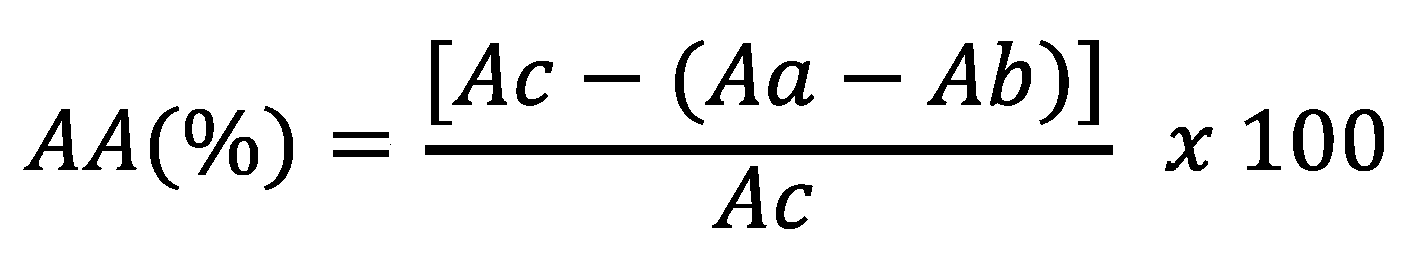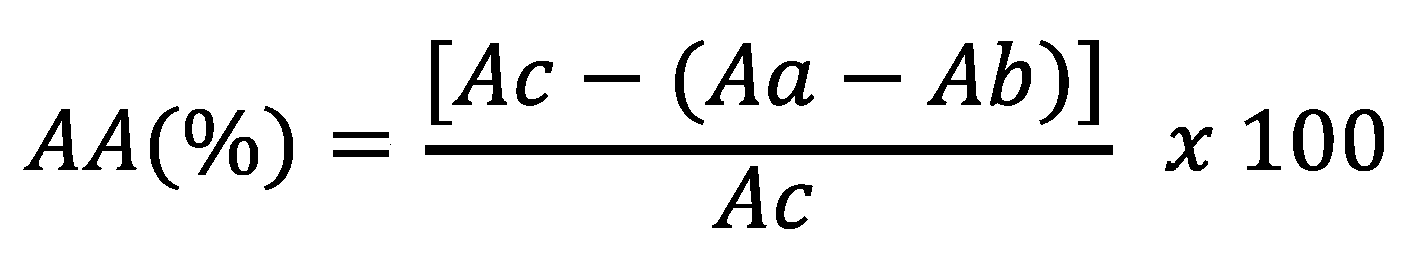1. Introduction
As a region of heterogeneous space, the Legal Amazon has an immense potential of natural, social and cultural resources. We must think of the Legal Amazon as a region for valuing its regional resources, encouraging its conservation by integrating the various economic and social interests with the need to preserve its ecosystem. The Legal Amazon provides a unique biodiversity, placing it in a prominent position in obtaining herbal medicines.
Herbal products offer limitless opportunities for new drug discoveries due to the unparalleled availability of chemical diversity. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), more than 80% of the world’s population depends on traditional medicine for their basic health needs.[
1]
The discovery of medicinal plant species in dentistry has piqued the interest of the scientific community, prompting research into the development of products with substantivity, minimal harm to oral tissues, reduced bacterial biofilm, and no favorable conditions for the development of resistant bacteria. Thus, phytotherapy has become well-known in the dental community for providing natural products with superior biocompatibility, lower toxicity, and high therapeutic activity that has been scientifically proven when compared to conventional medicines.
Given the wide range of benefits that plants from the Brazilian flora have in dentistry for humans, it’s critical to investigate their antimicrobial effects on the various microorganisms that cause oral infections, so that they can be used in the treatment of these diseases with efficacy and low cost for the population.[
2]
Medicinal plants from the Amazon region have a high antimicrobial potential and the identification of bioactive compounds may be an option against pathogenic microorganisms present in the oral cavity. Thus, finding scientific evidence of the effect of these plants and how they act against the bacteria present in the oral cavity is of great importance for dentistry.[
3]
The
Couroupita guianensis Aubl. is a native plant of the Legal Amazon popularly known in Brazil as abricó de macaco.[
4] Almost all parts of the plant (leaves, flowers, fruits, roots, stems and seeds) are known to have various medicinal properties. It is used in the treatment of malaria,[
5] hypertension and as an anti-inflammatory,[
6] in addition to presenting analgesic and antimicrobial activity.[
5]
Although flavonoids, saponins, quercetins, alkaloids, and volatile compounds have all been described in
C. guianensis,[
7] their potential for action against these pathogenic microorganisms in the oral cavity has yet to be investigated.
Thus, it is important for the scientific community to discover new products of natural origin, which may be used in dentistry, with action in the most important oral diseases, caries and periodontal disease.[
8] The goal of this work was to conduct a phytochemical and toxicological analysis and evaluation of the antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of extracts from the leaf of
Couroupita guianensis Aubl. focusing on microorganisms in the oral cavity.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chemical composition
The results obtained for the phytochemical screening of
C. guianensis leaf extracts are shown in
Table 1.
In all extracts, the presence of flavonoids, tannins and saponins was detected. Substances of natural origin such as flavonoids and tannins have proven antioxidant activity.[
9] Brunet et al.,[
10] and Kaiser et al.,[
11] point out the antimicrobial action of tannins, tissue repair and regulation of proteins and enzymes. Studies with gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria present in the oral biofilm show that tannins are important for antimicrobial activity as they interfere with the mechanism of bacterial adherence to the surface of teeth.[
12]
Triterpenoids were detected in CUE and CSE extracts and alkaloids were found in CSE and ESE extracts. Achika et al.,[
13] shows that terpenes and terpenoids are important for the control of multiresistant bacteria to conventional antimicrobials.
The presence of alkaloids, flavonoids, tannins and terpenoids found in
C. guianensis leaf extracts determine antiviral, antifungal, antiprotozoal, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory action, in addition to inhibiting cell growth and division, an important action in the treatment of oral disorders by inhibiting the formation of bacterial biofilm on the surface of teeth.[
14,
15,
16,
17]
2.2. Content of phenolic compounds, tannins, flavonoids, flavonols and evaluation of antioxidant activity
Table 2 presents the contents of phenolic compounds, tannins, flavonoids, flavonols and the results of the antioxidant activity of extracts from the leaves of
Couroupita guianensis.
In the determination of the flavonols and flavonoids contents, among all the analyzed extracts, the CUE presented the highest amount (100.89 ± 1.05 and 307.21 ±1.05 mgRE/g, respectively). Regarding the phenolic compounds and tannins, the three extracts analyzed did not show a statistically significant difference between them, with values of 85.58 ± 0.51mg GAE/g for the CUE, 90.19 ± 0.29mg GAE/g for the CSE and 92.31 ± 0.38mg GAE/g for ESE in the quantification of phenolic compounds, and 20.96 ± 0.62mg GAE/g for the CUE, 17.69 ± 0.29mg GAE/g for the CSEe19.62 ± 0.88 for the ESE in the quantification of tannins. In the DPPH• and ABTS•+ radical scavenging assay, the ESE extract statistically showed greater efficiency in the scavenging capacity of free radicals (IC50 of 2.98 ± 0.96a and 4.93 ± 0.90aμg/mL, respectively), obtaining better results than the standard (rutin for DPPH• and gallic acid for ABTS•+).
Phenolic compounds can help prevent various types of cancer and cardiovascular diseases due to their antioxidant effects.[
18] According to Duque,[
19] phenolic acids are promising agents for use in endodontics as healing agents between treatment sessions, with the goal of promoting root canals disinfection and preventing inflammation, allowing the repair of the periapical tissue.
In a study carried out by Sirisha and Jaishree,[
15] with extracts of
C. guianensis, the authors found a phenolic content of 96.90 mg EAG/g of methanolic extract showing antioxidant activity. The result of their study is in agreement with the results found in this work (CUE85.58 ± 0.51; CSE90.19 ± 0.29; ESE92.31 ± 0.38 mg GAE/g).
Akther et al.,[
7] quantified the flavonoid content from the methanolic extract of different parts of
C. guianensis and showed that the leaves have the highest flavonoid content, followed by the flower, fruit pulp, fruit peel and bark stem.
Sathishkumar et al.,[
20] determined the total phenolic content of
C. guianensis extract (343 ± 0.8 mg EAG/g) and high DPPH• radical scavenging antioxidant activity (IC
50 = 37 μg/mL) for a concentration of 100 μg/mL, highlighting evidence of the relationship between the total phenolic content and the antioxidant activity of the extract.
In similar studies, C. guianensis leaf extracts were analyzed and also exhibited DPPH• radical scavenging (IC
50 = 18 μg/mL).[
21]
Pinheiro et al.,[
22] found antioxidant activity of great pharmacological potential in the extracts of total ethanol, hexane, dichloromethane, ethyl acetate and n-butanol from the leaves of C. guianensis. Among the partitions used, ethyl acetate showed the best antioxidant activity (IC
50= 6.38 mg/mL), followed by partition in n-butanol (IC
50= 8.19 mg/mL), dichloromethane (IC
50= 39.83 mg/mL) and hexane (IC
50= 64.69 mg/mL), while the total ethanol extract presented IC
50= 19.74 mg/mL. These results are in agreement with the oxidizing activity found in this work.
The DPPH• and ABTS
•+ free radical scavenging potential of
C. guianensis leaf and flower extract was shown by Raghavendra et al.,[
23]. The extracts exhibited DPPH• and ABTS•
+ free radical scavenging dependent on the concentration variation of the extracts. Among the extracts, the extracts from the leaves (DPPH•: IC
50 19.61 μg/mL; ABTS•
+: IC
50 7.63μg/mL) were superior when compared to the extracts from the flowers (DPPH•: IC
50 of 257.13 μg/mL; ABTS•
+: IC
50 53.34 μg/mL), using ascorbic acid as a standard (DPPH: IC
50 8.89 μg/mL; ABTS: IC
50 3.59 μg/mL).
2.3. Analysis by LC-DAD
Table 3 shows the compounds identified by LC-DAD from
C. guianensis leaf extracts (CUE, CSE, ESE).
Among the compounds found in the analyzed extracts are caffeic acid, sinapic acid, rutin, quercetin, luteolin, kaempferol and apigenin. Only in the ESE a low amount (3.4 ± 0.1 mg/g) of the compound apigenin was found. Quercetin was the most abundant compound found in all extracts analyzed (CUE = 169.8 ± 0.6; CSE = 181.4 ± 0.7 and ESE = 177.3 ± 0.4mg/g).
All substances identified have important antioxidant activity, especially caffeic acid and sinapic acid.[
24] Rutin, in addition to antioxidant activity, has also been studied in relation to antibacterial activity.[
25]
In a study conducted by Oliveira et al.,[
25] the presence of rutin demonstrated antitumor activities and antibacterial properties. Stojkovic et al.,[
26] carried out a study with some phenolic compounds including rutin and observed that an amount of 1.87 mg/mL of this substance inhibited by up to 100% the growth of
Staphylococcus aureus at a temperature of 25 °C.
The flavonoids quercetin, luteolin, campefrol and apigenin have also been shown to have antioxidant potential, implying antimicrobial activity. [
7,
27]
The identified compounds are important in treatments against pathogens that affect the oral microbiota, mainly in the formation of bacterial biofilm on the dental surface.
There were no studies found in the literature using liquid chromatography by LC-DAD with extracts of the plant C. guianensis.
2.4. Analysis by GC-MS
Table 4 lists the compounds identified by GC-MS in
C. guianensis leaf extracts (CUE, CSE, ESE) obtained by ultrasound assisted and Soxhlet apparatus.
In the CUE and CSE extracts, the substances found were stigmasterol and β-sitosterol. No compounds were found in the ESE using this technique. The amount of the stigmasterol compound in the CSE was statistically higher than the CUE. On the other hand, the β-Sitosterol compound showed no statistical difference between the CUE and CSE extracts.
Phytosterols such as β-sitosterol and stigmasterol have antitumor, antifungal, analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties. These activities are important in the dental field as they largely affect oral diseases and the formation of bacterial oral microbiota [
28,
29,
30].
Using the same technique Araujo et al.,[
31] identified 8 different compounds (polyphenols and nitrogen-containing alkaloids) in extracts from leaves of
C. guianensis. Venkatraman and Sheba,[
32] analyzing the pulp of the fruit of
C. guianensis, confirmed the presence of about 30 chemical components, with 2,5-furandione-3-methyl- and 5-hydroxymethylfurfural being the main components of the ethanolic extract.
Volatile and semi-volatile compounds were analyzed in extracts from mature fruits of
C. guianensis in the studies by Lavanya and John,[
33] and identified 50 different compounds such as linalool, benzyl alcohol, terpineol, hexadecanoic acid and the predominant cis and transfuran oxides linalool.
2.5. Toxicity
Table 5 presents the values of toxicity of the extracts of the leaves of
C. guianensis against the specimens of
Allium cepa (onion) tested under different concentrations (50, 250, 750 µg/mL) and the control group.
When analyzing the results found for the average root length (ARL), it was possible to verify a significant difference for the studied samples, with the longest length presented by the ESE extract 50µg/mL and the smallest by the CUE extract 750µg/mL. Only in the extracts CUE 50µg/mL and ESE 50 µg/mL there was growth stimulus (GS) of the roots. In the concentration of 250µg/mL, all the samples of the studied extracts had the size of their roots similar to the control group. At a concentration of 750µg/mL, all extracts inhibited root growth.
In the analysis of the ICR, it was found that the lowest RGI was observed for the CUE 500 µg/mL extract. In all extracts, there was an inversely proportional pattern between RGI and extract concentrations, that is, the higher the concentration, the lower the growth rate (GR), so that the extracts with RGI <0.8 differ statistically from the other samples (p <0.05).
No studies were found in the literature with the use of Allium cepa against extracts of the plant C. guianensis.
Table 6 defines IC
50 values and toxicity rates for
C. guianensis leaf extracts in the
A. salina mortality test.
In this study, no toxicity was found even at the highest concentrations. The three extracts analyzed (CUE, CSE and ESE) presented IC
50 values above 1000μg/mL, giving them the denomination of non-toxic according to Young et al.[
34]
Few studies using the
A. salina test for the analysis of toxicity with
C. guianensis are reported. In the study evaluating the methanolic extract obtained from the leaves of
C. guianensis, Bhuvaneswari et al.,[
21] found weak activity against
A. salina, eliminating 60% of microcrustaceans at a concentration of 6 mg/mL.
Sivapragasam et al.,[
35] investigated the action of the
C. guianensis flower extract on the mortality of
A. salina and the general results showed that the methanolic extract of the
C. guianensis flower has neither cytotoxic nor genotoxic potential (IC
50 of 1210.65 μg/mL) suggesting its future development into a therapeutic agent.
2.6. Antimicrobial Activity
The result of the antibacterial activity through the agar-well diffusion test of the extracts from the leaves of
C. guianensis is shown in
Table 7.
CUE, CSE and ESE extracts from C. guianensis leaves induced the formation of inhibition halos against S. aureus and S. mutans bacteria, compared to the positive control. Regarding the fungicidal activity, none of the tested extracts was able to form inhibition halos against the fungus C. albicans. Regarding the microorganism, the inhibition halo of S. aureus had higher values compared to S. mutans. In relation to the analyzed extracts, the ESE and the CUE presented the best inhibition halos when compared to the CSE extract. The concentration of 200mg of the extracts was able to inhibit all the bacteria tested.
Against the
S. aureus strains, the CUE (200mg) and ESE (200mg and 100mg) extracts showed higher inhibition halos compared to the positive control chlorhexidine, being statistically superior. Against the strains of
S. mutans, the extracts analyzed were statistically inferior to the positive control chlorhexidine. In this work, the extracts from the leaves of
C. guianensis showed no action against the fungi
C. albicans, a result similar to that found by Singh et al.[
14]
These same authors observed that the leaf extract of C. guianensis has significant activity in different bacteria, including S. aureus.
Akther, Khan and Hemalatha,[
7] analyzed antibacterial activity using methanolic extracts from various parts of
C. guianensis and found that the zone of inhibition ranged between 08 and 22 mm. The leaf extract showed inhibition against the pathogens
Proteus mirabilis and
Acinetobacter baumannii (22 mm each).
Raghavendra et al.,[
23] evaluated the antimicrobial activity of hydroethanolic extracts of leaves and flowers of
C. guianensis against Gram-positive bacteria, Gram-negative bacteria and fungi, noting antifungal activity (
Fusarium sp.,
Alternaria sp. and
Curvularia sp). The authors observed marked antibacterial activity (
Staphylococcus epidermidis and
Escherichia coli) in the leaf extract (16.7 ± 0.06mm) when compared to the flower extract. When comparing with the findings in this study, the inhibition halos present statistically equal values (13.41 ± 1.76 mm).
In another study, Patel et al.,[
36] observed a greater activity of the methanolic extract of
C. guianensis leaf against
S. aureus (8 mm inhibition halo), which is in agreement with the finding in this study. The study by Lavanya and John,[
33] showed the potential of extracts from leaves of
C. guianensis against human pathogenic fungi (
Candida albicans, Cryptococcus sp., Microsporum canis and
Trichophyton rubrum) (inhibition halo between 7 to 17 mm), unlikely observed in our study.
The continuous and regular use of antibiotics causes antibiotic or multidrug resistance, therefore, the plant extract of C. guianensis can be an alternative source of antibiotics to inhibit bacterial infection.
2.7. Determination of the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC)
For the determination of MIC only the microorganisms S. aureus and S. mutans were studied because they showed inhibition halo in the well diffusion test. The CUE and ESE extracts were effective against the microorganisms S. aureus and S. mutans, at the lowest concentration analyzed (0.781mg/mL), showing bactericidal activity.
Singh et al.,[
14] found lower results, with a minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) for
S. aureus of 25 mg/mL for the ethanolic extract, 50 mg/mL for the methanolic extract and 100 mg/mL for the chloroform extract. In the consulted literature, no data on
S. mutans inhibition were found.
This result is important in dentistry as it prevents the growth of S. aureus and S. mutans, the main microorganisms responsible for the formation of bacterial plaque and, consequently, the development of caries and periodontal disease.
3. Conclusions
In all analyzed extracts of C. guianensis flavonoids, tannins and saponins were found. The CUE extract showed the highest content of flavonols and total flavonoids. The three extracts showed no statistically significant difference in tannins between them. Caffeic acid, sinapic acid, rutin, quercetin, luteolin, kaempferol and apigenin were identified by LC-DAD chromatography, substances with proven antioxidant and antimicrobial action. In the identification by GC-MS, stigmasterol and β-sitosterol were found in the CUE and CSE extracts. All extracts showed antioxidant activity, especially the ESE extract.
In the toxicity with Allium cepa, only the extracts CUE 50µg/mL and ESE 50 µg/mL showed root growth stimulation. There was no death of Artemia salina nauplii at the concentrations tested. Thus, the extracts were not considered toxic. The antibacterial action was verified against S. aureus and S. mutans, without detection of antifungal activity against C. albicans.
C. guianensis has the potential to be a source of great therapeutic interest, with applications in oral health research. The findings of this study are promising and provide a foundation for further research.
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Plant material
The leaves of C. guianensis were collected at Praça dos Girassóis in Palmas-Tocantins, Brazil (10º11’14” S and 48º19’56” W) and were listed and incorporated into the HUTO herbarium collection (Universidade Estadual do Tocantins - UNITINS) under number HTO 8057. The project was registered in SISGEN as A9D18D3.
4.2. Preparation of extracts
After the plant material was collected, it was sanitized and dried in an oven at 50 °C for 48 hours, then ground with a Willye-type knife mill (Fortinox STAR FT50 brand) and stored in amber glass bottles.
Three extracts were prepared by two different methods, Soxhlet and ultrasound bath. First, extraction was performed using 5g of leaf powder, 80mL of 70% ethanol in an ultrasound bath (USC1600, frequency 40 kHz, 135 W), for 5 cycles of 1 hour at room temperature, resulting in the Crude Ultrasound Extract (CUE). Soxhlet extraction was performed based on the method described by Soares et al.,[
37] with modifications, using 5g of leaf powder, 200 mL of 70% ethanol, heated to boiling temperature for a period of six hours, giving rise to the Cru Soxhlet Extract (CSE). By the same method, the Ethanol Soxhlet Extract (ESE) was obtained, after a previous degreasing process with hexane, the sample was dried at room temperature for 24 hours, before carrying out the extraction with 70% ethanol.
Solvents were removed using rotary evaporator (FISATOM) at -600mmHg and 45ºC. The extracts were frozen at -70 ºC, lyophilized in a benchtop lyophilizer (LIOTOP L101) and stored in airtight flasks for further analysis.
4.3. Phytochemical screening
Phytochemical screening was performed through qualitative tests based on chemical reactions of color change and/or precipitation to identify the main groups of secondary metabolites: flavonoids, tannins, phytosterols, triterpenoids, quinones, saponins and alkaloids.[
38,
39,
40]
4.4. Determination of the content of phenolic compounds
Total phenolic compounds were quantified using the Folin-Ciocalteu method, as described by Amorim et al.,[
41] with modifications, using gallic acid as a standard. 0.2 mL of methanolic solution of CUE, CSE and ESE extracts (1mg/mL) or standard (galic acid, 2-100 μg/mL) was mixed with 0.5 mL of Folin-Ciocalteu reagent (10%). 1 mL of sodium carbonate (75%, w/v) and 8.3 mL of distilled water, stirred gently and kept for 30 minutes in the dark. Absorbance was measured at 760 nm using a UV visible spectrophotometer (GLOBAL TRADE TECHNOLOGY, GTA-96). The total phenolic content was determined by interpolating the absorbance of the samples against a calibration curve constructed with different concentrations of gallic acid (y=0,0052x + 0,038, R
2 = 0,9915). The result was expressed as mg GAE/g of lyophilized extract. The assay was performed in triplicate on each extract.
4.5. Determination of tannin content
The tannin content was quantified using the Folin-Ciocalteu Method associated with casein precipitation, as described by Amorim et al.,[
42] with modification. To quantify the tannin content, the CUE, CSE and ESE extracts (1mL, 1mg/mL) were mixed with casein (0.1g) and distilled water (5mL), followed by vigorous stirring until homogenization. After 3 h at room temperature and without agitation, the solution was centrifuged at 1358 rpm for 10 min at 10°C. In the supernatant, the non-tannin phenolic constituents were determined similarly to the total phenolic content. The amount of tannin was calculated as the difference between the total phenolic content and the non-tannin phenolic content in the extract. The total tannin content was expressed as mg GAE/g of
C. guianensis extract. The experiment was performed in triplicate for each sample.
4.6. Determination of flavonoid content
The total flavonoid content was determined according to the methodology described by Soares et al.[
37] 0.5 mL of methanolic solution of the CUE, CSE and ESE extracts (1mg/mL) or the rutin standard (10-400 μg/mL) were mixed in an aqueous solution of acetic acid (0.5 mL, at 60%), methanolic pyridine solution (2 mL, 20%), aluminum chloride (1 mL, 5%) and 6 mL of distilled water. The blank was made by replacing aluminum chloride with methanol. The reaction complex and the blank were carefully shaken and kept for 30 min protected from light and the absorbance measured at 420nm in a spectrophotometer. The total flavonoid content was determined by interpolating the absorbances of the samples against a calibration curve of the rutin standard (y = 0,0019x + 0,0047, R
2 = 0,9984) and expressed in mg ER/g of lyophilized extract. The analysis was performed in triplicate for each sample.
4.7. Determination of flavonols
The total flavonol content was measured using the method described by Miliauskas, Venskutonis and Van Beek.[
43] Briefly, 0.5mL of extracts (1mg/mL) were mixed with 0.5mL of aluminum chloride (20mg/mL), followed by 1.5mL of sodium acetate (50mg/mL). The mixture was incubated at room temperature for 2.5h. Absorbance was measured by a spectrophotometer at 440 nm. The total flavonol content was determined by the interval in the decrease of samples against a calibration curve (y = 0,0019x + 0,0047, R
2 = 0,9984) constructed with different concentrations of rutin in methanol (2-400 μg/mL, w/v). The result was expressed as milligram of rutin equivalent per gram of lyophilized extract of
C. guianensis (mg RE/g). The experiment was performed in triplicate for each sample.
4.8. Assessment of antioxidant activity
The evaluation of the antioxidant capacity of the extracts was determined by the elimination methods of the DPPH• (2,2-difenil-1-picrilhidrazil) stable free radical and by the ABTS•+ by capturing the 2,2-azinobis radical (3-etilbenzotiazolina-6-ácido sulfônico).
The antioxidant capacity by the DPPH• method was measured following the descriptions of Peixoto-Sobrinho et al.,[
44] with the rutin pattern as a positive control. In triplicate, 0.5 mL of different concentrations of extracts or standards (10 – 200 μg/mL) were added to a methanolic solution of DPPH• (3 mL to 40 μg/mL). A blank was constructed by replacing DPPH• with methanol in the reaction medium. The reaction complex and the blank were stirred and kept protected from light for 30 minutes, and the absorbances were measured at 517 nm in a spectrophotometer calibrated with methanol. The absorbance of the 40 μg/mL DPPH solution was also measured and used as a negative control. Antioxidant activity (AA) was expressed as the percentage of inhibition determined by the equation:
where AA (%) is the percentage of antioxidant activity; Ac, the absorbance of the negative control; Aa, the absorbance of the sample; Ab, the absorbance of the blank.
The IC50 value was calculated denoting the sample concentration needed to decrease the absorbance by 50% at 517 nm. IC50 was expressed in μg/mL.
The antioxidant capacity by the ABTS•
+ method was determined according to the methodology described by Chen et al.,[
45] and updated by Rabêlo et al.[
46] The ABTS•
+ solution was prepared by reacting 7 mM ABTS (5 mL) and 2.45 mM (88 µL) potassium persulfate, after incubation at room temperature in the dark for 16 h. It was then diluted with 80% ethanol to obtain an absorbance of 0.700 ± 0.020 at 734 nm. ABTS•
+ solution (2.7 mL) was carefully mixed with 0.3 mL of test samples. The reaction mixture was allowed to stand at 30 °C for 30 min, and the absorbance at 734 nm was measured in a spectrophotometer. Percent inhibition was calculated by the following formula:
where: AA (%) is the percentage of antioxidant activity; Ac, the absorbance of the negative control; Aa, the absorbance of the sample; Ab, the absorbance of the blank. The IC50 value was also calculated to measure the concentration of a sample needed to decrease the absorbance by 50%. IC50 was expressed in μg/mL.
4.9. Analysis by liquid chromatography by diode array detection (LC-DAD)
C. guianensis leaf extracts were analyzed by LC-DAD using LC chromatograph (LC-6AD Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan) with photodiode array detector system (PDA) between wavelengths λ = 200-800 nm, in an apparatus analytical LC, with ODS HYPERSIL column (C-18, 150 mm long x 4.6 mm diameter, ThermoElectron Corporation). The injection flow and volume were, respectively, 1 mL/min and 10 µL. All chromatographic analyzes took place at a temperature of 25 °C. Eluent A was composed of a binary mobile phase of water with 6% acetic acid and 2 mM sodium acetate and eluent B, composed of acetonitrile and the following gradient was applied: 0 min 5% B; 20 min 15% B; 30 min 60% B; and 40 min 100% B. The identification of compounds was performed with the aid of a DAD scanning detector in the spectral range of 200-800 nm. Patterns were identified and quantified based on their absorption spectra in the UV region and retention time. Calibration curves were determined by linear regression using LC. The linearity of the standards was evaluated for 10 concentration ranges. The respective coefficients of determination R2 were 0.9994 for caffeic acid, ellagic acid, sinapic acid, vanillic acid, ferulic acid and gallic acid and R2 = 0.9996 for rutin, luteolin, apigenin, naringin, kampferol and quercetin. All standards were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich.
4.10. Analysis by gas chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry (GC-MS)
GC-MS analysis was performed using GC-2010 Plus, (Shimadzu, Kyoto-Japan) equipped with a mass spectrometry detector (GC-MS Ultra 2010), using LM-5 (5% phenyldimethylpolysiloxane), silica capillary column cast (15m long x 0.2mm and 0.2 µm thick film.
The analysis took place under the following conditions: helium carrier gas (99.999% and flow rate of 1 mL/min), 1 µL injection volume, split ratio (1:20), initial oven temperature set to 150 ºC and heating at 150 °C to 280 °C at 15 °C/min and a hold at 280 °C for 15 min. The temperature of the injector and detector was 280°C. MS scan parameters included an electron impact ionization voltage of 70 eV, a mass range of 45-600 nm m/z and a scan interval of 0.3s. Compound concentrations were determined by external calibration. The linearity of the standards was evaluated for 5 concentration ranges. The mean standard errors for the peak areas of replicate injections (n = 5) were less than 2%, thus showing good repeatability of the calibration curve. The coefficient of determination R2 was 0.9996 for stigmasterol and β-sitosterol. All standards were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich.
4.11. Toxicity evaluation
The evaluation of the toxicity of the extracts was determined by the Allium cepa and Artemia salina methods.
Toxicity analysis on
Allium cepa was carried out according to the methodology of Meneguetti et al.,[
47] with modifications. The specimens of
Allium cepa were acquired in the local market, with standardization of size, origin, not germinated and healthy aspect. After removing the peel, the bulbs were submerged in 50 mL of mineral water for 48 hours at 25 ºC to identify healthy onions. After this period, the onions had their roots trimmed and then submerged in 50 mL of aqueous extracts of
C. guianensis leaves under different concentrations (50, 250, 750 µg/mL), and the control group was submerged in 50 mL of mineral water at 25 ºC for five days. At the end of the period, the number of germinated roots of each onion was counted and the three largest were measured with a digital caliper. Analyzes were performed in triplicate.
The experimental design was completely randomized in a factorial scheme, arrangement (4×3) with 9 treatments: the control, three concentrations of each extract and three replications per treatment. The Relative Growth Index (RGI) was determined through the root growth of the control and the extracts according to Young et al.,[
34] obtained by the equation:
Where RLS is the root length sample and RLC is the root length control. The effect of the extract in relation to the control was determined as a function of the RGI, which is subdivided into 3 categories: RGI < 0.8: Growth inhibition (GI); 0.8 ≤ RGI ≤ 1.2: Same effect as control (SCE) and RGI > 1.2: Growth stimulus (GS).
In another toxicity test, Artemia salina L. nauplii were used, using the Mean Lethal Concentration (LC
50) as a parameter to evaluate the biological activity, according to the methodology of McLaughlin et al.[
48] About 25 mg of A. salina eggs were incubated in a container containing artificial sea water (NaCl 23 g/L, MgCl
2.6H
2O 11 g/L, Na
2SO
4 4 g/L, CaCl
2.2H
2O 1.3 g/L and KCl 0.7 g/L) at a temperature of 20 to 30 °C, with a pH between 8.0 and 9.0, using Na
2CO
3 to adjust the pH. After 24 hours of incubation for hatching, the nauplii considered viable, with the presence of motor activity, were used for the test.
The assays were performed in triplicate, seeking to determine the dose-response relationship. For the control group, it was used only with artificial sea water, and the test groups, artificial sea water with the CUE, CSE and ESE extracts of
C. guianensis at concentrations of 50, 500, 1,000 and 5,000 μg/mL. Each tube with the test group, containing 10 nauplii of
A. salina, including the control, were filled to a final volume of 5 mL with artificial sea water and incubated in the dark for 24 hours. After this period, the immobile nauplii were counted and the IC50 was calculated, determined by the statistical method of Probits. The extract classification followed the criteria established by NGUTA et al.,[
49] with values of: IC50< 100 µg/mL – high toxicity; 100 ≤ IC
50 ≤ 500 µg/mL – moderate toxicity; 500 < IC
50 ≤ 1000 µg/mL – weak toxicity; IC
50 > 1000 µg/mL – non-toxic.
4.12. Antimicrobial activity evaluation
For the bioassays, ATCC (American Type Culture Collection) reference strains were used, borrowed from the collection of the Faculty of Dentistry of the University of São Paulo (USP-Bauru). The strains selected for the study were Staphylococcus aureus (ATCC 6538), Streptococcus mutans (ATCC 25175), and the fungus Candida albicans (ATCC 90028).
The strains were stored under freezing at -70 ºC in Brain Heart Infusion (BHI) broth. For reactivation, they were subcultured in nutrient agar and incubated for 24 hours at 35 ºC and stored in a refrigerator at 2-8 ºC until the time of preparation and standardization for the tests.
4.13. Antimicrobial test by the Agar diffusion method (Well)
Antimicrobial activity was performed by the well diffusion method, in triplicate and in three replications, using petri dishes (140x15 mm) containing 50 mL of Mueller Hinton agar (AMH) medium for bacteria and Sabouraud agar medium for yeast. The extracts (CUE, CSE and ESE) were diluted in a mixture with 10% dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO) at concentrations (200, 100 and 50 mg/mL). Inoculum solutions were prepared using isolated strains, diluted in 0.85% saline solution until reaching a turbidity corresponding to 0.5 on the MacFarland scale, obtaining about 1.5 × 10
8 (CFU/mL) of bacteria and 2, 0 × 10
6 CFU mL of yeast. For the positive control, chlorhexidine (Periogard® 0.12%, Colgate, Brazil) (1.1 mg/mL to 0.00234 mg/mL) was used for the bacteria and nystatin (100,000UI/mL) for the fungus, for the negative control, the 10% DMSO solution (Oliveira et al.,[
50] with adaptations). With the aid of a sterile swab, the solutions containing the inoculum were seeded on the surface of the plates containing the culture medium and then wells were drilled with a 5mm diameter sterile plastic straw. These wells were filled with 50 μL of each extract diluted in 10% DMSO and with positive and negative controls.[
51] After 24 h (for the bacteria) and 48 h (for the fungus) of incubation at 37 ºC, the results were analyzed by measuring the diameters of the inhibition halos observed around the wells with a digital caliper model Starret 799.
4.14. Determination of the Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC)
The tests were performed in a 96-well microplate (ELISA Plate) sterilized, in triplicate and three replicates. The extract test was performed on each microplate,[
52] using the microorganisms
Staphylococcus aureus,
Streptococcus mutans and the fungus
Candida albicans.
100 μL of Mueller Hinton broth (M-H Broth) was added to each well, then different concentrations of the tested extracts were prepared in order to always obtain half the concentrations (serial dilution). The concentrations of the extracts tested in the experiment ranged from 100 to 0.78125 mg/mL (100; 50; 25; 12.5; 6.25; 3.125; 1.5625 and 0.78125 mg/mL). For the positive control (C+) 0.12% chlorhexidine was used, the negative control (C-) was used 10% DMSO solution. For the control of the culture medium (CM) only 100 μL of the M-H Broth medium was used. For the control of the microbial growth (C) 5 μL of bacterial suspension 107 UFC/mL was added to the culture medium. The plates were incubated at 37 ºC for 24 hours.[
50]
After the incubation period, 30 μL of sterile 0.03% (m/v) resazurin (m/v) were added to each microplate well and then the plates were reincubated for 2 to 4 hours or the time necessary for the dye overturning and then the reading. The presence of blue color represented absence of growth (inhibition of growth) and pink color, presence of bacterial growth (non-inhibition of growth).[
53] The lowest concentration of the extract capable of inhibiting bacterial growth was considered as MICa. After this period, an aliquot from the well with the lowest inhibitory concentration was plated in the culture medium to assess whether the extracts had a bacteriostatic/bactericidal effect.
4.15. Statistical analysis
The experiments performed in triplicate had their results expressed as mean ± standard deviation. The data obtained were submitted to statistical analysis using the SISVAR program version 5.6,[
54] and GraphPadPrism 8. Analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used to compare the mean values obtained in the analyses. P values < 0.05 were considered statistically significant by the Tukey test.
Author Contributions
M. A. C. A performed the experiments, analyzed the data and wrote the article. D. A. S. performed the experiments, analyzed the data and revised the manuscript. J. F. P. and M. A. N. R. revised the manuscript. R. M. N. F. guided and supervised the phytochemical analyzes. J. F. M. S. supervised the analysis of antimicrobial activity, analyzed the data and revised the manuscript. C. A. L. C. performed the GC-MS and LC-DAD analyzes, analyzed the data and revised the manuscript. E. S. supervised and coordinated all experiments, supervised, revised the manuscript, review and editing and funding acquisition. M. K. D. R. writing revision and funding acquisition
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the Federal University of Tocantins (UFT) for the support received. This publication received financial support from EDITAL Nº17/2021, of the Postgraduate Program in Environmental Science (PPGCiamb) by the UFT, of the Postgraduate Program in Environmental Science (PPGCiamb) by the UFT and from EDITAL Nº 40/2021 of the Pro-Rectory for Research (PROPESQ) by the UFT and the Foundation for Research Support of the State of Tocantins (FAPT) through the public notice number 01/2019.
References
- C. Rosa, S. G. Câmara, J. U. Béria, ‘Representações e intenção de uso da fitoterapia na atenção básica à saúde‘. Cien. Saude Colet. 2011, 16, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- L. Borzini, R. Condò, P. De Dominicis, A. Casaglia, L. Cerroni, ‘Root canal irrigation: chemical agents and plant extracts against Enterococcus faecalis’. Open. Dent. J. 2016, 10, 692–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- N. C. Conde, M. D. S. Vieira Pereira, M. F. Costa Lima Bandeira, G. Naura Venâncio, G. Palma de Oliveira, F. Correia Sampaio, ‘In vitro antimicrobial activity of plants of the Amazon on oral biofilm micro-organisms’. Ver. Odonto Ciênc. 2015, 30, 179–183. [Google Scholar]
- H. Lorenzi, ‘Árvores Brasileiras: Manual de Identificação e Cultivo de Plantas Arbóreas do Brasil’, in ‘Instituto Plantarum de Estudos da Flora LTDA‘, Ed. Nova Odessa, São Paulo, SP, 2000.
- N. K. Kaushik, A. Bagavan, A. A. Rahuman, A. A. Zahir, C. Kamaraj, G. Elango, C. Jayaseelan, A. V. Kirthi, T. Santhoshkumar, S. Marimuthu, G. Rajakumar, S. K. Tiwari, D. Sahal, ‘Evaluation of antiplasmodial activity of medicinal plants from North Indian Buchpora and South Indian Eastern Ghats’. Malar. J. 2015, 14. [Google Scholar]
- J. Sanz-Biset, J. Campos-de-la-Cruz, M. A. Epiquién-Rivera, S. Canigueral, ‘A first survey on the medicinal plants of the Chazuta valley (Peruvian Amazon)’. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2009, 122, 333–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- T. Akther, M. S. Khan, S. Hemalatha, ‘Extraction of flavonoid from various parts of Couroupita guianensis and its efficacy against pathogenic bacteria. Asian J. Pharm.Clin. Res. 2017, 10, 354–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- I. A. Freires, S. M. De Alencar, P. L. Rosalen, ‘A pharmacological perspective on the use of brazilian red propolis and its isolated compounds against human diseases’. Eur J. Med. Chem. 2016, 110, 267–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- C. Chen, H. C. CHANG, H. W. YANG, G. L. CHEN, ‘Evaluation of total antioxidant activity of several popular vegetables and chinese herbs: a fast approach with ABTS/H2O2/HRP system in microplates’. J. Food Drug Anal. 2004, 12, 29–33. [Google Scholar]
- J. R. Brunet, M. D. Echevarría, F. M. Luzardo, E. N. Romero, L. M. V. Guerra, J. L. S. Romero, ‘Inhibición de la replicación del virus de inmunodeficiencia humana por extractos de taninos de Pinus caribaea Morelet’. Rev. Cubana Farm. 2003, 37, 0–0. [Google Scholar]
- S. Kaiser, C. Pavei, G. G. Ortega, ‘Estudo da relação estrutura-atividade de saponinas hemolíticas e/ou imunoadjuvantes mediante uso de análise multivariada‘. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2010, 20, 300–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- C. Aleluia, V. de Cássia Procópio, M. T. G. Oliveira, P. G. S. Furtado, J. F. G. Giovannini, S. M. S. de Mendonça, ‘Fitoterápicos na odontologia’. Rev. Odont. Univers. Cidade Sao Paulo 2017, 27, 126–134. [Google Scholar]
- J. I. Achika, R.G. Ayo, J.D. Habila, A.O. Oyewale, ‘Terpenes with antimicrobial and antioxidant activities from Lannea humilis (Oliv.). Sci. Afri. 2020, 10, e00552. [Google Scholar]
- R. Singh, N. Kumari, M. Gangwar, G. Nath, ‘Qualitative characterization of phytochemicals and in vitro antimicrobial evaluation of leaf extract of Couroupita guianensis aubl. - a threatened medicinal tree’. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 7, 212–215. [Google Scholar]
- M. Sirisha, V. Jaishree, ‘Phytochemical screening, antioxidant and antiproliferative activities of successive extracts of Couroupita guianensis Aubl. Plant’. Ind. J. Nat. Prod. Res. 2018, 9, 22–27. [Google Scholar]
- P. Pandurangan, M. Sahadeven, S. Sunkar, S. K. N. M. Dhana, ‘Comparative analysis of biochemical compounds of leaf, flower and fruit of Couroupita guianensis and synthesis of silver nanoparticles’. Pharmacogn. J. 2018, 10, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A. Elumalai, K. Bargavi, S. Krishna, M. C. Eswaraiah, ‘Evaluation of anti-oxidant and hepatoprotective activity of Couroupita guianensis leaves’. J. Cell. Tissue Res. 2013, 13, 3745. [Google Scholar]
- F. R. P. Silva, S. S. M. F. R. P. Silva, S. S. M. Almeida, ‘Análise fitoquímica e microbiológica da atividade do extrato bruto etanólico da andiroba, Carapa guianensis aubl’. Biota Amazônia 2014, 4, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- C. Duque. Available online: https://bv.fapesp.br/pt/bolsas/186095/efeito-antimicrobiano-e-anti-inflamatorio-de-acidos-fenolicos-isolados-combinados-e-incorporados-em/ (accessed on 17 May 2022).
- G. Sathishkumar, K. J. Pradeep, V. Vignesh, C. Rajkuberan, M. Jeyaraj, M. Selvakumar, J. Rakhi, S. Sivaramakrishnan, ‘Cannonball fruit (Couroupita guianensis, Aubl.) extract mediated synthesis of gold nanoparticles and evaluation of its antioxidant activity’. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 215, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- S. Bhuvaneswari, K. R. Aravind, B. Ramkumar, N. V. Raja, A. Neelakandan, P. M. Kumar, N. K. U. Prakash, ‘Studies on the phytochemistry and bioactivity of leaves of trees in Chennai’. Int. J. Chem. Tech. Res. 2014, 6, 4078–4083. [Google Scholar]
- M. M..G. Pinheiro, S. B. O. Fernandes, C. E. Fingolo, F. Boylan, P. D. Fernandes, ‚Anti-inflammatory activity of ethanol extract and fractions from Couroupita guianensis Aublet leaves‘. J. Ethnopharm. 2013, 146, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- H. L. Raghavendra, T. R. P. Kekuda, D. Pushpavathi, M. Shilpa, T. Petkar, A. Siddiqha, ‚Antimicrobial, radical scavenging, and insecticidal activity of leaf and flower extracts of Couroupita guianensis Aubl’. Int. J.Green Pharm. 2017, 11, 171–179.
- D. M. Oliveira, D. H. M. Bastos, ‘Biodisponibilidade de ácidos fenólicos‘. Quim. Nova 2014, 34, 1051–1056. [Google Scholar]
- L. M. N. Oliveira, L. M. R. Silva, A. C. S. Lima, R. R. Almeida, N. M. P. S. Ricardo, E. A. T. Figueiredo, R. W. Figueiredo, ‘Characterization of rutin, phenolic compounds and antioxidant capacity of pulps and by-products of tropical fruits’. Res. Soc. Dev. 2020, 9, e42942812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D. Stojković, J. Petrović, M. Soković, J. Glamočlija, J. Kukić-Marković, S. Petrović, ‘In situ antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of naturally occurring caffeic acid, p-coumaric acid and rutin, using food systems’. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2013, 93, 3205–3208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- B. Gupta, B. Huang, ‘Mechanism of salinity tolerance in plants: physiological, biochemical, and molecular characterization’. Int. J. Genomics 2014, 2014, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- J. H. G. Lago, A. T. Ito, C. M. Fernandes, M. C. M. Young, M. J. Kato, ‘Secondary metabolites isolated from Piper chimonanti folium and their antifungal activity’. Nat. Prod. Res. 2012, 26, 770–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- V. A. Facundo, A. R. Pollli, R. V. Rodrigues, J. S. T. Militão, R. G. Stabelli, C. T. Cardoso, ‘Constituintes químicos fixos e voláteis dos talos e frutos de Piper tuberculatum Jacq. e das raízes de P. hispidum HBK’. Acta Amazon. 2008, 38, 743–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- H. D. S. Alves, G. E. D. Oliveira, M. D. G. Zoghbi, M. C. D. O. Chaves, ‘Flavonóides de Piper carniconnectivum C. DC.. Piperaceae’. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2010, 20, 160–164. [Google Scholar]
- M. Araujo, M. C. O. Pinheiro, I. E. A. Z. Teixeira, L. G. Riachi, C. B. Rocha, C. A. De Maria, R. F. A. Moreira, ‘Volatile and semi-volatile composition of the ripe Brazilian Couroupita guianensis fruit’. Nat. Product. J. 2014, 4, 280–289. [Google Scholar]
- A. Venkatraman, L. A. Sheba, ‘Antioxidant potential and chromatographic profiling of Couroupita guianensis fruit pulp‘. J. Adv. Sci. Res. 2022, 13, 286–293. [Google Scholar]
- R. Lavanya, S. A. John, ‘Investigation of secondary metabolites from Couroupita guianensis through GC-MS’. Int. J. Phytopharm. 2015, 5, 81–85.
- B. J. Young, N. I. Riera, M. E. Beily, P. A. Bres, D. C. Crespo, A. E. Ronco, ‘Toxicity of the effluent from an anaerobic bioreactor treating cereal residues on Lactuca sativa’. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 76, 82–186.
- G. Sivapragasam, V. Soundararajan, C. Yeng, S. L. Ngit, A. W. Habibah, F. Hariri, S. Subramaniam, S. Sreenivasan, ‘In vitro and in vivo-scientific evaluation on cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of traditional medicinal plant Couroupita guianensis aubl. Flower’. Pharmacol. online 2019, 2, 24–38. [Google Scholar]
- S. H. Patel, J. V. Suthar, R. K. Patel, U. S. Zankharia, V. R. Jani, K. N. Gajjar, ‘Antimicrobial activity investigation of Aegle marmelos, Couroupita guianesis, Manilkara hexandra, cow urine and dung’. Res. J. Pharm. Biol. Chem. Sci. 2015, 6, 1014–1022. [Google Scholar]
- I. M. Soares, M. F. Ribeiro, O. J. Costa, A. E. Souza, A. A. Aguiar, R. S. Barbosa, T. C. Alvim, S. D. Ascêncio, R. W. S. Aguiar, ‘Application of a degreasing process and sequential ultrasound-assisted extraction to obtain phenolic compounds and elucidate of the potential antioxidant of Siparuna guianensis Aublet’. J. Med. Plant. Res. 2017, 11, 357–366. [Google Scholar]
- L. C. F. Saraiva, W. M. N. Maia, F. R. Leal, A. L. M. Maia Filho, C. M. Feitosa, ‘Triagem fitoquímica das folhas de Moringa oleifera’. Boletim Informativo Geum 2018, 9, 12–19.
- C. M. O. Simões, E. P. Schenkel, J. C. P. de Mello, L. A. Mentz, P. R. Petrovick, ‘Farmacognosia: do produto natural ao medicamento’. Ed. Artmed, Porto Alegre, RS, 2016.
- L. C. O. Silva, R. A. Lima, ‘Identificação das classes de metabólitos segundários no extrato etanólico dos frutos e folhas de Eugenia uniflora L’, Ed Reget, Porto Velho, RO, 2016, 20, 381 – 288.
- E. L. Amorim, V. T. N. A. Castro, J. Melo, A. Corrêa, T. J. S. Peixoto Sobrinho, ‘Standard operating procedures (SOP) for the spectrophotometric determination of phenolic compounds contained in plant sample’, In ‘Latest Research into Quality Control’, Ed. Intechopen, Rijeka, Croatia, 2012, 1, 47 – 66.
- E. L. Amorim, J. E. Nascimento, J. M. Monteiro, T. J. S. Peixoto Sobrinho, T. A. Araújo, U. P. Albuquerque, ‘A simple and accurate procedure for the determination of tannin and flavonoid levels and some applications in ethnobotany and ethnopharmacology’. Functional Ecosystems and Communities 2008, 2, 88–94. [Google Scholar]
- G. Miliauskas, P. R. Venskutonis, T. A. Van Beek, ‘Screening of radical scavenging activity of some medicinal and aromatic plant extracts’. Food. Chem. 2004, 85, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- T. J. P. Sobrinho, V. T. Castro, A. M. Saraiva, D. M. Almeida, E. A. Tavares, E. L. Amorim, ‘Phenolic content and antioxidant capacity of four Cnidoscolus species (Euphorbiaceae) used as ethnopharmacologicals in Caatinga, Brazil’. African J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2011, 5, 2310–2316. [Google Scholar]
- Y. Chen, B. Huang, J. He, L. Han, Y. Zhan, Y. Wang, ‘In vitro and in vivo antioxidant effects of the ethanolic extract of Swertia chirayita’. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 136, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- S. V. Rabêlo, M. M. D. Costa, R. C. Libório, J. R. G. D. S. Almeida, ‘Antioxidant and antimicrobial activity of extracts from atemoia (Annona cherimola Mill. x A. squamosa L.)’. Rev. Bras. Fruticult. 2014, 36, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D. U. Meneguetti, F. C. da Silva, R. A. Zan, L. J. Ramos, ‘Adaptation of the micronucleus technique in Allium cepa, for mutagenicity analysis of the Jamari river valley, western Amazon, Brazil’. J. Environ. Anal. Toxicol. 2012, 2, 2161–0525. [Google Scholar]
- J. L. McLaughlin, L. L. Rogers, J. E. Anderson, ‘The use of biological assays to evaluate botanicals’. Drug Inf. J. 1998, 32, 513–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- J. M. Nguta, J. M. Mbaria, P. K. Gathumbi, J. D. Kabasa, S. G. Kiama, ‘Biological screening of Kenya medicinal plants using Artemia salina (ARTEMIIDAE)’. Pharmacologyonline 2011, 2, 458–478. [Google Scholar]
- A. I. T. D. Oliveira, T. S. Mahmoud, G. N. L. D. Nascimento, J. F. M. D. Silva, R. S. Pimenta, P. B. D. Morais, ‘Chemical composition and antimicrobial potential of palm leaf extracts from Babaçu (Attalea speciosa), Buriti (Mauritia flexuosa), and Macaúba (Acrocomia aculeata)’. Sci. World J. 2016, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- I. I. T. Oliveira, J. B. Cabral, T. S. Mahmoud, G. N. L. Do Nascimento, J. F. M. Da Silva, R. S. Pimenta, P. B. De Morais, ‘In vitro antimicrobial activity and fatty acid composition through gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) of ethanol extracts of Mauritia flexuosa (Buriti) fruits’. J. Med. Plants Res. 2017, 11, 635–641. [Google Scholar]
- M. A. Wikler, ‘Methods for dilution antimicrobial susceptibility tests for bacteria that grow aerobically: approved standard’, In ‘National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards (NCCLS)’, Wayne, PA, 2000, Vol. 26, pp. M7 – M5.
- J. C. Palomino, A. Martin, M. Camacho, H. Guerra, J. Swings, F. Portaels, ‘Resazurin microtiter assay plate: simple and inexpensive method for detection of drug resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis’. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2002, 46, 2720–2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D. F. Ferreira, ‘Sisvar: um programa para análises e ensino de estatística’. Rev. Cient. Symposium 2008, 6, 36–41. [Google Scholar]
Table 1.
Phytochemical screening of C. guianensis leaf extracts obtained by ultrasound and Soxhlet.
Table 1.
Phytochemical screening of C. guianensis leaf extracts obtained by ultrasound and Soxhlet.
| Chemical Group |
Extract |
| CUE |
CSE |
ESE |
| Flavonoids |
+ |
+ |
+ |
| Tannins |
+ |
+ |
+ |
| Phytosterols |
- |
- |
- |
| Triterpenoids |
+ |
+ |
+ |
| Quinones |
- |
- |
- |
| Saponins |
+ |
+ |
+ |
| Alkaloids |
- |
+ |
+ |
Table 2.
Contents of phenolic compounds, tannins, flavonoids, flavonols and antioxidant activity (DPPH• and ABTS•+) of extracts of leaves of Couroupita guianensis obtained by ultrasound and Soxhlet and positive controls rutin and gallic acid.
Table 2.
Contents of phenolic compounds, tannins, flavonoids, flavonols and antioxidant activity (DPPH• and ABTS•+) of extracts of leaves of Couroupita guianensis obtained by ultrasound and Soxhlet and positive controls rutin and gallic acid.
| |
Extract |
Control |
CUE
Mean ± SD |
CSE
Mean ± SD |
ESE
Mean ± SD |
Gallic acid
Mean ± SD |
Rutin
Mean ± SD |
Phenolic compounds
(mg GAE/g) |
85.58 ± 0.51a
|
90.19 ± 0.29a
|
92.31 ± 0.38a
|
- |
- |
Tannins
(mg GAE/g) |
20.96 ± 0.62a
|
17.69 ± 0.29a
|
19.62 ± 0.88a
|
- |
- |
Flavonoids
(mg RE/g) |
307.21 ± 1.05a
|
101.07 ± 1.99b
|
65.63 ± 0.53c
|
- |
|
Flavonols
(mg RE/g) |
100.89 ± 1.05a
|
88.61 ± 0.80b
|
56.33 ± 0.80c
|
- |
- |
DPPH•
IC50 (µg/mL) |
59.51 ± 0.26c
|
31.13 ± 0.55b
|
2.98 ± 0.96a
|
- |
11.92 ± 0.47 |
ABTS•+
IC50 (µg/mL) |
30.32 ± 1.60c
|
15.74 ± 1.45b
|
4.93 ± 0.90a
|
6.75 ± 0.01 |
- |
Table 3.
Identification of chemical composition by LC-DAD of C. guianensis leaf extracts (mg/g± DP) obtained by ultrasound and Soxhlet.
Table 3.
Identification of chemical composition by LC-DAD of C. guianensis leaf extracts (mg/g± DP) obtained by ultrasound and Soxhlet.
| Compound |
Concentration (mg/g) |
CUE
Mean ± SD |
CSE
Mean ± SD |
ESE
Mean ± SD |
| Cafeic acid |
37.6 ± 0.1a
|
39.4 ± 0.2a
|
38.5 ± 0.2a
|
| Sinapic acid |
37.1 ± 0.1a
|
38.6 ± 0.1a
|
38.1 ± 0.1a
|
| Rutin |
124.1 ± 0.4a
|
138.1 ± 0.6a
|
129.2 ± 0.5a
|
| Quercetin |
169.8 ± 0.6a
|
181.4 ± 0.7a
|
177.3 ± 0.4a
|
| Luteolin |
100.1± 0.2a
|
103.2 ± 0.4a
|
101.8 ± 0.3a
|
| Kampefrol |
94.8 ± 0.2a
|
97.4 ± 0.3a
|
96.3 ± 0.2a
|
| Apigenin |
75.2 ± 0.1a
|
78.8 ± 0.2a
|
3.4 ± 0.1b
|
Table 4.
Identification of chemical composition by GC-MS of extracts from leaves of C. guianensis (mg/g± DP) obtained by ultrasound and Soxhlet.
Table 4.
Identification of chemical composition by GC-MS of extracts from leaves of C. guianensis (mg/g± DP) obtained by ultrasound and Soxhlet.
| Compound |
Concentration (mg/g) |
CUE
Mean ± SD |
CSE
Mean ± SD |
ESE
Mean ± SD |
| Stigmasterol |
69.7 ± 0.1b
|
85.1 ± 0.2a
|
-* |
| β-sitosterol |
80.3 ± 0.2a
|
91.9 ± 0.3a
|
-* |
Table 5.
Toxicity analysis by the test of Allium cepa in and extracts of leaves of C. guianensis obtained by ultrasound and Soxhlet.
Table 5.
Toxicity analysis by the test of Allium cepa in and extracts of leaves of C. guianensis obtained by ultrasound and Soxhlet.
| Samples |
Concentration |
ARL ± DP (mm)
Mean ± SD |
ICR |
Effect |
GR (%) |
| Control |
|
43.08 ± 5.8 |
1 |
|
100 |
| CUE |
50µg/mL |
58.44 ± 1.29 |
1.36 |
GS |
135.6 |
| 250µg/mL |
41.11 ± 11.72 |
0.95 |
SCE |
95.4 |
| 750µg/mL |
19.24 ± 1.77 |
0.45 |
GI |
44.7 |
| CSE |
50µg/mL |
47.40 ± 11.40 |
1.10 |
SCE |
110 |
| 250µg/mL |
34.83 ± 7.41 |
0.81 |
SCE |
80.8 |
| 750µg/mL |
20.64 ± 3.06 |
0.48 |
GI |
47.9 |
| ESE |
50µg/mL |
60.29 ± 1.70 |
1.40 |
GS |
139.9 |
| 250µg/mL |
44.49 ± 11.20 |
1.03 |
SCE |
103.2 |
| 750µg/mL |
32.34 ± 2.00 |
0.75 |
GI |
75 |
Table 6.
50% lethal concentration (IC50) of C. guianensis leaf extracts obtained by ultrasound and Soxhlet by the Artemia salina test.
Table 6.
50% lethal concentration (IC50) of C. guianensis leaf extracts obtained by ultrasound and Soxhlet by the Artemia salina test.
| Extract |
IC50
(µg/mL) |
Toxicity |
| CUE |
2.318 |
Non toxic |
| CSE |
2.308 |
Non toxic |
| ESE |
1.478 |
Non toxic |
Table 7.
Antimicrobial activity of C. guianensis leaf extracts obtained by ultrasound and Soxhlet. Mean inhibition halo (in mm) during the action of the extracts against the microorganisms Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus mutans.
Table 7.
Antimicrobial activity of C. guianensis leaf extracts obtained by ultrasound and Soxhlet. Mean inhibition halo (in mm) during the action of the extracts against the microorganisms Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus mutans.
| Extrats |
Concentration
(mg) |
Microorganisms |
S. aureus
Mean ± SD |
S. mutans
Mean ± SD |
| |
|
Zone of inibition (mm) |
| CUE |
50 |
10.50 ± 0.70b |
7.83 ± 0.49b |
| 100 |
10.44 ± 1.75b |
7.87 ± 0.15b |
| 200 |
12.21 ± 1.23a |
10.31 ± 0.17a |
| CSE |
50 |
8.09 ± 0.22c |
4.48 ± 2.89b |
| 100 |
9.61 ± 0.15b |
9.16 ± 0.39a |
| 200 |
10.29 ± 0.04a |
9.99 ± 1.39a |
| ESE |
50 |
7.72 ± 2.83b |
8.13 ± 0.15b |
| 100 |
12.57 ± 0.74a |
8.69 ± 0.62b |
| 200 |
13.41 ± 1.76a |
9.06 ± 0.55a |
| Chlorhexidine (+) |
|
10.82 ± 0.81a |
12.37 ± 0.61a |
| DMSO (-) |
|
0.00 ± 0.00 |
0.00 ± 0.00 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).