1. Introduction
Alloys for different technological and highly specialized applications are required now day, specifically in dental industry copper-nickel based alloys can be these alloys due to their excellent mechanical and physical properties providing good structural resistance [
1,
2]. Copper can be easily alloyed with a wide range of metals, which makes it very useful element for several applications. However, binary alloys exhibit some mechanical limitations; hence, many of the investigations focus on the addition of a third or fourth element instead of the binary copper-nickel alloys, mainly to produce an effect on the microstructural [
1,
2,
3,
4] and mechanical properties [
5,
6,
7,
8,
9]. H. Fu [
10], studied the mechanical properties of Al-Cu-Ni alloys by controlling the solidification process and modifying the stress state of grain boundaries, restricting intergranular cracking caused by local stress concentration. Martinez [
11] developed an analysis with zirconium additions as ternary element in Cu-Ni-based alloy by means of mechanical alloying and hot-pressing conditions, achieving a significant increment in hardness but also in brittleness. On the other hand, nickel, as a reinforcing element, has been widely used in super-alloys due to its good mechanical and chemical properties, and extensive research has also been developed related to its corrosion resistance in different environments [
12,
13,
14,
15,
16,
17,
18,
19]. Density studies in materials and their correlation with thermal point defects, always has been an important issue to be considered to understand the cause of possible emerging structural defects. Then, due to aluminum has a density approximately one third lower in comparison with nickel and copper (2.7 and 8.96 g/cm
3, respectively), these alloys can be considered for applications like automotive, aerospace, dental industry, and in general where low density is required. It is well known that heat treatment under inert atmospheres may allow a better controlled cooling rate diminishing residual stresses formation. Thus, the novelty of this work lies in the influence of the aluminum additions as well in the heat treatment effect via vacuum and He atmosphere on the microstructure and physical-mechanic properties of the Cu-Ni and Cu-Ni-Al alloys as potential material in the dental industry.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials Synthesis
Copper-nickel alloys were obtained using high purity elements (99.999) employing an induction furnace unit, melted in a quartz crucible under vacuum conditions (10
-3 torr).
Table 1 shows the alloy designation taking in consideration the nominal compositions, considering an extra amount of aluminum due to evaporation. Heat treatments were performed under He atmosphere (3ml/min) at 600°C for 120 minutes. Specimens under these conditions were designated with TT.
2.2. Metallographic Evaluation
Specimens were ground up to 600 SiC paper grinding for posteriorly be polished with Alumina with a particle size of 0.03 µm. Samples were etched with a reactant of 5g Fe2Cl3, 25ml HCl and 70 ml deionized water. Microstructure and surface analyses were carried out in an LEO-1450VP scanning electron microscope, and chemical analyses were performed using the EDS system attached to the equipment.
2.3. Physical Properties
Density measurements were carried out by using an AccuPyc II 1340 Tec He-Pycnometer, developing 10 evaluations for each sample, while lattice parameter measurements were obtained from X-ray diffraction patterns with internal silicon powders as standard using a Bruker X-Ray Diffractometer equipment with CuK radiation 1.54 Å.
2.4. Mechanical Testing Evaluation
Hardness measurements were carried out on the sample´s surface (previously polished with diamond paste with 0.03 µm average size), using a LECO Microhardness tester Leco LM300AT, with 0.2 kg load and 15 s holding time. For compression tests, specimens with cross sections of 5x5 mm and 10 mm high were machined by using an electro-discharge machine. After that, specimens were ground up to 600 paper grinding, obtaining parallel opposites surfaces, and compressed using an Instron 4501 testing machine with a strain rate of 10-3 s-1.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Microstructural Characterization
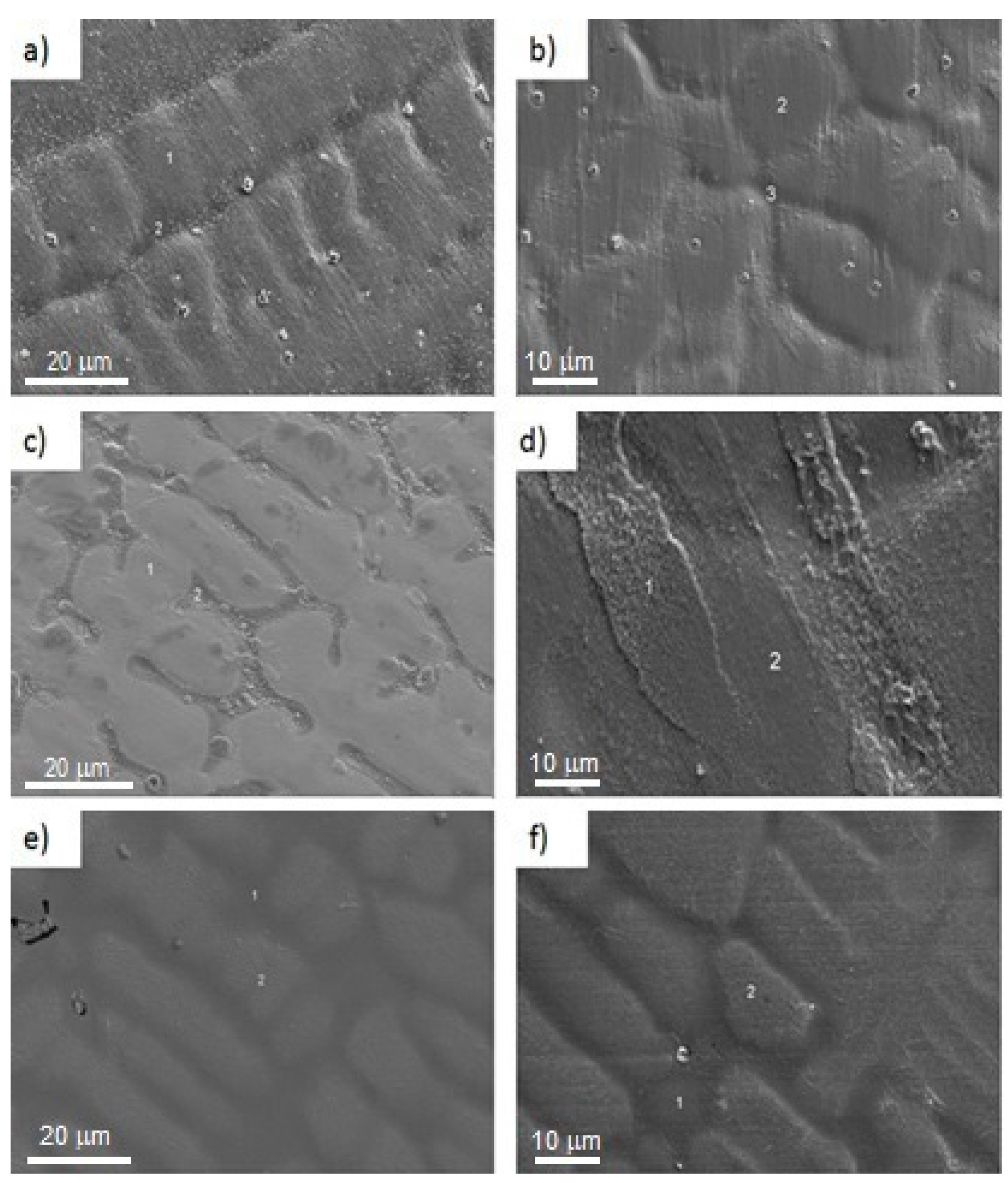
Figure 1 shows the alloy´s microstructure without and with heat treatment, where it can be observed that the microstructure is dendritic type in both conditions. However, in untreated alloys with 0, 5, and 10 at% Al, predominantly a coarse dendritic structure is observed. On the other hand, samples in the annealing condition present a refined dendritic structure. Lei [
2] reported a similar result in Cu-Ni-Si alloys. In these images, it can be observed a reduction in the inter-dendritic spacing as well as in the dendrite arm length, preferentially in samples with heat treatment. This effect is attributed to a saturation of aluminum atoms in the Cu-Ni structure where posteriorly aluminum segregation is promoted through the inter-dendritic regions, possibly due to a diffusion process. This mechanism occurs when aluminum atoms with lower atomic radii in comparison with Cu and Ni (0.5 Å) take preferential positions in the Cu-Ni lattice during the casting-solidification process; hence, analyzing the images in
Figure 1, it is observed the apparition of a second phase in samples with 10 at. % Al, indicating that aluminum solubility in the Cu-Ni alloy is lower than the mentioned composition. On the other hand, in the heat-treated samples, it is observed a significant amount of precipitates randomly distributed over the surface in comparison with samples untreated, it is important to take into consideration this observation due to the affectation on the mechanical properties of these alloys.
3.1.1. Lattice Parameter Analyses
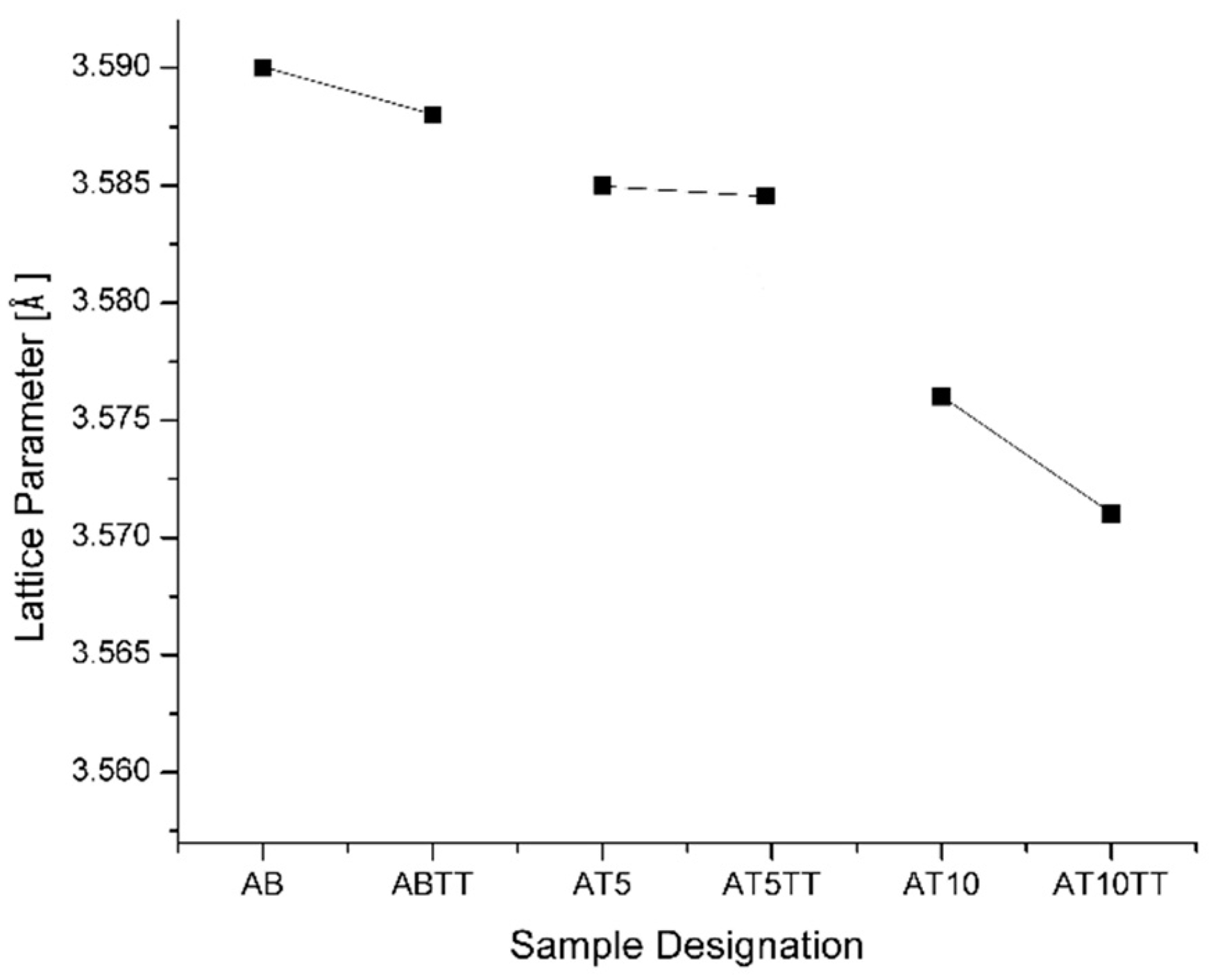
Lattice parameter measurements were carried out in order to understand the lattice parameter affectation in samples with different aluminum additions and also with and without thermal treatment. In
Figure 2 it can be observed that for alloys with 5 and 10 at. % Al, the lattice parameter decreases as the aluminum content increases, and the observed slope for heat-treated higher aluminum content (10 at.%) diminishes in comparison with the alloys of lower aluminum content, indicating a considerable lattice contraction. This was expected because the number of nickel atoms substituted by aluminum atoms in the lattice increases, obtaining the calculated reduction for 5 and 10 at.% Al of 0.012 and 0.011 Å, respectively. In addition to this observation, these variations indicate enough lattice distortion that may promotes dislocation generation, i.e., Burguers Vector has been affected as the lattice parameter was modified, which means that exists some interference on the dislocation mobility which produces plane misalignment. Thus, it is important to note in the plot that points for the different aluminum compositions do not fit a straight line along the aluminum compositions because this lattice parameter reduction is not only produced due to the aluminum saturation but for the presence of the observed precipitates on the sample´s surface.
3.2. Physical Properties
3.2.1. Density and Thermal defects evaluation
Materials with low density and good mechanical resistance are interesting from the engineering point of view, specifically in the present case for fabrication of dental post and core; the latest always has been designed to support artificial crowns showing excellent fracture resistance to the roots; therefore, to evaluate the aluminum effect on the alloys, density measurements were carried out in samples with different condition.
Table 2 shows that the density values decrease as the aluminum content increases, which is not surprising since aluminum atomic weight is lower in comparison with copper and nickel density in a ratio close to 3:1. Therefore, because aluminum addition is considered substitutional inner the alloy [
2], then it is necessary to evaluate if during solidification thermal defects were produced. Whereby, calculations of vacancy concentration were carried out taking in consideration the density values obtained in
Table 2 and using the following relation described by Zhu [
20].
where:
Cv= Vacancy concentration
ρXRD = Density obtained by X-ray diffraction
ρpyc= Density obtained by He-Pycnometry.
It is important to note that the obtained results of vacancies concentration (see
Table 2) are lower than 1.0 %, which means that minimal thermal defects exist. These results have shown to be lower than the experimental error. Among the mechanisms that can produce a lattice parameter reduction, vacancies are one of the most common defects during the casting process. Nevertheless, due to the low range of vacancy concentration obtained for all alloys, it is demonstrated that using this process under vacuum conditions and the applied heat treatments under He atmosphere, a considerable thermal defects reduction was obtained. Thus, it is observed that defects generation by the incorporation of aluminum atoms inner the structure was controlled in a low range (since He possesses small atomic radii), allowing aluminum atoms may occupy the most possible spaces in the crystal structure and therefore diminishing the vacancies generation.
Table 2.
Density values obtained from X-ray diffraction and He-pycnometer.
Table 2.
Density values obtained from X-ray diffraction and He-pycnometer.
| Alloy designation |
Density by X-ray Diffraction [g/cm3] |
Density by He-Pycnometry
[g/cm3] |
Vacancy Concentration
[%] |
| AB |
9.5601 |
9.5594 |
0.0073 |
| ABTT |
9.5581 |
9.5570 |
0.0115 |
| AT5 |
9.2085 |
9.2011 |
0.0804 |
| AT5TT |
9.2071 |
9.2038 |
0.0358 |
| AT10 |
8.9347 |
8.9307 |
0.0447 |
| AT10TT |
8.9304 |
8.9257 |
0.0526 |
The former results show that the alloys present a good performance due to the density values produced by the aluminum incorporation into the alloys. This fact permitted consideration of the use of the material in multiple posts without a considerable increment in weight on the jawbone. On the other hand, the knowledge of the low index of thermal defects found in the alloys gives the reliability of the structural integrity of the post-dental, and it will not develop micro-cracks formation when a chewing process is carried out.
3.3. Mechanical Characterization
3.3.1. Hardness Evaluation
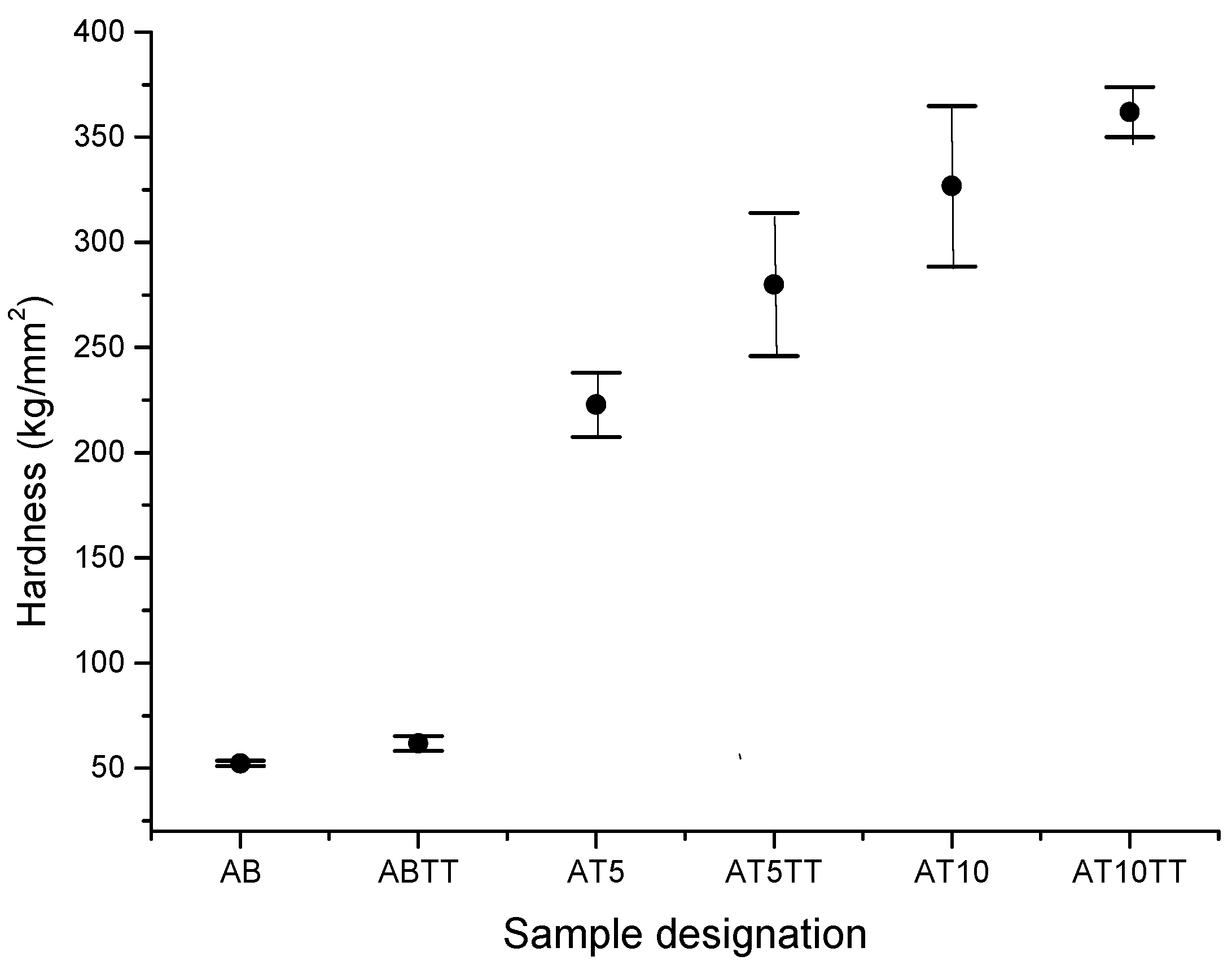
In dental applications, it is important a balance the hardness of the system components (dental post and crown); in other words, it is very important to get internal materials with a moderated hardness that supports the crown (hard material). This combination, in consequence, produces the necessary toughness to support the stresses generated by the contact between teeth. In this way, hardness evaluation was carried out in the as-cast and annealed samples. The results are shown in
Figure 3, where it can be observed for samples without heat treatment, the average hardness value of ternary AT5 and AT10 alloys is 260 kg/mm
2 and 350 kg/mm
2, respectively, which represent considerable increments with respect to the unalloyed sample (binary AB) which possess a hardness value of approximately 50 kg/mm
2. On the other hand, by analyzing the effect of heat treatment, it is observed that ABTT binary alloy does not present a significant variation. However, AT5TT and AT10TT alloys present a noticeable hardness increment (280 and 350 kg/mm
2, respectively) representing an increment of approximately 20 and 40 percent respectively compared with the binary alloy. This hardening effect is produced partially by a dendrite refinement due to applied heat treatment. Therefore, low plastic deformation is reached when grain boundaries inside the alloy partially inhibit dislocation movement. Due to the fact that a large amount of precipitates finely dispersed were observed on the surface sample in
Figure 1, thus, the possibility that a hardening effect by precipitation mechanism occurs is relatively high [
7].
Therefore, to corroborate the former statement, SEM surfaces analyses on the precipitates were carried out.
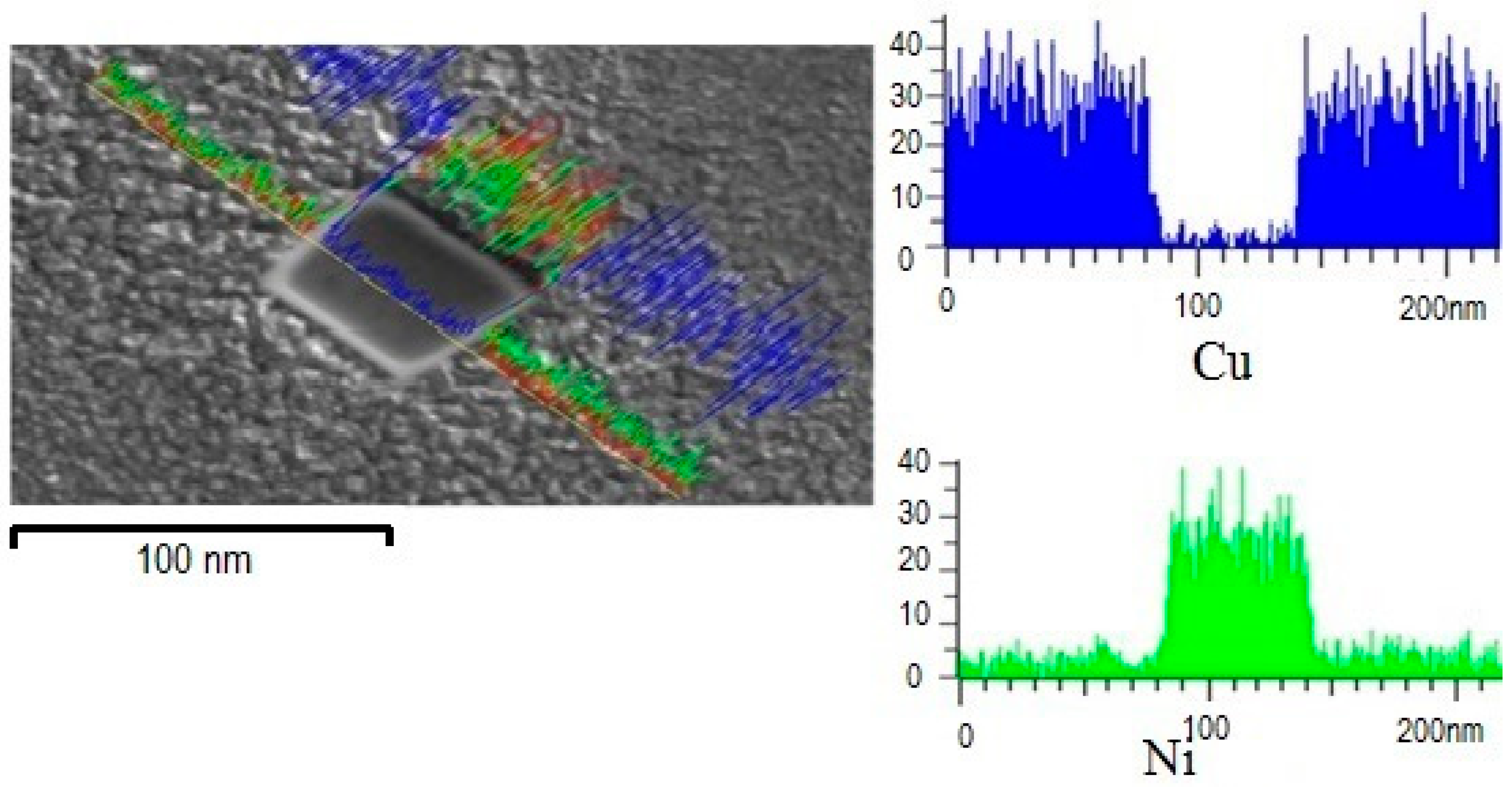
Figure 4 shows a line scan analysis carried out across the surface of a precipitate in the sample with 10 at. % Al. It was found that the precipitate composition is mainly of nickel with some copper traces with a square-type morphology with an average size of 60 nm. The area fraction calculation of the precipitates using the IPA (Image Processing Analysis) of the SEM, indicates a 15 percent in an average area of 400 µm
2. Such amount of precipitates may take part in the alloy strengthening, mainly when a dislocation impacts a precipitate. On the other hand, it is important to take into consideration that precipitates are not coherent with each other (i.e., oriented in a different direction), as can be observed in
Figure 1. Thus, the observed misorientation in the precipitates contributes to enhancing the alloy hardening by the precipitation mechanism working as an obstacle for dislocation mobility. This observation is postulated by Similar hardening behavior reported in Cu-Ni-Si alloys with a controlled aging treatment [
8].
3.3.2. Compression Tests Evaluation
Because teeth are exposed mainly to compressive forces, it is important to develop a deep study of the compression resistance that can be reached for the materials after being synthesized. Hence, to analyze the strengthening effect of aluminum additions in samples, compression tests were carried out using a moderate strain rate of 10
-3 s
-1.
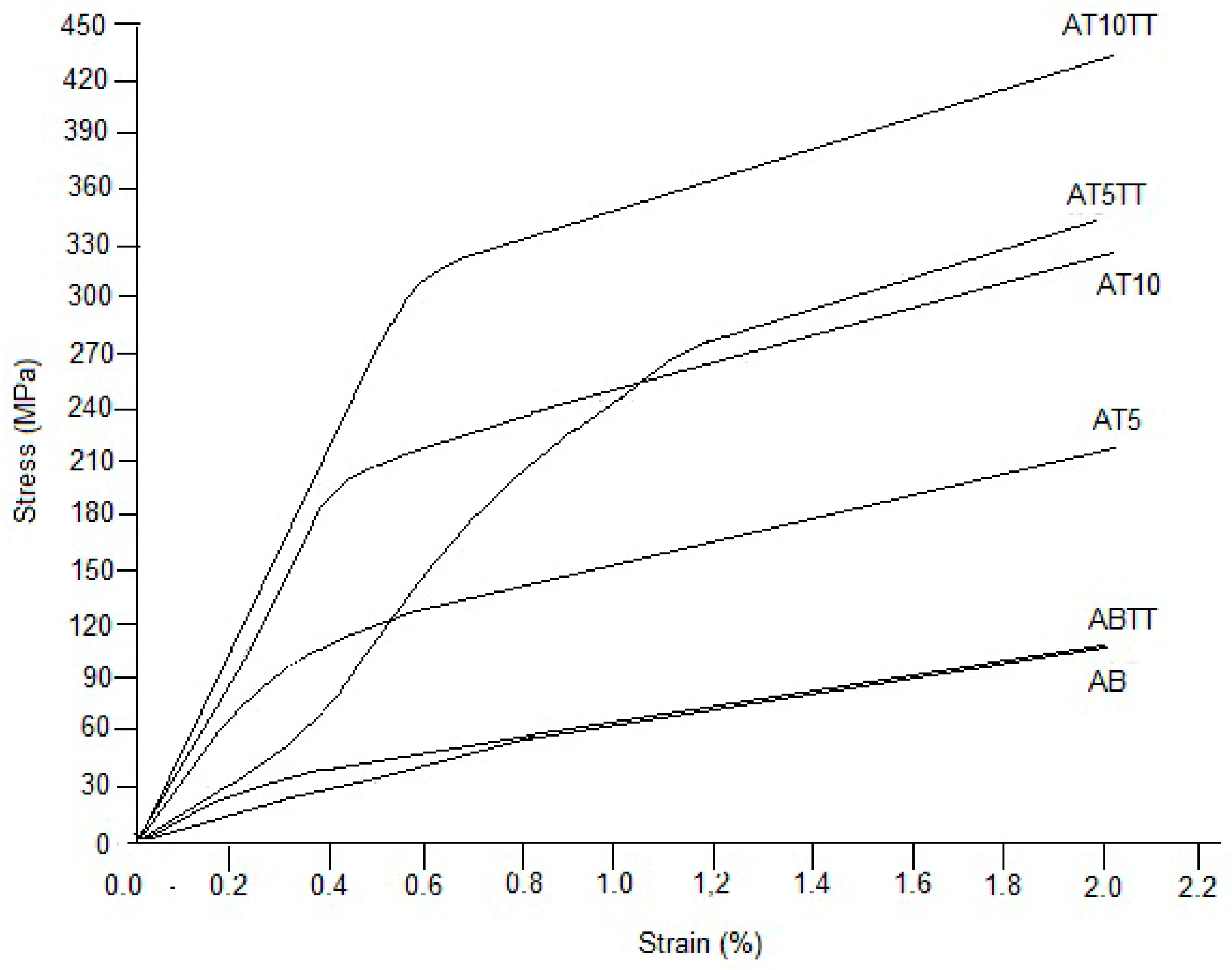
Figure 5 presents the σ-ε curves for the evaluated alloys, where it can be observed that binary alloy (AB) does not show a significant change in the yielding point as compared to the heat-treated sample. However, AT5TT alloy exhibits an important improvement in resistance compared to the untreated sample (at the same compositions). Similar behavior is observed in the AT10TT sample, where an increment in the stress value can be appreciated, attributed to the presence of precipitates and the lower grain size of treated samples compared to untreated samples. Additionally, Cahn [
21] established that the segregation of solute atoms produces deformation stacking faults in the lattice. Besides, if plastic deformation can be affected by the incorporation of an element that produces lattice distortion that does not allow the dislocation movement [
10,
11], then, this phenomenon can be one of the main causes for alloy strengthening. In fact, for all curves, strain continues above two percent, but after these values, it starts to drop down until it reaches the final fracture. From the evaluated curves (taking into account the aluminum concentration), it is determined that alloys with 5 and 10 at% Al exhibited the most important strengthening behavior in comparison with the unalloyed samples. A. Rittapai [
23], developed a study with Cu-Ni-Al, reporting promising results in this alloy to be considered for potential use as dental post and core applications
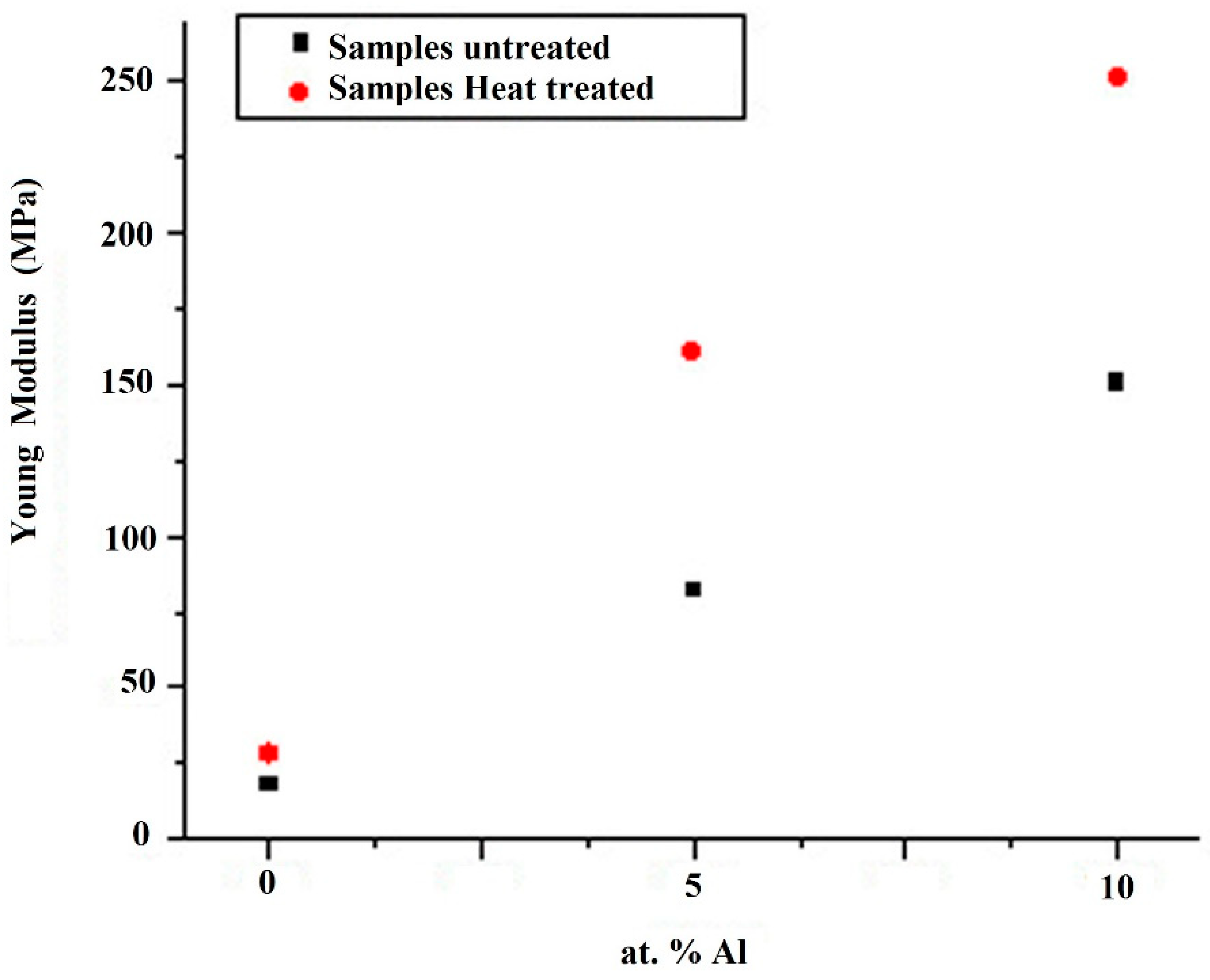
Due to the remarkable differences in slopes observed in the elastic zone of the curves of
Figure 5, Young’s modulus was evaluated to know the effect of the heat treatment and the aluminum addition. In the results of
Figure 6, it can be observed that heat-treated alloys present a significant increment compared to the untreated samples and that the elastic modulus increases proportionally as a function of aluminum addition. It is well known that a plastic deformation during the compression test process reflects the correlation between the applied stresses with dislocation mobility; then, the increment in aluminum addition promotes one of the characteristic hardening mechanisms observed in copper-based alloys [
22], namely the solute segregation to dislocation. This way, if Young ́s modulus is appropriately considered as the stiffness of a material, then a higher elastic modulus value directly reflects a small deformation behavior so that the noticeable increment of the slope in the elastic zone of the σ-ε curves is produced by the aluminum additions that produces crystal structure disorder with the consequent low index in plastic flow, reflected in the curves of the tested alloys.
The dependence of the yield strength on the heat treatment parameters and aluminum additions was found to be like that observed in the hardness behavior. Several authors postulated that a dental post should have a Young´s Modulus similar of the value to the human dentin, in order to distribute homogeneously the applied forces along the length of the post [
24,
25,
26].
Yielding behavior perhaps is the most important parameter in the alloys strengthening in which is obtained the value that will be used for structural calculations.
Figure 7 shows the resultant values of the yield strength variation obtained from compression tests evaluated at 0.2% offset of deformation. In this plot, it can be observed that the yield strength value increases also directly proportional with the aluminum content. For the as-casting samples, the following values were obtained, AB≈42 MPa, AT5≈124 MPa and AT10≈226 MPa, the former value represent a maximum increment of 5 times more in comparison with unalloyed sample. Similar tendency is observed for samples in annealing condition where it is observed that samples with thermal treatment present higher yielding value in comparison with untreated samples in at least 300 percent increment in comparison with the as-cast sample and much higher than the samples without heat treatment. (ABTT≈ 90 MPa, AT5TT≈ 290 MPa, and AT10TT≈333 MPa). However, due to the fact that compression process is governed by the creation and annihilation of dislocations produced by the applied stresses, then dislocation movement can be minimized when it crosses trough the grain boundaries reducing an easier dislocations mobility and combined with the precipitates presence that works as an obstacle for plastic deformation, then the result of a combination of these factors produces the improvement of the reported yielding behavior.
4. Conclusions
Copper-nickel alloys were synthetized by the induction melting technique. After controlled heat treatment under He atmosphere, a coarse dendritic structure was obtained in as-cast samples while refined dendritic structure was obtained in thermally treated specimens. Due to the aluminum addition it is expected an improved biocompatibility.
Thermal defects analyses demonstrated a minimum effect of the heat treatments with low range of defects concentration in the alloys basically below of the experimental error. Hardening precipitation result to be one of the main strengthening mechanisms in the alloys increasing this mechanical property approximately five times, Furthermore, compression tests indicate that heat-treated samples and with high aluminum addition presented enhanced yielding resistance, being sample with 10 at.% Al which showed the best alloy performance. In general, is stablished that strengthening observed in alloys is proportional with the increment of substitutional aluminum. Corrosion test evaluation is currently being developed in synthetic saliva.
Author Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation. Experiments, Data collection and analysis were performed by [Constancio Diaz, Rene Guardian, Juan Antonio. Ruiz-Ochoa]. The first draft of the manuscript was written by [Isai Rosales-Cadena] America Maria Ramirez-Arteaga, Roy Lopez-Sesenes commented on previous versions of the manuscript developing a complete discussion of results. The final version of the manuscript was performed by Isai Rosales-Cadena, Jose Gonzalo Gonzalez-Rodriguez. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Acknowledgments
Authors are thankful with A. Aguilar and J. Macedonio for helpful support in mechanical characterization. This project was partially supported by PRODEP under grant UAEM/ PTC-074
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Ricks, R.A., Howell, P.R., & Honeycombe, R.W. K. Formation of supersaturated ferrite during decomposition of austenite in iron–copper and iron–copper–nickel alloys. Metal Science. 1980, 14(12), 562-568. [CrossRef]
- Lei, Q., Li, Z., Dai, C., Wang, J., Chen, X., Xie, J.M., Chen, D.L. Effect of aluminum on microstructure and property of Cu–Ni–Si alloys. Materials Science and Engineering: A. 2013, 572, 65-74. [CrossRef]
- Schneider, M.S., Kad, B., Kalantar, D.H., Remington, B.A., Kenik, E., Jarmakani, H., & Meyers, M.A. Laser shock compression of copper and copper–aluminum alloys. International Journal of Impact Engineering. 2005, 32(1), 473-507. [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, K., Hashiba, M., & Yamashina, T. A quantitative analysis of surface segregation and in-depth profile of copper-nickel alloys. Surface Science. 1976, 61(2), 483-490. [CrossRef]
- McFadden, S.X., Mishra, R.S., Valiev, R.Z., Zhilyaev, A.P., & Mukherjee, A.K. Low-temperature superplasticity in nanostructured nickel and metal alloys. Nature. 1999, 398(6729), 684-686. [CrossRef]
- Brandstetter, S., Zhang, K., Escuadro, A., Weertman, J.R., & Van Swygenhoven, H. Grain coarsening during compression of bulk nanocrystalline nickel and copper. Scripta Materialia. 2008, 58(1), 61-64. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y., Ping, L.I.U., Tian, B.H., Yong, L.I. U., Li, R.Q., & Xu, Q.Q. Hot deformation behavior and processing map of Cu–Ni–Si–P alloy. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China. 2013, 23(8), 2341-2347. [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, S., Shibutani, N., Mimura, K., Isshiki, M., & Waseda, Y. Improvement in strength and electrical conductivity of Cu–Ni–Si alloys by aging and cold rolling. Journal of Alloys and Compounds. 2006, 417(1), 116-12. [CrossRef]
- Naghash, A.R., Etsell, T.H., & Xu, S. XRD and XPS study of Cu− Ni interactions on reduced copper− nickel− aluminum oxide solid solution catalysts. Chemistry of materials. 2006, 18(10), 2480-2488. [CrossRef]
- Fu, H., Song, S., Zhuo, L., Zhang, Z., & Xie, J Enhanced mechanical properties of polycrystalline Cu–Al–Ni alloy through grain boundary orientation and composition control. Materials Science and Engineering: A. 2016, 650, 218-224. [CrossRef]
- Martínez, C., Briones, F., Rojas, P., Aguilar, C., Guzman, D., & Ordoñez, S. Microstructural and mechanical characterization of copper, nickel, and Cu-based alloys obtained by mechanical alloying and hot pressing. Materials Letters. 2017, 209, 509-512. [CrossRef]
- Syrett, B.C. The mechanism of accelerated corrosion of copper-nickel alloys in sulphide-polluted seawater. Corrosion Science. 1981, 21(3), 187-209. [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, R.S., Azambuja, D.S., & Lucho, A.M. S. Electrochemical studies of propargyl alcohol as corrosion inhibitor for nickel, copper, and copper/nickel (55/45) alloy. Corrosion science. 2002, 44(3), 467-479. [CrossRef]
- Johansson, B.I., Lemons, J.E., & Hao, S.Q. Corrosion of dental copper, nickel, and gold alloys in artificial saliva and saline solutions. Dental Materials. 1989, 5(5), 324-328. [CrossRef]
- Kear, G., Barker, B.D., Stokes, K.R., & Walsh, F.C. Electrochemistry of non-aged 90–10 copper–nickel alloy (UNS C70610) as a function of fluid flow: Part 1: Cathodic and anodic characteristics. Electrochemica Acta. 2007, 52(5), 1889-1898. [CrossRef]
- Martinez, S., & Metikoš-Huković, M. The inhibition of copper–nickel alloy corrosion under controlled hydrodynamic condition in seawater. Journal of applied electrochemistry. 2006, 36(12), 1311-1315. [CrossRef]
- Metikoš-Huković, M., Babić, R., Škugor, I., & Grubač, Z. Copper–nickel alloys modified with thin surface films: Corrosion behaviour in the presence of chloride ions. Corrosion science. 2011, 53(1), 347-352. [CrossRef]
- Melchers, R.E. Temperature effect on seawater immersion corrosion of 90: 10 copper-nickel alloy. Corrosion. 2001, 57(5), 440-451. [CrossRef]
- El Din, A.S., El Dahshan, M.E., & El Din, A.T. Dissolution of copper and copper-nickel alloys in aerated dilute HCl solutions. Desalination. 2000, 130(1), 89-97. [CrossRef]
- J.H. Zhu, L.M. Pike, C.T. Liu and P.K. Liaw, Point Defects in Binary Laves Phase Alloys. Acta Mater. 1999, 47-7, 2003-2018. [CrossRef]
- R. W. Cahn, R.G. Davies X-ray evidence for segregation of solute to stacking faults in a copper-aluminum alloy. Philosophical Magazine. 1960, 5-59, 1119-1126. [CrossRef]
- J. M. Vitek, H. Warlimont The mechanism of anneal hardening in dilute copper alloys Metallurgical Transaction A. 1979, 10-12, 1889–1892. [CrossRef]
- Rittapai, S Urapepon, J. Kajornchaiyakul, Ch. Harniratisai. Properties of experimental copper-aluminum-nickel alloys for dental post-and-core applications The Journal of Advanced Prosthodontics 2014, 6, 215-23. [CrossRef]
- SR Potashnick, FS Weine, S Strauss. Restoration of the endodontically treated tooth. In: Weine FS, ed. Endodontic therapy. 4th ed. St. Louis; Mosby; 1989. p. 653-98.
- H Harold, JG Charles. Preparation for restoration. In: Torabinejad M, Walton RE eds. Endodontics: Principles and practice. 4th ed, Saunders; Elsiver Health Sciences; St. Louis, MO; 2009. p. 287-9.
- JL Gutmann. The dentin-root complex: anatomic and biologic considerations in restoring endodontically treated teeth. J Prosthet Dent 1992, 67, 458-67. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).