Submitted:
15 May 2023
Posted:
16 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Purification of recombinant P. falciparum enolase (rPfeno), preparation of Human RBC ghost, packed RBCs, and raising anti-rPfeno antibodies (α-rPfeno):
2.2. Erythrocytes binding Assays:
2.3. Blot Overlay assay:
2.4. Pull Down assay:
2.5. Immuno-precipitation (IP) and reverse IP using Protein-A (PrA):
2.6. Two-dimensional Gel Electrophoresis (2DE) of hRBC ghost and blot overlay:
2.7. In-gel Digestion of 2DE protein spots and Mass spectrometric analysis:
2.8. P. falciparum and P. berghei parasite preparations:
2.9. ELISA for monitoring protein-protein interaction:
2.10. Molecular Modelling:
3. Results
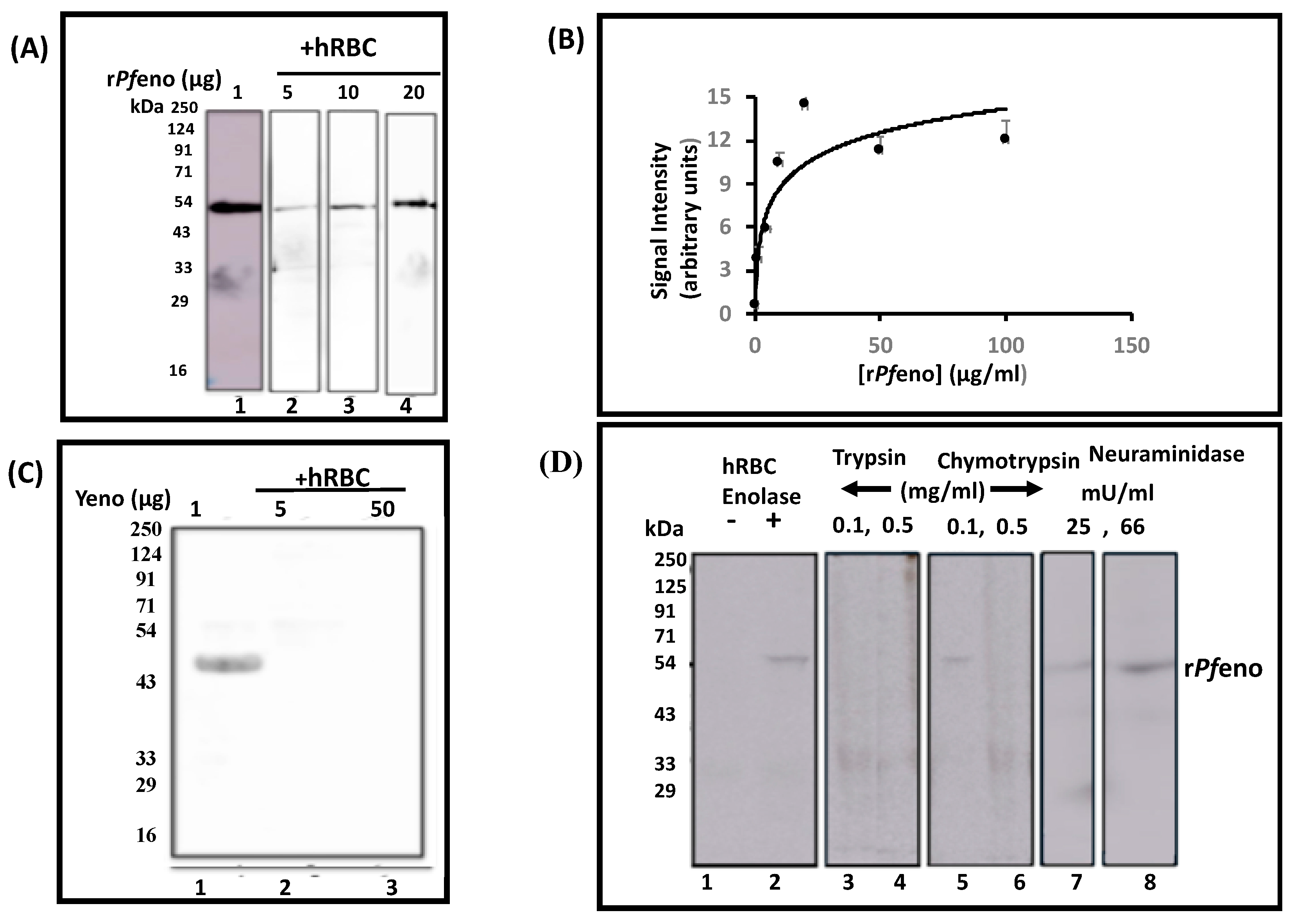
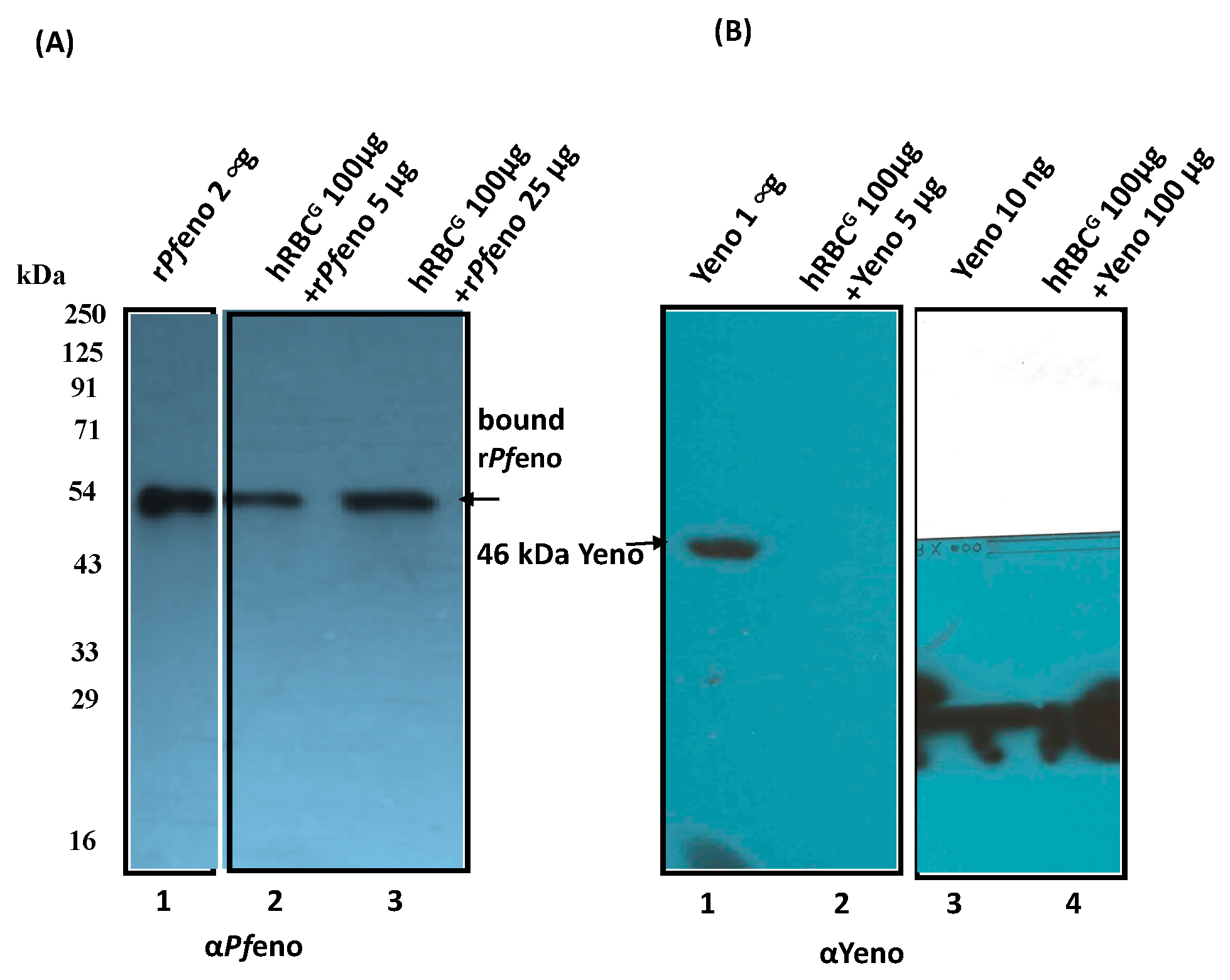
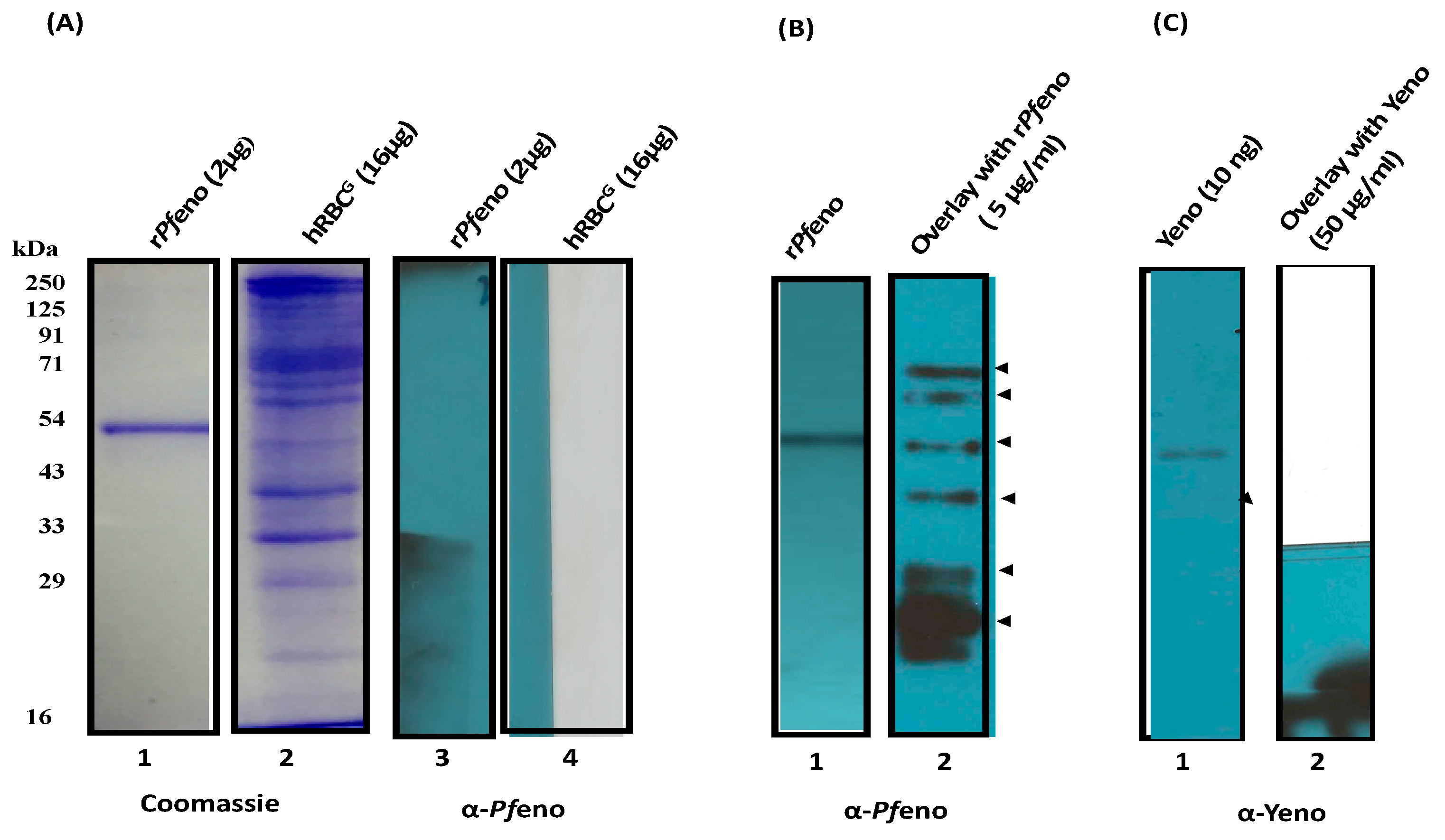
3.1. Binding of rPfeno to hRBCs and hRBC ghosts:
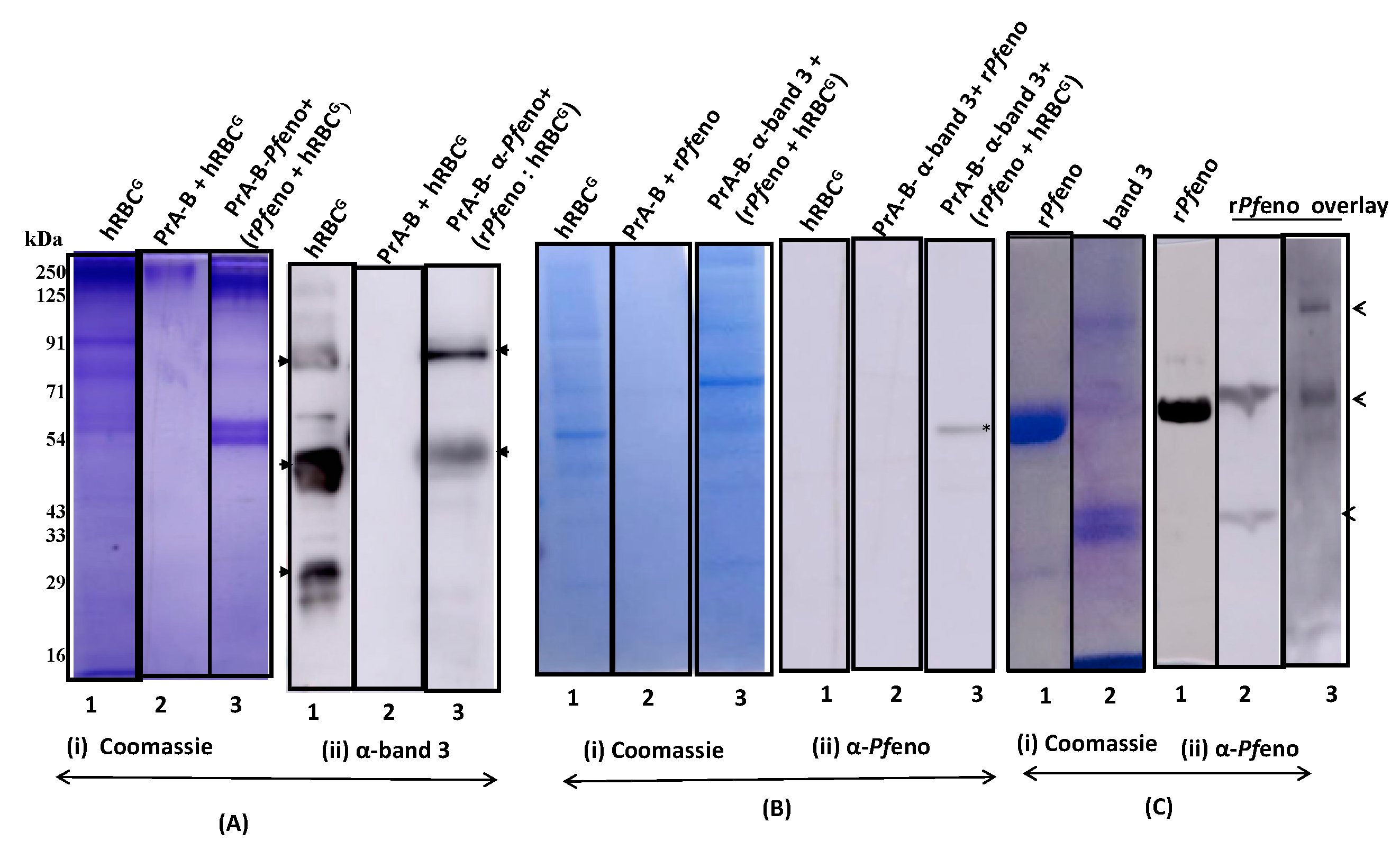
3.2. Pfeno interacting membrane proteins in hRBC:
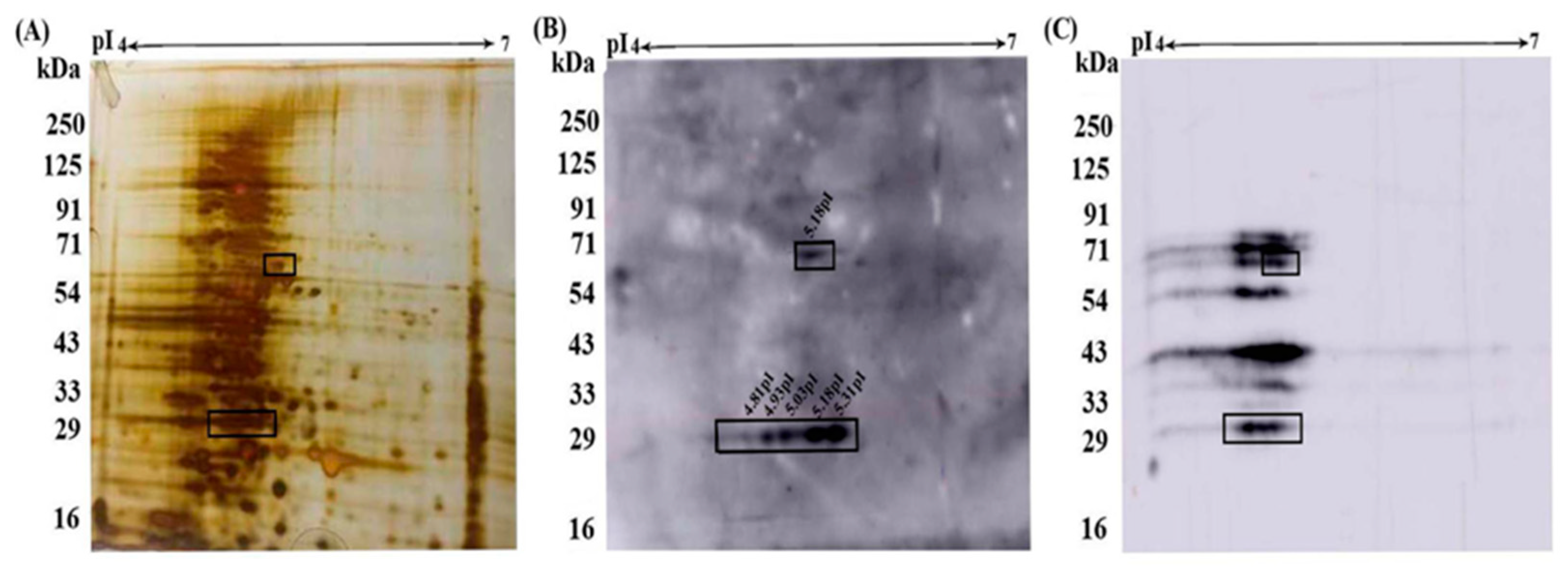
3.3. Molecular Identification of rPfeno binding proteins in hRBC ghosts:
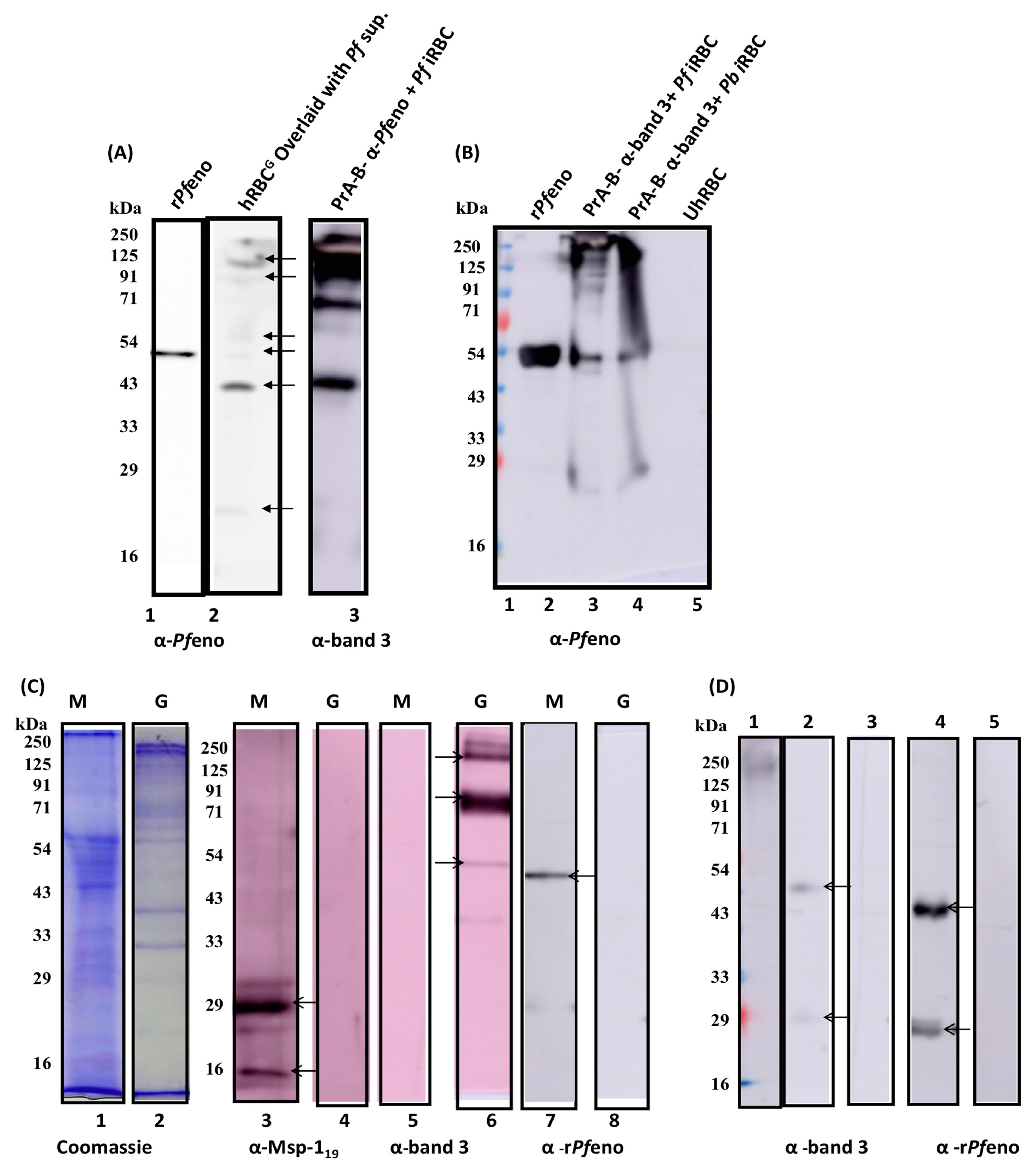
3.4. The band 3 of human erythrocytes interacts with rPfeno:
3.5. Native enolases from P. falciparum and P. berghei merozoites bind to hRBC band 3:
3.6. Post translationally modified variants of band 3 exhibit differential binding to rPfeno:
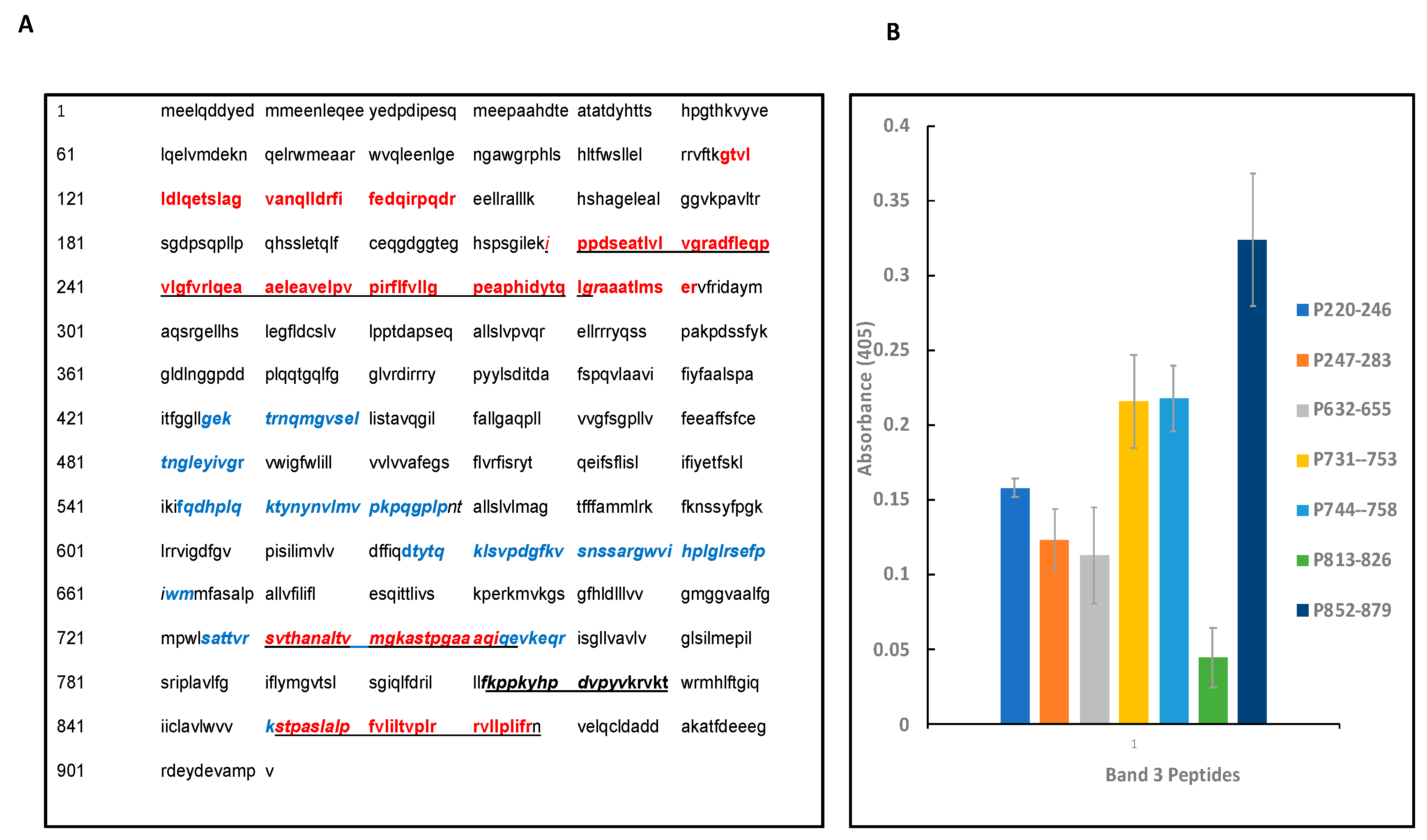
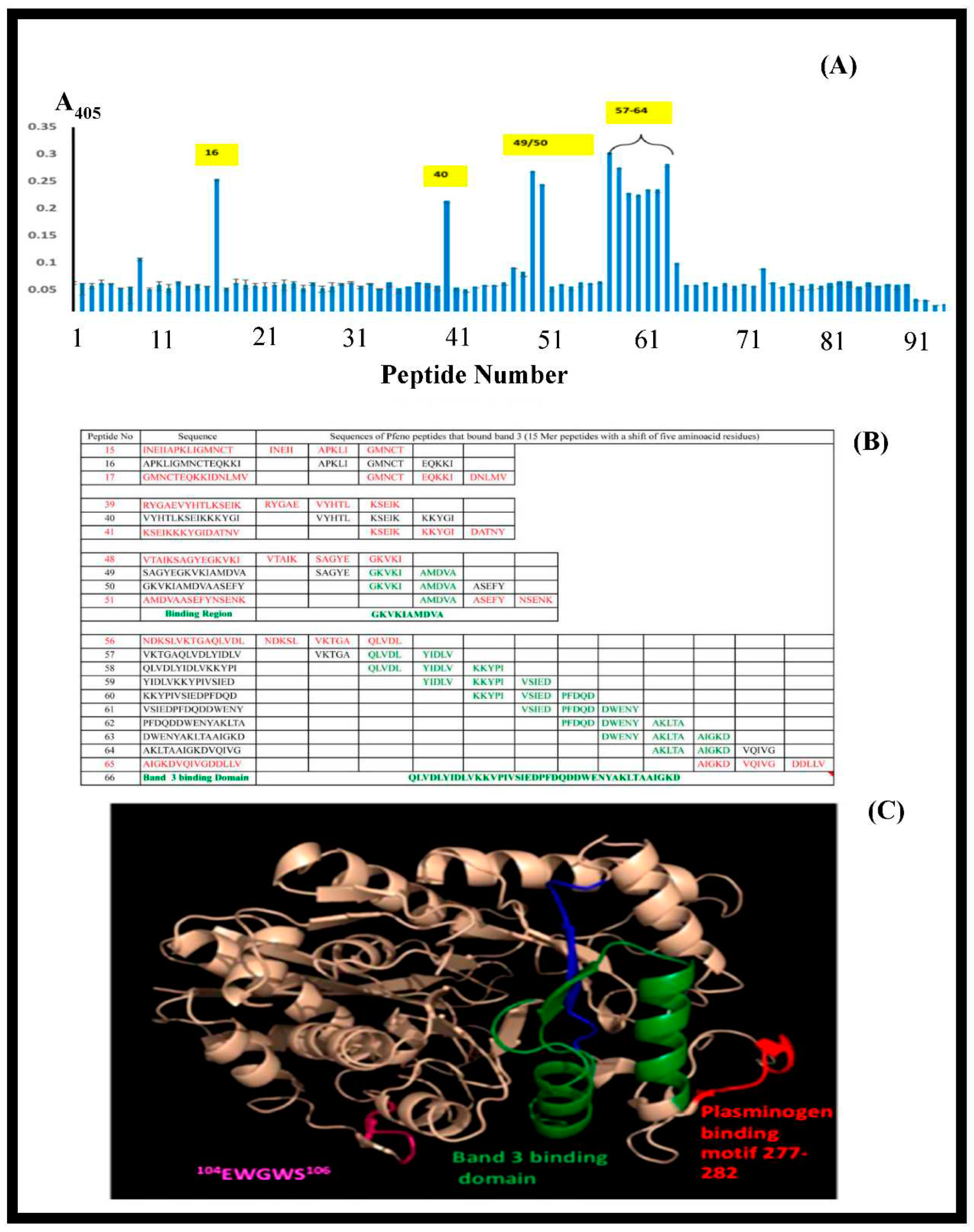
3.7. Synthetic peptide towards mapping the binding sites of band 3 and Pfeno:
4. Discussion:
Author Contributions
Funding
Ethical Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- WHO: World malaria report 2017. Available online: http://wwwwhoint/malaria/publications/world-malaria-report-2017/en/ (accessed on 10 April 2018).
- Iyer J, Gruner AC, Renia L, Snounou G, Preiser PR: Invasion of host cells by malaria parasites: a tale of two protein families. Mol Microbiol 2007, 65, 231–249. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul AS, Egan ES, Duraisingh MT: Host-parasite interactions that guide red blood cell invasion by malaria parasites. Curr Opin Hematol 2015, 22, 220–226. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tham WH, Healer J, Cowman AF: Erythrocyte and reticulocyte binding-like proteins of Plasmodium falciparum. Trends Parasitol 2012, 28, 23–30. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cowman AF, Tonkin CJ, Tham WH, Duraisingh MT: The Molecular Basis of Erythrocyte Invasion by Malaria Parasites. Cell Host Microbe 2017, 22, 232–245. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deas JE, Lee LT: Competitive inhibition by soluble erythrocyte glycoproteins of penetration by Plasmodium falciparum. Am J Trop Med Hyg 1981, 30, 1164–1167. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobo CA, Rodriguez M, Reid M, Lustigman S: Glycophorin C is the receptor for the Plasmodium falciparum erythrocyte binding ligand PfEBP-2 (baebl). Blood 2003, 101, 4628–4631. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perkins M: Inhibitory effects of erythrocyte membrane proteins on the in vitro invasion of the human malarial parasite (Plasmodium falciparum) into its host cell. J Cell Biol 1981, 90, 563–567. [CrossRef]
- Ord RL, Rodriguez M, Yamasaki T, Takeo S, Tsuboi T, Lobo CA: Targeting sialic acid dependent and independent pathways of invasion in Plasmodium falciparum. PLoS One 2012, 7, e30251.
- Awandare GA, Nyarko PB, Aniweh Y, Ayivor-Djanie R, Stoute JA: Plasmodium falciparum strains spontaneously switch invasion phenotype in suspension culture. Sci Rep 2018, 8, 5782. [CrossRef]
- Camus D, Hadley TJ: A Plasmodium falciparum antigen that binds to host erythrocytes and merozoites. Science 1985, 230, 553–556. [CrossRef]
- Li X, Marinkovic M, Russo C, McKnight CJ, Coetzer TL, Chishti AH: Identification of a specific region of Plasmodium falciparum EBL-1 that binds to host receptor glycophorin B and inhibits merozoite invasion in human red blood cells. Mol Biochem Parasitol 2012, 183, 23–31. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer DC, Cofie J, Jiang L, Hartl DL, Tracy E, Kabat J, Mendoza LH, Miller LH: Glycophorin B is the erythrocyte receptor of Plasmodium falciparum erythrocyte-binding ligand, EBL-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2009, 106, 5348–5352. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awandare GA, Spadafora C, Moch JK, Dutta S, Haynes JD, Stoute JA: Plasmodium falciparum field isolates use complement receptor 1 (CR1) as a receptor for invasion of erythrocytes. Mol Biochem Parasitol 2011, 177, 57–60. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spadafora C, Awandare GA, Kopydlowski KM, Czege J, Moch JK, Finberg RW, Tsokos GC, Stoute JA: Complement receptor 1 is a sialic acid-independent erythrocyte receptor of Plasmodium falciparum. PLoS Pathog 2010, 6, e1000968.
- Tham WH, Wilson DW, Lopaticki S, Schmidt CQ, Tetteh-Quarcoo PB, Barlow PN, Richard D, Corbin JE, Beeson JG, Cowman AF: Complement receptor 1 is the host erythrocyte receptor for Plasmodium falciparum PfRh4 invasion ligand. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2010, 107, 17327–17332. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crosnier C, Bustamante LY, Bartholdson SJ, Bei AK, Theron M, Uchikawa M, Mboup S, Ndir O, Kwiatkowski DP, Duraisingh MT, et al: Basigin is a receptor essential for erythrocyte invasion by Plasmodium falciparum. Nature 2011, 480, 534–537. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goel VK, Li X, Chen H, Liu SC, Chishti AH, Oh SS: Band 3 is a host receptor binding merozoite surface protein 1 during the Plasmodium falciparum invasion of erythrocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2003, 100, 5164–5169. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cowman AF, Berry D, Baum J: The cellular and molecular basis for malaria parasite invasion of the human red blood cell. J Cell Biol 2012, 198, 961–971. [CrossRef]
- Bartholdson SJ, Bustamante LY, Crosnier C, Johnson S, Lea S, Rayner JC, Wright GJ: Semaphorin-7A is an erythrocyte receptor for P. falciparum merozoite-specific TRAP homolog, MTRAP. PLoS Pathog 2012, 8, e1003031. [Google Scholar]
- Hu G, Cabrera A, Kono M, Mok S, Chaal BK, Haase S, Engelberg K, Cheemadan S, Spielmann T, Preiser PR, et al: Transcriptional profiling of growth perturbations of the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Nat Biotechnol 2010, 28, 91–98. [CrossRef]
- Le Roch KG, Zhou Y, Blair PL, Grainger M, Moch JK, Haynes JD, De La Vega P, Holder AA, Batalov S, Carucci DJ, Winzeler EA: Discovery of gene function by expression profiling of the malaria parasite life cycle. Science 2003, 301, 1503–1508. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhowmick IP, Kumar N, Sharma S, Coppens I, Jarori GK: Plasmodium falciparum enolase: stage-specific expression and sub-cellular localization. Malar J 2009, 8, 179. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh AK, Coppens I, Gardsvoll H, Ploug M, Jacobs-Lorena M: Plasmodium ookinetes coopt mammalian plasminogen to invade the mosquito midgut. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2011, 108, 17153–17158. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh AK, Jacobs-Lorena M: Surface-expressed enolases of Plasmodium and other pathogens. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 2011, 106 (Suppl. 1), 85–90. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal-Bhowmick I, Mehta M, Coppens I, Sharma S, Jarori GK: Protective properties and surface localization of Plasmodium falciparum enolase. Infect Immun 2007, 75, 5500–5508. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutta S, DasSarma P, DasSarma S, Jarori GK: Immunogenicity and protective potential of a Plasmodium spp. enolase peptide displayed on archaeal gas vesicle nanoparticles. Malar J 2015, 14, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutta S, Tewari A, Balaji C, Verma R, Moitra A, Yadav M, Agrawal P, Sahal D, Jarori GK: Strain-transcending neutralization of malaria parasite by antibodies against Plasmodium falciprum enolase. Malar J 2018, 17, 17.
- Vega-Rodriguez J, Ghosh AK, Kanzok SM, Dinglasan RR, Wang S, Bongio NJ, Kalume DE, Miura K, Long CA, Pandey A, Jacobs-Lorena M: Multiple pathways for Plasmodium ookinete invasion of the mosquito midgut. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2014, 111, E492–E500.
- Vora HK, Shaik FR, Pal-Bhowmick I, Mout R, Jarori GK: Effect of deletion of a plant like pentapeptide insert on kinetic, structural and immunological properties of enolase from Plasmodium falciparum. Arch Biochem Biophys 2009, 485, 128–138. [CrossRef]
- Pal-Bhowmick I, Sadagopan K, Vora HK, Sehgal A, Sharma S, Jarori GK: Cloning, over-expression, purification and characterization of Plasmodium falciparum enolase. Eur J Biochem 2004, 271, 4845–4854. [CrossRef]
- Marchesi VT, Palade GE: The localization of Mg-Na-K-activated adenosine triphosphatase on red cell ghost membranes. J Cell Biol 1967, 35, 385–404. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyagi RK, Sharma YD: Erythrocyte Binding Activity Displayed by a Selective Group of Plasmodium vivax Tryptophan Rich Antigens Is Inhibited by Patients' Antibodies. PLoS One 2012, 7, e50754.
- Wu Y, Li Q, Chen XZ: Detecting protein-protein interactions by Far western blotting. Nat Protoc 2007, 2, 3278–3284. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luche S, Santoni V, Rabilloud T: Evaluation of nonionic and zwitterionic detergents as membrane protein solubilizers in two-dimensional electrophoresis. Proteomics 2003, 3, 249–253. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shevchenko A, Jensen ON, Podtelejnikov AV, Sagliocco F, Wilm M, Vorm O, Mortensen P, Shevchenko A, Boucherie H, Mann M: Linking genome and proteome by mass spectrometry: large-scale identification of yeast proteins from two dimensional gels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1996, 93, 14440–14445. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jindal N, Balaji C, P.B. S, Dutta S, Jarori GK: Identification of Post-translational Modificatio ns of Plsmodium yoelii Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase by Mass Spectrometry. Adv Proteomics Bioinform: APBI - 103 2017.
- Moll K, Ljungstrom I, Perlman H, Scherf A, Wahlgren. M: Methods in Malaria Research (American Type Culture Collection, Manassas, VA).2008.
- Ruan J, Mouveaux T, Light SH, Minasov G, Anderson WF, Tomavo S, Ngo HM: The structure of bradyzoite-specific enolase from Toxoplasma gondii reveals insights into its dual cytoplasmic and nuclear functions. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 2015, 71, 417–426. [CrossRef]
- Neubig RR, Krodel EK, Boyd ND, Cohen JB: Acetylcholine and local anesthetic binding to Torpedo nicotinic postsynaptic membranes after removal of nonreceptor peptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1979, 76, 690–694. [CrossRef]
- Shevade S, Jindal N, Dutta S, Jarori GK: Food vacuole associated enolase in plasmodium undergoes multiple post-translational modifications: evidence for atypical ubiquitination. PLoS One 2013, 8, e72687.
- Arakawa T, Kobayashi-Yurugi T, Alguel Y, Iwanari H, Hatae H, Iwata M, Abe Y, Hino T, Ikeda-Suno C, Kuma H, et al: Crystal structure of the anion exchanger domain of human erythrocyte band 3. Science 2015, 350, 680–684. [CrossRef]
- Fujinaga J, Tang XB, Casey JR: Topology of the membrane domain of human erythrocyte anion exchange protein, AE1. J Biol Chem 1999, 274, 6626–6633. [CrossRef]
- Frank R: The SPOT-synthesis technique. Synthetic peptide arrays on membrane supports--principles and applications. J Immunol Methods 2002, 267, 13–26. [Google Scholar]
- Dutta S, Mukherjee D, Jarori GK: Replacement of Ser108 in Plasmodium falciparum enolase results in weak Mg(II) binding: role of a parasite-specific pentapeptide insert in stabilizing the active conformation of the enzyme. FEBS J 2015, 282, 2296–2308. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Read M, Hicks KE, Sims PF, Hyde JE: Molecular characterisation of the enolase gene from the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Evidence for ancestry within a photosynthetic lineage. Eur J Biochem 1994, 220, 513–520. [Google Scholar]
- Hamasaki N, Okubo K: Band 3 protein: physiology, function and structure. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand) 1996, 42, 1025–1039.
- Yu J, Steck TL: Isolation and characterization of band 3, the predominant polypeptide of the human erythrocyte membrane. J Biol Chem 1975, 250, 9170–9175. [CrossRef]
- Baldwin M, Yamodo I, Ranjan R, Li X, Mines G, Marinkovic M, Hanada T, Oh SS, Chishti AH: Human erythrocyte band 3 functions as a receptor for the sialic acid-independent invasion of Plasmodium falciparum. Role of the RhopH3-MSP1 complex. Biochim Biophys Acta 2014, 1843, 2855–2870. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharya S, Ploplis VA, Castellino FJ: Bacterial plasminogen receptors utilize host plasminogen system for effective invasion and dissemination. J Biomed Biotechnol 2012, 2012, 482096.
- Jong AY, Chen SH, Stins MF, Kim KS, Tuan TL, Huang SH: Binding of Candida albicans enolase to plasmin(ogen) results in enhanced invasion of human brain microvascular endothelial cells. J Med Microbiol 2003, 52, 615–622. [CrossRef]
- Liu K-J, Shih N-Y: The Role of Enolae in Tissue Invasion and Metastasis of Pathogens and Tumor Cells. J Cancer Mole 2007, 3, 45–48.
- Lahteenmaki K, Edelman S, Korhonen TK: Bacterial metastasis: the host plasminogen system in bacterial invasion. Trends Microbiol 2005, 13, 79–85. [CrossRef]
- Vinetz JM: Plasmodium ookinete invasion of the mosquito midgut. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 2005, 295, 357–382.
- Hernandez-Romano J, Rodriguez MH, Pando V, Torres-Monzon JA, Alvarado-Delgado A, Lecona Valera AN, Ramos RA, Martinez-Barnetche J, Rodriguez MC: Conserved peptide sequences bind to actin and enolase on the surface of plasmodium berghei ookinetes. Parasitology 2011, 138, 1341–1353. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee D, Mishra P, Joshi M, Thakur PK, Hosur RV, Jarori GK: EWGWS insert in Plasmodium falciparum ookinete surface enolase is involved in binding of PWWP containing peptides: Implications to mosquito midgut invasion by the parasite. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 2016, 68, 13–22. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Didiasova M, Schaefer L, Wygrecka M: When Place Matters: Shuttling of Enolase-1 Across Cellular Compartments. Front Ceell Dev Biol 2019, 7, 61.
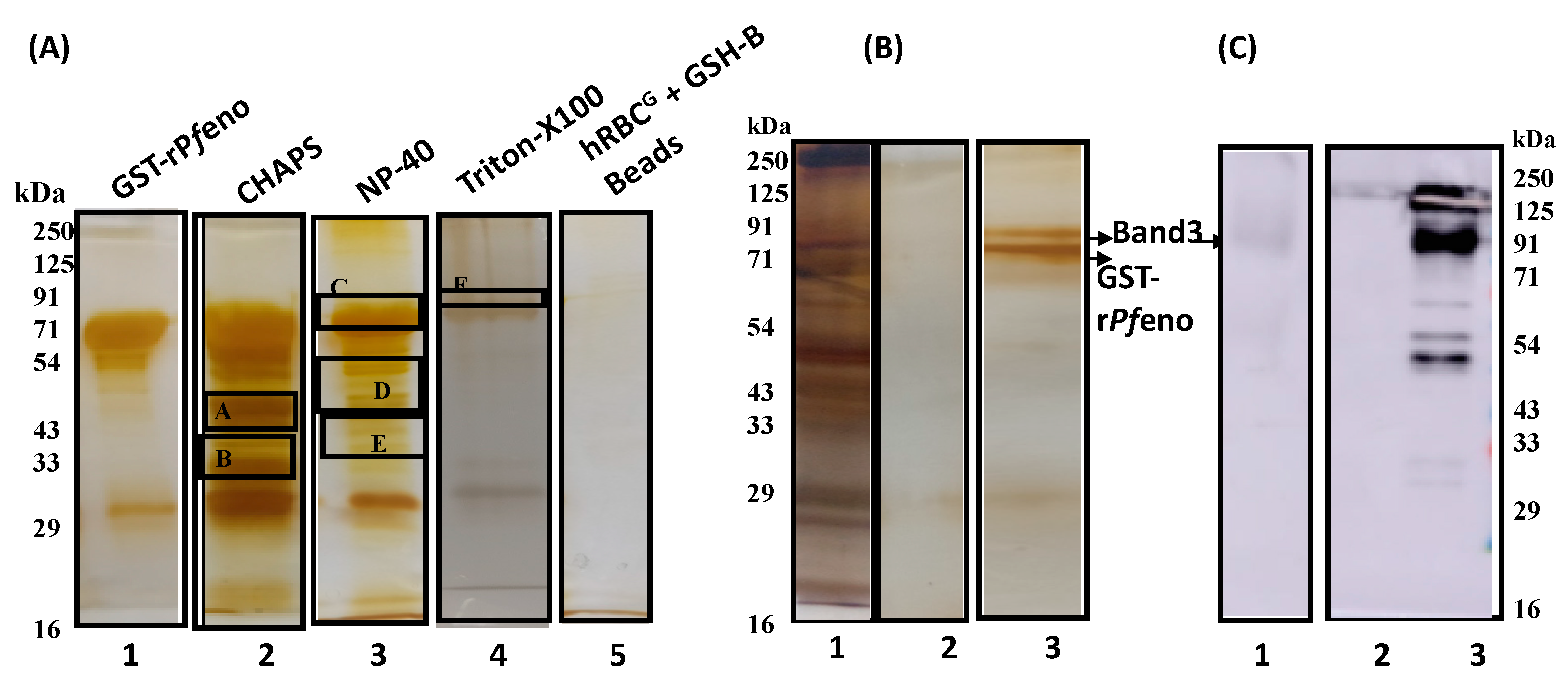
| S.No. | Detergents | Protein Bands | Proteins Identified | Protein Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CHAPS | A | Spectrin | 49 |
| B | Band 3 | 81 | ||
| 2 | NP-40 | C | Spectrin | 51 |
| D | Band 3 | 71 | ||
| E | Band 3 | 83 | ||
| 3 | Triton X100 |
F | Band 3 | 89 |
| Protein Spot | Proteins Identified | Protein Score | Mol.Wt (kDa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| A (pI~ 5.31 MW~25kDa) |
Diacylglycerol Kinase | 42 | 102 |
| Chromosome 20 ORF | 30 | 125 | |
| Cadherin 12 | 30 | 110 | |
| B (pI~ 5.18, MW~64 kDa) |
Spectrin α chain | 50 | 281 |
| Spectrin β chain | 31 | 247 | |
| Band 3 chain P | 33 | 102 |
| S. No. | Peptide positions and Sequences* |
|---|---|
| 1 | G117TVLLDLQETSLAGVANQLLDR138 |
| 2 | F139IFEDQIRPQDR150 |
| 3 | I220PPDSEATVLVGR233 |
| 4 | A234DFLEQPVLGFVR246 |
| 5 | L247QEAAELEAVELPVPIR263 |
| 6 | F264LFVLLGPEAPHIDYTQLGR283 |
| 7 | A284AATLMTER292 |
| 8 | S731VTHANALTVMGKASTPGAAAQ752 |
| 9 | S851TPALSLALPFVLILTVPLR870 |
| 10 | V872LLPLIFR879 |
| S. No. | Amino acid sequence of band 3 peptides |
|---|---|
| 1 | I220PPDSEATLVLVGRADFLEQPVLGFVR246 |
| 2 | L247QEAAELEAVELPVPIRFLFVLLGPEAPHIDYTQLGR283 |
| 3 | L632SVPDGPKVSNSSARGWVIHPLGL655 |
| 4 | S731VTHANALTVMGKASTPGAAAQ753 |
| 5 | A744STPGAAAQIQEVKE758 |
| 6 | F813KPPKYHPDVPYVK826 |
| 7 | S852TPASLALPFVLILTVPLRRVLLPLIFRN879 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




