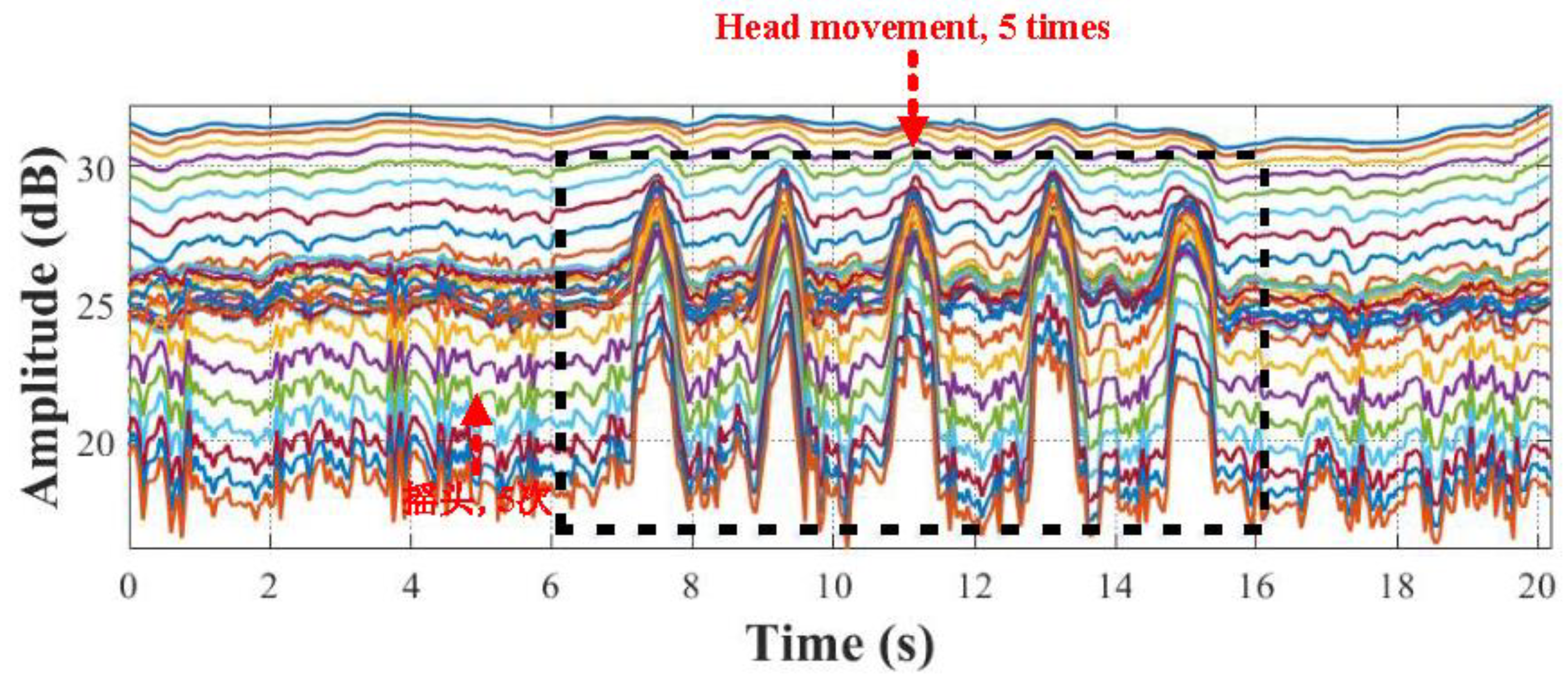
Figure 5, the CSI amplitude signals after mean filtering are smoother and more regular, the hierarchy between subcarriers is clearer, and all head motion-induced CSI amplitude fluctuations can be fully recorded. The experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of the mean filter used by Wi-Senser to filter out low-frequency interfering noise. In addition,
Figure 7 shows the comparison of CSI amplitude changes before and after data processing. It can be clearly seen that compared with the original CSI amplitude signal (as shown in
Figure 7(a)), the CSI amplitude signal obtained by Wi-Senser's filtering channel is smoother, and the CSI amplitude fluctuations caused by head motion are more obvious, while various noises are effectively filtered out (as shown in
Figure 7(b)). The experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of the filtering channel used by Wi-Senser to filter out various noises.
3.4. Carrier Selection
Due to different center frequencies/wavelengths of different subcarriers, the sensitivity of CSI amplitude fluctuations of different subcarriers to human head motion changes varies. Specifically,
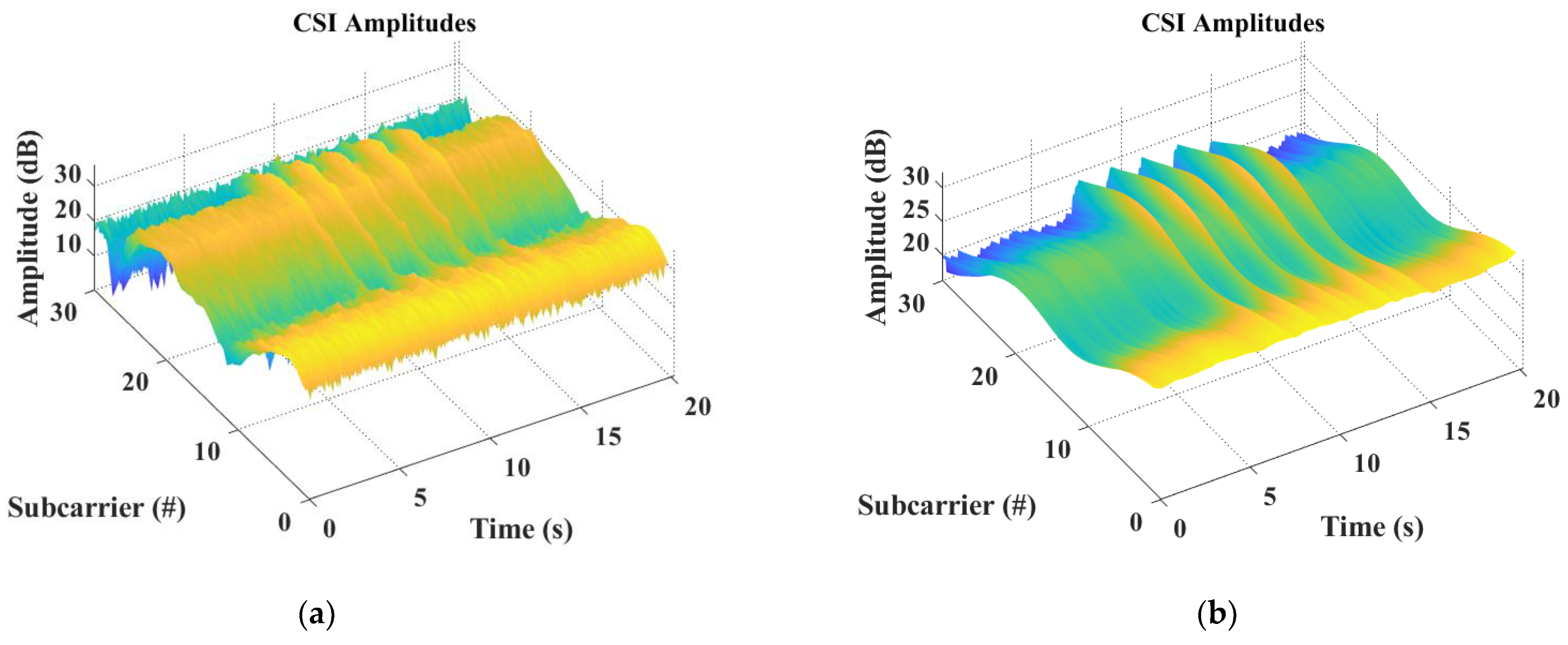
Figure 7(b) shows the CSI amplitude changes of each subcarrier with human head motion after data processing. It can be observed that human head motion has a smaller impact on the CSI amplitude changes of subcarriers with lower carrier numbers (i.e., subcarriers 1-10), indicating that these subcarriers are less sensitive to human head motion changes. However, human head motion has a greater impact on the CSI amplitude changes of subcarriers with higher carrier numbers (i.e., subcarriers 15-30), indicating that these subcarriers are more sensitive to human head motion changes. Therefore, before performing human head motion detection, Wi-Senser needs to select the optimal subcarrier with the highest sensitivity to human head motion changes from the CSI subcarriers after data processing.
To achieve this goal, Wi-Senser first defines a sensitivity metric to quantify the sensitivity of CSI amplitude changes of different subcarriers to human head motion changes. Specifically, given any processed CSI amplitude sequence
where
i is the ordinal of subcarrier and
n is the sample length, the sensitivity of
to human motion can be calculated as:
where
and
are the standard deviation and kurtosis of
respectively, and
is a weighting factor. Unlike reference [
24], which only utilizes the variance of the CSI amplitude sequence to quantify the sensitivity of different subcarriers to human motion. However, both human movement and non-motion interference can cause large changes in the variance of CSI amplitude, it is difficult for variance measurement to effectively identify whether the fluctuation of CSI amplitude (that is, large variance value) in a certain period of time is caused by human motion or by non-motion interference. Therefore, as shown in Equation 12, Wi-Senser introduces a joint sensitivity metric of the standard deviation and kurtosis of the CSI amplitude sequence for the first time. The reason for introducing this joint metric is twofold: first, the kurtosis metric can measure the sharpness of CSI amplitude fluctuations, and since the CSI amplitude fluctuations caused by human motion are sharper, this metric can better capture the CSI amplitude fluctuations that reflect human motion changes; second, compared with variance metrics, standard deviation metrics are more robust to CSI amplitude fluctuations.
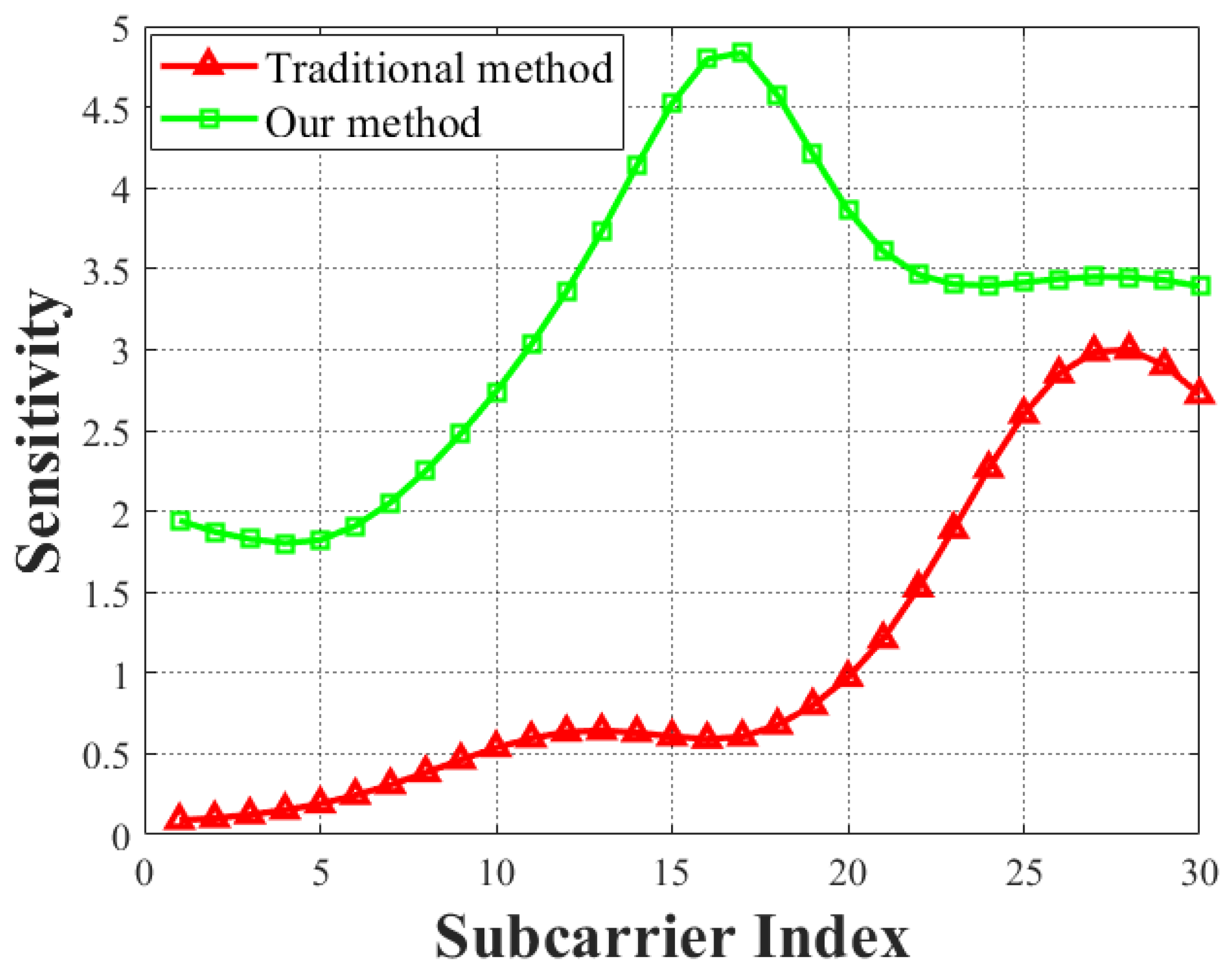
Figure 8 shows the sensitivity calculation results of different subcarriers under different sensitivity metrics. It can be observed that the optimal subcarrier selected by the traditional method (i.e., variance metric) is subcarrier 28, while the optimal subcarrier selected by Wi-Senser (i.e., joint metric) is subcarrier 17.
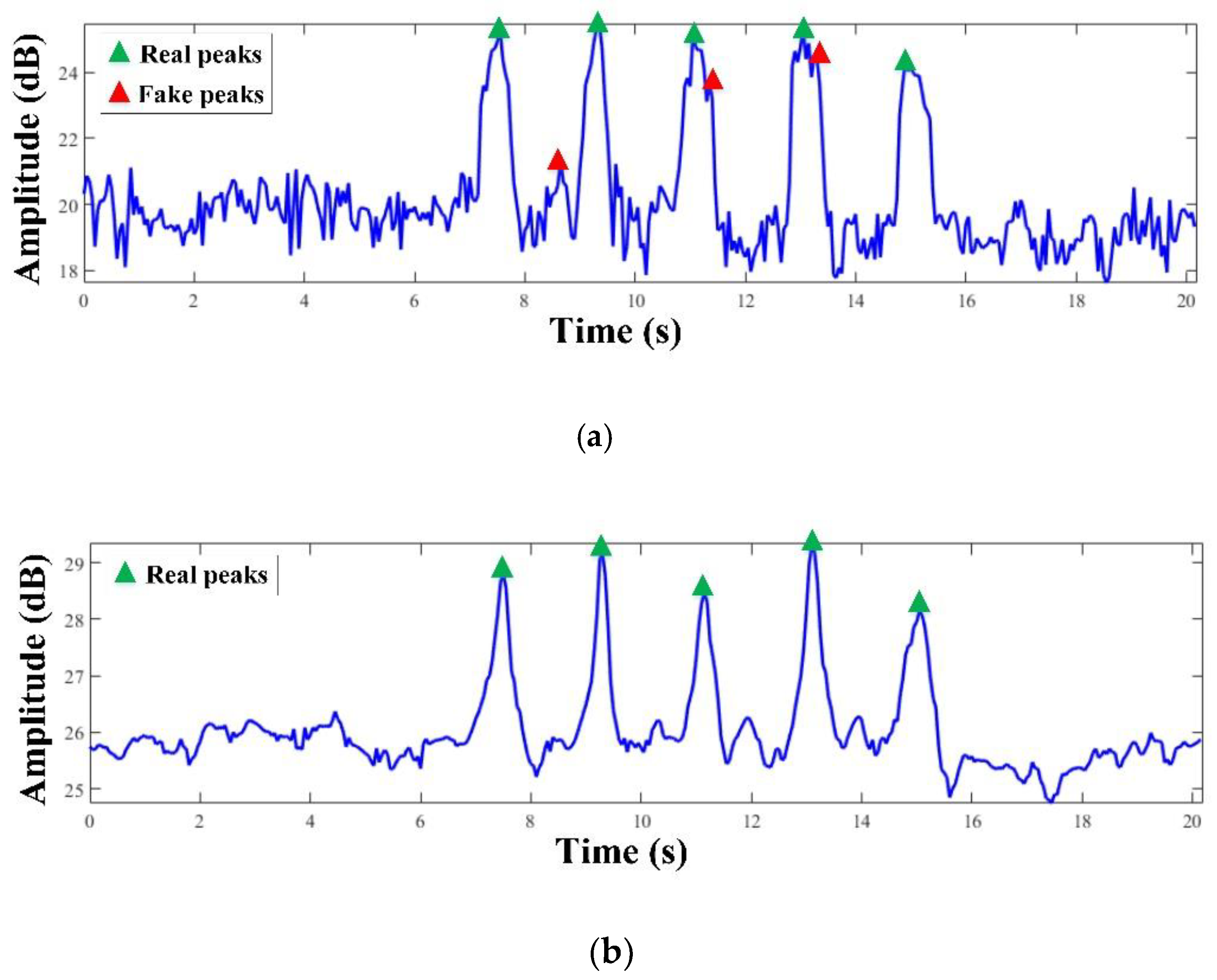
Figure 9 further shows the optimal subcarrier selected under different sensitivity metrics (i.e., subcarrier 28 and subcarrier 17). It can be clearly observed that, as shown in
Figure 9(a), although subcarrier 28 can fully record human head motion changes (i.e., the green triangle in the figure), it also introduces more spike signals unrelated to human head motion (i.e., the red triangle in the figure), which may lead to false detection. Compared with subcarrier 28, subcarrier 17 shown in
Figure 9(b) is smoother and more stable, especially, there are no spike signals around the peak of the CSI amplitude fluctuations that reflect human head motion, indicating that subcarrier 17 can more accurately detect human head motion (i.e., the green triangle in the figure) and greatly reduce the possibility of false detection. In conclusion, the joint standard deviation and kurtosis sensitivity metric proposed by Wi-Senser can better select the optimal subcarrier, which has the highest sensitivity to human head motion and is insensitive to irrelevant environmental changes.
3.5. Motion Detection
After Wi-Senser selects the optimal subcarrier with the highest sensitivity to human head motion changes from 30 CSI subcarriers by the joint metric, it further utilizes the algorithm called peak-finding to capture the true peak set caused by human head motion from the optimal subcarrier to achieve accurate detection of human head motion. The peak-finding algorithm is detailed in Algorithm 1. Specifically, for the processed CSI amplitude sequence
, Wi-Senser first uses the sensitivity measure given by Equation 12 to calculate the sensitivity values of each subcarrier to sleep head movement (lines 1-5 in Algorithm 1). Then, Wi-Senser selects the subcarrier with the highest sensitivity value as the optimal subcarrier (lines 6-10 in Algorithm 1). Next, for the selected optimal subcarrier, Wi-Senser sets a minimum peak height and uses a classical algorithm to find all local maxima as the candidate peak set (lines 11-12 in Algorithm 1). Finally, Wi-Senser filters out false peaks caused by large body movements (e.g., going to bed and turn over) from the candidate peak set based on a threshold-based approach to obtain the true peak set that records sleep head movement changes (lines 13-18 in Algorithm 1).
|
Algorithm 1: Peak-finding algorithm. |
Input: The processed CSI amplitude sequence: ;
weight factor: ; threshold used to discriminate large body movements: .
Output: The true peak set:
|
| 1: ; |
| 2: for =1: do
|
| 3: ; |
| 4: ; |
| 5: ; # Sensitivity calculation |
| 6: if then
|
| 7: ; # Optimal subcarrier selection |
| 8: end if
|
| 9: end for
|
| 10: ; |
| 11: ; #Set a minimum peak height used to filter out non-movement interferences |
| 12: ;/**/ |
| 13: for =1: do #Find the true peak set caused by head movements |
| 14: if then
|
| 15: add into ; |
| 16: end if
|
| 17: end for
|
| 18: return . |
4. Evaluation
4.1. Implementation
4.1.1. Hardware Implementation
The transmitter of Wi-Senser is a TP-Link commercial wireless router model TL-WDR5620, which is set to operate in the 2.4 GHz frequency band and use the IEEE 802.11n protocol standard. The receiver of Wi-Senser is a Lenovo laptop computer with an Intel 5300 wireless network card (3.3 GHz Intel(R) Core (TM) i5 CPU, 8 GB RAM, 512 GB solid-state drive), which has three antenna interfaces that we externally connect to enhance the received signal strength. The laptop computer is installed with Ubuntu 12.04 LTS and operates in client mode. The laptop computer sends ping commands to the wireless router at a data rate of 20 pkts/s, and the wireless router also transmits 2.4 GHz WiFi signals to the laptop computer at the same data transmission rate. We modify the firmware and driver of the network card using tools provided in reference [
14] to obtain CSI measurements of 30 subcarriers in the 2.4 GHz WiFi signal. MATLAB R2018b is used to process and analyze the collected CSI data. Wi-Senser uses a high-definition camera to record actual human head motion. The experimental deployment is shown in
Figure 2.
4.1.2. Software Implementation
To obtain rich experimental data to verify the detection performance of Wi-Senser on human head motion, a total of six volunteers were recruited for this experiment, including four adults (two males and two females) and two children (one boy and one girl) with ages ranging from 6 to 27 years and weights between 20 kg and 65 kg. During the experiment, the transmitter and receiver were initially placed on both sides of the area where human motion was expected, with an initial relative distance of 2.5 m between them. Each volunteer was asked to perform 60 human head movements freely and randomly over three days according to their personal sleeping habits, with each movement lasting 3 minutes. Therefore, Wi-Senser collected a total of 360 CSI amplitude data segments (60 times × 6 volunteers).
4.1.3. Performance Metric
We use the Detection Accuracy as the performance evaluation index of human head motion detection, which is defined as follows:
where
represents the number of true head movements detected by Wi-Senser using Peak-finding Algorithm, and
represents the actual number of head movements recorded by the high-definition camera.
4.2. Overall Performance
4.2.1. Evaluation of Sleep Head Movement Detection
The detection results of Wi-Senser on human head motion are shown in the green bar chart in
Figure 10. Specifically, the average detection accuracies of Wi-Senser for the six volunteers' head movements are 96.5%, 100%, 99%, 98%, 100%, and 100%, respectively. That is, Wi-Senser achieves an average detection accuracy of over 98.5% for all volunteer head movements. It should be noted that the detection accuracy of Wi-Senser for volunteer P1's head movements is relatively lower than that of other volunteers. The main reason for this result is that volunteer P1 is a female child, and her head movements have smaller amplitude and weaker swing force, resulting in less fluctuation in the received CSI amplitude values and causing Wi-Senser to miss some slight head movements of the child. Overall, Wi-Senser can achieve accurate detection of human head motion for both adults and children (with an average detection accuracy of over 98.5%).
4.2.2. In Comparison to the Existing Method
To verify the effectiveness of the sensitivity metric proposed by Wi-Senser in selecting the optimal subcarrier, we first used the traditional variance metric to select the optimal subcarrier from the collected 360 CSI data segments, then used the peak-finding algorithm to obtain the corresponding peak set, and finally calculated the detection accuracy. The red bar chart in
Figure 10 shows the human head motion detection performance under the variance metric. It can be observed clearly that the detection accuracy of the optimal subcarrier selected by the variance metric is significantly lower than that of Wi-Senser, with an average detection accuracy reduced from 98.5% to 93%. The experimental results confirm the effectiveness of the sensitivity metric proposed by Wi-Senser in improving the detection performance of human head motion.
5. Discussion
Wi-Senser utilizes the multipath propagation effect of WiFi signals and ubiquitous commercial wireless routers to implement non-contact, low-cost, easy-to-deploy and high-precision detection of human head movement. However, at present, there are also some limitations in practical applications.
-
Limitations on the positioning of sensing devices
To address the limitations on the positioning of sensing devices, Wi-Senser can try to deploy multiple pairs of transceivers in future work to expand the effective sensing range of the system, and fuse the CSI measurement values collected by multiple pairs of transceivers to achieve more comprehensive and three-dimensional detection of human movement.
-
Limitations on the distance of sensing devices
To address the limitations on the distance of sensing devices, Wi-Senser can try to use high-gain directional antennas to increase the transmission power of WiFi signals in future work, enabling receivers to collect effective CSI measurement values at greater distances.
-
Limitations on multi-person sensing
At present, Wi-Senser can only sense the head movements of a single person. In future work, Wi-Senser can try to use multi-signal classification algorithms such as MUSIC to achieve multi-person sleep movement sensing.
6. Conclusion
This paper designs and implements a non-contact human head movement detection system, Wi-Senser, using ubiquitous WiFi signals from commercial wireless routers. Firstly, the theoretical basis of using WiFi signals for detecting human limb movements is analyzed, which approximates the changes in CSI amplitude caused by human movement as the sum of a series of DC components and cosine signals whose frequencies vary with the dynamic path velocity and amplitudes vary with the dynamic path length. To obtain detailed CSI amplitude information, Wi-Senser first uses a filtering channel composed of Hampel filter, wavelet filter, and mean filter to filter out outliers and environmental noise in the raw CSI measurements. Then, Wi-Senser proposes a joint sensitivity measure of standard deviation and kurtosis, and selects an optimal subcarrier from 30 CSI subcarriers that can fully record the changes in human head movement based on this sensitivity measure. Finally, Wi-Senser captures the real peak set caused by head movement from the optimal subcarrier using the peak-finding algorithm, thus achieving accurate detection of human head movement. This paper builds an experimental platform in a university lab setting to verify the detection performance of Wi-Senser and evaluate the actual impact of transmitter-receiver location and distance on Wi-Senser's sensing performance. Experimental results show that Wi-Senser achieves an average detection accuracy of more than 98.5% for head movement data from six volunteers. Compared with traditional carrier selection methods, the proposed joint measurement-based carrier selection method improves the average detection accuracy of the system by 5.5%. The sensing method proposed by Wi-Senser in this paper provides a theoretical and experimental basis for subsequent sleep multi-movement detection and recognition.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization W.L.; methodology, W.L.; software, W.L.; validation, W.L., Y.F. and S.Z.; formal analysis, W.L. and S.Z.; investigation, W.L.; resources, W.L.; data curation, W.L.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.F.; writing—review and editing, Y.F.; visualization, Y.F.; supervision, W.L.; project administration, W.L.; funding acquisition, W.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under grant 62202001.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this paper are available from the
corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Wilkinson J N, Thanawala V U. Thoracic impedance monitoring of respiratory rate during sedation–is it safe?. Anaesthesia, 2009, 64(4): 455-456. [CrossRef]
- Nukaya S, Shino T, Kurihara Y, et al. Noninvasive bed sensing of human biosignals via piezoceramic devices sandwiched between the floor and bed. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2010, 12(3): 431-438. [CrossRef]
- Zhang Y, Pan G, Jia K, et al. Accelerometer-based gait recognition by sparse representation of signature points with clusters. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2014, 45(9): 1864-1875. [CrossRef]
- Abir F F, Faisal M A A, Shahid O, et al. Contactless human activity analysis: an overview of different modalities. Contactless Human Activity Analysis, 2021, 200: 83. [CrossRef]
- Liu A A, Xu N, Nie W Z, et al. Benchmarking a multimodal and multiview and interactive dataset for human action recognition. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2016, 47(7): 1781-1794. [CrossRef]
- Liu A A, Su Y T, Nie W Z, et al. Hierarchical clustering multi-task learning for joint human action grouping and recognition. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2016, 39(1): 102-114. [CrossRef]
- Cheng R, Heinzelman W, Sturge-Apple M, et al. A motion-tracking ultrasonic sensor array for behavioral monitoring. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2011, 12(3): 707-712. [CrossRef]
- Wang T, Zhang D, Zheng Y, et al. C-FMCW based contactless respiration detection using acoustic signal. Proceedings of the ACM on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies, 2018, 1(4): 1-20. [CrossRef]
- Wang T, Zhang D, Wang L, et al. Contactless respiration monitoring using ultrasound signal with off-the-shelf audio devices. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2018, 6(2): 2959-2973.1. [CrossRef]
- Graham D, Simmons G, Nguyen D T, et al. A software-based sonar ranging sensor for smartphones. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2015, 2(6): 479-489. [CrossRef]
- Lien J, Gillian N, Karagozler M E, et al. Soli: Ubiquitous gesture sensing with millimeter wave radar. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2016, 35(4): 1-19. [CrossRef]
- Liu C, Xiong J, Cai L, et al. Beyond respiration: Contactless sleep sound-activity recognition using RF signals. Proceedings of the ACM on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies, 2019, 3(3): 1-22. [CrossRef]
- Yang Y, Cao J, Liu X. ER-Rhythm: Coupling exercise and respiration rhythm using lightweight COTS RFID. Proceedings of the ACM on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies, 2019, 3(4): 1-24. [CrossRef]
- Halperin D, Hu W, Sheth A, et al. Tool release: Gathering 802.11 n traces with channel state information. ACM SIGCOMM Computer Communication Review, 2011, 41(1): 53-53. [CrossRef]
- Xie Y, Li Z, Li M. Precise power delay profiling with commodity Wi-Fi. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2018, 18(6): 1342-1355. [CrossRef]
- Xu Y, Yang W, Wang J, et al. WiStep: Device-free step counting with WiFi signals. Proceedings of the ACM on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies, 2018, 1(4): 1-23. [CrossRef]
- Wang X, Yang C, Mao S. TensorBeat: Tensor decomposition for monitoring multiperson breathing beats with commodity WiFi. ACM Transactions on Intelligent Systems and Technology (TIST), 2017, 9(1): 1-27. [CrossRef]
- Zeng Y, Wu D, Gao R, et al. FullBreathe: Full human respiration detection exploiting complementarity of CSI phase and amplitude of WiFi signals. Proceedings of the ACM on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies, 2018, 2(3): 1-19. [CrossRef]
- Zeng Y, Wu D, Xiong J, et al. FarSense: Pushing the range limit of WiFi-based respiration sensing with CSI ratio of two antennas. Proceedings of the ACM on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies, 2019, 3(3): 1-26. [CrossRef]
- Zhang D, Wang H, Wu D. Toward centimeter-scale human activity sensing with Wi-Fi signals. Computer, 2017, 50(1): 48-57. [CrossRef]
- Zhang F, Wu C, Wang B, et al. Smars: sleep monitoring via ambient radio signals. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2019, 20(1): 217-231. [CrossRef]
- Zeng Y, Wu D, Xiong J, et al. MultiSense: Enabling multi-person respiration sensing with commodity wifi. Proceedings of the ACM on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies, 2020, 4(3): 1-29. [CrossRef]
- XU Yang. Research on human walking perception technology based on channel state information. Doctor degree, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei city, Anhui Province, China, 2020.
- Liu J, Chen Y, Wang Y, et al. Monitoring vital signs and postures during sleep using WiFi signals. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2018, 5(3): 2071-2084. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).