1. Introduction
Colorectal cancer is the third most common cancer in the world, and it is currently treated by surgical removal of lesions [
1]. However, due to its high postoperative recurrence rate and frequent complications, medical treatment of colorectal cancer is not ideal [
2]. Therefore, with the rapid development of molecular biology, it is hoped to seek new materials and novel methods for treating colon cancer. Human colon cancer cell HCT116 is the most commonly used cell model in anti-colon cancer studies [
3].
As a normal flora in the intestine, lactic acid bacteria are usually added to food as starters or probiotics [
4]. Lactic acid bacteria can modulate the composition of intestinal microbiota, inhibit the growth of harmful microorganisms, and repair damages of the gastrointestinal tract [
5]. A large number of experiments have proved that extracellular polysaccharides secreted by lactic acid bacteria, heat inactivated lactic acid bacteria cells, and peptidoglycan in the cell wall of lactic acid bacteria have obvious inhibitory effects on colon cancer cells [
6,
7,
8,
9]. In recent years, lactic acid bacteria, as a popular material for anti-tumor, especially for colon cancer, have the advantages of low production cost, low extraction difficulty, and high product safety. They have attracted the attention of tumor researchers. Tuo et al. [
10] reported that the cell wall of Lactobacillus paracasei M5 could promote the release of IL-12, IFN-γ, TNF-α, and the components such as peptidoglycan and lipoteichoic acid in the cell wall could effectively inhibit the growth of colon cancer cells and induce their apoptosis. At present, studies have indicated that lactic acid bacteria have the effect of inhibiting colon cancer, but there are few reports on their anti-colon cancer mechanism. In this study, thus, the inhibitory effect and mechanism of heat-inactivated plant-derived lactic acid bacteria on human colon cancer cell HCT116 were investigated by using CCK-8 assay, Caspase3 enzyme activity detection, flow cytometry measurement, and Western blot analysis. The results will lay the foundation for applying plant-derived lactic acid bacteria in the prevention and treatment of colon cancer.
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Experimental subjects
The lactic acid bacteria used in this study were 577, 602, 722, 933, 664, 647, 662, 755, 6-12, 856, Z1-11, 729, Z22, yz16-3, 985, 674, Z1-6, H3D, LGG and 6D-16. These strains were obtained from the plant-derived probiotic strain library in the Department of Food Science and Technology, Hunan Agricultural University, China.
Human colon cancer cell HCT116 was purchased from Shanghai Cell Bank, China.
2.2. Experimental reagents
Caspase3 Activity Detection Kit (Biyuntian Biologics, China), Annexin V/PI Dual Staining Kit (Biyuntian Biologics, China), Procedural cooling box (Nalgene, America), Enhanced cell viability assay kit (CCK-8) (Shangbao Biologics, China), MCCOY'S 5A MEDIUM (Biological Industries, Israel), Phosphate Buffered Saline (Biological Industries, Israel), Pancreatic Enzyme (Biological Industries, Israel), dimethyl sulfoxide solution (Sigema, America), fetal bovine serum (Sigema, America), Ferrostatin-1 (Sigema, America), sodium chloride (Sinopharm Chemical Actual Co., Ltd, China), absolute ethanol (Sinopharm Chemical Actual Co., Ltd. , China), Tris-HCl buffer (Solaebio, China), gelab solution (30%) (Solaebio, China), TEMED (Aladdin), primary antibody / secondary antibody dilution (Aladdin), primary and secondary antibodies of GPX4 (Cell Signaling Technology, America), Xct (Cell Signaling Technology, America), and GAPDH (Cell Signaling Technology, America) were used in this study.
2.3. Instruments and Equipment
Cell culture incubator (ULTS1368, Thermo Scientific), high-speed refrigerated centrifuge (Heraeus Multifuge X1R, Thermo Scientific), mixed-spin oscillator (Thermo Scientific), full-wavelength microplate reader (1510, Thermo Scientific), Thermostatic bacterial incubator (SPL-250, Labortery), Water Bath Box (DZKW, Honour), automatic autoclave sterilizer (SQ810C, Chongqing Yamato Technology Co., Ltd.), 6-well plates (Nest), 12-well plates (Nest), 96-well plates (Nest), Ultra-low temperature freezer (DW-HL340, MELNG), Cell Flow Cytometry (MoFlo XDP, Beckman), Supply Electrophoresis Instrument (Mini Pro 300V Power, Major Science), and Electrophoresis Tank ( Labnet Sub System 70, Labnet) were used in this study.
2.4. Preparation of bacterial suspensions
After three consecutive activation at 37 °C, the test strain was thermally inactivated at 90°C for 30 min. After centrifugation at 12000 rpm for 15 min, the supernatant was removed. The pellet was washed with sterile saline and resuspended in MCCOY's 5A MEDIUM. The cell density was measured with UV spectrophotometer[
11]. The desired concentration of different heat inactivated bacterial suspension required for each experiment was obtained.
2.5. Determination of the inhibition rate of human colon cancer cell HCT116 by plant-derived lactic acid bacteria
The cell suspension of human colon cancer cell HCT116 at a density of 5×10
4 cells/mL was seeded in 96-well plates (100 μL/well), cultured at 37℃, 5% CO
2 for 18 h. Then, the supernatant was removed. The experiment was divided into control group (MCCOY'S 5A MEDIUM 100 μL per well), bacterial groups (100 μL of 1×10
6 CFU/mL or 1×10
8 CFU/mL heat-inactivated bacterial suspension), and blank group (PBS buffer 100 μL per well). Five parallel wells were set for each treatment. After being incubated at 37℃ with 5% CO
2 for 18 h, the supernatant was removed and 100 μL of 10-fold diluted CCK-8 reagent was added to each well, followed by incubation for 2 h in the dark. The absorbance (A) was measured by a microplate reader at 490 nm [
12,
13], and the inhibition rate was calculated according to the inhibition rate formula [
14].
2.6. Effect of the concentration of heat inactivated bacteria suspension of strain 729 on inhibition rate of HCT116 cells
The test method was the same as 2.5. Seven concentration gradients of heat inactivated bacteria suspension of strain 729 were set as 1×103 CFU/mL, 1×104 CFU/mL, 1×105 CFU/mL, 1×106 CFU/mL, 1×107 CFU/mL, 1×108 CFU/mL and 1×109CFU/mL. The proliferation inhibition rate of HCT116 cells was determined, and the relationship between the suspension concentration and the inhibition rate was plotted.
2.7. Effect of strain 729 on apoptosis of HCT116 cells based on caspase 3 activity
HCT116 cells suspension with a density of 5×10
4 cells /mL was seeded in 6-well plates (2 mL/well). For the control group, MCCOY'S 5A medium was added. For the bacterial group, serial dilutions of heat-inactivated strain 729 suspension (1×10
5 cfu/mL, 1×10
7 cfu/mL and 1×10
8 cfu/mL) were added (2 mL/well). Five parallel wells were set for each concentration and incubated at 37°C for 18 h in 5% CO
2. Cells were isolated and collected according to the instructions of Caspase3 activity assay kit. Lysate was added at the ratio of 100 μL lysate per 2 million cells, and the precipitate was resuspended in an ice bath for 15 min. After centrifugation at 16000 ×g at 4℃ for 15 min, the supernatant was transferred to a 96-well plate treated with ice bath in advance. According to the ratio of testing buffer: sample to be tested: Ac-DEVD-pNA (2mM) = 4:5:1, a total volume of 100 μL solution was prepared for each well. The absorbance value at 405 nm was measured with a microplate reader, and number of the activity unit of Caspase3 was calculated [
15,
16,
17].
2.8. Effect of strain 729 on cell cycle of HCT116 cells
Cell suspension of HCT116 with a density of 5×10
4 cells / mL was seeded in 12-well plates (1mL/well). 1mL of MCCOY's 5A medium was added to each well in the positive control group or the negative control group. 1 mL of heat-inactivated bacterial suspension of strain 729 at a concentration of 1×10
8 CFU/mL was added to each well in the bacterial group. Three parallel wells were set for each group and incubated at 37℃ with 5%CO
2 for 18 h. Cells in each group were isolated and collected in EP tubes (the positive control group was incubated with H
2O
2 medium for 5 min in advance), and 400μL of binding solution was added to each tube. Annexin V/PI double staining was performed for 15 min in darkness. One hundred microliter of binding solution was added to each tube and then analyzed by flow cytometry [
18,
19].
2.9. Ferroptosis induced by strain 729 in HCT116 cells
Cell suspension of HCT116 with a density of 5×10
4 cells /mL was seeded in 12-well plates (2 mL/well). 1 mL of MCCOY's 5A medium was added to each well in the positive control group or the negative control group. 1 mL of heat-inactivated suspension of strain 729 at a concentration of 1×10
8 CFU/mL was added to each well in the bacterial group. One milliliter of heat-inactivated suspension of strain 729 at a concentration of 1×10
8 CFU/mL prepared with 10 μmol/L Ferrostatin-1 was added to each well in the inhibitor group. Three parallel wells were set in each group [
20,
21,
22]. Cell handling, staining, and detection were the same as
Section 2.8.
2.10. Effect of strain 729 on related proteins in HCT116 cells
Cell plate, culture and grouping were the same as
Section 2.7. After the supernatant was removed in the bacterial group, 2 mL of heat inactivated suspension of strain 729 at a concentration of 1×10
8CFU/mL was added to each well and incubated at 37℃ with 5% CO
2 for 18 h. Cells were lysed and collected. After being incubated for 10 min in a dry bath at 100℃, 6× loading buffer was added to each sample and incubated at 100℃ for 10 min again, followed by storing at -20℃. The laminated gel and separation gel were prepared in a glass splint. Five microliter of protein marker was loaded, whereas 8 μL of each sample was loaded in each well. The samples were electrophoresed at 70V-110V for 2 h, and the protein gel was removed and transmembraned for 45 min (70V, 260mA). After being blocked for 1 h, the gel was incubated with primary antibody overnight at 4°C, and with secondary antibody for 1 h. Added developer, and the protein bands were photographed with an ultrasensitive chemiluminescence detector, and the grayscale values of each protein band were analyzed by ImageJ. [
23,
24,
25]. Relative content (%) of each target protein was calculated according to the formula using GAPDH as the reference protein [
26].
2.11. 16S rDNA sequencing and phylogenetic tree construction of strain 729
Total DNA was extracted from strain 729
and the V3–V4 region of the 16S ribosomal RNA (rRNA) gene of strain 729 was amplified
using a univeral primer
: 27F (5′-AGAGTTTGATCCTGGCTCAG-3′) and 1492R (5′-GGTTACCTTGTTACGACTT-3′). The PCR product was analyzed using an Agilent DNA 1000 Kit and an Agilent 2100 Bioanalyzer (Agilent Technologies, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Phylogenic tree was made according to the NCBI and RDP databanks methods [
27,
28,
29].
2.12. Statistical analysis of data
Cell flow cytometry data was analyzed using software Summit4.0, and grayscale analysis of protein bands was performed by software Image J. The 16S rDNA sequencing results were compared through the NCBI database, and the software MEGA-X 10.6.7 was used to analyze and map the phylogenic tree. All data were analyzed and processed by SPSS 20.0.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Inhibitory effect of plant derived lactic acid bacteria on the proliferation of human colon cancer cell HCT116
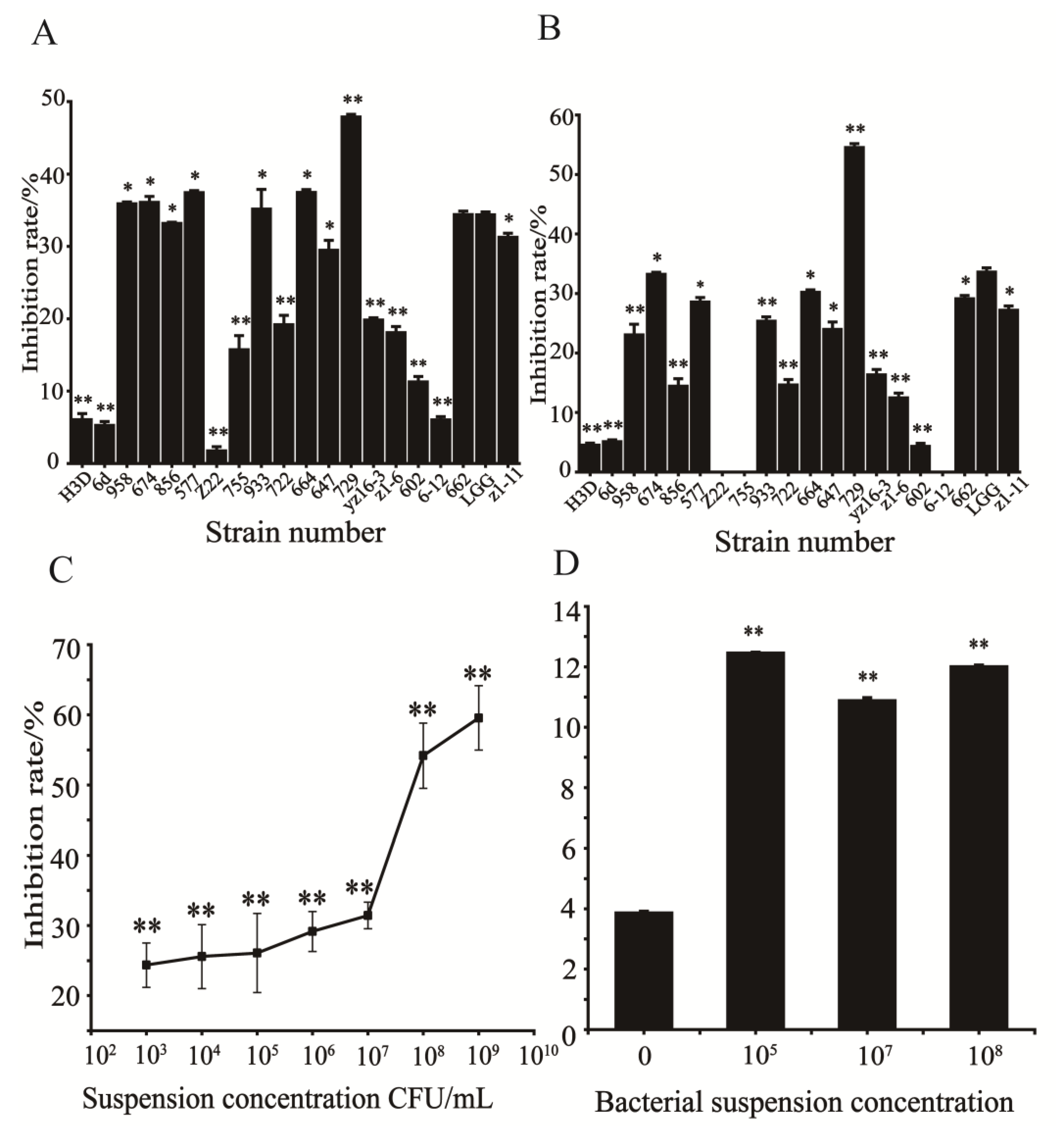
The inhibition rates of 19 plant-derived lactic acid bacteria on HCT116 cells are shown in
Figure 1A,B. The results showed that the inhibitory effect of each strain on HCT116 was not the same. Strain 729 had significantly stronger inhibitory effect, than that of probiotic LGG and other test strains. When the concentration of strain 729 was 1×10
8 CFU/mL, the inhibitory rate reached 54.52%. Therefore, the modulating effect of strain 729 on HCT116 cells was investigated in the following study. Consistent with our results, Wang S et al. have reported that different bacteria strains produced different effects against HCT116 cells due to they showed differs in cell body and cell wall structure[
30].
3.2. Effect of different concentrations of heat inactivated suspension of strain 729 on the proliferation of HCT116 cells
Seven different concentrations of heat-inactivated suspension of strain 729 were selected for the cell proliferation test, and the results are shown in
Figure 1C. The inhibitory effect of strain 729 suspension on HCT116 was dose-dependent. When the concentration of suspension of strain 729 increased from 1×10
3 CFU/mL to 1×10
7 CFU/mL, the inhibitory effect on HCT116 did not change significantly. When the concentration of suspension increased from 1×10
7 CFU /mL to 1×10
8 CFU/mL, the inhibition rate increased significantly. When the concentration of suspension increased from 1×10
8 CFU/mL to 1×10
9 CFU/mL, the inhibition rate did not show a significant increase either.
3.3. Effect of strain 729 on apoptosis of HCT116 cells
According to the test results from
Section 3.2, three different concentrations of heat inactivated suspensions (1×10
5 CFU/mL, 1×10
7 CFU/mL, and 1×10
8 CFU/ ml) of strain 729 were selected to act on HCT116, and the enzyme activity units of Caspase3 were determined by a microplate reader. The results showed that the enzyme activity units of Caspase3 of the bacterial groups were significantly higher than that of the control group (p<0.01). The relative enzyme activity units of Caspase3 of the bacterial groups were as follows: 1×10
5 CFU/mL group > 1× 10
8 CFU/mL group > 1×10
7 CFU/mL group, but the enzyme activity unit of caspase3 of 1×10
8 CFU/mL group (12.01) was only slightly lower than that of 1×10
5 CFU/mL group (12.45) (
Figure 1D). When the concentration of the suspension was 1×10
8 CFU/mL, the inhibitiory effect was significantly stronger than that of 1×10
5 CFU/mL group. The proliferation of HCT116 was hindered, and the total number of HCT116 was much lower than that of 1×10
5 CFU/mL, Therefore, the number of enzyme activity units in the 1×10
8CFU/mL group is slightly lower than that in the 1×10
5CFU/mL group. In conclusion, the optimal concentration of heat inactivated bacterial suspension of strain 729 against HCT116 was 1×10
8 CFU/mL.
3.4. Effect of strain 729 on apoptosis of HCT116 cells
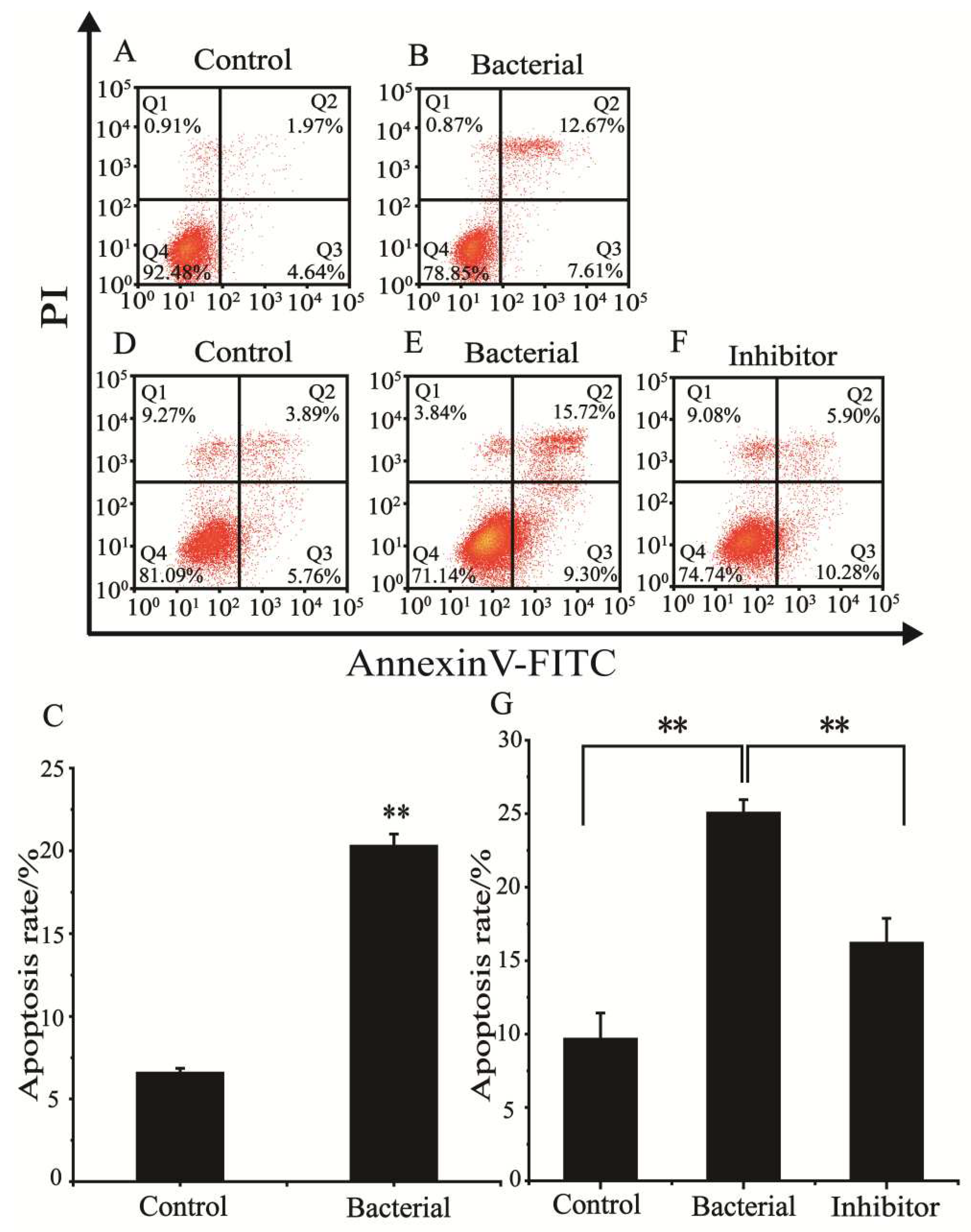
The effect of strain 729 on the cell cycle of HCT116 was determined by flow cytometry and the results are shown in
Figure 2A,B. The apoptosis rate in the cell cycle was shown in
Figure 2C.
The results showed that the apoptotic ratio (The sum of early apoptosis ratio in Q3 and late apoptosis ratio in Q2) of HCT116 treated with heat-inactivated strain 729 suspension (20.28%) was significantly higher than that of the control group (6.61%). It was evident that the heat-inactivated bacteria suspension of strain 729 could effectively block the cell cycle of human colon cancer cell HCT116 and induce apoptosis.
3.5. Effect of strain 729 on inducing ferroptosis of HCT116
The effect of strain 729 on inducing
ferroptosis of HCT116 was determined by flow cytometry, and the apoptosis ratio (The sum of early apoptosis ratio in Q3 and late apoptosis ratio in Q2) was shown in
Figure 2D–F and
Figure 2G. The proportion of HCT116 in the apoptotic phase (25.02%) for bacterial group was significantly higher than that for the control group (9.65%). The proportion of HCT116 in the apoptotic phase (16.18%) for inhibitor group was between the bacterial treatment group and the control group, indicating that the
ferroptosis inhibitor fer-1 reduced the positive regulatory effect of strain 729 on apoptosis. The results above suggested that strain 729 could induce ferroptosis of HCT116 cells.
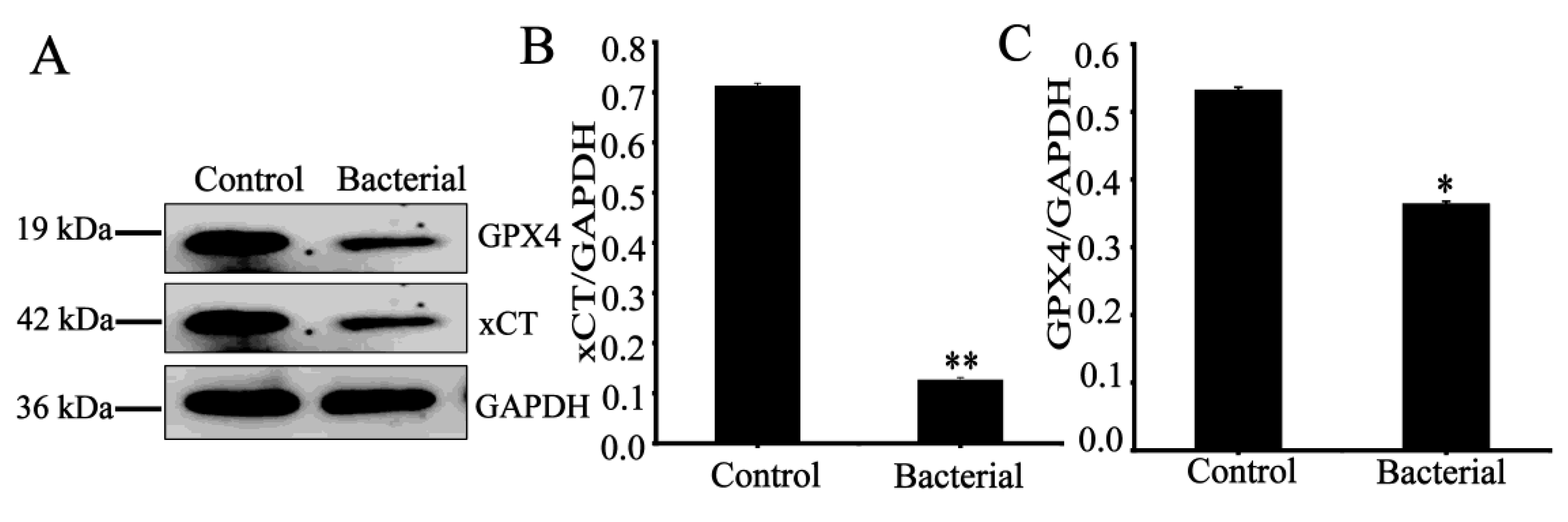
3.6. Effect of strain 729 on Ferroptosis related proteins in HCT116 cells
In order to further determine the mechanism of the inhibitory effect of strain 729 on HCT116 cells, the expressions of related proteins (GPX4 and xCT) were detected by Western blot. As shown in
Figure 3, strain 729 significantly down-regulated the expression of GPX4 and xCT.
Ferroptosis, a novel regulated cell death, is an iron-dependent and peroxidation-driven, non-apoptotic programmed cell death pattern characterized by the accumulation of lethal lipid reactive oxygen species (ROS) [
31]. GPX4 is one of the main regulators of ferroptosis. GPX4 uses glutathione (GSH) to convert toxic lipid peroxides into non-toxic lipid alcohols to reduce lipid peroxide accumulation and negatively regulate ferroptosis. xCT is also a negative regulator of ferroptosis When xCT is inhibited, it reduces intracellular cystine uptake and glutathione (GSH) synthesis. Decreased levels of GSH can inactivate GPX4, induce lipid peroxidation damage and abnormal accumulation of ROS, and eventually lead to ferrodeath. Heat-inactivated bacterial suspension (1×10
8CFU/mL) of strain 729 can induce ferroptosis in HCT116 by significantly down-regulating the expression of GPX4 and xCT.
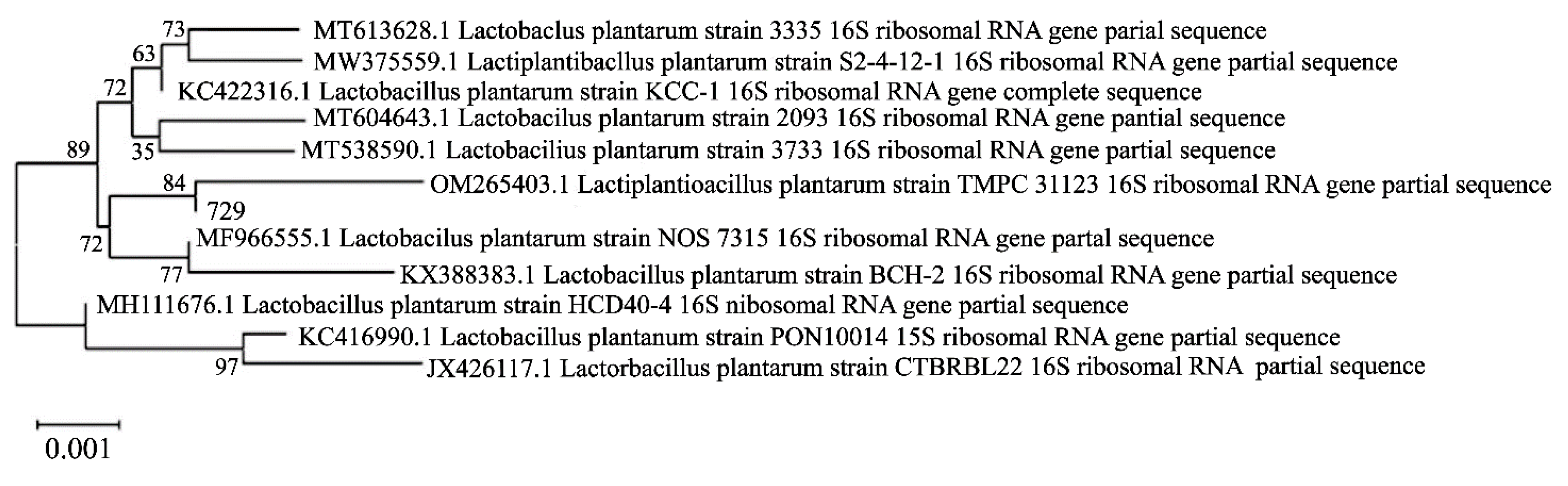
3.7. 16S rDNA sequence and phylogenetic tree of strain 729
Comparing the 16S rDNA sequence of strain 729 with the NCBI gene bank, the results showed that strain 729 had 99.86% homology with Lactobacillu plantarum, and was identified as Lactobacillus plantarum. Its phylogenetic tree is shown in
Figure 4.
4. Conclusion
Colon cancer is one of the most common cancers in the world, and the prevalence and mortality rate in China remain high. At present, the main treatment for colon cancer is resection of the lesion, but postoperative complications frequently occur, and the cure rate and 5-year survival rate are not up to expectations. A large number of experiments have proved that lactic acid bacteria can improve the immunity and fight infection and tumor.
In this study, strain 729 was screened out from 19 strains of plant-derived lactic acid bacteria by its strong inhibitory effect on human colon cancer cell HCT116 in cell proliferation assay. The inhibitory effect of strain 729 on HCT116 was significantly higher than that of probiotics LGG. Caspase3 enzyme activity test showed that the optimal inhibitory concentration of strain 729 on HCT116 was 1×108 CFU/mL. Flow cytometry result showed that heat-inactivated strain 729 could inhibit the proliferation of HCT116 by inducing cell apoptosis. The proportion of apoptotic cells in bacterial group decreased significantly when treated with Ferrostatin-1, which proved that the inhibition of HCT116 by strain 729 was related to the induction of ferroptosis in HCT116. Western blot analysis confirmed that strain 729 could down-regulate GPX4 and xCT expression in the ferroptosis and promote cell ferroptosis. Through 16S rDNA sequencing, strain 729 was identified as Lactobacillus plantarum. Lactobacillus plantarum 729 can potentially be used as probiotics for the prevention of colon cancer.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the national modern agricultural industrial technology system (Project No. CARS-24-E-02), the construction of the research center for green deep processing technology of fermented pepper (Project No. 2023ZYQ044), the structural characterization of glucosinolates in Huarong large leaf mustard and its mechanism for preventing colon cancer (Project No. 2021JJ30315).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors have declared that there is no conflict of interest.
References
- Chen SH, Ma TJ, Zhang GY, et al. Influencing factors of tumor metastasis after radical resection in patients with stage II.-III colon cancer. Practical Journal of Cancer 2022, 37, 650–652.
- Cui FC, Chen Yu, Hu Min, et al. Expression of NEK2 in colorectal cancer tissues and its effect on the proliferation, invasion and migration capacity of HCT116 cells. Cancer Prevention and Treatment Research 2021, 48, 159–165.
- Tian Y, Deng FM, Zhao LY, et al. Inhibitory effect of glucoside extract on HCT116 in human colon cancer cells. Food Science 2020, 41, 172–180.
- Liu Xian, Kang XH, Lingnan. Research progress on extracellular polysaccharides produced by fermentation of lactic acid bacteria. China Dairy 2012, 2, 46–48.
- Span A, Lagan P, Visalli G, et al. In vitro antibiofilm activity of an exopolysaccharide from the Marine thermophilic Bacillus licheniformis T14.Curr Microbiol 2016, 72, 518–28.
- Tuo YF, Zhang WQ, Zhang LW, et al. Study of probiotic potential of four wild Lactobacillus rhamnosus strains. Anaerobe 2013, 21, 22–27+34.
- Balansky, R.; Gyosheva, B.; Ganchev, G. Inhibitory effects of freezedried milk fermented by selected Lactobacillus bulgaricus strains on carcinogenesis induced by 1, 2-dimethylhydrazine in rats and by diethylnitrosamine in hamsters. Cancer Letter 1999, 147, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang S, Zhang L, Fan R, et al. Induction of HT-29 cells apoptosis by lactobacilli isolated from fermented Products. Research in Microbiology 2014, 165, 202–214.
- Wang, S.M.; Zhang, L.W.; Shan, Y.J. Lactic acid bacteria and colon cancer. Acta Microbiologica Sinica. 2015, 55, 667–674. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tuo YF, Zhang WQ, Zhang LW, et al. Study of probiotic potential of four wild Lactobacillus rhamnosus strains. Anaerobe 2013, 21, 22–27.
- Li SP, Yang HB, Wang Di, et al. Determination of concentrations of Aeromonas hydrophila by ultraviolet spectrophotometry. Journal of Fisheries 2013, 26, 40–42.
- Guo Tingting, Hu Jin, Zhu SY, et al. Synthesis and antitumor activity of carbonylpthiridin derivatives. Synthetic Chemistry 2021, 29, 905–911.
- Liu FX, Tan Feng, Fan Qiaoling, et al. Comparison of CCK-8 and MTT method for the detection of drug-containing serum in zuogui pill to intervene in the proliferation of BMSCs. Chinese Journal of Osteoporosis 2022, 28, 6–10.
- Ma NF, Shangguan FG, Zhou Hongfei, etal. 6-methoxydihydroavicine, the alkaloid extracted from Macleaya cordata (Willd.) R. Br. (Papaveraceae), triggers RIPK1/Caspase-dependent cell death in pancreatic cancer cells through the disruption of oxaloacetic acid metabolism and accumulation of reactive oxygen species. PhytomedicineVolume 2022, 102, 154164–15416.
- Liu MY, Yang YH, Wang JH, et al. Synthesis of novel 3-O-acetyl-11-β-boswellic acid derivatives and their antitumor activity in vitro. Synthetic Chemistry 2022, 30, 245–251.
- Sun Jing, Zhang Feng. Study on the regulatory capacity and mechanism of TPX2 on proliferation and apoptosis of non-small cell lung cancer cells. Hebei Medicine 2022, 44, 1184–1186.
- Liu Yue, Wang Yan, Gao Yanchao, et al. Effect of Circ-0041795 targeting miR-361-3p on high-glucose induced renal tubular epithelial cell damage. Hebei Medicine 2022, 44, 1136–1140.
- Tang Liang, Yin Min, Zhang Hai, et al. Effects of overexpression of miR-411 on proliferation, invasion and apoptosis of cervical cancer cells. Hebei Medicine 2022, 44, 1130–1135.
- Xu Jinrui, Zheng Xuedi, Ma Boli, et al. Regulatory effect of LXR-ABCA1/ABCG1 pathway on apoptosis and inflammatory response of macrophages infected with BCG. Journal of Immunology 2022, 38, 401–406.
- Xie Jinna, Ye Zehua, Li Lei, et al. Ferrostatin-1 alleviates oxalate-induced renal tubular epithelial cell injury, fibrosis and calcium oxalate stone formation by inhibiting ferroptosis. Molecular Medicine Reports 2022, 26, 256.
- Shi Qing, Liu Rui, Chen Li. Ferroptosis inhibitor ferrostatin-1 alleviates homocysteine -induced ovarian granulosa cell injury by regulating TET activity and DNA methylation. Molecular Medicine Reports 2022, 25, 1–9.
- Sun CF, Peng Fang, Li Jianfei, et al. Ferroptosis-specific inhibitor ferrostatin-1 relieves h2o2-induced redox imbalance in primary cardiomyocytes through the Nrf2/ARE pathway. Disease Markers 2022, 2022, 4539932–4539932.
- Valashedi Mehdi Rabiee, Roushandeh Amaneh Mohammadi, Tomita Kazuo, et al. CRISPR/Cas9-mediated knockout of Lcn2 in human breast cancer cell line MDA-MB-231 ameliorates erastin-mediated ferroptosis and increases cisplatin vulnerability. Life Sciences 2022, 304, 116586.
- Qin Binyu, Zeng Zhili, Xu JL, et al. Emodin inhibits invasion and migration of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via regulating autophagy-mediated degradation of snail and β-catenin. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 671–671.
- Wu Qian, Tong Le, Zou ZR, et al. Herceptin-functionalized SK-BR-3 cell membrane-wrapped paclitaxel nanocrystals for enhancing the targeted therapy effect of HER2-positive breast cancer. Materials & DesignVolume 2022, 219.
- Fan Zhimin, Liu LJ, Wang ZG, et al. Mechanisms for promoting iron necrosis in colon cancer cells and enhancing their sensitivity to cisplatin. Research in Medical Theory and Practice 2021, 34.
- Yan ZX, Zhang Kang, Zhang Kai, et al. Integrated 16S rDNA gene sequencing and untargeted metabolomics analyses to investigate the gut microbial composition and plasma metabolic phenotype in calves with dampness-heat diarrhea. Frontiers in Veterinary Science 2022, 9, 703051–703051.
- Li HY, Zhai RQ, Liang HY, et al. Analysis of the changes in intestinal microecology in the early stage of sepsis rat based on 16S rDNA sequencing. Chinese Critical Illness Emergency Medicine 2022, 34, 28–34.
- Nie ZY, Wu Yanyang, Wang ZG, et al. Screening and characteristics of plant-derived probiotic lactic acid bacteria. Food Science 2022, 1-14.
- Ver ghese m, Rao Dr, Chawan C B, et al. Dietary inulin suppresses azoxymethane-induced preneoplastic aberrant crypt foci in mature fisher 344 rats. J Nutr 2002, 132, 2804–2808.
- Huang JS,YAN Fuxia. Research progress on ferroptosis and its relationship with cell adaptive regulation. Medical Review 2022, 1–6.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).