1. Introduction
With the development of cancer research, although there are some clearly identified risk factors, such as smoking, drinking, obesity and so on, aging is another factor that needs to be paid attention[
1,
2,
3]. Therefore, as one age increases, the incidence rate of cancer increases sharply, which is due to the combination of high risk of specific cancer and low efficiency cell repair mechanism [
4,
5,
6]. In the context of the rapid development of global aging, if we can understand the process of aging and how they affect the development of cancer, and can achieve early detection and early treatment, the cancer mortality can be greatly reduced. Oxidative stress refers to an unbalanced and tend to oxidize state in the body, which is an important factor for aging and diseases, inducing destruction of the normal cell membrane and nuclear structure, protein structure changes and chromosome aberrations[
7,
8,
9]. In recent years, the application of biomarkers in patient status diagnosis and management has become a growing method, and the development of molecular biology has led to the continuous discovery of new circulating biomarkers [
10,
11]. At the same time, molecular epidemiological studies have also confirmed the relationship between oxidative stress and carcinogens [
12,
13].
Hydroxyl radical may attack cellular membranes, proteins, nucleic acids, nuclear, mitochondrial DNA and RNA, during which 8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine (8-OHdG) formed abundantly and stablely [
14]. At present, the most commonly used and promising biomarkers 8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine (8-OHdG) for oxidative stress have been investigated in medicine and toxicology [
15,
16]. It has proposed that the content of 8-OHdG is the most studied biomarker of DNA damage induced several diseases, including cancer[
17,
18,
19], neurodegenerative disorders [
20,
21], diabetes [
22,
23], cardiovascular [
24,
25] and infectious diseases [
26]. As early detection is still the most crucial determinant for successful treatment and survival. Therefore, oxidative stress biomarker 8-OHdG assays carried out in wide screening programs by POCT are very useful for early diagnosis and assessment of susceptible population. Researches showed that 8-OHdG had been detected in various biological samples, such as plasma, urine, saliva, and tissue [
27,
28,
29,
30,
31,
32]. Among them urinary biological samples were broadly used in preventive and occupational medicine due to their non-invasive sampling performances.
Various methods have been proposed to sense 8-OHdG in biological samples, shuch as gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS), high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), liquid chromatography-single mass spectrometry (HPLC-MS), enzyme-linked immunosorbant assay (ELISA), and resonance rayleigh scattering (RRS) [
33,
34,
35,
36,
37]. They showed high sensitivity in 8-OhdG quantitative study due to the professional equipment with the multiple reaction monitoring mode leading to a considerable reduction in the background ions-caused noise. However, the consumption of time, the requirment of sophisticated and laborious technologies, and the excessive handling of biological samples induced they not conducive to on-site screening needs in special environments. Therefore, the development of portable, fast, easy-to-use and low cost methods for 8-OHdG detection remains a challenge. As alternative, biosensor have been reported achieving through electrochemical or quartz crystal microbalance (QCM) detection techmologies [
38,
39,
40], by using the 8-OHdG active redox properties established direct reading modes. This is beneficical for establishing a POCT platform to transfer traditional diagnostic tests in the clinical laboratory setting to near-patient setting with timely diagnostic information enabling better informed decisions regarding diagnosis.
In this work, we proposed an sensitive oxidative stress biosensor by using the AuNTAs/PtNPs plasma-assembled ITO electrode for the detection of 8-OHdG. The sensing electrode adopted multi-layer screen printing process, and was made of special template printing carbon paste and silver paste on the flexible and transparent ITO material substrate. AuNTAs were modified on ITO electrode by electrostatic adsorption, and PtNPs were modified on ITO/AuNTAs electrode by electrochemical reduction. Based on square wave voltammetry (SWV), PtNPs were prepared by reduction with chloroplatinic acid hexahydrate on the AuNTAs modified electrode. Then a portable oxidative stress sensing system for the electrochemical detection was developed with screen printed sensing electrodes, printed circuit boards (PCBs), PCs/smartphones. Finally, the layer by layer self-assembled electrodes and the portable sensing system were applied for 8-OHdG detection from 10 ng/mL to 100 μg/mL by differential pulse voltammetry (DPV). Here, the strategy of applying ITO/AuNTAs/PtNPs electrode as sensing layer to achieve electrochemical analysis and enhance sensitivity is reported for the first time. Moreover, the fabricated oxidative stress sensing system exhibited good performance in POCT, demonstrating its promising application in biomarkers monitoring.
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
ITO-PET (resistance ≤6 ohm/sq) was obtained from HNXCKJ Co., Ltd (China). Hydrophobic layer was obtained from Neopro Co., Ltd (China). Silver-ink was obtained from UVTM Co., Ltd (China). Carbon-ink was obtained from JUJO Co., Ltd (Japan). Isopropanol (C3H8O), gold chloride trihydrate (HAuCl4·3H2O), chloroplatinic acid hexahydrate (H2PtCl6·6H2O), sodium thiosulfate pentahydrate (Na2S2O3·5H2O) were obtained from Sigma-Aldrich (United States). Phosphate buffer saline (PBS, pH = 7.4) was obtained from Standard information network (China). 8-OHdG, potassium ferricyanide (K3Fe(CN)6) and potassium hexacyanoferrate (II) (K4Fe(CN)6) were obtained from Sigma-Aldrich (United States).
2.2. Production of ITO Electrode
ITO electrodes were produced by automatic screen printing machine. Figure 1a showed the fabrication process of ITO electrode : (1) Clean the ITO substrate with isopropanol. Each electrode was 20.0 mm long and 8.5 mm wide. (2) Cover hydrophobic layer-Ⅰ on ITO substrate to expose the circular working electrode (WE) area and interface part. The diameter of WE was 4.0 mm. (3) Print three strips of silver-ink with a width of 1.0 mm, and the right one was as reference electrode (RE). (4) Print arc-shaped carbon-ink as counter electrode (CE) with a width of 0.8 mm. (5) Cover hydrophobic layer-Ⅱ on the upper area of ITO electrode to expose the detection area with CE and RE as boundary. Figure 1b showed the finished electrode product of batch printing and the great flexibility of ITO electrode.
2.3. Synthesis of AuNTAs
In seed preparation, 10mL 2mM HAuCl
4·3H
2O and 12mL 0.5mM Na
2S
2O
3·5H
2O were mixed in 50 mL conical bottle and gently stirred for 15 minutes at room temperature (
Figure 1c). Then 2mL 0.5mM Na
2S
2O
3·5H
2O was added into the solution for seed growth. After 90 minutes of stirring, the AuNTAs were formed. Finally, the AuNTAs solution was centrifugated at 6000 rpm for 10 minutes and stored at room temperature. Spectral analysis of AuNTAs was carried out by UV-vis-NIR (Lambda 750, Perkin Elmer, America). Triangular features in nanometer size of AuNTAs were observed by transmission electron microscope (TEM, Tecnai G2 F20, Netherlands).
2.4. Plasma-Assembled ITO Electrode
Before the modifying process, it was necessary to clean the electrode surface. At the start, deionized water was used to wash the electrode surface. Then 80 μL of PBS was dripped to the detection area of electrode, using DPV to get the electrochemical cleaning effect. Scan from 0.15 V to 0.35 V with 25 mV amplitude, 5 mV increment, 50 ms pulse width and 500 ms pulse period. After about 6-8 cycles scanning, the steady DPV response curve was observed. At last, deionized water was used to wash the electrode again. This cleaning process was very important to get stable electrochemistry response during further 8-OHdG detection process. After the cleaning process, the electrode should be dried by N2. Then 10 μL AuNTAs solution was evenly dripped on the WE and the whole electrode was put into the oven at 60 ℃ for 20 minutes (Figure 1d). Due to the electrostatic adsorption, AuNTAs were tightly adsorbed on the surface of WE so as to get AuNTAs modified electrode. In electrochemical reduction, 80 μL H14Cl6O6Pt was dripped to the detection area of electrode, using SWV to electrodeposit PtNPs. Scan from -0.2 V to -0.8V with 25 mV amplitude and 10 mV increment for 6 circles. Finally AuNTAs/PtNPs modified electrode was prepared. CV was used to describe electrochemical characterization of electrodes. 80 μL redox pairs (Fe2+/Fe3+) solution was scanned from -0.4 V to 0.6 V with scan rate of 50mV/s. All electrochemical methods were carried out on a CHI660E electrochemical workstation (China). The morphological characteristics of modified electrode were observed by scanning electron microscope (SEM, NanoSEM 430, United States). Elemental analysis was carried out by energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS, EMSA/MAS, United Kingdom).
2.5. 8-OHdG Detection
8-OHdG was dissolved in PBS to prepare standard solutions which concentrations ranged from 10 ng/mL to 100000 ng/mL. During the preparation, 5 minutes of the shaking was needed to make sure the full dissolution. DPV was used for 8-OHdG detection, scanning from 0.22 V to 0.53 V, with 25 mV amplitude, 5 mV increment, 50 ms pulse width and 500 ms pulse period. Before each scan, 80 μL of the standard solution was added to the detection area of the ITO/AuNTAs/PtNPs electrode and 8-OHdG in the solution would be oxidized gradually with the variation of potential and formed peak current. After each scan, deionized water was used to clean electrode. In order to obtain reliable and reproducible results, three electrodes need to be prepared and used to scan solutions of each concentration (10 ng/mL, 100 ng/mL, 1 μg/mL, 5 μg/mL, 10 μg/mL, 50 μg/mL, 100 μg/mL). All detections were performed at room temperature. In data processing, mathematical analysis means were used to calculate the peak current of standard solutions with different concentration and observe the correlation of concentration and peak current.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Oxidative Stress Sensing System
We have developed a portable oxidative stress sensing system for the electrochemical detection of 8-OHdG. The system consists of screen printed sensing electrodes, printed circuit boards (PCBs), PCs, or smartphones (
Figure 2a). The sensing electrode adopted multi-layer screen printing process, and was made of special template printing carbon paste and silver paste on the flexible and transparent ITO material substrate. It contained the WE of ITO material, the RE of Ag/AgCl material, and the CE of carbon material. The size of a single sensing electrode was 8.5mm × 20.0mm, and the circular detection area was about 0.5cm
2. The small size feature of the electrode ensureed that the detection of 8-OHdG concentration would be completed only by dripping about 50 μL test solution into the detection area. The sensing electrode was connected to the three electrode interface of the PCB head, and the PCB controled the electrode to output and collect electrical signals in electrochemical detection. The collected data was transmitted to a PC or smartphone through Bluetooth, and finally processed to obtain relevant concentration information. This portable electrochemical detection device had the characteristics of fast, accurate and low power consumption, and was a relatively common platform in electrochemical detection. It can realize a variety of electrochemical detection methods, such as CV, DPV, and SWV etc. It can carry different sensing electrodes to detect different biomarkers.
As shown in
Figure 2b, the PCB was composed of a power supply, microcontroller, potentiostat module, digital to analog conversion module (DAC), analog-to-digital conversion module (ADC), Bluetooth module, etc. The microcontroller controled the DAC to generate DPV voltage excitation and applied it to the sensor electrode through the potentiostat module. At the same time, the ADC collected the current signal generated in the chemical reaction (DPV response) and sent it to the upper computer through Bluetooth transmission for data processing and result display. The core circuit module was the potentiostat module, which was connected to the DAC and ADC inside the PCB, and directly connected to the sensing electrode through the RE/WECE interface.
Figure 2b showed the schematic diagram of the relevant circuit design. The potentiostat consisted of an in-phase amplifier, a voltage follower, a transimpedance amplifier (TIA), and a reference source. WE and RE formed a voltage control loop, using the voltage feedback effect of the amplifier to construct a in-phase amplifier and a voltage follower to accurately control the voltage. The voltage at the RE end was controlled by the DAC (DAC_RE), and the bias voltage at the WE end was controlled by the reference source chip AZ431 and ensured to be stable at 1.24V left to right. This way, the voltage difference between RE and WE can be adjusted within a certain positive and negative range. WE and CE formed a current loop and convert current to voltage through TIA, thereby outputting to ADC for signal acquisition (ADC_OUT). Adjusting the size of the resistor Rx can change the output voltage, thereby adjusting the detection sensitivity.
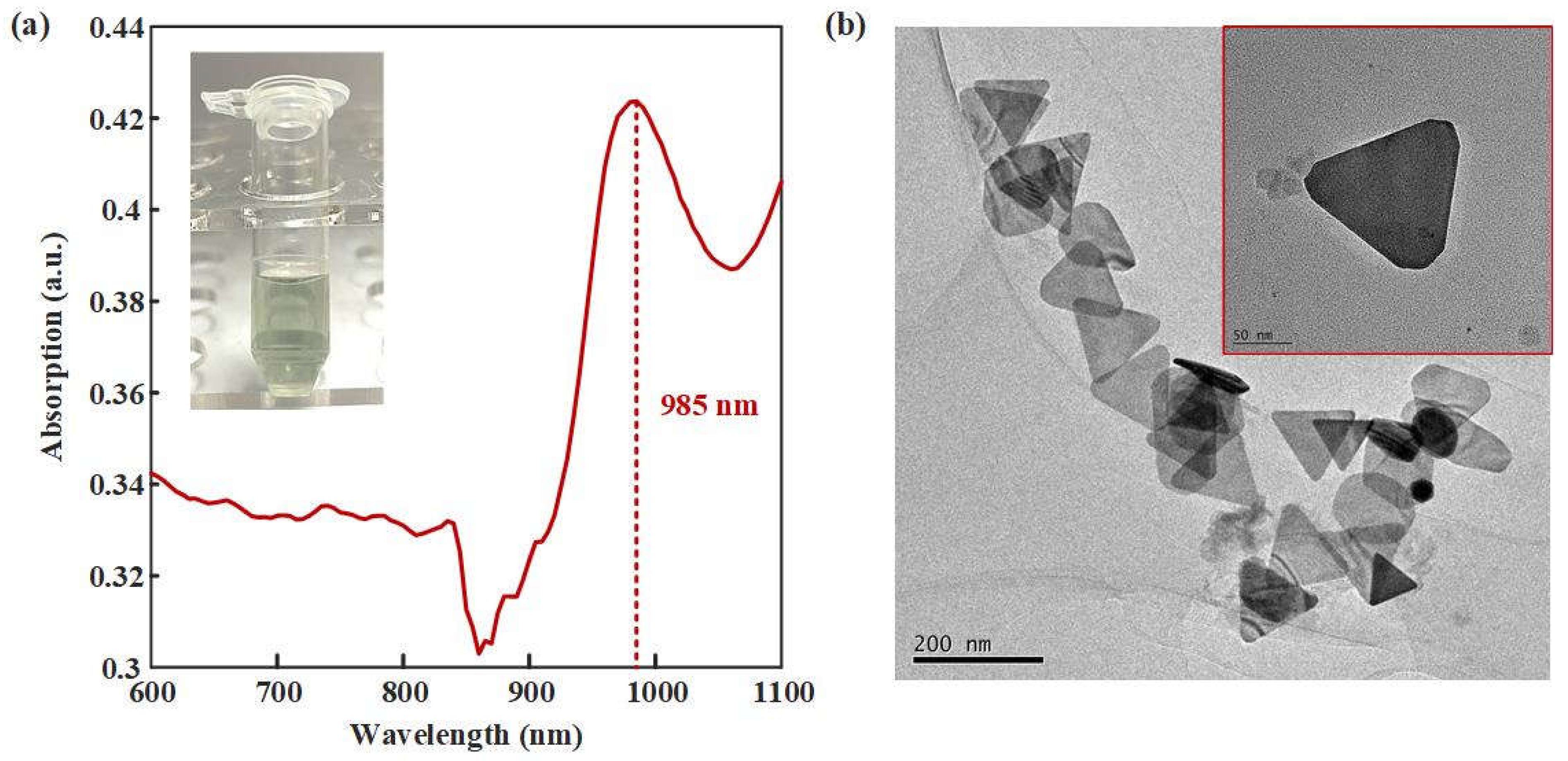
Figure 3.
Characteristics of AuNTAs. (a) UV-vis-NIR spectrum of AuNTAs. (b) TEM of AuNTAs.
Figure 3.
Characteristics of AuNTAs. (a) UV-vis-NIR spectrum of AuNTAs. (b) TEM of AuNTAs.
3.2. Characteristics of ITO/AuNTAs/PtNPs Electrode
UV-vis-NIR and TEM were used to verify the synthesis effect of AuNTAs. As shown in
Figure 3a, an obvious absorption peak appeared at 985 nm wavelength, which proved the successflu synthesized of AuNTAs.
Figure 3b showed the regular triangular shapes of AuNTAs under the TEM. The average particle size of AuNTAs was about 130 nm.
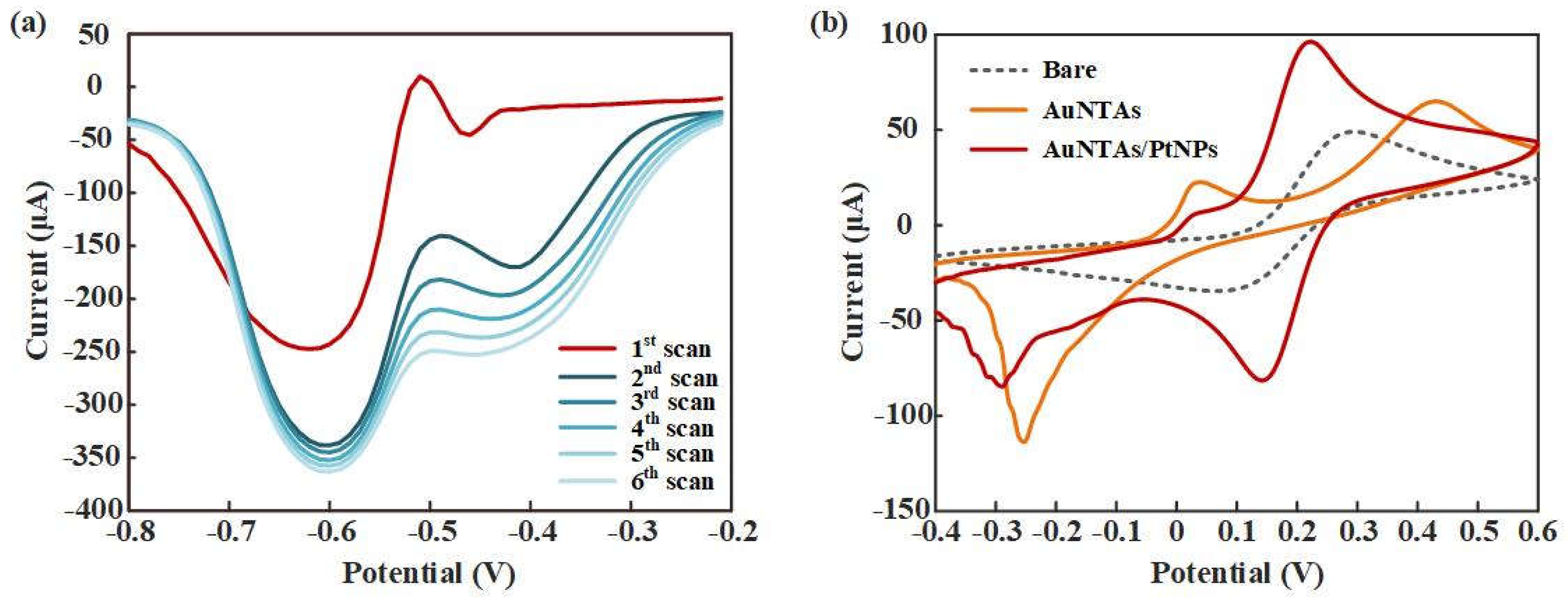
Figure 4a showed the SWV response curves of PtNPs electrodeposition. A great gap appeared in the first two scans and gradually decreased in next four scans, which indicated that PtNPs were ultimately deposited on the WE.
Figure 4b showed the CV response curves of bare electrode, AuNTAs modified electrode and AuNTAs/ PtNPs modified electrode. Compared with bare electrode (Ep=0.294 V, ip=4.907e-5 A), AuNTAs modified electrode showed a fact that oxidation peak current raised and the peak position shifted to the right (Ep=0.431 V, ip=6.495e-5 A). It indicated that AuNTAs had a specific enhancing effect to ITO electrode because of its nano triangular features. As expected, AuNTAs/PtNPs modified electrode showed a great current enhancement characteristic (Ep=0.222V, ip=9.636e-5 A) as a result of the formation of arranged PtNPs on the AuNTAs modified electrode. Also, a phenomenon could be observed was that the position of oxidation peak had shifted back to the left, which may be related to the fully covering of PtNPs on the WE surface.
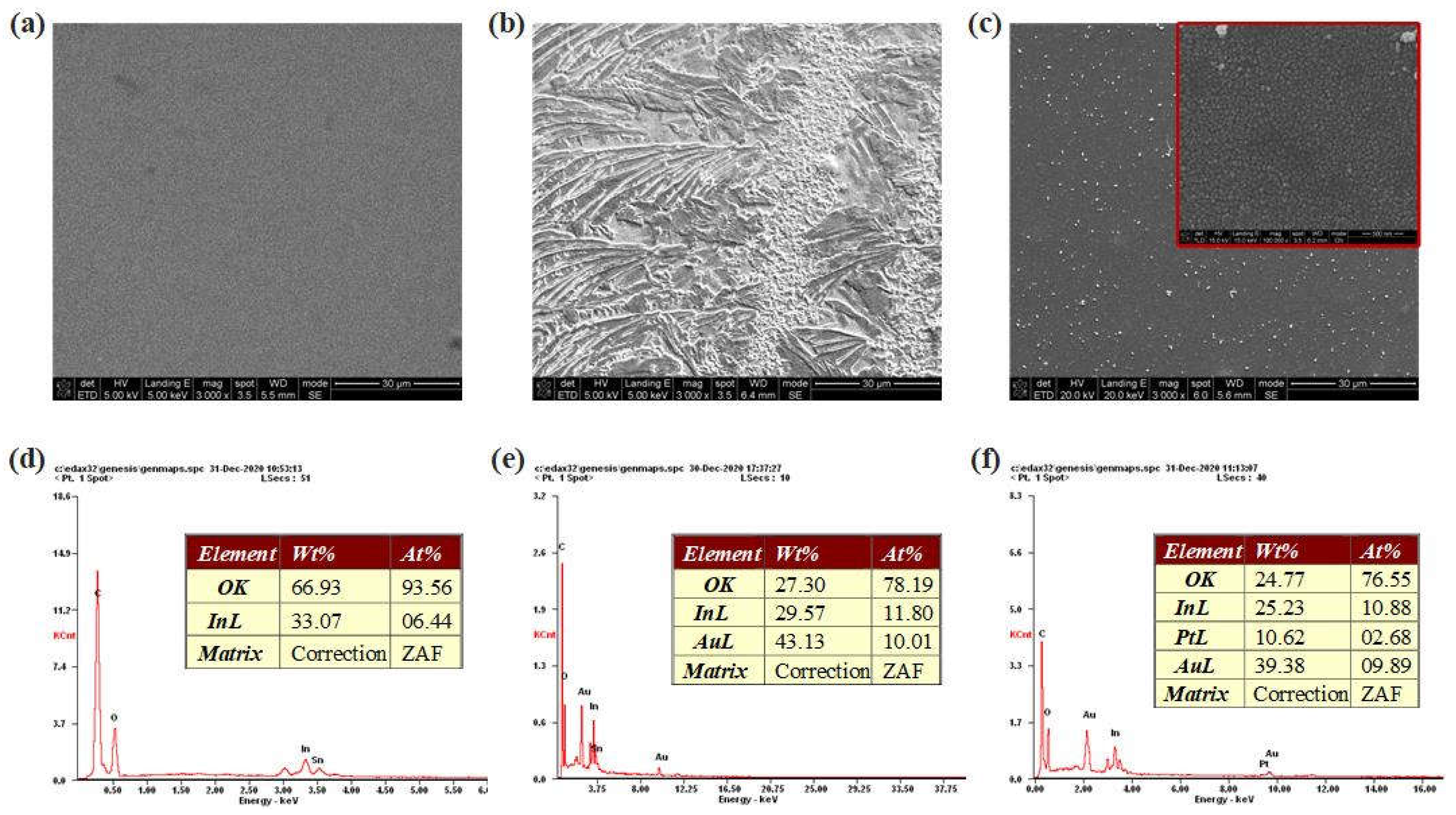
SEM images and EDS analyses of bare electrode, AuNTAs modified electrode and AuNTAs/PtNPs modified electrode were shown in
Figure 5a-c. Bare ITO electrode showed a clean and smooth surface while AuNTAs modified electrode had an apparently rough surface. Under the excitation of negative potential, PtNPs were evenly and densely tiled on the WE, which increased the contact area between test sample and electrode, so as to improve the sensitivity.
Figure 5d-f showed the elemental type and content changes in electrode modification through EDS. The element of bare ITO electrode mainly contained O and In, and the weight percentages were 66.93 % and 33.07 %, respectively. When AuNTAs were modified, Au became the main element of the electrode, whose weight percentage reached 43.13 % and atomic percentage reached 10.01 %. When PtNPs were electrodeposited on AuNTAs modified electrode, Pt element in the electrode showed up with 10.62 % weight percentage and 2.68 % atomic percentage. These results strongly proved the preparation success of ITO/AuNTAs/PtNPs electrode.
3.3. 8-OhdG Detection
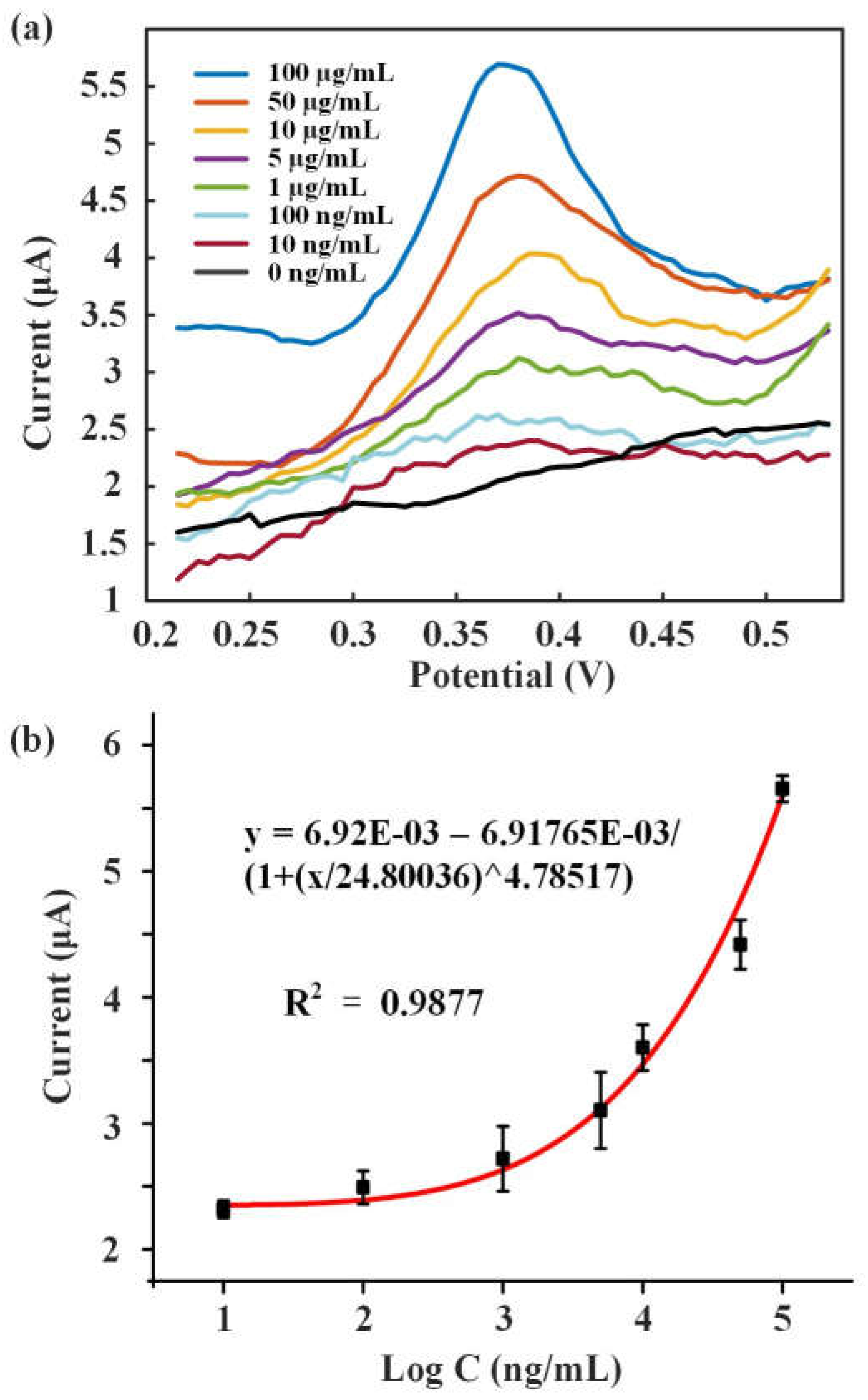
Different concentrations of 8-OHdG solutions (10 ng/mL, 100 ng/mL, 1 μg/mL, 5 μg/mL, 10 μg/mL, 50 μg/mL, 100 μg/mL) were detected.
Figure 6a showed the DPV response curves of these solutions. 8-OHdG was fully oxidized at around 0.38 V and formed the peak current. As the increase of 8-OHdG concentration, the peak current also improved.
Figure 6b showed fitting curve of the concentration of 8-OHdG and peak current, between which the logarithmic fitting relationship was y = 6.92E-03 – 6.91765E-03/(1+(x/24.80036)^4.78517). The results showed that this method was feasible to detect 8-OHdG.
4. Conclusions
In this study, plasma coupled electrochemistry electrode was proposed by transparent ITO/AuNTAs/PtNPs for oxidative stress sensing of 8-OHdG. ITO electrodes were prepared from layer-by-layer screen printing. Plasma-assembled ITO electrode was functionalized by electrostatic adsorption of AuNTAs and electrochemical reduction of PtNPs, which achieved high-precision sensing of 8-OHdG. Then a portable electrochemical detection device with power supply, microcontroller, potentiostat module, DAC, ADC, and Bluetooth module was designed for fast, accurate and low power consumption. The prepared oxidative stress sensing system exhibited good linearity in the concentration range of 8-OHdG from 10 ng/mL to 100000 ng/mL. Besides, it was a relatively common platform in electrochemical detection, can realize CV, DPV, and SWV with specific signal stimulus, showed great potential for further development in POCT.
Author Contributions
Yongchang Bai: Conceptualization, Methodology, Experiment, Data curation, Writing – original draft. Shuang Li: Conceptualization, Experimental design, Writing – review & editing, Supervision.
Funding
This work was funded by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2022YFF1202704), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 82001922), the HongKong Scholars Program (Grant No. XJ2021034).
Acknowledgments
Thank you to Ziyue Qin, Jie Fu and Qiya Gao for their assistance in Electrochemical Experiments and Data curation.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- [1] R.C. Kafle, D.Y. Kim, M.M. Holt, Gender-specific trends in cigarette smoking and lung cancer incidence: A two-stage age-stratified Bayesian joinpoint model, Cancer Epidemiology, 84(2023) 102364. [CrossRef]
- [2] J. Huang, E.O.-T. Chan, X. Liu, V. Lok, C.H. Ngai, L. Zhang, et al., Global Trends of Prostate Cancer by Age, and Their Associations With Gross Domestic Product (GDP), Human Development Index (HDI), Smoking, and Alcohol Drinking, Clinical Genitourinary Cancer, (2023). [CrossRef]
- [3] F. Cheng, J. He, J. Yang, Bone marrow microenvironment: roles and therapeutic implications in obesity-associated cancer, Trends in Cancer, (2023). [CrossRef]
- [4] D.J. Zabransky, E.M. Jaffee, A.T. Weeraratna, Shared genetic and epigenetic changes link aging and cancer, Trends in Cell Biology, 32(2022) 338-50. [CrossRef]
- [5] A.-H. Rezaeian, F. Dang, W. Wei, The circadian clock, aging and its implications in cancer, Neoplasia, 41(2023) 100904. [CrossRef]
- [6] K. Chatsirisupachai, C. Lagger, J.P. de Magalhães, Age-associated differences in the cancer molecular landscape, Trends in Cancer, 8(2022) 962-71. [CrossRef]
- [7] P. Rossner, A. Rossnerova, R.J. Sram, Oxidative stress and chromosomal aberrations in an environmentally exposed population, Mutation Research/Fundamental and Molecular Mechanisms of Mutagenesis, 707(2011) 34-41. [CrossRef]
- [8] S. Barathkumar, R.K. Padhi, P.K. Parida, S.R. Marigoudar, In vivo appraisal of oxidative stress response, cell ultrastructural aberration and accumulation in Juvenile Scylla serrata exposed to uranium, Chemosphere, 300(2022) 134561. [CrossRef]
- [9] J.Y. Song, J.W. Lim, H. Kim, T. Morio, K.H. Kim, Oxidative Stress Induces Nuclear Loss of DNA Repair Proteins Ku70 and Ku80 and Apoptosis in Pancreatic Acinar AR42J Cells*, Journal of Biological Chemistry, 278(2003) 36676-87. [CrossRef]
- [10] N.G. Than, M. Posta, D. Györffy, L. Orosz, G. Orosz, S.W. Rossi, et al., Early pathways, biomarkers, and four distinct molecular subclasses of preeclampsia: The intersection of clinical, pathological, and high-dimensional biology studies, Placenta, 125(2022) 10-9. [CrossRef]
- [11] S. Tang, K. Yuan, L. Chen, Molecular biomarkers, network biomarkers, and dynamic network biomarkers for diagnosis and prediction of rare diseases, Fundamental Research, 2(2022) 894-902. [CrossRef]
- [12] N. Sambiagio, A. Berthet, P. Wild, J.-J. Sauvain, R. Auer, A. Schoeni, et al., Associations between urinary biomarkers of oxidative stress and biomarkers of tobacco smoke exposure in smokers, Science of The Total Environment, 852(2022) 158361. [CrossRef]
- [13] G. Peris-Pastor, S. Alonso-Rodríguez, J.L. Benedé, A. Chisvert, High-throughput determination of oxidative stress biomarkers in saliva by solvent-assisted dispersive solid-phase extraction for clinical analysis, Advances in Sample Preparation, 6(2023) 100067. [CrossRef]
- [14] I. Marrocco, F. Altieri, I. Peluso, Measurement and Clinical Significance of Biomarkers of Oxidative Stress in Humans, Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity, 2017(2017) 6501046. [CrossRef]
- [15] G.V. Martins, A.C. Marques, E. Fortunato, M.G.F. Sales, 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG) biomarker detection down to picoMolar level on a plastic antibody film, Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 86(2016) 225-34. [CrossRef]
- [16] L. Bláhová, T. Janoš, V. Mustieles, A. Rodríguez-Carrillo, M.F. Fernández, L. Bláha, Rapid extraction and analysis of oxidative stress and DNA damage biomarker 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG) in urine: Application to a study with pregnant women, International Journal of Hygiene and Environmental Health, 250(2023) 114175.
- [17] T. Yano, F. Shoji, H. Baba, T. Koga, T. Shiraishi, H. Orita, et al., Significance of the urinary 8-OHdG level as an oxidative stress marker in lung cancer patients, Lung Cancer, 63(2009) 111-4. [CrossRef]
- [18] H. Sova, A. Jukkola-Vuorinen, U. Puistola, S. Kauppila, P. Karihtala, 8-Hydroxydeoxyguanosine: A new potential independent prognostic factor in breast cancer, British Journal of Cancer, 102(2010) 1018-23. [CrossRef]
- [19] J. Sheridan, L.M. Wang, M. Tosetto, K. Sheahan, J. Hyland, D. Fennelly, et al., Nuclear oxidative damage correlates with poor survival in colorectal cancer, British Journal of Cancer, 100(2009) 381-8. [CrossRef]
- [20] I. Zerr, J. Gawinecka, K. Gmitterowa, P2.028 8-OHdG in cerebrospinal fluid as a marker of oxidative stress in various neurodegenerative diseases, Parkinsonism & Related Disorders, 15(2009) S96. [CrossRef]
- [21] C. Feng, S. Liu, F. Zhou, Y. Gao, Y. Li, G. Du, et al., Oxidative stress in the neurodegenerative brain following lifetime exposure to lead in rats: Changes in lifespan profiles, Toxicology, 411(2019) 101-9. [CrossRef]
- [22] H. Chen, C. Sun, W. Guo, R. Meng, H. Du, Q. Qi, et al., AluYb8 insertion in the MUTYH gene is related to increased 8-OHdG in genomic DNA and could be a risk factor for type 2 diabetes in a Chinese population, Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology, 332(2011) 301-5. [CrossRef]
- [23] W. Liu, B. Wang, S. Yang, T. Xu, L. Yu, X. Wang, et al., Associations of propylene oxide exposure with fasting plasma glucose and diabetes: Roles of oxidative DNA damage and lipid peroxidation, Environmental Pollution, 292(2022) 118453. [CrossRef]
- [24] T. Myoren, S. Kobayashi, S. Oda, T. Nanno, H. Ishiguchi, W. Murakami, et al., An oxidative stress biomarker, urinary 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine, predicts cardiovascular-related death after steroid therapy for patients with active cardiac sarcoidosis, International Journal of Cardiology, 212(2016) 206-13. [CrossRef]
- [25] J. Song, J. Zhu, G. Tian, H. Li, H. Li, Z. An, et al., Short time exposure to ambient ozone and associated cardiovascular effects: A panel study of healthy young adults, Environment International, 137(2020) 105579. [CrossRef]
- [26] L.L. Wu, C.-C. Chiou, P.-Y. Chang, J.T. Wu, Urinary 8-OHdG: a marker of oxidative stress to DNA and a risk factor for cancer, atherosclerosis and diabetics, Clinica Chimica Acta, 339(2004) 1-9. [CrossRef]
- [27] P. Koivisto, A.L. Kosonen, J. Laakso, Oxidative damage marker 8-OHdG in urine of vegetarians and omnivores, Toxicology Letters, 238(2015) S72-S3. [CrossRef]
- [28] M.G. Trachioti, J. Hrbac, M.I. Prodromidis, Determination of 8−hydroxy−2ˊ−deoxyguanosine in urine with “linear” mode sparked graphite screen-printed electrodes, Electrochimica Acta, 399(2021) 139371.
- [29] D. Ekuni, T. Tomofuji, N. Tamaki, T. Sanbe, T. Azuma, R. Yamanaka, et al., Mechanical stimulation of gingiva reduces plasma 8-OHdG level in rat periodontitis, Archives of Oral Biology, 53(2008) 324-9. [CrossRef]
- [30] A. Sayal, A. Aydin, A. Savaser, O. Erdem, A. Eken, Z. Arsova-Sarafinovska, et al., Evaluation of plasma 8-OHdG levels in prostate cancer, benign prostatic hyperplasia patients and healthy individuals, Toxicology Letters, 180(2008) S81.
- [31] M. Yasuda, H. Ide, K. Furuya, T. Yoshii, K. Nishio, K. Saito, et al., Salivary 8-OHdG: A Useful Biomarker for Predicting Severe ED and Hypogonadism, The Journal of Sexual Medicine, 5(2008) 1482-91. [CrossRef]
- [32] R. Arunachalam, A.P. Reshma, V. Rajeev, S.B. Kurra, M.R.J. Prince, N. Syam, Salivary 8-Hydroxydeoxyguanosine – a valuable indicator for oxidative DNA damage in periodontal disease, The Saudi Journal for Dental Research, 6(2015) 15-20. [CrossRef]
- [33] S. Mei, Q. Yao, C. Wu, G. Xu, Determination of urinary 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine by two approaches - Capillary electrophoresis and GC/MS: An assay for in vivo oxidative DNA damage in cancer patients, Journal of Chromatography B: Analytical Technologies in the Biomedical and Life Sciences, 827(2005) 83-7. [CrossRef]
- [34] R. Yoshida, Y. Ogawa, H. Kasai, Urinary 8-oxo-7,8-dihydro-2′-deoxyguanosine values measured by an ELISA correlated well with measurements by high-performance liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection, Cancer Epidemiology Biomarkers and Prevention, 11(2002) 1076-81.
- [35] S. Koide, Y. Kinoshita, N. Ito, J. Kimura, K. Yokoyama, I. Karube, Determination of human serum 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG) by HPLC-ECD combined with solid phase extraction (SPE), Journal of Chromatography B, 878(2010) 2163-7. [CrossRef]
- [36] H. Guo, K. Xue, L. Yan, Resonance Rayleigh scattering spectral method for determination of urinary 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine using gold nanoparticles as probe, Sensors and Actuators, B: Chemical, 171-172(2012) 1038-45. [CrossRef]
- [37] D. Wu, B. Liu, J. Yin, T. Xu, S. Zhao, Q. Xu, et al., Detection of 8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine (8-OHdG) as a biomarker of oxidative damage in peripheral leukocyte DNA by UHPLC–MS/MS, Journal of Chromatography B, 1064(2017) 1-6. [CrossRef]
- [38] A. Gutiérrez, F.A. Gutierrez, M. Eguílaz, J.M. González-Domínguez, J. Hernández-Ferrer, A. Ansón-Casaos, et al., Electrochemical sensing of guanine, adenine and 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine at glassy carbon modified with single-walled carbon nanotubes covalently functionalized with lysine, RSC Advances, 6(2016) 13469-77.
- [39] P. Gupta, M. Oyama, R.N. Goyal, Electrochemical investigations of 8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine and its determination at an edge plane pyrolytic graphite electrode, RSC Advances, 6(2016) 1722-8. [CrossRef]
- [40] Rosy, R.N. Goyal, Determination of 8-Hydroxydeoxyguanosine: A potential biomarker of oxidative stress, using carbon-allotropic nanomaterials modified glassy carbon sensor, Talanta, 161(2016) 735-42. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).