Submitted:
20 May 2023
Posted:
23 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Materials and Methods
Materials
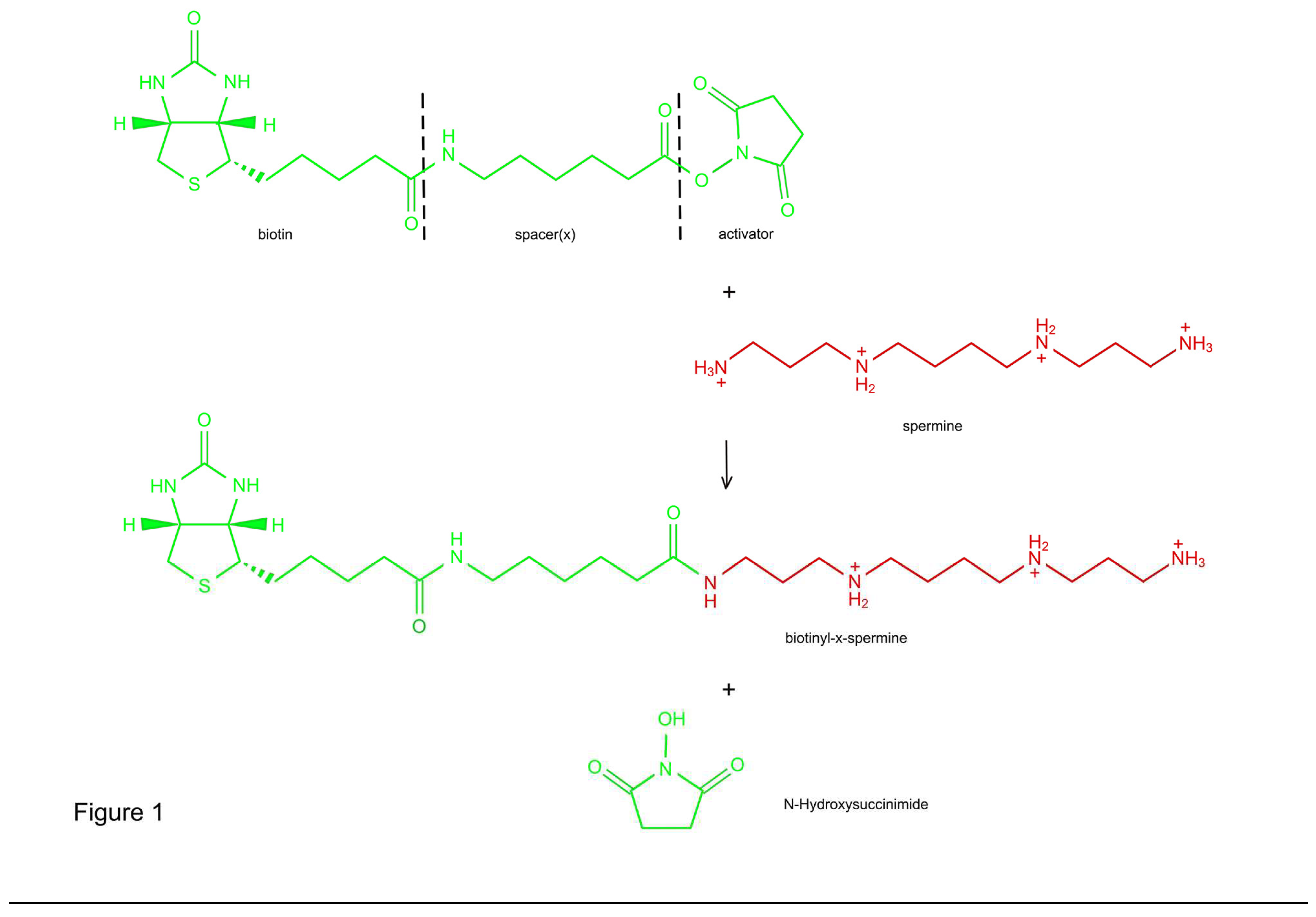
Synthesis of B-X-SPM
Characterization of B-X-SPM
Solutions and Drugs
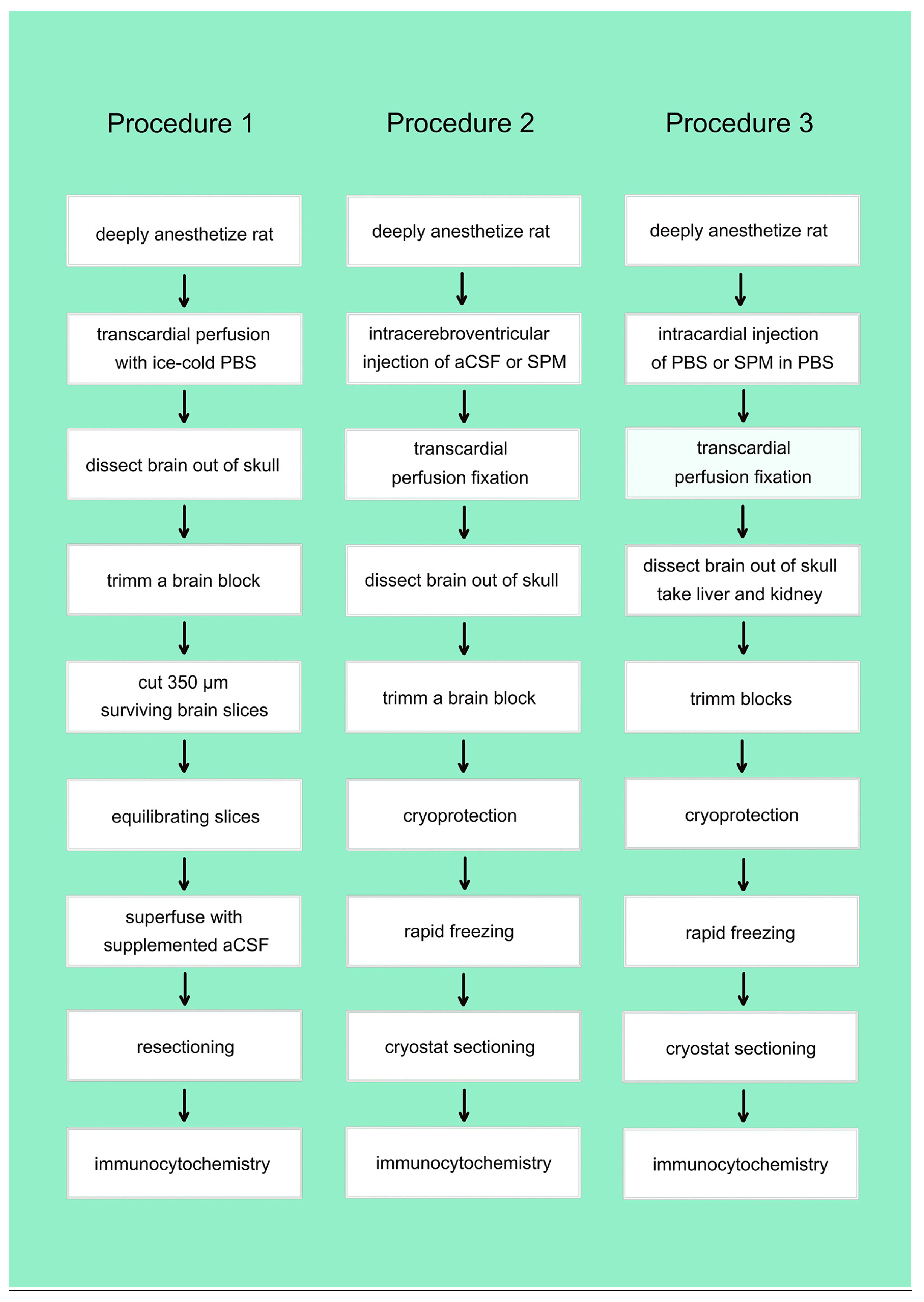
Preparation of Brain Slices
Superfusion of Brain Slices
In-Vivo Injections
Immunocytochemistry
Results
Synthesis and Characterization of Biotinylated and Extended Spermine (B-X-SPM)
In-Vitro Uptake of Native or Biotinylated SPM in Brain Slices
Uptake of Native SPM in Brain Slices
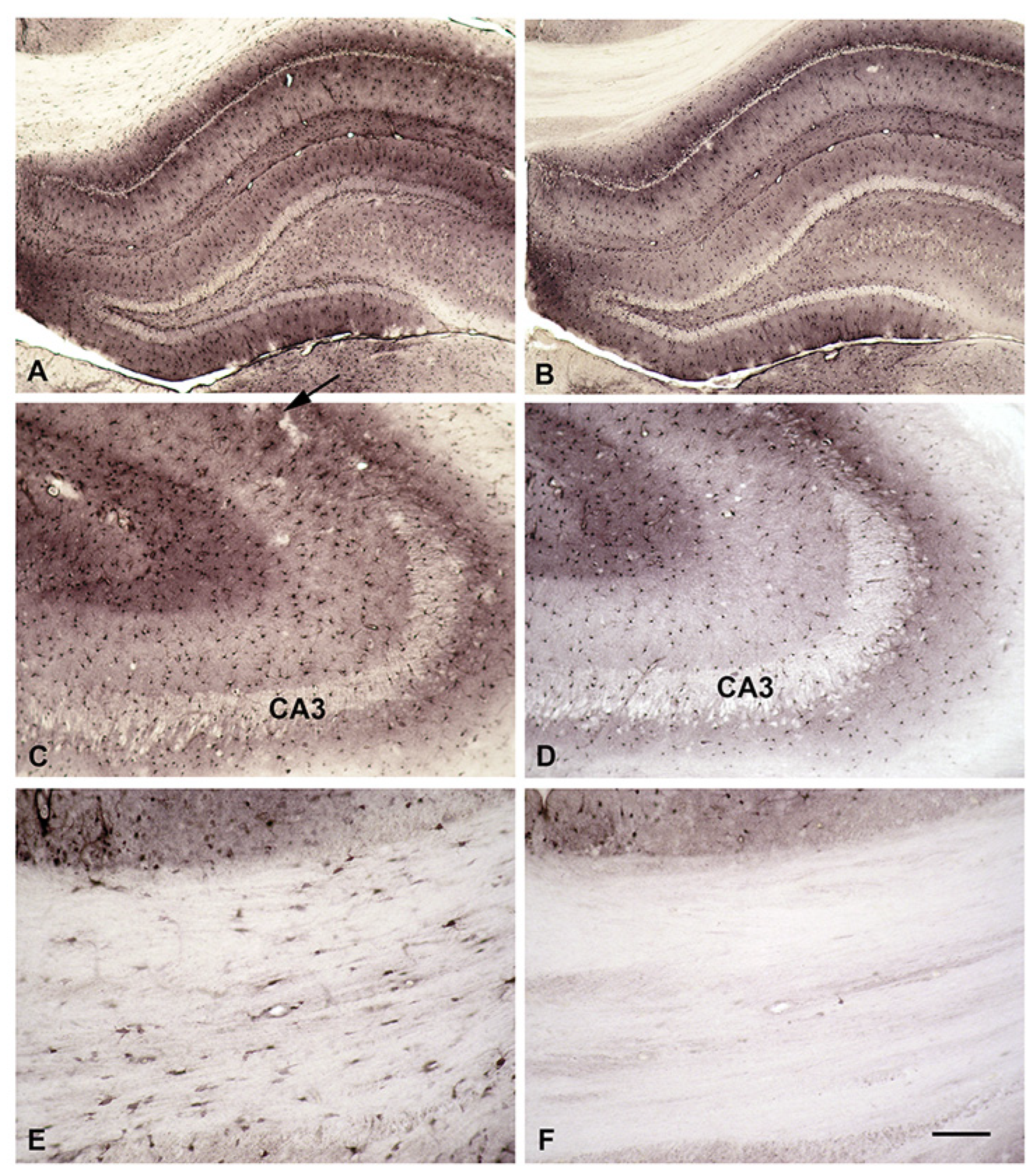
Uptake of Biotinylated SPM (B-X-SPM) in Brain Slices
Incorporation of B-X- SPM into Astrocytes Is Based on a PA-Specific Uptake System
In-Vivo Uptake of Native or Biotinylated SPM into the brain from intraventricular CSF or from the blood stream
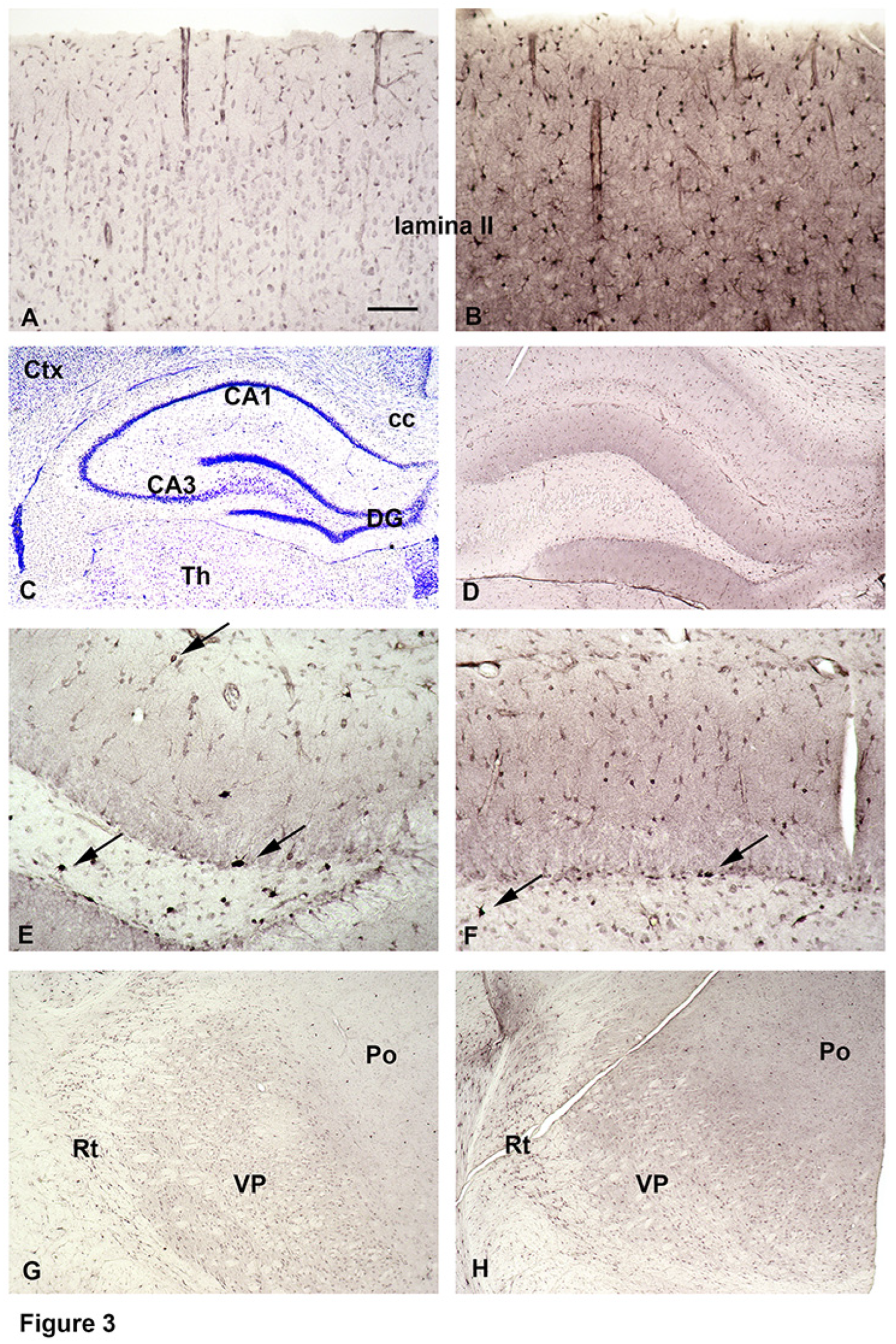
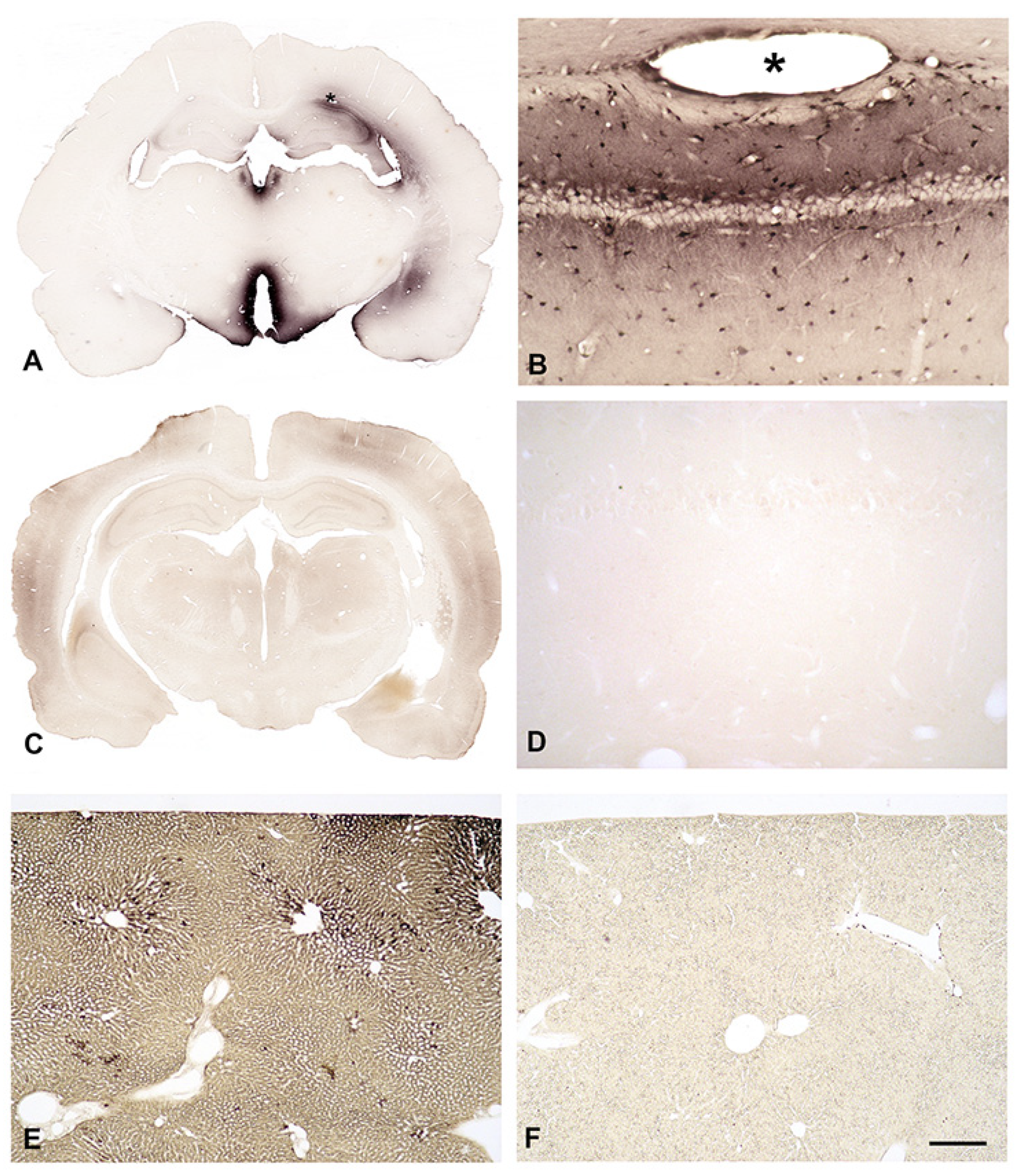
In-Vivo Uptake of Biotinylated SPM into the Brain from Intraventricular CSF
In-Vivo Uptake of Biotinylated SPM into the Brain from the Blood Stream
Discussion
Technical Considerations
Native and Biotinylated SPM Are Taken Up by Astrocytes and Neurons in Brain Slices
Uptake of Biotinylated SPM (B-X-SPM) by Brain Slices Is Different in Protoplasmic and Fibrous Astrocytes
Native or Biotinylated SPM Are not Taken Up into the Brain from the Blood Stream
Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
References
- Rieck, J.; Skatchkov, S.N.; Derst, C.; Eaton, M.J.; Veh, R.W. Unique Chemistry, Intake, and Metabolism of Polyamines in the Central Nervous System (CNS) and Its Body. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 501.
- Matsumoto, M.; Kakizoe, K.; Benno, Y. Comparison of Fecal Microbiota and Polyamine Concentration in Adult Patients with Intractable Atopic Dermatitis and Healthy Adults. Microbiology and Immunology 2007, 51, 37-46, . [CrossRef]
- Madeo, F.; Hofer, S.J.; Pendl, T.; Bauer, M.A.; Eisenberg, T.; Carmona-Gutierrez, D.; Kroemer, G. Nutritional Aspects of Spermidine. Annual Review of Nutrition 2020, 40, 135-159. [CrossRef]
- Kibe, R.; Kurihara, S.; Sakai, Y.; Suzuki, H.; Ooga, T.; Sawaki, E.; Muramatsu, K.; Nakamura, A.; Yamashita, A.; Kitada, Y.; et al. Upregulation of colonic luminal polyamines produced by intestinal microbiota delays senescence in mice. Scientific Reports 2014, 4, 4548. [CrossRef]
- Milovic, V. Polyamines in the gut lumen: bioavailability and biodistribution. European Journal of Gastroenterology & Hepatology 2001, 13, 1021-1025.
- Skatchkov, S.N.; Antonov, S.M.; Eaton, M.J. Glia and glial polyamines. Role in brain function in health and disease. Biochemistry (Moscow) Supplement Series A: Membrane and Cell Biology 2016, 10, 73-98. [CrossRef]
- Lajtha, A.; Sershen, H. Substrate specificity of uptake of diamines in mouse brain slices. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics 1974, 165, 539-547, . [CrossRef]
- Sershen, H.; Lajtha, A. Perinatal changes of transport systems for amino acids in slices of mouse brain. Neurochemical Research 1976, 1, 417-428. [CrossRef]
- Shin, W.-W.; Fong, W.-F.; Pang, S.-F.; Wong, P.C.-L. Limited Blood-Brain Barrier Transport of Polyamines. Journal of Neurochemistry 1985, 44, 1056-1059, . [CrossRef]
- Hopman, A.H.; Ramaekers, F.C.; Speel, E.J. Rapid synthesis of biotin-, digoxigenin-, trinitrophenyl-, and fluorochrome-labeled tyramides and their application for In situ hybridization using CARD amplification. Journal of Histochemistry & Cytochemistry 1998, 46, 771-777.
- Madai, V.I.; Poller, W.C.; Peters, D.; Berger, J.; Paliege, K.; Bernard, R.; Veh, R.W.; Laube, G. Synaptic localisation of agmatinase in rat cerebral cortex revealed by virtual pre-embedding. Amino Acids 2012, 43, 1399-1403. [CrossRef]
- Somogyi, P.; Takagi, H. A note on the use of picric acid-paraformaldehyde-glutaraldehyde fixative for correlated light and electron microscopic immunocytochemistry. Neuroscience 1982, 7, 1779-1783, . [CrossRef]
- Bernard, R.; Veh, R.W. Individual neurons in the rat lateral habenular complex project mostly to the dopaminergic ventral tegmental area or to the serotonergic raphe nuclei. Journal of Comparative Neurology 2012, 520, 2545-2558, . [CrossRef]
- Laube, G.; Veh, R.W. Astrocytes, not neurons, show most prominent staining for spermidine/spermine-like immunoreactivity in adult rat brain. Glia 1997, 19, 171-179, . [CrossRef]
- Malpica-Nieves, C.J.; Rivera, Y.; Rivera-Aponte, D.E.; Phanstiel, O.; Veh, R.W.; Eaton, M.J.; Skatchkov, S.N. Uptake of Biotinylated Spermine in Astrocytes: Effect of Cx43 siRNA, HIV-Tat Protein and Polyamine Transport Inhibitor on Polyamine Uptake. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1187.
- Krauss, M.; Langnaese, K.; Richter, K.; Brunk, I.; Wieske, M.; Ahnert-Hilger, G.; Veh, R.W.; Laube, G. Spermidine synthase is prominently expressed in the striatal patch compartment and in putative interneurones of the matrix compartment. Journal of Neurochemistry 2006, 97, 174-189. [CrossRef]
- Biedermann, B.; Skatchkov, S.N.; Brunk, I.; Bringmann, A.; Pannicke, T.; Bernstein, H.-G.; Faude, F.; Germer, A.; Veh, R.; Reichenbach, A. Spermine/spermidine is expressed by retinal glial (müller) cells and controls distinct K+ channels of their membrane. Glia 1998, 23, 209-220. [CrossRef]
- Skatchkov, S.N.; Eaton, M.J.; Krušek, J.; Veh, R.W.; Biedermann, B.; Bringmann, A.; Pannicke, T.; Orkand, R.K.; Reichenbach, A. Spatial distribution of spermine/spermidine content and K+-current rectification in frog retinal glial (Müller) cells. Glia 2000, 31, 84-90. [CrossRef]
- Kovács, Z.; Skatchkov, S.N.; Veh, R.W.; Szabó, Z.; Németh, K.; Szabó, P.T.; Kardos, J.; Héja, L. Critical Role of Astrocytic Polyamine and GABA Metabolism in Epileptogenesis. Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience 2022, 15, doi:10.3389/fncel.2021.787319.
- Bernstein, H.-G.; Müller, M. The cellular localization of the l-ornithine decarboxylase/polyamine system in normal and diseased central nervous systems. Progress in Neurobiology 1999, 57, 485-505. [CrossRef]
- Kilpeläinen, P.; Rybnikova, E.; Hietala, O.; Pelto-Huikko, M. Expression of ODC and its regulatory protein antizyme in the adult rat brain. Journal of Neuroscience Research 2000, 62, 675-685. [CrossRef]
- Laube, G.; Bernstein, H.-G.; Wolf, G.; Veh, R.W. Differential distribution of spermidine/spermine-like immunoreactivity in neurons of the adult rat brain. Journal of Comparative Neurology 2002, 444, 369-386. [CrossRef]
- Garcia, A.D.R.; Petrova, R.; Eng, L.; Joyner, A.L. Sonic Hedgehog Regulates Discrete Populations of Astrocytes in the Adult Mouse Forebrain. The Journal of Neuroscience 2010, 30, 13597-13608. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




