1. Introduction
Antibiotic resistance has emerged as a significant concern for public health which is likely to jeopardize the efficacy of life-saving antimicrobial treatments [
1,
2]. The World Health Organization (WHO) has identified antibiotic resistance as one of the most pressing global health threats, with an estimated 700,000 deaths occurring annually due to drug-resistant infections. Failure to address this problem is expected to lead to a projected increase in the annual death toll to 10 million by 2050 [
3]. Furthermore, the misuse or overuse of some antibiotics have exacerbated the situation [
4]. We are also seeing a decline in investments in antibiotic research which is visible in the form of sluggish growth of new antibiotics [
5,
6].
Amidst these concerns, the gut microbiota has gained significant attention as a crucial modulator of host health and disease [
7]. Human gut microbiota has a unique significance in human biology as it comprises trillions of microorganisms including bacteria, viruses, and fungi. Recent research has demonstrated that the gut microbiota exerts a profound influence on various aspects of human physiology including metabolism, immunity, and neurological function [
8]. The role of gut microbiota and brain has been extensively studied due to its significant role in human emotions and psychological health [
9,
10]. In 2013, Clarke et al. reported that early-life microbiota regulates the hippocampal serotonergic system which opened up multiple line of inquiries into the role of microbiome on neurodevelopment [
11].
The intricate interplay between the gut microbiota and the host immune system is essential to maintain homeostasis for optimal functioning of an individual. Imbalances in this interplay have been linked to a range of diseases including infectious diseases [
12]. Therefore, understanding the intricate relationship between the gut microbiota, antibiotic therapy selection, and resistance mitigation is of paramount importance for disease management. Thanks to the advancements in molecular biology techniques such as metagenomics, transcriptomics, and metabolomics, the composition of function of gut microbiota is becoming more clearer with each passing day [
13]. These cutting-edge technologies have shed light on the intricate interplay between the gut microbiota and the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of antibiotics [
14].
Furthermore, newer research has highlighted the potential of the gut microbiota to overcome antibiotic resistance through competitive exclusion, colonization resistance, and modulation of host immune responses [
15,
16,
17]. The emergence of next-generation sequencing (NGS) technologies has transformed the field of microbiome research which has enabled comprehensive and high-resolution characterization of the gut microbial community [
18]. Several studies have explored the potential of manipulating the gut microbiota to optimize antibiotic therapy and mitigate resistance [
19,
20,
21]. The use of prebiotics, probiotics, and fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) are some examples of interventions that have shown promise in modulating the gut microbiota, with potential implications for antibiotic therapy selection and resistance mitigation [
22,
23]. Moreover, the integration of gut microbiota research into clinical decision-making is beginning to gain traction, as evidenced by the increasing number of clinical trials and studies investigating the use of gut microbiota information to guide antibiotic therapy [
24,
25,
26].
The present review presents an extensive overview of the molecular mechanisms underlying the influence of gut microbiota on the selection of antibiotic therapy and the alleviation of antibiotic resistance. The article emphasizes the clinical significance, hurdles, and potential research pathways concerning gut microbiota in the context of infectious diseases. The knowledge in this review will improve clinical decision making and help design innovative therapeutic strategies.
2. Gut microbiota and antibiotic therapy selection
The gut microbiota can significantly influence the efficacy and toxicity of orally administered antibiotics as it plays a crucial role in modulation of their pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. Pharmacokinetics refers to the absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion of drugs, while pharmacodynamics deals with the relationship between drug concentration and its effect on the body [
27]. Both aspects are critical in determining the success of antibiotic therapy.
The gut microbiota also influences the absorption of antibiotics by metabolizing the drug or altering the intestinal environment which can lead to changes in drug bioavailability [
28]. For instance, certain bacterial species in the gut can metabolize beta-lactam antibiotics which can render them inactive and reduce their efficacy. Furthermore, the gut microbiota can affect drug distribution by altering the expression of efflux transporters and drug-metabolizing enzymes in the intestinal epithelium [
29]. These alterations can significantly affect the systemic availability and tissue distribution of antibiotics which can ultimately impact their efficacy and toxicity [
30]. The gut microbiota can also influence the bile acid pool which can affect the solubility and absorption of antibiotics [
31].
The gut microbiota can also impact the pharmacodynamics of antibiotics by modulating the host immune response. Several studies have revealed that the gut microbiota plays a crucial role in regulating both the innate and adaptive immune responses which are critical to control and resolve bacterial infections [
32]. The gut microbiota can facilitate the efficacy of specific antibiotics through the promotion of antimicrobial peptide production and regulation of immune cell differentiation and activation [
33]. Furthermore, the gut microbiota is capable of generating short-chain fatty acids that enhance immune cell function and amplify the effectiveness of antibiotics against bacterial infections [
34]. However, it is important to note that certain gut bacteria can produce enzymes that disable antibiotics which can reduce their potency and promote the development of antibiotic resistance [
35].
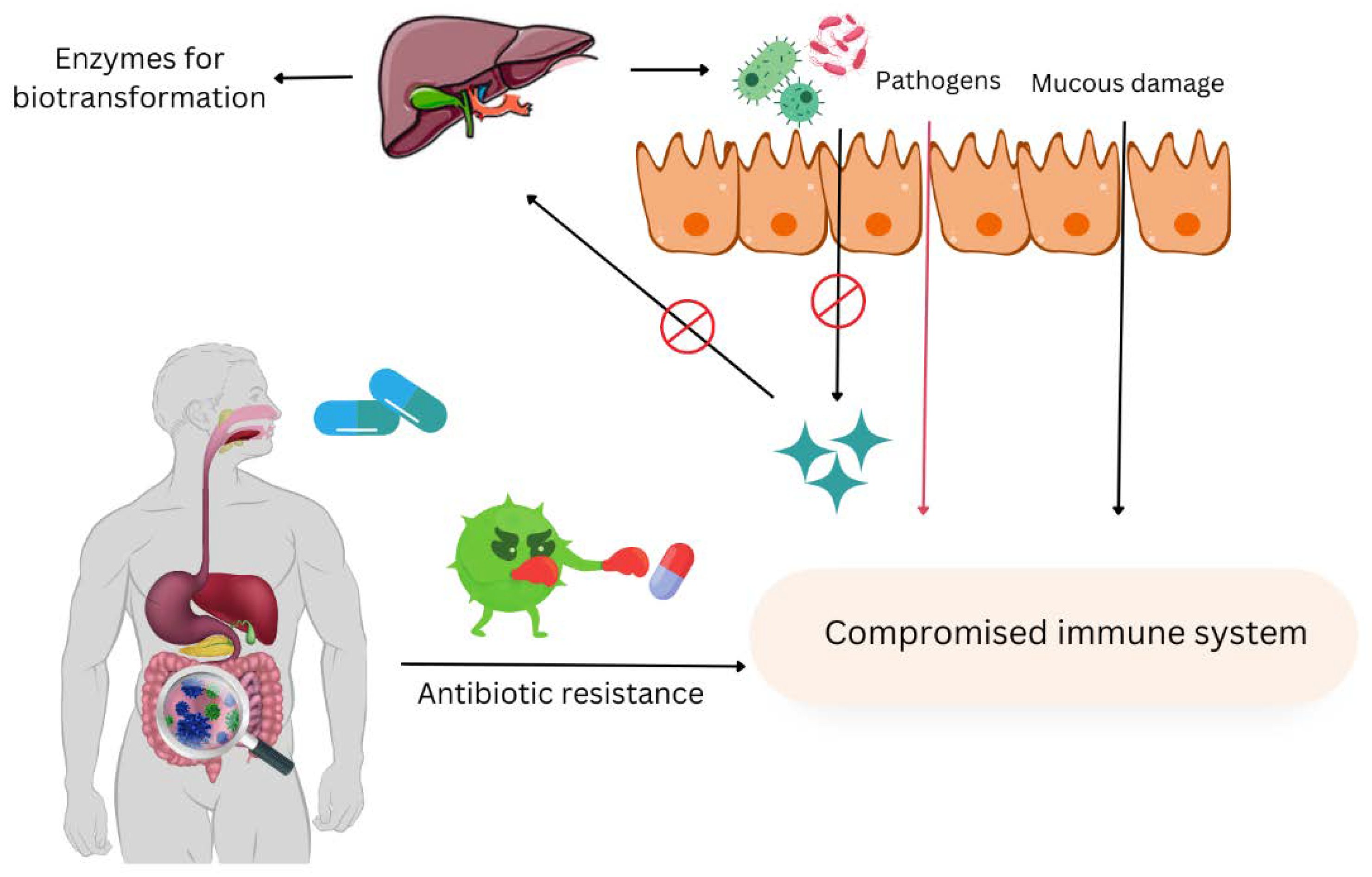
Figure 1.
The negative effects of antibiotic misuse on host health.
Figure 1.
The negative effects of antibiotic misuse on host health.
One of the key examples illustrating the impact of gut microbiota on antibiotic therapy selection is the interaction between the gut microbiota and the antibiotic vancomycin. The gut microbiota can modulate the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of vancomycin by altering its absorption, distribution, and metabolism, as well as its ability to elicit an immune response [
36]. Furthermore, gut microbiota dysbiosis caused by vancomycin treatment has been associated with increased susceptibility to
Clostridium difficile infection. A study by Buffie et al. reported that the administration of a single clindamycin dose resulted in a significant reduction in the diversity of the intestinal microbiota for a minimum of 28 days. Moreover, caused a long-term reduction of approximately 90% of the normal microbial taxa present in the cecum [
37].
An example of persistors is
Staphylococcus aureus, it acquires antibiotic resistance easily. Even the most susceptible
S. aureus survives and persists the antibiotic therapy. It requires prolonged surgical interventions and treatments. They tolerate high concentrations of antibiotics, display the phenotype of arrested growth, and are are linked with recurrent and chronic infections [
38]. Huemer et al. in their study characterize these persisters. Multiomics analysis recognized molecular fluctuations in
S. aureus in reaction to acid stress paving to a general infectious population. They persist also due to molecular reprogramming such as ribosomal protein upregulation, downregulation of virulence, amino acid pathways, cell division, ATP levels, lowered aconitase activity, and accretion of insoluble proteins used in translation, transcription, and energy production. They showed that a directed antipersister therapy by the use of retinoid byproducts and antibiotics helps to eliminate persistiors to some extent [
39].
Furthermore, it has been shown that gut microbiota can contribute to antibiotics-related toxicity. Antibiotics can disrupt the gut microbiota which leads to the overgrowth of pathogenic bacteria such as
Clostridium difficile, an etiological factor for severe diarrhea and colitis [
33]. Additionally, alterations in the gut microbiota can lead to changes in the production of microbial metabolites such as indoles and bile acids. These metabolites can modulate the absorption and distribution of antibiotics as well as influence the host immune response to infection [
40]. For example, a recent study by Chimerel et al. demonstrated that the gut microbiota-derived metabolite indole propionic acid can enhance the efficacy of certain antibiotics by increasing their penetration into bacterial cells and modulating the host immune response [
41].
Use of diagnostic techniques in understanding role of gut microbiota in antibiotic therapy
The recent advancements in various molecular techniques such as metagenomics, transcriptomics, and metabolomics have significantly contributed to our understanding of the role of gut microbiota in antibiotic therapy selection. Metagenomics has enabled the sequencing and analysis of total genomic content of microbiota which facilitate the identification of specific bacterial taxa and their functional genes [
42]. This approach has led to the discovery of particular genes associated with antibiotic resistance within the gut microbiota which can guide optimum antibiotic therapy selection to minimize resistance development [
43]. On the other hand, transcriptomics focuses on the analysis of the total RNA transcripts within a microbial community which reveals the active metabolic pathways and functions of the gut microbiota [
44]. Transcriptomic studies have demonstrated the differential expression of genes involved in antibiotic resistance and metabolism in response to antibiotic exposure [
45]. This approach can help identify differentially expressed genes involved in antibiotic resistance, metabolism, and host-microbiota interactions. For instance, transcriptomic analyses can reveal the expression of efflux pumps, enzymes, and other factors that contribute to antibiotic resistance in gut bacteria [
46]. Metabolomics is a field of study that employs a comprehensive analytical approach to elucidate the small molecules (metabolites) synthesized by the gut microbiota and their host [
47]. This discipline has facilitated the identification of specific metabolites such as short-chain fatty acids that can modulate the absorption and distribution of antibiotics. Furthermore, metabolomic analyses have uncovered the ability of gut microbiota-derived short-chain fatty acids to modulate the function of immune cells and enhance the efficacy of specific antibiotics against bacterial infections [
48].
3. Antibiotic resistance mitigation by gut microbiota
The gut microbiota has been shown to play a significant role in the development and mitigation of antibiotic resistance [
49]. Antibiotic resistance occurs when bacteria adapt to the effects of antibiotics which ultimately render them ineffective. The understanding of the mechanisms by which the gut microbiota mitigates antibiotic resistance is essential in order to develop novel therapeutic strategies to preserve the efficacy of existing antibiotics. The gut microbiota acts as a reservoir for antibiotic resistance genes that can be horizontally transferred between bacterial species. This process allows bacteria to acquire new resistance mechanisms and contribute to the spread of multidrug-resistant pathogens [
50].
3.1. Competitive exclusion
One of the mechanisms through which the gut microbiota mitigates antibiotic resistance is competitive exclusion where beneficial commensal bacteria in the gut prevent the colonization and growth of resistant pathogens [
51]. Beneficial commensal bacteria in the gut outcompete resistant pathogens by limiting their access to limited resources such as nutrients. This competitive environment can reduce the opportunity for horizontal gene transfer and limit the spread of resistance genes [
52]. By occupying essential niches and utilizing available nutrients, commensal bacteria can outcompete and inhibit the proliferation of antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Furthermore, certain commensal bacteria such as
Bifidobacterium and
Lactobacillus species produce antimicrobial compounds that directly target pathogenic bacteria which further restricts their growth and minimizes the emergence of resistance [
53].
3.2. Colonization resistance
Colonization resistance is a crucial mechanism that aids in reducing antibiotic resistance by impeding the colonization of pathogens in the gut through the production of antimicrobial agents and alteration of the local environment [
54]. The commensal microbiota generates bacteriocins which are protein toxins with antimicrobial properties that selectively inhibit the growth of related bacterial strains, including antibiotic-resistant strains [
55]. During colonization resistance, the gut microbiota helps maintain a stable and diverse microbial community, thereby limiting the establishment of antibiotic-resistant pathogens. A diverse gut microbiota also plays a critical role in maintaining a balanced immune response which can help prevent the overgrowth of resistant bacteria and maintain homeostasis [
56]. Commensal bacteria can stimulate the production of host-derived antimicrobial peptides, enhance the function of immune cells, and promote the clearance of pathogens [
57]. Antibiotic treatment and other disruptions to the gut microbiota can weaken colonization resistance which can result in the expansion of resistant pathogens. Therefore, preserving a diverse and healthy gut microbiota is necessary to combat antibiotic resistance [
58].
The use of narrow-spectrum antibiotics can preserve colonization resistance and minimize the emergence of antibiotic resistance [
59]. Certain commensal bacterial strains have been shown to degrade antibiotics which reduce their selective pressure on the gut microbiota and limit the development of resistance. This phenomenon can potentially slow down the development of resistance by lowering the exposure of bacteria to antibiotics. However, the extent to which the gut microbiota impacts the pharmacokinetics of antibiotics and the development of resistance remains an area of ongoing investigation [
60,
61].
Mechanisms of clonization resistance
There are two types of mechanisms in colonization resistance: direct and indirect. The direct mechanism is characterized by the ability of gut microbiota to limit colonization by intestinal pathogens, or the over progression of these pathogens after embedding, and those liberated from the host. Dietary complex carbohydrates and mucins are crucial colonic nutritious means to which commensal types have adapted through definite metabolic paths[
62]. Enteropathogens regularly use nourishing sources presented by commensal types [
63]. For instance,
Citrobacter rodentium and
E. coli may be in rivalry for the absorption of monosaccharides. Though, some pathogenic microbes may use gastrointestinal nutrients that commensals cannot digest. For instance, ethanolamine is a nitrogen and carbon source for Entero-Haemorrhagic
E. coli (EHEC),
S. Typhimurium,
Klebsiella,
C. difficile,
Listeria monocytogenes , and
Pseudomonas, however, cannot be utilized by a maximum of the commensal species [
64]. Particularly EHEC species have advanced metabolic paths for discrete sugar resources, more or less of which are unreachable to commensal
E. coli [
65]. Interestingly, EHEC can be disinterested from its metabolic position, in the existence of two dissimilar strains of
E. coli and might fail to form a colony in the gut [
66].
Cell wall-active bactericidal polypeptides produced by the commensal microbes generally are called bacteriocins. Bacteriocins produced by the Gram-negative bacteria are named microcins and they have a fine spectrum of action restricted to new Gram-negative microbes [
67]. Microcins cause internalization and thus apply their inhibitory influence and restrict the colonization of microbes [
68]. Indirect Mechanisms: host and commensal flora interaction result in colonization resistance indirectly. This happens through RegIIIγ and angiotensin-4 (antimicrobial peptides), bile acid metabolism, and epithelial barrier mechanism. The production of antimicrobial peptides is regulated by the microbes. Microbiota can stimulate the production of RegIIIγ by stimulating TLRs (Troll like receptors), mainly TLR-4 through the lipopolysaccharides [
69]. In the epithelial barrier mechanism, a decrease in the thickness of the mucus layer will result in enhanced pathogen colonization susceptibility. Antibiotic therapy, western-style diet, and drugs that have impacts on the microbiota will consequence in increased colonization susceptibility and thickness of the mucus layer [
70].
In the case of bile acid metabolisms, reabsorption of primary bile acids occur in the terminal of the ileum, however, only a small fraction also reaches the large intestine, where the subset of colonic bacteria converts primary bile acids into secondary bile acids. Different bile acids affect differently on the vegetative growth and germination process. For example, taurocholic acid, a primary bile acid has an impact on germination induction in the
C. difficile spores, while secondary bile acids are well known to cause an inhibition in the growth of toxin-producing, vegetative
C. difficile [
71].
Clostridium scindens can convert chenodeoxycholic acid and cholic acid (primary bile acids) to lithocholic acid and deoxycholic acid (secondary bile acids). As a result,
C. scindens increase resistance to infections by
C. difficile in both human patients and animals through secondary bile acid-dependent functions [
72].
3.3. Use of diagnostic techniques in antibiotic resistance mitigation by gut microbiota
The role of different molecular techniques has been instrumental in studying the role of gut microbiota in mitigating antibiotic resistance. Metagenomic analyses can identify the presence and abundance of antibiotic resistance genes within the gut microbiota [
73]. Transcriptomic and proteomic approaches can reveal the expression patterns of resistance genes and help elucidate the mechanisms through which gut microbes interact with antibiotics [
74,
75]. Metabolomics provides a functional readout of the gut microbiota by identifying metabolites involved in antibiotic resistance or those that could be used to enhance the efficacy of existing antibiotics [
76].
Furthermore, recent advances in NGS technologies such as long-read sequencing and metagenomic assembly have enabled the identification and characterization of novel antibiotic resistance genes and mobile genetic elements that contribute to the spread of antibiotic resistance within the gut microbiota [
77]. These technological advancements have also facilitated the discovery of previously unknown associations between commensal bacteria, pathogens, and host immune responses. In recent times, various research inquiries have employed molecular methodologies to investigate the interplay between the gut microbiota and the management of antibiotic resistance. Metagenomic analyses have been utilized to explore the gut microbiota's capacity to support resistance gene transfer, leading to the revelation that specific environmental factors such as antibiotic exposure may foster horizontal gene transfer and the evolution of resistance [
78].
3.4. Probiotics, Prebiotics, and fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT)
The modulation of gut microbiota is a promising strategy for mitigating antibiotic resistance. Probiotics, prebiotics, and fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) are potential interventions that can be used for this purpose. Probiotics are living microorganisms that when consumed in appropriate quantities bestow a health benefit on the host by enhancing the resistance of gut microbiota against pathogenic organisms and antibiotic-induced perturbations [
79]. Prebiotics, on the other hand are indigestible food components that selectively promote the growth and activity of beneficial bacteria in the gut [
80]. FMT involves the transfer of fecal material containing healthy donor microbiota into a recipient. This technique has been shown to restore the diversity and function of gut microbiota [
81]. Clinical studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of FMT in treating recurrent
Clostridioides difficile infections and reducing the prevalence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria in the gut [
82]. A randomized control trial by Huttner et al. showed that 5-day course of non-absorbable antibiotics followed by FMT decreased extended spectrum β-lactamase
Enterobacteriaceae (ESBL-E) and carbapenemase-producing
Enterobacteriaceae (CPE) carriage compared with controls [
83].
Additionally, the application of bacteriophages has been proposed as an alternative to conventional antibiotics with the potential to specifically target resistant bacteria without disrupting the overall gut microbial community [
84].
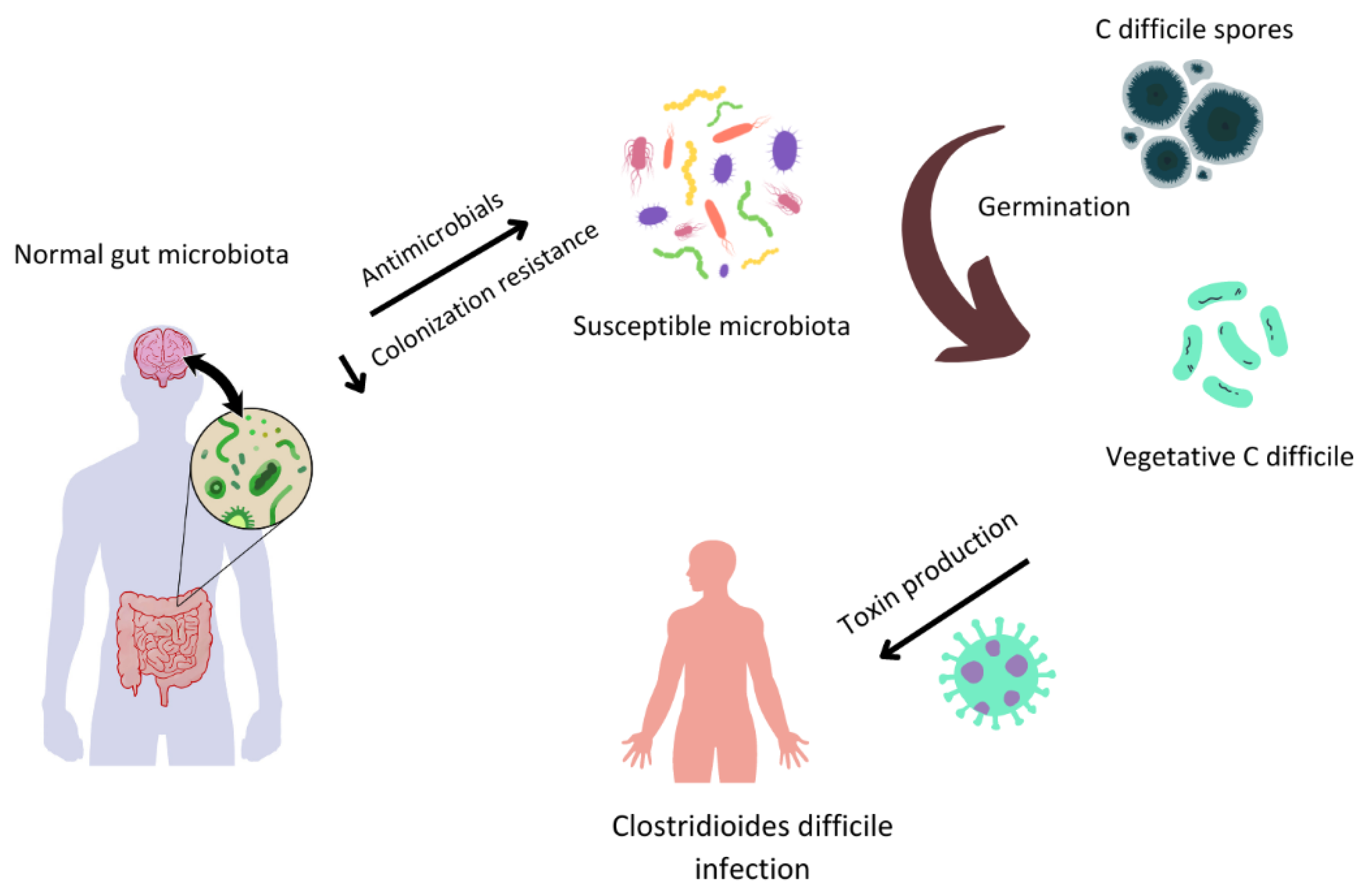
Figure 2.
Gut microbiota and Clostridioides difficile infection (CDI).
Figure 2.
Gut microbiota and Clostridioides difficile infection (CDI).
4. Clinical applications of gut microbiota research for antibiotic therapy selection
By understanding the complex interactions between the gut microbiota, antibiotics, and host immune responses, clinicians can attain greater acuity in antibiotic selection and implement measures to attenuate resistance. Furthermore, recent advances in omics technologies have facilitated the development of rapid diagnostic tools that can assess the gut microbiota's composition and function, providing real-time information to guide clinical decision-making [
85]. Gut microbiota research can contribute to clinical decision-making by pinpointing specific bacterial strains and their susceptibility profiles to antibiotics in an individual's gut microbiota. Such insights can facilitate personalized antibiotic therapy selection, curtail the risk of treatment failure or resistance emergence [
86]. For instance, metagenomic sequencing can furnish pertinent information about the prevalence of antibiotic resistance genes in a patient's gut microbial community, thereby empowering clinicians to opt for antibiotics that are less prone to favor resistant bacteria[
87]. These tools can help clinicians monitor the effects of antibiotics on the gut microbiota and identify early signs of resistance development or dysbiosis, allowing for timely intervention and adjustment of antibiotic regimens.
Moreover, research into the use of probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics as adjuvant therapies has shown promise in improving antibiotic efficacy and reducing resistance development. In a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, Reid et al. demonstrated that the administration of a
Lactobacillus rhamnosus probiotic alongside antibiotic treatment for bacterial vaginosis resulted in higher cure rates and fewer recurrences compared to the antibiotic treatment alone [
88]. Similarly, a study by Timmerman et al. found that synbiotic supplementation in critically ill patients receiving antibiotics led to improved gut permeability, a reduced incidence of antibiotic-associated diarrhea, and a lower abundance of potentially pathogenic bacteria in the gut [
89]. The integration of gut microbiota research into clinical decision-making for antibiotic therapy selection and resistance mitigation is still in its early stages, with many challenges remaining. For instance, translating research findings into clinically relevant guidelines and protocols requires a thorough understanding of the complex interactions between the gut microbiota, host immune system, and antibiotics, as well as the development of standardized methodologies for assessing the gut microbiota.
Furthermore, the implementation of gut microbiota-based diagnostics and therapeutics in clinical settings faces several practical barriers such as the need for specialized equipment, trained personnel, and rigorous quality control measures to ensure the accuracy and reproducibility of results [
90]. Furthermore, the use of FMT and other microbiota-targeted interventions raises questions about the long-term safety and efficacy of these therapies, as well as potential unintended consequences on the recipient's health [
91]. Despite the challenges, clinical applications of gut microbiota research for antibiotic therapy selection and resistance mitigation hold great promise for improving patient outcomes. By leveraging cutting-edge molecular techniques and a growing understanding of the complex interactions between the gut microbiota, antibiotics, and host immune responses, clinicians can make more informed decisions about antibiotic selection, dosing, and duration, as well as implement strategies to mitigate resistance and restore gut microbial health.
5. Current challenges and future directions
The investigation of gut microbiota has the potential to significantly influence the selection of antibiotic therapy and the mitigation of resistance. However, the field faces various challenges. One such challenge is the standardization of techniques and interpretation of results as the field currently lacks universally accepted methodologies and reporting standards. The inconsistency in sample collection, processing, sequencing, and data analysis can result in variations in findings which obstruct the translation of research outcomes into clinical practice [
92]. To address these challenges, researchers are working to develop new analytical methods and establish guidelines for reporting gut microbiota data. Projects like the International Human Microbiome Standards (IHMS) initiative aim to create standardized protocols for sample collection, processing, and data analysis [
93]. These protocols enable stronger comparisons across research and facilitate the integration of gut microbiota research into clinical decision-making. Furthermore, the advancement of bioinformatics tools and platforms, such as QIIME 2 and MetaPhlAn, can aid researchers in profiling and analyzing gut microbiota data with precision and facilitate dependable and reproducible outcomes [
94,
95].
Future research directions in the field include investigating the role of the gut microbiota in antibiotic stewardship and optimizing personalized medicine approaches. Antibiotic stewardship programs could greatly benefit from a better understanding of the role of the gut microbiota in antibiotic response and resistance development [
96]. By incorporating gut microbiota research into antibiotic stewardship efforts, healthcare providers can make more informed decisions about when and how to use antibiotics, ultimately preserving their effectiveness and minimizing the risk of resistance [
97]. Personalized medicine approaches that utilize individualized gut microbiota profiles to tailor antibiotic therapy have considerable potential for enhancing patient outcomes. The identification of specific bacterial strains and their susceptibility patterns within the gut microbiota of an individual via metagenomic and metatranscriptomic analyses can enable the selection of precisely targeted antibiotic regimens [
72]. Furthermore, the exploration of adjuvant therapies such as probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics may facilitate the development of customized strategies to re-establish gut microbial balance and ameliorate the deleterious effects of antibiotic therapy [
98].
7. Conclusions
In conclusion, the emerging field of gut microbiota research holds tremendous potential for revolutionizing antibiotic therapy selection and resistance mitigation strategies. The intricate interplay between the gut microbiota, antibiotic therapy, and antibiotic resistance underscores the importance of incorporating this research into clinical practice. By addressing the challenges and future directions associated with this field, including standardization of methodologies, ethical considerations, and interdisciplinary collaboration, we can pave the way for the integration of gut microbiota research into antibiotic therapy and resistance mitigation efforts. Harnessing the power of gut microbiota research can not only optimize antibiotic use and preserve the efficacy of these lifesaving drugs but also significantly contribute to combating the global threat of antibiotic resistance. Furthermore, the development and validation of novel diagnostic tools, therapeutic interventions, and predictive models will facilitate the practical implementation of gut microbiota research findings in clinical settings. By maintaining an agile and responsive research environment, the scientific community can swiftly adapt to new findings and challenges, driving the field of gut microbiota research forward and making significant strides towards better antibiotic therapy selection and resistance mitigation.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.A.; methodology, M.A..; validation, M.A.; formal analysis, M.A..; investigation, M.A..;. resources, M.A.; data curation M.A. ; writing—original draft preparation, M.A.; writing—review and editing M.A.; visualization, M.A.; supervision, M.A.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Dixit, A.; Kumar, N.; Kumar, S.; Trigun, V. Antimicrobial resistance: progress in the decade since emergence of New Delhi metallo-β-lactamase in India. Indian journal of community medicine: official publication of Indian Association of Preventive & Social Medicine 2019, 44, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, T.; Xu, N.; Lu, T.; Hong, W.; Penuelas, J.; Gillings, M.; Wang, M.; Gao, W.; et al. Assessment of global health risk of antibiotic resistance genes. Nature Communications 2022, 13, 1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O'Neill, J. Tackling drug-resistant infections globally: final report and recommendations. 2016.
- Micoli, F.; Bagnoli, F.; Rappuoli, R.; Serruto, D. The role of vaccines in combatting antimicrobial resistance. Nature Reviews Microbiology 2021, 19, 287–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luepke, K.H.; Mohr III, J.F. The antibiotic pipeline: reviving research and development and speeding drugs to market. Expert review of anti-infective therapy 2017, 15, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theuretzbacher, U.; Outterson, K.; Engel, A.; Karlén, A. The global preclinical antibacterial pipeline. Nature Reviews Microbiology 2020, 18, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cani, P.D. Gut microbiota—at the intersection of everything? Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology 2017, 14, 321–322. [Google Scholar]
- Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Gut microbes and depression: still waiting for godot. Brain, Behavior, and Immunity 2019, 79, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jameson, K.G.; Hsiao, E.Y. Linking the gut microbiota to a brain neurotransmitter. Trends in Neurosciences 2018, 41, 413–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deidda, G.; Biazzo, M. Gut and brain: investigating physiological and pathological interactions between microbiota and brain to gain new therapeutic avenues for brain diseases. Frontiers in Neuroscience 2021, 15, 753915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, G.; Grenham, S.; Scully, P.; Fitzgerald, P.; Moloney, R.D.; Shanahan, F.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. The microbiome-gut-brain axis during early life regulates the hippocampal serotonergic system in a sex-dependent manner. Molecular Psychiatry 2013, 18, 666–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schluter, J.; Peled, J.U.; Taylor, B.P.; Markey, K.A.; Smith, M.; Taur, Y.; Niehus, R.; Staffas, A.; Dai, A.; Fontana, E. The gut microbiota is associated with immune cell dynamics in humans. Nature 2020, 588, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Vos, W.M.; Tilg, H.; Van Hul, M.; Cani, P.D. Gut microbiome and health: mechanistic insights. Gut 2022, 71, 1020–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Treuren, W.; Dodd, D. Microbial contribution to the human metabolome: implications for health and disease. Annual Review of Pathology: Mechanisms of Disease 2020, 15, 345–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Covington, A.; Pamer, E.G. The intestinal microbiota: antibiotics, colonization resistance, and enteric pathogens. Immunological reviews 2017, 279, 90–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isaac, S.; Scher, J.U.; Djukovic, A.; Jiménez, N.; Littman, D.R.; Abramson, S.B.; Pamer, E.G.; Ubeda, C. Short-and long-term effects of oral vancomycin on the human intestinal microbiota. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 2016, 72, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sperandio, V.; Frankel, G. Editorial overview: Host-microbe interactions: friends, foes and frenemies. Current Opinion in Microbiology 2022, 65, viii. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, R.; Vrbanac, A.; Taylor, B.C.; Aksenov, A.; Callewaert, C.; Debelius, J.; Gonzalez, A.; Kosciolek, T.; McCall, L.-I.; McDonald, D. Best practices for analysing microbiomes. Nature Reviews Microbiology 2018, 16, 410–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Schwartzenberg, R.J.; Bisanz, J.E.; Lyalina, S.; Spanogiannopoulos, P.; Ang, Q.Y.; Cai, J.; Dickmann, S.; Friedrich, M.; Liu, S.-Y.; Collins, S.L. Caloric restriction disrupts the microbiota and colonization resistance. Nature 2021, 595, 272–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gacesa, R.; Kurilshikov, A.; Vich Vila, A.; Sinha, T.; Klaassen, M.; Bolte, L.; Andreu-Sánchez, S.; Chen, L.; Collij, V.; Hu, S. Environmental factors shaping the gut microbiome in a Dutch population. Nature 2022, 604, 732–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pamer, E.G. Resurrecting the intestinal microbiota to combat antibiotic-resistant pathogens. Science 2016, 352, 535–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooijevaar, R.E.; Terveer, E.M.; Verspaget, H.W.; Kuijper, E.J.; Keller, J.J. Clinical application and potential of fecal microbiota transplantation. Annual review of medicine 2019, 70, 335–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patangia, D.V.; Anthony Ryan, C.; Dempsey, E.; Paul Ross, R.; Stanton, C. Impact of antibiotics on the human microbiome and consequences for host health. MicrobiologyOpen 2022, 11, e1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirsepasi, H.; Persson, S.; Struve, C.; Andersen, L.O.; Petersen, A.M.; Krogfelt, K.A. Microbial diversity in fecal samples depends on DNA extraction method: easyMag DNA extraction compared to QIAamp DNA stool mini kit extraction. BMC research notes 2014, 7, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McOrist, A.L.; Miller, R.B.; Bird, A.R.; Keogh, J.B.; Noakes, M.; Topping, D.L.; Conlon, M.A. Fecal Butyrate Levels Vary Widely among Individuals but Are Usually Increased by a Diet High in Resistant Starch1,2. The Journal of Nutrition 2011, 141, 883–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scher, J.U.; Nayak, R.R.; Ubeda, C.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Abramson, S.B. Pharmacomicrobiomics in inflammatory arthritis: gut microbiome as modulator of therapeutic response. Nature Reviews Rheumatology 2020, 16, 282–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levison, M.E.; Levison, J.H. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of antibacterial agents. Infectious Disease Clinics 2009, 23, 791–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vrieze, A.; Out, C.; Fuentes, S.; Jonker, L.; Reuling, I.; Kootte, R.S.; van Nood, E.; Holleman, F.; Knaapen, M.; Romijn, J.A. Impact of oral vancomycin on gut microbiota, bile acid metabolism, and insulin sensitivity. Journal of hepatology 2014, 60, 824–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, R. Gut microbiota modulates drug pharmacokinetics. Drug metabolism reviews 2018, 50, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, E.M.; Ilhan, Z.E.; Herbst-Kralovetz, M.M. Microbiota–drug interactions: Impact on metabolism and efficacy of therapeutics. Maturitas 2018, 112, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enright, E.F.; Griffin, B.T.; Gahan, C.G.; Joyce, S.A. Microbiome-mediated bile acid modification: role in intestinal drug absorption and metabolism. Pharmacological Research 2018, 133, 170–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belkaid, Y.; Hand, T.W. Role of the microbiota in immunity and inflammation. Cell 2014, 157, 121–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becattini, S.; Taur, Y.; Pamer, E.G. Antibiotic-induced changes in the intestinal microbiota and disease. Trends in molecular medicine 2016, 22, 458–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.; Qie, Y.; Park, J.; Kim, Chang H. Gut Microbial Metabolites Fuel Host Antibody Responses. Cell Host & Microbe 2016, 20, 202–214. [CrossRef]
- Crofts, T.S.; Gasparrini, A.J.; Dantas, G. Next-generation approaches to understand and combat the antibiotic resistome. Nature Reviews Microbiology 2017, 15, 422–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmermann, M.; Zimmermann-Kogadeeva, M.; Wegmann, R.; Goodman, A.L. Mapping human microbiome drug metabolism by gut bacteria and their genes. Nature 2019, 570, 462–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buffie, C.G.; Jarchum, I.; Equinda, M.; Lipuma, L.; Gobourne, A.; Viale, A.; Ubeda, C.; Xavier, J.; Pamer, E.G. Profound alterations of intestinal microbiota following a single dose of clindamycin results in sustained susceptibility to Clostridium difficile-induced colitis. Infection and immunity 2012, 80, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.; Lee, R.-E.; Lee, W. A pursuit of Staphylococcus aureus continues: a role of persister cells. Archives of Pharmacal Research 2020, 43, 630–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huemer, M.; Mairpady Shambat, S.; Brugger, S.D.; Zinkernagel, A.S. Antibiotic resistance and persistence—Implications for human health and treatment perspectives. EMBO reports 2020, 21, e51034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Sperandio, V. Indole signaling at the host-microbiota-pathogen interface. MBio 2019, 10, e01031–01019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chimerel, C.; Emery, E.; Summers, D.K.; Keyser, U.; Gribble, F.M.; Reimann, F. Bacterial metabolite indole modulates incretin secretion from intestinal enteroendocrine L cells. Cell reports 2014, 9, 1202–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forslund, K.; Sunagawa, S.; Kultima, J.R.; Mende, D.R.; Arumugam, M.; Typas, A.; Bork, P. Country-specific antibiotic use practices impact the human gut resistome. Genome research 2013, 23, 1163–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quince, C.; Walker, A.W.; Simpson, J.T.; Loman, N.J.; Segata, N. Correction: Corrigendum: Shotgun metagenomics, from sampling to analysis. Nature biotechnology 2017, 35, 1211–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajilić-Stojanović, M.; De Vos, W.M. The first 1000 cultured species of the human gastrointestinal microbiota. FEMS microbiology reviews 2014, 38, 996–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plichta, D.; Juncker, A.; Bertalan, M.; Rettedal, E.; Gautier, L.; Varela, E.; Manichanh, C.; Fouqueray, C.; Levenez, F.; Nielsen, T. Metagenomics of the Human Intestinal Tract (MetaHIT) Consortium. 2016. Transcriptional interactions suggest niche segregation among microorganisms in the human gut. Nat Microbiol 1: 16152. 2016.
- Rajput, A.; Tsunemoto, H.; Sastry, A.V.; Szubin, R.; Rychel, K.; Chauhan, S.M.; Pogliano, J.; Palsson, B.O. Advanced transcriptomic analysis reveals the role of efflux pumps and media composition in antibiotic responses of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Nucleic acids research 2022, 50, 9675–9688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sartor, R.B.; Wu, G.D. Roles for intestinal bacteria, viruses, and fungi in pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel diseases and therapeutic approaches. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Z.; Li, M.; Qian, M.; Yang, Z.; Han, X. Co-Cultures of Lactobacillus acidophilus and Bacillus subtilis Enhance Mucosal Barrier by Modulating Gut Microbiota-Derived Short-Chain Fatty Acids. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, E.D.; Wright, G.D. Antibacterial drug discovery in the resistance era. Nature 2016, 529, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullany, P. Functional metagenomics for the investigation of antibiotic resistance. Virulence 2014, 5, 443–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassone-Corsi, M.; Raffatellu, M. No vacancy: how beneficial microbes cooperate with immunity to provide colonization resistance to pathogens. The Journal of Immunology 2015, 194, 4081–4087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchesi, J.R.; Ravel, J. The vocabulary of microbiome research: a proposal. Springer: 2015; Vol. 3, pp 1-3.
- Milani, C.; Duranti, S.; Bottacini, F.; Casey, E.; Turroni, F.; Mahony, J.; Belzer, C.; Delgado Palacio, S.; Arboleya Montes, S.; Mancabelli, L. The first microbial colonizers of the human gut: composition, activities, and health implications of the infant gut microbiota. Microbiology and molecular biology reviews 2017, 81, e00036–00017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawley, T. Сolonization resistance [Electronic resource]. Immunology 2013, 138, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.-C.; Lin, C.-H.; Sung, C.T.; Fang, J.-Y. Antibacterial activities of bacteriocins: application in foods and pharmaceuticals. Frontiers in microbiology 2014, 5, 241. [Google Scholar]
- Belkaid, Y.; Harrison, O.J. Homeostatic immunity and the microbiota. Immunity 2017, 46, 562–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honda, K.; Littman, D.R. The microbiota in adaptive immune homeostasis and disease. Nature 2016, 535, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunham, J.; Van Driel, N.; Eggen, B.J.; Paul, C.; ‘t Hart, B.A.; Laman, J.D.; Kap, Y.S. Analysis of the cross-talk of Epstein–Barr virus-infected B cells with T cells in the marmoset. Clinical & translational immunology 2017, 6, e127. [Google Scholar]
- Abt, M.C.; Buffie, C.G.; Sušac, B.; Becattini, S.; Carter, R.A.; Leiner, I.; Keith, J.W.; Artis, D.; Osborne, L.C.; Pamer, E.G. TLR-7 activation enhances IL-22–mediated colonization resistance against vancomycin-resistant enterococcus. Science translational medicine 2016, 8, 327ra325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maier, L.; Pruteanu, M.; Kuhn, M.; Zeller, G.; Telzerow, A.; Anderson, E.E.; Brochado, A.R.; Fernandez, K.C.; Dose, H.; Mori, H. Extensive impact of non-antibiotic drugs on human gut bacteria. Nature 2018, 555, 623–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palomo, A.; Jane Fowler, S.; Gülay, A.; Rasmussen, S.; Sicheritz-Ponten, T.; Smets, B.F. Metagenomic analysis of rapid gravity sand filter microbial communities suggests novel physiology of Nitrospira spp. The ISME journal 2016, 10, 2569–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Ho, S.B. Intestinal goblet cells and mucins in health and disease: recent insights and progress. Current gastroenterology reports 2010, 12, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamada, N.; Kim, Y.-G.; Sham, H.P.; Vallance, B.A.; Puente, J.L.; Martens, E.C.; Núñez, G. Regulated virulence controls the ability of a pathogen to compete with the gut microbiota. Science 2012, 336, 1325–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garsin, D.A. Ethanolamine utilization in bacterial pathogens: roles and regulation. Nature Reviews Microbiology 2010, 8, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabich, A.J.; Jones, S.A.; Chowdhury, F.Z.; Cernosek, A.; Anderson, A.; Smalley, D.; McHargue, J.W.; Hightower, G.A.; Smith, J.T.; Autieri, S.M. Comparison of carbon nutrition for pathogenic and commensal Escherichia coli strains in the mouse intestine. Infection and immunity 2008, 76, 1143–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maltby, R.; Leatham-Jensen, M.P.; Gibson, T.; Cohen, P.S.; Conway, T. Nutritional basis for colonization resistance by human commensal Escherichia coli strains HS and Nissle 1917 against E. coli O157: H7 in the mouse intestine. PloS one 2013, 8, e53957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boakes, S.; Ayala, T.; Herman, M.; Appleyard, A.N.; Dawson, M.J.; Cortés, J. Generation of an actagardine A variant library through saturation mutagenesis. Applied microbiology and biotechnology 2012, 95, 1509–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallares, R.M.; Carter, K.P.; Faulkner, D.; Abergel, R.J. Macromolecular crystallography for f-element complex characterization. In Methods in enzymology, Elsevier: 2021; Vol. 651, pp. 139–155.
- Mukherjee, S.; Zheng, H.; Derebe, M.G.; Callenberg, K.M.; Partch, C.L.; Rollins, D.; Propheter, D.C.; Rizo, J.; Grabe, M.; Jiang, Q.-X. Antibacterial membrane attack by a pore-forming intestinal C-type lectin. Nature 2014, 505, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, M.S.; Seekatz, A.M.; Koropatkin, N.M.; Kamada, N.; Hickey, C.A.; Wolter, M.; Pudlo, N.A.; Kitamoto, S.; Terrapon, N.; Muller, A. A dietary fiber-deprived gut microbiota degrades the colonic mucus barrier and enhances pathogen susceptibility. Cell 2016, 167, 1339–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarchum, I.; Liu, M.; Lipuma, L.; Pamer, E.G. Toll-like receptor 5 stimulation protects mice from acute Clostridium difficile colitis. Infection and immunity 2011, 79, 1498–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buffie, C.G.; Bucci, V.; Stein, R.R.; McKenney, P.T.; Ling, L.; Gobourne, A.; No, D.; Liu, H.; Kinnebrew, M.; Viale, A. Precision microbiome reconstitution restores bile acid mediated resistance to Clostridium difficile. Nature 2015, 517, 205–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G.; Li, B.; Li, L.-G.; Zhang, T.; Angelidaki, I. Antibiotic resistance genes and correlations with microbial community and metal resistance genes in full-scale biogas reactors as revealed by metagenomic analysis. Environmental science & technology 2017, 51, 4069–4080. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, H.; He, Q.-Y.; Shi, L.; Sleeman, M.; Baker, M.S.; Nice, E.C. Proteomics and the microbiome: pitfalls and potential. Expert review of proteomics 2019, 16, 501–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whon, T.W.; Shin, N.-R.; Kim, J.Y.; Roh, S.W. Omics in gut microbiome analysis. Journal of Microbiology 2021, 59, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, K.N.; Alexander, M.; Turnbaugh, P.J. Precision medicine goes microscopic: engineering the microbiome to improve drug outcomes. Cell host & microbe 2019, 26, 22–34. [Google Scholar]
- Staff, P.O. Correction: Inexpensive Multiplexed Library Preparation for Megabase-Sized Genomes. Plos one 2015, 10, e0131262. [Google Scholar]
- Von Wintersdorff, C.J.; Penders, J.; Van Niekerk, J.M.; Mills, N.D.; Majumder, S.; Van Alphen, L.B.; Savelkoul, P.H.; Wolffs, P.F. Dissemination of antimicrobial resistance in microbial ecosystems through horizontal gene transfer. Frontiers in microbiology 2016, 7, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.-Y.; Tsolis, R.M.; Bäumler, A.J. The microbiome and gut homeostasis. Science 2022, 377, eabp9960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, P.; Flint, H.J.; Michel, C. How to manipulate the microbiota: prebiotics. Microbiota of the human body: Implications in health and disease 2016, 119-142.
- Merrick, B.; Allen, L.; Zain, N.M.M.; Forbes, B.; Shawcross, D.L.; Goldenberg, S.D. Regulation, risk and safety of faecal microbiota transplant. Infection prevention in practice 2020, 2, 100069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Schooneveld, T.C.; Gross, A.; Kalil, A.C. Duodenal infusion of feces for recurrent Clostridium difficile. N Engl J Med 2013, 368, 2143. [Google Scholar]
- Huttner, B.D.; de Lastours, V.; Wassenberg, M.; Maharshak, N.; Mauris, A.; Galperine, T.; Zanichelli, V.; Kapel, N.; Bellanger, A.; Olearo, F.; et al. A 5-day course of oral antibiotics followed by faecal transplantation to eradicate carriage of multidrug-resistant Enterobacteriaceae: a randomized clinical trial. Clinical Microbiology and Infection 2019, 25, 830–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brives, C.; Pourraz, J. Phage therapy as a potential solution in the fight against AMR: obstacles and possible futures. Palgrave Communications 2020, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzosa, E.; Huang, K.; James, F.; Meadow, J.F.; Gevers, D.; Lemon, K.P.; Bohannan, B.J.M.; Huttenhower, C. Identifying personal microbiomes using metagenomic codes. PNAS 2015, 112, E2930–E2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettigrew, M.M.; Johnson, J.K.; Harris, A.D. The human microbiota: novel targets for hospital-acquired infections and antibiotic resistance. Annals of epidemiology 2016, 26, 342–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oniciuc, E.A.; Likotrafiti, E.; Alvarez-Molina, A.; Prieto, M.; Santos, J.A.; Alvarez-Ordóñez, A. The present and future of whole genome sequencing (WGS) and whole metagenome sequencing (WMS) for surveillance of antimicrobial resistant microorganisms and antimicrobial resistance genes across the food chain. Genes 2018, 9, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reid, G.; Younes, J.A.; Van der Mei, H.C.; Gloor, G.B.; Knight, R.; Busscher, H.J. Microbiota restoration: natural and supplemented recovery of human microbial communities. Nature Reviews Microbiology 2011, 9, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vickers, N.J. Animal communication: when i’m calling you, will you answer too? Current biology 2017, 27, R713–R715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topçuoğlu, B.D.; Lesniak, N.A.; Ruffin IV, M.T.; Wiens, J.; Schloss, P.D. A framework for effective application of machine learning to microbiome-based classification problems. MBio 2020, 11, e00434–00420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cammarota, G.; Ianiro, G.; Tilg, H.; Rajilic-Stojanovic, M.; Kump, P.; Satokari, R.; Sokol, H.; Arkkila, P.; Pintus, C.; Hart, A. European FMT Working Group. Proceedings of European consensus conference on faecal microbiota transplantation in clinical practice. Gut; p. 569.
- Weiss, S.; Amir, A.; Hyde, E.R.; Metcalf, J.L.; Song, S.J.; Knight, R. Tracking down the sources of experimental contamination in microbiome studies. Genome biology 2014, 15, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costea, P.I.; Zeller, G.; Sunagawa, S.; Pelletier, E.; Alberti, A.; Levenez, F.; Tramontano, M.; Driessen, M.; Hercog, R.; Jung, F.-E. Towards standards for human fecal sample processing in metagenomic studies. Nature biotechnology 2017, 35, 1069–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat Biotechnol 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, D.T.; Franzosa, E.A.; Tickle, T.L.; Scholz, M.; Weingart, G.; Pasolli, E.; Tett, A.; Huttenhower, C.; Segata, N. MetaPhlAn2 for enhanced metagenomic taxonomic profiling. Nat Methods 2015, 12, 902–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyar, O.; Huttner, B.; Schouten, J.; Pulcini, C. What is antimicrobial stewardship? ESGAP (ESCMID Study Group for Antimicrobial stewardshiP). Clin Microbiol Infect 2017, 23, 793–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulcini, C.; Tebano, G.; Mutters, N.T.; Tacconelli, E.; Cambau, E.; Kahlmeter, G.; Jarlier, V.; Presterl, E.; Gurbanov, A.; Piérard, D. Selective reporting of antibiotic susceptibility test results in European countries: an ESCMID cross-sectional survey. International journal of antimicrobial agents 2017, 49, 162–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taur, Y.; Pamer, E.G. Harnessing microbiota to kill a pathogen: Fixing the microbiota to treat Clostridium difficile infections. Nature Medicine 2014, 20, 246–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).