Submitted:
15 May 2023
Posted:
16 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Experimental section
2.1. Chemicals
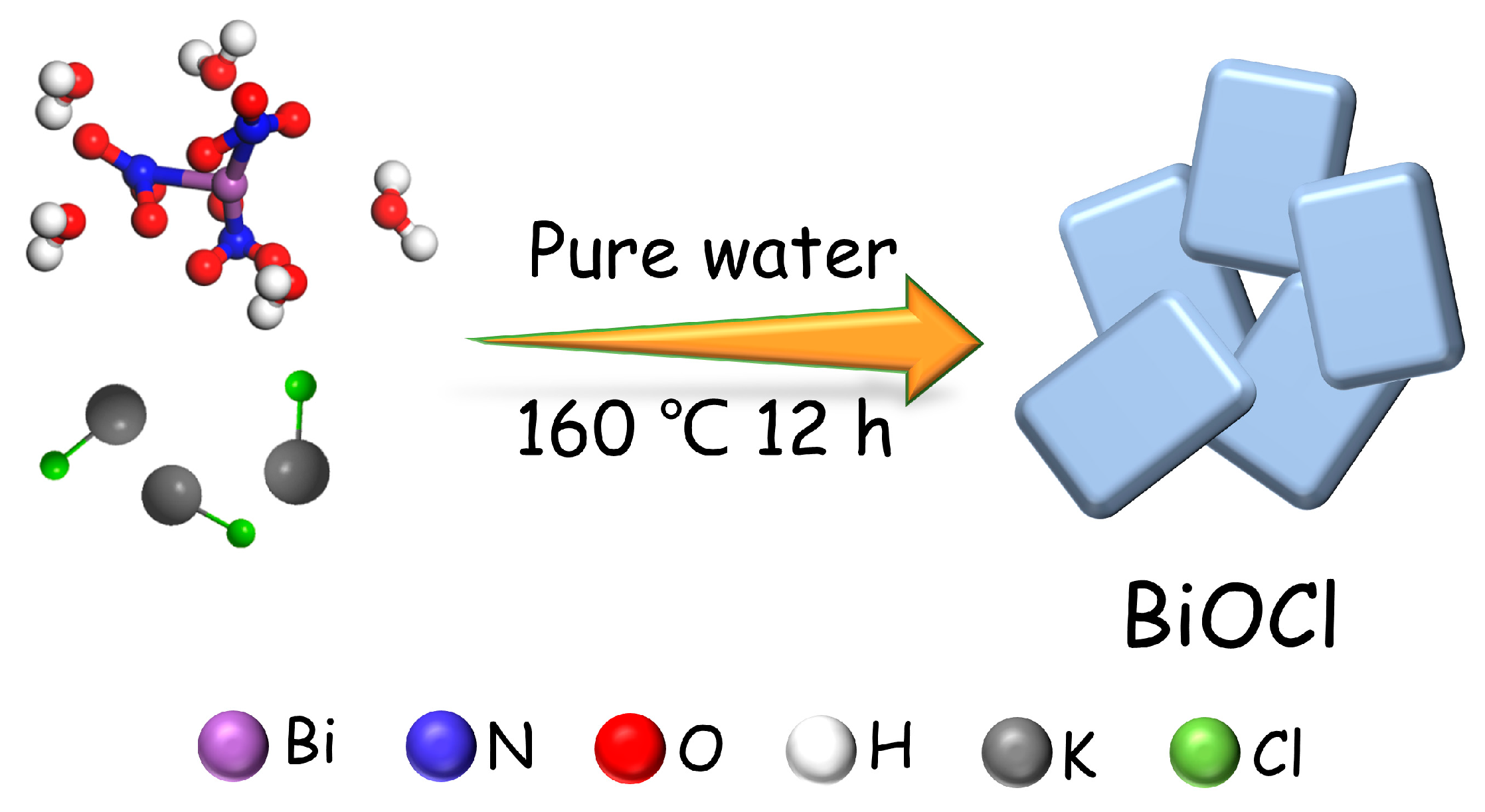
2.2. Synthesis
2.3. Photocatalytic performance test
3. Results and Discussion
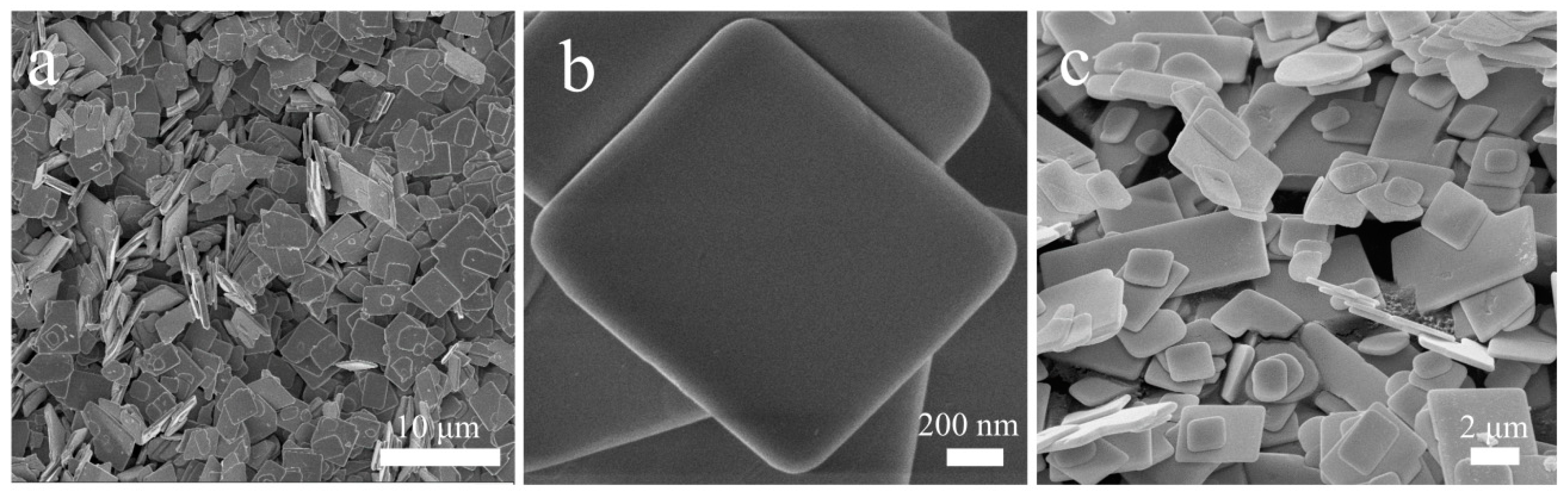
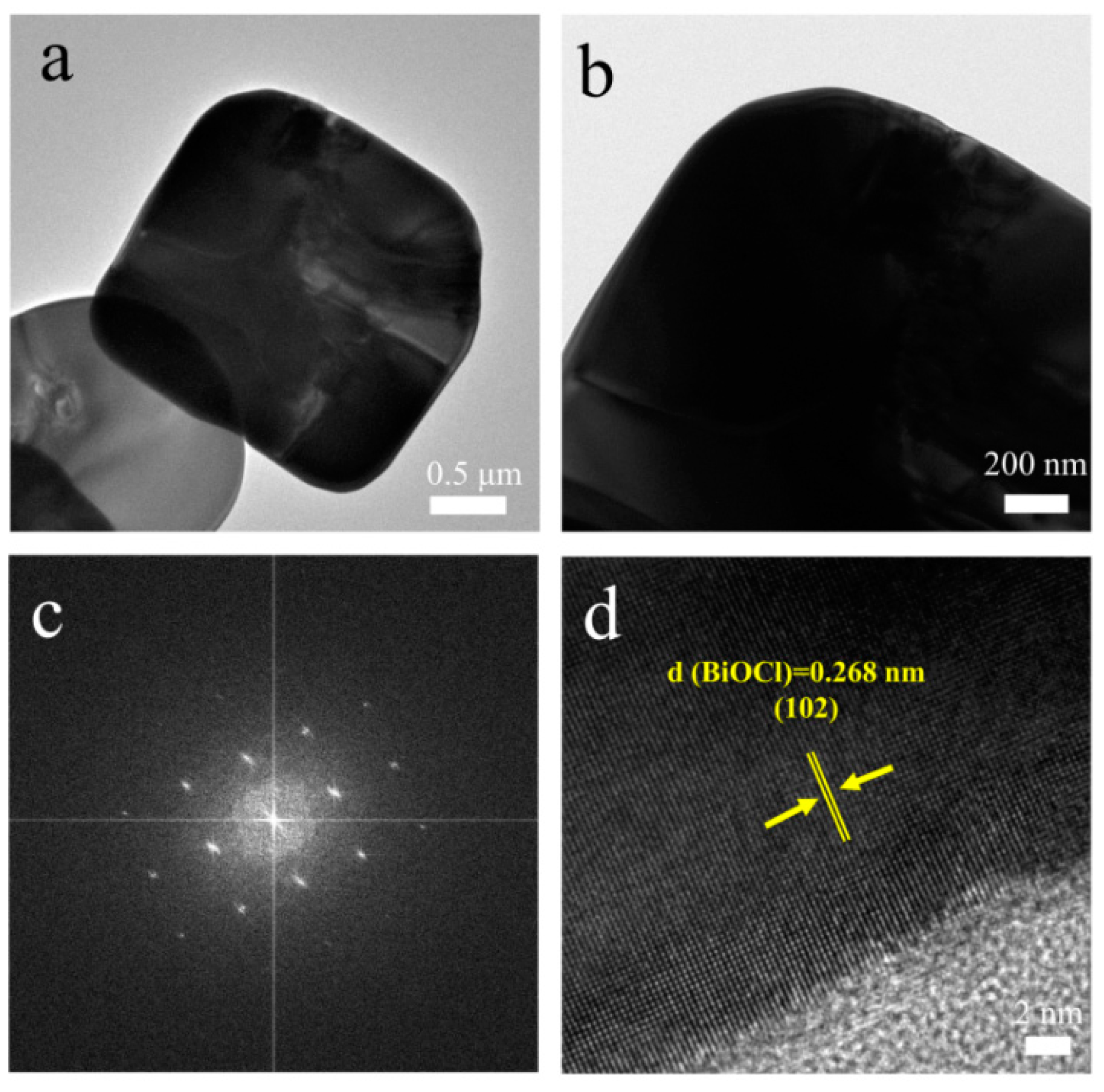
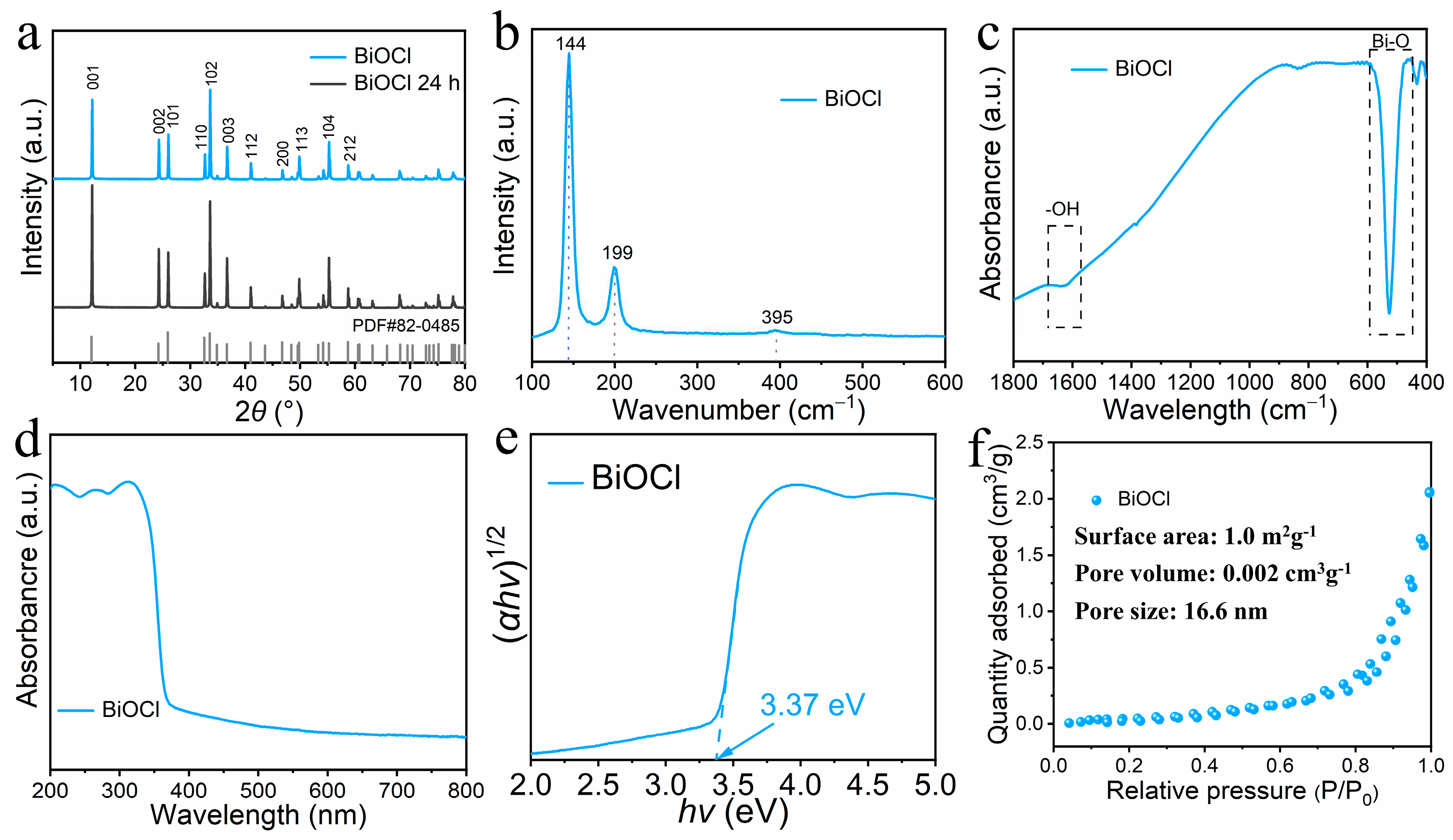
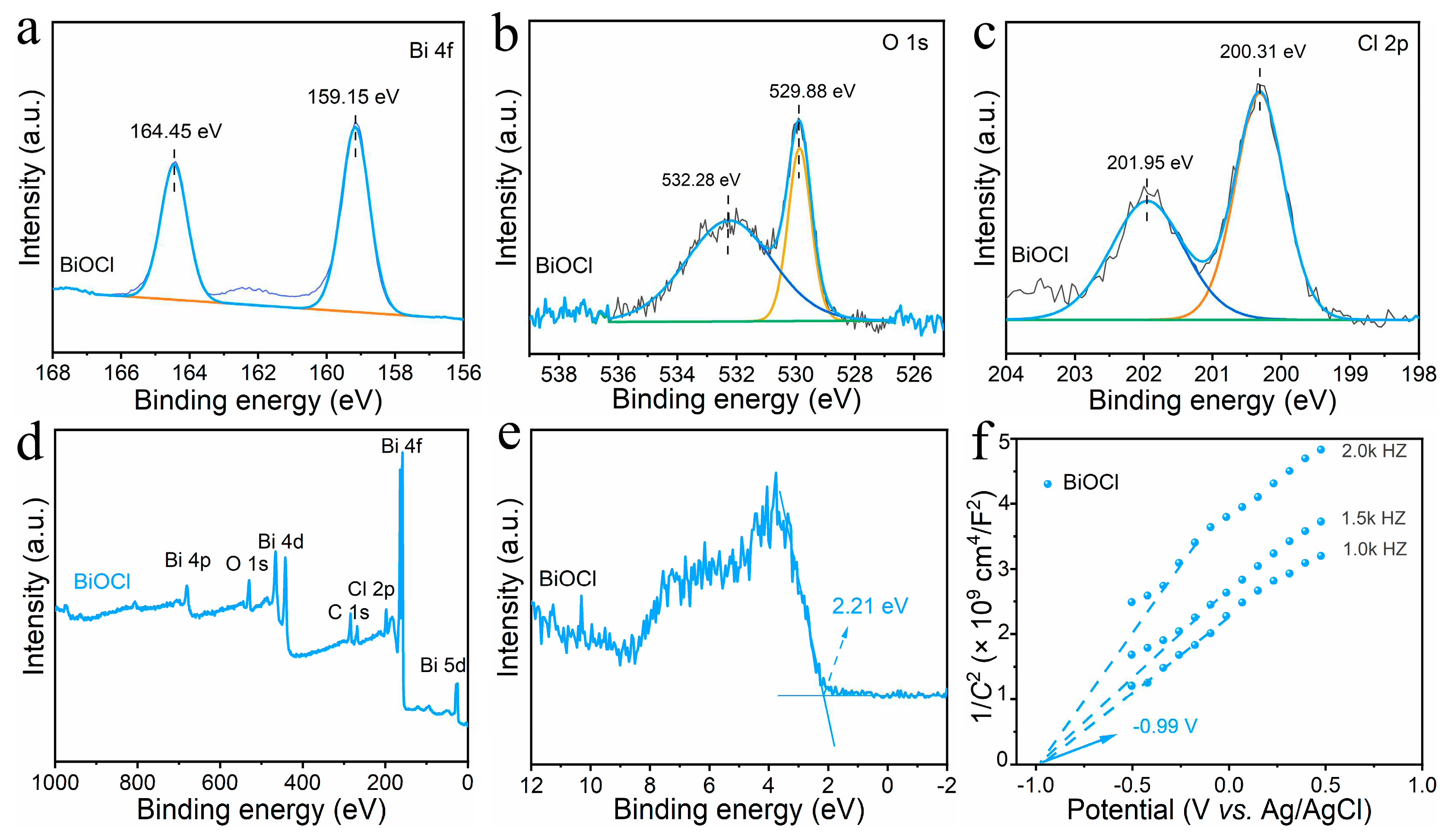
3.1. Morphology and microstructure
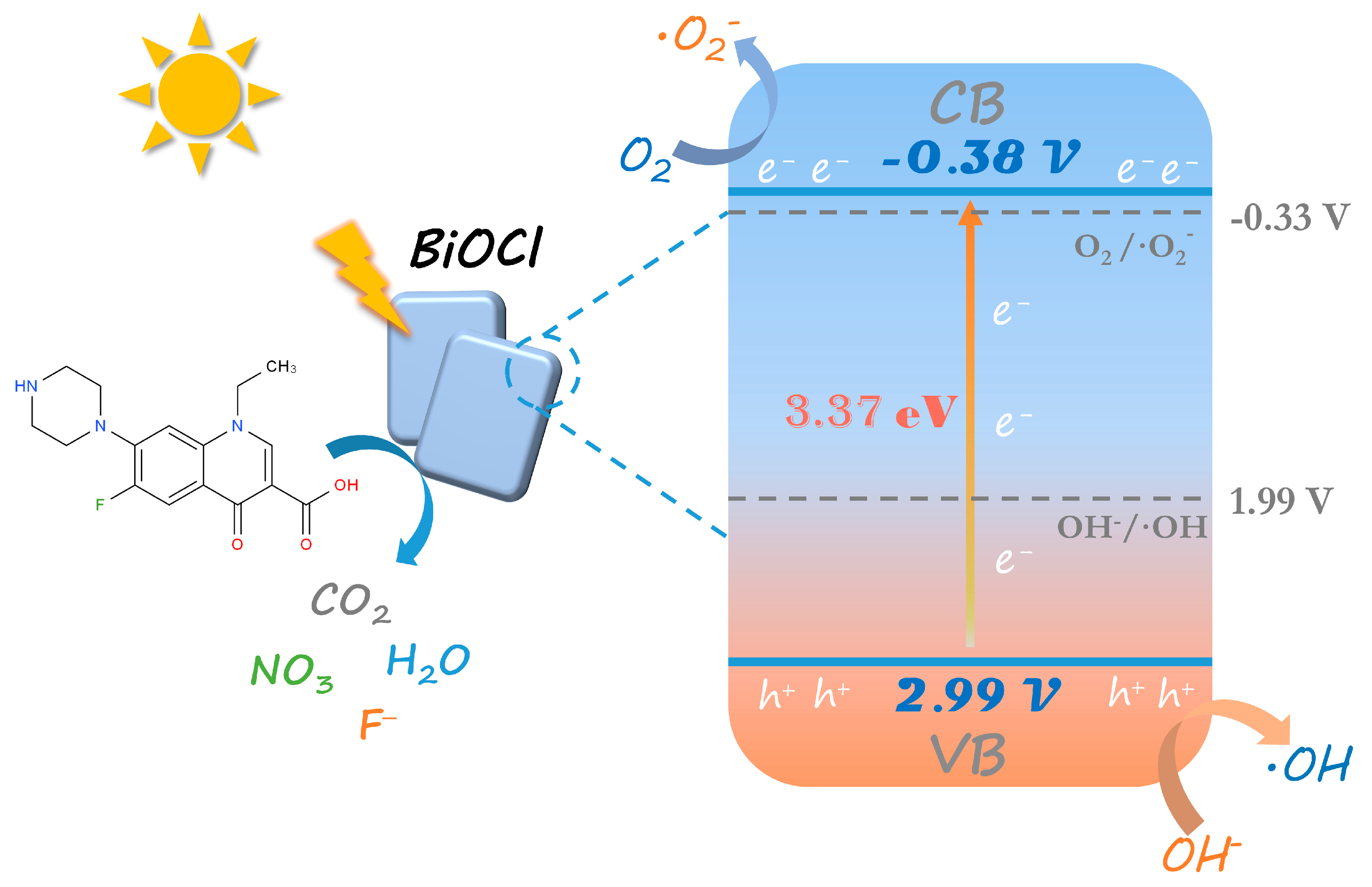
3.2. Photocatalytic activity and mechanism
4. Conclusions
Declaration of Competing Interest
Acknowledgements
References
- Kaiser, R.I.; Zhao, L.; Lu, W.; Ahmed, M.; Krasnoukhov, V.S.; Azyazov, V.N.; Mebel, A.M. Unconventional excited-state dynamics in the concerted benzyl (C(7)H(7)) radical self-reaction to anthracene (C(14)H(10)). Nat Commun 2022, 13, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, J.; Zhang, H.; Fu, S.; Jaroniec, M.; Shan, J.; Xia, B.; Qu, Y.; Qu, J.; Chen, S.; Song, L.; et al. NiPS(3) ultrathin nanosheets as versatile platform advancing highly active photocatalytic H(2) production. Nat Commun 2022, 13, 4600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theerthagiri, J.; Lee, S.J.; Karuppasamy, K.; Arulmani, S.; Veeralakshmi, S.; Ashokkumar, M.; Choi, M.Y. Application of advanced materials in sonophotocatalytic processes for the remediation of environmental pollutants. J Hazard Mater 2021, 412, 125245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.D.; Li, R.; Jiang, H.L. Metal-Organic Framework-Based Photocatalysis for Solar Fuel Production. Small Methods 2023, 7, e2201258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Wang, C.; Gao, C.; Fu, T.; Yang, C.; Ren, G.; Lu, J.; Zhou, S.; Xiong, Y. Solar-driven methanogenesis with ultrahigh selectivity by turning down H(2) production at biotic-abiotic interface. Nat Commun 2022, 13, 6612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.; Huang, D.; Qin, L.; Zeng, G.; Lai, C.; Cheng, M.; Ye, S.; Song, B.; Ren, X.; Guo, X. Selective prepared carbon nanomaterials for advanced photocatalytic application in environmental pollutant treatment and hydrogen production. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental 2018, 239, 408–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Li, J.; Kan, L.; Zhang, L.; Huang, Q.; Yan, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, S.L.; Lan, Y.Q. Linking oxidative and reductive clusters to prepare crystalline porous catalysts for photocatalytic CO(2) reduction with H(2)O. Nat Commun 2022, 13, 4681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.; Lyu, X.; Tong, T.; Lim, A.I.; Li, T.; Bao, J.; Hu, Y.H. Turning dead leaves into an active multifunctional material as evaporator, photocatalyst, and bioplastic. Nat Commun 2023, 14, 1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Cheng, C.; Yang, Z.; Wei, J. Encapsulated CdSe/CdS nanorods in double-shelled porous nanocomposites for efficient photocatalytic CO(2) reduction. Nat Commun 2022, 13, 6466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Pan, Z.; Kato, K.; Vequizo, J.J.M.; Yanagi, R.; Zheng, X.; Yu, W.; Yamakata, A.; Chen, B.; Hu, S.; et al. A general interfacial-energetics-tuning strategy for enhanced artificial photosynthesis. Nat Commun 2022, 13, 7783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, C.H.; Debnath, T.; Wang, Y.; Pohl, D.; Besteiro, L.V.; Meira, D.M.; Huang, S.; Yang, F.; Rellinghaus, B.; et al. Silver nanoparticle enhanced metal-organic matrix with interface-engineering for efficient photocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Nat Commun 2023, 14, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavasoli, A.; Gouda, A.; Zahringer, T.; Li, Y.F.; Quaid, H.; Viasus Perez, C.J.; Song, R.; Sain, M.; Ozin, G. Enhanced hybrid photocatalytic dry reforming using a phosphated Ni-CeO(2) nanorod heterostructure. Nat Commun 2023, 14, 1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Gao, S.; Guo, Y.; Wang, H.; Wei, J.; Su, X.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Z.; Wang, J. Designing covalent organic frameworks with Co-O(4) atomic sites for efficient CO(2) photoreduction. Nat Commun 2023, 14, 1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B.; Saeed, M.Z.; Li, Q.; Zhu, M.; Feng, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Fang, J.; Hossain, M.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; et al. General low-temperature growth of two-dimensional nanosheets from layered and nonlayered materials. Nat Commun 2023, 14, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, Q.D.; Manning, T.D.; Zanella, M.; Zhao, T.; Murgatroyd, P.A.E.; Robertson, C.M.; Jones, L.A.H.; McBride, F.; Raval, R.; Cora, F.; et al. Modular Design via Multiple Anion Chemistry of the High Mobility van der Waals Semiconductor Bi(4)O(4)SeCl(2). J Am Chem Soc 2020, 142, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, G.; Zhang, C.; Chen, Z.; Xu, Y. Nanoconfinement Synthesis of Ultrasmall Bismuth Oxyhalide Nanocrystals with Size-Induced Fully Reversible Potassium-Ion Storage and Ultrahigh Volumetric Capacity. Advanced Functional Materials 2022, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Sun, Y.; Li, M.; Cheng, X.; Yao, Y.; Huang, F.; Jiao, S.; Gu, M.; Rui, X.; Ali, Z.; et al. Rational Design of an Artificial SEI: Alloy/Solid Electrolyte Hybrid Layer for a Highly Reversible Na and K Metal Anode. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 16966–16975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Liu, N.; Wang, M.; Qiu, Y.; Guan, B.; Tian, D.; Guo, Z.; Fan, L.; Zhang, N. A Class of Catalysts of BiOX (X = Cl, Br, I) for Anchoring Polysulfides and Accelerating Redox Reaction in Lithium Sulfur Batteries. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 13109–13115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhao, X.; Lv, D.; Liu, C.; Lai, W.; Sun, C.; Su, Z.; Xu, X.; Hao, W.; Dou, S.X.; et al. Promoted Photocharge Separation in 2D Lateral Epitaxial Heterostructure for Visible-Light-Driven CO(2) Photoreduction. Adv Mater 2020, 32, e2004311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Zhang, G.; Fan, F.; Song, C.; Wang, F.; Xing, Q.; Wang, C.; Wu, H.; Yan, H. Strain-tunable van der Waals interactions in few-layer black phosphorus. Nat Commun 2019, 10, 2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Li, J.; Mao, C.; Liu, S.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Zhao, S.; Liu, X.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, L. Van Der Waals gap-rich BiOCl atomic layers realizing efficient, pure-water CO(2)-to-CO photocatalysis. Nat Commun 2021, 12, 5923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, E.; Wang, B.; Zhao, H.; Zeng, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, Y.; Gu, L.; Li, X.; et al. Determining the interlayer shearing in twisted bilayer MoS(2) by nanoindentation. Nat Commun 2022, 13, 3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, H.; Shi, G.; Zhong, L.; Liu, L.; Zhang, H.; Yang, C.; Yu, K.; Zhu, C.; Li, J.; Zhang, S.; et al. A Two-Dimensional van der Waals Heterostructure with Isolated Electron-Deficient Cobalt Sites toward High-Efficiency CO(2) Electroreduction. J Am Chem Soc 2022, 144, 21502–21511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; An, J.; Qi, L.; Xue, Y.; Li, G.; Lyu, Q.; Yang, W.; Li, Y. Synthesis of Crystalline Phosphine-Graphdiyne with Self-Adaptive p-pi Conjugation. J Am Chem Soc 2023, 145, 864–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Wei, B. Boosting photocatalytic hydrogen production from water by photothermally induced biphase systems. Nat Commun 2021, 12, 1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Lan, X.; Ni, N.; Yang, P.; Yang, Y.; Chen, X. Bismuth Oxychloride Nanowires for Photocatalytic Decomposition of Organic Dyes. ACS Applied Nano Materials 2021, 4, 3887–3892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yuan, L.; Liang, F.; An, D.; Chen, Z.; Feng, D.; Xian, M. Water-assisted synthesis of shape-specific BiOCl nanoflowers with enhanced adsorption and photosensitized degradation of rhodamine B. Environmental Chemistry Letters 2019, 18, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, F.; Saruyama, M.; Takahata, R.; Sato, R.; Matsumoto, K.; Teranishi, T. In Situ Control of Crystallinity of 3D Colloidal Crystals by Tuning the Growth Kinetics of Nanoparticle Building Blocks. J Am Chem Soc 2022, 144, 5871–5877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Shao, P.; Hu, L.; Sun, C.; Li, J.; Feng, X.; Wang, B. Construction of Interlayer Conjugated Links in 2D Covalent Organic Frameworks via Topological Polymerization. J Am Chem Soc 2021, 143, 7897–7902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greciano, E.E.; Calbo, J.; Orti, E.; Sanchez, L. N-Annulated Perylene Bisimides to Bias the Differentiation of Metastable Supramolecular Assemblies into J- and H-Aggregates. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 2020, 59, 17517–17524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, H.; Xu, Q.; Wu, J.; Lian, C.; Liu, H.; Zhang, B.; He, J.; Chen, D.; Lu, J. SuFEx-Enabled Elastic Polysulfates for Efficient Removal of Radioactive Iodomethane and Polar Aprotic Organics through Weak Intermolecular Forces. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 2022, 61, e202208577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, S.; Chen, B.; Xie, L.; Zheng, Z.; Liu, P. Facile in situ synthesis of a Bi/BiOCl nanocomposite with high photocatalytic activity. Journal of Materials Chemistry A 2013, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Wang, B.; Zhu, X.; Ding, P.; Zhao, J.; Li, H.; Chen, Z.; Zhu, W.; Xia, J. Edge-Site-Rich Ordered Macroporous BiOCl Triggers CO Activation for Efficient CO(2) Photoreduction. Small 2022, 18, e2105228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wang, R.; Qiu, T.; Yang, L.; Han, Q.; Shen, Q.; Zhou, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zou, Z. Bismuth Vacancy-Induced Efficient CO(2) Photoreduction in BiOCl Directly from Natural Air: A Progressive Step toward Photosynthesis in Nature. Nano Lett 2021, 21, 10260–10266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Huang, A.; Liang, C.; Chen, H.C.; Han, T.; Lin, R.; Peng, Q.; Zhuang, Z.; Shen, R.; Chen, H.M.; et al. Engineering Lattice Disorder on a Photocatalyst: Photochromic BiOBr Nanosheets Enhance Activation of Aromatic C-H Bonds via Water Oxidation. J Am Chem Soc 2022, 144, 3386–3397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiratsuka, T.; Tanaka, H.; Miyahara, M.T. Mechanism of Kinetically Controlled Capillary Condensation in Nanopores: A Combined Experimental and Monte Carlo Approach. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Favaro, M.; Chen, E.; Trotochaud, L.; Bluhm, H.; Choi, K.S.; van de Krol, R.; Starr, D.E.; Galli, G. Influence of Excess Charge on Water Adsorption on the BiVO(4)(010) Surface. J Am Chem Soc 2022, 144, 17173–17185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.; Zhang, P.; Kang, X.; Zheng, L.; Mo, G.; Wu, R.; Tai, J.; Han, B. Efficient Electrocatalytic Reduction of CO(2) to Ethane over Nitrogen-Doped Fe(2)O(3). J Am Chem Soc 2022, 144, 14769–14777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, R.; Lu, G.; Wang, M.; Dang, T.; Liu, J.; Yan, Z. Facet-dependent photoactivity of Mn3O4/BiOCl for naproxen detoxication: Strengthening effect of Mn valence cycle. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental 2021, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalawade, Y.; Pepper, J.; Harvey, A.; Griffin, A.; Caffrey, D.; Kelly, A.G.; Coleman, J.N. All-Printed Dielectric Capacitors from High-Permittivity, Liquid-Exfoliated BiOCl Nanosheets. ACS Applied Electronic Materials 2020, 2, 3233–3241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Li, H.; Zhang, H.; Shen, Z.; Ji, H. The role of Cs dopants for improved activation of molecular oxygen and degradation of tetracycline over carbon nitride. Chinese Chemical Letters 2022, 33, 4756–4760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, X.; Li, G.; Li, S.; Luo, Y.; Luo, W.; Wan, Q.; An, T. Highly efficient adsorption and catalytic degradation of ciprofloxacin by a novel heterogeneous Fenton catalyst of hexapod-like pyrite nanosheets mineral clusters. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental 2022, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Ren, J.; Hao, Y.-j.; Li, Y.-l.; Wang, X.-j.; Liu, Y.; Su, R.; Li, F.-t. Insight into reactive species-dependent photocatalytic toluene mineralization and deactivation pathways via modifying hydroxyl groups and oxygen vacancies on BiOCl. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental 2022, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




