1. Introduction
High-temperature superionic phases of acid salts of alkali metals are characterized by structural disordering of hydrogen bonds network, resulting in the high mobility of protons and the high conductivity values up to σ ~10
-3 to 10
-2 S/cm at 100–250°C [
1,
2]. For CsH
2PO
4 the phase transition from monoclinic (P2
1/m) to a cubic superionic (Pm-3m) phase with a conductivity σ~6·10
-2 S/cm is observed at 230°C [
3]. In superionic disordered phase all protons are participated in a transfer process provided by tetrahedra reorientation followed by a proton hopping [
4,
5]. Publications on acid salts of alkali metals have mainly focused on their use as electrolytes for medium temperature fuel cells SAFC [
6,
7,
8,
9]. Recently, the possibility of using of acid salt based solid electrolytes in the process of water electrolysis has been shown for the medium temperature range of 230–400°C. A higher operating temperature in a comparison with the low temperature devices allows to improve electrochemical performance and replace platinum catalysts [
10,
11,
12]. Also the medium-temperature range of 200–400°C is suitable for the synthesis of various organic substances, such as methane and methanol. It was shown that, during the combined electrolysis of CO
2 and H
2O using a nickel cathode and an IrO
2 anode, a CsH
2PO
4–SiC composite electrolyte, (T=300°C, pressure 8 bar) it is possible to carry out the synthesis of methane. The maximum efficiency for methane synthesis was obtained at a current density of 10–15 mA/cm
2 [
13].
The development of the flexible CsH
2PO
4-polymer films can significantly improve the disadvantageous properties of acid salt membranes such as insufficient mechanical properties and water solubility. Also the ohmic losses can be decreased by reduction of the thickness of the hybrid membrane. Various polymers were considered earlier as the effective additives for obtaining CsH
2PO
4 based membranes: SPEEK [
14], Butvar [
15], epoxy resin [
16,
17]. Fluoropolymers (FPs) are an extensive class of the functional materials with the perfect thermal stability and chemical inertness, hydrophobic properties and ability to operate in highly extreme conditions [
18]. Also, they are perspective as a polymer additive for CsH
2PO
4 based membranes. Polymer additive makes cesium-based electrolyte more stable to the deformation under the compressive loadings and creeps resulting in reduced fuel leaks and stable FC performance. The C-F bond provides the stability of fluoropolymers due to the high electronegativity of fluorine atoms and high bond dissociation energy. High content of fluorine in PTFE, PVDF and copolymers of various compositions provides a chemical resistivity to many aggressive media during prolonged heating at high temperatures, incombustibility and hydrophobicity. The main characteristics of fluoropolymers are presented in
Table 1.
Two main representatives of FPs are homopolymers polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) and polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) with fluorine mass fraction 0.76 and 0.594, respectively. The polymer density correlates with the mass fraction of fluorine, reaching the maximum for PTFE (2.12 g/cm
3) and the lowest values are for PVDF (1.78 g/cm
3) (
Table 1). PTFE has the highest decomposition temperature (more than 415°C) among the considered FPs. PTFE and PVDF are widely used in the various fields ranging from microelectronics to aerospace. Comprehensive overviews on the synthesis methods, properties, existing copolymers of the PTFE and PVDF are widely presented in the literature [
19,
20,
21,
22,
23].
According [
24,
25] the non-standard form of PTFE composed of ultrafine particles with the size ~0.6 μm with a trademark FORUM® can be obtained. The morphology of ultra-dispersed PTFE is related to the fact that during the synthesis of ultra-dispersed modification the condensation of the microspheres consisting of weakly connected films with a thickness of 5–10 nm occurs. Ultra-dispersed form is characterized by a high melting temperature of 275°C, excellent chemical stability and high degree of crystallinity similar to the bulk one. The crystal structure is comprised of (-CF
2-)
n chains arranged in a spirals directed along the z-axis. The difference of the bulk and ultra-dispersed forms is in the degree of the disordering consisted in relative shift of macromolecules and the rotation of CF
2-groups [
25,
26].
PVDF also exhibits a high degree of crystallinity reaching 50-70%. Polymer can crystallize in five different modifications depending on the implementation of various chain conformations (trans-, gauche-). Non-polar (α and δ) and polar (β and γ) phases can be realized. The structure of most commonly used polar β phase is composed of chains in the TTTT conformation and has the maximum dipole moment among all of the phases of PVDF.
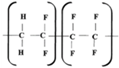
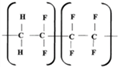
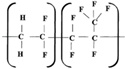
Unlike homopolymers, copolymers are made of the main polymer chain with the attached bulky groups that increase the degree of the disordering in the macromolecule, thereby reducing the crystallinity. The variation of the symmetry of the polymeric chain as a consequence of copolymerization modifies both intramolecular and intermolecular forces resulting in the changes of thermal characteristics (melting point, decomposition and glass transition temperature), elastic properties, solubility and permeability in a wide range [
20].
Copolymers F2M and F42 are PVDF-based polymers with the VDF/TFE mass ratio of components 92.75:7.25 and 61:39, respectively. As a rule mass fraction of fluorine and density of copolymers F2M and F42 are changed in the accordance to mass fraction of VDF/TFE (
Table 1). Fluoroplast-2M (F2M) is a primarily PVDF modified by small amount of TFE. The properties of F-2M copolymer are comparable to a pure homopolymer, but it has improved melt processability, greater elasticity, slightly lower strength.
Fluoroelastomers are high-molecular elastic polymers obtained by a radical copolymerization of the fluorine-containing monomers. Fluoroelastomer SKF-26 is a copolymer of VDF and hexafluoropropylene (HFP) with a mass ratio of 75:25 and a total fluorine weight of 66%. Copolymer can stretch beyond its original length, and returns to its initial size after unloading with maximum elongation at a break reaching values of 300%.
Unlike PTFE, the copolymers F2M, F42 and SKF26 are soluble in ketones, dimethylformamide (DMF), dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO). The solubility of polymers in various solvents opens up the possibility for the synthesis of thin films by the tape-casting method.
The first attempt to use a fluoropolymer as a polymer matrix for an acid salt was made for the PVDF–CsH
2PO
4 system [
27]. It was shown that the introduction of PVDF does not affect the crystal structure and thermal properties of the salt. The conductivity of the obtained samples reached 10 mS·cm
-1 at 270°C. The stability of the composite at a temperature of 259 °C and an atmosphere of 30% H
2O/Ar is maintained for at least 48 hours. The combination of proton conductivity and mechanical strength revealed the optimal content of polymer to be 30 wt. % [
27]. Of greatest interest are the membranes that have both a sufficiently high conductivity and improved mechanical strength.
The aim of this work is a comparative analysis of the composite polymer systems based on CsH2PO4 with the additives of different fluoropolymers, such as UPTFE and PVDF-based polymers (F2M, F42, SKF26) with high mechanical and thermal stability. The high conductive thin-film polymer composite systems were produced by different methods of the obtaining salt small particles, their mixing and applying to a matrix. More attention is paid to the analysis of the electrotransport and mechanical properties of compositions of the membranes (1-x)CsH2PO4-xFPs for which the thin high conductive films can be obtained (x=0.15-0.25).
2. Experimental
The CsH2PO4 crystals were grown from the aqueous solution of Cs2CO3 and H3PO4 with a molar ratio of 1:2. The CsH2PO4 particles of the size 1–5 µm were precipitated by anti-solvent technique using isopropanol.
Composite electrolytes with soluble fluoropolymers (F42, F2M, SKF26) were synthesized from a suspension of CsH2PO4 particles in a polymer solution with the further drying and uniaxial pressing at P~300 MPa (x≤0.15) or by tape-casting method (for x≥0.15). A small amount of polymer additive (x<0.15) is not enough to form a strong thin film membrane. The solvents with high-boiling point (DMF), low-boiling point (acetone) and their mixtures were used for the synthesis of the membranes. The homogenized suspension was spread on a fluoroplastic substrate by an automatic tape-casting machine (TOB-VFC-150). The gap height was 150-300 µm depending on the number of layers applied. The thickness of the membranes obtained by the tape-casting after drying was 50-150 μm. For UPTFE polymer solid-state method with the further hot-pressing at T=110–140°C, P~100 MPa was used due to the insolubility of the polymer in the common solvents.
Proton conductivity of the membranes was measured by the electrochemical impedance spectroscopy in a wide frequency range using the impedance meter P5X (1 mHz–0.5 MHz, Electrochemical Instruments, Russia) and Instek (12 Hz–200 kHz). The temperature dependencies of the conductivity are presented in the cooling mode. To prevent the acid salt dehydration during the measurements in the high temperature range (180–245°C), humid conditions were maintained (рН2О ~0.3 atm). Water vapor pressure was obtained by bubbling dry argon at a constant rate (50 ml/min) through the water at T=70°C.
Vickers microhardness test for the tablets and the tensile strength measurements for thin-film membranes have been performed. Vickers microhardness test for uniaxially pressed tablets (5 mm in diameter and 1 mm thickness) with the relative density of 91–99% was made on Microhardness tester DuraScan 50 (EMCO-TEST, Austria). The load was 0.5 kgf (4.9 N) with an application time of 10 seconds. The values of Vickers Hardness (HV) were obtained by division of the load applied by the area of the impression of the diamond pyramidal indenter.
For the preparation of the samples for tensile strength testing, a punching die of a certain size was used to obtain the samples with a form of a double blade with a 5 mm*20 mm working area. The membrane was stretched at a constant rate of 5 mm/min and the applied load and elongation were recorded. The measurements were performed on a Instron 5944 mechanical testing machine.
The phase composition of the membranes was analyzed by X-ray diffraction using a Bruker D8 Advance diffractometer (Cu
Kα radiation) with a one-dimensional Lynx-Eye detector and K
β filter. The evaluation of unit cell parameters and particle size of CsH
2PO
4 has been carried out from PXRD data by the Topas 4.2 software (Bruker AXS, Germany) [
28].
The cross-sectional morphology of the membranes was determined by scanning electron microscopy (Hitachi TM 1000). The membranes were preliminarily coated with gold sputtering to obtain a conductive surface. The FTIR-spectra in the attenuated total reflectance (ATR) mode were recorded on a Bruker Tensor 27 Spectrometer.
3. Results and discussion
The composition range for high conductive membranes of (1-x)CsH2PO4-xFPs was limited by x≤0.3. Note, that the compositions with x=0.3 correspond to the different volume fractions of the polymers due to the growth of its density in the PVDF<F2M<F42<PTFE sequence. With the further x increase the proton conductivity decreases sharply owing to the blocking of the proton transfer pathways by excess amount of the polymer resulting in «conductor-insulator» percolation effect.
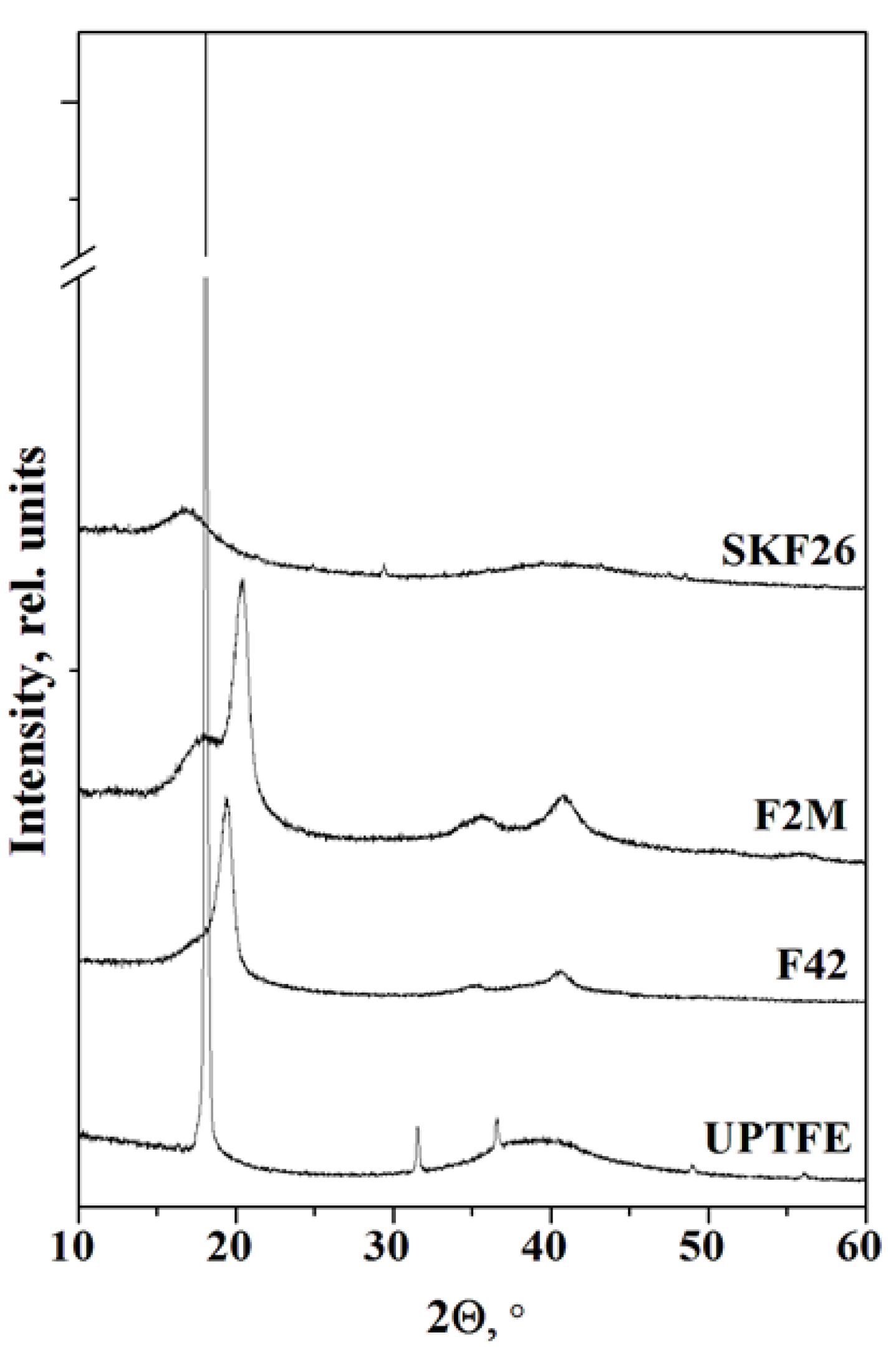
The experimental PXRD pattern for CsH
2PO
4 completely coincides with the calculated positions of the Bragg reflections, in accordance with [
29]. The positions of the main reflexes for fluoropolymers are in a good agreement with the literature data. The used fluoropolymers and differed by the degree of crystallinity (
Figure 1). Diffraction pattern of UPTFE powder is characterized by an intensive peak assigned to a crystalline phase (~18°) and the region of diffuse scattering observed at ~39° [
26]. Crystal structures of VDF/TFE copolymers of the different compositions have been discussed in [
30]. The main diffraction peaks of copolymers correspond to the slightly shifted positions of PVDF β-phase. XRD patterns for fluoroelastomer SKF26 consist of only by an amorphous halo at 2Θ ~17º due to the low crystallinity owing to bulky HFP parts in a VDF structure.
It was shown that P2
1/m structure of the acid salt retains in the composite electrolytes with different FPs (UPTFE, F42, SKF26 and PVDF) [
27,
31,
32,
33]. The more intensive peak of the polymer can be observed on the PXRD patterns only at x≥0.15 for the membranes based on FPs with a sufficiently high degree of the crystallinity. There is no chemical reaction between components in the polymer systems and only a slight deviation of 2θ peak positions was observed for the composites with UPTFE and F2M due to a decrease in the parameters of the crystal cell. Besides, the intensity of reflexes decreases more significantly than the mass fraction of CsH
2PO
4 in the polymer systems CsH
2PO
4-F-2M and UPTFE. Unusual morphology and rather high surface area of the UPTFE resulted in the disordering and amorphization of the salt [
31]. While for CsH
2PO
4-F2M membranes the dispersion due to the insignificant interface interaction takes place.
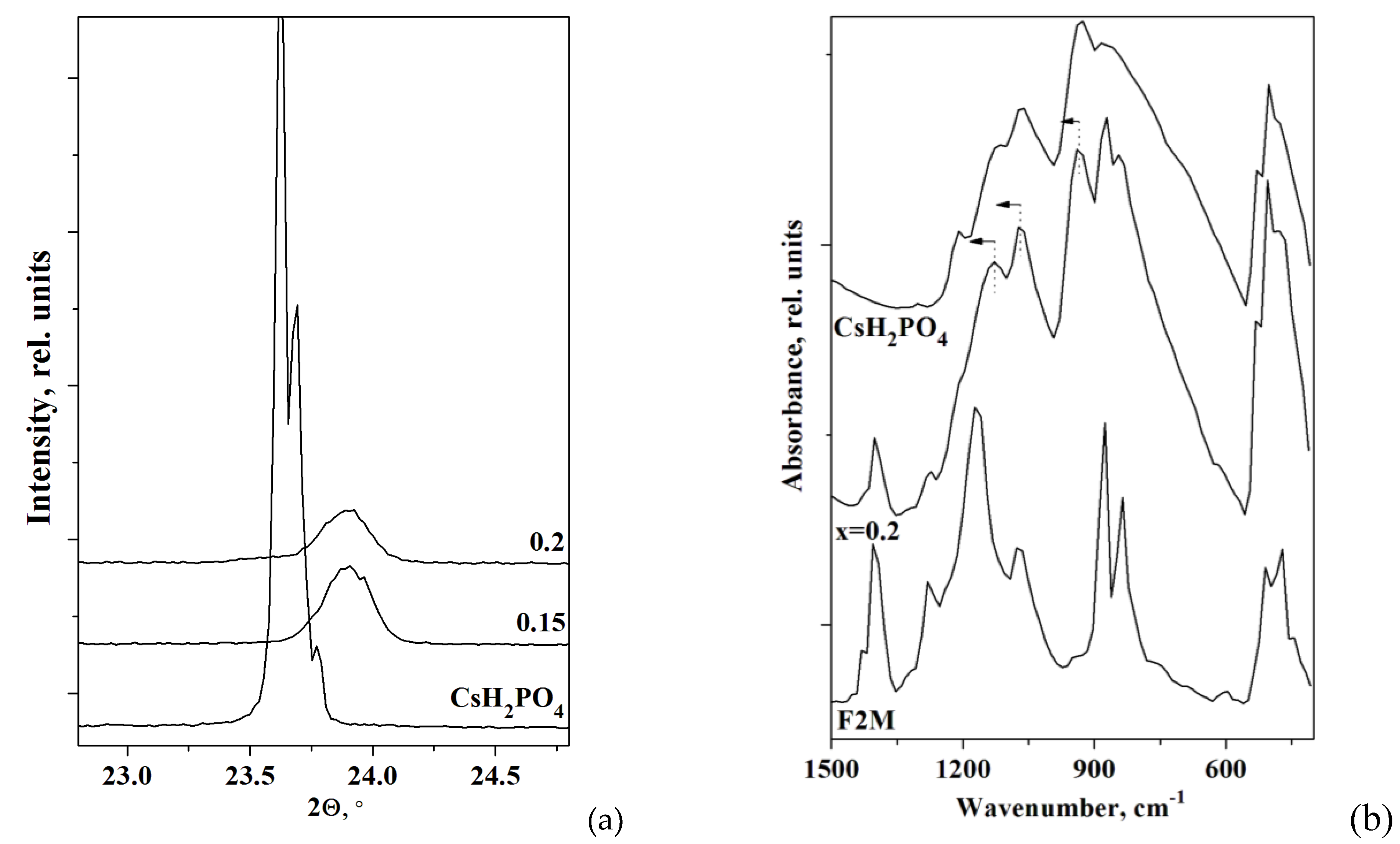
Figure 2a demonstrates the displacement of the main reflections (011 and -111) of CsH
2PO
4 phase in the composites with F2M and their decreasing. The reflections in the polymer composites move towards the larger angles due to a slight decrease of the unit cell parameters of CsH
2PO
4 in the volume of the polymer matrix.
FTIR spectra of the polymer electrolytes are similar to the pure CsH
2PO
4 (
Figure 2 b). The range of 1500–500 cm
−1 corresponds to the main characteristic absorption bands of F2M, and 1300–500 cm
−1 is related mainly to the spectral range of νPO
4 tetrahedra. Note, the FTIR spectrum at x=0.2 is the superposition of the absorption bands of CsH
2PO
4 and F2M. For x=0.2 the additional absorption bands in the range of 1400, 1274, 875, 835 and 509 cm
-1 appear to FTIR spectrum of CsH
2PO
4. The shift of the absorption bands of 930 and 1122 cm
-1 of CsH
2PO
4 in the composite to the 939 and 1133 cm
-1 (marked in
Figure 2b) is related to the insignificant strengthening of P-O bonds in the polymer membranes. Both FTIR and XRD data are consistent and confirm the insignificant CsH
2PO
4 changes due to the negligible interface interaction and the salt dispersion.
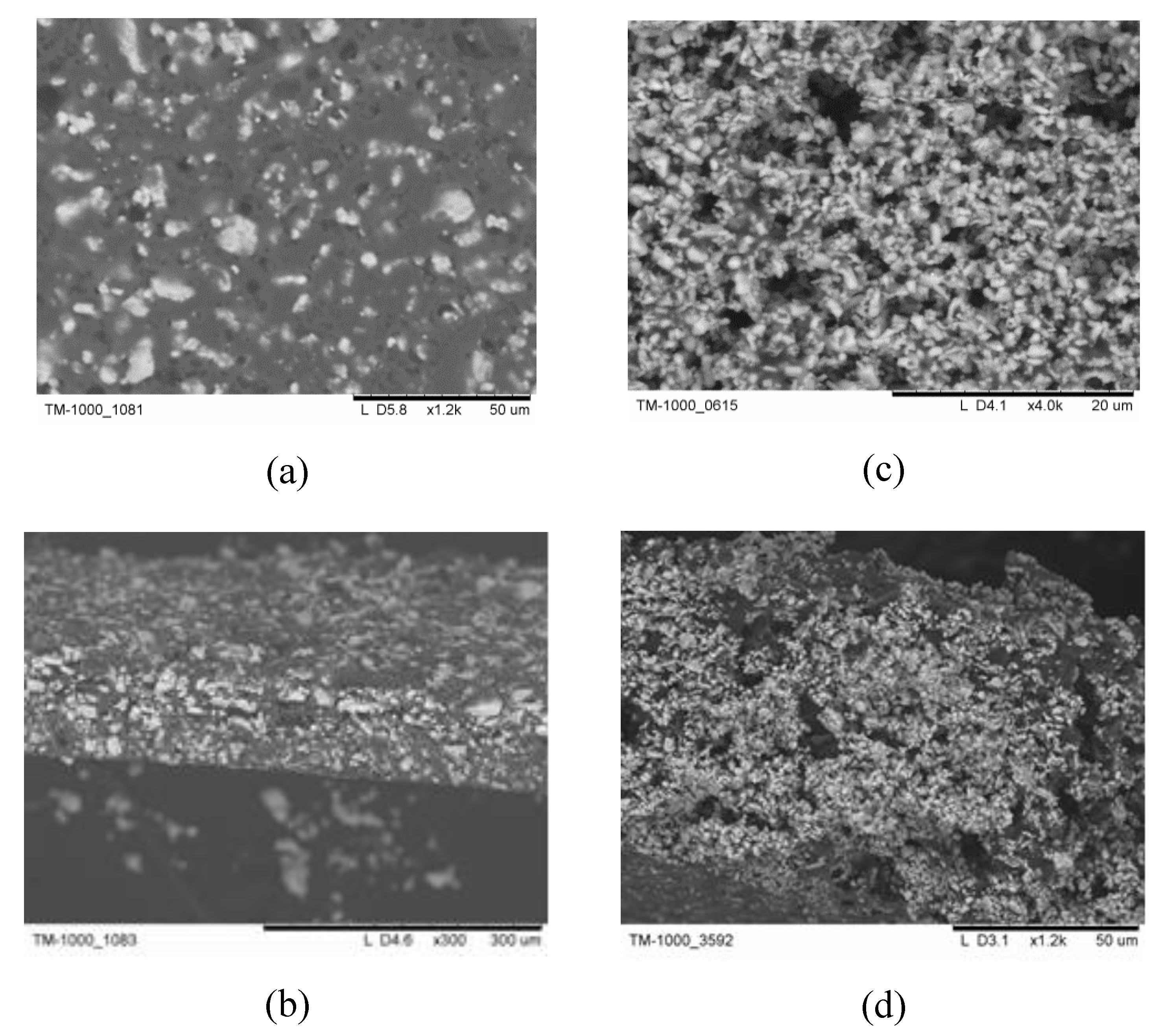
As a rule the membrane thickness and its mechanical characteristics can be limited by the particle size of the inorganic component and the uniformity of its distribution. SEM images (
Figure 3) present the differences in the morphology of the membranes with the salt particles obtained by various methods. The thickness of the membranes obtained by the tape-casting was 50-100 μm (
Figure 3 (b,d)). Note that durable thin films were obtained for the compositions x≥0.15. Thin-film with the mass fraction of F42, х=0.2, with salt particles precipitated by anti-solvent technique using the isopropanol is characterized by different size of the salt particles of 1-5 μm resulting in less even distribution (
Figure 3(a)). Thin film with x=0.2 obtained from the suspension of CsH
2PO
4 in the SKF26 polymer solution pretreated in a bead-mill is characterized by more uniform distribution and the smaller size of the salt particles (~300 nm,
Figure 3(c,d).
The microhardness test for the CsH
2PO
4-FPs polymer composites was used to evaluate the mechanical characteristics of the sample in the form of the tablet for x≤0.15 [
34] (
Figure 4). The microhardness value for the tablet of the pressed polycrystalline CsH
2PO
4 was HV~34 (333.4 MPa), whereas for the composite polymer membranes the size of the indenter impression on the membrane surface decreases, resulting in the lower values of microhardness (
Figure 4). The HV for F42 and UPTFE based membranes have close values of 11.8 and 12, respectively. For the membranes with SKF-26 (x=0.15) there was no visible impression of the indenter. It was quickly erased due to the elastomeric nature of the polymer and as a consequence a small recovery time of the membrane surface. It confirms that polymer composite membranes can resist plastic deformation and their mechanical properties are much higher than of the initial CsH
2PO
4 salt.
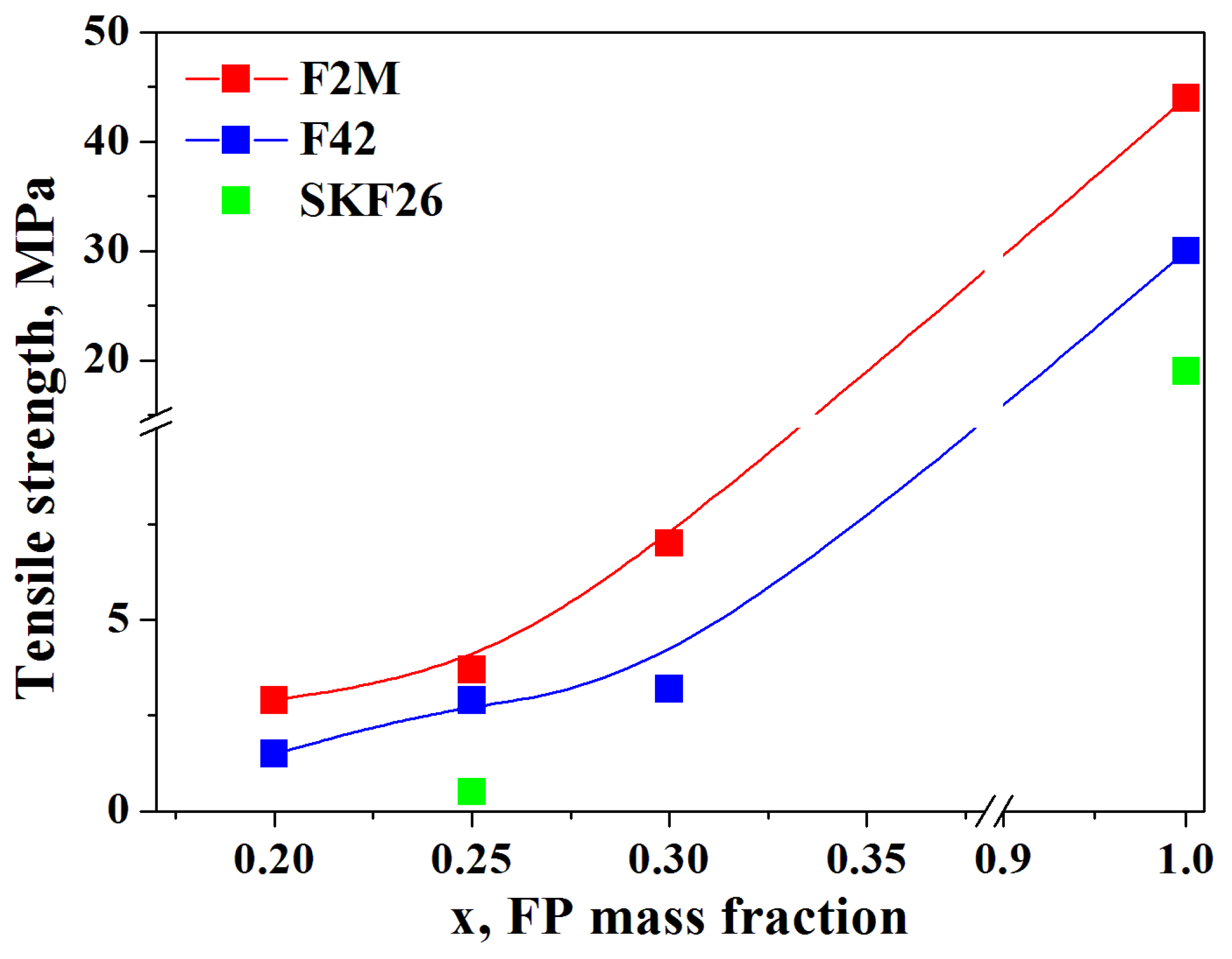
According the
Table 1, F2M copolymer is characterized by the highest value of tensile strength (34.3-55 MPa) among FPs considered. The same tendency was observed for CsH
2PO
4-FPs polymer composites.
Figure 5 presents the values of the tensile strength of the thin-film membranes in a comparison with literature data of the initial FPs. Maximum value of 7 MPa was obtained for 0.7CsH
2PO
4-0.3F2M membrane. The tensile strength values for 0.75CsH
2PO
4-0.25SKF26 were rather low and did not exceed 1 MPa, however the highest elongation before break of 170% was observed due to the elastomeric properties of the polymer.
Thus the obtained proton membranes are characterized by significantly increased mechanical strength and are comparable to the best polymer membranes.
Obviously, the size and shape of the particles, their distribution in the membrane influences both the mechanical strength and the values of proton conductivity. As for CsH
2PO
4 the difference in the morphology of its particles does not affect the proton conductivity since the surface conductivity for acid salt is comparable to the bulk one. In the same time in the polymer membranes a different aspect ratio of salt (length to diameter) provides a different number of the CsH
2PO
4 contacts in the volume of the matrix, which result in the more developed pathways for a proton transfer. For example the proton conductivity of (1-x)CsH
2PO
4-xSKF26 membranes with the platelet salt particles precipitated from the water solution by anti-solvent technique using ethyl alcohol in the presence of ethylene glycol was ~1 order of magnitude lower in the comparison with the small (about 300-500 nm) spherical particles obtained by ball-milling process. Obviously the small particles with the shape close to a spherical are the most prominent for the transport characteristics of the polymer composite membranes due to the maximum number of the salt contacts [
33].
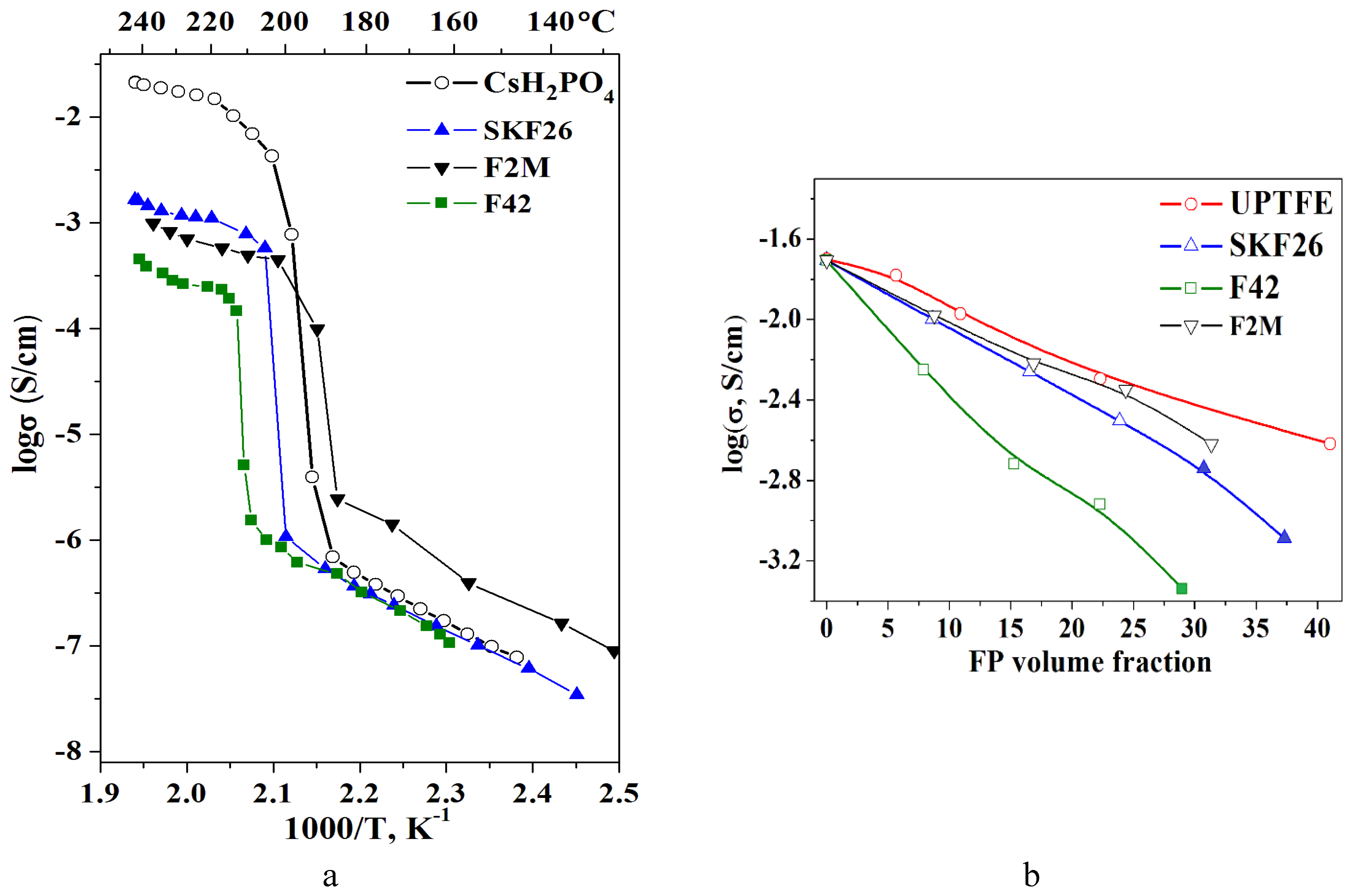
Temperature dependence of the proton conductivity of the composite polymer membranes is similar to the initial salt and can be characterized by the low- and high-temperature regions (
Figure 6a). In the high-temperature region CsH
2PO
4 exists in the superionic phase with the high proton conductivity reaching the value higher than ~3∙10
-2 S/cm. The observed jump in the proton conductivity of CsH
2PO
4 due to superproton phase transition is four orders of magnitude. The conductivity dependence for the low-temperature region (from the room temperature to the superionic phase transition) has an Arrhenius character with the activation energy of 0.8 eV. The activation energy of the conductivity of the polymer membranes in the high-temperature phase is about 0.4 eV similar to CsH
2PO
4. In the polymer composite electrolytes a decrease of the proton conductivity in the high temperature region close to linear is observed (
Figure 6a). The low temperature conductivity of SKF26 and F42 containing thin film membranes is close to pure CsH
2PO
4. In the same time the conductivity of CsH
2PO
4-F2M polymer system is 0.5-1 order of magnitude higher than CsH
2PO
4 due to the interface interaction and salt dispersion. With the further x increase the conductivity decreases both in the high- and the low-temperature regions of the polymer composite electrolytes. The decrease of the proton conductivity in the high-temperature region (
Figure 6a) is more significant due to the differences in the conductivity at higher temperatures. A slightly higher conductivity values for CsH
2PO
4-UPTFE membrane can be caused by another way of the synthesis that excludes the formation of a continuous polymer film on the surface of the salt particles. The conductivity jump due to the superproton transition to the monoclinic (P2
1/m) phase shifts to the lower temperatures more than 20°C for the membranes CsH
2PO
4-F2M due to the more pronounced interface interaction. The interface interaction with the negligible strengthening of the P-O bonds determines the shift of the phase transition temperature and the expansion of the range of CsH
2PO
4 superproton phase existence in the polymer electrolytes, which is important and perspective for SAFCs. The main tendency of the proton conductivity dependencies with different FPs volume fraction can be tracked for the tablet samples in the range up to 0.15 (f
V=0.20-0.25) (
Figure 6b). For all of the polymer systems, except UPTFE, the samples for the conductivity measurements were obtained by the same method. According
Figure 6 the change in the conductivity is close to linear. The selected FPs are dielectrics (
Table 1) and the addition of these polymers will inevitably lead to a decrease in the proton conductivity of the composite membranes due to the percolation effect of the "conductor-insulator". The polymer layer with sufficient thickness on the surface of the salt particles acts as a barrier for proton transport. The polymer systems based on F2M, UPTFE and SKF26 show the close and high conductivity values.
Despite the close nature of the polymers, they have some processing peculiarities. The temperature of the melting for F42 and F2M copolymers is preceded the temperature of the decomposition. However, at 150–180°C only the crystallites melt and the polymer does not pass into a viscous flow state up to the decomposition. Some softening of the polymer may contribute to a better coating of the surface of the salt particles with the polymer.
The boiling temperature of the solvent used can influence the morphology of the membranes. For the films casted with the low-boiling point solvent (acetone) the pores may be observed due to the high evaporation rate of the solvent. Therefore the high-boiling solvent DMF or the mixtures of DMF and acetone are preferrable for the obtaining the thin-film proton membranes by tape-casting technique. Another way to obtain denser thin-film proton membranes is pressing of the membranes. This is a simple and convenient way to densify the membranes for F42 and F2M polymers, however this method is not suitable for SKF26 membranes due to the elastomeric properties. Probably the absence of the phase transitions up to the decomposition temperature also affects the properties of the SKF26-containing membranes.
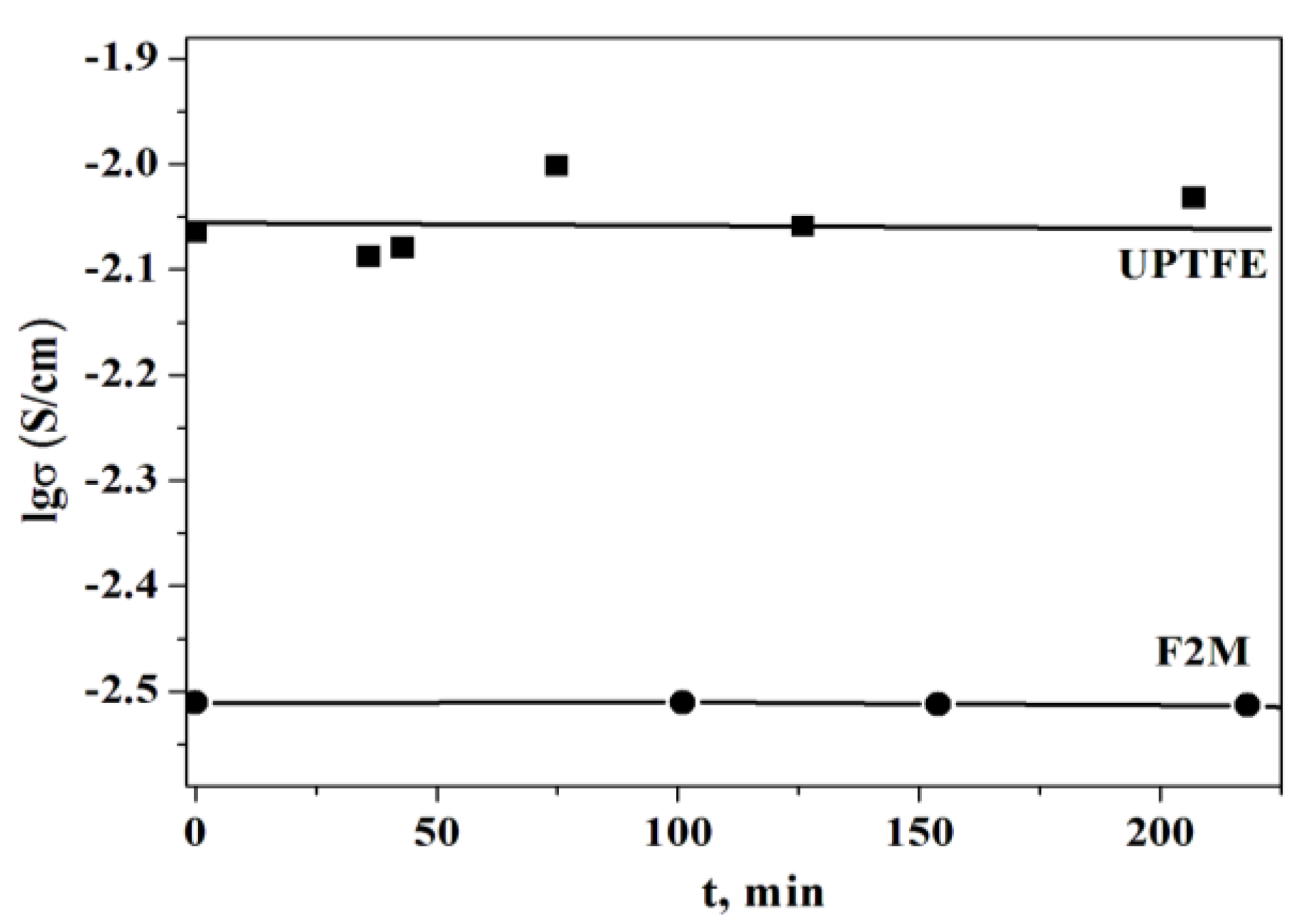
Despite the decrease in the conductivity the polymer membranes are chemically and thermally stable. Long-term thermal storage of the membranes revealed the stability of the proton conductivity at T=238°C and p
H2O~0.3 atm (
Figure 7).
Thus, there is a significant improvement in the mechanical properties of the polymer membranes, the synthesis of thin films (50 -100 μm) despite the decrease in the proton conductivity. Even small concentration of FPs can improve the mechanical properties of CsH2PO4 membranes, increase their hydrophobicity and stability in a humid environment, which is very important for SAFCs and other acid salt applications. At the same time, the higher FPs concentration creates the prospect of the synthesis of the thin-film membranes by the tape casting method. Also the sequential layer-by-layer deposition can be used for more reliable connection of the components for the dense thin films for both proton membranes and membrane-electrode assemblies.