Submitted:
25 May 2023
Posted:
29 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. A summary on 5-HT receptors
1.2. An overview of the effects of 5-HT in the cardiovascular system
1.3. The specific interactions of 5-HT at peripheral and central levels to induce cardiovascular effects
1.3.1. Sensory afferents
1.3.2. Sympathetic ganglia
1.3.3. Cardiac effects of 5-HT
1.3.3.1. Bradycardia
1.3.3.2. Tachycardia
1.3.4. Vascular and blood pressure effects of 5-HT
1.3.4.1. Initial transient vasodepressor effect
1.3.4.2. Vasopressor effect
1.3.4.3. Late long-lasting vasodepressor effect
1.3.5. Receptor-independent actions of 5-HT
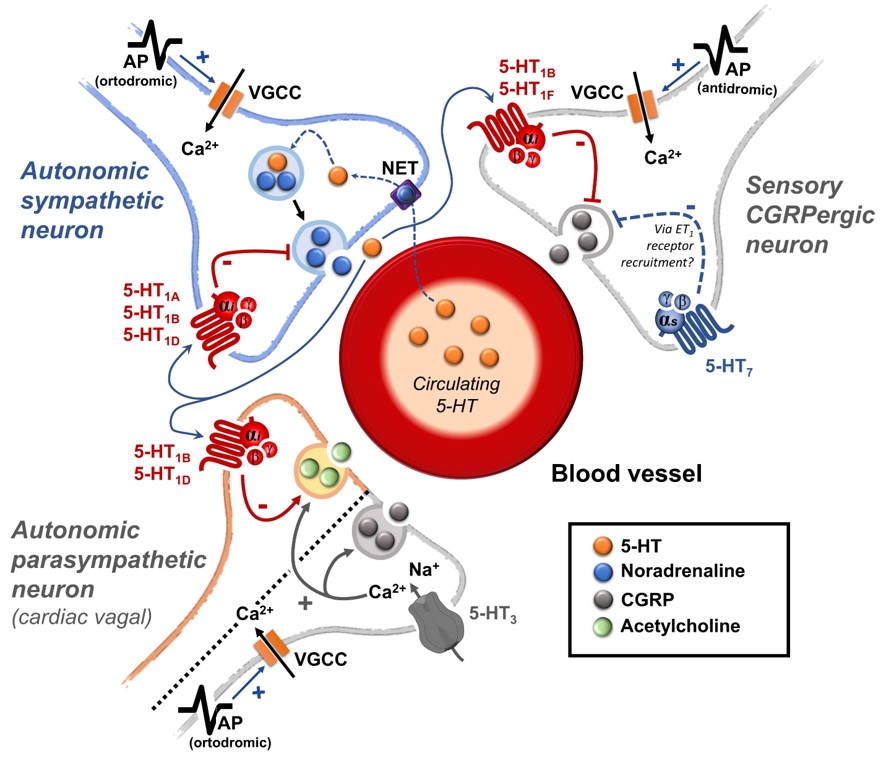
2. Peripheral autonomic nervous system and prejunctional 5-HT receptors
2.1. An overview of the peripheral actions of 5-HT regulating the vascular function
2.2. The role of prejunctional 5-HT receptors
2.2.1. The 5-HT receptors inhibiting the autonomic outflow
2.2.2. The 5-HT receptors as facilitators of the autonomic outflow
2.3. Clinical relevance and therapeutic potential
3. Sensory CGRPergic perivascular nerves and prejunctional 5-HT receptors
3.1. The sensory perivascular CGRPergic neurons as an intrinsic modulator of vascular tone
3.2. Prejunctional 5-HT receptors are mainly inhibitors of the perivascular sensory CGRPergic outflow
3.3. Clinical relevance
4. Future directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of interest
References
- Barnes, N.M.; Ahern, G.P.; Becamel, C.; Bockaert, J.; Camilleri, M.; Chaumont-Dubel, S.; Claeysen, S.; Cunningham, K.A.; Fone, K.C.; Gershon, M.; et al. International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. CX. Classification of Receptors for 5-hydroxytryptamine; Pharmacology and Function. Pharmacol Rev 2021, 73, 310–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, J.; Liu, F. The Role of Serotonin beyond the Central Nervous System during Embryogenesis. Front Cell Neurosci 2017, 11, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villalón, C.M. Chapter Three - The role of serotonin receptors in the control of cardiovascular function. In The Serotonin System, Tricklebank, M.D., Daly, E., Eds.; Academic Press: 2019; pp. 45-61.
- Villalón, C.M.; Centurión, D. Cardiovascular responses produced by 5-hydroxytriptamine:a pharmacological update on the receptors/mechanisms involved and therapeutic implications. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 2007, 376, 45–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saxena, P.R.; Villalón, C.M. Cardiovascular effects of serotonin agonists and antagonists. Journal of cardiovascular pharmacology 1990, 15 Suppl 7, S17–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyer, D.; Clarke, D.E.; Fozard, J.R.; Hartig, P.R.; Martin, G.R.; Mylecharane, E.J.; Saxena, P.R.; Humphrey, P.P. International Union of Pharmacology classification of receptors for 5-hydroxytryptamine (Serotonin). Pharmacol Rev 1994, 46, 157–203. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hoyer, D.; Hannon, J.P.; Martin, G.R. Molecular, pharmacological and functional diversity of 5-HT receptors. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 2002, 71, 533–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, P.R.; De Vries, P.; Villalón, C.M. 5-HT1-like receptors: a time to bid goodbye. Trends Pharmacol Sci 1998, 19, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saxena, P.R.; Villalón, C.M. 5-Hydroxytryptamine: a chameleon in the heart. Trends Pharmacol Sci 1991, 12, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalón, C.M.; Centurión, D.; Valdivia, L.F.; de Vries, P.; Saxena, P.R. Migraine: pathophysiology, pharmacology, treatment and future trends. Curr Vasc Pharmacol 2003, 1, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalón, C.M.; VanDenBrink, A.M. The Role of 5-Hydroxytryptamine in the Pathophysiology of Migraine and its Relevance to the Design of Novel Treatments. Mini Rev Med Chem 2017, 17, 928–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaumann, A.J.; Levy, F.O. 5-hydroxytryptamine receptors in the human cardiovascular system. Pharmacology & therapeutics 2006, 111, 674–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, S.W.; Davis, R.P. 5-hydroxtryptamine receptors in systemic hypertension: an arterial focus. Cardiovasc Ther 2011, 29, 54–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watts, S.W.; Morrison, S.F.; Davis, R.P.; Barman, S.M. Serotonin and blood pressure regulation. Pharmacol Rev 2012, 64, 359–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Hernández, A.; Marichal-Cancino, B.A.; Lozano-Cuenca, J.; López-Canales, J.S.; Muñoz-Islas, E.; Ramírez-Rosas, M.B.; Villalón, C.M. Heteroreceptors Modulating CGRP Release at Neurovascular Junction: Potential Therapeutic Implications on Some Vascular-Related Diseases. Biomed Res Int 2016, 2016, 2056786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramage, A.G.; Villalón, C.M. 5-hydroxytryptamine and cardiovascular regulation. Trends Pharmacol Sci 2008, 29, 472–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramage, A.G. Influence of 5-HT1A receptor agonists on sympathetic and parasympathetic nerve activity. Journal of cardiovascular pharmacology 1990, 15 Suppl 7, S75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramage, A.G. Central cardiovascular regulation and 5-hydroxytryptamine receptors. Brain Res Bull 2001, 56, 425–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Lopez, A.; Centurión, D.; Vázquez, E.; Arulmani, U.; Saxena, P.R.; Villalón, C.M. Pharmacological profile of the 5-HT-induced inhibition of cardioaccelerator sympathetic outflow in pithed rats: correlation with 5-HT1 and putative 5-ht5A/5B receptors. Br J Pharmacol 2003, 140, 725–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Pedraza, J.; Hernández-Abreu, O.; García, M.; Morán, A.; Villalón, C.M. Chronic 5-HT(2) receptor blockade unmasks the role of 5-HT(1F) receptors in the inhibition of rat cardioaccelerator sympathetic outflow. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 2018, 96, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-López, A.; Centurión, D.; Vázquez, E.; Arulmani, U.; Saxena, P.R.; Villalón, C.M. Further characterization of the 5-HT1 receptors mediating cardiac sympatho-inhibition in pithed rats: pharmacological correlation with the 5-HT1B and 5-HT1D subtypes. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 2004, 369, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Pedraza, J.; García, M.; Martín, M.L.; Gómez-Escudero, J.; Rodríguez-Barbero, A.; Román, L.S.; Morán, A. Peripheral 5-HT₁D and 5-HT₇ serotonergic receptors modulate sympathetic neurotransmission in chronic sarpogrelate treated rats. Eur J Pharmacol 2013, 714, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dabiré, H. Central 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) receptors in blood pressure regulation. Therapie 1991, 46, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bedi, U.S.; Arora, R. Cardiovascular manifestations of posttraumatic stress disorder. J Natl Med Assoc 2007, 99, 642–649. [Google Scholar]
- Tania, V.; Catherine, V. Roles of the Serotoninergic System in Coping with Traumatic Stress. In Serotonin and the CNS, Berend, O., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Paine, N.J.; Watkins, L.L.; Blumenthal, J.A.; Kuhn, C.M.; Sherwood, A. Association of depressive and anxiety symptoms with 24-hour urinary catecholamines in individuals with untreated high blood pressure. Psychosom Med 2015, 77, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brindley, R.L.; Bauer, M.B.; Blakely, R.D.; Currie, K.P.M. An interplay between the serotonin transporter (SERT) and 5-HT receptors controls stimulus-secretion coupling in sympathoadrenal chromaffin cells. Neuropharmacology 2016, 110, 438–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakatani, Y.; Sato-Suzuki, I.; Tsujino, N.; Nakasato, A.; Seki, Y.; Fumoto, M.; Arita, H. Augmented brain 5-HT crosses the blood-brain barrier through the 5-HT transporter in rat. Eur J Neurosci 2008, 27, 2466–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.M.; Wang, Y.; Liu, M.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, X.H.; Sun, Y.X.; Wang, H.L. Fluoxetine inhibits monocrotaline-induced pulmonary arterial remodeling involved in inhibition of RhoA-Rho kinase and Akt signalling pathways in rats. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 2012, 90, 1506–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.C.; Chou, C.C.; Tu, Z.; Yeh, L.F.; Wu, S.C.; Khoo, K.H.; Lin, C.H. Characterization of protein serotonylation via bioorthogonal labeling and enrichment. J Proteome Res 2014, 13, 3523–3529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penumatsa, K.C.; Fanburg, B.L. Transglutaminase 2-mediated serotonylation in pulmonary hypertension. American journal of physiology. Lung cellular and molecular physiology 2014, 306, L309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tjurmina, O.A.; Armando, I.; Saavedra, J.M.; Goldstein, D.S.; Murphy, D.L. Exaggerated adrenomedullary response to immobilization in mice with targeted disruption of the serotonin transporter gene. Endocrinology 2002, 143, 4520–4526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiradentes, R.V.; Pires, J.G.; Silva, N.F.; Ramage, A.G.; Santuzzi, C.H.; Futuro Neto, H.A. Effects of acute administration of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors on sympathetic nerve activity. Braz J Med Biol Res 2014, 47, 554–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroeter, S.; Levey, A.I.; Blakely, R.D. Polarized expression of the antidepressant-sensitive serotonin transporter in epinephrine-synthesizing chromaffin cells of the rat adrenal gland. Mol Cell Neurosci 1997, 9, 170–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furlan, A.; Dyachuk, V.; Kastriti, M.E.; Calvo-Enrique, L.; Abdo, H.; Hadjab, S.; Chontorotzea, T.; Akkuratova, N.; Usoskin, D.; Kamenev, D.; et al. Multipotent peripheral glial cells generate neuroendocrine cells of the adrenal medulla. Science 2017, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kameneva, P.; Melnikova, V.I.; Kastriti, M.E.; Kurtova, A.; Kryukov, E.; Murtazina, A.; Faure, L.; Poverennaya, I.; Artemov, A.V.; Kalinina, T.S.; et al. Serotonin limits generation of chromaffin cells during adrenal organ development. Nature Communications 2022, 13, 2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbone, E.; Borges, R.; Eiden, L.E.; García, A.G.; Hernández-Cruz, A. Chromaffin Cells of the Adrenal Medulla: Physiology, Pharmacology, and Disease. Compr Physiol 2019, 9, 1443–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brindley, R.L.; Bauer, M.B.; Blakely, R.D.; Currie, K.P.M. Serotonin and Serotonin Transporters in the Adrenal Medulla: A Potential Hub for Modulation of the Sympathetic Stress Response. ACS Chem Neurosci 2017, 8, 943–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linder, A.E.; Beggs, K.M.; Burnett, R.J.; Watts, S.W. Body distribution of infused serotonin in rats. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 2009, 36, 599–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, S.; Tsukahara, S.; Sugita, K.; Nagata, T. Adrenergic and cholinergic innervation of rat cerebral arteries. Consecutive demonstration on whole mount preparations. Histochemistry 1981, 70, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Y.; Zhu, L. The crosstalk between autonomic nervous system and blood vessels. Int J Physiol Pathophysiol Pharmacol 2018, 10, 17–28. [Google Scholar]
- Koep, J.L.; Taylor, C.E.; Coombes, J.S.; Bond, B.; Ainslie, P.N.; Bailey, T.G. Autonomic control of cerebral blood flow: fundamental comparisons between peripheral and cerebrovascular circulations in humans. The Journal of physiology 2022, 600, 15–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, N.; Hardebo, J.E. The cerebrovascular parasympathetic innervation. Cerebrovasc Brain Metab Rev 1993, 5, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Roloff, E.v.L.; Tomiak-Baquero, A.M.; Kasparov, S.; Paton, J.F.R. Parasympathetic innervation of vertebrobasilar arteries: is this a potential clinical target? The Journal of physiology 2016, 594, 6463–6485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, K.E.; Salvatierra, A.T. Apposition of enkephalin- and neurotensin-immunoreactive neurons by serotonin-immunoreactive varicosities in the rat spinal cord. Neuroscience 1998, 85, 837–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villalón, C.M.; Centurión, D.; Rabelo, G.; de Vries, P.; Saxena, P.R.; Sánchez-López, A. The 5-HT1-like receptors mediating inhibition of sympathetic vasopressor outflow in the pithed rat: operational correlation with the 5-HT1A, 5-HT1B and 5-HT1D subtypes. Br J Pharmacol 1998, 124, 1001–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rapport, M.M.; Green, A.A.; Page, I.H. Serum vasoconstrictor, serotonin; isolation and characterization. J Biol Chem 1948, 176, 1243–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rapport, M.M.; Green, A.A.; Page, I.H. Partial purification of the vasoconstrictor in beef serum. J Biol Chem 1948, 174, 735–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herr, N.; Bode, C.; Duerschmied, D. The Effects of Serotonin in Immune Cells. Front Cardiovasc Med 2017, 4, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palermo, A.; del Rosso, G.; Costantini, C.; Bertalero, P.; Rizzi, S.; Libretti, A. Platelet content of serotonin and response to stress. J Hypertens Suppl 1986, 4, S43–45. [Google Scholar]
- Teff, K.L.; Young, S.N. Effects of carbohydrate and protein administration on rat tryptophan and 5-hydroxytryptamine: differential effects on the brain, intestine, pineal, and pancreas. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 1988, 66, 683–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edvinsson, J.C.A.; Maddahi, A.; Christiansen, I.M.; Reducha, P.V.; Warfvinge, K.; Sheykhzade, M.; Edvinsson, L.; Haanes, K.A. Lasmiditan and 5-Hydroxytryptamine in the rat trigeminal system; expression, release and interactions with 5-HT1 receptors. The Journal of Headache and Pain 2022, 23, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, Y.; Sugiura, Y.; Magome, T.; Kamakura, T.; Takimoto, Y.; Hanada, Y.; Kitayama, K.; Nakamura, Y.; Shimada, S.; Ohta, N.; et al. Expression Analysis of Serotonin Receptors, Serotonin Transporter and l-Amino Acid Decarboxylase in the Mouse Sphenopalatine Ganglion by RT-PCR, Northern Blot Analysis and In Situ Hybridization. Neuroscience 2019, 411, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Punda, H.; Mardesic, S.; Filipovic, N.; Kosovic, I.; Benzon, B.; Ogorevc, M.; Bocina, I.; Kolic, K.; Vukojevic, K.; Saraga-Babic, M. Expression Pattern of 5-HT (Serotonin) Receptors during Normal Development of the Human Spinal Cord and Ganglia and in Fetus with Cervical Spina Bifida. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, T.; Satoh, S. Presynaptic inhibition by serotonin of cardiac sympathetic transmission in dogs. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 1983, 10, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Pedraza, J.; Hernández-Abreu, O.; Morán, A.; Carretero, J.; García-Domingo, M.; Villalón, C.M. Role of peripheral 5-HT(5A) receptors in 5-HT-induced cardiac sympatho-inhibition in type 1 diabetic rats. Sci Rep 2020, 10, 19358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morán, A.; Fernández, M.M.; Velasco, C.; Martín, M.L.; San Román, L. Characterization of prejunctional 5-HT1 receptors that mediate the inhibition of pressor effects elicited by sympathetic stimulation in the pithed rat. Br J Pharmacol 1998, 123, 1205–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilowsky, P.M. Chapter 16 - Serotonin in Central Cardiovascular Regulation: Ex Uno Plura (From One Comes Many). In Serotonin, Pilowsky, P.M., Ed.; Academic Press: Boston, 2019; pp. 335–347. [Google Scholar]
- Morán, A.; Velasco, C.; Salvador, T.; Martín, M.L.; San Román, L. Inhibitory 5-hydroxytryptamine receptors involved in pressor effects obtained by stimulation of sympathetic outflow from spinal cord in pithed rats. Br J Pharmacol 1994, 113, 1358–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villamil-Hernández, M.T.; Alcántara-Vázquez, O.; Sánchez-López, A.; Gutiérrez-Lara, E.J.; Centurión, D. Pharmacological evidence that 5-HT1A/1B/1D, α2-adrenoceptors and D2-like receptors mediate ergotamine-induced inhibition of the vasopressor sympathetic outflow in pithed rats. Eur J Pharmacol 2014, 740, 512–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marichal-Cancino, B.A.; González-Hernández, A.; Muñoz-Islas, E.; Villalón, C.M. Monoaminergic Receptors as Modulators of the Perivascular Sympathetic and Sensory CGRPergic Outflows. Curr Neuropharmacol 2020, 18, 790–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molderings, G.J.; Frölich, D.; Likungu, J.; Göthert, M. Inhibition of noradrenaline release via presynaptic 5-HT1D alpha receptors in human atrium. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 1996, 353, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morán, A.; Velasco, C.; Martín, M.L.; San Román, L. Pharmacological characterization of 5-HT receptors in parasympathetic innervation of rat heart. Eur J Pharmacol 1994, 252, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.J.; Liu, J.; Evans, M.S. Cholinergic-nitrergic transmitter mechanisms in the cerebral circulation. Microsc Res Tech 2001, 53, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackowski, A.; Crockard, A.; Burnstock, G. 5-Hydroxytryptamine demonstrated immunohistochemically in rat cerebrovascular nerves largely represents 5-hydroxytryptamine uptake into sympathetic nerve fibres. Neuroscience 1989, 29, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyle, S.H.; Brummett, B.H.; Kuhn, C.M.; Barefoot, J.C.; Siegler, I.C.; Williams, R.B.; Georgiades, A. The Effects of Tryptophan Enhancement and Depletion on Plasma Catecholamine Levels in Healthy Individuals. Psychosom Med 2019, 81, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Švec, J.; Švec, P.; Bencová, V.; Krčméry, V. [Anxio-depressive Syndrome - Biopsychosocial Model of Supportive Care]. Klin Onkol 2015, 28, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razzaque, Z.; Pickard, J.D.; Ma, Q.P.; Shaw, D.; Morrison, K.; Wang, T.; Longmore, J. 5-HT1B-receptors and vascular reactivity in human isolated blood vessels: assessment of the potential craniovascular selectivity of sumatriptan. Br J Clin Pharmacol 2002, 53, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villalón, C.M.; Sánchez-López, A.; Centurión, D. Operational characteristics of the 5-HT1-like receptors mediating external carotid vasoconstriction in vagosympathectomized dogs. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology 1996, 354, 550–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Hernandez, A.; Marichal-Cancino, B.A.; MaassenVanDenBrink, A.; Villalon, C.M. Side effects associated with current and prospective antimigraine pharmacotherapies. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol 2018, 14, 25–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marichal-Cancino, B.A.; González-Hernández, A.; Guerrero-Alba, R.; Medina-Santillán, R.; Villalón, C.M. A critical review of the neurovascular nature of migraine and the main mechanisms of action of prophylactic antimigraine medications. Expert Rev Neurother 2021, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidi, M.; Bevis, P.J.; Girgis, S.I.; Lynch, C.; Stevenson, J.C.; MacIntyre, I. Circulating CGRP comes from the perivascular nerves. Eur J Pharmacol 1985, 117, 283–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escott, K.J.; Connor, H.E.; Brain, S.D.; Beattie, D.T. The involvement of calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) and substance P in feline pial artery diameter responses evoked by capsaicin. Neuropeptides 1995, 29, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Schueren, B.J.; de Hoon, J.N.; Vanmolkot, F.H.; Van Hecken, A.; Depre, M.; Kane, S.A.; De Lepeleire, I.; Sinclair, S.R. Reproducibility of the capsaicin-induced dermal blood flow response as assessed by laser Doppler perfusion imaging. Br J Clin Pharmacol 2007, 64, 580–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dux, M.; Rosta, J.; Messlinger, K. TRP Channels in the Focus of Trigeminal Nociceptor Sensitization Contributing to Primary Headaches. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Julius, D.; Basbaum, A.I. Molecular mechanisms of nociception. Nature 2001, 413, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawasaki, H.; Nuki, C.; Saito, A.; Takasaki, K. Adrenergic modulation of calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP)-containing nerve-mediated vasodilation in the rat mesenteric resistance vessel. Brain research 1990, 506, 287–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawasaki, H.; Takasaki, K.; Saito, A.; Goto, K. Calcitonin gene-related peptide acts as a novel vasodilator neurotransmitter in mesenteric resistance vessels of the rat. Nature 1988, 335, 164–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taguchi, T.; Kawasaki, H.; Imamura, T.; Takasaki, K. Endogenous calcitonin gene-related peptide mediates nonadrenergic noncholinergic depressor response to spinal cord stimulation in the pithed rat. Circulation research 1992, 71, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawasaki, H.; Saito, A.; Takasaki, K. Age-related decrease of calcitonin gene-related peptide-containing vasodilator innervation in the mesenteric resistance vessel of the spontaneously hypertensive rat. Circulation research 1990, 67, 733–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avilés-Rosas, V.H.; Rivera-Mancilla, E.; Marichal-Cancino, B.A.; Manrique-Maldonado, G.; Altamirano-Espinoza, A.H.; Maassen Van Den Brink, A.; Villalón, C.M. Olcegepant blocks neurogenic and non-neurogenic CGRPergic vasodepressor responses and facilitates noradrenergic vasopressor responses in pithed rats. Br J Pharmacol 2017, 174, 2001–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, F.A.; King, R.; Smillie, S.J.; Kodji, X.; Brain, S.D. Calcitonin gene-related peptide: physiology and pathophysiology. Physiological reviews 2014, 94, 1099–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, A.F.; Hay, D.L. CGRP physiology, pharmacology, and therapeutic targets: migraine and beyond. Physiological reviews 2023, 103, 1565–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalón, C.M.; Albarrán-Juárez, J.A.; Lozano-Cuenca, J.; Pertz, H.H.; Görnemann, T.; Centurión, D. Pharmacological profile of the clonidine-induced inhibition of vasodepressor sensory outflow in pithed rats: correlation with alpha(2A/2C)-adrenoceptors. Br J Pharmacol 2008, 154, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Hernández, A.; Manrique-Maldonado, G.; Lozano-Cuenca, J.; Muñoz-Islas, E.; Centurión, D.; Maassen VanDenBrink, A.; Villalón, C.M. The 5-HT(1) receptors inhibiting the rat vasodepressor sensory CGRPergic outflow: further involvement of 5-HT(1F), but not 5-HT(1A) or 5-HT(1D), subtypes. Eur J Pharmacol 2011, 659, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Hernández, A.; Muñoz-Islas, E.; Lozano-Cuenca, J.; Ramírez-Rosas, M.B.; Sánchez-López, A.; Centurión, D.; Ramírez-San Juan, E.; Villalón, C.M. Activation of 5-HT1B receptors inhibits the vasodepressor sensory CGRPergic outflow in pithed rats. Eur J Pharmacol 2010, 637, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahimi, K.; Danser, A.; Terwindt, G.M.; van den Meiracker, A.H.; MaassenVanDenBrink, A. A human trigeminovascular biomarker for antimigraine drugs: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover trial with sumatriptan. Cephalalgia 2017, 37, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benemei, S.; Cortese, F.; Labastida-Ramírez, A.; Marchese, F.; Pellesi, L.; Romoli, M.; Vollesen, A.L.; Lampl, C.; Ashina, M. Triptans and CGRP blockade - impact on the cranial vasculature. J Headache Pain 2017, 18, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labastida-Ramírez, A.; Rubio-Beltrán, E.; Haanes, K.A.; Chan, K.Y.; Garrelds, I.M.; Johnson, K.W.; Danser, A.H.J.; Villalón, C.M.; MaassenVanDenBrink, A. Lasmiditan inhibits calcitonin gene-related peptide release in the rodent trigeminovascular system. Pain 2020, 161, 1092–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buzzi, M.G.; Carter, W.B.; Shimizu, T.; Heath, H., 3rd; Moskowitz, M.A. Dihydroergotamine and sumatriptan attenuate levels of CGRP in plasma in rat superior sagittal sinus during electrical stimulation of the trigeminal ganglion. Neuropharmacology 1991, 30, 1193–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Akerman, S.; van den Maagdenberg, A.M.; Saxena, P.R.; Goadsby, P.J.; van den Brink, A.M. Intravital microscopy on a closed cranial window in mice: a model to study trigeminovascular mechanisms involved in migraine. Cephalalgia 2006, 26, 1294–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limmroth, V.; Katsarava, Z.; Liedert, B.; Guehring, H.; Schmitz, K.; Diener, H.C.; Michel, M.C. An in vivo rat model to study calcitonin gene related peptide release following activation of the trigeminal vascular system. Pain 2001, 92, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, D.J.; Hargreaves, R.J.; Hill, R.G.; Shepheard, S.L. Sumatriptan inhibits neurogenic vasodilation of dural blood vessels in the anaesthetized rat--intravital microscope studies. Cephalalgia 1997, 17, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashina, M.; Hansen, J.M.; Do, T.P.; Melo-Carrillo, A.; Burstein, R.; Moskowitz, M.A. Migraine and the trigeminovascular system-40 years and counting. Lancet Neurol 2019, 18, 795–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Vries, T.; Villalón, C.M.; MaassenVanDenBrink, A. Pharmacological treatment of migraine: CGRP and 5-HT beyond the triptans. Pharmacology & therapeutics 2020, 211, 107528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goadsby, P.J.; Holland, P.R.; Martins-Oliveira, M.; Hoffmann, J.; Schankin, C.; Akerman, S. Pathophysiology of Migraine: A Disorder of Sensory Processing. Physiological reviews 2017, 97, 553–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Villalón, C.M. The relevance of preclinical research models for the development of antimigraine drugs: focus on 5-HT(1B/1D) and CGRP receptors. Pharmacology & therapeutics 2010, 128, 170–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Ajona, D.; Chan, C.; Villar-Martínez, M.D.; Goadsby, P.J. Targeting CGRP and 5-HT(1F) Receptors for the Acute Therapy of Migraine: A Literature Review. Headache 2019, 59 Suppl 2, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano-Cuenca, J.; González-Hernández, A.; Muñoz-Islas, E.; Sánchez-López, A.; Centurión, D.; Cobos-Puc, L.E.; Villalón, C.M. Effect of some acute and prophylactic antimigraine drugs on the vasodepressor sensory CGRPergic outflow in pithed rats. Life sciences 2009, 84, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, R.; Small, J.; Dixon, A.K.; Spanswick, D.; Lee, K. Serotonin receptor mRNA expression in rat dorsal root ganglion neurons. Neurosci Lett 2003, 337, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Islas, E.; Gupta, S.; Jiménez-Mena, L.R.; Lozano-Cuenca, J.; Sánchez-López, A.; Centurión, D.; Mehrotra, S.; MaassenVanDenBrink, A.; Villalón, C.M. Donitriptan, but not sumatriptan, inhibits capsaicin-induced canine external carotid vasodilatation via 5-HT1B rather than 5-HT1D receptors. Br J Pharmacol 2006, 149, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Islas, E.; Lozano-Cuenca, J.; González-Hernández, A.; Ramírez-Rosas, M.B.; Sánchez-López, A.; Centurión, D.; Maassenvandenbrink, A.; Villalón, C.M. Spinal sumatriptan inhibits capsaicin-induced canine external carotid vasodilatation via 5-HT1B rather than 5-HT1D receptors. Eur J Pharmacol 2009, 615, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio-Beltrán, E.; Labastida-Ramírez, A.; Villalón, C.M.; MaassenVanDenBrink, A. Is selective 5-HT(1F) receptor agonism an entity apart from that of the triptans in antimigraine therapy? Pharmacology & therapeutics 2018, 186, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, H.; Takatori, S.; Zamami, Y.; Hashikawa-Hobara, N.; Miyake, N.; Tangsucharit, P.; Mio, M.; Kawasaki, H. Adrenergic stimulation-released 5-HT stored in adrenergic nerves inhibits CGRPergic nerve-mediated vasodilatation in rat mesenteric resistance arteries. Br J Pharmacol 2012, 166, 2084–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Mancilla, B.; Cutler, N.R.; Leibowitz, M.T.; Spierings, E.L.; Klapper, J.A.; Diamond, S.; Goldstein, J.; Smith, T.; Couch, J.R.; Fleishaker, J.; et al. Safety and efficacy of PNU-142633, a selective 5-HT1D agonist, in patients with acute migraine. Cephalalgia 2001, 21, 727–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Hernández, A.; Marichal-Cancino, B.A.; Lozano-Cuenca, J.; MaassenVanDenBrink, A.; Villalón, C.M. Functional Characterization of the Prejunctional Receptors Mediating the Inhibition by Ergotamine of the Rat Perivascular Sensory Peptidergic Drive. ACS Chem Neurosci 2019, 10, 3173–3182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Jong, A.P.; Verhage, M. Presynaptic signal transduction pathways that modulate synaptic transmission. Current opinion in neurobiology 2009, 19, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuesta, C.; García-Pedraza, J.; García, M.; Villalón, C.M.; Morán, A. Role of 5-HT7 receptors in the inhibition of the vasodepressor sensory CGRPergic outflow in pithed rats. Vascul Pharmacol 2014, 63, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, A.K.; von der Weid, P.Y. 5-HT decreases contractile and electrical activities in lymphatic vessels of the guinea-pig mesentery: role of 5-HT 7-receptors. Br J Pharmacol 2003, 139, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, M.F.; Okun, I.; Stavros, F.L.; Hwang, E.; Wolff, M.E.; Balaji, V.N. Identification of a new class of ETA selective endothelin antagonists by pharmacophore directed screening. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1994, 201, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiklund, N.P.; Wiklund, C.U.; Cederqvist, B.; Ohlén, A.; Hedqvist, P.; Gustafsson, L.E. Endothelin modulation of neuroeffector transmission in smooth muscle. Journal of cardiovascular pharmacology 1991, 17 Suppl 7, S335–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippelli, A.; Falciani, M.; Piucci, B.; D'Amico, M.; D'Agostino, B.; Filippelli, W.; Rossi, F. Endothelin-1 affects capsaicin-evoked release of neuropeptides from rat vas deferens. Eur J Pharmacol 1999, 364, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenchat, A.; Zamanillo, D.; Hamon, M.; Romero, L.; Vela, J.M. Role of peripheral versus spinal 5-HT(7) receptors in the modulation of pain undersensitizing conditions. Eur J Pain 2012, 16, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.J.; Vasko, M.R.; Wu, X.; Staeva, T.P.; Baez, M.; Zgombick, J.M.; Nelson, D.L. Multiple subtypes of serotonin receptors are expressed in rat sensory neurons in culture. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1998, 287, 1119–1127. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pierce, P.A.; Xie, G.X.; Meuser, T.; Peroutka, S.J. 5-Hydroxytryptamine receptor subtype messenger RNAs in human dorsal root ganglia: a polymerase chain reaction study. Neuroscience 1997, 81, 813–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugiuar, T.; Bielefeldt, K.; Gebhart, G.F. TRPV1 function in mouse colon sensory neurons is enhanced by metabotropic 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor activation. J Neurosci 2004, 24, 9521–9530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Chen, T.; Gao, Y.; Quirion, R.; Hong, Y. Inhibition of SNL-induced upregulation of CGRP and NPY in the spinal cord and dorsal root ganglia by the 5-HT(2A) receptor antagonist ketanserin in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 2012, 101, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz-Islas, E.; Vidal-Cantú, G.C.; Bravo-Hernández, M.; Cervantes-Durán, C.; Quiñonez-Bastidas, G.N.; Pineda-Farias, J.B.; Barragán-Iglesias, P.; Granados-Soto, V. Spinal 5-HT₅A receptors mediate 5-HT-induced antinociception in several pain models in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 2014, 120, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tramontana, M.; Giuliani, S.; Del Bianco, E.; Lecci, A.; Maggi, C.A.; Evangelista, S.; Geppetti, P. Effects of capsaicin and 5-HT3 antagonists on 5-hydroxytryptamine-evoked release of calcitonin gene-related peptide in the guinea-pig heart. Br J Pharmacol 1993, 108, 431–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smillie, S.J.; Brain, S.D. Calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) and its role in hypertension. Neuropeptides 2011, 45, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arulmani, U.; Schuijt, M.P.; Heiligers, J.P.; Willems, E.W.; Villalón, C.M.; Saxena, P.R. Effects of the calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) receptor antagonist BIBN4096BS on alpha-CGRP-induced regional haemodynamic changes in anaesthetised rats. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 2004, 94, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.T.; Son, Y.J.; Lee, J.; Jetton, T.L.; Shiota, M.; Moscoso, L.; Niswender, K.D.; Loewy, A.D.; Magnuson, M.A.; Sanes, J.R.; et al. Mice lacking alpha-calcitonin gene-related peptide exhibit normal cardiovascular regulation and neuromuscular development. Mol Cell Neurosci 1999, 14, 99–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, T.H.; Wu, J.; Diedrich, A.; Garland, E.M.; Robertson, D. Calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) in autonomic cardiovascular regulation and vascular structure. Journal of the American Society of Hypertension : JASH 2014, 8, 286–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudrow, D.; Pascual, J.; Winner, P.K.; Dodick, D.W.; Tepper, S.J.; Reuter, U.; Hong, F.; Klatt, J.; Zhang, F.; Cheng, S.; et al. Vascular safety of erenumab for migraine prevention. Neurology 2020, 94, e497–e510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Vries Lentsch, S.; van der Arend, B.W.H.; Maassen VanDenBrink, A.; Terwindt, G.M. Blood Pressure in Patients With Migraine Treated With Monoclonal Anti-CGRP (Receptor) Antibodies: A Prospective Follow-up Study. Neurology 2022, 99, e1897–e1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Potts, J.D.; DiPette, D.J. Protective Role of α-Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide in Cardiovascular Diseases. Frontiers in physiology 2019, 10, 821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Williamson, M.; Hess, A.; DiPette, D.J.; Potts, J.D. Alpha-Calcitonin Gene Related Peptide: New Therapeutic Strategies for the Treatment and Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease and Migraine. Frontiers in physiology 2022, 13, 826122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MaassenVanDenBrink, A.; Meijer, J.; Villalón, C.M.; Ferrari, M.D. Wiping Out CGRP: Potential Cardiovascular Risks. Trends Pharmacol Sci 2016, 37, 779–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MaassenVanDenBrink, A.; Terwindt, G.M.; van den Maagdenberg, A. Calcitonin gene-related peptide (receptor) antibodies: an exciting avenue for migraine treatment. Genome Med 2018, 10, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, Y.T. [Plasma calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) level in patients with essential hypertension]. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi 1990, 29, 616–618. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.; Wang, X.A.; Wang, J.P. [Calcitonin gene-related peptide in normotensive and spontaneously hypertensive rats]. Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi 1989, 17, 174–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, R.E.; Supowit, S.C.; Zhao, H.; Katki, K.A.; Dipette, D.J. Role of sensory nervous system vasoactive peptides in hypertension. Braz J Med Biol Res 2002, 35, 1033–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyton, A.C.; Coleman, T.G.; Cowley, A.V., Jr.; Scheel, K.W.; Manning, R.D., Jr.; Norman, R.A., Jr. Arterial pressure regulation. Overriding dominance of the kidneys in long-term regulation and in hypertension. Am J Med 1972, 52, 584–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, B.B. Catecholamines, sympathomimetic drugs, and adrenergic receptor antagonists. In Goodman & Gilman´s The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics (10th Edition). Hardman JG, L.L., Goodman Gilman A (eds), Ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, 2001; pp. pp. 215-268.
- Gardiner, S.M.; Compton, A.M.; Bennett, T. Regional hemodynamic effects of calcitonin gene-related peptide. Am J Physiol 1989, 256, R332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.P.; Naes, L.; Westfall, T.C. Calcitonin gene-related peptide is the endogenous mediator of nonadrenergic-noncholinergic vasodilation in rat mesentery. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1990, 255, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Han, S.P.; Naes, L.; Westfall, T.C. Inhibition of periarterial nerve stimulation-induced vasodilation of the mesenteric arterial bed by CGRP (8-37) and CGRP receptor desensitization. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1990, 168, 786–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holzer, P. Local effector functions of capsaicin-sensitive sensory nerve endings: involvement of tachykinins, calcitonin gene-related peptide and other neuropeptides. Neuroscience 1988, 24, 739–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machida, T.; Iizuka, K.; Hirafuji, M. 5-hydroxytryptamine and its receptors in systemic vascular walls. Biol Pharm Bull 2013, 36, 1416–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marichal-Cancino, B.A.; Gonzalez-Hernandez, A.; Manrique-Maldonado, G.; Ruiz, S., II; Altamirano-Espinoza, A.H.; MaassenVanDenBrink, A.; Villalon, C.M. Intrathecal dihydroergotamine inhibits capsaicin-induced vasodilatation in the canine external carotid circulation via GR127935- and rauwolscine-sensitive receptors. Eur J Pharmacol 2012, 692, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumner, M.J. Characterization of the 5-HT receptor mediating endothelium-dependent relaxation in porcine vena cava. Br J Pharmacol 1991, 102, 938–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivasi, G.; Menale, S.; Turrin, G.; Coscarelli, A.; Giordano, A.; Ungar, A. The Effects of Pain and Analgesic Medications on Blood Pressure. Curr Hypertens Rep 2022, 24, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| 5-HT receptor | Receptor subtype | Agonists | Antagonists | Some functions | Canonical transduction system |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5-HT1 | 5-HT1A | 8-OH-DPAT | WAY 100635 | Central hypotension |
G-protein coupled receptor (Gi)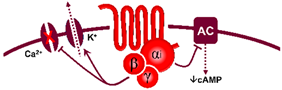
|
| 5-HT1B | Sumatriptan CP-93,129 (rodents) |
SB224289 | Vasoconstriction, sympatho-inhibition | ||
| 5-HT1D | PNU-109291 PNU-142633 |
BRL15572 | Autoreceptor, sympatho-inhibition | ||
| 5-HT1e* | 5-HT >> 5-CT LY334370 | Methiothepin (non-selective) | Unknown | ||
| 5-HTF | LY344864 lasmiditan, LY334370 | Methysergide (non-selective) | (-) Trigeminal system | ||
| 5-HT5 | 5-HT5A | 5-HT, ergotamine | SB699551 | Cardiac sympatho-inhibition in rats | |
| 5-HT5b* | 5-CT (non-selective) | Unknown | Unknown | ||
| 5-HT4 | - | Renzapride BIMU8, ML10302 SC53116 | GR 113808 SB204070 | (+) Neuronal activity, vasodilatation, tachycardia in pigs and humans |
G-protein coupled receptor (Gs)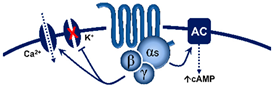
|
| 5-HT6 | - | 5-MeO-T ≥ 5-HTSB357134 SB271046 | Ro 630563 | Memory, not involved in cardiovascular regulation by 5-HT | |
| 5-HT7 | - | 5-CT>>5-HT AS-19 |
SB269970 SB258719 | Circadian rhythm, vasodilatation, tachycardia in cats | |
| 5-HT2 | 5-HT2A | DOI, DOB α-methyl-5-HT |
MDL100907 ketanserin | Vasoconstriction, platelet aggregation |
G-protein coupled receptor (Gq)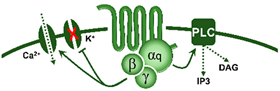
|
| 5-HT2B | DOI, BW723C86α-methyl-5-HT | SB204741 RS-127445 |
Vasoconstriction, release of NO | ||
| 5-HT2C | DOI, Ro 60-0175α-methyl-5-HT | SB242084 RS-102221 |
CSF production | ||
| 5-HT3 | Pentameric ion channel** | Phenylbiguanideα-methyl-5-HT | Tropisetron Granisetron MDL-72222 | (+) Neuronal activity, reflex bradycardia |
Ligand-gated ion channel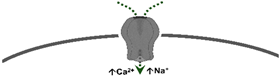
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





