Submitted:
08 May 2023
Posted:
15 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
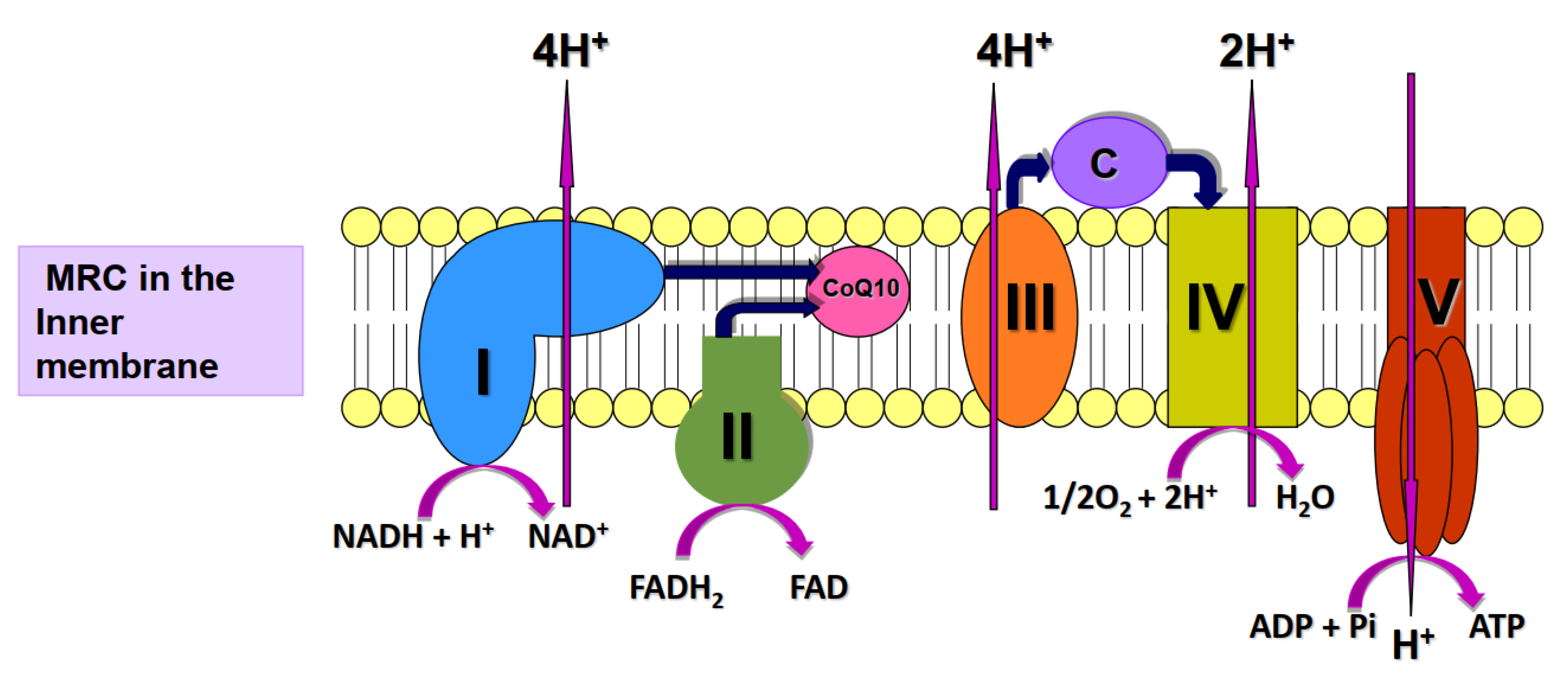
2. Biosynthesis of CoQ10
3. Assessment of primary CoQ10 deficiency
4. Clinical studies relating to COQ mutations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Crane, FL. Biochemical functions of coenzyme Q10. Journal of the American College of Nutrition 2001, 20, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salviati, L. , Trevisson E., Doimo M., Navas P. Primary Coenzyme Q10 Deficiency. In: Adam M.P., Ardinger H.H., Pagon R.A., Wallace S.E., Bean L.J.H., Mirzaa G., Amemiya A., editors. GeneReviews((R)) University of Washington; Seattle, WA, USA: 2017.
- Hughes BG, Harrison PM, Hekimi S. Estimating the occurrence of primary ubiquinone deficiency by analysis of large-scale sequencing data. Sci Rep. 2017, 7, 17744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefely JA, Pagliarini DJ. Biochemistry of mitochondrial coenzyme Q biosynthesis. Trends Biochem Sci. 2017, 42, 824–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allan CM, Awad AM, Johnson JS, Shirasaki DI, Wang C, Blaby-Haas CE, Merchant SS, Loo JA, Clarke CF. Identification of Coq11, a new coenzyme Q biosynthetic protein in the CoQ-synthome in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 2015, 290, 7517–7534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awad AM, Bradley MC, Fernández-Del-Río L, Nag A, Tsui HS, Clarke CF. Coenzyme Q 10 deficiencies: pathways in yeast and humans. Essays Biochem. 2018, 62, 361–376. [CrossRef]
- Yen HC, Yeh WY, Lee SH, Feng YH, Yang SL. Characterization of human mitochondrial PDSS and COQ proteins and their roles in maintaining coenzyme Q10 levels and each other's stability. Biochim Biophys Acta Bioenerg. 2020, 1861, 148192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsgren M, Attersand A, Lake S, Grünler J, Swiezewska E, Dallner G, Climent I. Isolation and functional expression of human COQ2, a gene encoding a polyprenyl transferase involved in the synthesis of CoQ. Biochem J. 2004, 382, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonassen T, Clarke CF. Isolation and functional expression of human COQ3, a gene encoding a methyltransferase required for ubiquinone biosynthesis J Biol Chem. 2000, 275, 12381–12387. [CrossRef]
- Nguyen TP, Casarin A, Desbats MA, Doimo M, Trevisson E, Santos-Ocaña C, Navas P, Clarke CF, Salviati L. Molecular characterization of the human COQ5 C-methyltransferase in coenzyme Q10 biosynthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014, 1841, 1628–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozeir M, Pelosi L, Ismail A, Mellot-Draznieks C, Fontecave M, Pierrel F. Coq6 is responsible for the C4-deamination reaction in coenzyme Q biosynthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 2015, 290, 24140–24151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marbois BN, Clarke CF. The COQ7 gene encodes a protein in saccharomyces cerevisiae necessary for ubiquinone biosynthesis. J Biol Chem. 1996, 271, 2995–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belogrudov GI, Lee PT, Jonassen T, Hsu AY, Gin P, Clarke CF. Yeast COQ4 encodes a mitochondrial protein required for coenzyme Q synthesis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2001, 392, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang A, Ruiz-Lopez M, Slow E, Tarnopolsky M, Lang AE, Munhoz RP. ADCK3-related Coenzyme Q10 Deficiency: A potentially treatable genetic disease. Mov Disord Clin Pract. 2018, 5, 635–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohman DC, Forouhar F, Beebe ET, Stefely MS, Minogue CE, Ulbrich A, et al. Mitochondrial COQ9 is a lipid-binding protein that associates with COQ7 to enable coenzyme Q biosynthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014, 111, E4697–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 16. Tsui HS, Pham NVB, Amer BR, Bradley MC, Gosschalk JE, Gallagher-Jones M, Ibarra H, Clubb RT, Blaby-Haas CE, Clarke CF. Human COQ10A and COQ10B are distinct lipid-binding START domain proteins required for coenzyme Q function. 60, 2019; 60. [CrossRef]
- Yubero, D. , Montero R., Artuch R., Land J.M., Heales S.J., Hargreaves I.P. Biochemical diagnosis of coenzyme q10 deficiency. Mol. Syndromol. 2014, 5, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan AJ, Heales SJ, Mills K, Eaton S, Land JM, Hargreaves IP. Determination of coenzyme Q10 status in blood mononuclear cells, skeletal muscle, and plasma by HPLC with di-propoxy-coenzyme Q10 as an internal standard. Clin Chem. 2005, 51, 2380–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yubero D, Montero R, Ramos M, Neergheen V, Navas P, Artuch R, Hargreaves I. Determination of urinary coenzyme Q10 by HPLC with electrochemical detection: Reference values for a paediatric population. Biofactors. 2015, 41, 424–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollet J, Giurgea I, Schlemmer D, Dallner G, Chretien D, Delahodde A, Bacq D, de Lonlay P, Munnich A, Rötig A. Prenyldiphosphate synthase, subunit 1 (PDSS1) and OH-benzoate polyprenyltransferase (COQ2) mutations in ubiquinone deficiency and oxidative phosphorylation disorders. J Clin Invest. 2007, 117, 765–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasta V, Merritt JL 2nd, Saneto RP, Hahn SH. Next-generation sequencing for mitochondrial diseases: a wide diagnostic spectrum. Pediatr Int. 2012, 54, 585–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardecchia F, De Giorgi A, Palombo F, Fiorini C, De Negri AM, Carelli V, Caporali L, Leuzzi V. Missense PDSS1 mutations in CoenzymeQ10 synthesis cause optic atrophy and sensorineural deafness. Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2021, 8, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellusci M, García-Silva MT, Martínez de Aragón A, Martín MA. Distal phalangeal erythema in an infant with biallelic PDSS1 mutations: Expanding the phenotype of primary Coenzyme Q 10 deficiency. JIMD Rep. 2021, 62, 3–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López LC, Schuelke M, Quinzii CM, Kanki T, Rodenburg RJ, Naini A, Dimauro S, Hirano M. Leigh syndrome with nephropathy and CoQ10 deficiency due to decaprenyl diphosphate synthase subunit 2 (PDSS2) mutations. Am J Hum Genet. 2006, 79, 1125–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iványi B, Rácz GZ, Gál P, Brinyiczki K, Bódi I, Kalmár T, Maróti Z, Bereczki C. Diffuse mesangial sclerosis in a PDSS2 mutation-induced coenzyme Q10 deficiency. Pediatr Nephrol. 2018, 33, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadowski CE, Lovric S, Ashraf S, Pabst WL, Gee HY, Kohl S, et al. A single-gene cause in 29.5% of cases of steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2015, 26, 1279–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman S, Clarke C, Hirano M. 176th ENMC international workshop on the diagnosis and treatment of CoQ10 disorders. Neuromusc Disord. 2011, 22, 76–86. [Google Scholar]
- Quinzii C, Naini A, Salviati L, Trevisson E, Navas P, Dimauro S, Hirano M. A mutation in para-hydroxybenzoate-polyprenyl transferase (COQ2) causes primary coenzyme Q10 deficiency. Am J Hum Genet. 2006, 78, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diomedi-Camassei F, Di Giandomenico S, Santorelli FM, Caridi G, Piemonte F, Montini G, et al. COQ2 nephropathy: a newly described inherited mitochondriopathy with primary renal involvement. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007, 18, 2773–2780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scalais E, Chafai R, Van Coster R, Bindl L, Nuttin C, Panagiotaraki C, et al. Early myoclonic epilepsy, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and subsequently a nephrotic syndrome in a patient with CoQ10 deficiency caused by mutations in para-hydroxybenzoate-polyprenyl transferase (COQ2). Eur J Paediatr Neurol. 2013, 17, 625–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desbats MA, Vetro A, Limongelli I, Lunardi G, Casarin A, Doimo M, et al. Primary coenzyme Q10 deficiency presenting as fatal neonatal multiorgan failure. Eur J Hum Genet. 2015, 23, 1254–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eroglu FK, Ozaltin F, Gönç N, Nalçacıoğlu H, Özçakar ZB, Yalnızoğlu D, Güçer Ş, Orhan D, Eminoğlu FT, Göçmen R, Alikaşifoğlu A, Topaloğlu R, Düzova A. Response to Early Coenzyme Q10 Supplementation Is not Sustained in CoQ10 Deficiency Caused by CoQ2 Mutation. Pediatr Neurol. 2018, 88, 71–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu K, Mao XY, Yao Y, Cheng H, Zhang XJ. Clinical analysis of one infantile nephrotic syndrome caused by COQ2 gene mutation and literature review. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2018, 56, 662–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starr MC, Chang IJ, Finn LS, Sun A, Larson AA, Goebel J, Hanevold C, Thies J, Van Hove JLK, Hingorani SR, Lam C. COQ2 nephropathy: a treatable cause of nephrotic syndrome in children. Pediatr Nephrol. 2018, 33, 1257–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu X, Wang W, Liu Y, Chen W, Zhao L. A steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome in an infant resulting from a consanguineous marriage with COQ2 and ARSB gene mutations: a case report. BMC Med Genet. 2019, 20, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 36. Abdelhakim AH, Dharmadhikari AV, Ragi SD, de Carvalho JRL Jr, Xu CL, Thomas AL, Buchovecky CM, Mansukhani MM, Naini AB, Liao J, Jobanputra V, Maumenee IH, Tsang SH. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2020 Nov 13;15, 320. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13023-020-01600-8.Compound heterozygous inheritance of two novel COQ2 variants results in familial coenzyme Q deficiency. Orphanet J Rare Dis.
- Li M, Yue Z, Lin H, Wang H, Chen H, Sun L. COQ2 mutation associated isolated nephropathy in two siblings from a Chinese pedigree. Ren Fail. 2021, 43, 97–101. [CrossRef]
- Rosado Santos R, Rodrigues M, Loureiro T. Prenatal diagnosis of lissencephaly associated with biallelic pathologic variants in the COQ2 gene. Prenatal diagnosis of lissencephaly associated with biallelic pathologic variants in the COQ2 gene. Acta Med Port. 2022. [CrossRef]
- 39. Stallworth JY, Blair DR, Slavotinek A, Moore AT, Duncan JL, de Alba Campomanes AG. Retinopathy and optic atrophy in a case of COQ2-related primary coenzyme Q10 deficiency. Ophthalmic Genet. [CrossRef]
- Drovandi S, Lipska-Ziętkiewicz BS, Ozaltin F, Emma F, Gulhan B, Boyer O, et al. Variation of the clinical spectrum and genotype-phenotype associations in Coenzyme Q10 deficiency associated glomerulopathy. Kidney Int. 2022, 102, 592–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drovandi S, Lipska-Ziętkiewicz BS, Ozaltin F, Emma F, Gulhan B, Boyer O, et al. Oral Coenzyme Q10 supplementation leads to better preservation of kidney function in steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome due to primary Coenzyme Q10 deficiency. Kidney Int. 2022, 102, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantle, D. Turton N, Hargreaves I. Multiple system atrophy: role of CoQ10. J Clin Med Res.
- Salviati L, Trevisson E, Rodriguez Hernandez MA, Casarin A, Pertegato V, Doimo M, et al. Haploinsufficiency of COQ4 causes coenzyme Q10 deficiency. Med Genet. 2012, 49, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brea-Calvo G, Haack TB, Karall D, Ohtake A, Invernizzi F, Carrozzo R, et al. COQ4 mutations cause a broad spectrum of mitochondrial disorders associated with CoQ10 deficiency. Am J Hum Genet. 2015, 96, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung WK, Martin K, Jalas C, Braddock SR, Juusola J, Monaghan KG, et al. Mutations in COQ4, an essential component of coenzyme Q biosynthesis, cause lethal neonatal mitochondrial encephalomyopathy. J Med Genet. 2015, 52, 627–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Moya D, Castaño J, Santos-Ocaña C, Navas P, Menendez P. Generation, genome edition and characterization of iPSC lines from a patient with coenzyme Q 10 deficiency harboring a heterozygous mutation in COQ4 gene. Stem Cell Res. 2017, 24, 144–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sondheimer N, Hewson S, Cameron JM, Somers GR, Broadbent JD, Ziosi M, Quinzii CM, Naini AB. Novel recessive mutations in COQ4 cause severe infantile cardiomyopathy and encephalopathy associated with CoQ 10 deficiency. Mol Genet Metab Rep. 2017, 12, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch AM, Kamsteeg EJ, Rodenburg RJ, van Deutekom AW, Buis DR, Engelen M, Cobben JM. Coenzyme Q10 deficiency due to a COQ4 gene defect causes childhood-onset spinocerebellar ataxia and stroke-like episodes. Mol Genet Metab Rep. 2018, 17, 19–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caglayan AO, Gumus H, Sandford E, Kubisiak TL, Ma Q, Ozel AB, Per H, Li JZ, Shakkottai VG, Burmeister M. COQ4 Mutation Leads to Childhood-Onset Ataxia Improved by CoQ10 Administration. Cerebellum. 2019, 18, 665–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 50. Ling TK, Law CY, Yan KW, Fong NC, Wong KC, Lee KL, Chu WC, Brea-Calvo G, Lam CW. Clinical whole-exome sequencing reveals a common pathogenic variant in patients with CoQ 10 deficiency: An underdiagnosed cause of mitochondriopathy. Clin Chim Acta. [CrossRef]
- Lu M, Zhou Y, Wang Z, Xia Z, Ren J, Guo Q. Clinical phenotype, in silico and biomedical analyses, and intervention for an East Asian population-specific c.370G>A (p.G124S) COQ4 mutation in a Chinese family with CoQ10 deficiency-associated Leigh syndrome. J Hum Genet. 2019, 64, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu MH, Tsang MH, Lai S, Ho MS, Tse DML, Willis B, et al. Primary coenzyme Q10 deficiency-7: expanded phenotypic spectrum and a founder mutation in southern Chinese. NPJ Genom Med. 2019, 4, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen XR, Xu JP, Yao YH. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. Primary coenzyme Q10 deficiency-7: a case report and literature review. 2020, 58, 928–932. [CrossRef]
- Mero S, Salviati L, Leuzzi V, Rubegni A, Calderan C, Nardecchia F, et al. New pathogenic variants in COQ4 cause ataxia and neurodevelopmental disorder without detectable CoQ 10 deficiency in muscle or skin fibroblasts. J Neurol. 2021, 268, 3381–3389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laugwitz L, Seibt A, Herebian D, Peralta S, Kienzle I, Buchert R, et al. Human COQ4 deficiency: delineating the clinical, metabolic and neuroimaging phenotypes. J Med Genet. 2022, 59, 878–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malicdan MCV, Vilboux T, Ben-Zeev B, Guo J, Eliyahu A, Pode-Shakked B, et al. A novel inborn error of the coenzyme Q10 biosynthesis pathway: cerebellar ataxia and static encephalomyopathy due to COQ5 C-methyltransferase deficiency. Hum Mutat. 2018, 39, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heeringa SF, Chernin G, Chaki M, Zhou W, Sloan AJ, Ji Z, et al. COQ6 mutations in human patients produce nephrotic syndrome with sensorineural deafness. Clin Invest. 2011, 121, 2013–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park E, Ahn YH, Kang HG, Yoo KH, Won NH, Lee KB, Moon KC, Seong MW, Gwon TR, Park SS, Cheong HI. COQ6 Mutations in Children With Steroid-Resistant Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis and Sensorineural Hearing Loss. Am J Kidney Dis. 2017, 70, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li GM, Cao Q, Shen Q, Sun L, Zhai YH, Liu HM, An Y, Xu H. Gene mutation analysis in 12 Chinese children with congenital nephrotic syndrome. BMC Nephrol. 2018, 29, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao Q, Li GM, Xu H, Shen Q, Sun L, Fang XY, Liu HM, Guo W, Zhai YH, Wu BB. Coenzyme Q(10) treatment for one child with COQ6 gene mutation induced nephrotic syndrome and literature review. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2017, 55, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song CC, Hong Q, Geng XD, Wang X, Wang SQ, Cui SY, Guo MD, Li O, Cai GY, Chen XM, Wu D. New Mutation of Coenzyme Q 10 Monooxygenase 6 Causing Podocyte Injury in a Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis Patient. Chin Med J (Engl). 2018, 131, 2666–2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stańczyk M, Bałasz-Chmielewska I, Lipska-Ziętkiewicz B, Tkaczyk M. CoQ10-related sustained remission of proteinuria in a child with COQ6 glomerulopathy-a case report. Pediatr Nephrol. 2018, 33, 2383–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuruk Yildirim Z, Toksoy G, Uyguner O, Nayir A, Yavuz S, Altunoglu U, et al. Primary coenzyme Q10 Deficiency-6 (COQ10D6): Two siblings with variable expressivity of the renal phenotype. Eur J Med Genet. 2020, 63, 103621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 64. Justine Perrin R, Rousset-Rouvière C, Garaix F, Cano A, Conrath J, Boyer O, Tsimaratos M. COQ6 mutation in patients with nephrotic syndrome, sensorineural deafness, and optic atrophy. JIMD Rep. [CrossRef]
- Wang N, Zheng Y, Zhang L, Tian X, Fang Y, Qi M, Du J, Chen S, Chen S, Li J, Shen B, Wang L. A Family Segregating Lethal Primary Coenzyme Q10 Deficiency Due to Two Novel COQ6 Variants. Front Genet. 2022, 12, 811833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leeuwen L, Lubout CMA, Nijenhuis HP, Meiners LC, Vos YJ, Herkert JC. Expanding the clinical spectrum of primary coenzyme Q10 deficiency type 6: The first case with cardiomyopathy. Clin Genet. 2022, 102, 350–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam DW, Park SS, Lee SM, Suh MW, Park MK, Song JJ, Choi BY, Lee JH, Oh SH, Moon KC, Ahn YH, Kang HG, Cheong HI, Kim JH, Lee SY. Effects of CoQ10 replacement therapy on the audiological characteristics of pediatric patients with COQ6 variants. Biomed Res Int. 2022, 2022, 5250254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freyer C, Stranneheim H, Naess K, Mourier A, Felser A, Maffezzini C, et al. Rescue of primary ubiquinone deficiency due to a novel COQ7 defect using 2,4-dihydroxybensoic acid. J Med Genet. 2015, 52, 779–783. 52. [CrossRef]
- Wang Y, Smith C, Parboosingh JS, Khan A, Innes M, Hekimi S. Pathogenicity of two COQ7 mutations and responses to 2,4-dihydroxybenzoate bypass treatment. J Cell Mol Med. 2017, 21, 2329–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwong AK, Chiu AT, Tsang MH, Lun KS, Rodenburg RJT, Smeitink J, Chung BH, Fung CW. A fatal case of COQ7-associated primary coenzyme Q 10 deficiency. JIMD Rep. 2019, 47, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang Y, Gumus E, Hekimi S. Mol Genet Metab Rep. A novel COQ7 mutation causing primarily neuromuscular pathology and its treatment options. Mol Genet Metab Rep. 2022, 31, 100877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollet J, Delahodde A, Serre V, Chretien D, Schlemmer D, Lombes A, Boddaert N, Desguerre I, de Lonlay P, de Baulny HO, Munnich A, Rötig A. CABC1 gene mutations cause ubiquinone deficiency with cerebellar ataxia and seizures. Am J Hum Genet. 2008, 82, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagier-Tourenne C, Tazir M, López LC, Quinzii CM, Assoum M, Drouot N, et al. ADCK3, an ancestral kinase, is mutated in a form of recessive ataxia associated with coenzyme Q10 deficiency. Am J Hum Genet. 2008, 82, 661–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumkin L, Leshinsky-Silver E, Zerem A, Yosovich K, Lerman-Sagie T, Lev D. Heterozygous Mutations in the ADCK3 Gene in Siblings with Cerebellar Atrophy and Extreme Phenotypic Variability. JIMD Rep. 2014, 12, 103–107. [CrossRef]
- Hikmat O, Tzoulis C, Knappskog PM, Johansson S, Boman H, Sztromwasser P, Lien E, Brodtkorb E, Ghezzi D, Bindoff LA. ADCK3 mutations with epilepsy, stroke-like episodes and ataxia: a POLG mimic? Eur J Neurol. 2016, 23, 1188–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen JC, Whitford W, Swan B, Taylor J, Love DR, Hill R, Molyneux S, George PM, Mackay R, Robertson SP, Snell RG, Lehnert K. Compound Heterozygous Inheritance of Mutations in Coenzyme Q8A Results in Autosomal Recessive Cerebellar Ataxia and Coenzyme Q 10 Deficiency in a Female Sib-Pair. JIMD Rep. 2018, 42, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang A, Ruiz-Lopez M, Slow E, Tarnopolsky M, Lang AE, Munhoz RP. ADCK3-related Coenzyme Q10 Deficiency: A Potentially Treatable Genetic Disease. Mov Disord Clin Pract. 2018, 5, 635–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair P, Lama M, El-Hayek S, Abou Sleymane G, Stora S, Obeid M, Al-Ali MT, Delague V, Mégarbané A. COQ8A and MED25 Mutations in a Child with Intellectual Disability, Microcephaly, Seizures, and Spastic Ataxia: Synergistic Effect of Digenic Variants? Mol Syndromol. 2019, 9, 319–323. [CrossRef]
- Schirinzi T, Favetta M, Romano A, Sancesario A, Summa S, Minosse S, Zanni G, Castelli E, Bertini E, Petrarca M, Vasco G. One-year outcome of coenzyme Q10 supplementation in ADCK3 ataxia (ARCA2). Cerebellum Ataxias. 2019, 6, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 80. Uccella S, Pisciotta L, Severino M, Bertini E, Giacomini T, Zanni G, Prato G, De Grandis E, Nobili L, Mancardi MM. Photoparoxysmal response in ADCK3 autosomal recessive ataxia: a case report and literature review. Epileptic Disord. [CrossRef]
- Paprocka J, Nowak M, Chuchra P, Śmigiel R. COQ8A-Ataxia as a manifestation of primary Coenzyme Q deficiency. Metabolites. 2022, 12, 955. [CrossRef]
- 82. Değerliyurt A, Gülleroğlu NB, Kibar Gül AE. Primary CoQ10 deficiency with a severe phenotype due to the c.901 C > T (p.R301W) mutation in the COQ8A gene. Int J Neurosci. [CrossRef]
- Traschütz A, Schirinzi T, Laugwitz L, Murray NH, Bingman CA, Reich S, et al. Clinico-Genetic, Imaging and Molecular Delineation of COQ8A-Ataxia: A Multicenter Study of 59 Patients. Ann Neurol. 2020, 88, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horvath R, Czermin B, Gulati S, Demuth S, Houge G, Pyle A, et al. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2012, 83, 174–178. [CrossRef]
- 85. Mignot C, Apartis E, Durr A, Marques Lourenço C, Charles P, et al. Phenotypic variability in ARCA2 and identification of a core ataxic phenotype with slow progression. Orphanet J Rare Dis. [CrossRef]
- Mallaret M, Renaud M, Redin C, Drouot N, Muller J, Severac F, et al. Validation of a clinical practice-based algorithm for the diagnosis of autosomal recessive cerebellar ataxias based on NGS identified cases. J Neurol. 2016, 263, 1314–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 87. Ashraf S, Gee HY, Woerner S, Xie LX, Vega-Warner V, Lovric S, et al. ADCK4 mutations promote steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome through CoQ10 biosynthesis disruption. J Clin Invest. 5189. [CrossRef]
- Korkmaz E, Lipska-Ziętkiewicz BS, Boyer O, Gribouval O, Fourrage C, Tabatabaei M, et al. ADCK4-Associated Glomerulopathy Causes Adolescence-Onset FSGS. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016, 27, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atmaca M, Gülhan B, Atayar E, Bayazıt AK, Candan C, Arıcı M, Topaloğlu R, Özaltın F. Long-term follow-up results of patients with ADCK4 mutations who have been diagnosed in the asymptomatic period: effects of early initiation of CoQ10 supplementation. Turk J Pediatr. 2019, 61, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng C, Wang Q, Wang J, Liu F, Shen H, Fu H, Mao J. Coenzyme Q10 supplementation therapy for 2 children with proteinuria renal disease and ADCK4 mutation: Case reports and literature review. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017, 96, e8880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song X, Fang X, Tang X, Cao Q, Zhai Y, Chen J, et al. COQ8B nephropathy: Early detection and optimal treatment. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2020, 8, e1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 92. Duncan AJ, Bitner-Glindzicz M, Meunier B, Costello H, Hargreaves IP, López LC, et al. A nonsense mutation in COQ9 causes autosomal-recessive neonatal-onset primary coenzyme Q10 deficiency: a potentially treatable form of mitochondrial disease. Am J Hum Genet. [CrossRef]
- Danhauser K, Herebian D, Haack TB, Rodenburg RJ, Strom TM, Meitinger T, et al. Fatal neonatal encephalopathy and lactic acidosis caused by a homozygous loss-of-function variant in COQ9. Eur J Hum Genet. 2016, 24, 450–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith AC, Ito Y, Ahmed A, Schwartzentruber JA, Beaulieu CL, Aberg E, et al. A family segregating lethal neonatal coenzyme Q 10 deficiency caused by mutations in COQ9. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2018, 41, 719–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olgac A, Öztoprak Ü, Kasapkara ÇS, Kılıç M, Yüksel D, Derinkuyu EB, et al. A rare case of primary coenzyme Q10 deficiency due to COQ9 mutation. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2020, 33, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 96. Vrablik M, Zlatohlavek L, Stulc T, Adamkova V, Prusikova M, Schwarzova L, Hubacek JA, Ceska R. Statin-associated myopathy: from genetic predisposition to clinical management. Physiol Res. [CrossRef]
- López-Lluch G, Del Pozo-Cruz J, Sánchez-Cuesta A, Cortés-Rodríguez AB, Navas P. Bioavailability of coenzyme Q10 supplements depends on carrier lipids and solubilization. Nutrition. 2019, 57, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Author | Gene | Condition | Number of patients | CoQ10 dose and Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mollet et al [20] |
COQ1 (PDSS1) |
Infantile neurosensorial deafness and optic atrophy | 2 | |
| Vasta et al [21] | Kidney failure and death at 16 months | 1 | ||
| Nardecchia et al [22] | Sensorineural deafness and optic atrophy (ages 6 and 14 years) | 2 | ||
| Bellusci et al [23] | Numerous morbidities; death aged 3 years | 1 | 15 mg/Kg/day No effect on disease progression | |
| Lopez et al [24] |
COQ1 (PDSS2) |
Nephrotic syndrome & encephalopathy; died at 8 months | 1 | 50 mg/day. No effect on disease progression |
| Ivanyi et al [25] | Numerous morbidities; death at 7 months | 1 | ||
| Sadowski et al [26] | Less severe morbidities | 2 _________ 2 |
||
| Rahman et al [27] | Infantile onset encephalopathy | |||
| Quinzii et al [28] | COQ2 | Infantile nephropathy | 2 | |
| Diomedi-Camassei et al [29] | Encephalopathy and nephropathy in first patient who died at 6 months. Non-fatal nephropathy in second patient. | 2 | 30 mg/Kg/day clinical stabilisation in second patient | |
| Mollet et al [20] | Fatal neonatal nephropathy | 1 | ||
| Scalais et al [30] | Myoclonic epilepsy and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy; died at 5 months | 1 | 5 mg/Kg/day did not prevent fatality | |
| Desbats et al [31] | Newborn multi-organ failure and death | 1 | ||
| Eroglu et al [32] | Infantile renal and neurological symptoms | 4 | Supplement normalised renal function in 2 patients | |
| Xu et al [33] | Infantile nephrotic syndrome | 1 | 30 mg/Kg/day improved renal function | |
| Starr et al [34] | Nephrotic syndrome (patients 2-10 years old) | 3 | 30mg/Kg/day restored renal function in 2 patients | |
| Wu et al [35] | Fatal neuropathy at 6 months | 1 | ||
| Abdelhakim et al [36] | Nephropathy and retinopathy | 3 | Visual deterioration prevented after 30 mg/Kg/day CoQ10 for 6 months | |
| Li et al [37] |
Infantile nephropathy | 2 | Proteinuria reduced after 30 mg/Kg/day CoQ10 | |
| Rosado-Santos et al [38] |
Newborn fatality with severe fetal growth restriction | 1 | ||
| Stallworth et al [39] | 8 year old with nephropathy and optic atrophy | 1 | ||
| Drovandi et al [40, 41] |
Review articles to include many of the above studies relating to COQ2, plus some previously unreported cases. | 63 | Partial or complete remission of proteinuria in more than half of patients after CoQ10 | |
| No reports identified |
COQ3 | |||
| Salviati et al [43] | COQ4 | 3 year old with neuromuscular symptoms | 1 | Significant symptomatic improvement after 30mg/kg/day CoQ10 |
| Brea-Calvo et al [44] | Neurological deterioration with neonatal or early infancy fatality | 5 | ||
| Chung et al [45] | Neurological deterioration and early deaths | 6 | ||
| Romero-Moya et al [46] | Mental retardation and lethal rhabdomyolysis aged 4 | 1 | ||
| Sondheimer et al [47] | Seizures, cardiomyopathy and death in infancy | 1 | ||
| Bosch et al [48] | Infantile spinocerebellar ataxia and stroke-like episodes | 1 | No improvement after 1000 mg/day CoQ10 | |
| Caglayan et al [49] | Childhood onset slow progressive ataxia | 2 | One sibling improved after 200 mg/day CoQ10 for 1 month | |
| Ling et al [50] | Infantile encephalopathy or cardiomyopathy | 3 | ||
| Lu et al [51] | 2 month old with Leigh syndrome | 1 | Patient stabilised after CoQ10 | |
| Yu et al [52] | Numerous morbidities with neonatal or infantile onset | 11 | Seizure control improved in 2 patients after 15-40 mg/Kg/day CoQ10; no benefit in 5 patients who subsequently died | |
| Chen et al [53] | 5 month old with epileptic seizures | 1 | ||
| Mero et al [54] | Motor impairment and ataxia | 2 | ||
| Malicdan et al [56] | COQ5 | Seizures, ataxia and cognitive disability in early childhood | 3 | Symptomatic improvement in all cases after 15 mg/Kg/day CoQ10 for 6 months |
| Heeringa et al [57] | COQ6 | Early onset (1-2 years) nephrotic and sensory syndromes | 13 | Symptomatic improvement in some patients with 100mg/day CoQ10 |
| Sadowski et al [26] | Infancy/early childhood onset nephropathy | 6 | ||
| Park et al [58] | Renal disease (onset 15-47 months) requiring transplant | 6 | ||
| Li et al [59] | One year old with proteinuria | 1 | Proteinuria completely resolved after 30 mg/day CoQ10 for 3 months | |
| Cao et al [60] | Infantile nephrotic syndrome | 1 | Normal renal function restored after 30 mg/Kg/day CoQ10 for 3 months | |
| Song et al [61] | Proteinuria in 16 year old | 1 | 50% reduction in proteinuria after CoQ10 | |
| Stanczyk et al [62] | Glomerulopathy ion 4 year old | 1 | Complete symptomatic remission after 30 mg/Kg/day CoQ10 for 1 month | |
| Yildirim et al [63] | Nephrotic syndrome and sensorineural deafness in 7 year old | 1 | ||
| Perrin et al [64] | Renal disease, deafness and optic neuropathy | 1 | CoQ10 analogue, idebenone, improved vision | |
| Wang et al [65] | Numerous morbidities: died in infancy | 2 | ||
| Leeuwen et al [66] | 19 month old with fatal cardiomyopathy | 1 | ||
| Nam et al [67] | Patients (<18 years) with nephropathy and deafness | 12 | Hearing loss in some patients responded well after 30mg/kg CoQ10 | |
| Freyer et al [68] | COQ7 | Numerous morbidities oin 9 year old; muscle CoQ10 levels severely decreased | 1 | |
| Wang et al [69] | Spasticity and sensorineural hearing loss in 6 yesar old; moderate decrease in CoQ10 levels | 1 | ||
| Kwong et al [70] | Fatal morbidities at 1 year | 1 | Poor response to treatment after 10 mg/Kg/day CoQ10 | |
| Wang et al [71] | 4 year old with numerous morbidities: 45% reduction in fibroblast CoQ10 levels | 1 | ||
| Mollet et al [72] |
COQ8A | Seizures and cerebellar atrophy (ages 18-36 months) | 4 | Not improved after 15 mg/Kg/day CoQ10 |
| Lagier-Tourenne et al [73] | Childhood onset cerebellar atrophy and ataxia | 6 | ||
| Blumkin et al [74] |
Ataxia and mild dysarthria | 2 | Ataxia partially resolved after 20 mg/Kg/day CoQ10 | |
| Hikmat et al [75] | Childhood onset cerebellar ataxia and epilepsy | 3 | ||
| Jacobsen et al [76] | Childhood onset cerebellar atrophy and ataxia | 2 | Improvement in ataxia and mental capacity after 20mg/kg/day CoQ10 | |
| Nair et al [78] |
5 year old with intellectual disability and ataxia | 1 | Improved motor performance following 15 mg/kg/day CoQ10 | |
| Schirinzi et al [79] | Ataxia in patients aged 4-12 months | 4 | ||
| Uccella et al [80] |
Childhood onset ataxia | 1 | Disease progression slowed after CoQ10 | |
| Paprocka et al [81] | Cerebellar ataxia and developmental regression in 22 month old | 1 | Improved communi-cation and growth after 300 mg/day CoQ10 | |
| Degerliyurt et al [82] | 16 year old with ataxia, cerebellar atrophy and cardiomyopathy | 1 | treatment with CoQ10 started at too late a stage to prevent death of the patient. | |
| Traschutz et al 2020 | Review incorporating some previously published data; cerebellar ataxia in all patients with mean onset age 7 years | 64 | 50% of patients responded after mean dose of 11 mg/Kg/day CoQ10 | |
| Ashraf et al [87] | COQ8B | Nephropathy | 1 | Partial remission after CoQ10 |
| Korkmaz et al [88] | Adolescent nephropathy | 26 | Improved proteinuria after 15 mg/kg/day CoQ10 in 2 patients | |
| Atmaca et al [89] | Nephropathy | 8 | Improved proteinuria after CoQ10 | |
| Feng et al [90] | Patients aged 9 months and 11 years with proteinuria | 2 | Younger subject ahowed good response after 15 mg/kg/day CoQ10 | |
| Song et al [91] | Patients aged 1-18 years with renal disease | 20 | Reduced proteinuria in trial group of 5 subjects after 15-30 mg/Kg/day CoQ10 | |
| Duncan et al [92] | COQ9 | Multiple morbidities; died aged 2 years | 1 | Up to 300mg/day CoQ10 did not prevent fatality |
| Danhauser et al [93] | Fatal neonatal lactic acidosis and encephalopathy | 1 | ||
| Smith et al [94] | Multisysystem disease in 4 siblings, 2 of whom died soon after birth | 4 | ||
| Olgac et al [95] | Microcephaly and seizures in 9 month old | 1 | No improvement after 5-50 mg/Kg/day CoQ10 | |
| No reports identified |
COQ 10A and 10B |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




