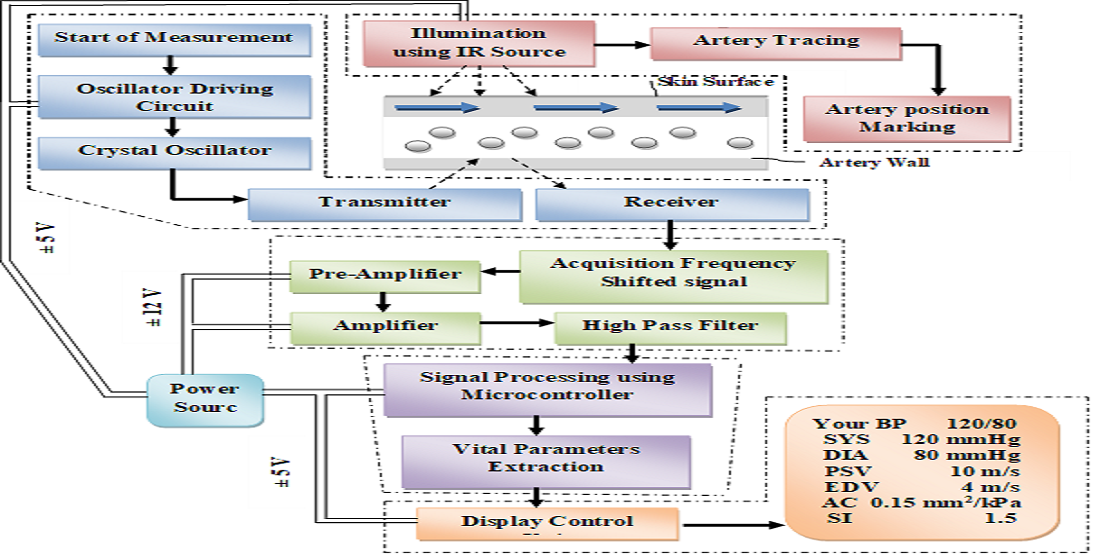
In this paper, the feasibility of automated and accurate in vivo measurements of vascular parameters continuously and non-invasively using ultrasound sensor is presented. Vascular parameters such as pulse wave velocity (PWV), blood pressure (BP), arterial compliance (AC) and stiffness index (SI) are affluent indicators of cardiovascular disorders and needs to be monitored non-invasively and continuously during surgeries and follow-up procedures. Cuff based or invasive catheter techniques are considered as gold standard to measure BP and are fed manually to compute AC and SI which employ imaging algorithms. In this context, a Continuous and Non-Invasive Vascular Stiffness and Arterial Compliance Screener (CaNVAS) is developed to measure said parameters continuously and non-invasively using ultrasound sensor. Acoustic waves of 5 MHz (2.2 – 10 MHz) are driven through target arterial walls, reflected echoes captured, pre-processed and frequency shift is used to calculate PWV. It is observed that PWV measured using CaNVAS varies exponentially with BP values obtained from sphygmomanometer (BPMR-120) and this relationship is used to compute instantaneous values of BP. The proposed device is validated by performing measurements on 250 subjects in pre and post exercise conditions and found to have 95% accuracy and an average of 12.5% coefficient of variation.