Submitted:
11 May 2023
Posted:
12 May 2023
Read the latest preprint version here
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- The speed of aging is increasing;
- In the year 2020, people aged more than sixty years outnumbered young kids under the age of five;
- By 2050 the population of geriatrics is expected to double from 12% to 22%. People over 60 are expected to be around 2.1 billion, and the number of people above 80 is expected to reach 426 million.
- Two-thirds of the aging population is expected to be in the low- and middle-income range.
2. Background of Work
2.1. Sensors
2.1.1. Ambient Sensors
2.1.2. Wearable Sensors
2.2. Data-Sets
3. Data Collection Methodology
- Very few public datasets available that have readings from multiple sensors. Most public datasets only have the linear acceleration data.
- Very few datasets available that have wide diversity in terms of age, gender, height, weight and health issues
- Even in datasets where there is diversity, no information is available on the ratio of gender, age, height or weight
- The number of volunteers are usually less. In most cases less than 20.
- The list of ADLs and falls are not completely provided
- The details of how long each activities lasted is not available.
- The data collection methodology is not described
- The details of the sensors used is not provided, hence using multiple datasets becomes a major issue as they cannot be fused together.
3.1. Volunteers statistics
- No of volunteers: 41
- Age range: 18-50
- Number of female volunteers: 14.
- Weight: 50 Kg – 120 Kg.
- Height: 4ft 11 inches – 6ft 4 inches.
3.1.1. ADL
- Walking Slowly (2 min)
- Walking Quickly (2 mins)
- Jogging (2 min)
- Jogging (2 min)
- Climbing up slowly (2 mins)
- Climbing down slowly (2 mins)
- Climbing up normal (2 mins)
- Climbing down normal (2 mins)
- Slowly sitting on a chair (nil)
- Rapidly sitting down on a chair (na(not applicable))
- Nearly Sitting on the chair getting up (na)
- Swinging Hands (2 mins)
- Lying on the bed (2 min)
- Lying on the back and getting up slowly (na)
- Lying on the back and getting up quickly (na)
- Transition from sideways to one’s back while lying down (na)
3.1.2. Fall
- Forward fall landing on the knees (30 secs on the ground)
- Right fall (30 secs on the ground)
- Left fall (30 secs on the ground)
- Forward fall (30 secs on the ground)
- Seated on the bed and falling on the ground (30 secs on the ground)
- Forward fall body weight on the hand (30 secs on the ground)
- Backward fall from seated position (30 secs on the ground)
- Grabbing while falling (30 secs on the ground)
| Sr no. | Parameter | Values and Nos |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Gender | Male = 27 Female = 14 |
| 2 | Age-range | 20-30 years = 29 30-40 years = 6 >40 years = 6 |
| 3 | Weight-range | 50 Kg – 65 Kg = 21 65 Kg – 80 Kg = 16 80 Kg – 100 Kg = 3 100 Kg – 120 Kg = 1 |
| 4 | Height Range | 5ft – 5ft 5in = 23 5ft 5in – 6ft = 16 >6ft = 2 |
| 5 | Health Issues | No. of subjects with health issues = 17 No. of subjects without health issues = 24 Health Conditions of subjects: Sinus Tachycardia, High Blood Pressure, Overweight, Folic acid allergy, Obese, Thyroid, Hypochondria, extreme anxiety Low Blood Pressure, Prostrate, Sinusitis and Genetic Diabetes |
4. Experimental methodology
5. Results and Discussion
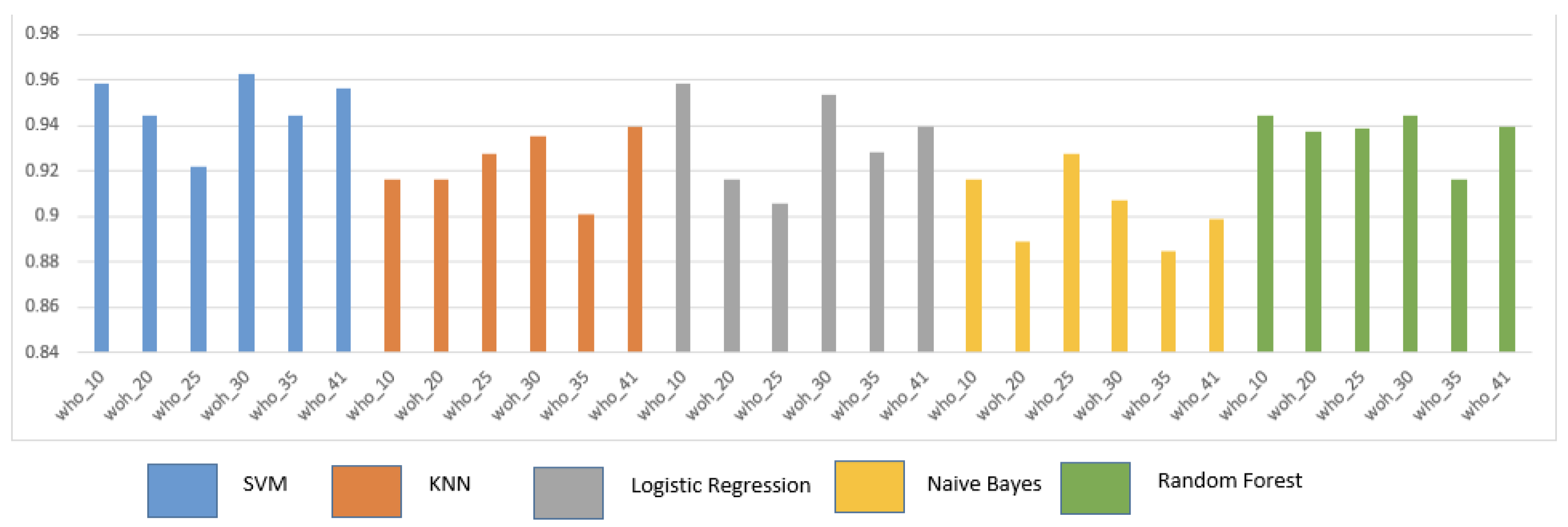
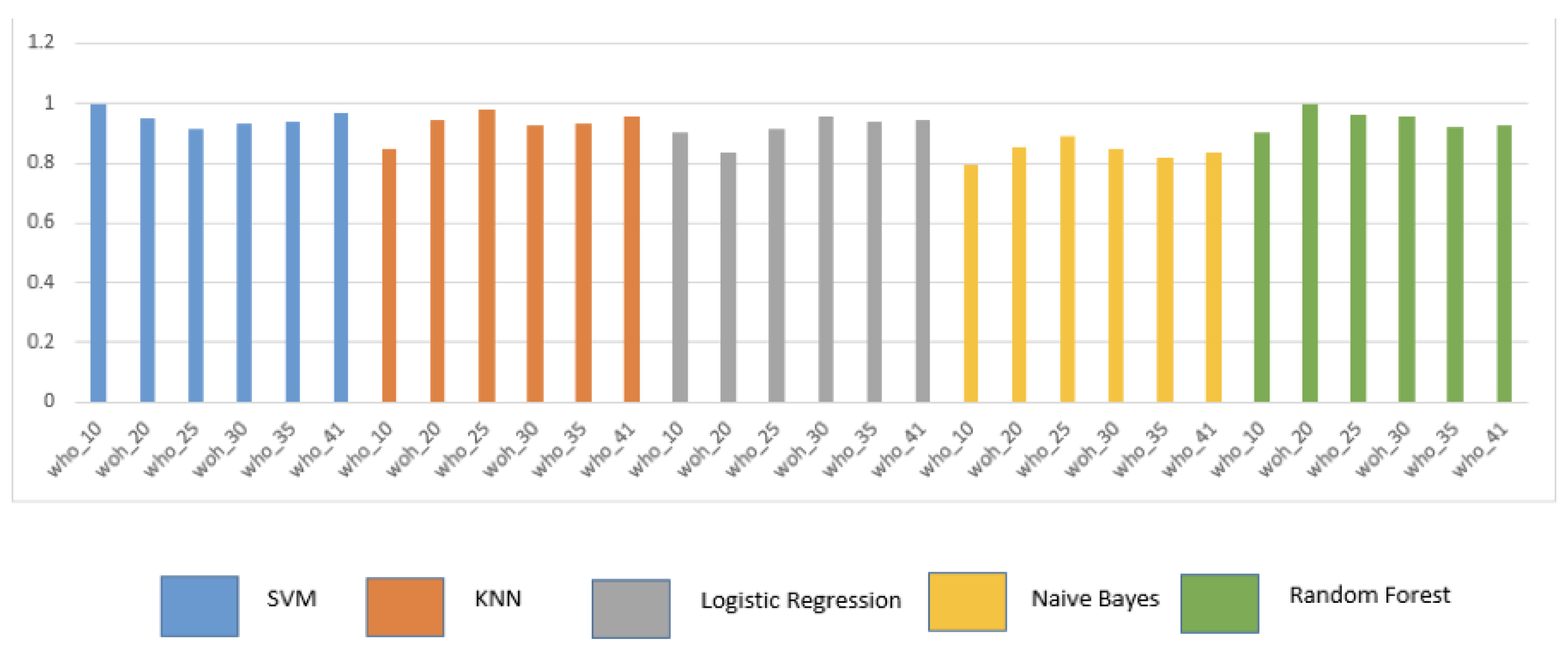
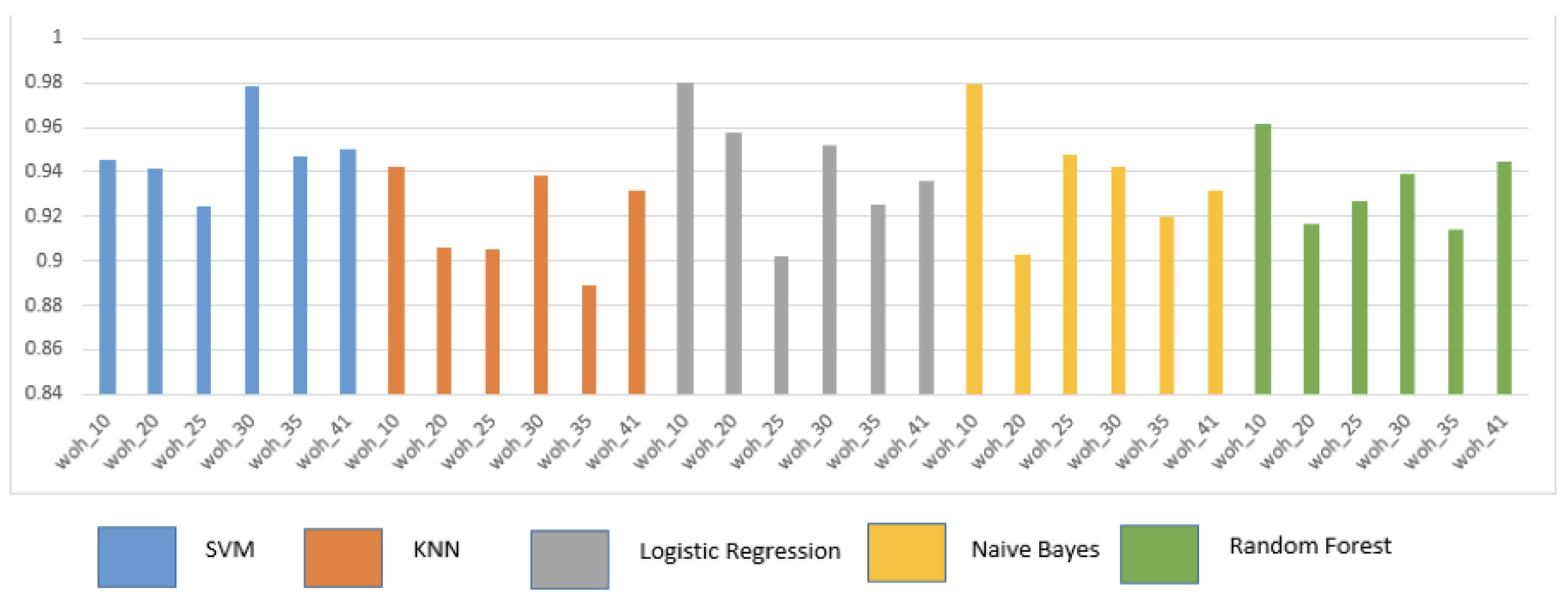
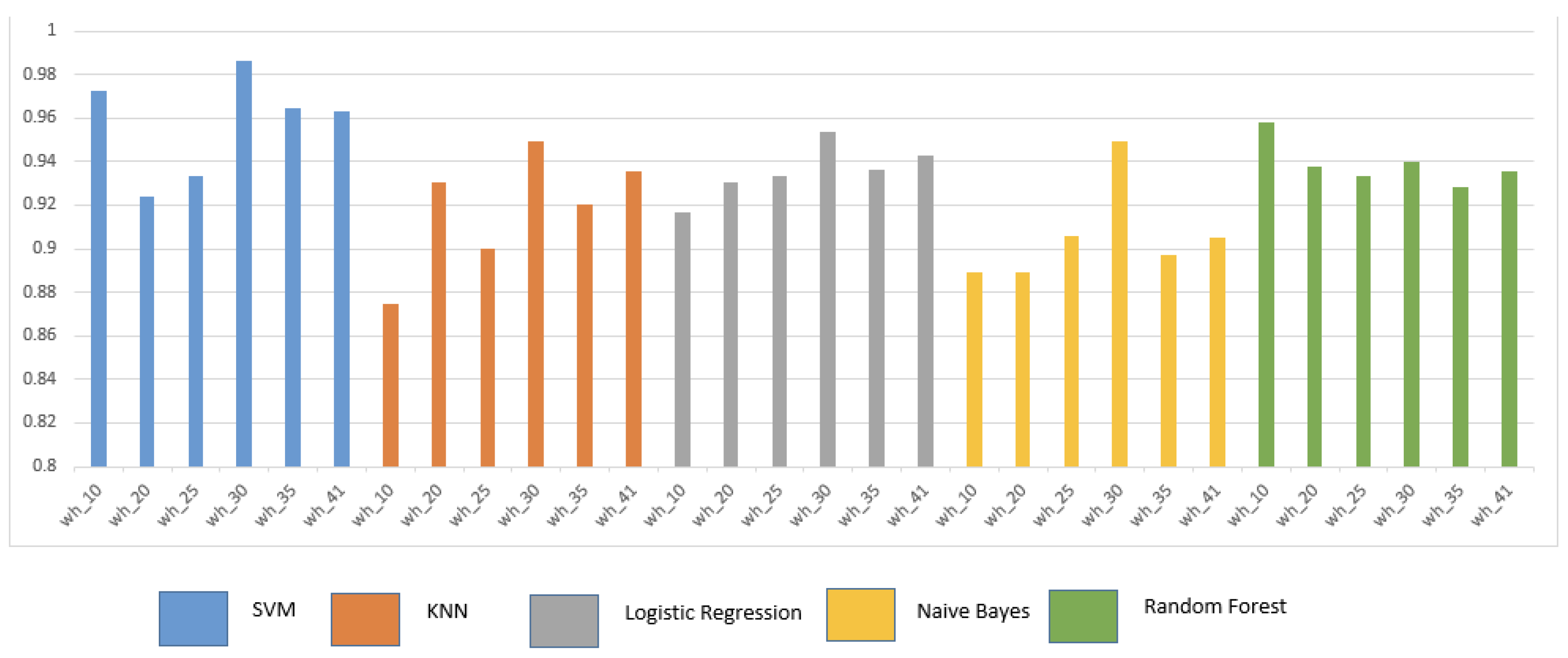
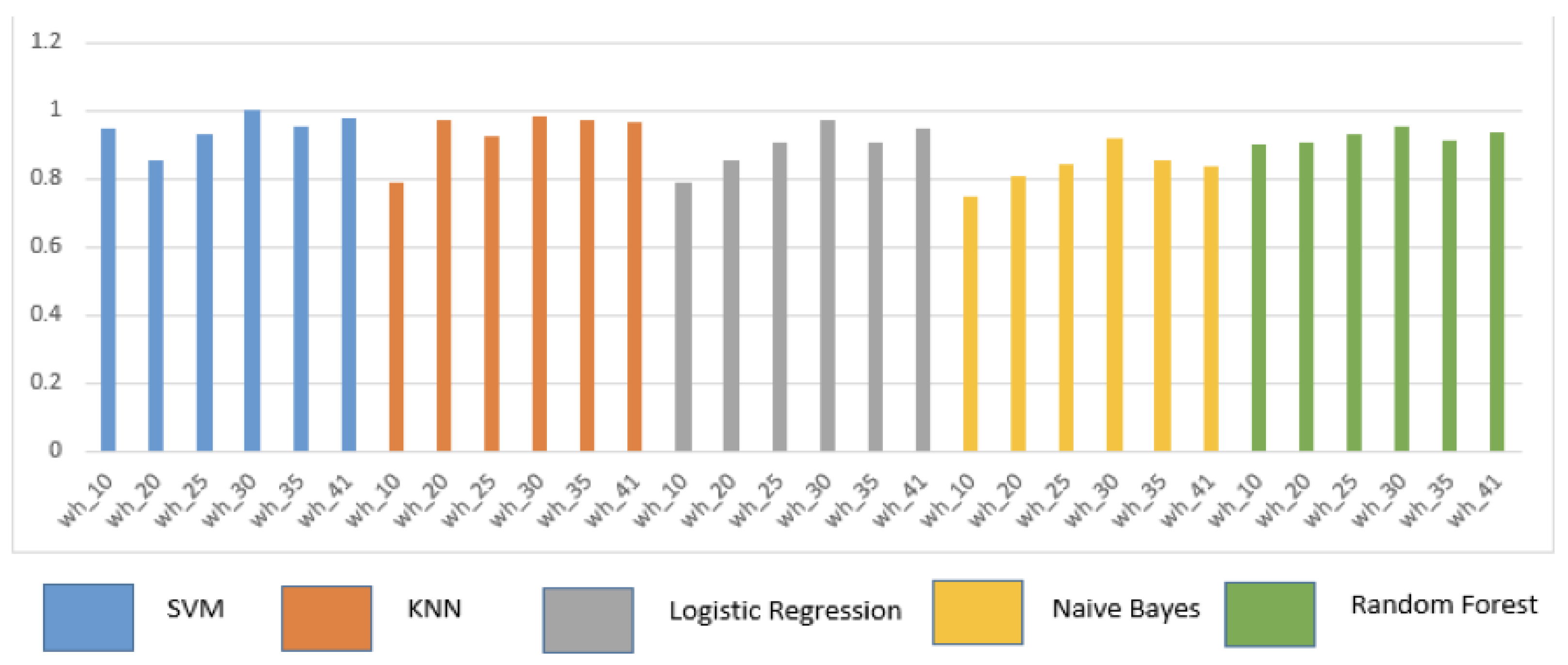
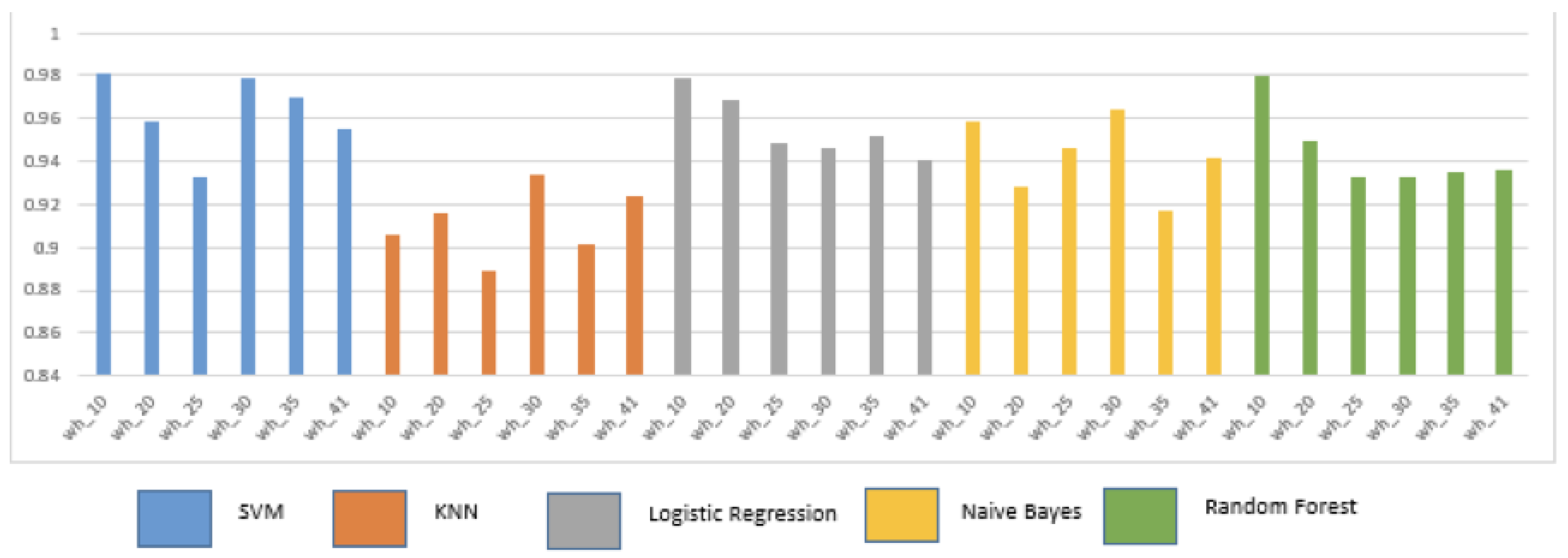
5.1. Overall Performance Analysis for various ML algorithms with varying data sizes
6. Conclusion
References
- United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs, World Population Ageing 2020. https://www.un.org/development/desa/pd/sites/www.un.org.development.desa.pd/files/undesa_pd-2020_world_population_ageing_highlights.pdf. [Accessed 31-Mar-2023].
- Nandi, P.; Bajaj, A.; Anupama, K.R. Application of KNN for Fall Detection on Qualcomm SoCs. IoT Technologies for HealthCare; Spinsante, S., Iadarola, G., Paglialonga, A., Tramarin, F., Eds.; Springer Nature Switzerland: Cham, 2023; pp. 148–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snapdragon 820c Development Board | Qualcomm — qualcomm.com. https://developer.qualcomm.com/hardware/dragonboard-820c. [Accessed 31-Mar-2023].
- Nandi, P.; Anupama, K.; Bajaj, A.; Shukla, S.; Musale, T.; Kachadiya, S. Performance evaluation of Machine Learning algorithms on System on Chips in Wearables for Healthcare Monitoring. Procedia Computer Science 2023, 218, 2755–2766. International Conference on Machine Learning and Data Engineering. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Jiang, Z.; Su, X.; Benzoni, S.; Maxwell, A. Detection of Human Fall Using Floor Vibration and Multi-Features Semi-Supervised SVM. Sensors 2019, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salman Khan, M.; Yu, M.; Feng, P.; Wang, L.; Chambers, J. An unsupervised acoustic fall detection system using source separation for sound interference suppression. Signal Processing 2015, 110, 199–210. Machine learning and signal processing for human pose recovery and behavior analysis. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.L.; Chu, E.T.H. An Image-Based Fall Detection System for the Elderly. Applied Sciences 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luque, R.; Casilari, E.; Morón, M.J.; Redondo, G. Comparison and Characterization of Android-Based Fall Detection Systems. Sensors 2014, 14, 18543–18574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.; Ralhan, A.S.; Ko, S. A Study on Machine Learning Algorithms for Fall Detection and Movement Classification. 2011 International Conference on Information Science and Applications, 2011, pp. 1–8. [CrossRef]
- Albert, M.V.; Kording, K.; Herrmann, M.; Jayaraman, A. Fall Classification by Machine Learning Using Mobile Phones. PLOS ONE 2012, 7, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özdemir, A.T.; Barshan, B. Detecting Falls with Wearable Sensors Using Machine Learning Techniques. Sensors 2014, 14, 10691–10708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koshmak, G.; Linden, M.; Loutfi, A. Dynamic Bayesian Networks for Context-Aware Fall Risk Assessment. Sensors 2014, 14, 9330–9348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chetty, G.; White, M.; Akther, F. Smart phone based data mining for human activity recognition. Proceedings of the International Conference on Information and Communication Technologies, ICICT 2014; Samuel, P., Ed.; Elsevier: Netherlands, 2015; Vol. 46, Procedia Computer Science, pp. 1181–1187. International Conference on Information and Communication Technologies : ICICT 2014 ; Conference date: 03-12-2014 Through 05-12-2014. [CrossRef]
- Genoud, D.; Cuendet, V.; Torrent, J. Soft Fall Detection Using Machine Learning in Wearable Devices. 2016 IEEE 30th International Conference on Advanced Information Networking and Applications (AINA), 2016, pp. 501–505. [CrossRef]
- Vallabh, P.; Malekian, R.; Ye, N.; Bogatinoska, D.C. Fall detection using machine learning algorithms. 2016 24th International Conference on Software, Telecommunications and Computer Networks (SoftCOM), 2016, pp. 1–9. [CrossRef]
- Kostopoulos, P.; Nunes, T.; Salvi, K.; Deriaz, M.; Torrent, J. F2D: A fall detection system tested with real data from daily life of elderly people. 2015. [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, M.; Li, J.; Cao, J.; Wang, Z. An improved fall detection approach for elderly people based on feature weight and Bayesian classification. 2016, pp. 471–476. [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Bai, S.; Wang, X. An Unobtrusive Fall Detection and Alerting System Based on Kalman Filter and Bayes Network Classifier. Sensors 2017, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guvensan, M.A.; Kansiz, A.O.; Camgoz, N.C.; Turkmen, H.I.; Yavuz, A.G.; Karsligil, M.E. An Energy-Efficient Multi-Tier Architecture for Fall Detection on Smartphones. Sensors 2017, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, C.Y.; Liu, K.C.; Huang, C.N.; Chu, W.C.; Chan, C.T. Novel Hierarchical Fall Detection Algorithm Using a Multiphase Fall Model. Sensors 2017, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahanjoo, A.; Tahan, M.N.; Rashti, M.J. Accurate fall detection using 3-axis accelerometer sensor and MLF algorithm. 2017 3rd International Conference on Pattern Recognition and Image Analysis (IPRIA), 2017, pp. 90–95. [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Chen, H.; Brown, R.A. Hidden Markov Model-Based Fall Detection With Motion Sensor Orientation Calibration: A Case for Real-Life Home Monitoring. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics 2018, 22, 1847–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, H.; Usaha, W. Fall detection using lifting wavelet transform and support vector machine. 2017 Federated Conference on Computer Science and Information Systems (FedCSIS), 2017, pp. 877–883. [CrossRef]
- Jefiza, A.; Pramunanto, E.; Boedinoegroho, H.; Purnomo, M.H. Fall detection based on accelerometer and gyroscope using back propagation. 2017 4th International Conference on Electrical Engineering, Computer Science and Informatics (EECSI), 2017, pp. 1–6. [CrossRef]
- Kao, H.C.; Hung, J.C.; Huang, C.P. GA-SVM applied to the fall detection system. 2017 International Conference on Applied System Innovation (ICASI), 2017, pp. 436–439. [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Shrestha, A.; Fioranelli, F.; Le Kernec, J.; Heidari, H.; Pepa, M.; Cippitelli, E.; Gambi, E.; Spinsante, S. Multisensor data fusion for human activities classification and fall detection. 2017 IEEE SENSORS, 2017, pp. 1–3. [CrossRef]
- Fakhrulddin, A.H.; Fei, X.; Li, H. Convolutional neural networks (CNN) based human fall detection on Body Sensor Networks (BSN) sensor data. 2017 4th International Conference on Systems and Informatics (ICSAI), 2017, pp. 1461–1465. [CrossRef]
- Hakim, A.; Huq, M.S.; Shanta, S.; Ibrahim, B. Smartphone Based Data Mining for Fall Detection: Analysis and Design. Procedia Computer Science 2017, 105, 46–51. 2016 IEEE International Symposium on Robotics and Intelligent Sensors, IRIS 2016, 17-20 December 2016, Tokyo, Japan. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Dinh, A.; Chen, L. A wearable real-time fall detector based on Naive Bayes classifier. CCECE 2010, 2010, pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsinganos, P.; Skodras, A. A smartphone-based fall detection system for the elderly. Proceedings of the 10th International Symposium on Image and Signal Processing and Analysis, 2017, pp. 53–58. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Li, W.; Niu, W.; Gravina, R.; Fortino, G. Recognition of human fall events based on single tri-axial gyroscope. 2018, pp. 1–6. [CrossRef]
- Putra, I.P.E.S.; Brusey, J.; Gaura, E.; Vesilo, R. An Event-Triggered Machine Learning Approach for Accelerometer-Based Fall Detection. Sensors 2018, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.C.; Hsieh, C.Y.; Hsu, S.; Chan, C.T. Impact of Sampling Rate on Wearable-Based Fall Detection Systems Based on Machine Learning Models. IEEE Sensors Journal 2018, PP, 1–1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, A.; Adarsh, R.; Pahwa, P.; Anupama, K.R. Machine Learning-based Fall Detection in Geriatric Healthcare Systems. 2018 IEEE International Conference on Advanced Networks and Telecommunications Systems (ANTS), 2018, pp. 1–6. [CrossRef]
- Torti, E.; Fontanella, A.; Musci, M.; Blago, N.; Pau, D.; Leporati, F.; Piastra, M. Embedded Real-Time Fall Detection with Deep Learning on Wearable Devices. 2018 21st Euromicro Conference on Digital System Design (DSD), 2018, pp. 405–412. [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, T.B.; Salgado, D.P.; Cordeiro, M.C.; Osterwald, K.M.; Filho, T.F.; de Lucena, V.F.; Naves, E.L.; Murray, N. Fall Detection System by Machine Learning Framework for Public Health. Procedia Computer Science 2018, 141, 358–365. The 9th International Conference on Emerging Ubiquitous Systems and Pervasive Networks (EUSPN-2018) / The 8th International Conference on Current and Future Trends of Information and Communication Technologies in Healthcare (ICTH-2018) / Affiliated Workshops. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yacchirema, D.; de Puga, J.S.; Palau, C.; Esteve, M. Fall detection system for elderly people using IoT and Big Data. Procedia Computer Science 2018, 130, 603–610. The 9th International Conference on Ambient Systems, Networks and Technologies (ANT 2018) / The 8th International Conference on Sustainable Energy Information Technology (SEIT-2018) / Affiliated Workshops. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musci, M.; De Martini, D.; Blago, N.; Facchinetti, T.; Piastra, M. Online Fall Detection Using Recurrent Neural Networks on Smart Wearable Devices. IEEE Transactions on Emerging Topics in Computing 2021, 9, 1276–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawar, N.; Kehtarnavaz, N. A Convolutional Neural Network-Based Sensor Fusion System for Monitoring Transition Movements in Healthcare Applications. 2018 IEEE 14th International Conference on Control and Automation (ICCA), 2018, pp. 482–485. [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.L.; Le, T.A.; Pham, C. The Internet-of-Things based Fall Detection Using Fusion Feature. 2018 10th International Conference on Knowledge and Systems Engineering (KSE), 2018, pp. 129–134. [CrossRef]
- Chelli, A.; Pätzold, M. A Machine Learning Approach for Fall Detection and Daily Living Activity Recognition. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 38670–38687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, F.; Hussain, F.; Ehatisham-ul Haq, M.; Azam, M.A. Activity-Aware Fall Detection and Recognition Based on Wearable Sensors. IEEE Sensors Journal 2019, 19, 4528–4536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, G.L.; Endo, P.T.; Monteiro, K.H.d.C.; Rocha, E.d.S.; Silva, I.; Lynn, T. Accelerometer-Based Human Fall Detection Using Convolutional Neural Networks. Sensors 2019, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cahoolessur, D.; Rajkumarsingh, B. Fall Detection System using XGBoost and IoT. R and D Journal 2020, 36, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrozek, D.; Koczur, A.; Małysiak-Mrozek, B. Fall detection in older adults with mobile IoT devices and machine learning in the cloud and on the edge. Information Sciences 2020, 537, 132–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, A.; Ramesh, A.; Karuppiah, A. Evaluation of Feature Engineering on Wearable Sensor-based Fall Detection. 2020 International Conference on Information Networking (ICOIN), 2020, pp. 110–114. [CrossRef]
- Usmani, S.; Saboor, A.; Haris, M.; Khan, M.A.; Park, H. Latest Research Trends in Fall Detection and Prevention Using Machine Learning: A Systematic Review. Sensors 2021, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahian, M.J.A.; Ghosh, T.; Banna, M.H.A.; Aseeri, M.A.; Uddin, M.N.; Ahmed, M.R.; Mahmud, M.; Kaiser, M.S. Towards an Accelerometer-Based Elderly Fall Detection System Using Cross-Disciplinary Time Series Features. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 39413–39431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şengül, G.; Karakaya, M.; Misra, S.; Abayomi-Alli, O.O.; Damaševičius, R. Deep learning based fall detection using smartwatches for healthcare applications. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control 2022, 71, 103242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansoor, M.; Amin, R.; Mustafa, Z.; Sengan, S.; Aldabbas, H.; Alharbi, M.T. A machine learning approach for non-invasive fall detection using Kinect. Multimedia Tools and Applications 2022, 81, 15491–15519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karar, M.E.; Shehata, H.I.; Reyad, O. A Survey of IoT-Based Fall Detection for Aiding Elderly Care: Sensors, Methods, Challenges and Future Trends. Applied Sciences 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- New Galaxy Watch 5 Smartwatch | Specs | Samsung UK — samsung.com. https://www.samsung.com/uk/watches/galaxy-watch/galaxy-watch5-44mm-sapphire-bt-sm-r910nzbaeua/. [Accessed 31-Mar-2023].
- Vembandasamy, K.; Sasipriya, R.; Deepa, E. Heart diseases detection using Naive Bayes. IJISET - Int. J. Innov. Sci. Eng. Tech 2015, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Alpaydin, E. Voting over Multiple Condensed Nearest Neighbors. Artificial Intelligence Review 1997, 11, 115–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosmer, D.W.; Lemeshow, S. Applied Logistic Regression, 2nd edn. Wiley-Interscience; Wiley-Interscience: Hoboken, NJ, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Breiman, L. Classification and Regression Trees (1st ed.); Routledge, 1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.H.; Cheng, W.C. Fall detection with the support vector machine during scripted and continuous unscripted activities. Sensors (Basel) 2012, 12, 12301–12316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
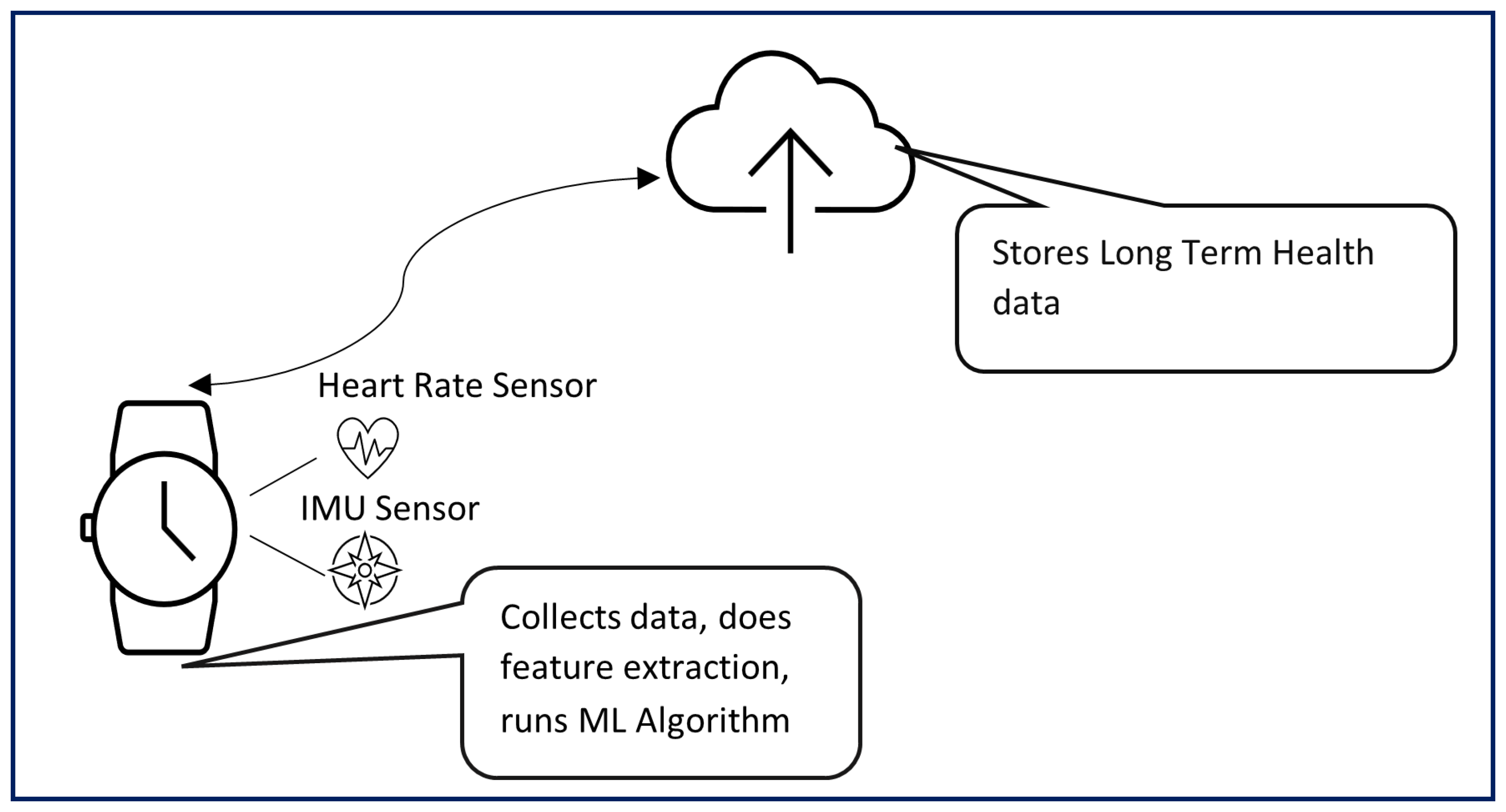
| Ref | Year | Dataset used | Sensor used | Sensor placement | Methodology | Performance parameter and details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [9] | 2011 | UCI dataset | 3-Axes accelerometer, 2-axis gyroscope | Chest, thigh | Comparison of ML algorithms for fall detection using single node and two nodes | Accuracy of classification = 99.8% with two nodes(one on waist and one on knee). Naïve Bayes gaves the worst result, others gave comparable |
| [10] | 2012 | Generated from experiments | Accelerometer | Smartphones carried along with the user | Comparison of SVM, SMLR, Naive Bayes, decision trees, kNN, and regularized logistic regression for fall detection | Support vector machines and regularized logistic regression were able to identify a fall with 98% accuracy and classify the type of fall (trips, left lateral, slips, right lateral) with 99% accuracy. Naïve Bayes reported least accuracy |
| [11] | 2014 | Generated from experiments | Accelerometer gyroscope and magnetometers | 6 different positions on the body | Comparison of k-NN, classifier, LSM, SVM,BDM, DTW and ANN algorithms | k-NN classifier and LSM gave above 99% for sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy |
| [12] | 2014 | Generated from experiments | Accelerometer | Smartphones carried along with the user | Accelerometer data from wearable sensors to generate alarms for falls, combined with context recognition using sensors in an apartment, for inferring regular ADLs, using Bayesian networks | Provides statistical information regarding the fall risk probability for a subject |
| [13] | 2015 | Publicly available activity recognition dataset | Accelerometer, gyroscope | Smartphone | Comparison of Naive Bayes classifier, decision trees, random forests, classifiers based on ensemble learning (random committee), and lazy learning (IBk) algorithms for activity detection carried along with the user | Naive Bayes classifier performs reasonably well for a large dataset, with 79% accuracy, and it is fastest in terms of building the model taking only 5.76 seconds Random forests are better in terms of both accuracy and model building time, with 96.3% accuracy and 14.65 seconds model building time. k-Means clustering performs poorly with 60% classification accuracy and 582 seconds model building time |
| [14] | 2016 | Generated from experiments | 3-Axis Accelerometer | Not specified | Comparison of decision tree, decision tree ensemble, kNN, neural networks, MLP algorithms for soft fall detection | Decision tree ensemble was able to detect soft falls at more than 0.9 AUC |
| [15] | 2016 | MobiFall dataset | Accelerometer, gyroscope | User’s trouser pocket | Comparison of Naive Bayes, LSM, ANN, SVM, kNN algorithms for fall detection | k-NN, ANN, SVM had the best accuracy—results for kNN: Accuracy = 87.5% Sensitivity = 90.70% Specificity = 83.78% |
| [16,17] | 2016 | Generated from experiments | 3-Axis Accelerometer | Smartwatch | Threshold-based analysis of acceleration | Accuracy = 96.01% |
| [17] | 2016 | Generated from experiments | 3-Axis Accelerometer | Different parts of the body | Bayesian framework for feature selection, Naive-Bayes, C4.5 | Better accuracy with improved classification than Naive-Bayes and C4.5 |
| [18] | 2017 | Generated from experiments | Accelerometer gyroscope | Smart - Vest | Kalman filter for noise reduction, sliding window, and Bayes network classifier for fall detection | With Kalman filter Accuracy = 95.67%, Sensitivity = 99.0% Specificity = 95.0% |
| [19] | 2017 | Generated from experiments | 3-Axis Accelerometer | Smartphone | Combination of threshold-based and ML-based algorithms—K-Star, Naive Bayes, J48 | Energy saving = 62% compared with(ML only) techniques Sensitivity =77% (thresholding only), 82% (ML only), 86% (hybrid) Specificity = 99.8% (thresholding only), 98% (ML only), 99.5% (hybrid) Accuracy = 88.4% (thresholding only), 90% (ML only), 92.75% (hybrid) |
| [20] | 2017 | Generated from experiments | 3-Axis Accelerometer | Waist | Combination of threshold-based and knowledge-based approach based on SVM to detect a fall event | Using a knowledge based algorithm: Sensitivity = 99.79% Specificity = 98.74% Precision = 99.05% Accuracy = 99.33% |
| [21] | 2017 | MobiFall dataset | 3-Axis Accelerometer | Not specified | Comparison of multilevel fuzzy minmax neural network, MLP, KNN, SVM, PCA for fall detection | Multilevel fuzzy min-max neural network gave best results: Sensitivity = 97.29% Specificity = 98.70% |
| [22] | 2017 | FARSEEING dataset | 3-Axis Accelerometer | 5 locations on the upper body, neck, chest, waist, right side, and left side | Sensor orientation calibration algorithm to resolve issues arising out of misplaced sensor locations and misaligned sensor orientations, HMM classifiers | Sensitivity = 99.2% (experimental dataset), 100% (real-world fall dataset) |
| [23,24] | 2017 | Generated from experiments | 3-Axis Accelerometer | Chest | LWT based frequency domain analysis and SVM-based time domain analysis of RMS of acceleration | Accuracy = 100% Sensitivity = 100% Specificity = 100% |
| [25] | 2017 | Generated from experiments | 3-Axis accelerometer, 3-axis gyroscope | Waist | Back propagation neural network (BPNN) for fall detection | Accuracy = 98.2% Precision = 98.3% Sensitivity= 95.1% Specificity= 99.4% |
| [26] | 2017 | Generated from experiments | Accelerometer, radar, depth camera | Wrist | Ensemble subspace discriminant, linear discriminant, kNN, SVM | Overall accuracy of ensemble classifier was the highest, after fusion of radar, accelerometer, and camera = 91.3%. This is an improvement of 11.2% compared to radar-only and 16.9% compared to accelerometer-only results |
| [27] | 2017 | Public datasets | 3-Axis accelerometer | Not specified | CNN-based analysis on time series accelerometer data converted to images | Accuracy = 92.3% |
| [28] | 2017 | Generated from experiments | Accelerometer, gyroscope, proximity sensor and compass | Right, left, and front pockets | SVM, decision tree, kNN, discriminant analysis | Highest accuracy = 99% for SVM |
| [29] | 2010 | Generated from experiments | 3-Axis accelerometer | Chest, thigh | Naive-Bayes, SVM, OneR, C4.5 (J48), neural networks | Naive-Bayes gave best results Accuracy = 100% |
| [30] | 2017 | Generated from experiments | Accelerometer (MobiAct dataset) | Not applicable | ENN+ kNN (where ENN was applied to remove outliers), ANN, SVM, and J48 | For ENN+ kNN: Sensitivity = 95.52% Specificity = 97.07% Precision = 91.83% |
| [31] | 2018 | Generated from experiments | Triaxial gyroscope | Waist | Decision tree | Accuracy = 99.52% Precision = 99.3% Recall = 99.5% |
| [32] | 2018 | Cogent dataset, SisFall dataset | 3D accelerometer , 3D gyroscope- Cogent dataset Accelerometer, gyroscope (SisFall) dataset | Chest, waist | Event-ML, classification and regression tree (CART), kNN, logistic regression, SVM | Better precision and F-scores with Event-ML than FOSW and FNSW-based approaches |
| [33] | 2018 | SisFall dataset, generated from experiments | 3-Axis accelerometer | Chest/thigh, waist | SVM, kNN, Naïve- Bayes, decision tree | Accuracy and sensitivity of SVM were the highest (97.6% and 98.3%, respectively) for both datasets. |
| [34] | 2018 | UMA Datasheet | Accelerometer, gyroscope, magnetometer | Wrist, waist, chest, ankle | kNN, Naive-Bayes, SVM, ANN, decision tree | Without risk categorization: 81% for decision tree With risk categorization: 85% for decision tree |
| [35] | 2018 | SisFall dataset original and manually labelled | 3-Axis accelerometer | Not specified | RNN | Highest accuracy reported for fall detection: 83.68% (before manual labelling), 98.33% (after manual labelling) |
| [36] | 2018 | Generated from experiments | Accelerometer, gyroscope, magnetometer | Near the waist | kNN | Accuracy = 99.4% |
| [37] | 2018 | Generated from Experiments | 3-Axis accelerometer | Waist | Decision tree | Accuracy = 91.67% Precision = 93.75% |
| [38] | 2018 | SiSFall dataset | 3-Axis accelerometer | Waist | RNN with LSTM | Highest accuracy after hyperparameter Optimization (97.16%) |
| [39] | 2018 | Generated from experiments | Depth camera, accelerometer | Waist | CNN | Accuracy of fall detection = 100% |
| [40] | 2018 | Generated from experiments | Accelerometer, gyroscope, magnetometer | Hip | SVM, random forest | Without sensor fusion: Accelerometer |
| [41] | 2019 | Public datasets | Accelerometer, gyroscope | Chest, thigh | ANN, kNN, QSVM, ensemble bagged tree (EBT) | Extraction of new features from acceleration and angular velocity improved the accuracy of all 4 classifiers. Accuracy of EBT was highest (97.7%) |
| [42] | 2019 | SisFall dataset | Accelerometer, gyroscope | Waist | kNN, SVM, random forest | Accuracy for fall detection was the highest for kNN (99.8%). Accuracy for recognizing fall activities was the highest for random forest (96.82%) |
| [43] | 2019 | Public datasets | Accelerometer | Not specified | CNN-based models for feature extraction | Highest accuracy reported = 99.86% |
| [44] | 2020 | SiSfall dataset | Two triaxle accelrometers and gyroscope | Wrist | The XGBoost was implemented on spyder software with a 75-25 train-test split | Overall accuracy using XGBoost = 94.6% |
| [45] | 2020 | SiSFall dataset | Accelerometer and Gyroscope sensors inbuilt with Smartphone | Carrying smartphone on hand or pockets | Features were extracted from raw data and person’s correlation was implemented, on the features RF,ANN, SVM and Boosted decision tree was implemented | Accuracies Random Forest = 99.7% ANN = 99.2% SVM = 98.5% Boosted decision tree = 99.9%. |
| [46] | 2020 | Generated from experimentation | All IMU sensors and heart-rate sensor | Wrist | Mean and median was calculated from Raw dataset and ANN, KNN, XGB, NB and Random Forest | Accuracy on mean and median ANN = 85.69% KNN = 94.3% XGB = 85.3% NV = 66% Random Forest = 99.7% |
| [47] | 2021 | Combination of experimentally Generated and publicly available datset | IMU Based sensor on wristwatch and smartphones | Wrist, waist pelvis | SVM,KNN and ANN was implemented | SVM (wrist placement) = 91.3% (waist placement) = 98% KNN (Wrist placement) = 99% (waist placement) = 99.8% ANN (Wrist placement) = 95.25% (Waist placement) = 92.96% |
| [48] | 2021 | UR Fall, MOBIFALL, UP Fall | Accelerometer, magnetometer, gyroscope, ECG sensor | MOBIFALL = trouser, pocket Up Fall = wrist, ankle Ur Fall = pelvis | Feature extraction was performed on the raw dataset and basic ML methods like RF,SVM,KNN, LR,BB and DT were implemented | UR Fall dataset = 99%(RF) UP Fall dataset = 99%(LR) MOBIFALL dataset = 99%(for nearly all mentioned algorithm) |
| [49] | 2022 | Generated from experiments | Accelerometer and gyroscope sensor | Wrist | Data augmentation to solve the imbalance of data set, classification was done by BiLSTM model | Combined sensor accuracy KNN = 74.70% RF = 75.64% SVM = 73.74% BiLSTM = 97.35% |
| [50] | 2022 | Generated from experiments | Image based, External placement | Camera based | Multiple images were captured of the subject’s skeletal orientation, Standard deviation was calculated and fed into KNN based classifier | Overall accuracy of 95% was obtained |
| [51] | 2022 | SisFall, DaLiaC, UMAFall and Epilepsy | IMU based sensors | Wrist and Waist placement | Multiple algorithms were run like ANN, SVM, Decision Trees, Naïve Bayes and Deep learning based | Overall accuracy obtained by the classifier was 92.5% |
| Sr no. | User Demographics | Range | Train | Test |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Age | <30 30-40 40-50 |
<30 (70% Train) <30 <30 30-40 30-40 40-50 |
<30 (30% test) 30 -40 40 - 50 30 - 40 40 - 50 40 - 50 |
| 2 | Gender | Male Female |
Female Male Male Female |
Female Male Female Male |
| 3 | Health Issues | With Without |
Without With With Without |
Without With Without With |
| 4 | Height | <5.5ft >5.5ft |
<5.5ft >5.5ft <5.5ft >5.5ft |
<5.5ft >5.5ft <5.5ft >5.5ft |
| 5 | Weight | 50-65 65-80 80-120 |
50-65 65-80 80-120 50-65 50-65 65-80 65-80 80-120 80-120 |
50-65 65-80 80-120 65-80 80-120 50-65 80-120 50-65 65-80 |
| Train | Test | Accuracy (%) | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SVM | KNN | LR | NV | RF | SVM | KNN | LR | NV | RF | SVM | KNN | LR | NV | RF | ||
| < 30 | < 30 | 94.60 | 92.15 | 92.64 | 86.76 | 92.15 | 93.38 | 89.51 | 93.18 | 91.80 | 91.24 | 97.06 | 98.36 | 91.67 | 79.27 | 94.03 |
| < 30 | 30-40 | 92.50 | 90.00 | 89.38 | 87.50 | 90.63 | 92.37 | 89.34 | 90.60 | 89.66 | 90.76 | 92.86 | 92.11 | 86.05 | 81.82 | 90.24 |
| < 30 | 40-50 | 96.53 | 95.14 | 95.83 | 93.75 | 99.31 | 95.96 | 93.20 | 95.92 | 93.94 | 98.97 | 97.78 | 100 | 95.65 | 93.33 | 100 |
| 30-40 | 30-40 | 85.42 | 81.25 | 83.33 | 72.92 | 87.50 | 84.21 | 78.57 | 83.78 | 85.71 | 84.62 | 90.00 | 100 | 81.82 | 55 | 100 |
| 30-40 | 40-50 | 90.28 | 89.58 | 90.97 | 88.89 | 95.83 | 91.84 | 86.49 | 91.92 | 97.62 | 94.12 | 86.96 | 100 | 88.89 | 76.67 | 100 |
| 40-50 | 40-50 | 93.18 | 88.64 | 93.18 | 84.09 | 90.91 | 90.32 | 84.85 | 93.10 | 92.00 | 92.86 | 100 | 100 | 93.33 | 73.68 | 87.50 |
| Train | Test | Accuracy (%) | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SVM | KNN | LR | NV | RF | SVM | KNN | LR | NV | RF | SVM | KNN | LR | NV | RF | ||
| < 30 | < 30 | 95.10 | 91.67 | 93.14 | 87.25 | 92.16 | 92.81 | 89.44 | 93.23 | 93.28 | 90.07 | 100 | 96.77 | 92.96 | 78.82 | 96.83 |
| < 30 | 30-40 | 92.50 | 90.52 | 89.38 | 87.50 | 90.63 | 92.37 | 90.08 | 90.60 | 89.66 | 89.43 | 92.86 | 92.31 | 86.05 | 81.82 | 94.60 |
| < 30 | 40-50 | 95.83 | 95.14 | 95.14 | 94.44 | 99.31 | 95.92 | 93.20 | 94.95 | 96.81 | 98.97 | 95.65 | 100 | 95.56 | 90 | 100 |
| 30-40 | 30-40 | 87.50 | 81.25 | 79.17 | 72.92 | 87.50 | 86.49 | 78.57 | 82.86 | 85.71 | 84.62 | 90.91 | 100 | 69.23 | 55 | 100 |
| 30-40 | 40-50 | 90.97 | 88.89 | 90.28 | 88.19 | 93.75 | 91.09 | 85.71 | 91.84 | 98.77 | 92.23 | 90.70 | 100 | 86.96 | 74.60 | 97.56 |
| 40-50 | 40-50 | 90.91 | 86.36 | 93.18 | 84.09 | 93.18 | 90 | 82.35 | 93.10 | 88.89 | 93.10 | 92.86 | 100 | 93.33 | 76.47 | 93.33 |
| Train | Test | Accuracy (%) | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SVM | KNN | LR | NV | RF | SVM | KNN | LR | NV | RF | SVM | KNN | LR | NV | RF | ||
| Female | Female | 93.07 | 86.14 | 88.12 | 84.16 | 93.07 | 96.92 | 92.19 | 95.16 | 94.83 | 95.52 | 86.11 | 75.68 | 76.92 | 69.77 | 88.24 |
| Male | Male | 93.33 | 92.82 | 95.90 | 89.23 | 92.82 | 93.13 | 90.00 | 94.70 | 91.34 | 91.79 | 93.75 | 100.00 | 98.41 | 85.29 | 95.08 |
| Male | Female | 94.35 | 90.48 | 94.35 | 89.58 | 93.45 | 94.37 | 88.40 | 94.76 | 89.21 | 93.16 | 94.29 | 96.51 | 93.46 | 90.53 | 94.12 |
| Female | Male | 91.82 | 92.59 | 92.90 | 91.05 | 93.83 | 90.58 | 91.20 | 93.47 | 93.29 | 92.79 | 95.03 | 96.15 | 91.67 | 86.57 | 96.32 |
| Train | Test | Accuracy (%) | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SVM | KNN | LR | NV | RF | SVM | KNN | LR | NV | RF | SVM | KNN | LR | NV | RF | ||
| Female | Female | 95.04 | 89.10 | 89.10 | 85.14 | 93.06 | 98.46 | 93.84 | 95.23 | 94.91 | 95.52 | 88.88 | 80.55 | 78.94 | 71.42 | 88.23 |
| Male | Male | 92.30 | 92.82 | 95.38 | 88.71 | 92.82 | 93.02 | 90.57 | 94.65 | 91.26 | 92.42 | 90.90 | 98.24 | 96.87 | 84.05 | 93.65 |
| Male | Female | 93.75 | 92.26 | 94.05 | 89.29 | 92.56 | 93.94 | 91.25 | 94.74 | 89.17 | 92.34 | 93.33 | 94.79 | 92.59 | 89.58 | 93.07 |
| Female | Male | 92.44 | 92.28 | 92.44 | 90.43 | 94.14 | 90.83 | 90.81 | 93.03 | 93.43 | 93.20 | 96.56 | 96.11 | 91.13 | 84.68 | 96.35 |
| Train | Test | Accuracy (%) | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SVM | KNN | LR | NV | RF | SVM | KNN | LR | NV | RF | SVM | KNN | LR | NV | RF | ||
| Without | Without | 96.11 | 93.33 | 93.89 | 92.22 | 95.56 | 95.80 | 93.33 | 94.12 | 95.54 | 95.00 | 96.72 | 93.33 | 93.44 | 86.76 | 96.67 |
| With | With | 91.38 | 83.62 | 90.52 | 84.48 | 91.38 | 93.75 | 82.80 | 93.67 | 86.90 | 91.67 | 86.11 | 86.96 | 83.78 | 78.13 | 90.63 |
| With | Without | 95.00 | 91.50 | 94.17 | 90.83 | 94.00 | 95.12 | 89.21 | 95.06 | 91.17 | 94.17 | 94.74 | 98.06 | 92.31 | 90.06 | 93.62 |
| Without | With | 94.27 | 92.19 | 92.71 | 89.06 | 94.53 | 94.32 | 91.85 | 92.54 | 91.80 | 93.04 | 94.17 | 92.98 | 93.10 | 83.59 | 98.20 |
| Train | Test | Accuracy (%) | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SVM | KNN | LR | NV | RF | SVM | KNN | LR | NV | RF | SVM | KNN | LR | NV | RF | ||
| Without | Without | 93.33 | 92.22 | 93.89 | 94.44 | 96.11 | 93.33 | 91.13 | 94.87 | 95.69 | 95.80 | 93.33 | 94.64 | 92.06 | 92.19 | 96.72 |
| With | With | 90.52 | 85.34 | 88.79 | 83.62 | 92.24 | 93.67 | 83.87 | 92.41 | 86.75 | 91.76 | 83.78 | 91.30 | 81.08 | 75.76 | 93.55 |
| With | Without | 96.50 | 92.00 | 94.50 | 90.00 | 93.83 | 97.73 | 90.18 | 95.76 | 90.67 | 94.38 | 94.09 | 96.91 | 91.96 | 88.46 | 92.67 |
| Without | With | 93.49 | 92.45 | 92.71 | 88.80 | 93.75 | 94.25 | 92.19 | 92.54 | 91.44 | 92.65 | 91.87 | 93.04 | 93.10 | 83.46 | 96.43 |
| Train | Test | Accuracy (%) | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SVM | KNN | LR | NV | RF | SVM | KNN | LR | NV | RF | SVM | KNN | LR | NV | RF | ||
| < 5.5 | < 5.5 | 92.77 | 91.57 | 91.57 | 89.76 | 91.57 | 93.69 | 90.60 | 92.79 | 91.82 | 90.60 | 90.91 | 93.88 | 89.09 | 85.71 | 93.88 |
| > 5.5 | > 5.5 | 93.85 | 90.77 | 91.54 | 86.15 | 93.08 | 97.56 | 89.36 | 97.47 | 91.46 | 93.26 | 87.50 | 94.44 | 82.35 | 77.08 | 92.68 |
| > 5.5 | < 5.5 | 93.12 | 90.40 | 92.93 | 90.76 | 91.85 | 93.19 | 87.77 | 92.51 | 89.92 | 90.27 | 92.94 | 98.52 | 93.94 | 92.90 | 96.03 |
| < 5.5 | > 5.5 | 94.91 | 92.82 | 94.68 | 89.81 | 93.75 | 94.93 | 91.05 | 95.22 | 92.36 | 93.94 | 94.85 | 97.48 | 93.53 | 84.72 | 93.33 |
| Train | Test | Accuracy (%) | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SVM | KNN | LR | NV | RF | SVM | KNN | LR | NV | RF | SVM | KNN | LR | NV | RF | ||
| < 5.5 | < 5.5 | 95.18 | 93.98 | 92.17 | 90.36 | 91.57 | 97.20 | 93.04 | 93.64 | 92.66 | 90.60 | 91.53 | 96.08 | 89.29 | 85.96 | 93.88 |
| > 5.5 | > 5.5 | 94.62 | 90.77 | 90.00 | 83.85 | 93.08 | 96.47 | 89.36 | 96.20 | 89.16 | 93.26 | 91.11 | 94.44 | 80.39 | 74.47 | 92.68 |
| > 5.5 | < 5.5 | 92.93 | 90.40 | 93.12 | 90.40 | 93.30 | 92.73 | 88.14 | 92.53 | 90.28 | 91.69 | 93.41 | 97.12 | 94.51 | 90.68 | 97.42 |
| < 5.5 | > 5.5 | 95.14 | 93.06 | 94.68 | 89.35 | 93.98 | 94.95 | 91.35 | 95.22 | 92.01 | 94.26 | 95.56 | 97.50 | 93.53 | 84.03 | 93.38 |
| Train | Test | Accuracy (%) | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SVM | KNN | LR | NV | RF | SVM | KNN | LR | NV | RF | SVM | KNN | LR | NV | RF | ||
| 50-65 | 50-65 | 96.35 | 94.89 | 94.89 | 89.78 | 93.43 | 94.68 | 93.62 | 94.57 | 95.18 | 92.55 | 100.00 | 97.67 | 95.56 | 81.48 | 95.35 |
| 65-80 | 65-80 | 91.67 | 87.96 | 88.89 | 84.26 | 92.59 | 93.75 | 87.50 | 95.89 | 91.89 | 94.94 | 85.71 | 90.00 | 74.29 | 67.65 | 86.21 |
| 80-120 | 80-120 | 94.12 | 90.20 | 90.20 | 90.20 | 92.16 | 92.11 | 91.67 | 91.67 | 96.88 | 91.89 | 100.00 | 86.67 | 86.67 | 78.95 | 92.86 |
| 50-65 | 65-80 | 93.89 | 94.17 | 92.78 | 91.39 | 93.61 | 93.60 | 92.94 | 94.21 | 92.65 | 92.22 | 94.55 | 97.14 | 89.83 | 88.70 | 97.09 |
| 50-65 | 80-120 | 89.29 | 90.48 | 86.90 | 86.90 | 88.69 | 91.23 | 89.34 | 88.79 | 90.91 | 89.74 | 85.19 | 93.48 | 82.69 | 79.31 | 86.27 |
| 65-80 | 50-65 | 94.74 | 91.01 | 93.64 | 91.45 | 93.42 | 95.45 | 89.25 | 94.50 | 92.88 | 93.35 | 93.24 | 95.87 | 91.84 | 88.44 | 93.57 |
| 65-80 | 80-120 | 94.64 | 89.29 | 91.07 | 88.69 | 90.48 | 94.78 | 87.30 | 93.69 | 91.15 | 90.00 | 94.34 | 95.24 | 85.96 | 83.64 | 91.67 |
| 80-120 | 50-65 | 88.60 | 87.06 | 92.54 | 90.57 | 92.76 | 88.41 | 85.30 | 93.27 | 92.23 | 91.44 | 89.06 | 92.66 | 90.97 | 87.07 | 96.12 |
| 80-120 | 65-80 | 91.94 | 88.06 | 92.50 | 90.00 | 93.06 | 92.37 | 86.08 | 92.77 | 92.50 | 91.19 | 90.99 | 94.25 | 91.89 | 85.00 | 97.98 |
| Train | Test | Accuracy (%) | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SVM | KNN | LR | NV | RF | SVM | KNN | LR | NV | RF | SVM | KNN | LR | NV | RF | ||
| 50-65 | 50-65 | 94.89 | 95.62 | 94.89 | 89.78 | 93.43 | 93.62 | 94.62 | 95.56 | 95.18 | 92.55 | 97.67 | 97.73 | 93.62 | 81.48 | 95.35 |
| 65-80 | 65-80 | 92.59 | 87.04 | 91.67 | 83.33 | 92.59 | 94.94 | 85.71 | 96.05 | 90.67 | 94.94 | 86.21 | 94.12 | 81.25 | 66.67 | 86.21 |
| 80-120 | 80-120 | 90.20 | 88.24 | 92.16 | 90.20 | 92.16 | 89.47 | 87.18 | 94.29 | 96.88 | 91.89 | 92.31 | 91.67 | 87.50 | 78.95 | 92.86 |
| 50-65 | 65-80 | 94.44 | 94.44 | 93.06 | 91.11 | 93.06 | 94.72 | 92.97 | 94.61 | 91.60 | 91.19 | 93.86 | 98.08 | 89.92 | 90.00 | 97.98 |
| 50-65 | 80-120 | 90.48 | 90.48 | 89.29 | 87.50 | 89.29 | 92.11 | 90.00 | 90.52 | 89.57 | 89.83 | 87.04 | 91.67 | 86.54 | 83.02 | 88.00 |
| 65-80 | 50-65 | 95.18 | 92.11 | 94.30 | 91.45 | 93.64 | 96.08 | 90.61 | 94.84 | 93.44 | 93.93 | 93.33 | 96.03 | 93.15 | 87.42 | 93.01 |
| 65-80 | 80-120 | 93.45 | 89.29 | 89.88 | 87.50 | 90.48 | 93.91 | 87.30 | 91.30 | 89.57 | 90.00 | 92.45 | 95.24 | 86.79 | 83.02 | 91.67 |
| 80-120 | 50-65 | 90.35 | 87.72 | 92.54 | 89.47 | 92.54 | 91.67 | 86.05 | 94.41 | 92.11 | 91.41 | 87.50 | 92.86 | 88.82 | 84.21 | 95.38 |
| 80-120 | 65-80 | 91.94 | 86.11 | 92.50 | 89.44 | 92.22 | 92.37 | 84.17 | 92.77 | 91.74 | 90.46 | 90.99 | 92.68 | 91.89 | 84.75 | 96.94 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




