Submitted:
19 May 2023
Posted:
22 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
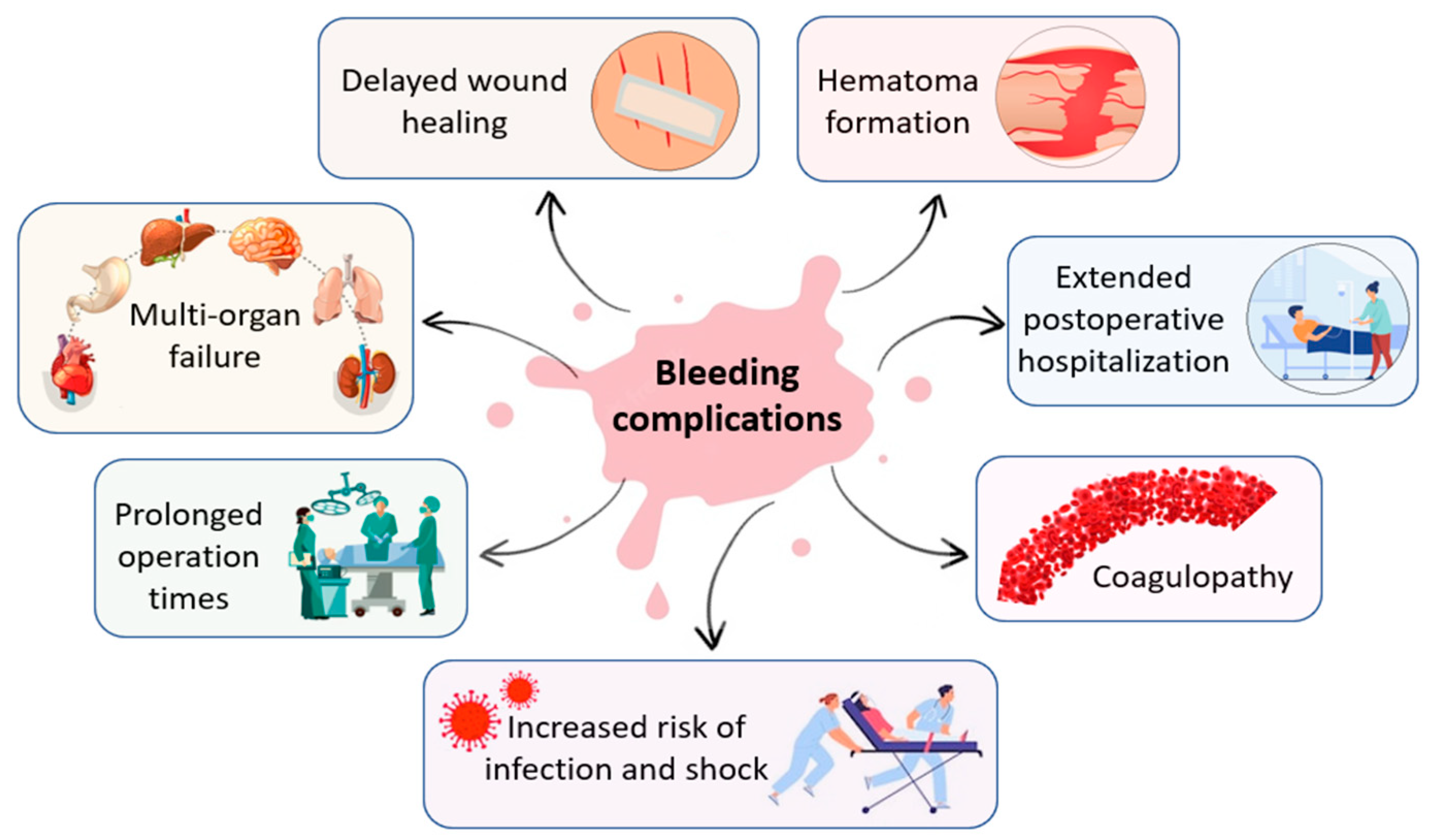
1.1. Hemorrhage in Surgical and Trauma Setting
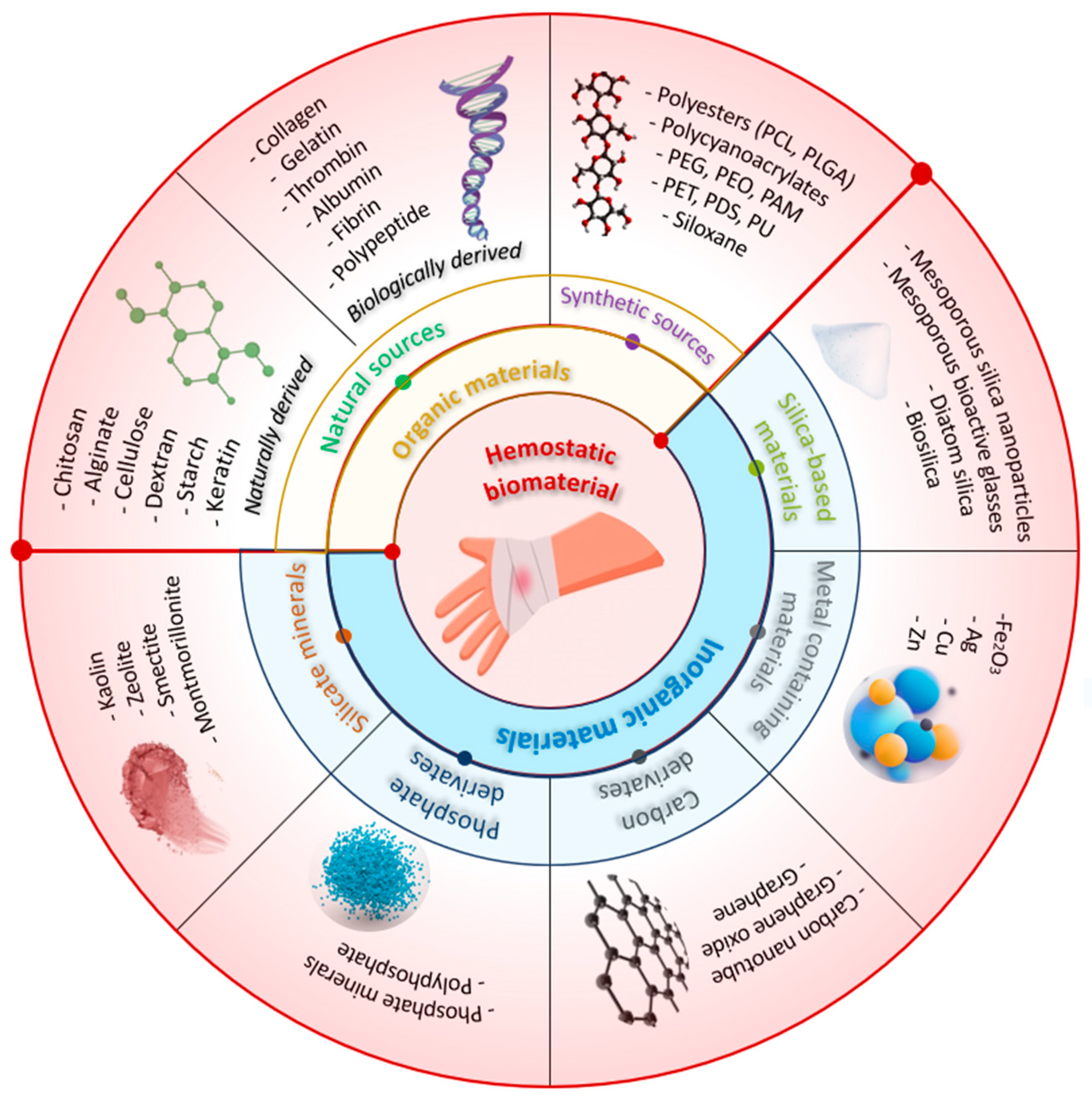
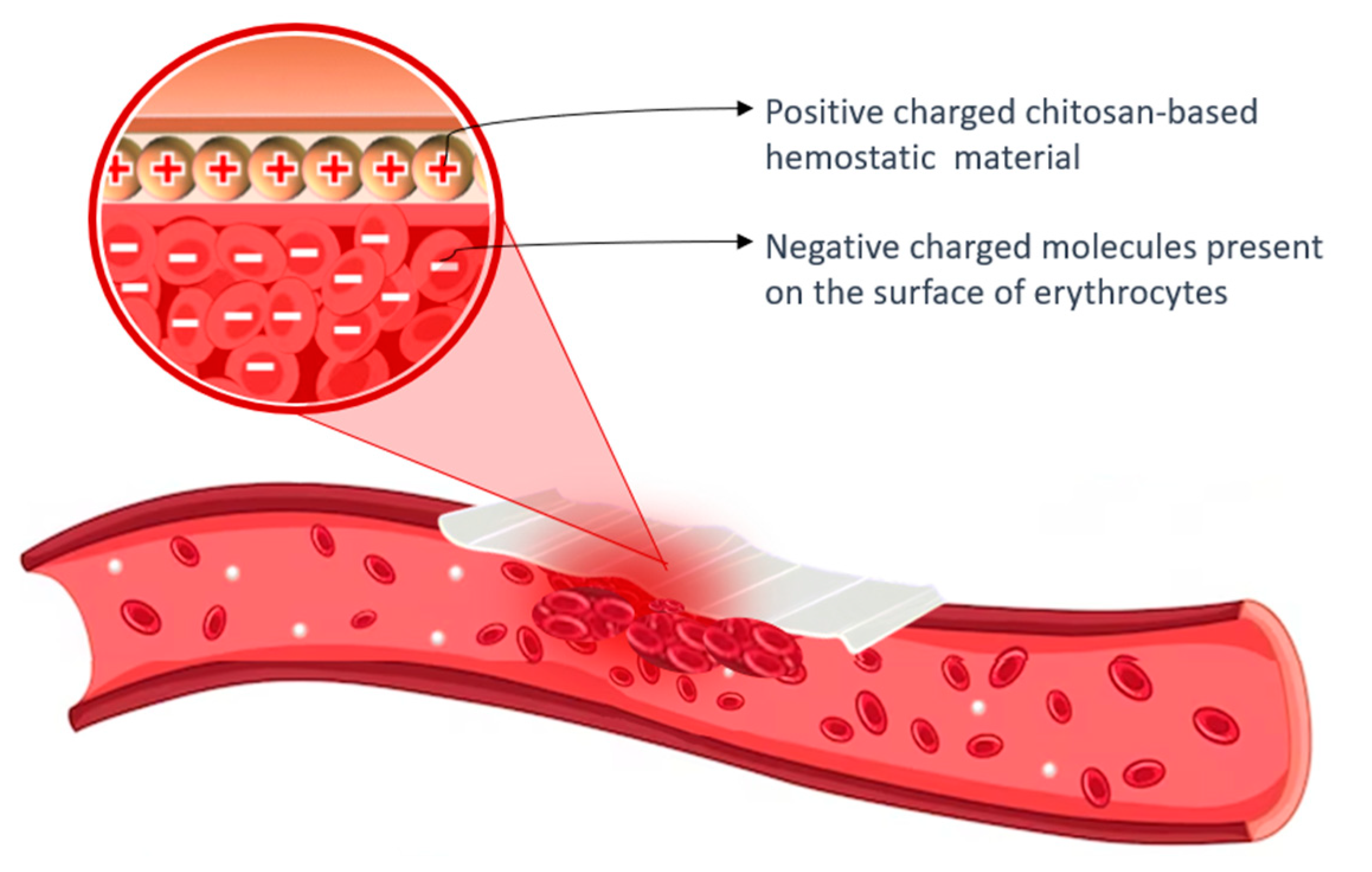
1.2. Achieving Hemostasis
| Materials and trademarks | Hemostatic mechanism | Characteristics | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chitosan-based materials ChitoFlex, Axiostat, PosiSep X, Celox, TraumaStat, HemCon. |
Positive surface charge enables it to bind with negatively charged blood components, promoting platelet activation and agglutination of blood proteins to facilitate fibrin clot formation, while also forming a strong physical barrier that adheres to wet tissues and seals wounds. |
Biocompatible, biodegradable, antibacterial ability, stimulatory effect on tissue regeneration, hemostatic effect, cost-effective, easy to store and long shelf-life; suitable for patients with coagulopathy, although it may not be entirely effective in extensive bleeding wounds. |
[33,34,35,36,37] |
| Cellulose-based materials BloodSTOP, WoundClot, Surgicel, Suntouch, ActCel. |
Absorbs fluids, forms a physical barrier to prevent blood loss, exhibits anti-microbial activity, is bioabsorbable, and aids clotting by binding to calcium ions, initiating the clotting cascade through contact activation and decreasing pH at the wound site, leading to platelet activation and aggregation. |
Appropriate for achieving hemostasis in cases of capillary, arteriolar, venous, and bone bleeding, and is also biocompatible, non-immunogenic, and bactericidal, conforming well to the wound site. However, it may not be effective in managing severe bleeding. | [2,38,39,40,41] |
| Starch-based materials PerClot, EndoClot |
Absorbs water from the blood, leading to the formation of a gel-like matrix that can adhere to tissue and promote the aggregation of platelets and activation of clotting factors, ultimately resulting in the formation of a stable fibrin clot that can help to stop bleeding. | Reduces bleeding and the need for transfusions, minimizes the risk of blood infections and has no known immune or allergic reactions or toxic side effects. Should not be used in blood vessels to avoid the risk of embolism and is suitable for minor injuries. It is easy to use, lightweight, has a long shelf life, is inexpensive. |
[42,43,44,45,46,47] |
| Collagen-based materials Avitene, Helitene, Hemopad, Helistat, Collastat, Instat, CoStasis, D-stat. |
Forms a physical matrix, triggers the process of coagulation cascade and induces the activation of platelets, leading to the release of clotting factors like thrombin and fibrinogen. | Promotes tissue regeneration and repair, and possesses characteristics such as biocompatibility, cell adhesion, biodegradability, non-toxicity, and low antigenicity. Effective in heparinized patients, not suitable for use in patients with thrombocytopenia. |
[2,20,33,48,49] |
| Gelatin-based materials Gelfoam, Surgifoam, Gelfilm, Gelita-spon. |
Triggers the activation and aggregation of platelets, expedites the formation of clots, and provides structural support to the clot formed by enhancing thrombin generation and subsequently propagating the coagulation cascade. | Applicable for treating various types of wounds and injuries, but caution must be taken when used in restricted areas or near nerve structures due to the potential risk of compressive complications. It is a cost-effective solution that remains stable at room temperature, non-toxic, and non-antigenic. Furthermore, it has a strong adsorption capability, can stick to the wound surface, and can increase its volume up to twice its original size by absorbing fluids. | [23,50,51,52,53] |
| Fibrin-based materials Artiss, Tissel, Evicel, Tissucol, TachoSil. |
Major protein component of blood clots, is formed as the final step in the coagulation cascade, serving as a scaffold for tissue repair and providing cues for cell behavior during injury healing. | Exhibits excellent hemostatic and adhesive properties, biocompatibility, and can be used for severe bleeding and patients with coagulation disorders but is not recommended for application on blood vessels. It also aids in tissue regeneration following injury due to its fast polymerization dynamics and ease of tunability. | [54,55,56,57] |
| Polycyanoacrylates-based materials Dermabond, Omnex, Glubran, Histoacryl, GLUture. |
Rapidly polymerize upon contact with fluids to create a mechanical barrier or plug that occludes the bleeding vessel or tissue, resulting in hemostasis. | Presents bactericidal and bacteriostatic effects, non-toxic, non-carcinogenic, and good histocompatibility, with considerable hemostatic ability and can be applied in anastomosis, wound hemostasis, wound adhesion, and tendon repair, however, it may result in vascular embolization and release of toxic substances. | [52,58,59,60] |
| PEG-based materials Coseal |
Upon contact with tissue fluids to form a gel-like matrix, which adheres to the tissue and provides a mechanical barrier to prevent bleeding. | Favorable biocompatibility, minimal cytotoxicity, and excellent hemostatic properties, commonly utilized in surgical settings to reduce bleeding and facilitate wound healing with a low occurrence of unfavorable consequences. | [48,61,62,63,64] |
| Polyurethane-based materials Bioclusive, Opsite Flexigrid, Tegaderm, Allevyn, Tegaderm (3M Science), TissuGlu (Cohera Medical, Inc.), ResQFoam (Arsenal Medical, Inc.), Nanosan-Sorb (SNS Nano Fiber Technology) |
It triggers activation and aggregation of thrombocytes, initiating both coagulation cascade. |
Polyurethane dressings can maintain a moist wound environment by allowing the transmission of moisture, oxygen, and air while blocking fluids and bacteria, and provide thermal insulation, promoting autolytic debridement; their high absorbency is due to a hydrophilic contact surface, microporous foam, and hydrophobic backing. Maintains its shape and firmness when exposed to blood, | [51,65,66,67] |
| Zeolite and kaolin powder based materials Quikclot, Woundstat Combat Gauze |
Has a hygroscopic action, which allows it to quickly absorb water from blood to concentrate coagulation factors; it can also release Ca++ in blood and activate FXII to trigger the intrinsic coagulation pathway, and potentially induce contact activation of platelets. | Ease of use, stability, no biological toxicity or disease transmission, provide deep tissue access, are inert, and do not elicit an immune response. Not bioabsorbable and are less effective for arterial bleeding or coagulopathic patients. Their success is dependent on the patient's blood clotting activity. May cause thrombotic complications if particles enter the bloodstream. |
[26,48,68,69,70] |
| PEG – Polyethylene glycol; PU – Polyurethane; FXII – Coagulation factor XII; | |||
2. Chitosan Properties and Hemostasis Efficiency
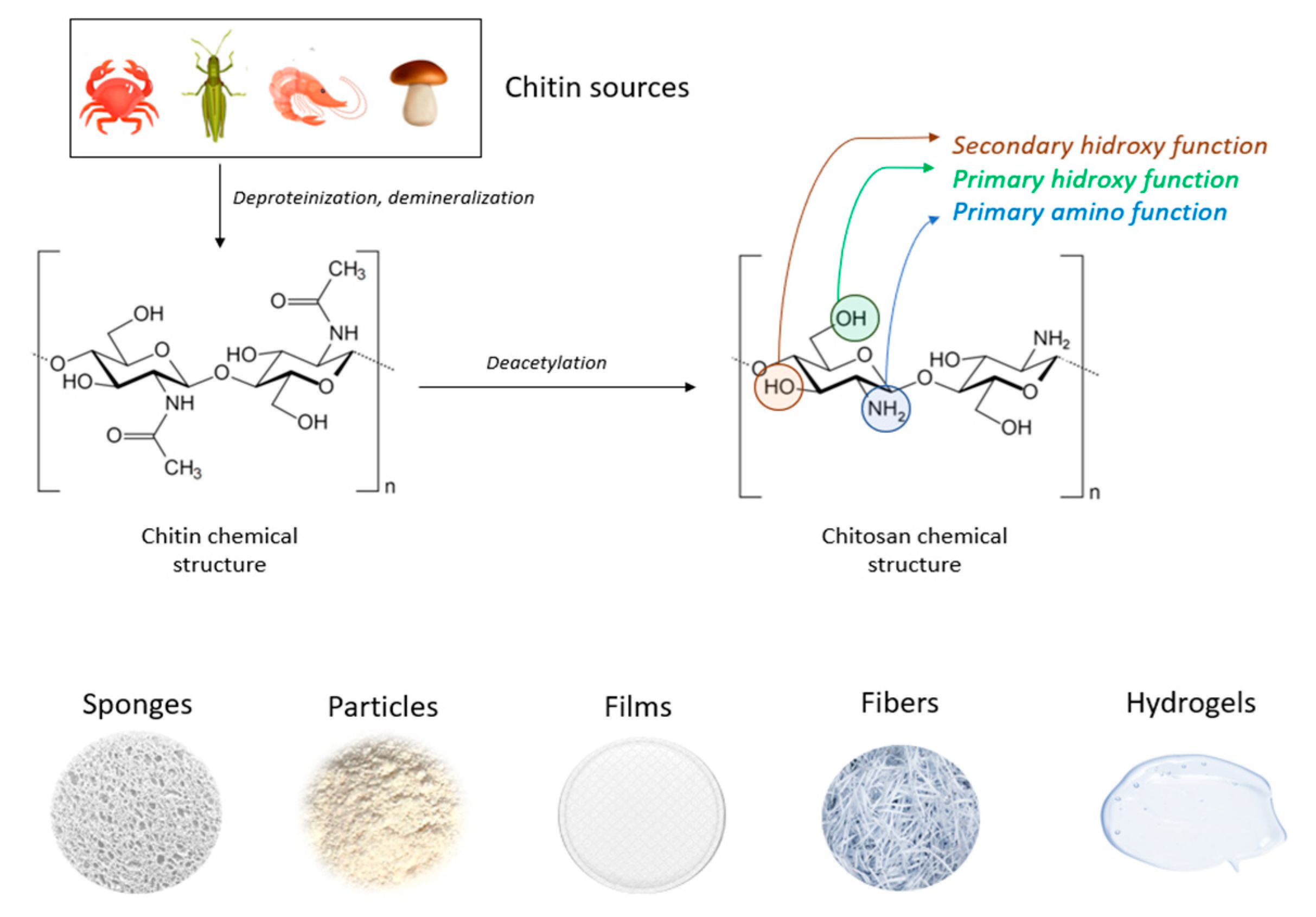
3. Current Trends on Chitosan Based Hemostatics
| Forms | Composition | Characteristics | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dressing | CS, Aluminum chloride | The microporous structure of the dressing is irregular, which allows it to absorb the maximum amount of blood and promote clot formation. | [35] |
| Carrageenan, CS | The composite dressing's greater swelling, larger surface area, and mesoporous structure result in superior hemostatic activity by promoting increased adhesion of blood cells and platelets. | [99] | |
| CS, Calcium Alginate | Biocompatibility, antibacterial, moisture retention, healing promotion, and noncytotoxicity characteristics make chitosan-calcium alginate dressing a superior option for wound care. | [100] | |
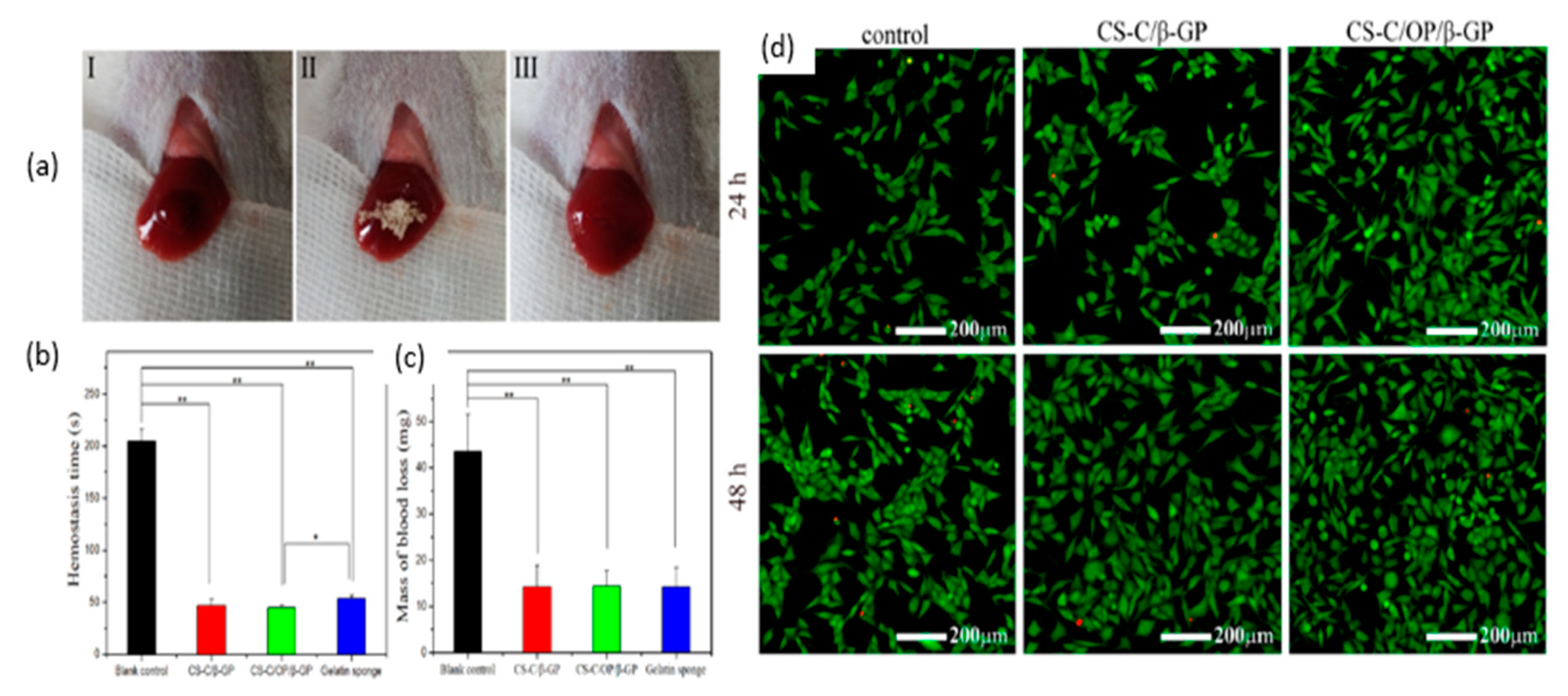
| Hydrogel | CS, PEG | The combination of biodegradability, self-adhesiveness, self-healing ability, stretchability, antibacterial properties, and biocompatibility makes it a promising material for emergency hemostasis, particularly for joint and limb injuries. The hydrogel showed strong adhesion to various substrates (PTFE, pigskin, and glass tubes) and provided long-term stability when applied to bleeding wounds in both static and dynamic humid environments. | [101] |
| Hydroxybutyl-functionalized CS | The material possesses thermosensitive characteristics, strong adhesion ability, effective hemostasis, appropriate mechanical properties, self-healing capability, easy removal as needed, antioxidant properties, as well as photothermal and intrinsic antibacterial activity. | [102] | |
| FCMCS, PDA, PAM | The hydrogel exhibited a variety of functions including tissue adhesion, biocompatibility, self-healing, and antibacterial properties. It also maintained its mechanical characteristics while offering broad-spectrum antibacterial activity. | [103] | |
| CMCS, OHA | The material exhibits favorable biodegradability and biosafety profiles, and possesses strong hemostatic and sealing capabilities, making it a promising candidate for clinical hemostatic sealant applications. | [104] | |
| Sponge | Cs, AgNPs | The chitosan/Ag nanocomposite sponges demonstrated outstanding antibacterial activity against Staphylococcus aureus and E. coli in the antibacterial test. They also displayed good mechanical properties and noncytotoxicity, with cell viability values exceeding 90%. | [105] |
| CS, Cellulose | The sponge demonstrates favorable biocompatibility and hemostatic capability, making it a promising option for prompt hemostasis in cases of severe bleeding. | [106] | |
| CS/PVA-PD-FeO NPs | The sponge demonstrated high porosity and water absorption properties, as well as significant antibacterial activity. It facilitated gaseous exchange, absorbed wound exudate, and inhibited microbial growth in diabetic wounds. Therefore, it can be inferred that the chitosan composite sponge's antioxidant, antidiabetic, and antibacterial properties can contribute to the healing of diabetic wounds. | [107] | |
| CS/ AgNPs /Alginate | The material demonstrated notable absorbency and a significant antimicrobial impact, particularly in assays involving Bacillus cereus and Staphylococcus aureus. | [108] | |
| CS, SIP | The material exhibits a strong ability to absorb fluids, as well as significant procoagulant effects, making it effective in promoting wound healing. | [109] | |
| CS – Chitosan; PEG – Polyethylene glycol; CMCS – Carboxymethyl chitosan; PDA – Polydopamine; PAM – Polyacrylamide; FCMCS – Fungal mushroom-derived carboxymethyl chitosan; OHA – Oxidized hyaluronic acid; AgNPs – Silver nanoparticles; PD – aqueous leaves extract of Pinus densiflora; FeO – Iron oxide; PVA – Poly vinyl alcohol; SIP – Squid ink polysaccharide. | |||
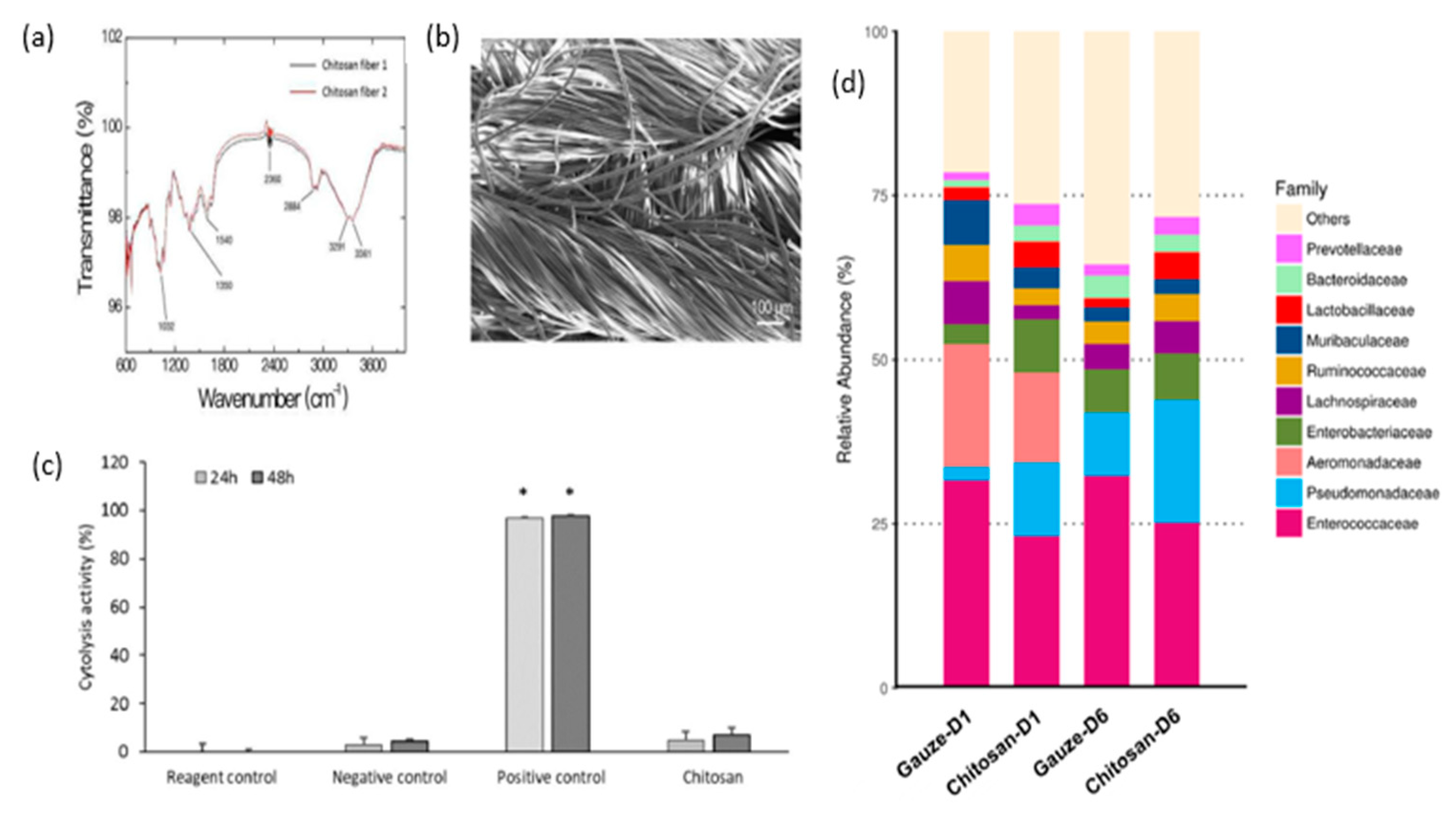
3.2. Hydrogel
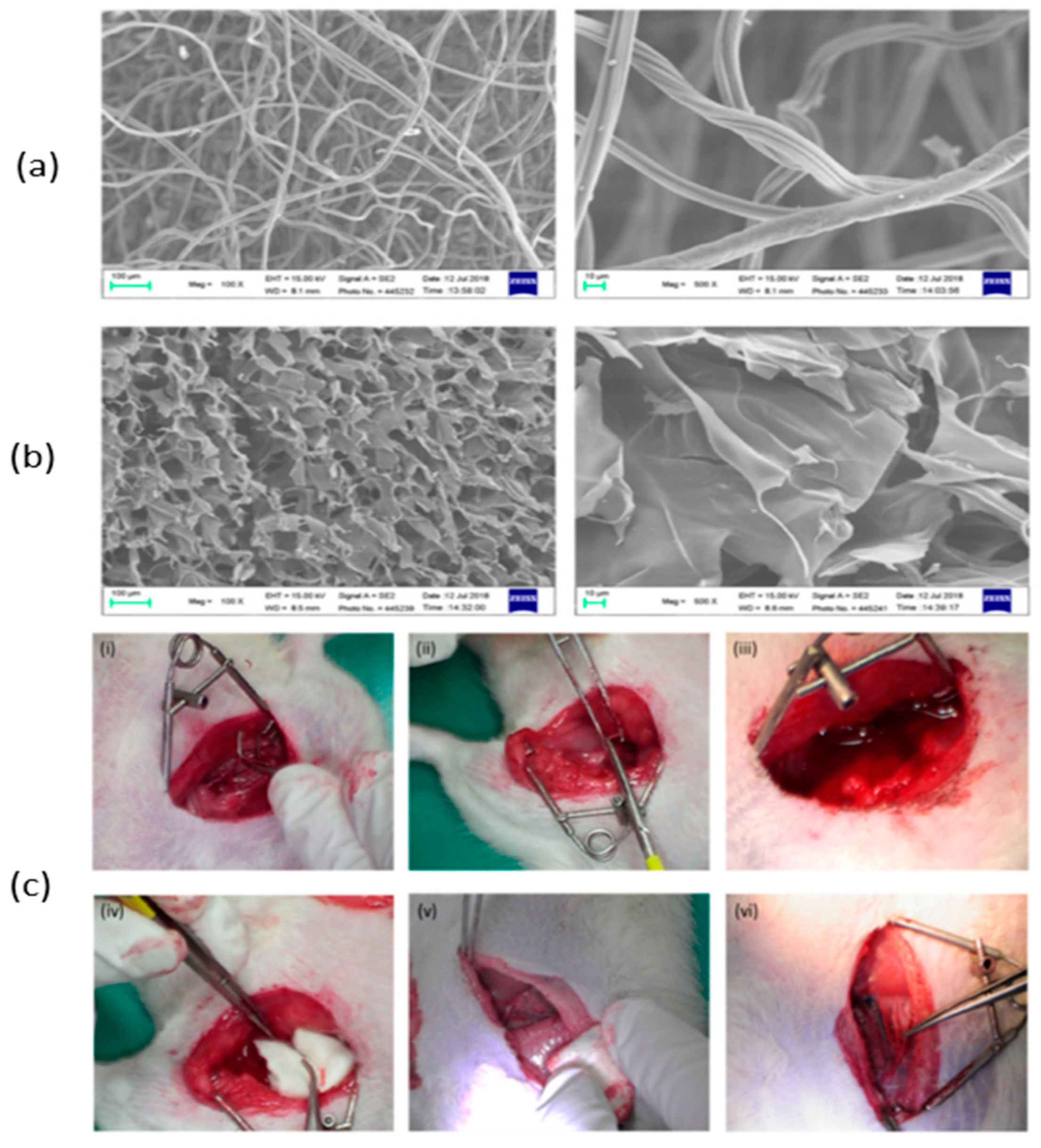
3.3. Sponge
4. Conclusion and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Malik, A.; Rehman, F.U.; Shah, K.U.; Naz, S.S.; Qaisar, S. Hemostatic Strategies for Uncontrolled Bleeding: A Comprehensive Update. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater 2021, 109, 1465–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, E.; Fitzgerald, A.; Tsuzuki, T. The Role of Nanoscale Structures in the Development of Topical Hemostatic Agents. Mater Today Nano 2021, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, E.E.; Moore, H.B.; Kornblith, L.Z.; Neal, M.D.; Hoffman, M.; Mutch, N.J.; Schöchl, H.; Hunt, B.J.; Sauaia, A. Trauma-Induced Coagulopathy. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2021, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yesudasan, S.; Averett, R.D. Recent Advances in Computational Modeling of Fibrin Clot Formation: A Review. Comput Biol Chem 2019, 83, 107148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pariza, G.; Mavrodin, C.; Antoniac, I. Dependency between the Porosity and Polymeric Structure of Biomaterials Used in Hernia Surgery and Chronic Mesh-Infection. MATERIALE PLASTICE 2015, 52, 484–486. [Google Scholar]
- Brătilă, E.; Comandasu, D.; Milea, C.; Berceanu, C.; Vasile, E.; Antoniac, I.; Mehedintu, C. Effect of the Surface Modification of the Synthetic Meshes Used in the Surgical Treatment of Pelvic Organ Prolapse on the Tissue Adhesion and Clinical Functionality. J Adhes Sci Technol 2017, 31, 2028–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iliuta, L.; Rac-Albu, M.; Rac-Albu, M.-E.; Andronesi, A. Impact of Pulmonary Hypertension on Mortality after Surgery for Aortic Stenosis. Medicina (B Aires) 2022, 58, 1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crișan, R.-M.; Băcilă, C.I.; Morar, S. The Role of Psychological Autopsy in Investigating a Case of Atypical Suicide in Schizophrenia: A Case Report with a Brief Review of Literature. Egypt J Forensic Sci 2022, 12, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iliuta, L. Predictors of Persistent Severe Diastolic Dysfunction after Aortic Valve Replacement in Aortic Stenosis Compared with Aortic Regurgitation. Eur Heart J 2012, 33, 667–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costache, V.S.; Moldovan, H.; Arsenescu, C.; Costache, A. Aortic Valve Surgery of the 21st Century: Sutureless AVR versus TAVI. Minerva Cardiology and Angiology 2018, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobritoiu, F.; Moldovan, H.; Oncica, R.; Vasile, G.; Nechifor, E.; Copaescu, C. Giant Cavernous Hemangioma of the Right Atrium - A Rare Case and Literature Review. Chirurgia (Bucur) 2020, 115, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costache, V.S.; Meekel, J.P.; Costache, A.; Melnic, T.; Solomon, C.; Chitic, A.M.; Bucurenciu, C.; Moldovan, H.; Antoniac, I.; Candea, G.; et al. Geometric Analysis of Type B Aortic Dissections Shows Aortic Remodeling After Intervention Using Multilayer Stents. Materials 2020, 13, 2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renkens, K.L.; Payner, T.D.; Leipzig, T.J.; Feuer, H.; Morone, M.A.; Koers, J.M.; Lawson, K.J.; Lentz, R.; Shuey, H.; Conaway, G.L.; et al. A Multicenter, Prospective, Randomized Trial Evaluating a New Hemostatic Agent for Spinal Surgery; Vol. 26.
- Moldovan, H.; Ciomaga, I.; Nechifor, E.; Tigănașu, R.; Badea, A.; Dobra, I.; Nica, C.; Scarlat, C.; Gheorghiță, D.; Antoniac, I.; et al. A Rare Case of Left Ventricular Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumour—Case Report and Review of the Literature. Medicina (B Aires) 2022, 58, 1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moldovan, H.; Antoniac, I.; Gheorghiță, D.; Safta, M.S.; Preda, S.; Broască, M.; Badilă, E.; Fronea, O.; Scafa-Udrişte, A.; Cacoveanu, M.; et al. Biomaterials as Haemostatic Agents in Cardiovascular Surgery: Review of Current Situation and Future Trends. Polymers (Basel) 2022, 14, 1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Wang, S. Advances in Hemostatic Hydrogels That Can Adhere to Wet Surfaces. Gels 2022, 9, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, N.C.; Ardehali, A.; Bruckner, B.A.; Parrino, P.E.; Gillen, D.L.; Hoffman, R.W.; Spotnitz, R.; Cavoores, S.; Shorn, I.J.; Manson, R.J.; et al. Prospective, Multicenter, Randomized, Controlled Trial Evaluating the Performance of a Novel Combination Powder vs Hemostatic Matrix in Cardiothoracic Operations. J Card Surg 2020, 35, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, R.; Niezgoda, J.; Niezgoda, J.; Madetipati, N.; Gopalakrishnan, S. Advances in Hemostatic Wound Dressings: Clinical Implications and Insight. Adv Skin Wound Care 2022, 35, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldovan, H.; Gheorghita, D.; Antoniac, I.; Gheorghe, D.; Fiori, F.; Mohan, A.; Raftu, G.; Ionel, C.; Costache, V. Bioadhesives Used in Cardiovascular Surgery. Revista De Chimie 2018, 69, 2799–2803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.M.; Kang, D.R.; Lee, J.H.; Jeong, Y.H.; Shin, D.A.; Yi, S.; Ha, Y.; Kim, K.N. Efficacy and Safety of a Thrombin-Containing Collagen-Based Hemostatic Agent in Spinal Surgery: A Randomized Clinical Trial. World Neurosurg 2021, 154, e215–e221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scridon, A. Platelets and Their Role in Hemostasis and Thrombosis—From Physiology to Pathophysiology and Therapeutic Implications. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moldovan, H.; Antoniac, I.; Gheorghiță, D.; Safta, M.S.; Preda, S.; Broască, M.; Badilă, E.; Fronea, O.; Scafa-Udrişte, A.; Cacoveanu, M.; et al. Biomaterials as Haemostatic Agents in Cardiovascular Surgery: Review of Current Situation and Future Trends. Polymers (Basel) 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Hao, F.; Tian, S.; Dong, H.; Nie, J.; Ma, G. Targeting Polysaccharides Such as Chitosan, Cellulose, Alginate and Starch for Designing Hemostatic Dressings. Carbohydr Polym 2022, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Du, Y.; Yin, Z.; Li, L.; Peng, H.; Zheng, H.; Yang, A.; Li, H.; Lv, G. Preparation and the Hemostatic Property Study of Porous Gelatin Microspheres Both in Vitro and in Vivo. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 2020, 187, 110641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biologically Responsive Biomaterials for Tissue Engineering; Antoniac, I. , Ed.; Springer New York: New York, NY, 2013; ISBN 978-1-4614-4327-8. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, C. Inorganic-Based Biomaterials for Rapid Hemostasis and Wound Healing. Chem Sci 2022, 14, 29–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baharlouei, P.; Rahman, A. Chitin and Chitosan: Prospective Biomedical Applications in Drug Delivery, Cancer Treatment, and Wound Healing. Mar Drugs 2022, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mecwan, M.; Li, J.; Falcone, N.; Ermis, M.; Torres, E.; Morales, R.; Hassani, A.; Haghniaz, R.; Mandal, K.; Sharma, S.; et al. Recent Advances in Biopolymer-Based Hemostatic Materials. Regen Biomater 2022, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; He, Y.; Lin, X.; Xie, M.; Liu, M.; Lvov, Y. Assembly of Clay Nanotubes on Cotton Fibers Mediated by Biopolymer for Robust and High-Performance Hemostatic Dressing. Adv Healthc Mater 2023, 12, 2202265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakiba-Marani, R.; Ehtesabi, H. A Flexible and Hemostatic Chitosan, Polyvinyl Alcohol, Carbon Dot Nanocomposite Sponge for Wound Dressing Application. Int J Biol Macromol 2023, 224, 831–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, G.; Torris, A.; Suresha, P.R.; Jadhav, S.; Badiger, M. V.; Ghormade, V. Design and Synthesis of a New Topical Agent for Halting Blood Loss Rapidly: A Multimodal Chitosan-Gelatin Xerogel Composite Loaded with Silica Nanoparticles and Calcium. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 2021, 198, 111454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Fang, Y.; Tang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Liu, X.; Liu, H. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Carried on Chitosan Microspheres for Traumatic Bleeding Control. Int J Biol Macromol 2019, 127, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Wang, M.; Liu, Q.; Liu, G.; Wang, S.; Li, J. Recent Advances in the Medical Applications of Hemostatic Materials. Theranostics 2023, 13, 161–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behrens, A.M.; Sikorski, M.J.; Kofinas, P. Hemostatic Strategies for Traumatic and Surgical Bleeding. J Biomed Mater Res A 2014, 102, 4182–4194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koumentakou, I.; Terzopoulou, Z.; Michopoulou, A.; Kalafatakis, I.; Theodorakis, K.; Tzetzis, D.; Bikiaris, D. Chitosan Dressings Containing Inorganic Additives and Levofloxacin as Potential Wound Care Products with Enhanced Hemostatic Properties. Int J Biol Macromol 2020, 162, 693–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sultankulov, B.; Berillo, D.; Sultankulova, K.; Tokay, T.; Saparov, A. Progress in the Development of Chitosan-Based Biomaterials for Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine. Biomolecules 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, G.; Torris, A.; Suresha, P.R.; Jadhav, S.; Badiger, M. V.; Ghormade, V. Design and Synthesis of a New Topical Agent for Halting Blood Loss Rapidly: A Multimodal Chitosan-Gelatin Xerogel Composite Loaded with Silica Nanoparticles and Calcium. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 2021, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uranues, S.; Fingerhut, A.; Levin, E.; Spazierer, D.; Rahimi, N.; Baumgartner, B. Effectiveness of Hemopatch® versus Surgicel® Original to Control Mild and Moderate Liver Bleeding. BMC Surg 2022, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponsen, A.C.; Proust, R.; Soave, S.; Mercier-Nomé, F.; Garcin, I.; Combettes, L.; Lataillade, J.J.; Uzan, G. A New Hemostatic Agent Composed of Zn2+-Enriched Ca2+ Alginate Activates Vascular Endothelial Cells in Vitro and Promotes Tissue Repair in Vivo. Bioact Mater 2022, 18, 368–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kliuk-Ben Bassat, O.; Schwartz, D.; Zubkov, A.; Gal-Oz, A.; Gorevoy, A.; Romach, I.; Grupper, A. WoundClot® Hemostatic Gauze Reduces Bleeding Time after Arterial Venous Fistula Decannulation. Blood Purif 2021, 50, 952–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mena-Álvarez, J.; Quispe-López, N.; Zubizarreta-Macho, Á.; Rico-Romano, C.; Rodero-Villanueva, R.; Fernández-Aceñero, M.J. Histological Analysis of Different Local Haemostatic Agents Used for Periapical Surgery: An Experimental Study with Sprague-Dawley Rats. Australian Endodontic Journal 2019, 45, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, K.; Gomati, A.; Yuen Hao Tong, E.; W Ah-See, K.; Shakeel, M. Use of PerClot® in Head and Neck Surgery: A Scottish Centre Experience. European Archives of Oto-Rhino-Laryngology 2021, 278, 1965–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.B.; Wang, H.J.; Raza, A.; Liu, C.; Yu, J.; Wang, J.Y. Preparation and Evaluation of Chitosan/Polyvinylpyrrolidone/Zein Composite Hemostatic Sponges. Int J Biol Macromol 2022, 205, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capella-Monsonís, H.; Shridhar, A.; Chirravuri, B.; Figucia, M.; Learn, G.; Greenawalt, K.; Badylak, S.F. A Comparative Study of the Resorption and Immune Response for Two Starch-Based Hemostat Powders. Journal of Surgical Research 2023, 282, 210–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Wu, J.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, D.; Chen, F.; Liu, C. A Self-Gelling Starch-Based Sponge for Hemostasis. J Mater Chem B 2022, 11, 1331–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimi BCDEF, N.; Amooee ACEF, A.; SafiDahaj BDEF, F. Comparison of the Effect of PerClot® Powder and a Chitosan Derivative on Postoperative Intra-Abdominal Adhesions in Rat Animal Models. [CrossRef]
- Goldis, A.; Goldis, R.; Chirila, T. V. Biomaterials in Gastroenterology: A Critical Overview. Medicina (Lithuania) 2019, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Cheng, N.; Sun, H.; Hou, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, D.; Zhang, W.; Chen, Z. Advances in the Development and Optimization Strategies of the Hemostatic Biomaterials. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 2023, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cziperle, D.J. AviteneTM Microfibrillar Collagen Hemostat for Adjunctive Hemostasis in Surgical Procedures: A Systematic Literature Review. Medical Devices: Evidence and Research 2021, 14, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Hu, H.; Min, N.; Wei, Y.; Li, X.; Li, X. Application and Outlook of Topical Hemostatic Materials: A Narrative Review. Ann Transl Med 2021, 9, 577–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghimire, S.; Sarkar, P.; Rigby, K.; Maan, A.; Mukherjee, S.; Crawford, K.E.; Mukhopadhyay, K. Polymeric Materials for Hemostatic Wound Healing. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, B.M.; Bortoto, J.B.; Fraga, G.P. Topical Hemostatic Agents in Surgery: Review and Prospects. Rev Col Bras Cir 2018, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salama, N.M.; Tabashy, R.H.; Mahmoud, I.H.; Rahman, A.E.R.M.A. El; Mohamed, D.N.E.; Kassas, H. El Does Gelfoam Slurry Embolization Post-Pulmonary Biopsy Reduce Risk of Pneumothorax? A Prospective Randomized Control Study. Egyptian Journal of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine 2023, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekyi-Djan, N.; Chapple, C.; Hammond-Kenny, A.; Hilger, A. The Use of ARTISS Fibrin Sealant in Thyroid Surgery: Case Series and Review of the Literature. British Journal of Surgery 2022, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somani, S.N.; Moshirfar, M.; Shmunes, K.M.; Ronquillo, Y.C. Comparison and Application of Commercially Available Fibrin Sealants in Ophthalmology. Ocular Surface 2020, 18, 418–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jolly, K.; Gupta, K.K.; Egbuji, O.; Naik, P.P.; Ahmed, S.K. Endoscopic Transsphenoidal Surgery Reconstruction Using the Fibrin Sealant Patch Tachosil®. Br J Neurosurg 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carretta, A.; Epskamp, M.; Ledermann, L.; Staartjes, V.E.; Neidert, M.C.; Regli, L.; Stienen, M.N. Collagen-Bound Fibrin Sealant (TachoSil®) for Dural Closure in Cranial Surgery: Single-Centre Comparative Cohort Study and Systematic Review of the Literature. Neurosurg Rev 2022, 45, 3779–3788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eichinger, J.K.; Oldenburg, K.S.; Lin, J.; Wilkie, E.; Mock, L.; Tavana, M.L.; Friedman, R.J. Comparing Dermabond PRINEO versus Dermabond or Staples for Wound Closure: A Randomized Control Trial Following Total Shoulder Arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 2022, 31, 2066–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, Y.; Hagemeister, K.; Tolba, R.H.; Steitz, J. Novel In Vitro Study to Assess Microbial Barrier Properties of Polyurethane-Based Tissue Adhesives in Comparison to the Gold Standard Dermabond®. Biomed Res Int 2022, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, M.; Liu, Z.; Kong, J.; Zhao, B.; He, X.; Gu, J.; Su, H. Transcatheter Arterial Embolization Using N-Butyl-2 Cyanoacrylate Glubran® 2 for Acute Massive Pancreati Coduodenal Arterial Hemorrhage. Front Mater 2022, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slezak, P.; Klang, A.; Ferguson, J.; Monforte, X.; Schmidt, P.; Bauder, B.; Url, A.; Osuchowski, M.; Redl, H.; Spazierer, D.; et al. Tissue Reactions to Polyethylene Glycol and Glutaraldehyde-Based Surgical Sealants in a Rabbit Aorta Model. J Biomater Appl 2020, 34, 1330–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhandapani, V.; Ringuette, V.; Desrochers, M.; Sirois, M.; Vermette, P. Composition, Host Responses and Clinical Applications of Bioadhesives. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater 2022, 110, 2779–2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keskin, E.; Aydin, H.A.; Kalayci, M.; Işik, E.; Özgen, U.; Şimşek, K.; Baklaci, D.; Gökçe, M. The Histopathological Effects of Reabsorbable Polyethylene Glycol Hydrogel (Coseal) on Epidural Fibrosis in an Experimental Postlaminectomy Model in Rats. Turk J Med Sci 2021, 51, 1512–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.F.; Lu, P.; Jia, H.R.; Li, G.; Zhu, B.; Wang, X.; Wu, F.G. Emerging Materials for Hemostasis. Coord Chem Rev 2023, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohlinger, R.; Rutkowski, R.; Kohlmann, T.; Paepke, S.; Alwafai, Z.; Flieger, C.; Moller, S.; Lenz, F.; Zygmunt, M.; Unger, J. Impact of the Lysine-Urethane Adhesive Tissuglu® on Postoperative Complications and Interventions after Drain-Free Mastectomy. Anticancer Res 2020, 40, 2801–2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yılmaz, G.; Özdenkaya, Y.; Karatepe, O.; Tanrıkulu, Y.; Kamalı, G.; Yalçın, O. Effects of Polyurethane Membrane on Septic Colon Anastomosis and Intra-Abdominal Adhesions. Ulusal Travma ve Acil Cerrahi Dergisi 2021, 27, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.; Siddiqui, Z.; Acevedo-Jake, A.M.; Roy, A.; Choudhury, M.; Grasman, J.; Kumar, V. Angiogenic Hydrogels to Accelerate Early Wound Healing. Macromol Biosci 2022, 22, 2200067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, F.C.; Lee, C.Y. Safety and Efficiency of Femoral Artery Access Closure Using QuikClot Combat Gauze in Patients with Severe Arterial Calcification of Access Sites. Quant Imaging Med Surg 2023, 13, 282–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Y. jun; Du, W. qiong; Zong, Z. wen; Jiang, R. qing; Zhong, X.; Ye, Z.; Li, T. shi; Yang, H. yang; Xiao, L. ping; Fan, J. Hemostatic Effects of Bio-Zeolite Gauze and QuikClot Combat Gauze on Major Bleeding in Rabbits Acutely Exposed to High Altitude. Prehospital Emergency Care 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Wei, X.; Yang, K.; Lin, S.; Tian, F.; Li, F. Ca-Ga Double Doping Strategy to Fabricate Hemostatic Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles (MSN) with Antibacterial Activity. [CrossRef]
- Milić, M.; Vuković, B.; Barbir, R.; Pem, B.; Milić, M.; Šerić, V.; Frőhlich, E.; Vinković Vrček, I. Effect of Differently Coated Silver Nanoparticles on Hemostasis. Platelets 2021, 32, 651–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, L.; Chen, W.-T.; Lai, C.-W.; Ye, F.-Y.; Lai, P.-S.; Lin, J.-J.; Yasuda, K.; Song, T.-T.; Song, J.-M. Biocompatibility and Antimicrobial Activity of Copper(II) Oxide Hybridized with Nano Silicate Platelets. Surf Coat Technol 2022, 435, 128253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milić, M.; Cvetić, Ž.; Bendelja, K.; Vuković, B.; Galić, E.; Ćurlin, M.; Dobrošević, B.; Jurak Begonja, A.; Vinković Vrček, I. Response of Platelets to Silver Nanoparticles Designed with Different Surface Functionalization. J Inorg Biochem 2021, 224, 111565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metwally, W.M.; El-Habashy, S.E.; El-Nikhely, N.A.; Mahmoud, H.E.; Eltaher, H.M.; El-Khordagui, L. Nano Zinc Oxide-Functionalized Nanofibrous Microspheres: A Bioactive Hybrid Platform with Antimicrobial, Regenerative and Hemostatic Activities. Int J Pharm 2023, 638, 122920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shefa, A.A.; Taz, M.; Hossain, M.; Kim, Y.S.; Lee, S.Y.; Lee, B.-T. Investigation of Efficiency of a Novel, Zinc Oxide Loaded TEMPO-Oxidized Cellulose Nanofiber Based Hemostat for Topical Bleeding. Int J Biol Macromol 2019, 126, 786–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.M.; Lee, J.; Lee, S.Y.; Lee, H.; Chathuranga, K.; Lee, J.; Park, W. Silk Fibroin/Tannin/ZnO Nanocomposite Hydrogel with Hemostatic Activities. Gels 2022, 8, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbonell-Blasco, P.; Martín-Martínez, J.M.; Antoniac, I.V. Synthesis and Characterization of Polyurethane Sealants Containing Rosin Intended for Sealing Defect in Annulus for Disc Regeneration. Int J Adhes Adhes 2013, 42, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- <, *!!! REPLACE !!!*; i>, *!!! REPLACE !!!*; Bioceramics and, Biocomposites< /i>, *!!! REPLACE !!!*; Antoniac, I. (Eds.) Bioceramics and Biocomposites; Antoniac, I., Ed.; Wiley, 2019; ISBN 9781119049340.
- Iannitti, D.A.; Kim, C.; Ito, D.; Epstein, J. Impact of an Active Hemostatic Product Treatment Approach on Bleeding-Related Complications and Hospital Costs among Inpatient Surgeries in the United States. J Med Econ 2021, 24, 514–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennington, Z.; Ehresman, J.; Westbroek, E.M.; Lubelski, D.; Cottrill, E.; Sciubba, D.M. Interventions to Minimize Blood Loss and Transfusion Risk in Spine Surgery: A Narrative Review. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 2020, 196, 106004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PRISADA, R.M. PERSPECTIVES TO DESCRIBE SURFACE PROPERTIES OF RAW PHARMACEUTICAL MATERIALS. A FRACTAL APPROACH ON THE WETTING OF POWDERS. Farmacia 2020, 68, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biranje, S.S.; Sun, J.; Shi, Y.; Yu, S.; Jiao, H.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Q.; Wang, J.; Liu, J. Polysaccharide-Based Hemostats: Recent Developments, Challenges, and Future Perspectives. Cellulose 2021, 28, 8899–8937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elieh-Ali-Komi, D.; Hamblin, M.R.; Daniel, E.-A.-K. Chitin and Chitosan: Production and Application of Versatile Biomedical Nanomaterials HHS Public Access; 2016; Vol. 4.
- Khan, M.A.; Mujahid, M. A Review on Recent Advances in Chitosan Based Composite for Hemostatic Dressings. Int J Biol Macromol 2019, 124, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Rooqi, M.M.; Hassan, M.M.; Moussa, Z.; Obaid, R.J.; Suman, N.H.; Wagner, M.H.; Natto, S.S.A.; Ahmed, S.A. Advancement of Chitin and Chitosan as Promising Biomaterials. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2022, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motelica, L.; Ficai, D.; Ficai, A.; Truşcă, R.D.; Ilie, C.I.; Oprea, O.C.; Andronescu, E. Innovative Antimicrobial Chitosan/Zno/Ag Nps/Citronella Essential Oil Nanocomposite—Potential Coating for Grapes. Foods 2020, 9, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janvikul, W.; Uppanan, P.; Thavornyutikarn, B.; Krewraing, J.; Prateepasen, R. In Vitro Comparative Hemostatic Studies of Chitin, Chitosan, and Their Derivatives. J Appl Polym Sci 2006, 102, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiplea, R.E.; Lemnaru, G.M.; Trușcă, R.D.; Holban, A.; Kaya, M.G.A.; Dragu, L.D.; Ficai, D.; Ficai, A.; Bleotu, C. Antimicrobial Films Based on Chitosan, Collagen, and Zno for Skin Tissue Regeneration. Biointerface Res Appl Chem 2021, 11, 11985–11995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radu, E.R.; Pandele, A.M.; Tuncel, C.; Miculescu, F.; Voicu, S.I. Preparation and Characterization of Chitosan/LDH Composite Membranes for Drug Delivery Application. Membranes (Basel) 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, Y.; Yano, R.; Miyatake, K.; Tomohiro, I.; Shigemasa, Y.; Minami, S. Effects of Chitin and Chitosan on Blood Coagulation. Carbohydr Polym 2003, 53, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crini, G.; Lichtfouse, Eric. Sustainable Agriculture Reviews. 35, Chitin and Chitosan: History, Fundamentals and Innovations; ISBN 9783030165376.
- Spoială, A.; Ilie, C.I.; Dolete, G.; Croitoru, A.M.; Surdu, V.A.; Trușcă, R.D.; Motelica, L.; Oprea, O.C.; Ficai, D.; Ficai, A.; et al. Preparation and Characterization of Chitosan/TiO2 Composite Membranes as Adsorbent Materials for Water Purification. Membranes (Basel) 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, A.; Krishnan, U.M.; Sethuraman, S. Skin Tissue Regeneration. In Electrospinning for Tissue Regeneration; Elsevier, 2011; pp. 298–316.
- Jiménez-Gómez, C.P.; Cecilia, J.A. Chitosan: A Natural Biopolymer with a Wide and Varied Range of Applications. Molecules 2020, 25, 3981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szatmári, V. Chitosan Hemostatic Dressing for Control of Hemorrhage from Femoral Arterial Puncture Site in Dogs. J Vet Sci 2015, 16, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, M.; Tang, Z.; Tu, J.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Q.; Xiao, R.; Liu, H. Porous Chitosan Microspheres Containing Zinc Ion for Enhanced Thrombosis and Hemostasis. Materials Science and Engineering C 2018, 85, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karahaliloğlu, Z.; Demirbilek, M.; Ulusoy, İ.; Gümüşkaya, B.; Denkbaş, E.B. Active Nano/Microbilayer Hemostatic Agents for Diabetic Rat Bleeding Model. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater 2017, 105, 1573–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Luo, W.; Li, P.; Li, S.; Yang, Z.; Hu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Ao, N. Preparation and Evaluation of Chitosan/Alginate Porous Microspheres/Bletilla Striata Polysaccharide Composite Hemostatic Sponges. Carbohydr Polym 2017, 174, 432–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biranje, S.S.; Madiwale, P. V.; Patankar, K.C.; Chhabra, R.; Dandekar-Jain, P.; Adivarekar, R. V. Hemostasis and Anti-Necrotic Activity of Wound-Healing Dressing Containing Chitosan Nanoparticles. Int J Biol Macromol 2019, 121, 936–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.Y.; Fang, Q.Q.; Wang, X.F.; Wang, X.W.; Zhang, T.; Shi, B.H.; Zheng, B.; Zhang, D.D.; Hu, Y.Y.; Ma, L.; et al. Chitosan-Calcium Alginate Dressing Promotes Wound Healing: A Preliminary Study. Wound Repair and Regeneration 2020, 28, 326–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, F.; Kong, Y.; Shao, C.; Cheng, Y.; Lu, J.; Tao, Y.; Du, J.; Wang, H. Chitosan-Based Multifunctional Flexible Hemostatic Bio-Hydrogel. Acta Biomater 2021, 136, 170–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shou, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yan, S.; Xia, P.; Xu, P.; Li, G.; Zhang, K.; Yin, J. Thermoresponsive Chitosan/DOPA-Based Hydrogel as an Injectable Therapy Approach for Tissue-Adhesion and Hemostasis. ACS Biomater Sci Eng 2020, 6, 3619–3629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, K.M.; Narayanan, K.B.; Uthappa, U.T.; Park, P.H.; Choi, I.; Han, S.S. Tissue Adhesive, Self-Healing, Biocompatible, Hemostasis, and Antibacterial Properties of Fungal-Derived Carboxymethyl Chitosan-Polydopamine Hydrogels. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, L.; Wang, S.; Jiang, Z.; Chi, J.; Yu, S.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, L.; Zhou, C.; Liu, W.; et al. Hemostatic Performance of Chitosan-Based Hydrogel and Its Study on Biodistribution and Biodegradability in Rats. Carbohydr Polym 2021, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, P.; Xia, Z.; Qi, C.; He, M.; Yu, T.; Shi, L. Construction of Chitosan/Ag Nanocomposite Sponges and Their Properties. Int J Biol Macromol 2021, 192, 272–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, X.; Li, Y.; Li, N.; Wan, G.; Ali, M.A.; Tang, K. Rapid Hemostatic Chitosan/Cellulose Composite Sponge by Alkali/Urea Method for Massive Haemorrhage. Int J Biol Macromol 2020, 164, 2769–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sathiyaseelan, A.; Saravanakumar, K.; Mariadoss, A.V.A.; Wang, M.H. Antimicrobial and Wound Healing Properties of Feo Fabricated Chitosan/Pva Nanocomposite Sponge. Antibiotics 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordienko, M.G.; Palchikova, V. V.; Kalenov, S. V.; Lebedev, E.A.; Belov, A.A.; Menshutina, N. V. The Alginate–Chitosan Composite Sponges with Biogenic Ag Nanoparticles Produced by Combining of Cryostructuration, Ionotropic Gelation and Ion Replacement Methods. International Journal of Polymeric Materials and Polymeric Biomaterials 2022, 71, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.; Lin, J.; Li, S.; Deng, Y.; Kong, S.; Hong, P.; Yang, P.; Liao, M.; Hu, Z. Preparation and Evaluation of Squid Ink Polysaccharide-Chitosan as a Wound-Healing Sponge. Materials Science and Engineering: C 2018, 82, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buriuli, M.; Kumari, W.G.; Verma, D. Evaluation of Hemostatic Effect of Polyelectrolyte Complex-Based Dressings. J Biomater Appl 2017, 32, 638–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misgav, M.; Lubetszki, A.; Brutman-Barazani, T.; Martinowitz, U.; Kenet, G. The Hemostatic Efficacy of Chitosan-Pads in Hemodialysis Patients with Significant Bleeding Tendency. Journal of Vascular Access 2017, 18, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Yan, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C. Preparation and Properties of Electrospun Chitosan/Polybutylenes Succinate Nanofiber Membrane for Wound Hemostatic Dressing. J. Ind. Text. 2022, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akram, A.M.; Omar, R.A.; Ashfaq, M. Chitosan/Calcium Phosphate-Nanoflakes-Based Biomaterial: A Potential Hemostatic Wound Dressing Material. Polymer Bulletin 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.W.; Liu, C.C.; Cherng, J.H.; Lin, C.S.; Chang, S.J.; Hong, Z.J.; Liu, C.C.; Chiu, Y.K.; Hsu, S. Der; Chang, H. Biological Effects of Chitosan-Based Dressing on Hemostasis Mechanism. Polymers (Basel) 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.H.; Cherng, J.H.; Liu, C.C.; Fang, T.J.; Hong, Z.J.; Chang, S.J.; Fan, G.Y.; Hsu, S. Der Procoagulant and Antimicrobial Effects of Chitosan in Wound Healing. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Zeng, Y.; Wu, H.; Wang, S.; Zhao, J. Multifunctional Carboxymethyl Chitosan/Oxidized Dextran/Sodium Alginate Hydrogels as Dressing for Hemostasis and Closure of Infected Wounds. Int J Biol Macromol 2022, 219, 1337–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elangwe, C.N.; Morozkina, S.N.; Olekhnovich, R.O.; Krasichkov, A.; Polyakova, V.O.; Uspenskaya, M. V. A Review on Chitosan and Cellulose Hydrogels for Wound Dressings. Polymers (Basel) 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Hu, Z.; Li, S.; Zhang, L.; Lu, S.; Liang, F. Chitosan-Based Thermo-Sensitive Hydrogel Loading Oyster Peptides for Hemostasis Application. Materials 2020, 13, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, G.; Pawar, R.; Jadhav, S.; Ghormade, V. A Chitosan Based Multimodal “Soft” Hydrogel for Rapid Hemostasis of Non-Compressible Hemorrhages and Its Mode of Action. Carbohydrate Polymer Technologies and Applications 2022, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Acosta, H.; Tapia-Rivera, J.M.; Guerrero-Guzmán, A.; Hernández-Elizarraráz, E.; Hernández-Díaz, J.A.; Garza-García, J.J.O.; Pérez-Ramírez, P.E.; Velasco-Ramírez, S.F.; Ramírez-Anguiano, A.C.; Velázquez-Juárez, G.; et al. Chronic Wound Healing by Controlled Release of Chitosan Hydrogels Loaded with Silver Nanoparticles and Calendula Extract. J Tissue Viability 2022, 31, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Shen, Y.; Wang, L. Multi-Scale Photoacoustic Assessment of Wound Healing Using Chitosan–Graphene Oxide Hemostatic Sponge. Nanomaterials 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Ryu, J.H.; Koh, M.-Y.; Yun, S.P.; Kim, S.; Park, J.P.; Jung, C.-W.; Lee, M.S.; Seo, H.-I.; Kim, J.H.; et al. Coagulopathy-Independent, Bioinspired Hemostatic Materials: A Full Research Story from Preclinical Models to a Human Clinical Trial. Sci Adv 2021, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Zhou, W.; Deng, W.; Xu, C.; Cai, Y.; Wang, X. Antibacterial and Hemostatic Thiol-Modified Chitosan-Immobilized AgNPs Composite Sponges. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2020, 12, 20307–20320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deineka, V.; Sulaieva, O.; Pernakov, M.; Korniienko, V.; Husak, Y.; Yanovska, A.; Yusupova, A.; Tkachenko, Y.; Kalinkevich, O.; Zlatska, A.; et al. Hemostatic and Tissue Regeneration Performance of Novel Electrospun Chitosan-Based Materials. Biomedicines 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bal-Ozturk, A.; Karal-Yilmaz, O.; Akguner, Z.P.; Aksu, S.; Tas, A.; Olmez, H. Sponge-like Chitosan-Based Nanostructured Antibacterial Material as a Topical Hemostat. J Appl Polym Sci 2019, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Gu, B.; Li, S.; Luo, B.; Wen, Y.; Chen, M.; Li, X.; Zha, Z.; Zhang, H.T.; Wang, X. An Antibacterial Hemostatic AuNPs@corn Stalk/Chitin Composite Sponge with Shape Recovery for Promoting Wound Healing. Carbohydr Polym 2022, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
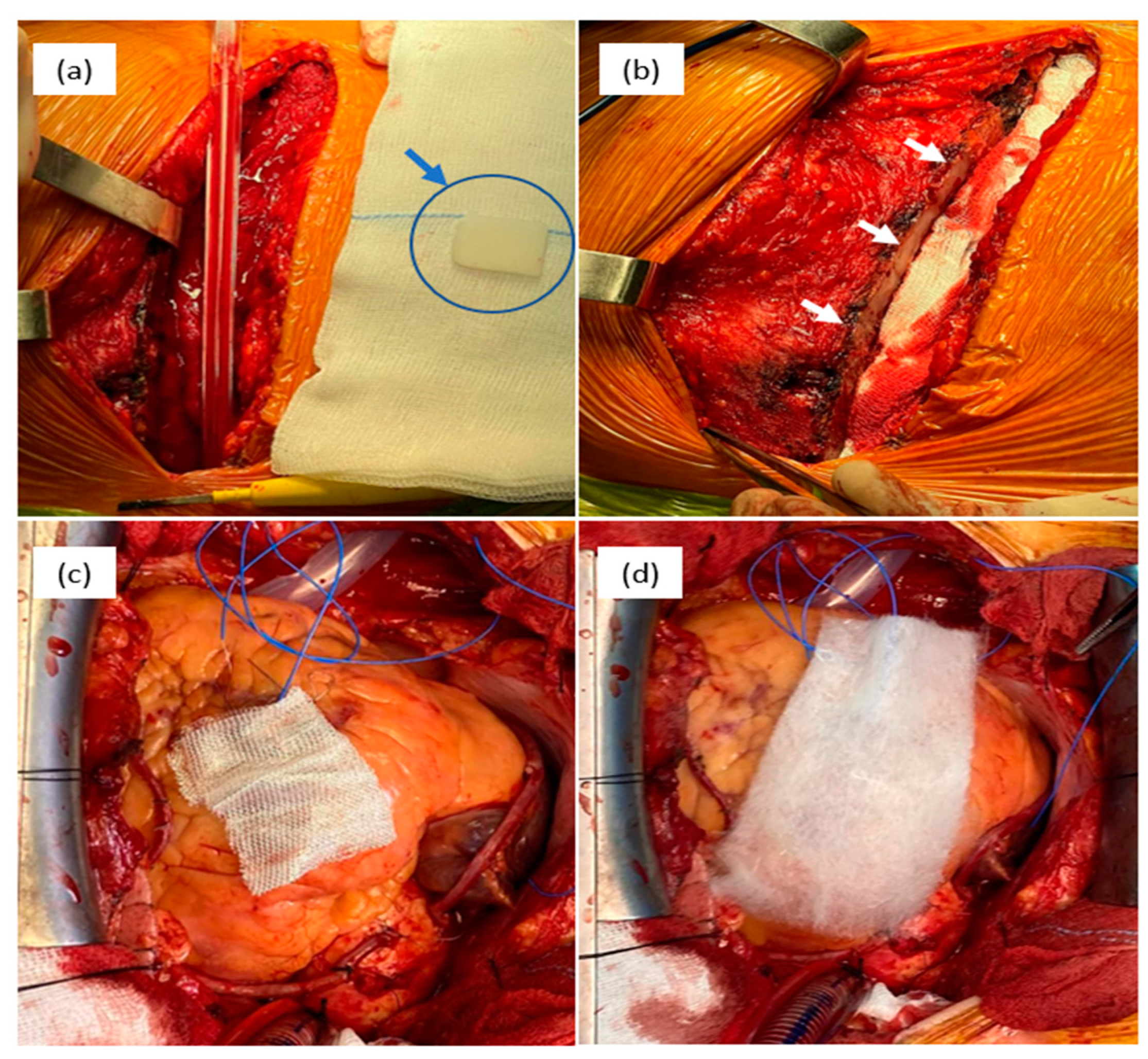
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





