1. Introduction
The use of underground warehouses for the storage of grains comprises a traditional practice that dates back to ancient Indian and Egyptian civilizations [
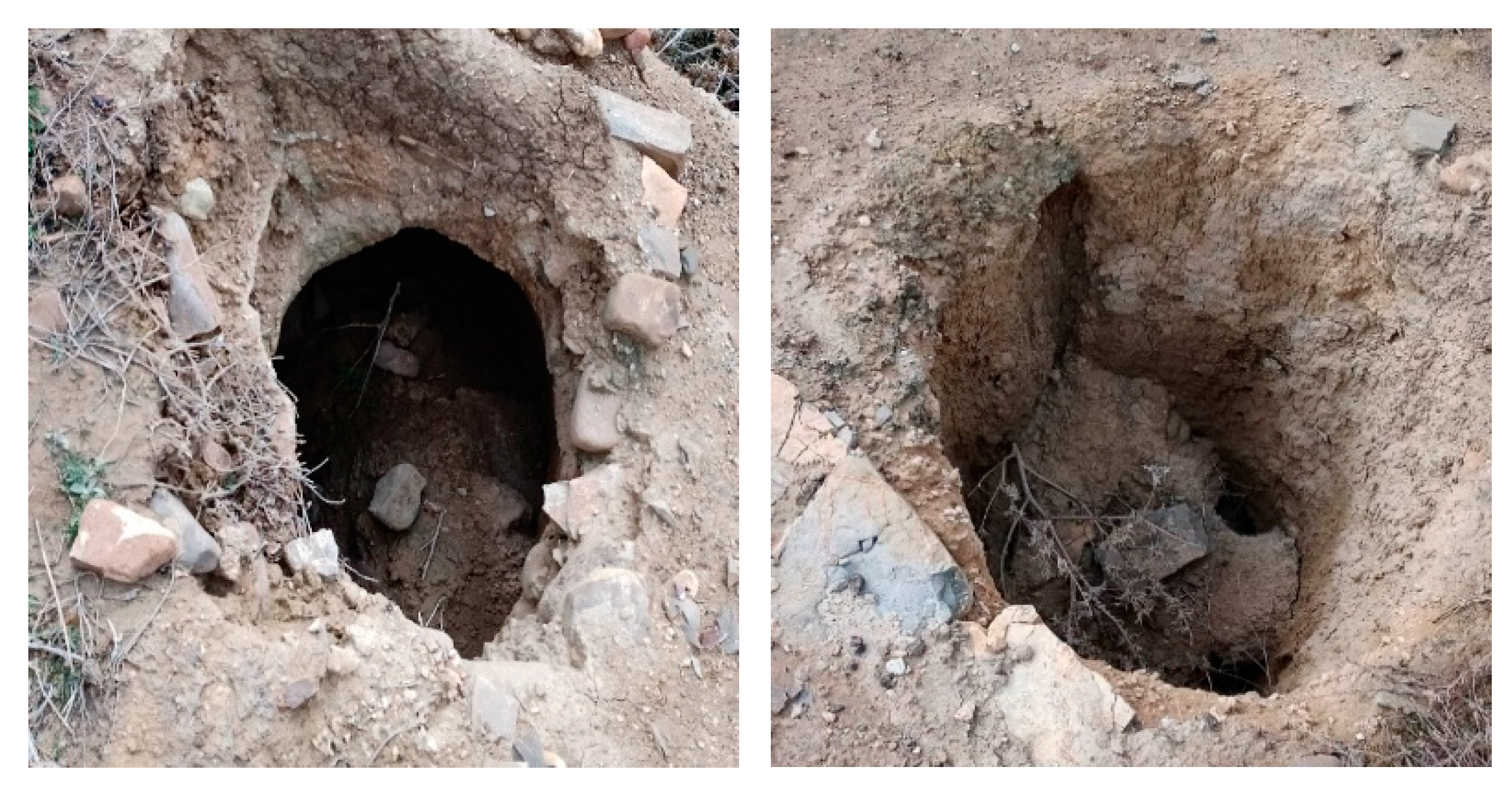
1]. The peasants that live in the high plateaus of Algeria preserve barley and wheat products in enclosures comprising basic cylindrical or rectangular holes dug in stable soil from dry areas. These underground holes are called ‘Matmoura’ (
Figure 1). They are constructed in supervised places or near farms, with a variable storage capacity, normally of just a few cubic meters, an archaic technique that is still employed in these remote regions [
2]. These storage techniques are very efficient due associated low human power required and costs, excellent thermal insulation, protection against rodents’ attacks, as well as effective protection against infestations thanks to their airtightness relative to the storage area, which reduces the gas exchange with the outside air [
3]. The downsides of these storage facilities are the associated difficulties whenever emptying the pits, the damages induced by humidity infiltrating through the soil profile, as well as the water condensation on the top of the enclosures. However, this latter shortcoming is balanced sometimes by the proliferation of fungi developed at the surface, which reduces the oxygen concentration in the underground atmosphere, therefore creating the premises for efficient conservation of the stock by reducing the gas exchange with the exterior [
4,
5].
Following the recent classification of the Couscous dish by UNESCO as a unique cultural heritage, we found it worth focusing on this topic in the current article, namely on the rare couscous type called Hammoum. The etymology of this word remains unknown, unfortunately, with origins perhaps dating back to prehistoric Algerian times. This type of dish remains unfortunately unknown for most Algerian citizens, deserving in our opinion more credit.
The wheat is obtained through natural fermentation by acidic lactic bacteria, a process still employed by a few local scattered tribes, but mainly by the populations from the communes El Maien off Oued El Fodda, situated in the western parts of Zakar.
The Hammoum comprises neutral barley that is buried and watered regularly to ensure an efficient fermentation process. The seeds of the Hamoum are brown and with a strong odor, which resembles the one found in the hops of breweries, and also have a rather peculiar taste. Then, the seeds are air-dried in rooms before they are grounded into flour. The end product is a tasty dish with a peculiar and atypical taste, very appreciated by local gastronomy [
6,
7].
Currently, lactic acid bacteria are of great interest due to their high nutritional and therapeutic value in the food and pharmaceutical industries. In-depth studies focused on the biotechnological characteristics of these bacteria increased their preservation capacities and improved the nutritional value of food and probiotics. These bacteria are also considered microorganisms with great probiotic potential that induce a feel-good effect [
8].
Currently, Fermented foods are very rich in probiotics. They support your digestion and strengthen your immune system, lactic acid bacteria are of great interest due to their high nutritional and therapeutic value in the food and pharmaceutical industries. In-depth studies focused on the biotechnological characteristics of these bacteria increased their preservation capacities and improved the nutritional value of food and probiotics. These bacteria are also considered microorganisms with great probiotic potential that induces a feel-good effect [
8,
9]. This research aims to study the physicochemical properties of fermented wheat, to characterize the physicochemical properties of the walls of Matmora, then we identify the fermentable germs and describe their inhibitory effects against some pathogenic bacteria.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study areas
Three study zones were selected to achieve our study, the town of Tiaret in Algeria, which is located at 1,143 m altitude of the Pass, on the flanks of Jebel Guezoul, which is part of the Tell Atlas chain, comprising woods dominated by various species and varieties of cypress and Aleppo pines. The climate is continental, dry, and harsh during winter, with temperatures varying from subfreezing values to above 35°C during summer; the annual mean temperatures are 6°C during winter and 25.9°C during summer. The second one was the town of Mascara, which is located in the northwest part of Algeria, 360 km west of Algiers, 100 km southeast of Oran, 89 km from Sidi Bel Abbès, and 154 km from Tiaret. The area is located on the southern slope of the Beni-Chougrane mountains (bearing the name of Chareb Errih, in translation “the lip of the wind”), part of the Tell Atlas chain and dominating the plains of Ghriss in the South. Besides, the third zone is the territory of the commune of Ghardaïa, which is located north of the wilaya of Ghardaïa, in the center of Algeria, and north of the Algerian Sahara, 600 km south of Algiers, 190 km south of Laghouat, 270 km of El Menia and 190 km west of Ouargla. Ghardaïa is the most important city of the Pentapolis (five cities) of Mzab. It is located upstream of the valley and is organized around a hill [
10].
2.2. Biological material
Three samples of Hamoum of Algerian origin were selected. The information related to their provenance and storage duration is indicated in
Table 1 and
Figure 2, respectively.
Relating to pathogenic strains, Enteropathogenic germs as indicator bacteria were used in the current study as inhibitors of lactic acid bacteria. Three bacterial strains were ATCC reference strains: Escherichia coli (ATCC 25922), Psodomonas aeroginosa (ATCC 9027), Bacillus cereus (ATCC 14579), and Staphylococcus aureus (ATCC 43300), from the Laboratory of Microbiology, Faculty of Natural and Life Sciences, Tiaret University. The purification of pathogenic bacteria was carried out by seeding streaks on the selective media of each pathogenic bacteria. The dishes were incubated at 37°C for 24 hours.
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Physicochemical and organoleptic analyses of fermented wheat (Hamoum)
The physicochemical determinations were performed using diverse parameters such as thousand-grain mass by manual or automatic counting of grains contained in a test sample of known mass, which are expressed in grams (g) according to [
11], while, pH measurement and readings were conducted directly with a pH meter. Although, acidity was measured by adding 50 mL of distilled water to 5 g of flour, homogenizing with a stirrer, then filtration was carried out on filter paper, and a volume of 10 mL of filtrate associated with a few drops of phenolphthalein was titrated with an acidimeter until the color turned pink [
12] and the acidity was given in °D. Concerning ash rate determination was conducted by incinerating 5 g of flour and grain at 900 °C for 2 hours until complete combustion of the organic matter, the ash content was determined by weighing the residue [
11], and the ash content was expressed as a percentage of mass relative to the overall dry mass. Finally, water content steaming the atmospheric pressure of a test sample of 5 g of flour and grain at 130 °C for 90 minutes in a multicellular oven [
12], the water content was expressed as a percentage of the product mass. The organoleptic qualities and characteristics of fermented wheat (Hamoum) were based on the following traits: appearance, smell, and taste.
2.3.2. Matmora walls physicochemical analyses
The analyzed soil was obtained from Matmora, which is located in the region of Hacine in Mascara, pH, granulometry, and humidity parameters were controlled, regarding pH, 10 g of soil/50 mL of distilled water after 2 hours of rest, the reading was carried out with a calibrated pH meter [
13]. For the granulometry test, the method of Robinson Kohn was applied for this analysis, by measuring the distribution of mineral particles with a diameter smaller than 2 mm, as well as the distribution of sediment size classes higher than 2 mm [
14], the particle size classes were expressed as percentages. Finally, the humidity control was by drying the seeds at 105 °C and expressed as a percentage (or per thousand) relative to air-dried soil, this measurement is easy to carry, simply by weighing, following drying in an oven for a sufficient period (verification of constant weight), on an analytical scale, it is also called residual humidity (e.g., amount of water remaining in the sample, see [
13].
2.3.3. Isolation and identification of lactic acid bacteria
We have further proceeded with the isolation and identification of lactic acid bacteria, as follows: 10 g of Hamoum fermented wheat grains were immersed in 9 mL of saline solution and incubated at 30°C for 24 hours. From the original culture, a series of decimal dilutions were carried out on the liquid MRS or M17 media (audited with a fungicide) and then inoculated on the surface of Petri dishes containing the solid MRS or M17 media with 0.1 mL of each dilution, incubated at 30°C and 37°C for 24 to 48 hours [
13]. The purification was undertaken for several subcultures on liquid M17 and MRS media from catalase-negative and Gram-positive strains. The identification of isolates was based on morphological, physiological, and biochemical characteristics.
To prepare supernatant from bacterial interactions against enteropathogenic germs, 18 h young cultures of lactic acid bacteria were inoculated in MRS and M17 broth and incubated at 37° C for 18 h. Following incubation, the tubes were centrifuged at 4,000 rpm for 15 min and the supernatant was collected for further antibacterial tests [
15].
2.3.4. Antibacterial activity
The study of bacterial properties against the pathogenic germs
E. coli (ATCC 25922),
P. aeroginosa (ATCC 9027), and
B. cereus (ATCC 14579) was carried out according to Bouzaine et al., 2004, known as the good method. The method is based on the diffusion of antimicrobial compounds within a solid medium. The wells were filled with 0.5 mL supernatant of retained lactic acid bacteria that produced the antimicrobial substance in the Muller Hinton agar medium. The plates were incubated at 37ºC and observed after 24 and 48 hours. The antibacterial activity was expressed in terms of the mean diameter of the inhibition zone around the wells. Amoxicillin (AMX) and Gentamicin (GM) were used as standard antibiotics as control. The antimicrobial effect on the target was assessed by measuring the inhibition zone and, depending on the diameter of inhibition, the strain was qualified as sensitive, intermediate, or resistant, due to the presence of competition between the growth of strains and diffusion of the tested supernatant [
16,
17]. Hcl acid and distilled water were used as positive and negative controls, respectively
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of fermented wheat (Hamoum)
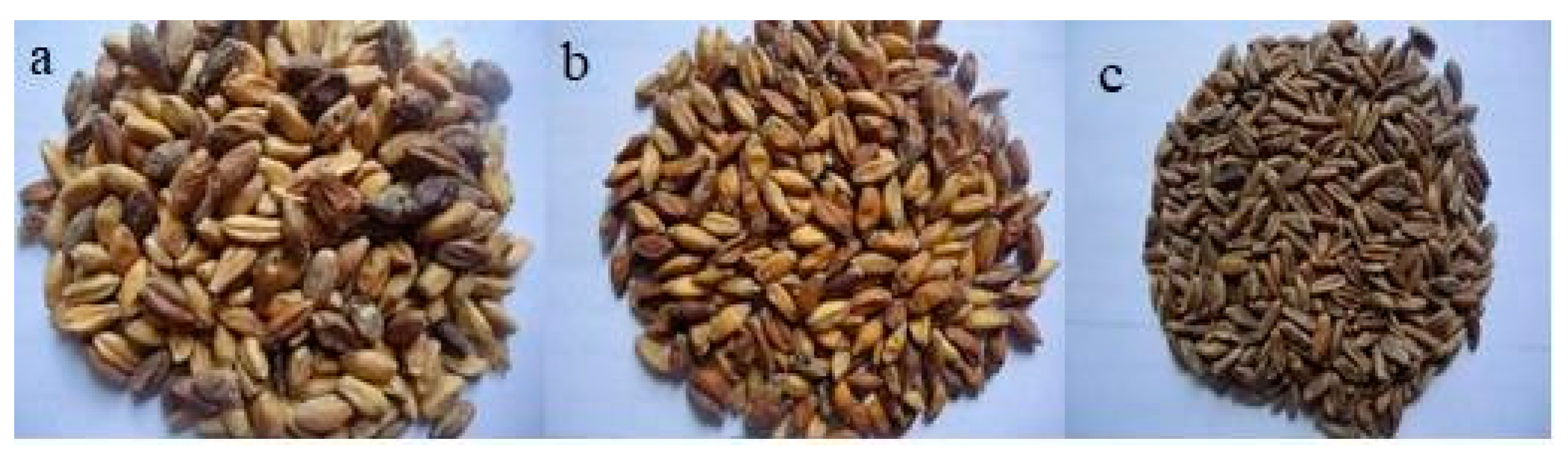
There were obvious differences among the three varieties of _kijfermented wheat samples (Hamoum) for the main parameters studied in
Table 2.
Regarding organoleptic characteristics, the aspect of Hamoum was generally gray in color or blackish, with a tendency towards the latter color as the residence time progressed, whereas, the peculiar smell of “Hamoum” fermentation was very similar to that of potatoes in advanced stages of petrification, explainable by the production of volatile and aromatic compounds during the fermentation process. While, the taste was similar to white couscous, with a more or less acidic aftertaste, which gives them a specific taste.
The results of the physicochemical parameters of the three samples of Hamoum (grain and flour) are given in
Table 2 and show a significant difference (p <0.05) among the samples.
Both varieties of wheat studied, with an average 1000 grain count, weighed 40.24 g, with the lowest value (28.07 g) recorded for the third sample of the Simeto variety, which is characterized by its elongated and fine shape. This parameter represents a limiting factor of semolina yield. The mass of 1000 grains corresponding to the quantity requested and that is transformed into semolina by the flour mill. The water content was variable in all three samples, the second sample comprising lower values compared to the first and the third sample, explicable by prolonged storage times of six months. However, the water content in the third sample was higher, despite its storage for nine years. Concerning the ash content of grains, it varied between 1.43 % to 1.44 % for Ofanto and Simeto, with 1.55 as the upper limit, thus affecting the quality of semolina due to strong contamination in the bites of bran. The flour ash content of the Simeto variety was relatively rich in Ash (1.63), whereas the Ofanto variety was intermediate (1.42 and 1.48).
According to
Table 2, the pH of grain and flour was relatively stable in the first two samples, but higher in the third sample because of its prolonged residence time. The first sample had a lower acidity (0.03) compared to the second (0.17) and the third (0.25) samples. These standard NF ISO 7035-V03-712 sets the lower acceptable acidity threshold of semolina at 0.05 %.
3.2. Physicochemical characteristics of the soil of the walls of Matmora
Our analyzes of various physicochemical parameters of samples from the Mascara region (Hacine) are given in
Table 3. The results of the particle size analysis showed that the soil sample from Matmoura has a clay-loamy texture, with the clay fraction dominant due to an increased percentage of silt. According to
Table 3, it can be noticed that the pH value was 8.2.
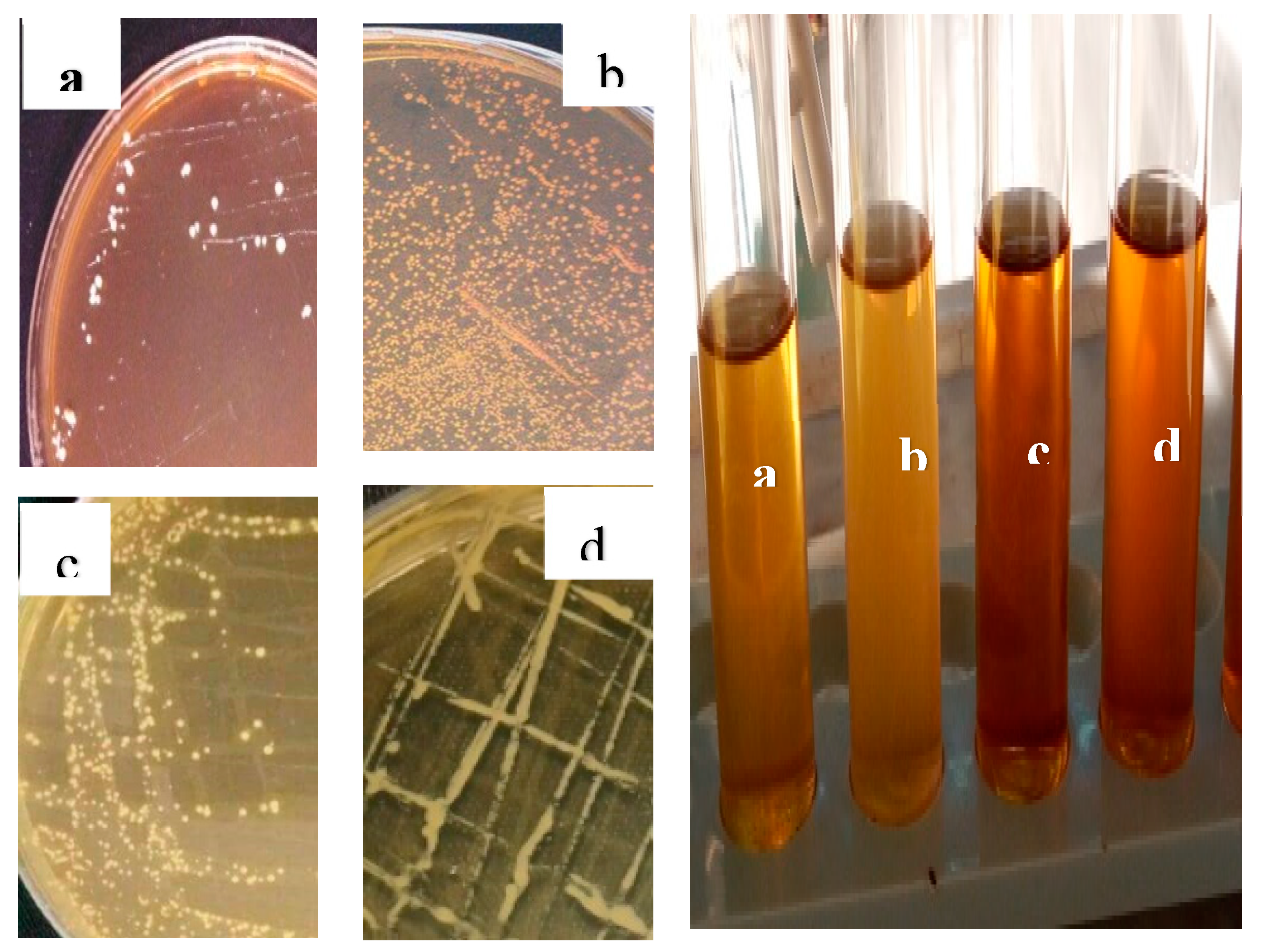
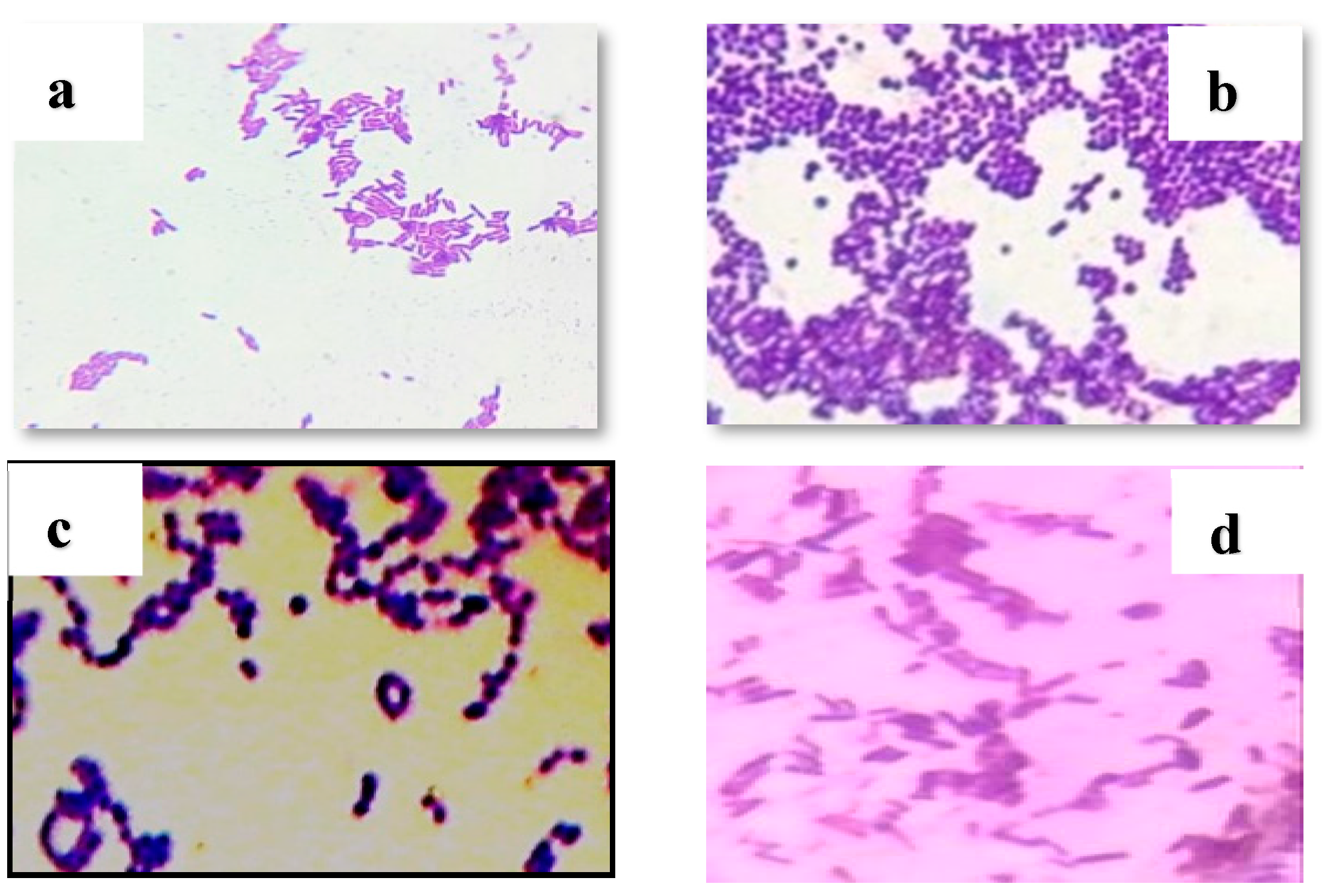
3.3. Results of isolation and identification of lactic acid bacteria
Following morphological (both macroscopic and microscopic
Figure 3 and
Figure 4), physiological, and biochemical tests on pure cultures, the results showed that the isolated lactic acid bacteria belonged to genera
Lactobacillus (59%),
Pediococcus (18%),
Leuconostoc (17%), and
Streptococcus (6%).
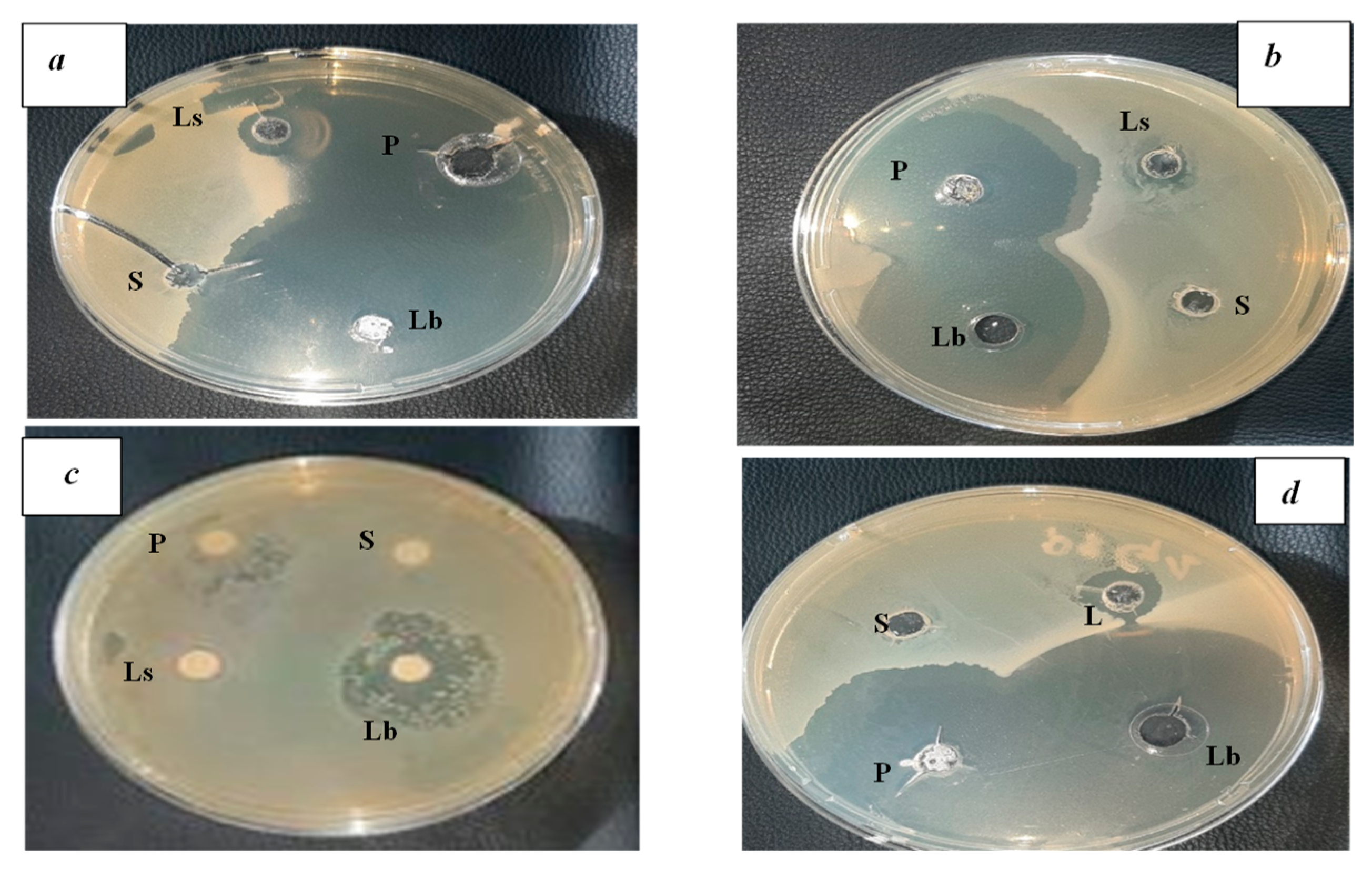
3.4. Results of antibacterial activity of fermented wheat (Hamoum)
The antibacterial activities of the isolated acid bacteria revealed the presence of strong inhibiting power against the pathogenic germs
E. coli (ATCC 25922),
P. aeroginosas (ATCC 9027),
B. cereus (ATCC 14579), and
S. aureus (ATCC 43300), as well as the appearance of clear and distinct halos around the wells (
Figure 4). The diameters of the inhibition zones are given in
Table 4 and
Figure 5.
According to [
18], the distribution of isolates was carried out according to the diameter of the inhibition zones as follows:37.5 % of interactions revealed resistance of pathogenic bacteria, mainly B. cereus, 62.5 % of interactions were positive, 10 % of the interactions showed inhibitions with a diameter < 10 mm, 90 % of interactions with inhibition diameter ≥ 10 mm and finally, 100% of pathogenic bacteria (Gram-positive and Gram-negative), were inhibited by
Lactobacillus with inhibition zones reaching 55 mm in diameter, thus reflecting a strong inhibitory potential.
4. Discussion
The fermented wheat Hamoum was kept for thousands of years in underground silos called “Matmour”. Following the accidental infiltration of precipitation water in matmora, the humidified wheat grains undergo fermentation that depends on the microorganisms present in the wheat or soil profile [
19]. The results of organoleptic tests revealed a very pronounced musty smell of volatile and aromatic compounds during the fermentation process [
10,
21,
22]. The observed brown color can be explained by non-enzymatic browning, as was observed during other food fermentation studies [
23]. The lactic and alcoholic fermentations induced by microorganisms produce enzymes, flavor components, as well as other alcohols [
24,
25]. The molds produce extracellular proteolytic and lipolytic enzymes that contribute to the development of product flavor and texture [
26]. According to [
7], the fermented wheat found near the walls of the “Matmora” had high water content. The variation in water content was due to the storage duration of wheat in the “Matmora” warehouses. [
1], observed changes in the humidity of extracted samples following different storage times in straw-lined “Matmora”. The results showed an increase in wheat moisture as a function of storage time. This increase was due to the relative humidity in the straw-lined warehouses. The values of the water content of fermented wheat were within the range quoted by [
27] (i.e., 9-13 %) and by [
28] (i.e., ≤ 16 %). These values are also in agreement with those of [
29], observed on the same variety of wheat (i.e., 13-15 %). The results from the current study showed a significant increase in the moisture of fermented wheat as a function of storage time and are similar to previous findings [
30] and consistent with the standards for optimal use [
31]. The results also indicated that the ash values for fermented wheat remained within the range (i.e., 1.5-2.5 %) cited by [
32]. Similarly, the decrease in the level of fermented wheat ash percentage always remained within the range of relative values and was similar to the results reported by [
33].
The fermentation enhanced the activities of the hydrolytic enzymes and changed the grain structure [
34]. The reduction in mineral substances could be explained by the interaction of minerals with environmental factors during storage in “Matmora” [
35,
36]. [
37], indicated that the reduction in mineral substances resulted in the diffusion of these micronutrients within the intercellular space, in particular at high temperatures. pH and acidity results were also in good agreement with the findings described by several authors who have worked on fermented products. However, in the fermented wheat Hamoum from the current investigation, the acidity increased to a maximum value of 0.25. According to [
32], the evolution of acidity is also adjusted by the biochemical modifications that the wheat undergoes during storage. The increase in acidity during the fermentation period is induced by the release of organic acids, such as lactic acid, acetic, butyric, formic, propionic acid, and short-chain fatty acids [
38,
39,
40]. The alkaline pH creates favorable conditions for several types of microorganisms and increases the role of biomass and their activity [
13]. An acidic pH can inhibit the development of certain microbial germs and their activity [
31].
An alkaline pH reflects the limestone content in this type of soil. An alkaline pH can promote the immobilization of certain nutrients. The pH in the presence of calcium carbonate can immobilize phosphorus as insoluble calcium phosphates [
12]. It is noteworthy to mention that the moisture was low due to the general characteristics of our Matmoura soil, with fine to medium water retention capacity, increasing its filtering capacity. According to the results from the current study, the value of the soil of Matmoura was 12.1 %, which could be explained by the depth and air currents, which increase the evapotranspiration rates [
41,
42].
In the current soil samples, there were observed high contents of clay (which reduces aeration). In the underground silos with a depth of 2.5 m, the air is absent and the temperature is high, leading to a deficiency in nutrients due to the absence of its natural sources, such as plants and organic matter debris specific to this environment. The current study revealed the existence of lactic flora that allowed the fermentation of wheat during its storage in matmoura. [
43], isolated lactic acid bacteria from the Italian wheat variety.
Our results indicate that 62.5 % of the pathogenic bacteria were inhibited, confirming the important role played by lactic acid bacteria in spontaneous fermentation, with results similar to [
44]. This type of fermented food is manufactured by microbial growth and enzymatic conversions [
45,
46], and is a well-documented process, known to lead to high acidification rates generally accompanied by rapid growth rates of lactic acid bacteria in fermented wheat [
38,
39,
40,
41,
42,
43,
44,
45,
46,
47]. According to [
48], various antimicrobial agents that inhibit the development of pathogenic bacteria and/or food degradation flora are produced by lactic acid bacteria during milk fermentation. These include organic acids from homo and heterofermentative mechanisms of lactic bacteria, hydrogen peroxide, and bacteriocins produced by some lactic strains.
5. Conclusions
This work, which aims to promote a quality product, is based on physicochemical and microbiological quality control, as well as on the isolation of fermentable germs. The results obtained show that fermented wheat (Hamoum) is beneficial for human consumption and this research should be further investigated to reflect the role of lactic acid bacteria in the prevention of gastric. The production of fermented wheat (Hamoum) gives an economic advantage to local farmers because it is generally sold at a price three times higher than durum wheat and it is precisely this price that makes farmers bear the additional production efforts.
Acknowledgments
The author would like also to sincerely thank the personnel of the laboratory of the Department of Nature and Life Sciences, University of Tiaret- Algeria, and Kaid Nahéda Engineer in the Directorate of Agricultural Services of Tiaret-Algeria.
Conflicts of interest: The author announce no conflict of interest.
References
- Bartali, E.H. Systèmes de stockages traditionnels « matmoras » et « sellas ». Hommes, Terre et Eaux. Rev. Maro. Sci. Tec. Dév. Rur 1995, 25, 16–22. [Google Scholar]
- Doumandji, A.; Mitiche, B.; Salahddined, M. Cereal technology course and wheat processing technology and storage insect problems. Univ Pub Off 2003, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Bartali, E.H. Structures de stockage des céréales, des légumineuses et de leurs dérivés. Séminaire international de la 2éme section de la commission internationale de génie rurale. INs Agri et Vete HASSANE II 1990, 16–19. [Google Scholar]
- Shejbal, J.D.E.; Boislambert, J.N. Stockage en atmospheres modifies. In. Multon JL., conservation et stockages des grains et graines et produits dérivées. Ed.Lavoisier, Paris, 1982, p 777.
- Ndiaye, D.S.B. Manuel de stockage et de conservation des céréales et des oléagineux, Coopérative Autrichienne pour le développement, Décolé Sidy Baba, Cellule centrale d’appui technique PADER, 1999, p 61.
- Mokhtari, B.S.; Taghouti, M.; Saidi, D.; Kheroua, O. Traditional Algerian fermented food: first data on nutritional characteristics of wheat (Triticum durum) fermented in underground silos matmora (mascara, Algeria) compared to unfermented wheat. Journal of Advances in Biology & Earth Sciences, 2020, 5, 176–192. [Google Scholar]
- Bartali EH, Afie S, Persoons E. 1989. Stockage des céréales dans des entrepôts souterrains. Cereals en régions chaudes. Aupele-UREF. Eds John Libbey Eurotext. Paris, pp 27-38.
- FAO/OMS. Guidelines for the evaluation of probiotics in foods: report of a joint FAO/WHO working group on drafting guidelines for the evaluation of probiotics in food. London, Ontario, Canada, 2002, p 134.
- Tamang, J.P.; Kailasapathy, K. Fermented Foods and Beverages of the World, CRC Press, 2010, p. 449.
- http://www.carte-algerie.co-algerie.com/ consulted the.
- NF V03-702. (1981). French standard volume 03-702.
- NF V03-702. (1976). French standard volume 03-702.
- Merad, Y. Study of the indices of a hard wheat crop on the microbiological behavior of different soil cropping precedents in the SEBAIN region. Engineering thesis in agronomic sciences option: plant production University of Tiaret, 2006, pp34-35.
- Bouktab, M. Contribution to the physicochemical and microbiological study of desert soils in the Zmalet El Amir Abd El Kader region, 2009, pp 68-70.
- Barefoot, S.F.; Klaenhammer, R. Detection and activity of lacticin B, a bacteriocin produced by Lactobacillus acidophilus, App, Env. Microbiol, 1983, 45, 1808–1815. [Google Scholar]
- Bouzaine, T.; ELMajdoub, T.; Thort, P.H.; Damdi, M. Sélection des bactéries lactiques probiotiques d’origine animale. Microbio. Hyg.Alim, 2004, 16, 28. [Google Scholar]
- Tabak, S.; Maghnia, D.; Bensoltane, A. The Antagonistic Activity of the Lactic Acid Bacteria (Streptococcus thermophilus, Bifidobacterium bifidum and Lactobacillus bulgaricus) against Helicobacter pylori Responsible for the Gastroduodenals Diseases. J.Agr. Sci. Tec 2012, A2, 709–715. [Google Scholar]
- Servin, A.L. Antagonistic activities of Lactobacilli and bifidobacteria against microbial pathogens. FEMS Microbiol Rev, 2004, 28, 405–440. [Google Scholar]
- Parker, M.; Zobrist, S.; Donahue, C.; Edick, C.; Mansen, K.; Hassan Zade Nadjari, M.; Kort, R. Naturally fermented milk from northern Senegal: Bacterial community composition and probiotic enrichment with Lactobacillus rhamnosus. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2018, 9, 2218. [Google Scholar]
- Blandino, A.; Al-Aseeri, ME.; Pandiella, S.; Cantero, D.; Webb, C. Cereal-based fermented foods and beverages. Food. Res. Int, 2003, 36, 527–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, A.; Egounlety, M.; Kouame, L.P.; Thonart, P. Les bactéries lactiques dans les aliments ou boissons amylacés et fermentés de l’Afrique de l’Ouest : leur utilisation actuelle. Annales de Médecine Vétérinaire, 2009, 153, 54–65. [Google Scholar]
- Tankoano, A.; Diop, M.B.; Sawadogo-Lingani, H.; Kaoré, D.; Savadogo, A. Les aspects technologiques, microbiogiques et nutritionnels de saliments fermentés à base de lait de millet en Afrique de l’ouest. Inter. Jour. Ad. Res 2017, 5, 1509–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faithong, N.; Benjakul, S. Changes in antioxidant activities and physicochemical properties of Kapi, a fermented shrimp paste, during fermentation. J. Foof Sciences. Technology, 2012, 51, 2463–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bintsis, T. Lactic acid bacteria: their applications in foods. J. Bacteriol. Mycol 2018, 6, 89–94. [Google Scholar]
- Holt, S.; Miks, M.H.; Carvalho, B.T.; Foulquié-Moreno, M.R.; Thevelein, J.M. The molecular biology of fruity and floral aromas in beer and other alcoholic beverages. FEMS Microbiology Reviews 2019, 43, 193–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamang, J.P.; Fleet, G.H. Yeast diversity in fermented foods and beverages. In Yeast Biotechnology: Diversity and Applications, Springer, Dordrecht, 2009, pp. 169–198.
- Jeantet, R.; Croguennec, T.; Schuck, P.; Brule, G. Sciences des Aliments 2- Technologie des Produits Alimentaires. Paris: Lavoisier Tec & Doc, 2007, p 760.
- Dubois, M. Les farines : caractéristiques des farines et des pates. Derniers développements dans le domaine analytique. In Industries des céréales Paris, Lavoisier, 1996, pp. 19–30.
- Hobamahoro, A.F. Etude comparative des caractéristiques physicochimiques, phytochimiques et technologiques des blés non fermentés et fermenté (El-hammoum), (Mémoire de fin d’études). Univ Ibn Khal Tiaret, 2013, p 124.
- Bartali, H.; Debbarh, A. Evaluation et amélioration de la technique traditionnelle du stockage souterrain des céréales au Maroc, Terre et Eaux. Rev Mar Sci Tec Dév Rur, 1991, 82, 3–20. [Google Scholar]
- Fredot, E. Connaissance des aliments. Bases alimentaires et nutritionnelles de la diététique, Tec. Doc. Lavoisier, Paris, 2006, p 397.
- Feillet, P. Le grain de blé : Composition et utilisation.Paris: Edition Quae. INRA, 2000. p 312.
- Bekhouche, F.; Merabti, R.; Bailly, J.D. Lemzeiet traditional couscous manufacture from fermented wheat (Algeria): investigation of the process and estimation of the technological and nutritional quality. Afr. J. Fd; Sci. Tec, 2013, 4, 167–175. [Google Scholar]
- Tou, E.H.; Guyot, J.P.; Mouquet-Rivier, C.; Rochette, I.; Counil, E. ; Traore, A ;S. Study through surveys and fermentation kinetics of the traditional processing of pearl millet (Pennisetum glaucum) into ben-saga, a fermented gruel from Burkina Faso. International j. food. micro, 2006, 106, 52–60. [Google Scholar]
- Dupin, H.; Cuq, J.L.; Malewiak, M.I.; Leynaud-Rouaud, C.; Berthier, A.M. Alimentation et nutrition humaines, Paris: ESF Ed, 1992, p 1533.
- Prescott, L.M. , Harley, J.P.; Klein, D.A., Wiley, J.M., Sherwood, L.M., Eds.; Woolverton, C.J. Microbiologie (éd. 3émé). Bruxelles: De Boeck, 2018, p 1120. [Google Scholar]
- Muanda, FN. Identification de polyphénols, évaluation de leur activité antioxydante et étude de leurs propriétés biologiques. Université Paul Verlaine-Metz, 2010, p 296.
- Faid, M.; Boraam, F.; Zyani, I.; Larpent, J.P. Characterization of sourdough bread ferments made in the laboratory by traditional methods. Zeitschrift für Lebensmittel- Untersuchung und Forschung 1994, 198, 287–291. [Google Scholar]
- Karovičová, Z.; Kohajdova, J. Fermentation of cereals for a specific purpose, J. Food. Nut. Res 2007, 46, 51–57. [Google Scholar]
- Ould El Hadj, M.D.; Sebihi, A.H.; Siboukeur, O. Qualité Hygiénique et Caractéristiques Physico-Chimiques du Vinaigre Traditionnel de Quelques Variétés de Dattes de la Cuvette de Ourgla. Rеvuе des Enеrgies Renouvеlablеs : Production et Valorisation-Biomasse, 2001, 87-92.
- Mokhtari, S. Effet protecteur de certaines bactéries lactiques isolées à partir de blé fermenté type Hamoum. Faculté des Sciences : Université d’Oran, 2012, p 209.
- Lery, F. L’agriculture au Maghreb ou pour une agronomie méditerranéenne. Ed. Maisonneuve et Larose, 1982; 338. [Google Scholar]
- Corsetti, A.; Settani, L.; Chavez Lopez, C.; Felis GE, Mastrangelo, M.; Suzzi, G. A taxonomy survey of lactic acid bacteria isolated from wheat (Triticum durum) kernels. Syst Appl Microbiol 2007, 30, 561–71. [CrossRef]
- Mokhtari S, Kheroua O, Saidi D. 2016. Isolation and Identification of Lactic Acid Bacteria from Algerian durum wheat (Triticum durum) naturally fermented in underground silos Matmora” El-Hammoum” and their antimicrobial activity again pathogenic germs. J. Nut. Health Sci, 2016, 3, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Marco, M.L.; Heeney, D.; Binda, S.; Cifelli, C.J.; Cotter, P.D.; Foligne, B.; Hutkins, R. Health benefit of fermented foods: Microbiota and beyond. Current Opinion in Biotechnology 2017, 44, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prückler, M.; Lorenz, C.; Endo, A.; Kraler, M.; Dürrschmid, K. , Hendriks, K. Comparison of homo-and heterofermentative lactic acid bacteria for implementation of fermented wheat bran in bread. Food microbiology 2015, 49, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyot, J.P. Fermented Cereal Products. In J. P. Tamang, & K. Kailasapathy, Fermented Foods and Beverages of the World, New York: CRC Press, 2010, pp. 247–262.
- Gomez, A.M.P.; Malcata, F.X. Bifidobacterium sp and Lactobacillus acidophilus: biological, technological, biochemical and therapeutical properties relevant for use as probiotics”. Trends in Food Sci & Tec 1999, 10, 139–157. [Google Scholar]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).