Submitted:
26 May 2023
Posted:
30 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Materials and Methods
Antibodies
Compounds
Cell Culture
siRNA
Western Blotting and Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction
Microarray
RNA-seq analysis
Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Assays
Sulforhodamine B Growth Analysis
Gamma H2AX assay
Results
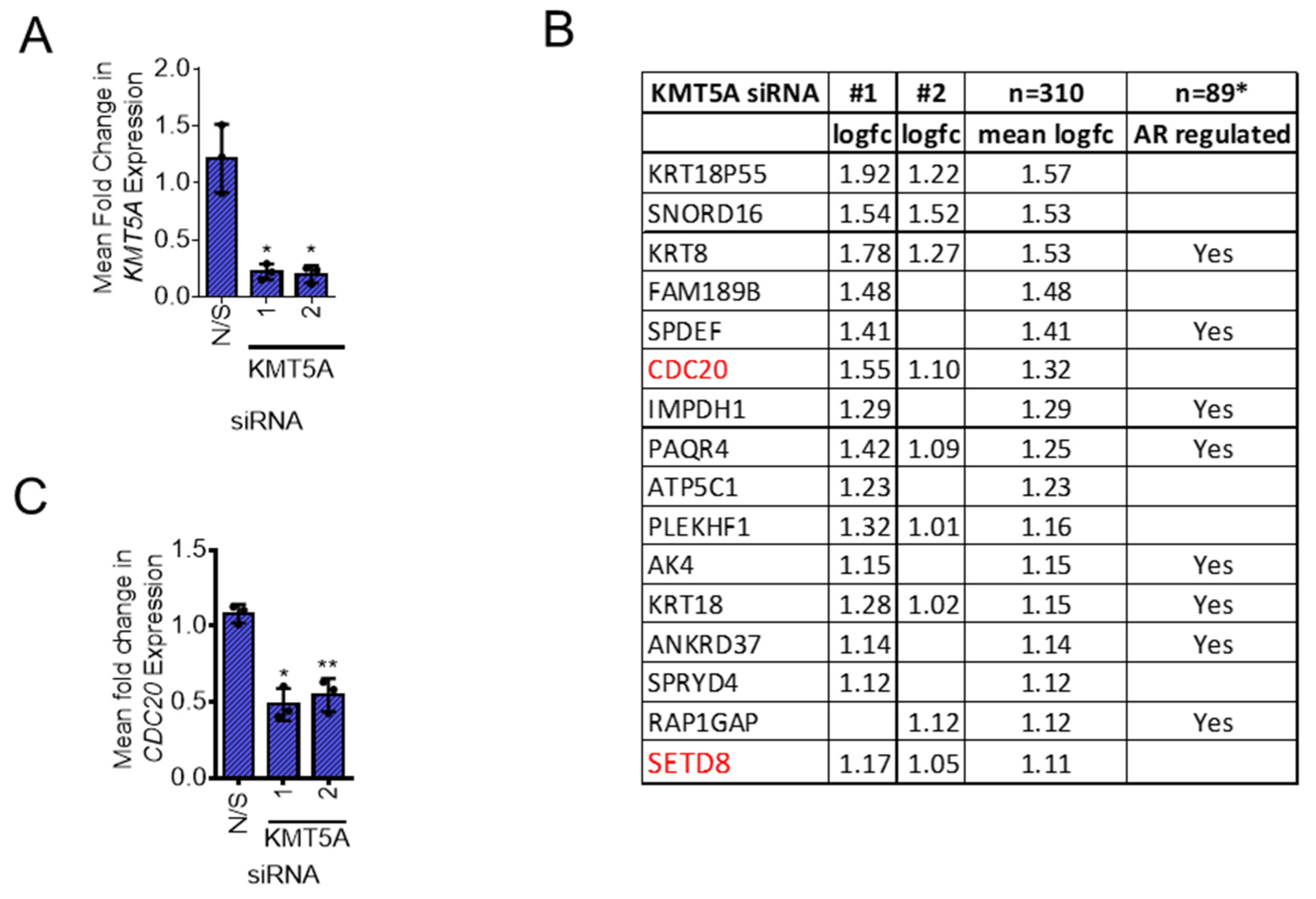
Identification of KMT5A regulated genes in androgen-independent prostate cancer
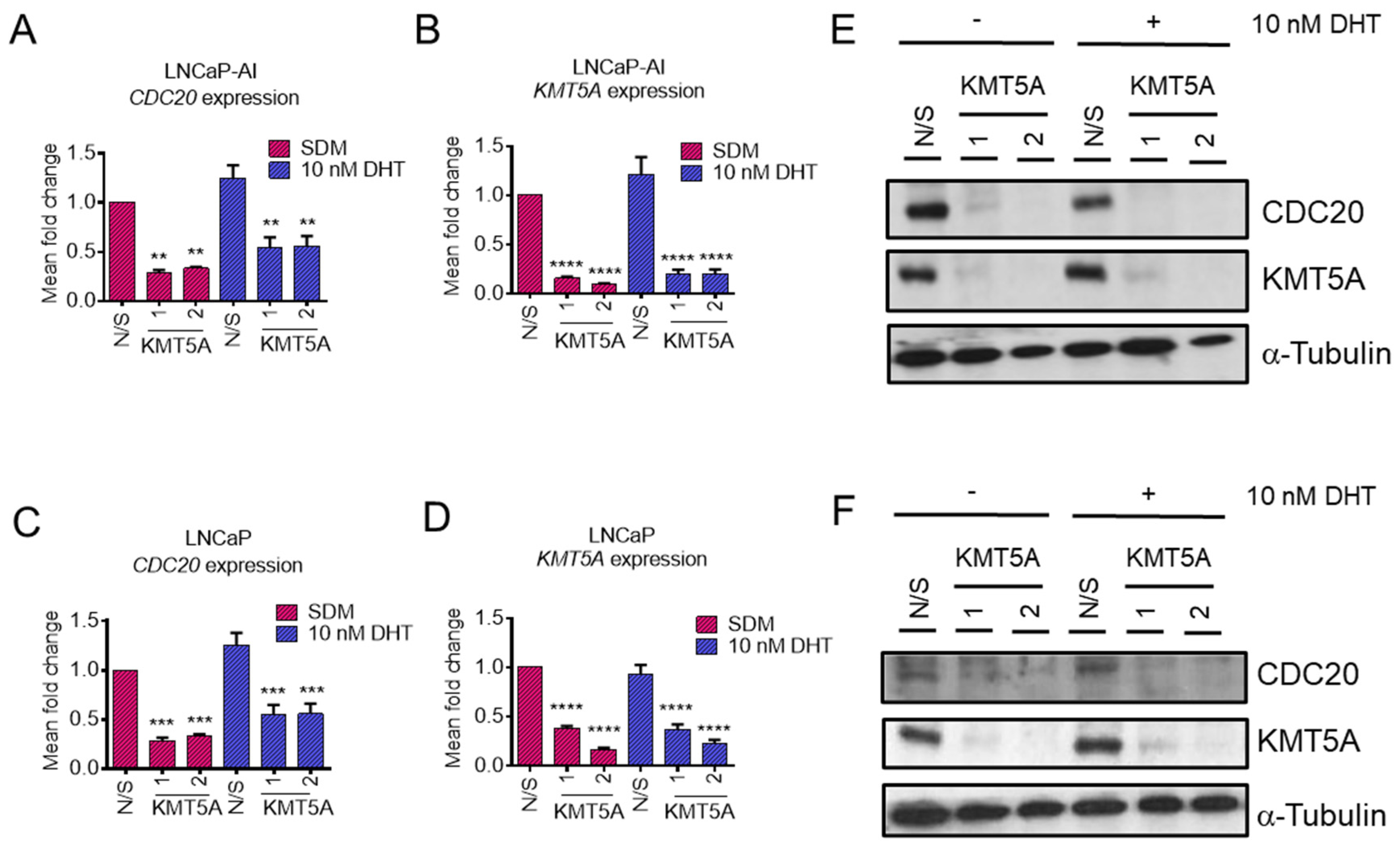
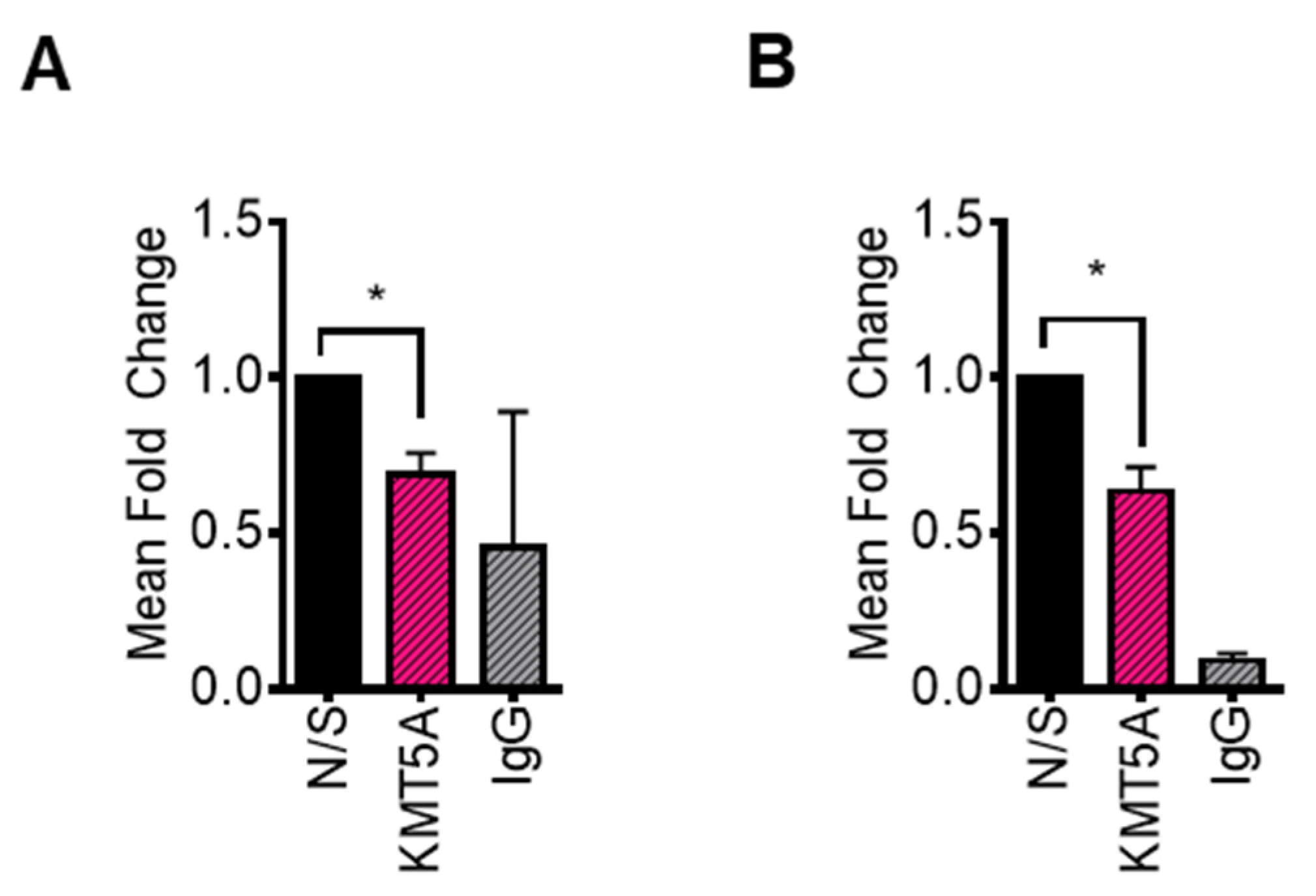
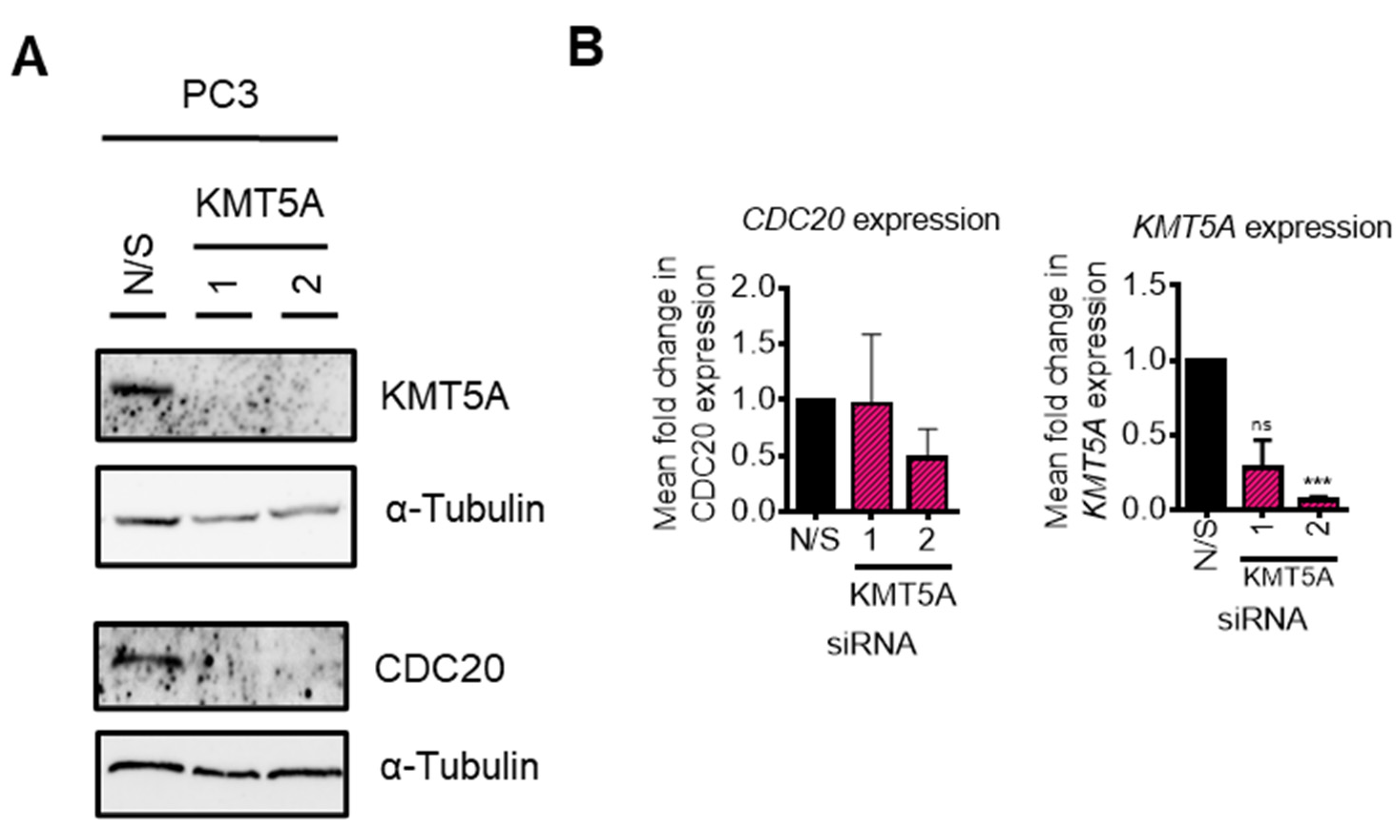
KMT5A depletion reduces CDC20 expression
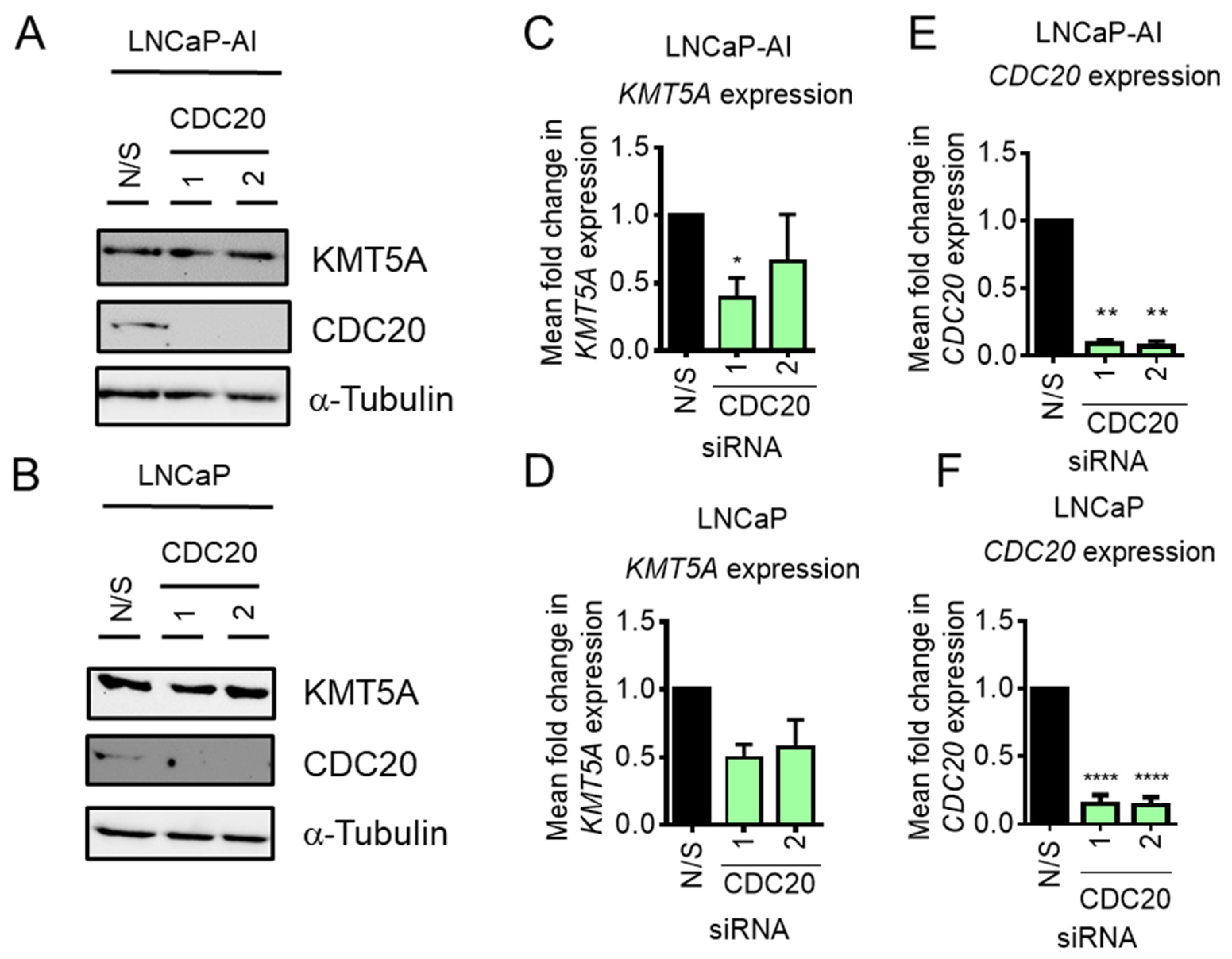
CDC20 depletion does not enhance KMT5A protein expression
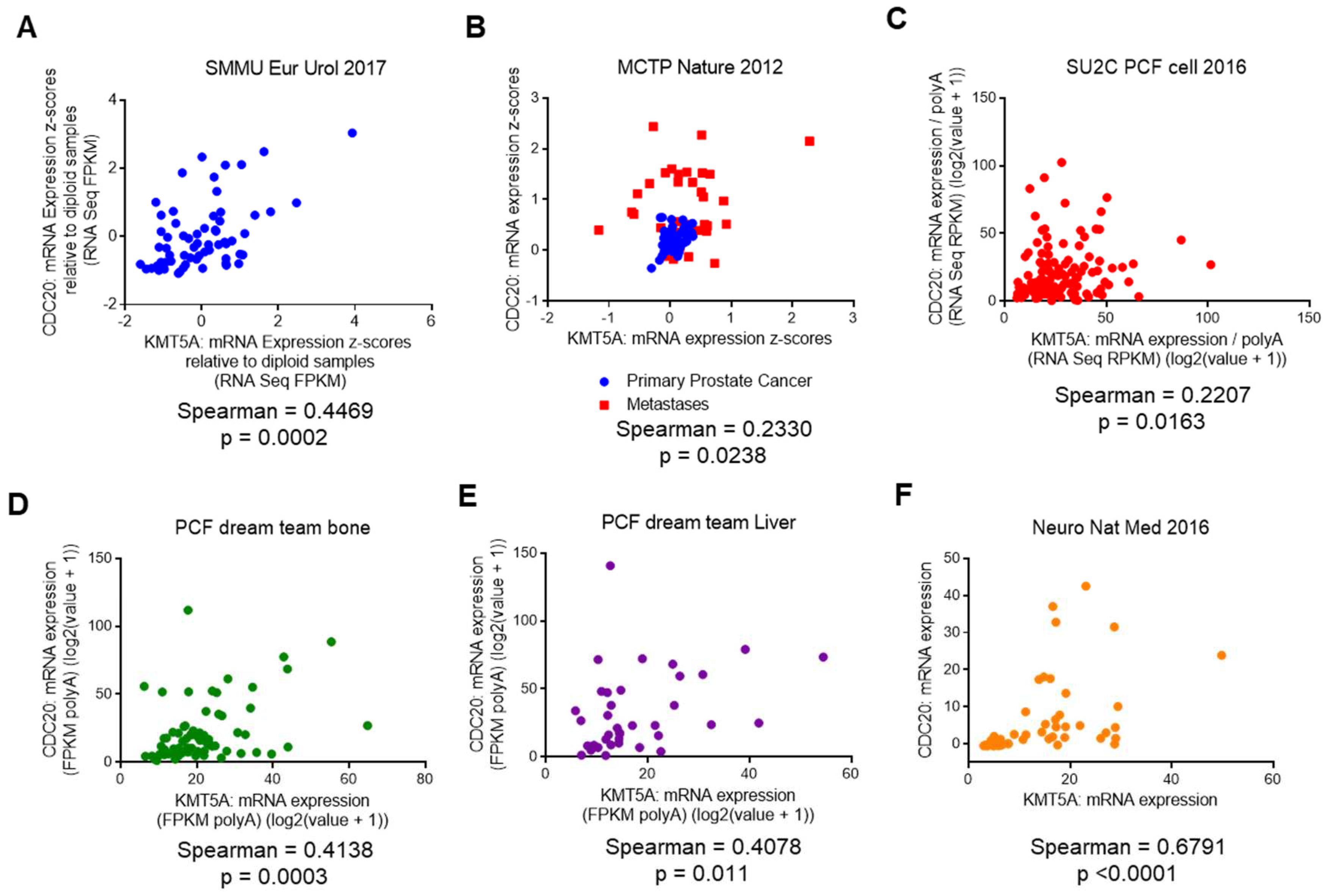
KMT5A expression correlates with CDC20 expression in prostate cancer patients
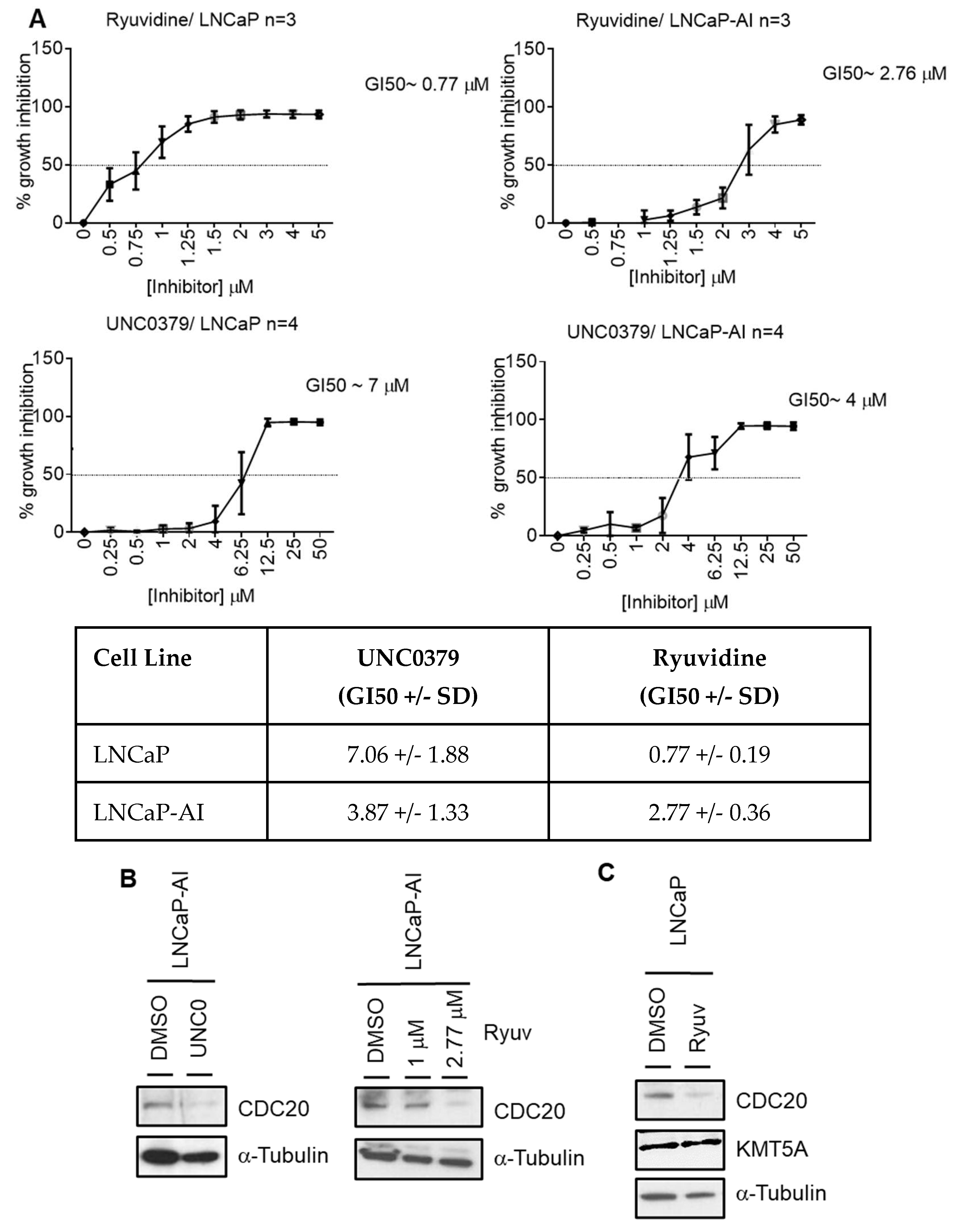
KMT5A inhibition reduces CDC20 expression and reduces prostate cancer cell proliferation.
KMT5A knockdown reduces H4K20Me1 at the CDC20 promoter
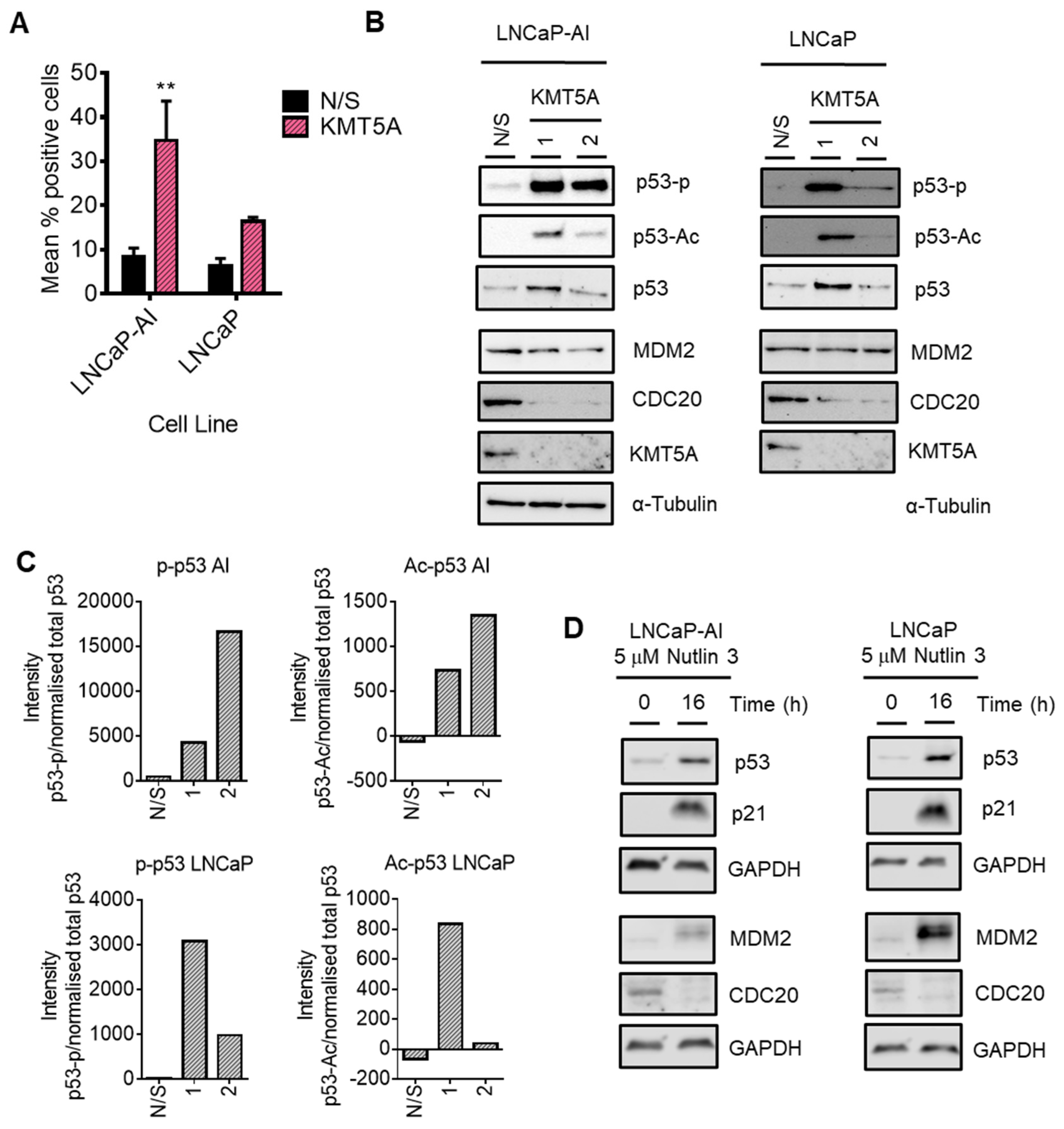
P53 mediates KMT5A regulation of CDC20 expression
CDC20 is down-regulated by protein turnover in the absence of p53.
Discussion
Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgements
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Veschi, V.; Liu, Z.; Voss, T.C.; Ozbun, L.; Gryder, B.; Yan, C.; Hu, Y.; Ma, A.; Jin, J.; Mazur, S.J.; et al. Epigenetic siRNA and Chemical Screens Identify SETD8 Inhibition as a Therapeutic Strategy for p53 Activation in High-Risk Neuroblastoma. Cancer Cell 2017, 31, 50–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Qiao, K.; Du, Y.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, H.; Peng, L.; Guo, Z. Downregulation of histone methyltransferase SET8 inhibits progression of hepatocellular carcinoma. Sci Rep 2020, 10, 4490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Hou, W.; Chai, M.; Zhao, H.; Jia, J.; Sun, X.; Zhao, B.; Wang, R. MicroRNA-127-3p inhibits proliferation and invasion by targeting SETD8 in human osteosarcoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2016, 469, 1006–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, L.; Li, Y.; Du, F.; Han, X.; Li, X.; Niu, Y.; Ren, S.; Sun, Y. Histone H4 Lys 20 methyltransferase SET8 promotes androgen receptor-mediated transcription activation in prostate cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2014, 450, 692–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Li, Q.; Yu, Y.; Li, M.; Zhang, D. SET8 induces epithelialmesenchymal transition and enhances prostate cancer cell metastasis by cooperating with ZEB1. Mol Med Rep 2016, 13, 1681–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Kachirskaia, I.; Yamaguchi, H.; West, L.E.; Wen, H.; Wang, E.W.; Dutta, S.; Appella, E.; Gozani, O. Modulation of p53 function by SET8-mediated methylation at lysine 382. Mol Cell 2007, 27, 636–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Wang, W.; Kong, X.; Congdon, L.M.; Yokomori, K.; Kirschner, M.W.; Rice, J.C. Dynamic regulation of the PR-Set7 histone methyltransferase is required for normal cell cycle progression. Genes Dev 2010, 24, 2531–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Rice, J.C. A new regulator of the cell cycle: the PR-Set7 histone methyltransferase. Cell Cycle 2011, 10, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.J.; Lee, E.H.; Han, S.H.; Chung, H.J.; Jeong, J.H.; Kwon, J.; Kim, H. Degradation of human RAP80 is cell cycle regulated by Cdc20 and Cdh1 ubiquitin ligases. Mol Cancer Res 2012, 10, 615–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, A.C.; Kok, K.H.; Jin, D.Y. REV7 is required for anaphase-promoting complex-dependent ubiquitination and degradation of translesion DNA polymerase REV1. Cell Cycle 2013, 12, 365–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, T.; Nath, S.; Roychoudhury, S. DNA damage induced p53 downregulates Cdc20 by direct binding to its promoter causing chromatin remodeling. Nucleic Acids Res 2009, 37, 2688–2698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidokoro, T.; Tanikawa, C.; Furukawa, Y.; Katagiri, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Matsuda, K. CDC20, a potential cancer therapeutic target, is negatively regulated by p53. Oncogene 2008, 27, 1562–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.J.; Dimova, N.V.; Tan, M.K.; Sigoillot, F.D.; King, R.W.; Shi, Y. The G2/M regulator histone demethylase PHF8 is targeted for degradation by the anaphase-promoting complex containing CDC20. Mol Cell Biol 2013, 33, 4166–4180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Wan, L.; Zhou, X.; Wang, Z.; Wei, W. Targeting Cdc20 as a novel cancer therapeutic strategy. Pharmacol Ther 2015, 151, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Li, K.; Lu, L.; Si-Tu, J.; Lu, M.; Gao, X. Overexpression of Cdc20 in clinically localized prostate cancer: Relation to high Gleason score and biochemical recurrence after laparoscopic radical prostatectomy. Cancer Biomark 2016, 16, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Dai, X.; Gan, W.; Wan, L.; Li, M.; Mitsiades, N.; Wei, W.; Ding, Q.; Zhang, J. Prostate cancer-associated mutation in SPOP impairs its ability to target Cdc20 for poly-ubiquitination and degradation. Cancer Lett 2017, 385, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Mao, Y.; Lu, L.; Hu, C.; Wang, D.; Si-Tu, J.; Lu, M.; Peng, S.; Qiu, J.; Gao, X. Silencing of CDC20 suppresses metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer growth and enhances chemosensitivity to docetaxel. Int J Oncol 2016, 49, 1679–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Karki, A.; Hodges, K.B.; Ahmad, N.; Zoubeidi, A.; Strebhardt, K.; Ratliff, T.L.; Konieczny, S.F.; Liu, X. Cotargeting Polo-Like Kinase 1 and the Wnt/beta-Catenin Signaling Pathway in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Mol Cell Biol 2015, 35, 4185–4198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coffey, K.; Rogerson, L.; Ryan-Munden, C.; Alkharaif, D.; Stockley, J.; Heer, R.; Sahadevan, K.; O'Neill, D.; Jones, D.; Darby, S.; et al. The lysine demethylase, KDM4B, is a key molecule in androgen receptor signalling and turnover. Nucleic Acids Res 2013, 41, 4433–4446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bainbridge, A.; Walker, S.; Smith, J.; Patterson, K.; Dutt, A.; Ng, Y.M.; Thomas, H.D.; Wilson, L.; McCullough, B.; Jones, D.; et al. IKBKE activity enhances AR levels in advanced prostate cancer via modulation of the Hippo pathway. Nucleic Acids Res 2020, 48, 5366–5382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coffey, K.; Blackburn, T.J.; Cook, S.; Golding, B.T.; Griffin, R.J.; Hardcastle, I.R.; Hewitt, L.; Huberman, K.; McNeill, H.V.; Newell, D.R.; et al. Characterisation of a Tip60 specific inhibitor, NU9056, in prostate cancer. PLoS One 2012, 7, e45539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple hypothesis testing. J R Stat Soc B 1995, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labaf, M.; Li, M.; Ting, L.; Karno, B.; Zhang, S.; Gao, S.; Patalano, S.; Macoska, J.A.; Zarringhalam, K.; Han, D.; et al. Increased AR expression in castration-resistant prostate cancer rapidly induces AR signaling reprogramming with the collaboration of EZH2. Front Oncol 2022, 12, 1021845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobin, A.; Davis, C.A.; Schlesinger, F.; Drenkow, J.; Zaleski, C.; Jha, S.; Batut, P.; Chaisson, M.; Gingeras, T.R. STAR: ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anders, S.; Pyl, P.T.; Huber, W. HTSeq--a Python framework to work with high-throughput sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 166–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, D.; Wilson, M.D.; Spyrou, C.; Brown, G.D.; Hadfield, J.; Odom, D.T. ChIP-seq: using high-throughput sequencing to discover protein-DNA interactions. Methods 2009, 48, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.; Wu, Q.; Mack, S.C.; Yang, K.; Kim, L.; Hubert, C.G.; Flavahan, W.A.; Chu, C.; Bao, S.; Rich, J.N. CDC20 maintains tumor initiating cells. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 13241–13254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.W.; Sherman, B.T.; Tan, Q.; Collins, J.R.; Alvord, W.G.; Roayaei, J.; Stephens, R.; Baseler, M.W.; Lane, H.C.; Lempicki, R.A. The DAVID Gene Functional Classification Tool: a novel biological module-centric algorithm to functionally analyze large gene lists. Genome Biol 2007, 8, R183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.W.; Sherman, B.T.; Tan, Q.; Kir, J.; Liu, D.; Bryant, D.; Guo, Y.; Stephens, R.; Baseler, M.W.; Lane, H.C.; et al. DAVID Bioinformatics Resources: expanded annotation database and novel algorithms to better extract biology from large gene lists. Nucleic Acids Res 2007, 35, W169–W175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerami, E.; Gao, J.; Dogrusoz, U.; Gross, B.E.; Sumer, S.O.; Aksoy, B.A.; Jacobsen, A.; Byrne, C.J.; Heuer, M.L.; Larsson, E.; et al. The cBio cancer genomics portal: an open platform for exploring multidimensional cancer genomics data. Cancer Discov 2012, 2, 401–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Aksoy, B.A.; Dogrusoz, U.; Dresdner, G.; Gross, B.; Sumer, S.O.; Sun, Y.; Jacobsen, A.; Sinha, R.; Larsson, E.; et al. Integrative analysis of complex cancer genomics and clinical profiles using the cBioPortal. Sci Signal 2013, 6, pl1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, S.; Wei, G.H.; Liu, D.; Wang, L.; Hou, Y.; Zhu, S.; Peng, L.; Zhang, Q.; Cheng, Y.; Su, H.; et al. Whole-genome and Transcriptome Sequencing of Prostate Cancer Identify New Genetic Alterations Driving Disease Progression. Eur Urol 2018, 73, 322–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasso, C.S.; Wu, Y.M.; Robinson, D.R.; Cao, X.; Dhanasekaran, S.M.; Khan, A.P.; Quist, M.J.; Jing, X.; Lonigro, R.J.; Brenner, J.C.; et al. The mutational landscape of lethal castration-resistant prostate cancer. Nature 2012, 487, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, D.; Van Allen, E.M.; Wu, Y.M.; Schultz, N.; Lonigro, R.J.; Mosquera, J.M.; Montgomery, B.; Taplin, M.E.; Pritchard, C.C.; Attard, G.; et al. Integrative clinical genomics of advanced prostate cancer. Cell 2015, 161, 1215–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abida, W.; Cyrta, J.; Heller, G.; Prandi, D.; Armenia, J.; Coleman, I.; Cieslik, M.; Benelli, M.; Robinson, D.; Van Allen, E.M.; et al. Genomic correlates of clinical outcome in advanced prostate cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2019, 116, 11428–11436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltran, H.; Prandi, D.; Mosquera, J.M.; Benelli, M.; Puca, L.; Cyrta, J.; Marotz, C.; Giannopoulou, E.; Chakravarthi, B.V.; Varambally, S.; et al. Divergent clonal evolution of castration-resistant neuroendocrine prostate cancer. Nat Med 2016, 22, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgensen, S.; Elvers, I.; Trelle, M.B.; Menzel, T.; Eskildsen, M.; Jensen, O.N.; Helleday, T.; Helin, K.; Sorensen, C.S. The histone methyltransferase SET8 is required for S-phase progression. J Cell Biol 2007, 179, 1337–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tardat, M.; Murr, R.; Herceg, Z.; Sardet, C.; Julien, E. PR-Set7-dependent lysine methylation ensures genome replication and stability through S phase. J Cell Biol 2007, 179, 1413–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blum, G.; Ibanez, G.; Rao, X.; Shum, D.; Radu, C.; Djaballah, H.; Rice, J.C.; Luo, M. Small-molecule inhibitors of SETD8 with cellular activity. ACS Chem Biol 2014, 9, 2471–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, A.; Yu, W.; Xiong, Y.; Butler, K.V.; Brown, P.J.; Jin, J. Structure-activity relationship studies of SETD8 inhibitors. Medchemcomm 2014, 5, 1892–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, S.; Chowdhury, A.; Dey, S.; Roychoudhury, A.; Ganguly, A.; Bhattacharyya, D.; Roychoudhury, S. Deregulation of Rb-E2F1 axis causes chromosomal instability by engaging the transactivation function of Cdc20-anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome. Mol Cell Biol 2015, 35, 356–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, K.; Christensen, J.; Rappsilber, J.; Nielsen, A.L.; Johansen, J.V.; Helin, K. The histone lysine demethylase JMJD3/KDM6B is recruited to p53 bound promoters and enhancer elements in a p53 dependent manner. PLoS One 2014, 9, e96545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trojer, P.; Li, G.; Sims, R.J., 3rd; Vaquero, A.; Kalakonda, N.; Boccuni, P.; Lee, D.; Erdjument-Bromage, H.; Tempst, P.; Nimer, S.D.; et al. L3MBTL1, a histone-methylation-dependent chromatin lock. Cell 2007, 129, 915–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoaib, M.; Walter, D.; Gillespie, P.J.; Izard, F.; Fahrenkrog, B.; Lleres, D.; Lerdrup, M.; Johansen, J.V.; Hansen, K.; Julien, E.; et al. Histone H4K20 methylation mediated chromatin compaction threshold ensures genome integrity by limiting DNA replication licensing. Nat Commun 2018, 9, 3704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oda, H.; Hubner, M.R.; Beck, D.B.; Vermeulen, M.; Hurwitz, J.; Spector, D.L.; Reinberg, D. Regulation of the histone H4 monomethylase PR-Set7 by CRL4(Cdt2)-mediated PCNA-dependent degradation during DNA damage. Mol Cell 2010, 40, 364–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishioka, K.; Rice, J.C.; Sarma, K.; Erdjument-Bromage, H.; Werner, J.; Wang, Y.; Chuikov, S.; Valenzuela, P.; Tempst, P.; Steward, R.; et al. PR-Set7 is a nucleosome-specific methyltransferase that modifies lysine 20 of histone H4 and is associated with silent chromatin. Mol Cell 2002, 9, 1201–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Sun, L.; Li, Q.; Han, X.; Lei, L.; Zhang, H.; Shang, Y. SET8 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and confers TWIST dual transcriptional activities. EMBO J 2012, 31, 110–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Nie, F.; Wang, S.; Li, L. Histone H4 Lys 20 monomethylation by histone methylase SET8 mediates Wnt target gene activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2011, 108, 3116–3123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vakoc, C.R.; Sachdeva, M.M.; Wang, H.; Blobel, G.A. Profile of histone lysine methylation across transcribed mammalian chromatin. Mol Cell Biol 2006, 26, 9185–9195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoaib, M.; Chen, Q.; Shi, X.; Nair, N.; Prasanna, C.; Yang, R.; Walter, D.; Frederiksen, K.S.; Einarsson, H.; Svensson, J.P.; et al. Histone H4 lysine 20 mono-methylation directly facilitates chromatin openness and promotes transcription of housekeeping genes. Nat Commun 2021, 12, 4800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor-Vazirani, P.; Vertino, P.M. A dual role for the histone methyltransferase PR-SET7/SETD8 and histone H4 lysine 20 monomethylation in the local regulation of RNA polymerase II pausing. J Biol Chem 2014, 289, 7425–7437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hori, T.; Shang, W.H.; Toyoda, A.; Misu, S.; Monma, N.; Ikeo, K.; Molina, O.; Vargiu, G.; Fujiyama, A.; Kimura, H.; et al. Histone H4 Lys 20 monomethylation of the CENP-A nucleosome is essential for kinetochore assembly. Dev Cell 2014, 29, 740–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.; Sun, Y.; Chen, J.; Li, H.; Yao, K.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Q.; Lu, J. The Oncogenic Role of APC/C Activator Protein Cdc20 by an Integrated Pan-Cancer Analysis in Human Tumors. Front Oncol 2021, 11, 721797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.; Hu, K.; Li, D.; Wang, Y.; Liu, M.; Wang, X.; Zhu, W.; Wang, X.; Yang, Z.; Lu, J. Identification of Core Genes and Potential Drugs for Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer Based on Bioinformatics Analysis. DNA Cell Biol 2020, 39, 836–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Song, Z.X.; Wei, D.P.; Zhang, J.D.; Liang, J.Q.; Wang, B.B.; Ma, W.T.; Li, L.Y.; Dang, Y.L.; Zhao, L.; et al. CDC20 and PTTG1 are Important Biomarkers and Potential Therapeutic Targets for Metastatic Prostate Cancer. Adv Ther 2021, 38, 2973–2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, P.; Yang, D.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, M.; He, X. Bioinformatics analysis identified hub genes in prostate cancer tumorigenesis and metastasis. Math Biosci Eng 2021, 18, 3180–3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Yin, Y.; Deng, Q.; Zhou, J.; Wang, Y.; Yin, G.; Yang, J.; Tang, Y. Integrative Analysis of MicroRNA and Gene Interactions for Revealing Candidate Signatures in Prostate Cancer. Front Genet 2020, 11, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Chen, J.; Chen, L. Exploration of gene expression profiles and immune microenvironment between high and low tumor mutation burden groups in prostate cancer. Int Immunopharmacol 2020, 86, 106709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbieri, C.E.; Baca, S.C.; Lawrence, M.S.; Demichelis, F.; Blattner, M.; Theurillat, J.P.; White, T.A.; Stojanov, P.; Van Allen, E.; Stransky, N.; et al. Exome sequencing identifies recurrent SPOP, FOXA1 and MED12 mutations in prostate cancer. Nat Genet 2012, 44, 685–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Ma, J.; Chang, K.; Ding, D.; Bai, Y.; Gao, K.; Zhang, P.; Mo, R.; Feng, K.; et al. Prostate Cancer-associated SPOP mutations enhance cancer cell survival and docetaxel resistance by upregulating Caprin1-dependent stress granule assembly. Mol Cancer 2019, 18, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.; Lin, Y.; Cui, P.; Li, H.; Zhang, L.; Sun, Z.; Huang, S.; Li, S.; Huang, S.; Zhao, Q.; et al. Cdc20/p55 mediates the resistance to docetaxel in castration-resistant prostate cancer in a Bim-dependent manner. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 2018, 81, 999–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuzon, C.T.; Spektor, T.; Kong, X.; Congdon, L.M.; Wu, S.; Schotta, G.; Yokomori, K.; Rice, J.C. Concerted activities of distinct H4K20 methyltransferases at DNA double-strand breaks regulate 53BP1 nucleation and NHEJ-directed repair. Cell Rep 2014, 8, 430–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dulev, S.; Tkach, J.; Lin, S.; Batada, N.N. SET8 methyltransferase activity during the DNA double-strand break response is required for recruitment of 53BP1. EMBO Rep 2014, 15, 1163–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Xu, M.; Zhu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Liu, G.; Bao, Y.; Gu, L.; Tian, Y.; Wen, H.; Zhu, W.G. RNF8-ubiquitinated KMT5A is required for RNF168-induced H2A ubiquitination in response to DNA damage. FASEB J 2021, 35, e21326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez-Vacas, J.M.; Herrero-Aguayo, V.; Montero-Hidalgo, A.J.; Gomez-Gomez, E.; Fuentes-Fayos, A.C.; Leon-Gonzalez, A.J.; Saez-Martinez, P.; Alors-Perez, E.; Pedraza-Arevalo, S.; Gonzalez-Serrano, T.; et al. Dysregulation of the splicing machinery is directly associated to aggressiveness of prostate cancer. EBioMedicine 2020, 51, 102547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




