1. Introduction
There is growing evidence that standard-of-care medical images obtained from modalities such as CT, MRI and PET contain more information than is visible to the human eye [
1]. The high throughput extraction and processing of the underlying information from radiological images is known as "radiomics". The quantitative data obtained (imaging biomarkers) could be used alongside the current gold standard of tumor evaluation and staging tools including TNM staging [
2] to aid clinical decision making such as personalized treatment planning.
The predictive power of radiomics features is dependent on having a large set of data. However, due to the nature of medical images, the size of the studies is often relatively small and based on a single dataset, restricting the impact of the results. To find candidates for reproducible biomarkers from the hundreds of features available from first, second and higher order statistical features of images, it is necessary for researchers to validate the results published by other groups [
3]. This should be carried out using a separate dataset from the original study and considered to be a retrospective investigation. However, at least 50% of published studies have been described as poorly reported with incomplete methodologies and results for successful validation when an analysis of biomedical research was performed by Chalmers and Glasziou [
3]. The precise cause of this serious lack of reproducibility in validation is unclear. The lack of standards for validating results, incomplete reporting of methodologies and results, and unrecognized confounding variables in the dataset used could all be to blame.
A recent systematic review of full-text articles in PubMed published in 2018 primarily addressed non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and oropharyngeal cancer [
4] and found only 7 out of 41 studies reported every methodology used in image acquisition, pre-processing, and feature extraction in detail. Out of 21 studies on NSCLC, 4 studies using CT images [
5,
6,
7,
8] and 1 study using PET images reported every methodologic aspect. The results identified the sensitivity of radiomics features in terms of repeatability and reproducibility to processing details such as the settings used in image acquisition, image reconstruction algorithm, image preprocessing and software used to extract radiomic features. First-order features were reported to be more reproducible than shape metrics and texture features.
Our previously published study [
9] analyzing radiomics features extracted from the CT component of PET/CT scans of patients with NSCLC, treated at the Royal Surrey NHS Foundation Trust (RSFT). The radiomics features were calculated using the toolkit of Vallières et al [
10]. which is available in the Matlab package. This study found that a set of radiomics features were stable to settings used in image acquisition and reconstruction algorithms used in different scanner models. Features were also stable to variations in tumor delineation. However, features were sensitive to intensity quantization parameters including i) the number of intensity levels, ii) the method of quantization to select the intensity levels and iii) the use of an intensity threshold around the tumor or organ being analyzed. These results show that different parameter choices in different datasets may help to explain the results in the two afore-mentioned review papers [
4,
5]. Therefore, a question is would these features be successfully reproduced and validated under different conditions such as with a different lung cancer dataset, or for a different disease site or using a different implementation of radiomics feature extraction?
2. Materials and Methods
The purpose of this paper is to investigate the generalizability of the findings from the initial study[
9] and if a common set of CT radiomics features is stable. This was achieved firstly by evaluating which radiomics features are stable from the originally used the 43 features of the Vallières toolkit, for a publicly available lung cancer dataset: the Reference Image Database to Evaluate Therapy Response (RIDER)[
11]. As Pyradiomics is one of the most used radiomics toolkits and provides the 43 features of the Vallières [
10] plus 59 other original features, the RIDER dataset was also evaluated using Pyradiomics [
12] and the results of the two toolkits were compared to study generalizability across radiomics implementations plus the extra features from Pyradiomics. As with the original study this was carried using the full intensity range in the images and thresholding to analyze the tumor intensity region only. To explore the applicability to other disease sites, a head and neck dataset was analyzed using MATLAB toolkit and Pyradiomics. The dataset used was the HN1 dataset made publicly available in The Cancer Imaging Archive [
1]. The stable features for HN1 were compared with those from RIDER.
2.1. Imaging Datasets
Two publicly available datasets were used in this study.
2.1.1. RIDER Dataset
The Reference Image Database to Evaluate Therapy Response (RIDER) dataset consists of 31 non-contrast enhanced PET/CT images from pathologically confirmed NSCLC patients scanned in the Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, New York, United States [
11]. All patients received conventional radiotherapy, none received SABR. Each patient had a repeat scan 15 minutes after the first scan using the same scanner and imaging protocol. These are referred to as RIDER Scan 1 and RIDER Scan 2. The image datasets were acquired using two scanner types: GE LightSpeed RT16 and GE VCT. Each CT image size was 512 by 512 pixels, with pixel size ranging from 0.58 mm by 0.58 mm to 0.87 mm by 0.87 mm and a slice thickness of 1.25 mm.
2.1.2. HN1 dataset
The HN1 dataset contains PET/CT images of 137 head and neck patients with squamous cell carcinoma. The patients were treated with definitive radiotherapy or concurrent chemoradiation. All patients underwent a treatment planning free-breathing 18F FDG-PET-CT scan (Biograph, SOMATOM Sensation-16 with an ECAT ACCEL PET scanner; Siemens, Erlangen, Germany), 45 minutes after uptake. A spiral CT (3 mm slice thickness) was performed covering the complete thoracic region. Slice thickness 1.5 - 3.0 mm in-plane resolution 0.9 x 0.98 mm2 to 1.09 x 1.09 mm2. The data also includes gross tumor volume (GTV) delineation by an experienced radiologist and a radiotherapy structure set. Further details are given here. [
1]
2.2. Texture Features Analyzed
To mimic the methodology of our previous study, the Matlab texture analysis toolkit of Vallières et al. [
13] was used to extract 43 standard features from the CT defined GTV for the RIDER dataset. 3 were first order features and 40 were second or higher order, of which 9 were from the grey level correlation matrix (GLCM), 13 from the grey level run length matrix (GLRLM), 13 from the grey level size zone matrix (GLSZM) and 5 from the neighborhood grey tone difference matrix (NGTDM). For the second and higher order features, matrices were generated to assess the relationship between the center voxel and its neighbors. One matrix was generated for each of the 13 directions in 3D space, the texture features were calculated then averaged over the GTV volume. A full list of the features and equations defining them used for the 43 radiomics features can be found in the literature [
10].
Using Pyradiomics a total of 103 features were extracted from the segmented GTV. These features encompassed eight types: 18 first-order, 14 shape,14 gray-level dependence matrix (GLDM), 22 gray-level co-occurrence matrix (GLCM), 16 gray-level run length matrix (GLRLM), 16 gray-level size zone matrix (GLSZM) and 5 neighboring gray tone difference matrix (NGTDM).
2.3. Experimental Set-up and Statistical Analysis
The 43 features from the Matlab toolkit were generated for both RIDER Scan 1 and Scan 2. Secondly the results were also compared with and without an intensity threshold applied to the CT scan. The threshold used was -200 to 300 HU as in our previous study [
9]. Thirdly stability was measured by comparing global uniform quanitizer (GUQ – with the same quantizer applied to each scan) and individual uniform quantizer (IUQ – with the quantizer optimized for each scan). All these were uniform quantizers which quantized the intensity range of each GTV into equal width bins.
The same features were generated for the two RIDER scans using Pyradiomics with the same thresholding and Fixed Bin Width (equivalent to Global Uniform quantizer) and Fixed Bin Count (equivalent to Individual Uniform Quantizer).
Results were compared between the Matlab and Pyradiomics implementations and between the two RIDER scans, with and without intensity threshold. No outcome information was available; hence validation of the features was based on assessing reproducibility of the rank ordering using each feature to changes to the quantization parameters for all datasets. Changes in the rank ordering indicate low reproducibility, leading to unreproducible predictions of biomarkers. In addition, the stability of the other 59 features available in Pyradiomics was also studied. Although these cannot be used to comment on the consistency with the MATLAB toolkit, it is instructive to determine if they are candidate stable features.
A feature was considered reproducible if it produces the same rank ordering for the cohort regardless of the quantization parameters. Spearman's rank correlation, rs, was used to measure the rank ordering quantized using IUQ against GUQ at 128 intensity levels used as a reference with and without intensity thresholding, for all datasets. The rank ordering quantized with GUQ at 128 intensity levels as a reference was used as the standard comparator as it was found to be the most stable quantization combination [
9]. Validation was considered successful if a feature which expressed high or low correlation for the Matlab toolkit also expressed high or low correlation in Pyradiomics.
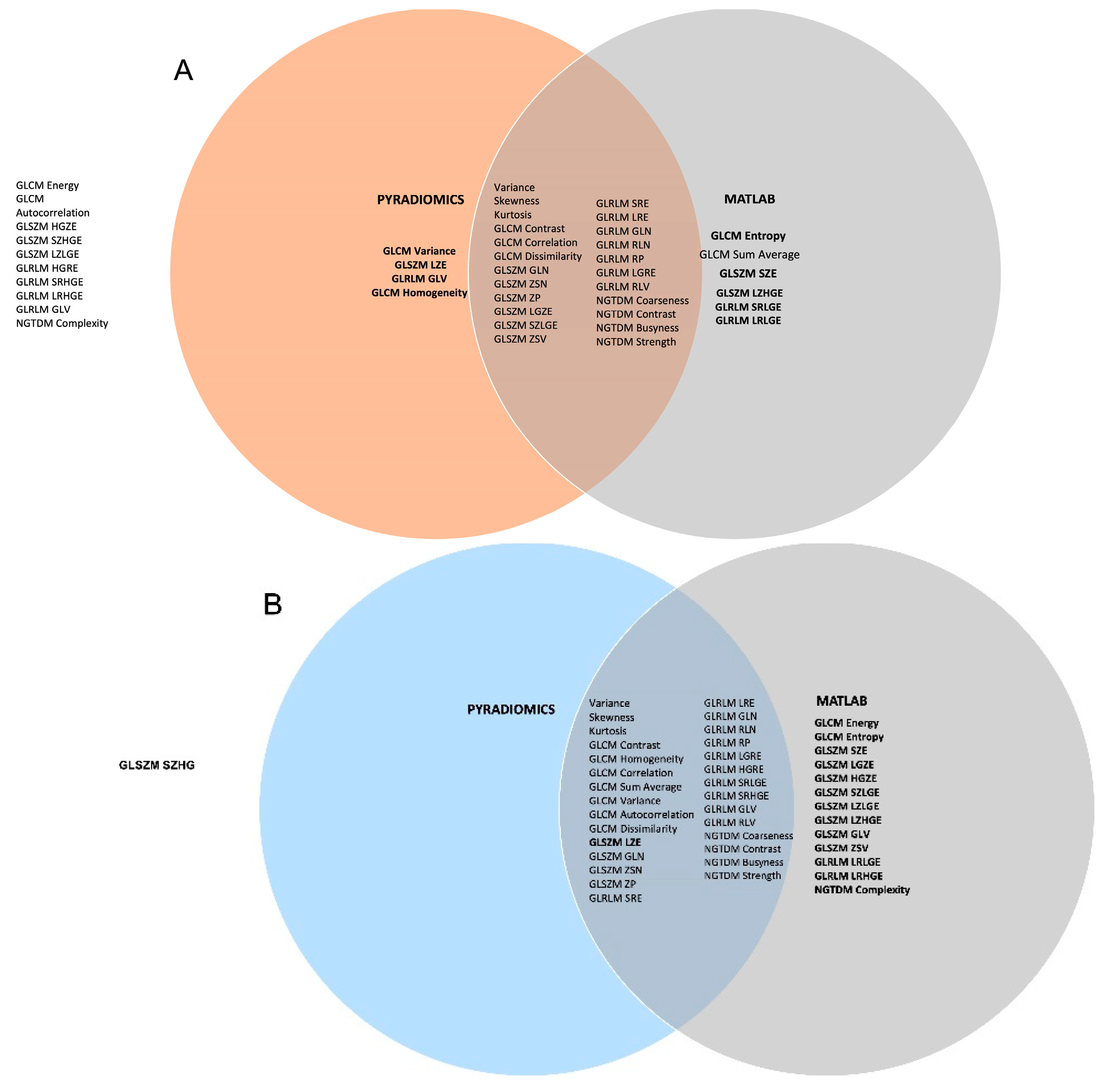
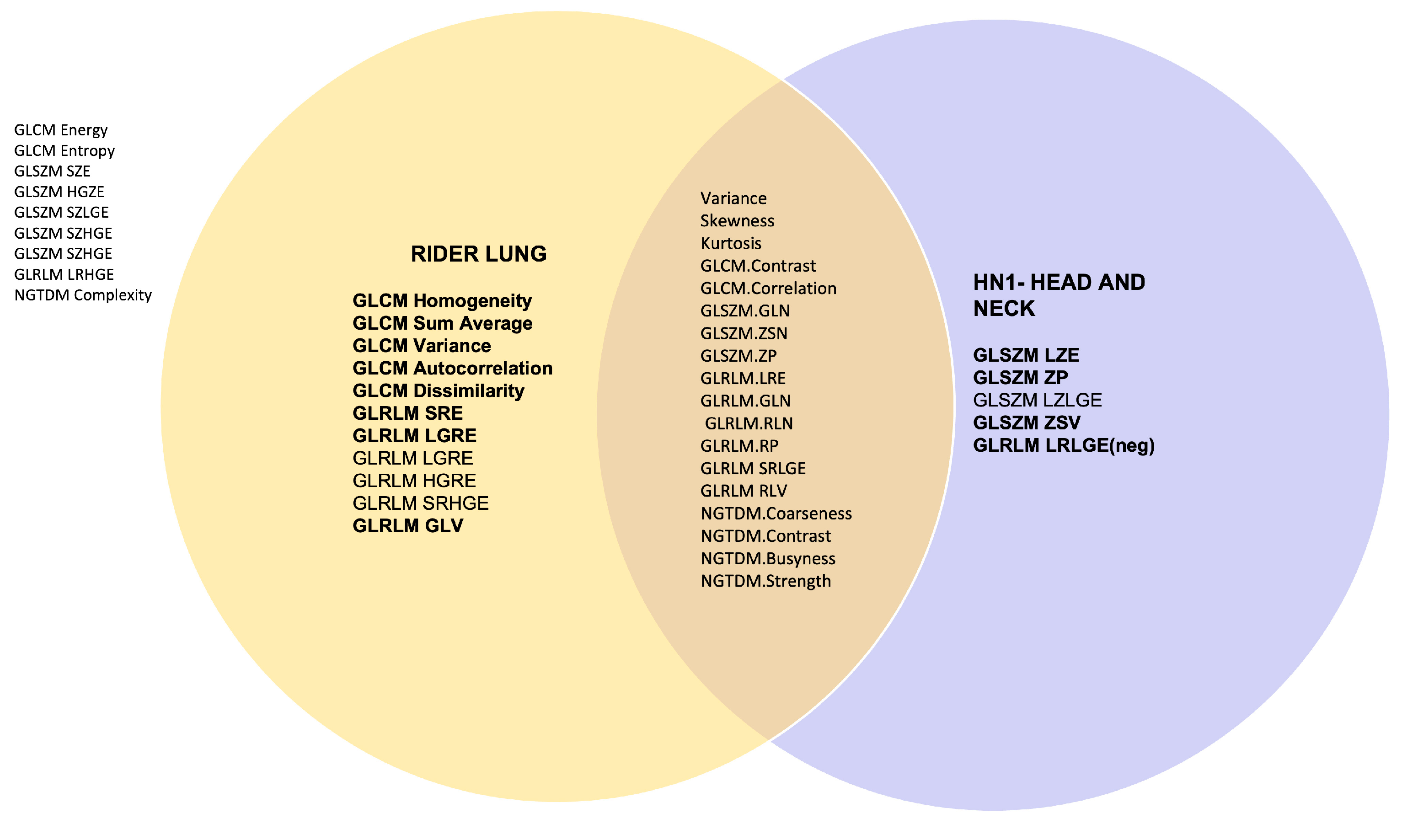
In the comparison of stable features between arms of the study in the results, e.g. between radiomics toolkits and disease sites, Venn diagrams are used to illustrate which features show promise as stable features in multiple arms.
Research manuscripts reporting large datasets that are deposited in a publicly available database should specify where the data have been deposited and provide the relevant accession numbers. If the accession numbers have not yet been obtained at the time of submission, please state that they will be provided during review. They must be provided prior to publication.
Interventionary studies involving animals or humans, and other studies that require ethical approval, must list the authority that provided approval and the corresponding ethical approval code.
3. Results
Table 1 lists all features that were reproducible, with high correlation, for RIDER Scans 1 and 2 based on the Spearman's correlation coefficient with (blue) and without threshold (red) using the two quantizers GUQ and IUQ. Features with rs >= 0.8 were classified as highly correlated. This was a subjective decision as no published guidance was available. 34 features were found to be reproducible; 29 and 21 with and without intensity threshold applied, respectively and 21 features were found to be reproducible for all data. This suggests that including intensity threshold around the region of interest as a pre-processing step tends to increase the stability of some radiomics features.
Figure 1 shows a Venn diagram plotting the overlap in highly correlated features quantized with GUQ versus IUQ for 43 features that are commonly available in the MATLAB toolkit and Pyradiomics. Panels A and B plot the correlation of rank ordering quantized between GUQ and IUQ without and with the use of an intensity threshold. The correlation value for most shape, first order, GLCM, GLRLM, GLZSM and NGTDM texture features were high (>0.8) for the RIDER Scan 1, with 9 and 14 features with rs >0.9 without and with intensity threshold. The number of features that overlapped between Matlab toolkit and Pyradiomics were higher when intensity threshold was applied. A similar trend was seen for RIDER scan 2 data.
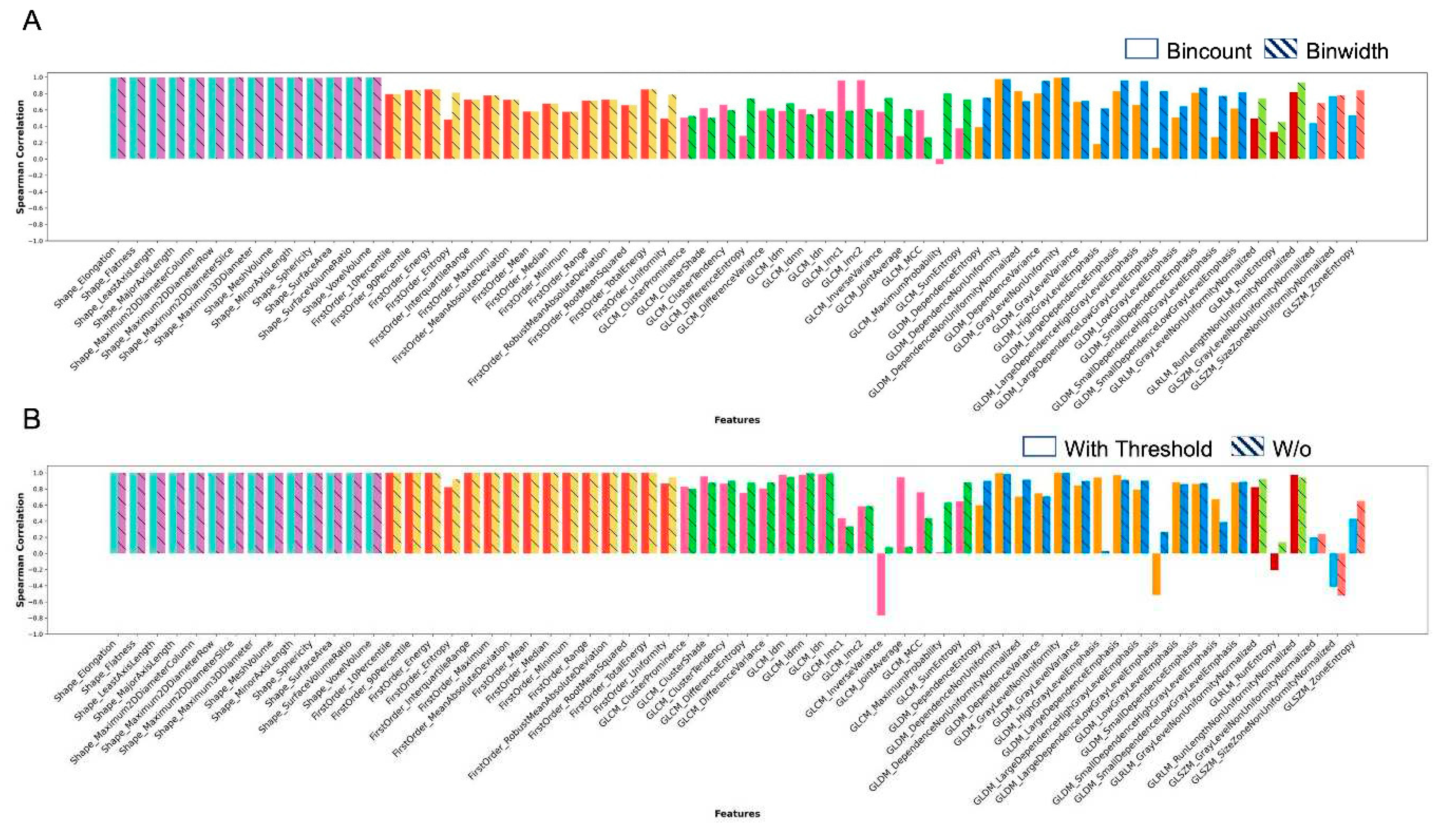
Figure 2 presents the results for features that were uniquely available in Pyradiomics.
Figure 2A shows correlation of rank order between features extracted with and without intensity threshold with the use of GUQ and IUQ quantization. Similarly, Fig. 2B shows the correlation of ranks quantized between GUQ and IUQ with and without intensity threshold being applied. Shape features were found to be invariant to intensity threshold or quantization techniques. For all other classes, the features showed more variance based on application of an intensity threshold and less so on the quantization used. A few features showed negative correlation with the choice of quantization used namely GLCM Inverse Variance, GLDM Large Dependence Low Gray Level Variance, GLRLM Run Entropy, and GLZSM Size Zone Nonuniformity Normalized. This negative correlation was seen only in GLCM Maximum Probability when an intensity threshold was applied.
Figure 3 plots a Venn diagram with the overlap in the highly correlated features quantized between GUQ and IUQ and with an intensity threshold applied for datasets RIDER Lung 1 and Head and Neck HN1.The features were extracted using Pyradiomics 18/43 features were agnostic of the disease site and 4/5 from HN1 and 8/11 from RIDER lung had rank correlation above 0.9, respectively.
4. Discussion
This study was to verify the robustness of the methods reported earlier for improving stability of radiomic features. The study used two different datasets with different pixel sizes acquired in a different center using different scanners and protocols, one lung cancer and the other head and neck cancer, both available publicly while additionally testing for reproducibility of stability to implementation of radiomic features. High levels of correlation were achieved for more than half of the features for both Matlab and Pyradiomics implementations for the RIDER lung data and more than one third features stable for lung and head and neck datasets suggesting that some features are agnostic to the disease site and generally robust.
In the literature, low reproducibility is one of the biggest challenges in radiomics [
3,
4]. Features identified to be predictive may be biased to the specific dataset and have limited predictive power on another dataset. Possible causes for the low reproducibility may include pre-existing differences in the dataset used, for example different acquisition parameters, reconstruction methods, pixel sizes and slice thickness, low reproducibility of features to variations in quantization parameters and low repeatability of the features. Other considerations include the preprocessing of the imaging data. For instance, Mottola et al. studied the effects of image resampling and showed that different resampling approaches produced very different error metrics, with Lanczos interpolation performing substantially better than simple linear interpolation [
14]. In our previous work [
9] we have shown that some radiomics features are reproducible across different scanner models, acquisition parameters, reconstruction methods, and modest variations in slice thickness, provided pixel sizes are resampled to a fixed standard. It was identified that feature reproducibility was highly sensitive to the choice of quantization parameters.
The imaging biomarker standardization initiative was set up to ensure features are reproducible across implementations [
15]. PyRadiomics does not exactly comply completely with all IBSI requirements including quantization parameters and although care was taken to keep the suggested stability parameters as close as possible, the implementation would have affected the present study. Hence, IBSI compliance is strongly recommended to allow better reproduction and validation of the results externally.
The aim of many radiomics studies including those of by our group is to predict an outcome such as response to treatment or disease-free survival using one or multiple features referred to as biomarkers. Predictions are often performed using statistical approaches including Kaplan-Meier analysis based on a single feature of the data at a time [
16] and machine learning approaches with multiple features from a large set of features up to hundreds [
1,
17]. Outcome prediction accuracy is heavily reliant upon having highly reproducible features. For instance, the widely used Kaplan-Meier analysis method involves ordering the dataset based on a feature and dichotomizing it into two sets for prediction. It is vital for the rank ordering to be consistent, as changes in the rank order may change the dichotomization and hence results in Kaplan-Meier studies, leading to low reproducibility and low predictive power.
Unreproducible features lead to even bigger challenges with big data driven methods. Machine learning approaches with medical images are prone to overfitting since the number of features available may be large compared to the number of cases available for study. Overfitting potentially increases the false discovery rate and limits the predictive power of the model to new datasets. It is a common practice to pre-select the features available for analysis using methods such as inter-feature correlation, interclass correlation (ICC) and LASSO Regularization. However, these methods are statistical, without any knowledge of the underlying radiomics features. Based on our results, we recommend excluding unreproducible features from analysis to reduce dimensionality and computational burden.
This study has successfully validated our previous results [
9] and reproduced the changes in radiomics features using different quantization parameters, suggesting the methodology used for the study9 is robust. These results highlight the importance of using the same quantization parameters for all analyses and reporting detailed methodology used.
5. Conclusions
Radiomics features reported as stable were analyzed for reproducibility using RIDER lung dataset with. 29 of 43 features found to be reproducible to changes in the feature extraction toolkits when intensity threshold was applied maintaining stable rank ordering (rs > 0.8) and are recommended for use for biomarker analysis. 1843 reported features were common in RIDER and HN1 datasets, suggesting they may be agnostic to disease site. Useful radiomics features should be selected based on reproducibility. This study identified a set of features that meet this requirement and validated the methodology for evaluating reproducibility between datasets.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.M.T, E.M.D. ,C.P.S., A.N., V.P. and P.M.E; methodology, H.M.T., H.Y.C.W., E.M.D., C.P.S., A.N. and P.M.E.; software, H.M.T. and H.Y.C.W.; validation, H.M.T., H.Y.C.W and H.S.; formal analysis, H.M.T. and H.Y.C.W.; investigation, V.P, A.J.V., S.B.K., S.P.P., D.D., M.M. and R.I.; resources, A.N., V.P., P.M.E. and D.D.; data curation, H.M.T. and H.Y.C.W.; writing—original draft preparation, H.M.T, H.Y.C.W and P.M.E..; writing—review and editing, H.M.T and P.M.E.; visualization, V.P, A.J.V., S.B.K., S.P.P., D.D., M.M. and R.I.; supervision, E.M.D., C.P.S., A.N., V.P. and P.M.E.; project administration, H.M.T., V.P. and P.M.E.; funding acquisition, H.M.T., A.N., V.P. and P.M.E. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the DBT/Wellcome Trust India Alliance Early Career Fellowship [Grant number: IA/E/18/1/504306] awarded to HMT Thomas. HMT Thomas acknowledges the support from the University of Surrey IAS fellowship for external academics 2022-23. HYC Wang acknowledges PhD funding from Alliance Medical Ltd.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethical review and approval were waived for this study due to its use of solely publicly available datasets.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was not applicable for this study.
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
The authors have no relevant conflicts of interest to disclose.
References
- Aerts, H.J.W.L.; Velazquez, E.R.; Leijenaar, R.T.H.; Parmar, C.; Grossmann, P.; Carvalho, S.; et al. Decoding tumour phenotype by noninvasive imaging using a quantitative radiomics approach. Nature Communications 2014, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Sullivan, B.; Brierley, J.; Byrd, D.; Bosman, F.; Kehoe, S.; Kossary, C.; et al. The TNM classification of malignant tumours—towards common understanding and reasonable expectations. Lancet Oncol 2017, 18, 849–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalmers, I.; Glasziou, P. Avoidable waste in the production and reporting of research evidence. The Lancet 2009, 374, 86–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traverso, A.; Wee, L.; Dekker, A. ; GilliesR. Repeatability and Reproducibility of Radiomic Features: A Systematic Review. International Journal of Radiation Oncology, Biology, Physics 2018, 102, 1143–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balagurunathan, Y.; Gu, Y.; Wang, H.; Kumar, V.; Grove, O.; Hawkins, S.; et al. Reproducibility and Prognosis of Quantitative Features Extracted from CT Images. Translational Oncology 2014, 7, 72–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coroller, T.P.; Agrawal, V.; Narayan, V.; Hou, Y.; Grossmann, P.; Lee, S.W.; et al. Radiomic phenotype features predict pathological response in non-small cell lung cancer. Radiother Oncol 2016, 119, 480–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fave, X.; Mackin, D.; Yang, J.; Zhang, J.; Fried, D.; Balter, P.; et al. Can radiomics features be reproducibly measured from CBCT images for patients with non-small cell lung cancer? Med Phys 2015, 42, 6784–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fave, X.; Zhang, L.; Yang, J.; Mackin, D.; Balter, P.; Gomez, D.; et al. Delta-radiomics features for the prediction of patient outcomes in non–small cell lung cancer. Scientific Reports 2017, 7, 588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.Y.C.; Donovan, E.M.; Nisbet, A.; South, C.P.; Alobaidli, S.; Ezhil, V.; et al. The stability of imaging biomarkers in radiomics: a framework for evaluation. Phys Med Biol 2019, 64, 165012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallières, M.; Kay-Rivest, E.; Perrin, L.J.; Liem, X.; Furstoss, C.; Aerts, H.J.W.L.; et al. Radiomics strategies for risk assessment of tumour failure in head-and-neck cancer. Scientific Reports 2017, 7, 10117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, B.; James, L.P.; Moskowitz, C.S.; Guo, P.; Ginsberg, M.S.; Lefkowitz, R.A.; et al. Evaluating variability in tumor measurements from same-day repeat CT scans of patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Radiology 2009, 252, 263–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welcome to pyradiomics documentation! — pyradiomics v3.0.1.post15+g2791e23 documentation n.d. https://pyradiomics.readthedocs.io/en/latest/ (accessed January 27, 2023). 27 January.
- Vallières, M.; Kay-Rivest, E.; Perrin, L.; Liem, X.; Furstoss, C.; Khaouam, N.; et al. Data from Head-Neck-PET-CT 2017. [CrossRef]
- Mottola, M.; Ursprung, S.; Rundo, L.; Sanchez, L.E.; Klatte, T.; Mendichovszky, I.; et al. Reproducibility of CT-based radiomic features against image resampling and perturbations for tumour and healthy kidney in renal cancer patients. Sci Rep 2021, 11, 11542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatt, M.; Vallieres, M.; Visvikis, D.; Zwanenburg, A. IBSI: an international community radiomics standardization initiative. J Nucl Med 2018, 59, 287–287. [Google Scholar]
- Win, T.; Miles, K.A.; Janes, S.M.; Ganeshan, B.; Shastry, M.; Endozo, R.; et al. Tumor heterogeneity and permeability as measured on the CT component of PET/CT predict survival in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2013, 19, 3591–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coroller, T.P.; Agrawal, V.; Huynh, E.; Narayan, V.; Lee, S.W.; Mak, R.H.; et al. Radiomic-Based Pathological Response Prediction from Primary Tumors and Lymph Nodes in NSCLC. Journal of Thoracic Oncology 2017, 12, 467–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).