Submitted:
10 May 2023
Posted:
15 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
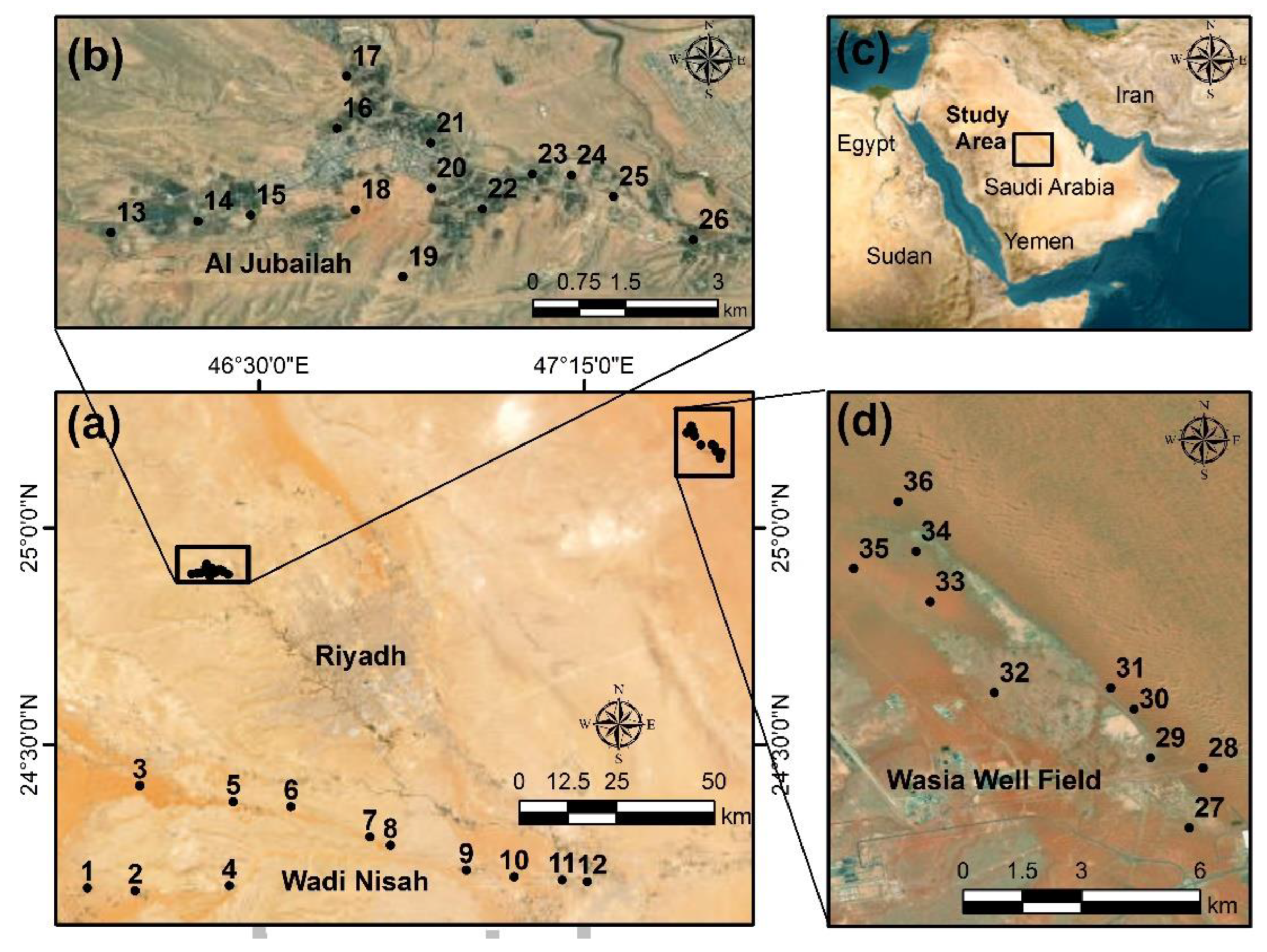
2. Geological Setting
3. Material and Methods
4. Results and Discussion
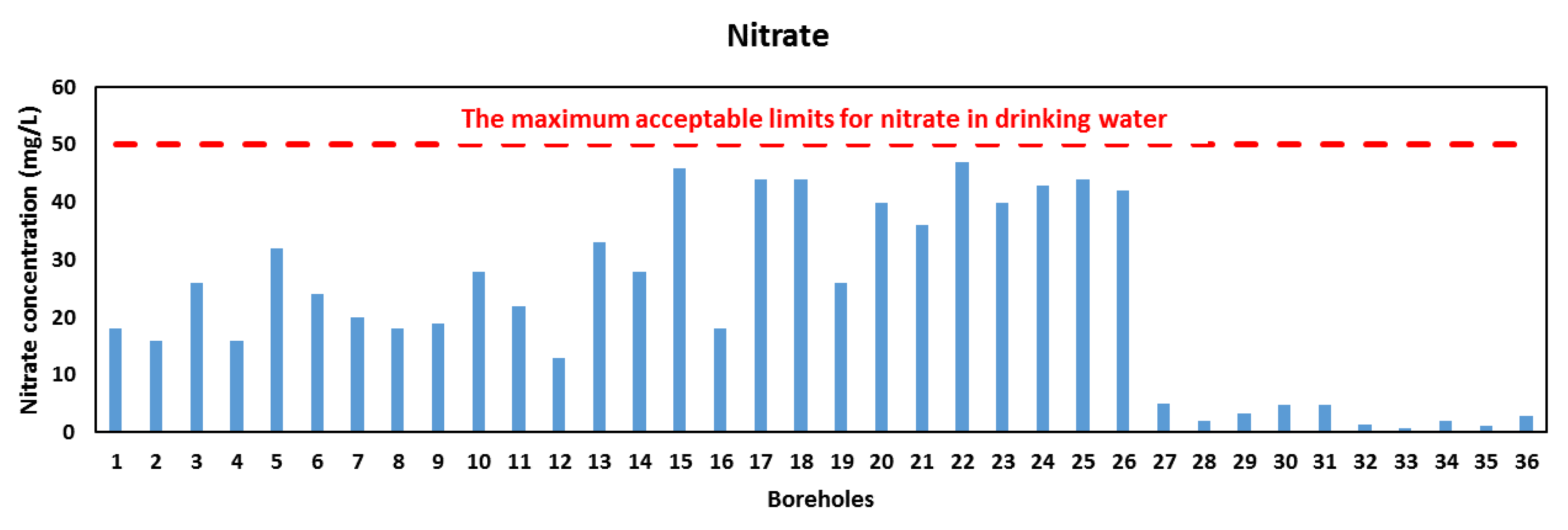
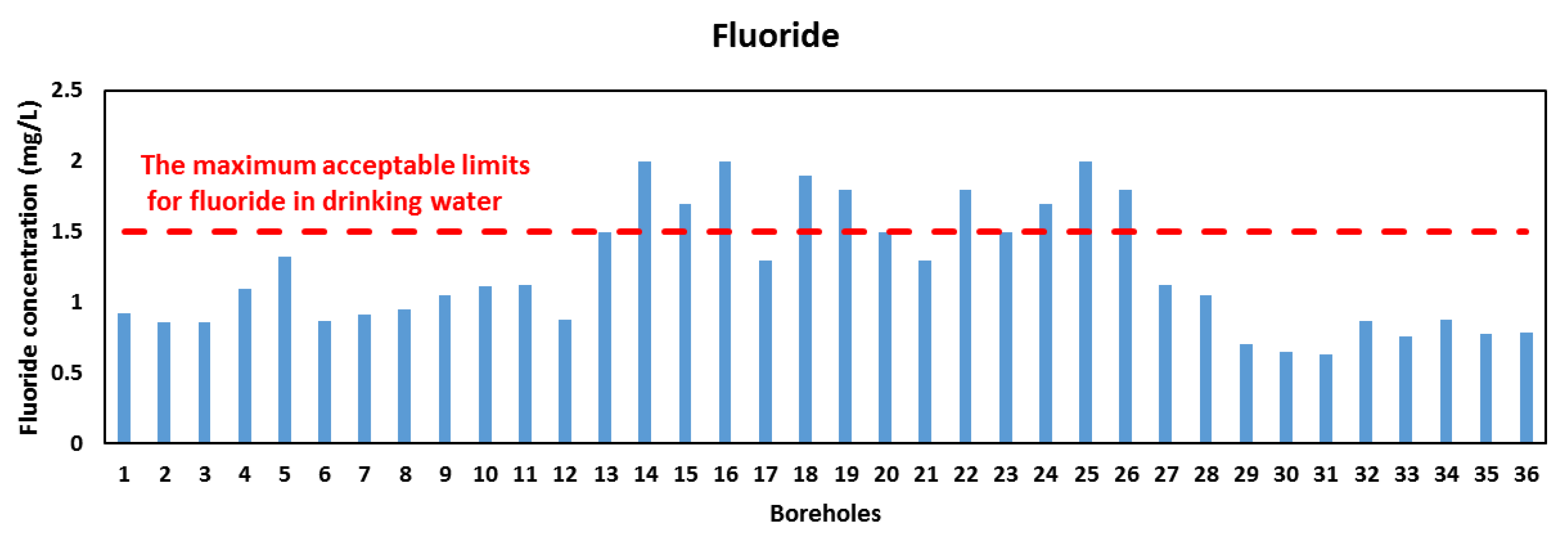
4.1. Concentration and Distribution of Nitrate and Flouride
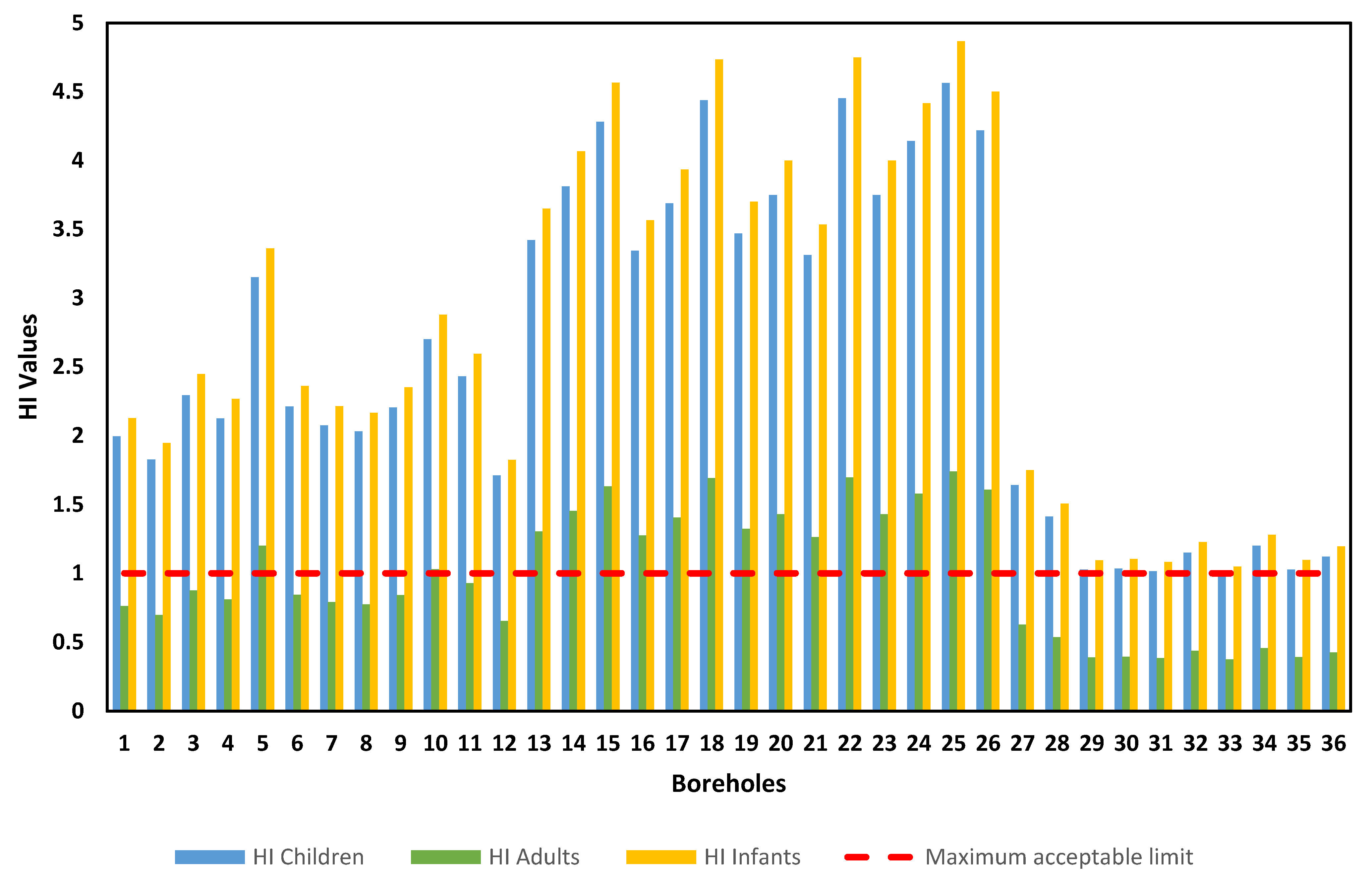
4.2. Human Health Risk
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Patel, P.M.; Saha, D.; Shah, T. Sustainability of groundwater through community-driven distributed recharge: An analysis of arguments for water scarce regions of semi-arid India. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2020, 29, 100680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kom, K.P.; Gurugnanam, B.; Bairavi, S. Non-carcinogenic health risk assessment of nitrate and fluoride contamination in the groundwater of Noyyal basin, India. Geodesy Geodyn. 2022, 13, 619–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dippong, T.; Mihali, C.; Hoaghia, M.-A.; Cical, E.; Cosma, A. Chemical modeling of groundwater quality in the aquifer of Seini town—Someș Plain, Northwestern Romania. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 168, 88–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Qian, H.; Ren, W.; Wang, H.; Liu, F.; Yang, F. Hydrogeochemical characterization and quality assessment of groundwater based on integrated-weight water quality index in a concentrated urban area. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 260, 121006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawale, V.; Malpe, D.; Marghade, D.; Yenkie, R. Non-carcinogenic health risk assessment with source identification of nitrate and fluoride polluted groundwater of Wardha sub-basin, central India. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 208, 111548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toolabi, A.; Bonyadi, Z.; Paydar, M.; Najafpoor, A.A.; Ramavandi, B. Spatial distribution, occurrence, and health risk assessment of nitrate, fluoride, and arsenic in Bam groundwater resource, Iran. Groundw Sustain. Dev. 2021, 12, 100543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briki, M.; Zhu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Shao, M.; Ding, H.; Ji, H. Distribution and health risk assessment to heavy metals near smelting and mining areas of Hezhang, China. Environ. Monit. Assess 2017, 189, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- inling, Wu; Yin, Y.; Wang, J. Hydrogen-based membrane biofilm reactors for nitrate removal from water and wastewater. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2018, 43(1–4),1–15.
- Eggers, M.J.; Doyle, J.T.; Lefthand, M.J.; Young, S.L.; Moore-Nall, A.L.; Kindness, L.; Ford, T.E.; Dietrich, E.; Parker, A.E.; Hoover, J.H.; Camper, A.K. Community engaged cumulative risk assessment of exposure to inorganic well water contaminants, crow reservation, montana. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018. [CrossRef]
- Amiri, V.; Berndtsson, R. Fluoride occurrence and human health risk from groundwater use at the west coast of Urmia Lake, Iran. Arab. J. Geosci. 2020, 13, 921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duvva, L.K.; Panga, K.K.; Dhakate, R.; Himabindu, V. Health risk assessment of nitrate and fluoride toxicity in groundwater contamination in the semi-arid area of Medchal, South India. Appl. Water Sci. 2022, 12, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Kang, W.; Li, Y.; Li, Z. Fluoride and nitrate contamination of groundwater in the Loess Plateau, China: Sources and related human health risks. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 286, 117287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.F.; Srinivasamoorthy, K.; Prakash, R.; Gopinath, S.; Saravanan, K.; Vinnarasi, F.; Babu, C.; Rabina, C. Human health risk assessment for fluoride and nitrate contamination in the groundwater: A case study from the east coast of Tamil Nadu and Puducherry, India. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimambo, V.; Bhattacharya, P.; Mtalo, F.; Ahmad, A. Fluoride occurrence in groundwater systems at global scale and status of defluoridation-State of the art. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2019, 9, 100223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vithanage, M.; Bhattacharya, P. Fluoride in the environment: Sources, distribution and defluoridation. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2015, 13, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, M.; Gurugnanam, B.; Vasudevan, S.; Dharanirajan, K.; Raj, N.J. Drinking and irrigational feasibility of groundwater, GIS spatial mapping in upper Thirumanimuthar sub-basin, Cauvery River, Tamil Nadu, J. Geol. Soc. India 75, 2010 518e526. [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, T. Hydrochemical Evaluation of Wasia Well Field in Riyadh Area. Master’s Thesis, King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, 2005. 139p. [Google Scholar]
- Alharbi, T.G. Identification of hydrogeochemical processes and their influence on groundwater quality for drinking and agricultural usage in Wadi Nisah, Central Saudi Arabia. Arab. J. Geosci. 2018, 11, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, S.; Al-Zahrani, M. Implications of climate change on water resources in Saudi Arabia. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2013, 38, 1959–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, T.G.; Zaidi, F.K. Hydrochemical classification and multivariate statistical analysis of groundwater from Wadi Sahba area in central Saudi Arabia. Arab. J. Geosci. 2018, 11, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aly, A.A.; Alomran, A.; Alharby, M.M. The water quality index and hydrochemical characterization of groundwater resources in Hafar Albatin, Saudi Arabia. Arab. J. Geosci. 2014, 8, 4177–4190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, T.; El-Sorogy, A.S.; Qaysi, S.; Alshehri, F. Evaluation of groundwater quality in central Saudi Arabia using hydrogeochemical characteristics and pollution indices. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 53819–53832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallick, J.; Singh, C.K.; AlMesfer, M.K.; Singh, V.P.; Alsubih, M. Groundwater Quality Studies in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia: Prevalent Research and Management Dimensions. Water 2021, 13, 1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, R.W.; Ramirez, L.F.; Redmond, C.D.; Elberg, E.L. Geology of the Arabian Peninsula Sedimentary Geology of Saudi Arabia; United States Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Al Husseini, M.I.; Mathews, R. Stratigraphic note: Orbital calibration of the Arabian plate second order sequence stratigraphy. GeoArabia 2006, 11, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, M.T.; Al Yousif, M.M.; Awad, H.S. Potentiality of secondary aquifers in Saudi Arabia: Evaluation of groundwater quality in Jubaila limestone. Int. J. Geosci. 2012, 3, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, M.; El Sorogy, A.S. Palaeoecology of benthic foraminifera in coral reefs recorded in the Jurassic Tuwaiq Mountain Formation of the Khashm Al-Qaddiyah area, central Saudi Arabia. J. Earth Sci. 2015, 26, 224–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gameil, M.; El-Sorogy, A.S. Gastropods from the Campanian–Maastrichtian Aruma Formation, Central Saudi Arabia. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2015, 103, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Asmar, H.M.; Assal, E.M.; El-Sorogy, A.S.; Youssef, M. Facies analysis and depositional environments of the Upper Jurassic Jubaila Formation, Central Saudi Arabia. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2015, 110, 34–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sorogy, A.S.; Al-Kahtany, K.M. Contribution to the scleractinian corals of Hanifa Formation, Upper Jurassic, Jabal al-Abakkayn central Saudi Arabia. Hist. Biol. 2015, 27, 90–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawfik, M.; Al-Dabbagh, M.E.; El-Sorogy, A.S. Sequence stratigraphy of the late middle Jurassic open shelf platform of the Tuwaiq Mountain Limestone Formation, central Saudi Arabia. Proc. Geol. Assoc. Proc. Geol. Assoc. 2016, 127, 395–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sorogy, A.S.; Al-Kahtany, K.h.M.; El-Asmar, H. Marine benthic invertebrates of the Upper Jurassic Tuwaiq Mountain Limestone, Khashm Al-Qaddiyah, Central Saudi Arabia. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2014, 97, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sorogy, A.S.; Almadani, S.A.; Al-Dabbagh, M.E. Microfacies and diagenesis of the reefal limestone, Callovian Tuwaiq Mountain Limestone Formation, central Saudi Arabia. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2016, 115, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özer, S.; El-Sorogy, A.S.; Al-Dabbagh, M.; Al-Kahtany, K. Campanian-Maastrichtian unconformities and rudist diagenesis, Aruma Formation, Central Saudi Arabia. Arab. J. Geosci. 2019, 12, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sorogy, A.; Al-Kahtany, K.; Almadani, S.; Tawfik, M. Depositional architecture and sequence stratigraphy of the Upper Jurassic Hanifa Formation, central Saudi Arabia. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2018, 139, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sorogy, A.S.; Gameil, M.; Youssef, M.; Al-Kahtany, K.M. Stratigraphy and macrofauna of the Lower Jurassic (Toarcian) Marrat Formation, central Saudi Arabia. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2017, 134, 476–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Dabbagh, M.E.; El-Sorogy, A.S. Diagenetic alterations of the Upper Jurassic scleractinian corals, Hanifa Formation, Jabal Al-Abakkayn, Central Saudi Arabia. J. Geol. Soc. India 2016, 87, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalifa, M.; Al-Kahtany, K.; Farouk, S.; El-Sorogy, A.S.; Al Qahtani, A. Microfacies architecture and depositional history of the Upper Jurassic (kimmeridgian) Jubaila Formation in central Saudi Arabia. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2021, 174, 104076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qasemi, M.; Afsharnia, M.; Zarei, A.; Farhang, M.; Allahdadi, M. Non-carcinogenic risk assessment to human health due to intake of fluoride in the groundwater in rural areas of Gonabad and Bajestan, Iran: A case study. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2018, 25, 1222–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaiphei, S.P.; Kurakalva, R.M. Hydrochemical characteristics and nitrate health risk assessment of groundwater through seasonal variations from an intensive agricultural region of upper Krishna River basin, Telangana, India. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 213, 112073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- USEPA. Human Health Evaluation Manual, Supplemental Guidance: Update of Standard Default Exposure Factors, OSWER Directive 9200.1–120; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2014.
- Narsimha, A.; Rajitha, S. Spatial distribution and seasonal variation in fluoride enrichment in groundwater and its associated human health risk assessment in Telangana State, South India. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2018, 24, 2119–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almodaresi, S.A.; Jafari, S.J.; Hosseinzadeh, E.; Miri, M.; Taghavi, M.; Khosravi, R.; Eslami, H.; Minaee, R.P.; Fallahzadeh, R.A. Investigation of fluoride concentration in rural drinking water resources of Bardaskan county using geographic information system (GIS) in 2014. J. Torbat Heydariyeh Univ. Med. Sci. 2016, 3, 32–41. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Wu, H.; Qian, H.; Gao, Y. Assessing Nitrate and Fluoride Contaminants in Drinking Water and Their Health Risk of Rural Residents Living in a Semiarid Region of Northwest China. Expo. Health 2016, 9, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qasemi, M.; Afsharnia, M.; Farhang, M.; Ghaderpoori, M.; Karimi, A.; Abbasi, H.; Zarei, A. Spatial distribution of fluoride and nitrate in groundwater and its associated human health risk assessment in residents living in Western Khorasan Razavi, Iran. Desalination Water Treat. 2019, 170, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Risk Exposure Factors | Unit | Adults | Children | Infants |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DI | L/d | 2 | 1.5 | 0.8 |
| F | d/year | 365 | 365 | 365 |
| ED | years | 40 | 10 | 1 |
| BW | kg | 70 | 20 | 10 |
| AT | d | 14,600 | 3650 | 365 |
| HI ≤1 | no health risk to humans | |||
| HI >1 | higher level of hazard | |||
| S.N. | Lat. | Long. | Nitrates | Fluoride | S.N. | Lat. | Long. | Nitrates | Fluoride |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 24.16958 | 46.10469 | 18 | 0.92 | 21 | 24.90678 | 46.39139 | 36 | 1.3 |
| 2 | 24.16344 | 46.21425 | 16 | 0.86 | 22 | 24.89717 | 46.39886 | 47 | 1.8 |
| 3 | 24.40542 | 46.22508 | 26 | 0.86 | 23 | 24.90225 | 46.40614 | 40 | 1.5 |
| 4 | 24.17483 | 46.43194 | 16 | 1.1 | 24 | 24.90211 | 46.41181 | 43 | 1.7 |
| 5 | 24.36869 | 46.44094 | 32 | 1.32 | 25 | 24.899 | 46.41792 | 44 | 2 |
| 6 | 24.35672 | 46.57375 | 24 | 0.87 | 26 | 24.89272 | 46.42953 | 42 | 1.8 |
| 7 | 24.28703 | 46.75603 | 20 | 0.91 | 27 | 25.16055 | 47.5633 | 5.1 | 1.12 |
| 8 | 24.26814 | 46.80336 | 18 | 0.95 | 28 | 25.17417 | 47.56645 | 2.1 | 1.05 |
| 9 | 24.21053 | 46.97817 | 19 | 1.05 | 29 | 25.17642 | 47.55445 | 3.2 | 0.7 |
| 10 | 24.19528 | 47.08814 | 28 | 1.11 | 30 | 25.18752 | 47.55073 | 4.7 | 0.65 |
| 11 | 24.1885 | 47.19881 | 22 | 1.12 | 31 | 25.19228 | 47.54542 | 4.8 | 0.63 |
| 12 | 24.18442 | 47.25731 | 13 | 0.88 | 32 | 25.19123 | 47.51897 | 1.3 | 0.87 |
| 13 | 24.89375 | 46.34486 | 33 | 1.5 | 33 | 25.21192 | 47.50437 | 0.7 | 0.76 |
| 14 | 24.89539 | 46.3575 | 28 | 2 | 34 | 25.2234 | 47.50117 | 2.1 | 0.88 |
| 15 | 24.89628 | 46.36517 | 46 | 1.7 | 35 | 25.2195 | 47.487 | 1.1 | 0.78 |
| 16 | 24.90889 | 46.37775 | 18 | 2 | 36 | 25.23465 | 47.49712 | 2.8 | 0.79 |
| 17 | 24.9165 | 46.37911 | 44 | 1.3 | Min. | 0.7 | 0.63 | ||
| 18 | 24.89706 | 46.38039 | 44 | 1.9 | Max. | 47 | 2 | ||
| 19 | 24.88733 | 46.38731 | 26 | 1.8 | Aver. | 22.59 | 1.23 | ||
| 20 | 24.90019 | 46.39144 | 40 | 1.5 | |||||
| S.N. | NO3− | CDI | F− | CDI | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Infants | Children | Adults | Infants | Children | Adults | |||
| 1 | 18 | 1.44 | 1.35 | 0.514 | 0.92 | 0.074 | 0.069 | 0.026 |
| 2 | 16 | 1.28 | 1.2 | 0.457 | 0.86 | 0.069 | 0.065 | 0.025 |
| 3 | 26 | 2.08 | 1.95 | 0.743 | 0.86 | 0.069 | 0.065 | 0.025 |
| 4 | 16 | 1.28 | 1.2 | 0.457 | 1.1 | 0.088 | 0.083 | 0.031 |
| 5 | 32 | 2.56 | 2.4 | 0.914 | 1.32 | 0.106 | 0.099 | 0.038 |
| 6 | 24 | 1.92 | 1.8 | 0.686 | 0.87 | 0.07 | 0.065 | 0.025 |
| 7 | 20 | 1.6 | 1.5 | 0.571 | 0.91 | 0.073 | 0.068 | 0.026 |
| 8 | 18 | 1.44 | 1.35 | 0.514 | 0.95 | 0.076 | 0.071 | 0.027 |
| 9 | 19 | 1.52 | 1.43 | 0.543 | 1.05 | 0.084 | 0.079 | 0.03 |
| 10 | 28 | 2.24 | 2.1 | 0.8 | 1.11 | 0.089 | 0.083 | 0.032 |
| 11 | 22 | 1.76 | 1.65 | 0.629 | 1.12 | 0.09 | 0.084 | 0.032 |
| 12 | 13 | 1.04 | 0.98 | 0.371 | 0.88 | 0.07 | 0.066 | 0.025 |
| 13 | 33 | 2.64 | 2.48 | 0.943 | 1.5 | 0.12 | 0.113 | 0.043 |
| 14 | 28 | 2.24 | 2.1 | 0.8 | 2 | 0.16 | 0.15 | 0.057 |
| 15 | 46 | 3.68 | 3.45 | 1.314 | 1.7 | 0.136 | 0.128 | 0.049 |
| 16 | 18 | 1.44 | 1.35 | 0.514 | 2 | 0.16 | 0.15 | 0.057 |
| 17 | 44 | 3.52 | 3.3 | 1.257 | 1.3 | 0.104 | 0.098 | 0.037 |
| 18 | 44 | 3.52 | 3.3 | 1.257 | 1.9 | 0.152 | 0.143 | 0.054 |
| 19 | 26 | 2.08 | 1.95 | 0.743 | 1.8 | 0.144 | 0.135 | 0.051 |
| 20 | 40 | 3.2 | 3 | 1.143 | 1.5 | 0.12 | 0.113 | 0.043 |
| 21 | 36 | 2.88 | 2.7 | 1.029 | 1.3 | 0.104 | 0.098 | 0.037 |
| 22 | 47 | 3.76 | 3.53 | 1.343 | 1.8 | 0.144 | 0.135 | 0.051 |
| 23 | 40 | 3.2 | 3 | 1.143 | 1.5 | 0.12 | 0.113 | 0.043 |
| 24 | 43 | 3.44 | 3.23 | 1.229 | 1.7 | 0.136 | 0.128 | 0.049 |
| 25 | 44 | 3.52 | 3.3 | 1.257 | 2 | 0.16 | 0.15 | 0.057 |
| 26 | 42 | 3.36 | 3.15 | 1.2 | 1.8 | 0.144 | 0.135 | 0.051 |
| 27 | 5.1 | 0.408 | 0.38 | 0.146 | 1.12 | 0.09 | 0.084 | 0.032 |
| 28 | 2.1 | 0.168 | 0.16 | 0.06 | 1.05 | 0.084 | 0.079 | 0.03 |
| 29 | 3.2 | 0.256 | 0.24 | 0.091 | 0.7 | 0.056 | 0.053 | 0.02 |
| 30 | 4.7 | 0.376 | 0.35 | 0.134 | 0.65 | 0.052 | 0.049 | 0.019 |
| 31 | 4.8 | 0.384 | 0.36 | 0.137 | 0.63 | 0.05 | 0.047 | 0.018 |
| 32 | 1.3 | 0.104 | 0.1 | 0.037 | 0.87 | 0.07 | 0.065 | 0.025 |
| 33 | 0.7 | 0.056 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.76 | 0.061 | 0.057 | 0.022 |
| 34 | 2.1 | 0.168 | 0.16 | 0.06 | 0.88 | 0.07 | 0.066 | 0.025 |
| 35 | 1.1 | 0.088 | 0.08 | 0.031 | 0.78 | 0.062 | 0.059 | 0.022 |
| 36 | 2.8 | 0.224 | 0.21 | 0.08 | 0.79 | 0.063 | 0.059 | 0.023 |
| S.N. | HQ Nitrates | HQ Fluoride | HI | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Infants | Children | Adults | Infants | Children | Adults | Infants | Children | Adults | |
| 1 | 0.9 | 0.844 | 0.321 | 1.227 | 1.15 | 0.438 | 2.127 | 1.994 | 0.76 |
| 2 | 0.8 | 0.75 | 0.286 | 1.147 | 1.075 | 0.41 | 1.947 | 1.825 | 0.695 |
| 3 | 1.3 | 1.219 | 0.464 | 1.147 | 1.075 | 0.41 | 2.447 | 2.294 | 0.874 |
| 4 | 0.8 | 0.75 | 0.286 | 1.467 | 1.375 | 0.524 | 2.267 | 2.125 | 0.81 |
| 5 | 1.6 | 1.5 | 0.571 | 1.76 | 1.65 | 0.629 | 3.36 | 3.15 | 1.2 |
| 6 | 1.2 | 1.125 | 0.429 | 1.16 | 1.088 | 0.414 | 2.36 | 2.213 | 0.843 |
| 7 | 1 | 0.938 | 0.357 | 1.213 | 1.138 | 0.433 | 2.213 | 2.075 | 0.79 |
| 8 | 0.9 | 0.844 | 0.321 | 1.267 | 1.188 | 0.452 | 2.167 | 2.031 | 0.774 |
| 9 | 0.95 | 0.891 | 0.339 | 1.4 | 1.313 | 0.5 | 2.35 | 2.203 | 0.839 |
| 10 | 1.4 | 1.313 | 0.5 | 1.48 | 1.388 | 0.529 | 2.88 | 2.7 | 1.029 |
| 11 | 1.1 | 1.031 | 0.393 | 1.493 | 1.4 | 0.533 | 2.593 | 2.431 | 0.926 |
| 12 | 0.65 | 0.609 | 0.232 | 1.173 | 1.1 | 0.419 | 1.823 | 1.709 | 0.651 |
| 13 | 1.65 | 1.547 | 0.589 | 2 | 1.875 | 0.714 | 3.65 | 3.422 | 1.304 |
| 14 | 1.4 | 1.313 | 0.5 | 2.667 | 2.5 | 0.952 | 4.067 | 3.813 | 1.452 |
| 15 | 2.3 | 2.156 | 0.821 | 2.267 | 2.125 | 0.81 | 4.567 | 4.281 | 1.631 |
| 16 | 0.9 | 0.844 | 0.321 | 2.667 | 2.5 | 0.952 | 3.567 | 3.344 | 1.274 |
| 17 | 2.2 | 2.063 | 0.786 | 1.733 | 1.625 | 0.619 | 3.933 | 3.688 | 1.405 |
| 18 | 2.2 | 2.063 | 0.786 | 2.533 | 2.375 | 0.905 | 4.733 | 4.438 | 1.69 |
| 19 | 1.3 | 1.219 | 0.464 | 2.4 | 2.25 | 0.857 | 3.7 | 3.469 | 1.321 |
| 20 | 2 | 1.875 | 0.714 | 2 | 1.875 | 0.714 | 4 | 3.75 | 1.429 |
| 21 | 1.8 | 1.688 | 0.643 | 1.733 | 1.625 | 0.619 | 3.533 | 3.313 | 1.262 |
| 22 | 2.35 | 2.203 | 0.839 | 2.4 | 2.25 | 0.857 | 4.75 | 4.453 | 1.696 |
| 23 | 2 | 1.875 | 0.714 | 2 | 1.875 | 0.714 | 4 | 3.75 | 1.429 |
| 24 | 2.15 | 2.016 | 0.768 | 2.267 | 2.125 | 0.81 | 4.417 | 4.141 | 1.577 |
| 25 | 2.2 | 2.063 | 0.786 | 2.667 | 2.5 | 0.952 | 4.867 | 4.563 | 1.738 |
| 26 | 2.1 | 1.969 | 0.75 | 2.4 | 2.25 | 0.857 | 4.5 | 4.219 | 1.607 |
| 27 | 0.255 | 0.239 | 0.091 | 1.493 | 1.4 | 0.533 | 1.748 | 1.639 | 0.624 |
| 28 | 0.105 | 0.098 | 0.038 | 1.4 | 1.313 | 0.5 | 1.505 | 1.411 | 0.538 |
| 29 | 0.16 | 0.15 | 0.057 | 0.933 | 0.875 | 0.333 | 1.093 | 1.025 | 0.39 |
| 30 | 0.235 | 0.22 | 0.084 | 0.867 | 0.813 | 0.31 | 1.102 | 1.033 | 0.393 |
| 31 | 0.24 | 0.225 | 0.086 | 0.84 | 0.788 | 0.3 | 1.08 | 1.013 | 0.386 |
| 32 | 0.065 | 0.061 | 0.023 | 1.16 | 1.088 | 0.414 | 1.225 | 1.148 | 0.438 |
| 33 | 0.035 | 0.033 | 0.013 | 1.013 | 0.95 | 0.362 | 1.048 | 0.983 | 0.374 |
| 34 | 0.105 | 0.098 | 0.038 | 1.173 | 1.1 | 0.419 | 1.278 | 1.198 | 0.457 |
| 35 | 0.055 | 0.052 | 0.02 | 1.04 | 0.975 | 0.371 | 1.095 | 1.027 | 0.391 |
| 36 | 0.14 | 0.131 | 0.05 | 1.053 | 0.988 | 0.376 | 1.193 | 1.119 | 0.426 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





