Submitted:
12 May 2023
Posted:
15 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Quorum sensing: bacterial communication network
2.1. LuxR receptors
2.2. Bicomponent Quorum sensing receptors
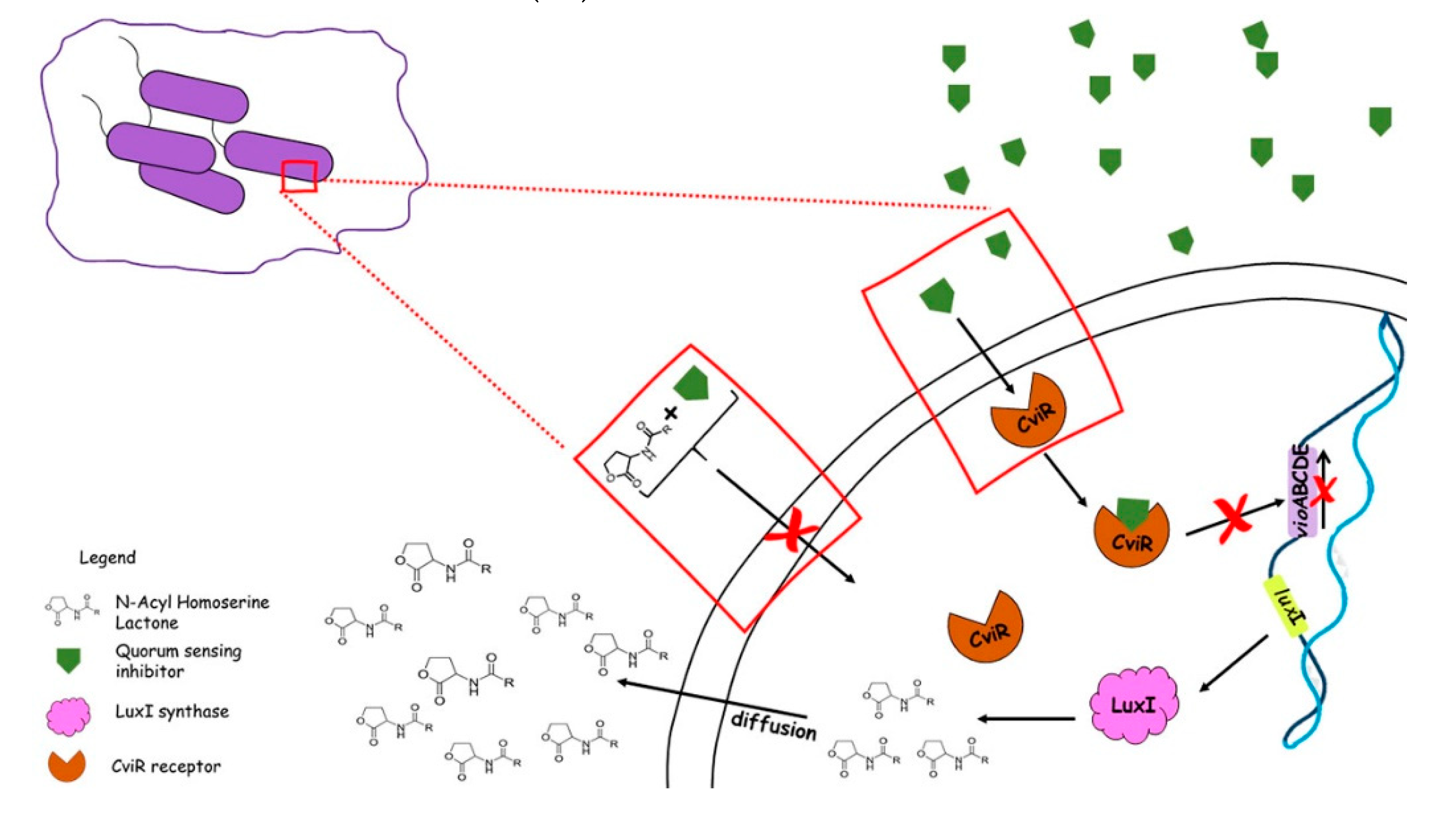
3. Quorum-Sensing system in Chromobacterium violaceum
3.1. Quorum sensing mechanisms in Chromobacterium violaceum
3.2. Pigment production
4. Plant Inhibitors: a new way to control bacterial communication
4.1. Quorum sensing inhibitory potential by plants
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Kumar, P.; Sharma, S.; Tripathi, V.N. Quorum sensing in bacteria of rice rhizospheres from Chhattisgarh, India. Bioinformation 2023, 19, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouyahya, A.; Dakka, N.; Et-Touys, A.; Abrini, J.; Bakri, Y. Medicinal plant products targeting quorum sensing for combating bacterial infections. Asian Pac J Trop Med 2017, 10, 729–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.; Hu, W.; Tian, Z.; Yuan, D.; Yi, G.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Developing natural products as potential anti-biofilm agents. Chin Med 2019, 14, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, T.B.; Manefield, M.; Andersen, J.B.; Eberl, L.; Anthoni, U.; Christophersen, C.; et al. How Delisea pulchra furanones affect quorum sensing and swarming motility in Serratia liquefaciens MG1. Microbiology 2000, 146, 3237–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, C.T.; Sperandio, V. Cell-to-cell signalling during pathogenesis. Cell Microbiol 2009, 11, 363–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutherford, S.T.; Bassler, B.L. Bacterial Quorum Sensing: Its Role in Virulence and Possibilities for Its Control. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2012, 2, a012427–a012427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalia, V.C. Quorum sensing inhibitors: An overview. Biotechnol Adv 2013, 31, 224–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, L.; Dong, X.; Grenier, D.; Wang, K.; Wang, Y. Research progress of bacterial quorum sensing receptors: Classification, structure, function and characteristics. Sci Total Environ 2021, 763, 143031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoitsova, S.R.; Paunova-Krasteva, T.S.; Borisova, D.B. Modulation of Biofilm Growth by Sub-Inhibitory Amounts of Antibacterial Substances. In: Dhanasekaran, D.; Thajuddin, N., Eds.;. Microbial Biofilms - Importance and Applications. InTech; 2016. ISBN978-953-51-2436-8. [CrossRef]
- Trendafilova, A.; Ivanova, V.; Rangelov, M.; Todorova, M.; Ozek, G.; Yur, S.; et al. Caffeoylquinic Acids, Cytotoxic, Antioxidant, Acetylcholinesterase and Tyrosinase Enzyme Inhibitory Activities of Six Inula Species from Bulgaria. Chem Biodivers 2020, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoitsova, S.; Paunova-Krasteva, T.; Dimitrova, P.D.; Damyanova, T. The concept for the antivirulence therapeutics approach as alternative to antibiotics: hope or still a fiction? Biotechnol Biotechnol Equip 2022, 36, 697–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemdan, B.A.; Mostafa, A.; Elbatanony, M.M.; El-Feky, A.M.; Paunova-Krasteva, T.; Stoitsova, S.; et al. Bioactive Azadirachta indica and Melia azedarach leaves extracts with anti-SARS-CoV-2 and antibacterial activities. PLOS ONE 2023, 18, e0282729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paunova-Krasteva, T.; Hemdan, B.A.; Dimitrova, P.D.; Damyanova, T.; El-Feky, A.M.; Elbatanony, M.M.; et al. Hybrid Chitosan/CaO-Based Nanocomposites Doped with Plant Extracts from Azadirachta indica and Melia azedarach: Evaluation of Antibacterial and Antibiofilm Activities. BioNanoScience 2023, 13, 88–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nealson, K.H.; Platt, T.; Hastings, J.W. Cellular Control of the Synthesis and Activity of the Bacterial Luminescent System. J Bacteriol 1970, 104, 313–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nealson, K.H.; Hastings, J.W. Bacterial Bioluminescence: Its Control and Ecological Significance. Microbiol rev 1979, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papenfort, K.; Bassler, B.L. Quorum sensing signal–response systems in Gram-negative bacteria. Nat Rev Microbiol 2016, 14, 576–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, M.B.; Bassler, B.L. Quorum Sensing in Bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol 2001, 55, 165–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abisado, R.G.; Benomar, S.; Klaus, J.R.; Dandekar, A.A.; Chandler, J.R. Bacterial Quorum Sensing and Microbial Community Interactions. mBio 2018, 9, e02331–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chugani, S.; Greenberg, E.P. An evolving perspective on the Pseudomonas aeruginosa orphan quorum sensing regulator QscR. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2014, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durán, N.; Justo, G.Z.; Durán, M.; Brocchi, M.; Cordi, L.; Tasic, L.; et al. Advances in Chromobacterium violaceum and properties of violacein-Its main secondary metabolite: A review. Biotechnol Adv 2016, 34, 1030–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajamanikandan, S.; Srinivasan, P. Exploring the selectivity of auto-inducer complex with LuxR using molecular docking, mutational studies and molecular dynamics simulations. J Mol Struct 2017, 1131, 281–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadakkan, K.; Choudhury, A.A.; Gunasekaran, R.; Hemapriya, J.; Vijayanand, S. Quorum sensing intervened bacterial signaling: Pursuit of its cognizance and repression. J Genet Eng Biotechnol 2018, 16, 239–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pena, R.T.; Blasco, L.; Ambroa, A.; González-Pedrajo, B.; Fernández-García, L.; López, M.; et al. Relationship Between Quorum Sensing and Secretion Systems. Front Microbiol 2019, 10, 1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeki, E.K.; Kobayashi, R.K.T.; Nakazato, G. Quorum sensing system: Target to control the spread of bacterial infections. Microb Pathog 2020, 142, 104068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haque, S.; Ahmad, F.; Dar, S.A.; Jawed, A.; Mandal, R.K.; Wahid, M.; et al. Developments in strategies for Quorum Sensing virulence factor inhibition to combat bacterial drug resistance. Microb Pathog 2018, 121, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majdura, J.; Jankiewicz, U.; Gałązka, A.; Orzechowski, S. The Role of Quorum Sensing Molecules in Bacterial–Plant Interactions. Metabolites 2023, 13, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waters, C.M.; Bassler, B.L. Quorum sensing: Cell-to-Cell Communication in Bacteria. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2005, 21, 319–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Keersmaecker, S.C.J.; Sonck, K.; Vanderleyden, J. Let LuxS speak up in AI-2 signaling. Trends Microbiol. 2006, 14, 114–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, K.; Bentley, W.E. Quorum Sensing from Two Engineers’ Perspectives. Isr J Chem 2023, e202200083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, C.; Park, S.J.; Im, S.J.; Park, S.J.; Lee, J.H. Interspecies signaling through QscR, a quorum receptor of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mol Cells 2012, 33, 53–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stauff, D.L.; Bassler, B.L. Quorum Sensing in Chromobacterium violaceum: DNA Recognition and Gene Regulation by the CviR Receptor. J Bacteriol, 3871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kothari, V.; Sharma, S.; Padia, D. Recent research advances on Chromobacterium violaceum. Asian Pac J Trop Med. 2017, 10, 744–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatramanan, M.; Sankar Ganesh, P.; Senthil, R.; Akshay, J.; Veera Ravi, A.; Langeswaran, K.; et al. Inhibition of Quorum Sensing and Biofilm Formation in Chromobacterium violaceum by Fruit Extracts of Passiflora edulis. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 25605–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenz, N.; Shin, J.Y.; Jung, K. Activity, Abundance, and Localization of Quorum Sensing Receptors in Vibrio harveyi. Front Microbiol. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Lu, Y.; Ye, X.; Emam, M.; Zhang, H.; Wang, H. Current advances in Vibrio harveyi quorum sensing as drug discovery targets. Eur J Med Chem. 2020, 207, 112741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watve, S.; Barrasso, K.; Jung, S.A.; Davis, K.J.; Hawver, L.A.; Khataokar, A.; et al. Parallel quorum-sensing system in Vibrio cholerae prevents signal interference inside the host. PLOS Pathog, 0831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brazilian National Genome Project Consortium. The complete genome sequence of Chromobacterium violaceum reveals remarkable and exploitable bacterial adaptability. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2003, 100, 11660–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamaeva, A.A.; Vasilchenko, A.S.; Deryabin, D.G. Atomic Force Microscopy Reveals a Morphological Differentiation of Chromobacterium violaceum Cells Associated with Biofilm Development and Directed by N-Hexanoyl-L-Homoserine Lactone. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaniyarakkal, V.; Orvankundil, S.; Lalitha, S.K.; Thazhethekandi, R.; Thottathil, J. Chromobacterium violaceum Septicaemia and Urinary Tract Infection: Case Reports from a Tertiary Care Hospital in South India. Case Rep Infect Dis. 2016, 2016, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oca-Mejía, M.M.; Castillo-Juárez, I.; Martínez-Vázquez, M.; Soto-Hernandez, M.; García-Contreras, R. Influence of quorum sensing in multiple phenotypes of the bacterial pathogen Chromobacterium violaceum. Pathog Dis. 2015, 73, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durán, M. ; Faljoni-Alario, A,; Durán, N. Chromobacterium violaceum and its important metabolites — review. Folia Microbiol (Praha). [CrossRef]
- Batista, J.H.; da Silva Neto, J.F. Chromobacterium violaceum Pathogenicity: Updates and Insights from Genome Sequencing of Novel Chromobacterium Species. Front Microbiol. 2017, 10, 2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, K.C.; Benomar, S.; Camuy-Vélez, L.A.; Nasseri, E.B.; Wang, X.; Neuenswander, B.; et al. Quorum-sensing control of antibiotic resistance stabilizes cooperation in Chromobacterium violaceum. ISME J. 2018, 12, 1263–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng WJ, Zhou JW, Zhang PP, Luo HZ, Tang S, Li JJ, et al. Quorum sensing inhibition and tobramycin acceleration in Chromobacterium violaceum by two natural cinnamic acid derivatives. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020 Jun;104:5025–37. [CrossRef]
- Gohil N, Bhattacharjee G, Gayke M, Narode H, Alzahrani KJ, Singh V. Enhanced production of violacein by Chromobacterium violaceum using agro-industrial waste soybean meal. J Appl Microbiol. 2022 Feb;132:1121–33. [CrossRef]
- Devescovi, G.; Kojic, M.; Covaceuszach, S.; Cámara, M.; Williams, P.; Bertani, I.; et al. Negative Regulation of Violacein Biosynthesis in Chromobacterium violaceum. Front Microbiol. 2017, 8, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.P.; Zeng, H.; Wan, C.X.; Zhou, Z.B. Amicoumacins from a desert bacterium: quorum sensing inhibitor against Chromobacterium violaceum. Nat Prod Res. 2021, 35, 5508–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassler, B.L.; Losick, R. Bacterially Speaking. Cell. 2006, 125, 237–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassler, B.L. How bacteria talk to each other: regulation of gene expression by quorum sensing. Curr Opin Microbiol. 1999, 2, 582–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Meng, F.; Gu, W.; Li, F.; Tao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Effects of Natural Products on Bacterial Communication and Network-Quorum Sensing. BioMed Res Int. 2020, 2020, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, T.B. ; Givskov. M. Quorum sensing inhibitors: a bargain of effects. Microbiology. [CrossRef]
- Fleitas Martínez, O.; Rigueiras, P.O. ; Pires Á da, S,; Porto, W.F.; Silva, O.N.; de la Fuente-Nunez, C.; et al. Interference With Quorum-Sensing Signal Biosynthesis as a Promising Therapeutic Strategy Against Multidrug-Resistant Pathogens. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 8. [CrossRef]
- Rasko, D.A.; Sperandio, V. Anti-virulence strategies to combat bacteria-mediated disease. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2010, 9, 117–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, M.; Teplitski, M.; Robinson, J.B.; Bauer, W.D. Production of Substances by Medicago truncatula that Affect Bacterial Quorum Sensing. Mol Plant-Microbe Interactions. [CrossRef]
- Hentzer, M.; Givskov, M. Pharmacological inhibition of quorum sensing for the treatment of chronic bacterial infections. J Clin Invest. 2003, 112, 1300–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frisvad, J.C.; Andersen, B.; Thrane, U. The use of secondary metabolite profiling in chemotaxonomy of filamentous fungi. Mycol Res. 2008, 112, 231–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobretsov, S.; Teplitski, M.; Bayer, M.; Gunasekera, S.; Proksch, P.; Paul, V.J. Inhibition of marine biofouling by bacterial quorum sensing inhibitors. Biofouling. 2011, 27, 893–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahjudi, M.; Papaioannou, E.; Hendrawati, O.; van Assen, A.H.G.; van Merkerk, R.; Cool, R.H.; et al. PA0305 of Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a quorum quenching acylhomoserine lactone acylase belonging to the Ntn hydrolase superfamily. Microbiology. 2011, 157, 2042–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terwagne, M.; Mirabella, A.; Lemaire, J.; Deschamps, C.; De Bolle, X.; Letesson, J.J. Quorum Sensing and Self-Quorum Quenching in the Intracellular Pathogen Brucellamelitensis. PLoS ONE. 2013, 8, e82514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teiber, J.F.; Horke, S.; Haines, D.C.; Chowdhary, P.K.; Xiao, J.; Kramer, G.L.; et al. Dominant Role of Paraoxonases in Inactivation of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa Quorum-Sensing Signal N -(3-Oxododecanoyl)- l -Homoserine Lactone. Infect Immun. 2008, 76, 2512–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinelli, D.; Grossmann, G.; Séquin, U.; Brandl, H.; Bachofen, R. Effects of natural and chemically synthesized furanones on quorum sensing in Chromobacterium violaceum. BMC Microbiol. 2004, 4, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaya, S.; Pereira, J.A.; Borkosky, S.A.; Valdez, J.C.; Bardón, A.; Arena, M.E. Inhibition of quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa by sesquiterpene lactones. Phytomedicine. 2012, 19, 1173–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín-Rodríguez, A.J.; Ticona, J.C.; Jiménez, I.A.; Flores, N.; Fernández, J.J.; Bazzocchi, I.L. Flavonoids from Piper delineatum modulate quorum-sensing-regulated phenotypes in Vibrio harveyi. Phytochemistry. 2015, 117, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majik, M.S.; Gawas, U.B.; Mandrekar, V.K. Next generation quorum sensing inhibitors: Accounts on structure activity relationship studies and biological activities. Bioorg Med Chem. 2020, 28, 115728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, S.O.; Zedan, H.H.; Ibrahim, Y.M. Quorum sensing inhibitory effect of bergamot oil and aspidosperma extract against Chromobacterium violaceum and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Arch Microbiol. 2021, 203, 4663–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazemian, H.; Ghafourian, S.; Heidari, H.; Amiri, P.; Yamchi, J.K.; Shavalipour, A.; et al. Antibacterial, anti-swarming and anti-biofilm formation activities of Chamaemelum nobile against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop. 2015, 48, 432–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacha, K.; Tariku, Y.; Gebreyesus, F.; Zerihun, S.; Mohammed, A.; Weiland-Bräuer, N.; et al. Antimicrobial and anti-Quorum Sensing activities of selected medicinal plants of Ethiopia: Implication for development of potent antimicrobial agents. BMC Microbiol. 2016, 16, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolova, I.; Paunova-Krasteva, T.; Petrova, Z.; Grozdanov, P.; Nikolova, N.; Tsonev, G.; et al. Bulgarian Medicinal Extracts as Natural Inhibitors with Antiviral and Antibacterial Activity. Plants. 2022, 11, 1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivero-Verbel, J.; Barreto-Maya, A.; Bertel-Sevilla, A.; Stashenko, E.E. Composition, anti-quorum sensing and antimicrobial activity of essential oils from Lippia alba. Braz J Microbiol. 2014, 45, 759–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choo, J.H.; Rukayadi, Y.; Hwang, J.K. Inhibition of bacterial quorum sensing by vanilla extract. Lett Appl Microbiol. 2006, 42, 637–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Hussaini, R.; Mahasneh, A. Microbial Growth and Quorum Sensing Antagonist Activities of Herbal Plants Extracts. Molecules. 2009, 14, 3425–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 72. Singh ,B.N.; Singh, B.R.; Singh, R.L.; Prakash, D.; Sarma, B.K.; Singh, H.B. Antioxidant and anti-quorum sensing activities of green pod of Acacia nilotica L. Food Chem Toxicol. [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.N.; Singh, B.R.; Singh, R.L.; Prakash, D.; Dhakarey, R.; Upadhyay, G.; et al. Oxidative DNA damage protective activity, antioxidant and anti-quorum sensing potentials of Moringa oleifera. Food Chem Toxicol. 2009, 47, 1109–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandclément, C.; Tannières, M.; Moréra, S.; Dessaux, Y.; Faure, D. Quorum quenching: role in nature and applied developments. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2016, 40, 86–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asfour, H. Anti-quorum sensing natural compounds. J Microsc Ultrastruct. 2018, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Swem, L.R.; Swem, D.L.; Stauff, D.L.; O’Loughlin, C.T.; Jeffrey, P.D.; et al. A Strategy for Antagonizing Quorum Sensing. Mol Cell. 2011, 42, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliyu, A.B.; Koorbanally, N.A.; Moodley, B.; Singh, P.; Chenia, H.Y. Quorum sensing inhibitory potential and molecular docking studies of sesquiterpene lactones from Vernonia blumeoides. Phytochemistry. 2016, 126, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, K.H.; Tham, F.Y. Screening of traditional Chinese medicinal plants for quorum-sensing inhibitors activity. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2011, 44, 144–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatima, Q.; Zahin, M.; Khan, M.S.A.; Ahmad, I. Modulation of quorum sensing controlled behaviour of bacteria by growing seedling, seed and seedling extracts of leguminous plants. Indian J Microbiol. 2010, 50, 238–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Ma, H.; Zhao, Q.; Song, S.; Jia, Z. Inhibition of Quorum Sensing Activity by Ethanol Extract of Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi. J Plant Pathol Microbiol. 2012, 09. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, Y.M.; Yin, W.F.; Ho, C.Y.; Mustafa, M.R.; Hadi, A.H.A.; Awang, K.; et al. Malabaricone C from Myristica cinnamomea Exhibits Anti-Quorum Sensing Activity. J Nat Prod. 2011, 74, 2261–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musthafa, K.S.; Ravi, A.V.; Annapoorani, A.; Packiavathy, I.S.V.; Pandian, S.K. Evaluation of Anti-Quorum-Sensing Activity of Edible Plants and Fruits through Inhibition of the N-Acyl-Homoserine Lactone System in Chromobacterium violaceum and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Chemotherapy. 2010, 56, 333–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chenia, H. Anti-Quorum Sensing Potential of Crude Kigelia africana Fruit Extracts. Sensors. 2013, 13, 2802–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivero, V.; Jesús, T.; Pájaro, C.; Nerlis. P.; Stashenko, E. Antiquorum sensing activity of essential oils isolated from different species of the genus Piper. Vitae. 2011, 18, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zheng, H.; Tang, Y.; Yu, W.; Gong, Q. Eugenol inhibits quorum sensing at sub-inhibitory concentrations. Biotechnol Lett. 2013, 35, 631–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musthafa, K.S.; Sahu, S.K.; Ravi, A.V.; Kathiresan, K. Anti-quorum sensing potential of the mangrove Rhizophora annamalayana. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2013, 29, 1851–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaki, A.A. Assessment of Anti-Quorum Sensing Activity for Some Ornamental and Medicinal Plants Native to Egypt. Sci Pharm. 2013, 81, 251–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasavi, H.S.; Arun, A.B.; Rekha, P.D. Inhibition of quorum sensing in Chromobacterium violaceum by Syzygium cumini L. and Pimenta dioica L. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed. 2013, 3, 954–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceylan, O.; Sahin, M.; Akdamar, G. Antioxidant and Anti-quorum Sensing Potential of Acer monspessulanum subsp. monspessulanum Extracts. Planta Med. 2016, 82, 1335–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamfu, A.N.; Kucukaydin, S.; Ceylan, O.; Sarac, N.; Duru, M.E. Phenolic Composition, Enzyme Inhibitory and Anti-quorum Sensing Activities of Cinnamon (Cinnamomum zeylanicum Blume) and Basil (Ocimum basilicum Linn). Chem Afr. 2021, 4, 759–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, F.; Hadi, N.; Bazargani, A. Evaluation of quorum-sensing inhibitory effects of extracts of three traditional medicine plants with known antibacterial properties. New Microbes New Infect. 2020, 38, 100769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alibi, S.; Ben Selma, W.; Ramos-Vivas, J.; Smach, M.A.; Touati, R.; Boukadida, J.; et al. Anti-oxidant, antibacterial, anti-biofilm, and anti-quorum sensing activities of four essential oils against multidrug-resistant bacterial clinical isolates. Curr Res Transl Med. 2020, 68, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Xiao, P.; Wang, Y.; Hao, Y. Mechanisms and Control Measures of Mature Biofilm Resistance to Antimicrobial Agents in the Clinical Context. ACS Omega. 2020, 5, 22684–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qais, F.A.; Khan, M.S.; Ahmad, I. Broad-spectrum quorum sensing and biofilm inhibition by green tea against gram-negative pathogenic bacteria: Deciphering the role of phytocompounds through molecular modelling. Microb Pathog. 2019, 126, 379–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, S.R.M.; Asfour, H.Z.; Elshali, K.Z.; Shaaban, M.I.A.; Al-Attas, A.A.M.; Mohamed, G.A.A. Antimicrobial, antiquorum sensing, and antiproliferative activities of sesquiterpenes from Costus speciosus rhizomes. Pak J Pharm Sci. 2019, 32, 109–115. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, M.R.T.; Lou, Z.; Yu, F.; Wang, P.; Wang, H. Anti-quorum sensing and anti-biofilm activity of Amomum tsaoko (Amommum tsao-ko Crevost et Lemarie) on foodborne pathogens. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2017, 24, 324–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Wang, L.; Gao, J.; Liu, X.; Feng, Y.; Wu, Q.; et al. Tannin-Rich Fraction from Pomegranate Rind Inhibits Quorum Sensing in Chromobacterium violaceum and Biofilm Formation in Escherichia coli. Foodborne Pathog Dis. 2016, 13, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poli, J.P.; Guinoiseau, E.; de Rocca Serra, D.; Sutour, S.; Paoli, M.; Tomi, F.; et al. Anti-Quorum Sensing Activity of 12 Essential Oils on Chromobacterium violaceum and Specific Action of cis-cis-p-Menthenolide from Corsican Mentha suaveolens ssp. Insularis. Molecules. 2018, 23, 2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noumi, E.; Merghni, A.; M Alreshidi, M.; Haddad, O.; Akmadar, G.; De Martino, L.; et al. Chromobacterium violaceum and Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1: Models for Evaluating Anti-Quorum Sensing Activity of Melaleuca alternifolia Essential Oil and Its Main Component Terpinen-4-ol. Molecules. 2018, 23, 2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, V.; Bhathena, Z. Broad Spectrum Anti-Quorum Sensing Activity of Tannin-Rich Crude Extracts of Indian Medicinal Plants. Scientifica. 2016, 2016, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Rui, X.; Wang, L.; Guan, Y.; Sun, X.; Dong, M. Polyphenolic extract from Rosa rugosa tea inhibits bacterial quorum sensing and biofilm formation. Food Control. 2014, 42, 125–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Yan, C.; Xu, Y.; Feng, Y.; Wu, Q.; Lv, X.; et al. Punicalagin Inhibits Salmonella Virulence Factors and Has Anti-Quorum-Sensing Potential. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2014, 80, 6204–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deryabin, D.; Tolmacheva, A. Antibacterial and Anti-Quorum Sensing Molecular Composition Derived from Quercus cortex (Oak bark) Extract. Molecules. 2015, 20, 17093–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paliya, B.S.; Mathew, J.; Singh, B.N. Evaluation of Anti-quorum Sensing Potential of Saraca asoca (Family Caesalpiniaceae) against Chromobacterium violaceum and Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA01. J Pharm Res Int. 2021, 33, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Yao, L. Antiviral Effects of Plant-Derived Essential Oils and Their Components: An Updated Review. Molecules. 2020, 25, 2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Jurado, F.; Navarro-Cruz, A.R.; Ochoa-Velasco, C.E.; Palou, E.; López-Malo, A.; Ávila-Sosa, R. Essential oils in vapor phase as alternative antimicrobials: A review. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2020, 60, 1641–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhao, X. Effects of quorum sensing on the biofilm formation and viable but non-culturable state. Food Res Int. 2020, 137, 109742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sources of QSIs | Active component | Bacteria | Inhibition characteristics | Ref.: |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Prunella vulgaris (whole plant), Imperata cylindrica (underground stem), Nelumbo nucifera (leaf), Panax notoginseng (flower), Punica granatum (bark), Areca catechu (seed) |
Acetone/water extracts | C. violaceum CV026 | QS and antimicrobial activity | (78) |
|
Pisum sativum L. (seedling), Trigonella foenum graecum (seed) |
Methanol, ethanol seed extracts | C. violaceum CV026, C. violaceum ATCC 12472 | Violacein production | (79) |
| Acacia nilotica (L.) (green pod) | Phenol and polyphenol compounds |
C. violaceum ATCC 12472 |
Violacein production |
(72) |
| Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi | Ethanol extract | C. violaceum CV026 | Violacein production | (80) |
| Myristica cinnamomea King (bark) | Methanol extract, Malabaricone C | C. violaceum CV026 | Violacein |
(81) |
|
Ananas comosus, Musa paradiciaca, Manilkara zapota, Ocimum sanctum |
Fruit aqueous extracts |
C. violaceum CV026, C. violaceum ATCC 12472 |
Violacein production | (82) |
| Kigelia africana (Lam.) Benth. | Fruit ethyl acetate, dichloromethane, hexane, methanol extracts |
C. violaceum ATCC 12472, C. violaceum CV026, C. violaceum ATCC 31532 |
Antimicrobial activity, Violacein production | (83) |
|
Laurus nobilis L., Populus alba L., Populus nigra L., Lavandula angustifolia, Rosmarinus officinalis L., Sonchus oleraceus L., Tecoma capensis Thunb. Lindl., Jasminum sambac Ait. |
Ethanolic extracts |
C. violaceum | Antimicrobial activity | (71) |
|
Piper bredemeyer, Piper bogotense, Piper brachypodon (Benth.) |
Essential oils | C. violaceum CV026 | Violacein production, cell growth | (84) |
|
Syzygium aromaticum (L.) Merrill, Perry (clove) |
Extracts | C. violaceum CV026 | Violacein production | (85) |
| Rhizophora annamalayana Kathiresan (bark) | Bark extracts | C. violaceum ATCC 12472 | Violacein production | (86) |
|
Adhatoda vasica L. (leaves) Bauhinia purpurea L. (leaves) Myoporum laetum G. Forst. (leaves) Lantana camara L. (leaves) Piper longum L. (fruits) Taraxacum officinale F.H. Wigg. (aerial parts) |
Ethanol fractions |
C. violaceum ATCC 12472 |
Antimicrobial activity | (87) |
|
Syzygium cumini (L.) Skeels. Pimenta dioica (L.) Merr. |
Ethyl acetate fractions |
C. violaceum ATCC 12472, C. violaceum ATCC 31532, C. violaceum CV026 |
Violacein production | (88) |
|
Acer monspessulanum subsp. monspessulanum |
Ethanol, ethyl acetate extracts |
C. violaceum CV026, C. violaceum ATCC 12472 |
Violacein production, Antimicrobial activity | (89) |
|
Cinnamomum zeylanicum, Ocimum basilicum |
Ethanol extracts | C. violaceum CV026, C. violaceum ATCC 12472 | Anti-QS activities, Violacein production | (90) |
| Rubus rosaefolius | Phenolic extracts | C. violaceum ATCC 12472 | Cluster movement, Biofilm formation, Violacein production |
(50) |
|
Astilbe rivularis, Fragaria nubicola, Osbeckia nepalensis |
Extracts | C. violaceum MTCC 2656 | Violacein | |
|
Melicope lunuankenda (Gaertn.) T. G. Hartley |
Hexane, chloroform and methanol extracts |
C. violaceum CV026 | Violacein production | |
| Nymphaea tetragona | Water extracts | C. violaceum | Violacein production | |
| Camellia sinensis L. | Water extracts | C. violaceum ATCC 12472 | Violacein production | |
| Allium cepa Lineu | Phenolic compounds | C. violaceum | Violacein production, Swarming motility | |
| Elletaria cardamomum | Essential oils | C. violaceum | Violacein production | (24) |
| Eucalyptus radiate | ||||
| Origanum vulgare | ||||
| Rubus rosaefolius | Phenolic extracts | |||
| Syzygium aromaticum | Extracts | C. violaceum CV026 | QS inhibition assay, Violacein production | (91) |
| Dionysia revoluta Boiss. | ||||
| Eucalyptus camaldulensis Dehnh. | ||||
| Cinnamomum verum | Essential oils | C. violaceum CV026 | Violacein production | (92) |
| Origanum majorana | ||||
| Thymus vulgaris | ||||
| Eugenia caryophyllata | ||||
| Lemon | Essential oils | C. violaceum SZMC 6269 | Biofilm formation | (93) |
| Juniper | ||||
| Cuminum cyminum | Methanol extract | C. violaceum ATCC 12472 | Violacein production | |
| Green tea | Extracts | C. violaceum ATCC 12472 | Violacein production | (94) |
| Costus speciosus | Methanol extract | C. violaceum | Violacein production | (95) |
| Amomum tsaoko | Crude extract | C. violaceum ATCC 12472 | Violacein production | (96) |
| Punica granatum | Tannin-rich fraction | C. violaceum ATCC 12472 | Violacein production | (97) |
| Mentha suaveolens ssp. insularis | Essential oils | C. violaceum wild-type strain - 103350T | Violacein production, Biofilm formation | (98) |
| Melaleuca alternifolia | Essential Oils | C. violaceum ATCC 12472 | Violacein production | (99) |
|
Syzygium cumini, Embelia ribes |
Tannin-Rich extracts |
C. violaceum ATCC 12472, C. violaceum ATCC 31532, C. violaceum CV026 |
Violacein production | (100) |
|
Phyllanthus emblica, Terminalia bellirica, Terminalia chebula | ||||
| Punica granatum | Pericarp | |||
| Mangifera indica | Flowers, seed kernel | |||
|
Acacia arabica, Terminalia arjuna, Thespesia populnea, Casuarina equisetifolia |
Barks | |||
| Rosa rugosa tea | Polyphenol (RTP) extract | C. violaceum CV026 | Violacein production | (101) |
| Punica granatum L. | Punicalagin | C. violaceum ATCC 12472 | Violacein production, Growth |
(102) |
| Quercus cortex (Oak bark) | Phytochemicals | C. violaceum CV026 | Violacein production, Growth |
(103) |
| Saraca asoca barks (stem) | Extracts | C. violaceum ATCC 12472 | Violacein production, Anti-QS activities |
(104) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





