1. Introduction
Fire has always been a major threat and disaster throughout the world, and early prevention and rapid detection of fire are the most important methods of reducing the serious harm caused by the occurrence and spread of fires [
1,
4], which is why it is particularly important to be able to warn of fire in a timely and accurate manner. It is well known that forests, grasslands, and wild slopes serve as nature's best "seasoning" system, and they are gaining increased attention due to the benefits they provide for the natural carbon and water cycles as well as for maintaining the balance of an ecosystem and improving its ecology. Although China has a vast land area, the proportion of stored forest, grassland and wild slope resources is tiny. For example, the per capita forest area is less than a quarter of the world average [
1,
2]. Fires are extremely destructive, not only burning large areas of trees and causing species extinction but also causing soil erosion and threatening people's lives and property [
3]. Therefore, inspection technology for fire has received more and more attention from scholars and related departments. Early detection of fires and an accurate grasp of the fire environment posture allows the command center to take effective suppression measures for fire control and extinguishment. The task of fire detection can be divided into the task of detecting both fire and smoke targets [
4]. Fire detection is initially performed using the response values of temperature and smoke detectors as the detection results. However, the detection of temperature and smoke detectors has a certain lag [
5], which is insufficient to fulfill the purpose of early fire prediction, is not resilient enough to environmental changes, and is susceptible to false alarms caused by electromagnetic interference[
6].
Computer vision-based fire detection has made significant progress in recent years [
7,
8,
9], allowing the detection of both flame targets and smoke targets in images rather than just a single target. In early computer vision-based fire detection methods, the task is decomposed into two parts, flame detection and smoke detection, using static appearance information, such as color [
10], texture [
11], and shape [
12]. Flames and smoke are exhibited during a fire, and motion information of flames and smoke in time order [
13,
14,
15,
16] to construct discriminative features of flames or smoke targets, and these discriminative features are then used to detect these targets. Most original flame and smoke detection methods rely on hand-crafted features, achieving good results on early single-category datasets with small amounts of data. Still, in realistic scenes flames and smoke exhibit features such as color, texture, and shape that are unstable and have some variability, making hand-designed features more arduous [
17]. In addition, hand-crafted features rely mainly on a priori information about the target and do not have high abstraction and invariance; thus, their detection accuracy is limited. In addition, most flame and smoke detection methods are proposed for single fire types or fixed scenes, which are not robust, have significantly lower detection accuracy when lighting, scenes, and fire types change, and cannot meet the needs of practical scenarios. There is still a high rate of missed detection for tunnels, forests, dim light, long distances, and small targets, and the performance needs to be further improved to cope with complex real-world scenarios.
The paper [
18] designed a 12-layer convolutional neural network for forest fire detection that is pre-trained with the ImageNet dataset before training and testing it with a self-built dataset (500 images for training and 100 images for testing). During the training process, a dropout operation is performed on the hidden layer of the network to reduce the probability of overfitting. However, its self-built dataset has only 600 images, and it is still possible to overfit when using iterative training. Then its dataset scenarios are single and its robustness is not good in generic scenarios. Additionally, its final output is simply the probability of fire and no fire, and does not contain other information about fire and smoke targets. The paper [
19] has been reported that the classical convolutional neural network combined with convolution and maximum pooling can be used to determine whether the image contains flame or smoke. The algorithm improves the speed of detection by moving a 12×12 sliding window over the feature map. Compared with the method of Zhang et al., it contains more data sets, covers a wider range of scenarios and has a lighter and faster network. However, it only includes three categories (flame, smoke, and normal), and it is not friendly to scenes with both smoke and fire. Similarly, the final output of this method does not contain the location information of the flame and smoke target, leading to the inaccurate perception to the fire state. Through the global and local fire detection of the pictures, the method proposed by [
20] further improves the classification precision. But it only uses fire detection results as a basis for fire classification, and cannot identify smoke, leading to a poor effect with smoke obscuring the flames. As well, it is just a categorization and does not contain the location information of flame and smoke targets.
2. Related work
2.1. Target detection algorithms
The deep learning approach can extract target features from a large number of images and obtain generalized information with better learning ability and adaptability. Target detection is one of the main branches of computer vision based on deep learning, and YOLO, proposed by Redmon et al. [
21], is an outstanding representative of the target detection algorithm. By a convolutional neural network, the method extracts and classifies the features of the input image. The method frames the target on the original image and gives the categories with a good recognition effect but slightly poor accuracy. In order to improve accuracy, Redmon et al. [
22] proposed YOLOv2 algorithm, which used K-means to cluster prior boxes. It improves detection accuracy by splitting the prior frames into three size categories, each of which is further subdivided into three categories, corresponding to three sizes of targets, large and small, respectively. For small targets, however, this algorithm performs poorly. Redmon et al. [
23] then proposed the YOLOv3 algorithm. Based on YOLOv2, feature pyramid networks (FPN) [
24] were used to improve detection performance by fusing features of different sizes. The detection effect was significantly improved in small target detection. Wang et al. [
25] proposed a DSE-YOLO model with good results based on YOLOv3 for strawberry detection. However, the detection of YOLOv3 is not satisfactory for targets with complex features. Bochkovskiy et al. [
26] proposed YOLOv4 based on the optimization of the YOLO series in various aspects and achieved better performance indexes in terms of applications. Jocher et al. [
27] proposed YOLOv5 based on YOLOv4 with a modified loss function, including a Focus structure, adaptive anchor frame calculation at the input, and other optimization methods. Compared with the previous YOLO model, it has a lighter structure and more accurate precision. However, since it uses an anchor frame as the initial preset frame, the computation will increase, affecting the model performance. Although YOLOv5 has a relatively good performance in target detection, it needs to be improved in the area of forest fire detection. Part of the fire area is very small and needs to be detected on time, making it better to ensure accuracy and real-time forest fire detection. This study proposes a fire detection method, YOLOv5-IFFDM, to address the shortcomings of YOLOv5, and confirms its feasibility for detecting forest fires by experiments.
2.2. Methods of this paper
In order to detect both fire and smoke in fire detection tasks and to ensure the effectiveness of small target detection, the following contributions are made in this paper. 1) Darknet-53 of YOLOv5 is used as the backbone feature extraction network, and the attention mechanism is added to the backbone. The flame and smoke detection accuracy and the perception accuracy of small targets are improved. 2) An improved function is adopted to enhance the loss and gradient weights of high IoU, thus improving the regression accuracy and detection of the model. 3) The model adopts a spatial pyramidal pooling structure and replaces all MaxPool pooling layers with more efficient SoftPool to improve the robustness of the model to spatial layout and object variability. 4) The model is augmented using the stochastic Mosaic augmentation technique to enhance the data and the model generalization. 5) The parameters of the convolutional and normalization layers of a trained model are merged to reduce the model complexity, improve detection speed, and reduce hardware requirements. 6) We use the K-means algorithm for fire and smoke a priori frame clustering because the a priori frame is often relevant to the detection task, and the appropriate size of the a priori frame improves the accuracy and speed of detection.
3. Materials and algorithms
3.1. Feature-strengthening structure based on attention mechanism
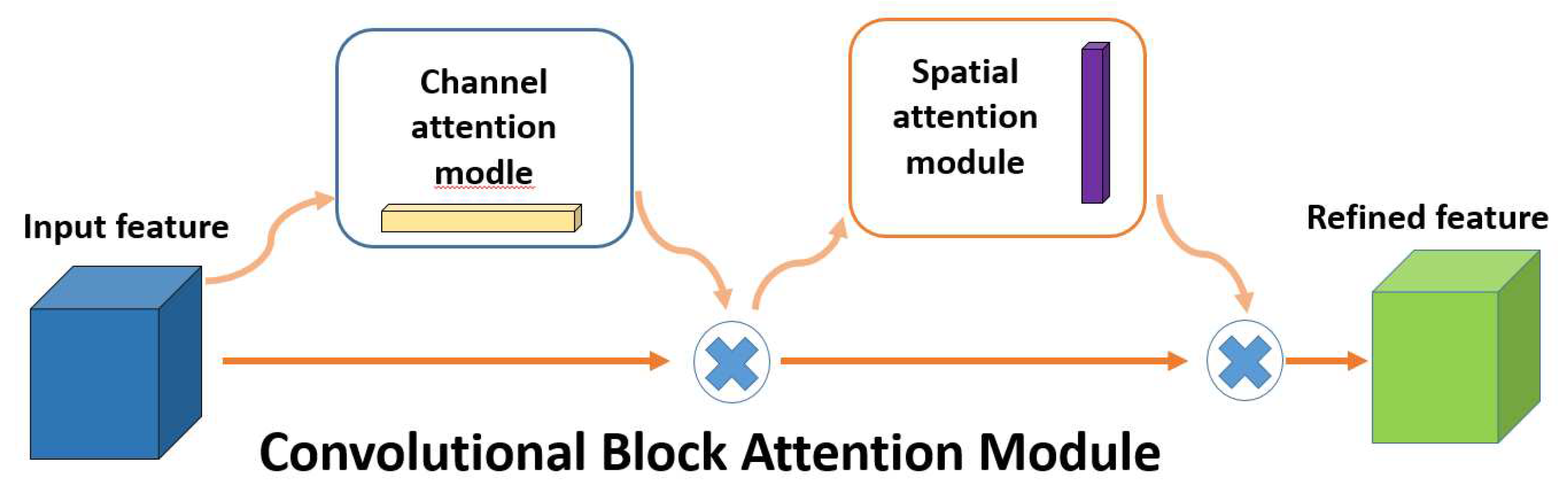
Attentional mechanisms focus on obtaining local information, which works by imitating the way humans pay attention. It devotes more attentional resources to the target region to obtain more target information and suppresses background information. The main ones are squeeze-and-excitation networks (SE) proposed by Hu et al. [
28]; and the convolutional block attention module (CBAM) [
29], which was advanced by Woo et al. The mechanism used in this paper is CBAM, which is a combination of channel and spatial attention mechanisms. It obtains more information about the channel where the target is located by performing an attention operation on the channel; it performs an attention operation on the space to ensure that the target location information is better obtained and improves the accuracy of target detection. The CBAM attention mechanism is shown in
Figure 1.
It has been shown by Foggia et al. [
30] that the feature information of the fire differs on different channels, as well as the location information on each feature map. Therefore, CBAM, which combines channel attention and spatial attention mechanisms, can be used to process them, improve the interest of the model for the target, and enhance the effectiveness of acquiring feature targets.
3.2. Improved
The CIoU loss function used in YOLOv5 is an improvement of the DIoU loss. Because the DIoU increases the height and width loss of the prior frame, the prediction accuracy is higher. The equation is as follows.
The three components in CIoU correspond to the calculation of the IoU, centroid distance, aspect ratio β and aspect ratio, and the calculation procedure is shown above. w, h and wgt, hgt denote the height and width of the predicted and real frames, respectively.
increases the loss and gradient weights of high IoU by performing a power operation on the IoU and its penalty term expression, thus improving the regression accuracy of the model. Its equation is as follows.
In this paper, we define the value of as 3. The power operation focuses more on the high IOU target, which not only enhances the accuracy of the regression but also accelerates the convergence of the network. Therefore, we use the loss function for boundary regression in this paper.
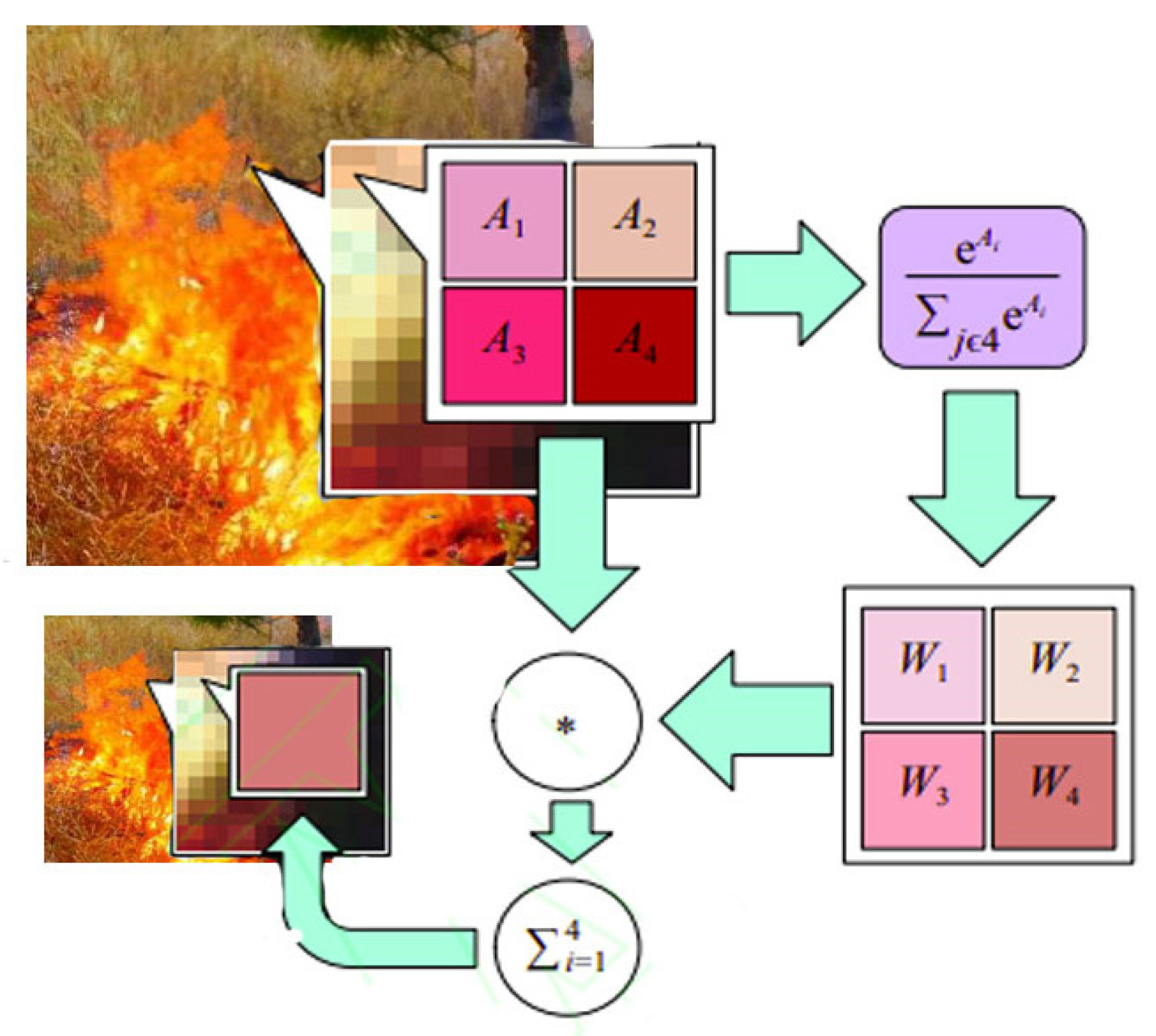
3.2. Improved Spatial Pyramidal Pooling Structure
Spatial pyramid pooling is a multi-scale feature fusion pooling method that can well preserve object features [
31,
32], maintain feature map shape, and output fixed-size features with any feature image size as input. Pooling operation, as one of the most basic algorithms for image processing in the field of deep learning, can reduce the size of the feature map of the model by retaining some features while reducing the computational cost, preventing overfitting, and improving the model's generalization ability. In CNN, the common pooling methods are average pooling and maximum pooling. Averaging pooling is an averaging operation on the neighborhood feature points, which can preserve the background information well and make the image smoother. Still, it will cause feature information loss. Maximum pooling is to obtain the maximum value of neighboring feature points, which can extract obvious texture feature information well. So, it is more suitable as a convolutional neural network to retain prominent features and speed up the model response. It is also easy to ignore some detailed feature information. SoftPool is a variant of a pooling structure with the original pooling layer function while retaining more feature information. The SoftPool can reduce the loss risk of detailed features during pooling and has good feature retention for small targets. Thus, we propose using SoftPool instead of MaxPool in spatial pyramid pooling to better preserve the detailed features of the fire and enhance its detection[
33,
34,
35]. The calculation process of SoftPool is shown in
Figure 2.
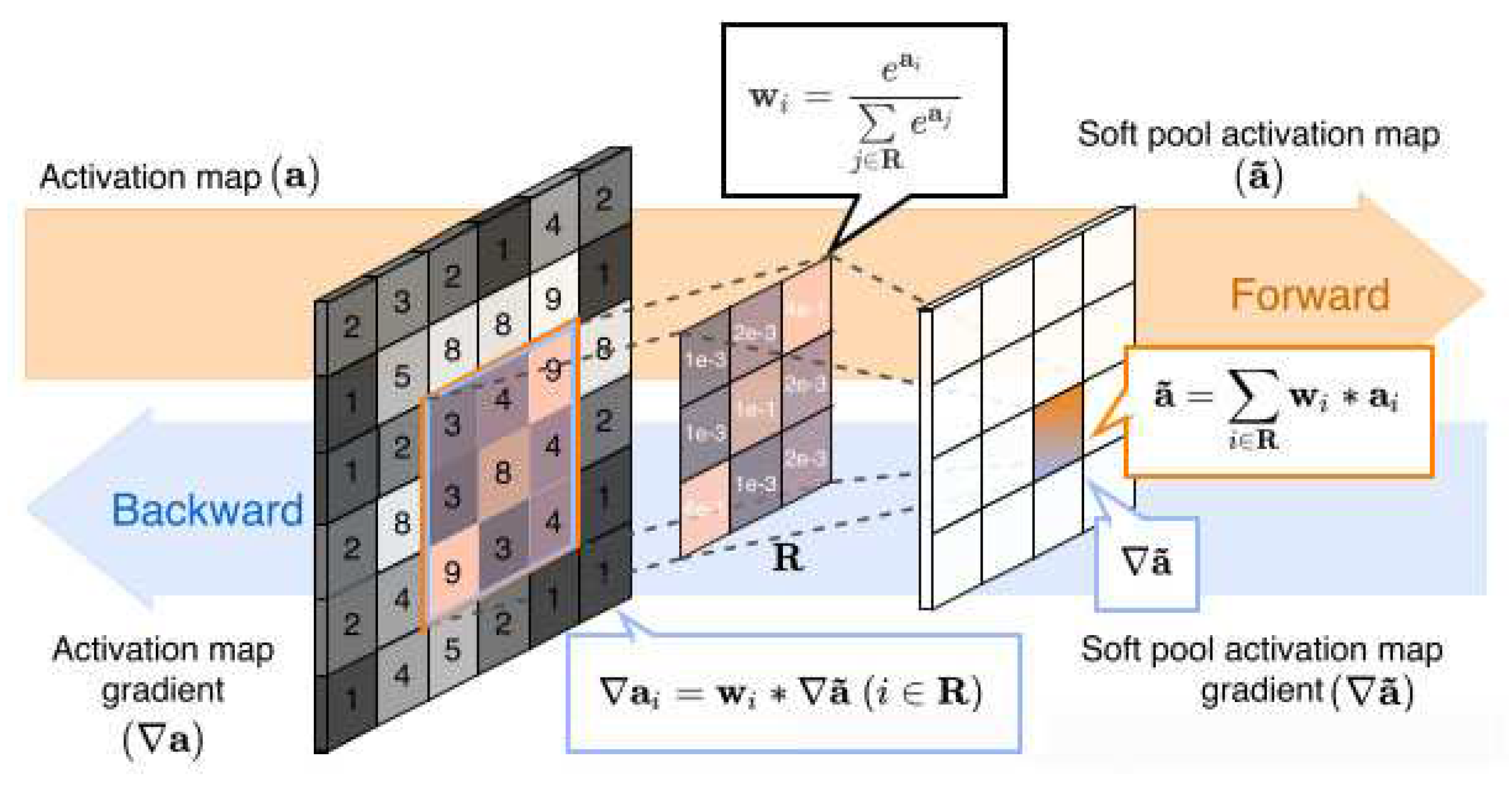
The local feature region is Defined as
.
is a pooling kernel of size
, and the dimension is denoted as
, where
denotes the number of channels,
denotes the height of the feature map, and
denotes the width of the feature map. The corresponding feature weights are calculated nonlinearly based on the values of each feature point, and the equation is shown as follows.
where
denotes the weight,
represents the eigenvalue of a point, and
denotes the activation value. Calculating the weights ensures that the feature texture information can be passed and activates the feature values in the region
to be passed backwards. After obtaining the weights, they are summed with the region's feature values
to obtain the output results.
where
denotes the output value of feature points after SoftPool, obtained by the standard summation of all weighted activations in the kernel neighborhood R, as shown in
Figure 3.
3.3. Mosaic random data enhancement method
Mosaic enhancement technology takes 4 or 6 images, first zoom, pan, flip, color gamut transformation, etc., and then performs the stitching operation. Each image has a corresponding target frame. After stitching by the mosaic method, a picture containing 4 or 6 target frames is obtained, which not only greatly enriches the environment in which the target appears but also increases the pre-trained Batch in disguise. This is helpful in improving detection accuracy. The implementation process is shown in
Figure 4.
3.4. Merge BN layers to convolutional layers to improve network detection speed
In the training of deep network models, the BN (Batch Normalization) layer accelerates the convergence of the network and prevents overfitting. It is usually placed after the convolutional layer. The BN layer normalizes the data and can effectively solve the gradient disappearance and gradient explosion problems. Although the BN layer plays a positive role in training, the extra layers of operations in the network's forward inference affect the model's performance and take up more memory or video memory space. BN (Batch Normalization) layer parameters are merged into the convolutional layer to improve model forward inference speed. Therefore, after training, it is merged with the convolutional layer to improve the speed of forward inference.
The principle of merging is as follows.
A batch data
, we perform the normalization operation on them.
where
is the data mean and
is the data variance. Mean and variance are calculated separately for each channel.
and
are the parameters that can be learned for each different batch of data,
is the scaling factor,
is the translation factor.
is a very small number, approximately 10
-6, which is intended to prevent the denominator from being zero. The above equation can be deformed as follows.
In order to combine BN and convolution, the above equation can be written as the following
The feature map F, after normalization, is also the result equivalent to a 1*1*C convolution.
is the matrix of C X C and
is the matrix of C X 1. Therefore, the BN process can be written as the following equation
In addition
So
Therefore ,,The fusion of convolutional and BN layers is achieved.
3.5. Re-clustering anchor
The YOLOv5 network still uses the anchor boxes mechanism to preset three initial a priori boxes with different areas and aspect ratio sizes for each feature point. According to the K-means clustering algorithm, these are the priori boxes. For the target detection algorithm, a suitable set of prior frames will reduce the tuning of the network to obtain the prediction frames faster. Flame and smoke detection can only be achieved with high accuracy and speed when the priori frame of YOLOv5 is optimized to fit the dataset and scenarios of the detection task[
36,
37,
38,
39,
40]. In this paper, we decided to analyze the true boxes of labeled flames and smoke by an improved K-means clustering algorithm so that the dimensions of the a priori boxes better match the dimensions of the forest flame and smoke dataset in this paper. The number of clusters K is the number of a priori boxes to be selected, and the width and height of the central box of the clusters are the width and height of the a priori boxes.
4. Experiment
4.1. Experimental environment
To implement the training and testing of the proposed method and other target detection methods in this paper, an 11th Gen Intel(R) Core(TM) i5-11260H@ 2.60 GHz CPU with 8 GB of RAM is used as the experimental device and an NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3090 24G GPU as the graphics device. The training parameters are as follows: the Adam optimizer is used, and a total of 100 iteration cycles are set. 1-50 cycles of freeze training on the backbone network with an initial learning rate of 0.001, weight decay of 0.0005, and batches of 8. 51-100 cycles were trained for thawing, with an initial learning rate of 0.0001, a weight decay of 0.0005, and a batch size of 2.
Table 1.
Experimental conditions.
Table 1.
Experimental conditions.
| Experimental environment |
Details |
| Operating System |
Windows 10 |
| CPU |
11th Gen Intel(R) Core(TM) i5-11260H@ 2.60 GHz |
| Deep Learning Framework |
Pytorch 1.12.1 |
| Programming Language |
Python 3.9 |
| GPU |
NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3090 |
| CUDA Version |
CUDA 10.2 |
| Initial learning rate |
0.001 |
| Epochs |
200 |
| batch-size |
8 |
| Img-size |
640*640 |
Table 2.
Details of dataset.
Table 2.
Details of dataset.
| Dataset |
Train |
Val |
Test |
| forest |
11090 |
1238 |
1360 |
| forest fire |
6892 |
679 |
978 |
| forest smoke |
873 |
128 |
212 |
| forest fire and smoke |
3325 |
431 |
170 |
4.2. Data set
The dataset used is the fire and smoke dataset (
http://www.yongxu.org/databases.html) as well as images downloaded from the web and taken in reality. The acquired images are annotated by the dataset annotation tool Labelme. VOC2007 dataset format used for dataset format. The dataset includes a total of 13688 images of flames and smoke from various scenes, some of which are shown in
Figure 5.
4.2.1. Data set widening
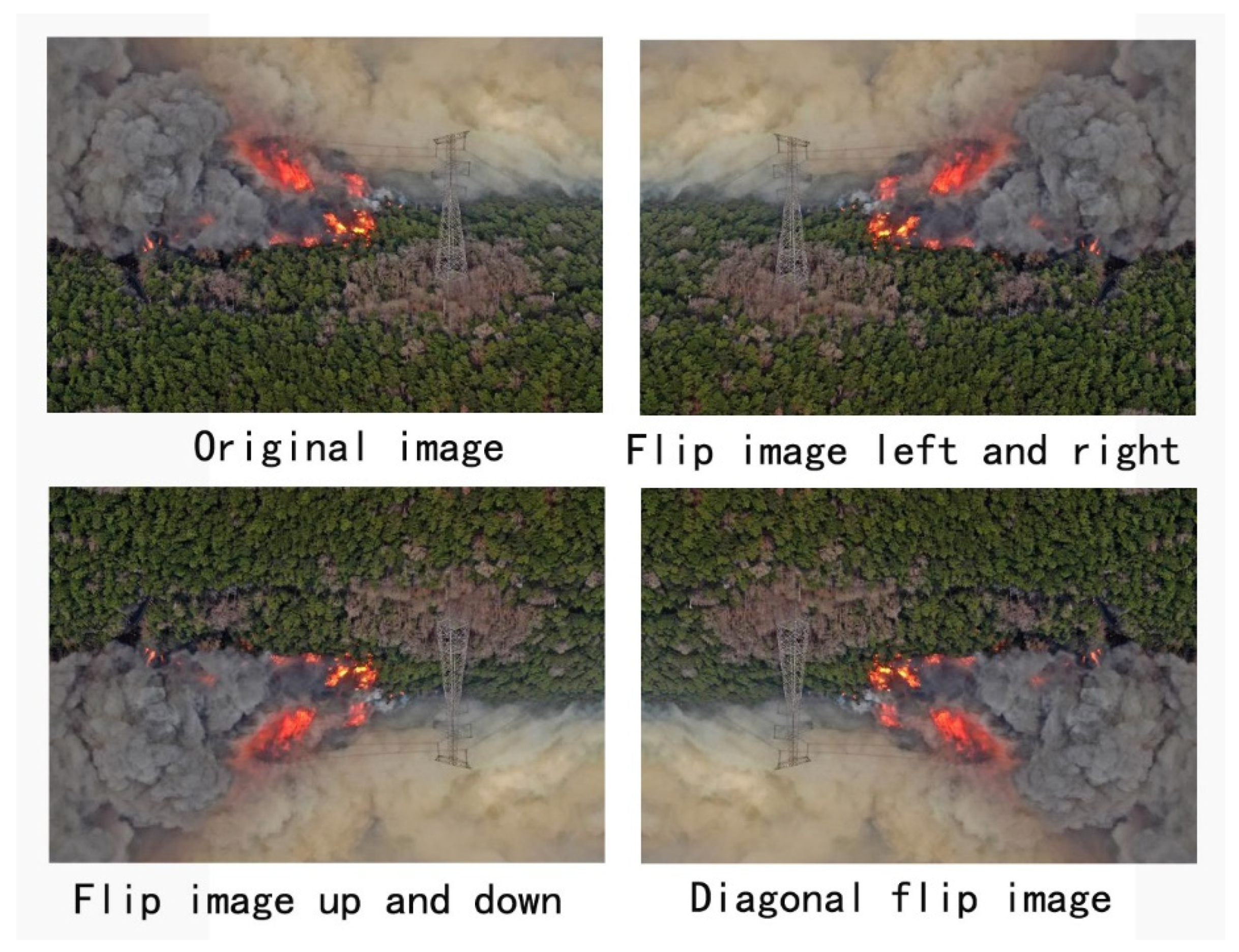
①Flip to increase the width
Image flip simulation can be used to obtain images collected from different flight directions due to the limited data set material. In this way, we use image flipping to get the image when flying from different directions, thus achieving the purpose of data widening[
41].
②Mixing and widening
Since the acquired image scenes are limited, to enrich the scenes, the images are augmented by the method of blending backgrounds. Firstly, a forest image is randomly selected as the background. Secondly, a fire image is obtained by keying out the flames on the image and then fusing the flames with the background image using an image fusion technique[
42].
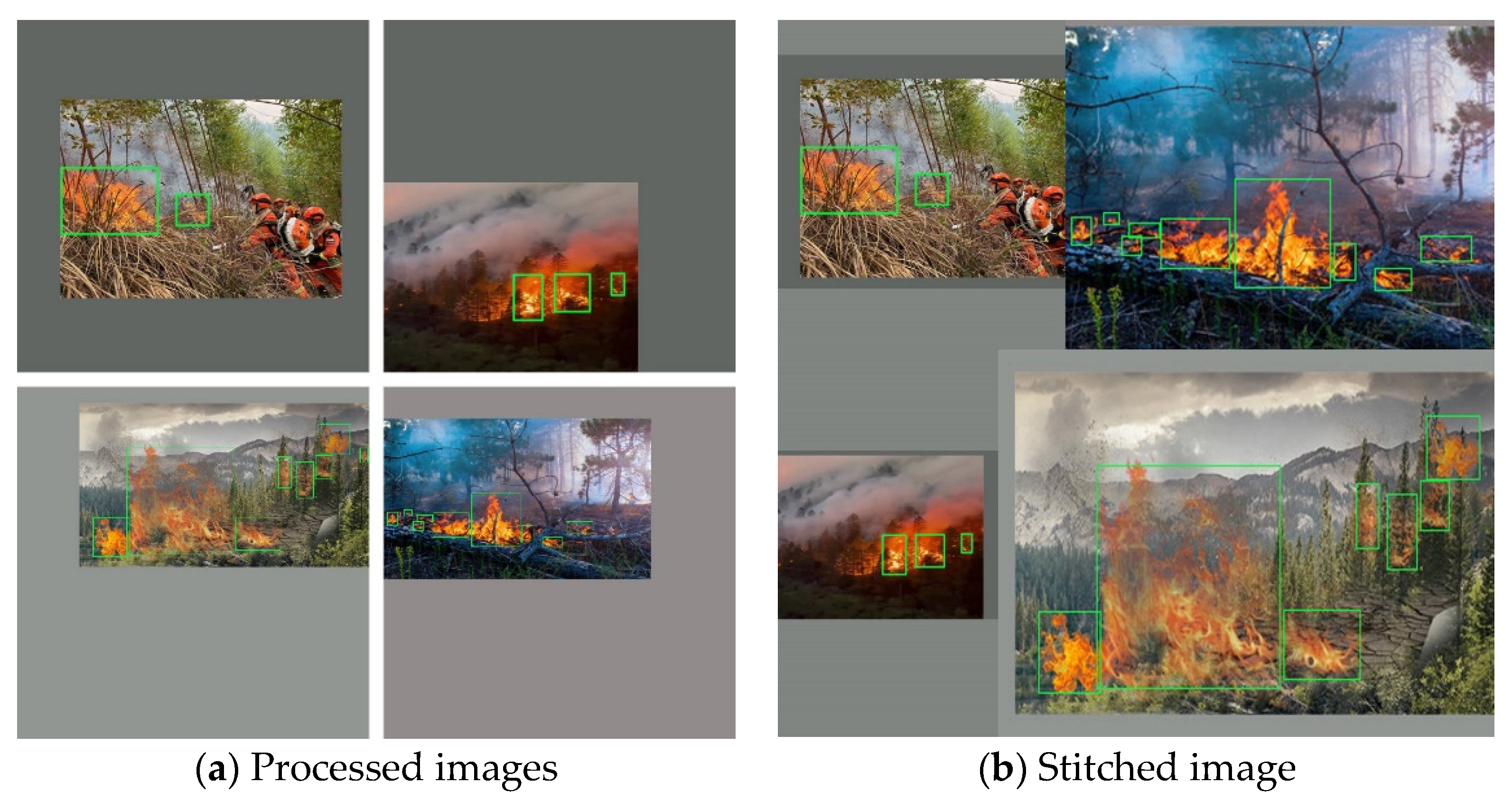
③Image Mosaic stitching enhancement technology
When processing the dataset with the Mosaic stitching enhancement technique, 4 or 6 images are randomly selected to be stitched together into one image. By using this method, the pre-trained batch is increased in disguise, and the complexity of the image is increased, which affects the accuracy of image detection.
In addition, the dataset was partitioned in the ratio of 9:1 for training and testing, respectively. The training dataset part is further divided into training and validation sets with a ratio of 9:1 to prevent the occurrence of overfitting during the training process.
4.3. Evaluation indicators
To evaluate the YOLOv5-IFFDM network as well as other network performance, we use the following performance metrics as comprehensive evaluation metrics[
43]: Precision, recall, F1 score, and mean average precision (mAP). We use Size to measure the model's size and FPS to measure the model in real time. Some of its formulas are defined as follows.
where
denotes true positive samples,
denotes false positive samples, and
denotes false negative samples. The
score is the summed average of the precision and recall rates. The higher the F1 score, the higher the precision and recall.
indicates the performance of each target object class. The
metric is the average of the mean accuracy, which is used to measure the overall detection accuracy of the target detection algorithm model. Time represents the time spent for the whole training, consisting of three parts. FPS indicates how many forest fire images can be processed in one second.
Taking forest fire detection as an example, TP indicates how many forest fire images are correctly predicted, i.e., the detection object and the model detection result are both forest fires.FP means the detection object is a non-forest fire, and the model detection result is a non-forest fire. FN indicates that the detection object is a forest fire, and the model detection result is a non-forest fire. NMS, also known as non-maximum suppression, is the post-frame processing time.
The experimental procedure is as follows. First, the original YOLOv5 detection model is trained using a homemade forest fire classification dataset and evaluated using a test set. The CBAM attention mechanism is then added for experimental comparison. Again, the maxpool in YOLOv5 was replaced with Softpool for evaluation. The fourth experiment is to modify the loss function to α-IoU based on experiment III. The fifth experiment is to add Mosaic data enhancement for experimental comparison based on experiment IV. Following is a table that shows the experimental test results for the sixth and seventh experiments, which add the frame re-clustering and convolutional layer merging again in turn.
Table 3.
Model experimental results.
Table 3.
Model experimental results.
| Model |
Forest Fire |
Forest Smoke |
FPS |
Time |
| YOLOv5 |
0.820 |
0.790 |
59 |
16.9 |
| YOLOv5+CBAM |
0.852 |
0.805 |
62 |
16.1 |
| YOLOv5+CBAM+SoftPool |
0.870 |
0.823 |
63 |
15.9 |
| YOLOv5+CBAM+SoftPool +α-IoU |
0.885 |
0.822 |
63 |
15.9 |
| YOLOv5+CBAM+SoftPool +α-IoU +Mosaic |
0.896 |
0.835 |
63 |
15.9 |
| YOLOv5+CBAM+SoftPool +α-IoU +Mosaic + Re-clustering class anchor |
0.906 |
0.842 |
62 |
16.1 |
| YOLOv5+CBAM+SoftPool +α-IoU +Mosaic + Re-clustering class anchor + Convolution, BN merge(YOLOv5-IFFDM,ours) |
0.905 |
0.843 |
75 |
13.3 |
4.4. Detection performance analysis
From the above results, we found that YOLOv5, one of the more advanced single-stage target detection models, has a good mAP@0.5 for forest fire classification and recognition, but there is still room for improvement. YOLOv5 has a detection accuracy of 0.820 and 0.729 for forest fire and forest smoke, respectively, which is slightly lower, but there is still room for improvement. In addition, the FPS value of YOLOv5 is 59, and the detection time is 16.9 ms, which is slow in real-time detection. In Experiment 2, we added the attention mechanism CBAM in YOLOv5, and both forest fire and forest smoke were improved by 3.2% and 1.5%, respectively, showing the effectiveness of the CBAM attention mechanism in the detection process.
Experiment 3 further improves detection accuracy by replacing the spatial pyramidal pooling structure of maxpool with SoftPool. In experiment 4, the loss function in YOLOv5 is changed to α-IoU, the forest fire accuracy is improved, and the forest smoke detection accuracy is basically unchanged. The detection accuracy of forest fires and forest smoke was improved after adding dataset mosaic preprocessing and re-clustering anchors to Experiments V and VI. The merging of the convolution and BN layers was performed in Experiment 7, and the detection accuracy did not improve, but the detection speed increased substantially, indicating that the prediction speed is indeed affected when the convolution and BN layers are separated, as expected. The model's accuracy in this paper is 90.5% and 84.3% for forest fire and forest smoke, respectively. Compared with the YOLOv5 model, the mAP of this model is improved by 8.5% and 5.3%, respectively, suggesting that the model has better results in forest fire classification detection.
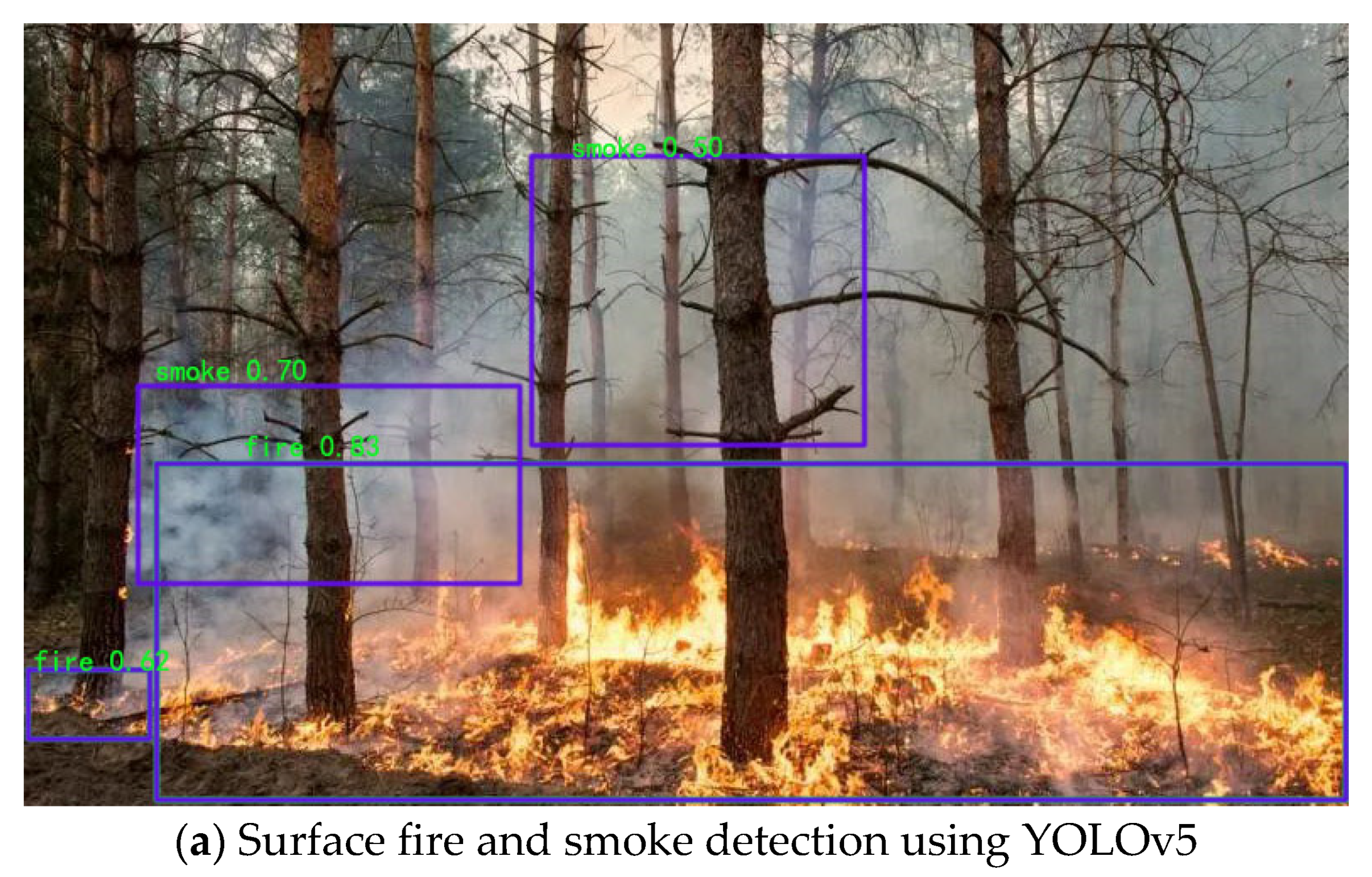
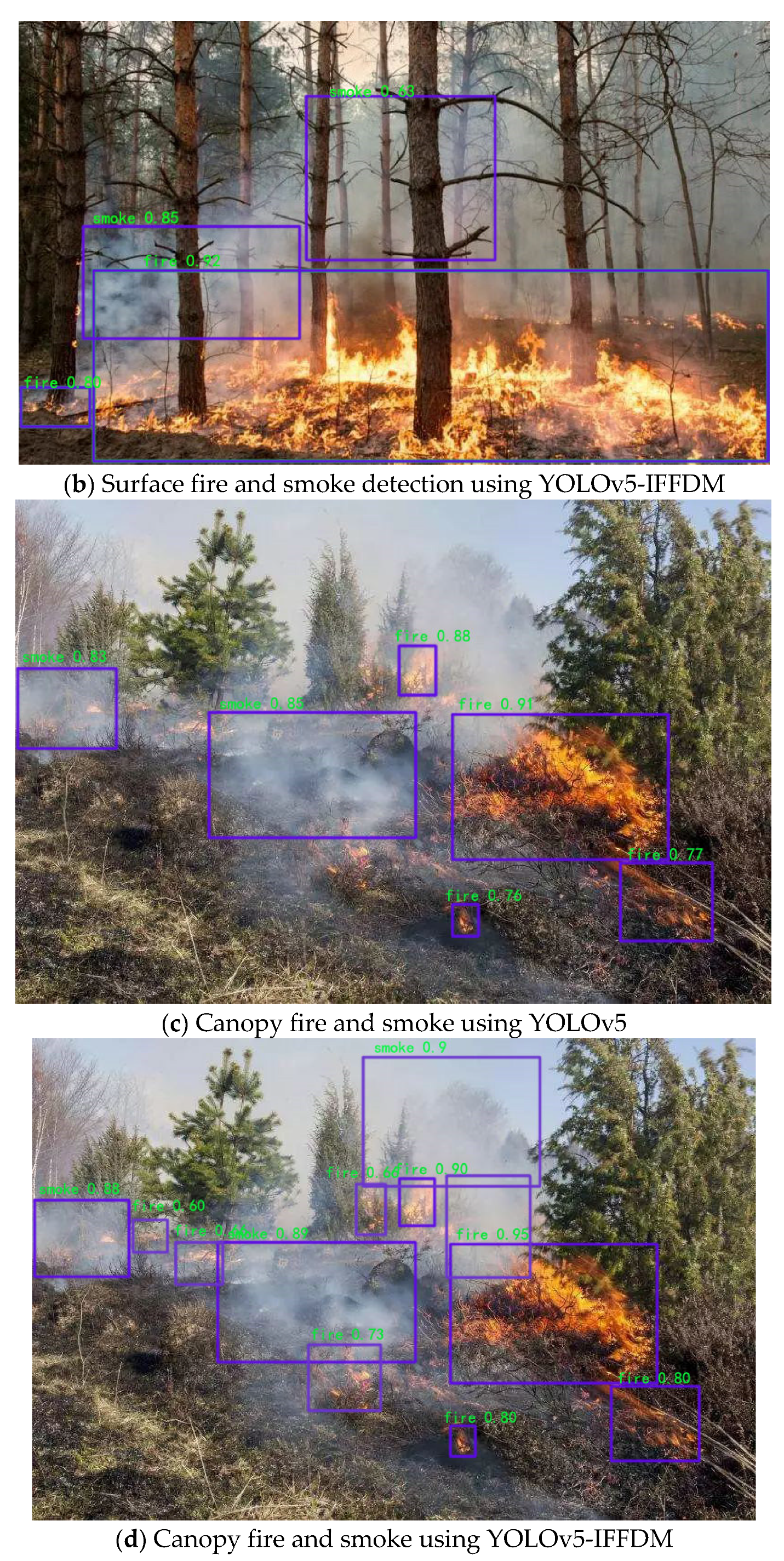
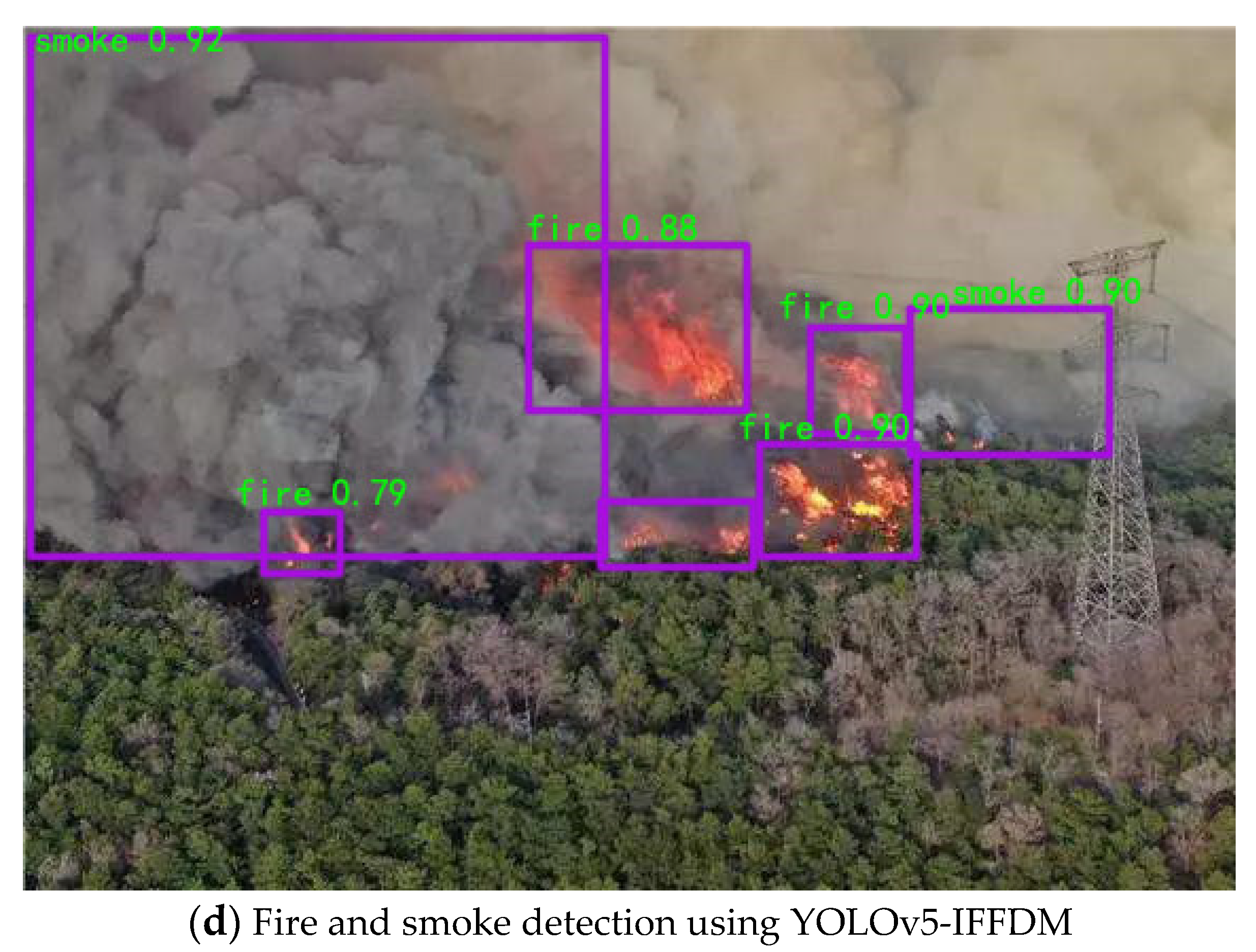
The results of the YOLOv5 model and the YOLOv5-IFFDM forest fire classification and detection model are shown in
Figure 7 and
Figure 8.
Figure 7 shows the detection effect of a sample of forest fire training images with typicality, and
Figure 8 shows the detection of forest fire image samples from the UAV camera view. From the detection effect, the YOLOv5 model detects that the rectangular box of the forest fire is not located in the same place as the real box. As a result, the missing detection problem will occur, and the detection effect will be poor. YOLOv5-IFFDM model detection aligns more with the real forest fire target frame. The model has better detection of forest fire types and fewer false detections of leakage. Experiments show that the model YOLOv5-IFFDM proposed in this paper is more suitable for forest fire classification detection.
5. Discussion
The forest fire detection model proposed in this paper has been improved compared with YOLOv5 regarding detection accuracy and detection speed, but the model still has room for improvement. For example, in low illumination, some small fire areas may be missed, and some fire points may only be a few dozen pixels in size when taken from a high altitude and distance, which may result in their misdetection as well. Further research is needed to improve the detection accuracy and speed up the detection of small fire spots.
The experimental results show that the forest fire detection model proposed in this paper has good application prospects. The model can be fitted to drones or watchtowers for forest image acquisition to detect quickly if a forest fire occurs. Compared with the traditional method of arranging sensors to detect forest fires or manual inspection, this method has a larger detection range, lower cost, better and more efficient detection on time, and has a positive effect on protecting forests from the threat of forest fires.
6. Conclusion and outlook
This paper focuses on improving the feature extraction network to address the shortcomings of YOLOv5 in fire detection applications by improving the attention mechanism, prior frame, loss function, convolutional layer and BN layer merging to make YOLOv5 more efficient in fire detection. The algorithm has experimented with a self-designed and labeled fire-detection dataset. The experimental results show that the improved method in this paper has better fire detection robustness than the original YOLOv5 detection algorithm, both in terms of accuracy and speed. Based on the dataset, the detection algorithm achieved 91.6% accuracy, 83.2% recall, 84.5% mAP, and an average detection speed of 13.3ms. In the future, in addition to optimizing and improving the network, we will expand the existing fire dataset to increase sample diversity and improve the sample quality of the training set, as well as expand the existing fire dataset.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.L. and X.L.; methodology, J.L. and X.L.; software, J.L.; validation, J.L.; formal analysis, J.L.; data curation, J.L.; writing— original draft preparation, J.L.; writing—review and editing, J.L. and X.L.; visualization, J.L.; supervision, X.L.; project administration, J.L. and X.L.; funding acquisition, X.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by 2020 Beijing Higher Education "Undergraduate Teaching Reform and Innovation Project " (Project No. 173), 2020 Teaching Reform Research Project of the Teaching Instruction Committee of Electronic Information (Project No. 2020-YB-09), 2020 Education Teaching Reform Research Project of Beijing Technology and Business University (Project No. jg205105), 2021 Talent Training Quality Construction Project of Beijing Technology and Business University (Project No. 9008021060).
Data Availability Statement
The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the School of Artificial Intelligence, Beijing Technology and Business University for assistance with simulation verifications related to this work.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Wen xiao rong. Research on key techniques and methods of forest resources second class survey [D]. NAN JING: Nanjing Forestry University, 2017.
- Dong xiao rui. Research on forest fire detection system based on FY3 remote sensing images[D]. Harbin: Harbin Engineering University, 2018.
- Yan Yang. Application of Visual Information Network Foundation Platform in Forest Fire Prevention [J]. Forest Science and Technology Information 2019, 51, 18–21. [Google Scholar]
- WANG M W, et al. Fire recognition based on multi-Channel convolutional neural Network [J]. Fire Technology 2018, 54, 531–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang Xu Bin. The research of smoke detection algorithm on video [D]. Han Zhou: Zhe jiang University,2017.
- Xiao xiao, Kong fan zhi, Liu jin hua. Monitoring Video Fire Detection Algorithm Based on Dynamic Characteristics and Static Characteristics. Computer Science 2019, 284–286. [Google Scholar]
- CHEN T H, WU P H, CHIOU Y C. An early fire-detection method based on image processing [C]. 2004 International Conference on Image Processing, 2004. ICIP’04, IEEE,2004.
- CHEN J, HE Y, WANG J. Multi-feature fusion based fast video flame detection [J]. Building and Environment 2010, 45, 1113–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CELIK T, DEMIREL H, OZKARMANLI H. Automatic fire detection in video sequences [J]. Fire Safety Journal 2006, 6, 233–240. [Google Scholar]
- LI Z, MIHAYLOVA L S, ISUPOVA O, et al. Autonomous flame detection in videos with a dirichlet process Gaussian mixture color model [J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics 2017, 14, 1146–1154. [Google Scholar]
- EMMY P C, VINSLEY S S, SURESH S. Efficient flame detection based on static and dynamic texture analysis in forest fire detection [J]. Fire Technology 2018, 54, 255–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foggia, P.; Saggese, A.; Vento, M. Real-Time Fire Detection for Video-Surveillance Applications Using a Combination of Experts Based on Color, Shape, and Motion. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2015, 25, 1545–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HAN X F, JIN J S, WANG M J, et al. Video fire detection based on Gaussian mixture model and multi-color features [J]. Signal Image & Video Processing 2017, 11, 1419–1425. [Google Scholar]
- Jian wen lin. Research on fire detection method based on video smoke motion detection [D]. NAN CHANG: Nanchang Aviation University, 2018.
- DIMITROPOULOS K, BARMPOUTIS P, GRAMMALIDIS N. Higher order linear dynamical systems for smoke detection in video surveillance applications [J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology 2017, 27, 1143–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WANG S, HE Y, YANG H, et al. Video smoke detection using shape, color and dynamic features [J]. Journal of Intelligent & Fuzzy Systems 2017, 33, 305–313. [Google Scholar]
- APPANA D K, ISLAM R, KHAN S A, et al. A Video based smoke detection using smoke flow pattern and spatial-temporal energy analyses for alarm systems [J]. Information Sciences 2017, 418, 91–101. [Google Scholar]
- 18. FU Tian-ju, ZHENG Chang-e, TIAN Ye, QIU Qi-min, LIN Si-jun. Forest Fire Recognition Based on Deep Convolutional Neural Network Under Complex Background [J]. Computers and Modernization, 2016; 5257.
- Frizzi S, Kaabi R, Bouchouicha M, et al. Convolutional neural network for video fire and smoke detection [C]∥IECON 2016-42nd Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, -26, 2016, Florence, Italy. New York: IEEE Press, October 23-26 2016: 877-882.
- Sandler, M.; Howard, A.; Zhu, M. Mobilenetv2: Inverted Residuals and Linear Bottlenecks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 4510–4520. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. You Only Look Once: Unified, Real-Time Object Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 779–788. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon J, Farhadi A. YOLO9000: Better, faster, stronger. Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu: IEEE, 2017. 6517–6525.
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. YOLOv3: An Incremental improvement. In Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Lin TY, Dollár P, Girshick R, et al. Feature pyramid networks for object detection. Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu: IEEE, 2017. 936–944.
- Wang, Y.; Yan, G.; Meng, Q.; Yao, T.; Han, J.; Zhang, B. DSE-YOLO: Detail semantics enhancement YOLO for multi-stage strawberry detection. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 198, 107057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochkovskiy A, Wang CY, Liao HYM. YOLOv4: Optimal speed and accuracy of object detection. arXiv:2004.10934, 2020.
- Jocher, G. YOLOv5. https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5.
- Hu J, Shen L, Sun G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City: IEEE, 2018. 7132–7141.
- Wang QL, Wu BG, Zhu PF, et al. ECA-Net: Efficient channel attention for deep convolutional neural networks. Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Seattle: IEEE, 2020. 11531–11539.
- Foggia, P.; Saggese, A.; Vento, M. Real-Time Fire Detection for Video-Surveillance Applications Using a Combination of Experts Based on Color, Shape, and Motion. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2015, 25, 1545–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.; Xu, R.; Li, J.; Lv, Y.; Lin, H.; Liu, Y. A Vision-Based Detection and Spatial Localization Scheme for Forest Fire Inspection from UAV. Forests 2022, 13, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Ou, X.; Xu, L. A Collaborative Region Detection and Grading Framework for Forest Fire Smoke Using Weakly Supervised Fine Segmentation and Lightweight Faster-RCNN. Forests 2021, 12, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xin, J.; Mu, L.; Yi, Y.; Liu, H.; Liu, D. A Deep Learning Based Forest Fire Detection Approach Using UAV and YOLOv3. In Proceedings of the1st International Conference on Industrial Artificial Intelligence (IAI), Shenyang, China, 23–27 July 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Mukhiddinov, M.; Abdusalomov, A.B.; Cho, J. A Wildfire Smoke Detection System Using Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Images Based on the Optimized YOLOv5. Sensors 2022, 22, 9384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouguettaya, A.; Zarzour, H.; Taberkit, A.M.; Kechida, A. A review on early wildfire detection from unmanned aerial vehicles using deep learning-based computer vision algorithms. Signal Process. 2021, 190, 108309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almalki, F.A.; Soufiene, B.O.; Alsamhi, S.H.; Sakli, H. A Low-Cost Platform for Environmental Smart Farming Monitoring System Based on IoT and UAVs. Sustainability 2021, 13, 5908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zhan, J.; Zhou, G.; Chen, A.; Cai, W.; Guo, K.; Hu, Y.; Li, L. Fast forest fire smoke detection using MVMNet. Knowledge-Based Syst. 2022, 241, 108219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahyono; Harjoko, A. ; Dharmawan, A.; Adhinata, F.D.; Kosala, G.; Jo, K.-H.G. Real-Time Forest Fire Detection Framework Based on Artificial Intelligence Using Color Probability Model and Motion Feature Analysis. Fire 2022, 5, 23.
- Guede-Fernández, F.; Martins, L.; de Almeida, R.V.; Gamboa, H.; Vieira, P. A Deep Learning Based Object Identification System for Forest Fire Detection. Fire 2021, 4, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzekri, W.; El Moussati, A.; Moussaoui, O.; Berrajaa, M. Early Forest Fire Detection System using Wireless Sensor Network and Deep Learning. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2020, 11, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Yang, F.; Tang, Q.; Lu, X. An Attention Enhanced Bidirectional LSTM for Early Forest Fire Smoke Recognition. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 154732–154742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinaneva, D.; Hristov, G.; Raychev, J.; Zahariev, P. Early Forest Fire Detection Using Drones and Artificial Intelligence. In Proceedings of the 42nd International Convention on Information and Communication Technology, Electronics and Microelectronics (MIPRO), Opatija, Croatia, 20–24 May 2019; pp. 1060–1065. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Hua, C.; Ding, W.; Wu, R. Real-time detection of flame and smoke using an improved YOLOv4 network. Signal, Image Video Process. 2022, 16, 1109–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).