1. Introduction
Sheep and goats are an important source of nutrition and income to smallholder famers, notably rural women and children, especially in tropical Africa. One of the major factors affecting efficient sheep and goats’ production is the presence of high impact transboundary animal diseases (TADs) (Mdetele, et al., 2021). Among the deadliest diseases of sheep and goats is the Peste des Petits Ruminants (PPR). The presence of this disease is a major obstacle to the development of the livestock industry because of its adverse effects on production, productivity and on trade of animals and animal products into lucrative export markets (Mdetele et al., 2021). This disease is presented clinically with difficulty in breathing and coughing, hence termed as a respiratory disease of small ruminants. Laboratory diagnoses is complicated with limited laboratory facilities and cost associated with sample collection preservation, transportation and reagents used in the laboratories. Emergency of Artificial intelligence (AI) technology could be an efficient, cost effective for early identification and prediction of these diseases affecting small ruminants. However, data scarcity to support development of PPR predictive models has become a hindrance. As such, this study experiments the synthesis of accurate data to support the prediction of PPR based on Machine Learning techniques. The reliability of the synthesized data is tested and results are presented.
2. Summary
Machine learning is a significant field in the Fourth Industrial Revolution (4IR), it uses models and statistical algorithms to enable computers learn from data and become better at a given task without having to be explicitly programmed (Alpaydin, 2010). This field has been engaged with many scholars for research and practitioners to solve real world problems for instance in agriculture and livestock (Nyambo et al., 2019).
Machine learning algorithms use data to learn and make predictions, and the quality of the predictions is directly related to the quality, quantity and relevance of the data used to train the model (Sarker, 2021). Hence, more data means more variation and diversity, which allows machine learning models to generalize better and make more accurate predictions on new and unseen data.
In the real world there is a challenge of data scarcity, especially data that can be used to accurately predict and surveillance infectious disease by using Machine Learning techniques. This is because data collection can be expensive, time consuming and sometimes difficult. Although many researchers in developing countries use data from developed countries, it has been shown that problems solved with locally obtained data tends to address the problem well (Mduma, Kalegele, & Machuve, 2019).
Data scarcity is detrimental to any machine learning project because a small dataset may not capture all the relevant patterns and relationships, leading to overfitting and poor performance of the machine learning model on new data. The efforts to solve data scarcity in the field has led to the development of data synthesis methods that aim to generate new data samples from few real-world data. Some of the data synthesis methods include Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) (Goodfellow & Pouget-Abadie, 2014) and Variational autoencoders (VAE) (Kingma & Welling, 2013).
This work focuses on data synthesis of categorical data for training a machine learning model using Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), mainly the conditional tabular generative adversarial network to synthesize categorical data for training machine learning models for prediction of the Pestes des Petits Ruminants (PPR) disease.
Pestes des Petits Ruminants (PPR) disease is a fatal and highly contagious disease that affects small ruminants like goats and sheep. In Tanzania, the disease has been prevalent among the pastoralist’s communities in the Northern Tanzania zone since 2008 when it was first introduced. The disease affects herds instantly after one of the animals gets infected. Current means to combat it are through vaccines which shows a good seroconversion rate of 98% but endless interactions with unvaccinated animals or wild animals causes the endemic disease to erupt again (Mdetele, et al., 2021).
2.1. Generative Adversarial Networks (GAN)
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) are a type of deep learning algorithm that are used to generate new data that is similar to a given set of data mostly tabular data. The fundamental concept underlying GANs is to simultaneously train a generator network and a discriminator network. The discriminator network tries to differentiate between the generated data and the training data while the generator network generates fresh data (Goodfellow I. , et al., 2020). In a process known as adversarial training, the two networks are trained together, with the discriminator network learning to discern between real and produced data while the generator network learns to generate data that can trick the discriminator network.
Initially the GAN architecture was described by (Goodfellow & Pouget-Abadie, 2014) but there has been a numerous extension to it (Goodfellow I. , et al., 2020). Research on this area has grown resulting to modifications like: Conditional GANs that is based on the generation of data conditioned on some input variables (Mirza & Osindero, 2014), (Yu, Wang, Fang, & Zhang, 2020), (Ates, Karwan, Okraschevski, Koch, & Bauer, 2023), . Wasserstein GANs that uses a new loss function to enhance training stability and convergence (Arjovsky, Chintala, & Bottou, 2017) and Conditional Wasserstein GAN that uses an auxiliary classifier loss (Engelmann & Lessmann, 2021). CycleGANs that is used mostly on images and is used to learn image-to-image translation without paired data Zhu et al. (2017).
2.2. Related Works
Bakhshipour at al. (2022) developed a GAN model to generate synthetic time-series data from the limited time-series data that they recorded for predicting combined sewer flow. Bayesian Optimization Hyper Band Algorithm was used for hyperparameter tuning. The authors employed Jensen-Shannon Divergence and the Kullback-Leiber divergence used as an assessment method to weakly evaluate the performance of the GAN. The forecasting model was built using Tensorflow with LSTM layers, ADAM was used as an optimizer and MAE cost function was included. The results showed that although the model without synthetic data performed better than the model with synthetic data, the model with synthetic data had higher accuracy for predicting the peak values (Bakhshipour, et al., 2022).
Furthermore, Wang et al. (2021) used Synthetic Data Vaulting (SDV) to generate synthetic data for predicting the progression of COVID-19. The study trained an SDV model on a small COVID-19 dataset and generated synthetic data to increase the size of the dataset. Synthetic data vaulting was used and generally led to improved accuracy of the model. A similar work is done by Bannur, et al., (2020) using the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) Curve fit model to generate data that will be fed into SIR model for the forecasting. The model was evaluated using Absolute Percentage Error (APE).
Similarly, Giacomo & David (2021) presents a novel approach for generating synthetic tabular data that addresses the challenges of maintaining privacy while ensuring statistical similarity to the original data. The study incorporated differential privacy into the GAN framework to ensure that the privacy of individuals in the original dataset is preserved. The study evaluated the model by passing synthetic data to train the model and real-world data to test the model and measuring the utility, detection and privacy metrics. The proposed approach was shown to be effective in several real-world datasets, and has the potential to be used in a variety of applications where privacy preservation is a concern.
Xu et al. (2019) describes the challenges of modelling tabular data, including the need to capture complex dependencies and interactions between variables. The study proposed an approach that uses a Conditional GAN (CGAN) to model the joint distribution of the input variables and the target variable. This study used the likelihood fitness metric to evaluate the model. The proposed approach demonstrated that it is effective in modelling tabular data and generating realistic samples.
3. Methods
3.1. Study Site and Data Description
The study area was Northern zone of Tanzania particularly in 6 districts: Ngorongoro, Karatu, Longido, Monduli, Meatu and Serengeti. This area was selected because it is the introductory point of PPR in Tanzania and also it is characterised by pastoralist communities. The villages in the six districts engaged in the study were selected randomly. Farmers were selected to participate in the study and assist in locating herds. Animals were observed for clinical symptoms of PPR and the RT-qPCR rapid test conducted on site to verify the PPR suspects. The ground truth data was collected by a PPR expert by filling in the observed symptoms in an excel sheet. The dataset initially had 161 samples of clinical symptoms observed on sheep and goats that were affected with the Pestes des Petits Ruminants (PPR) disease.
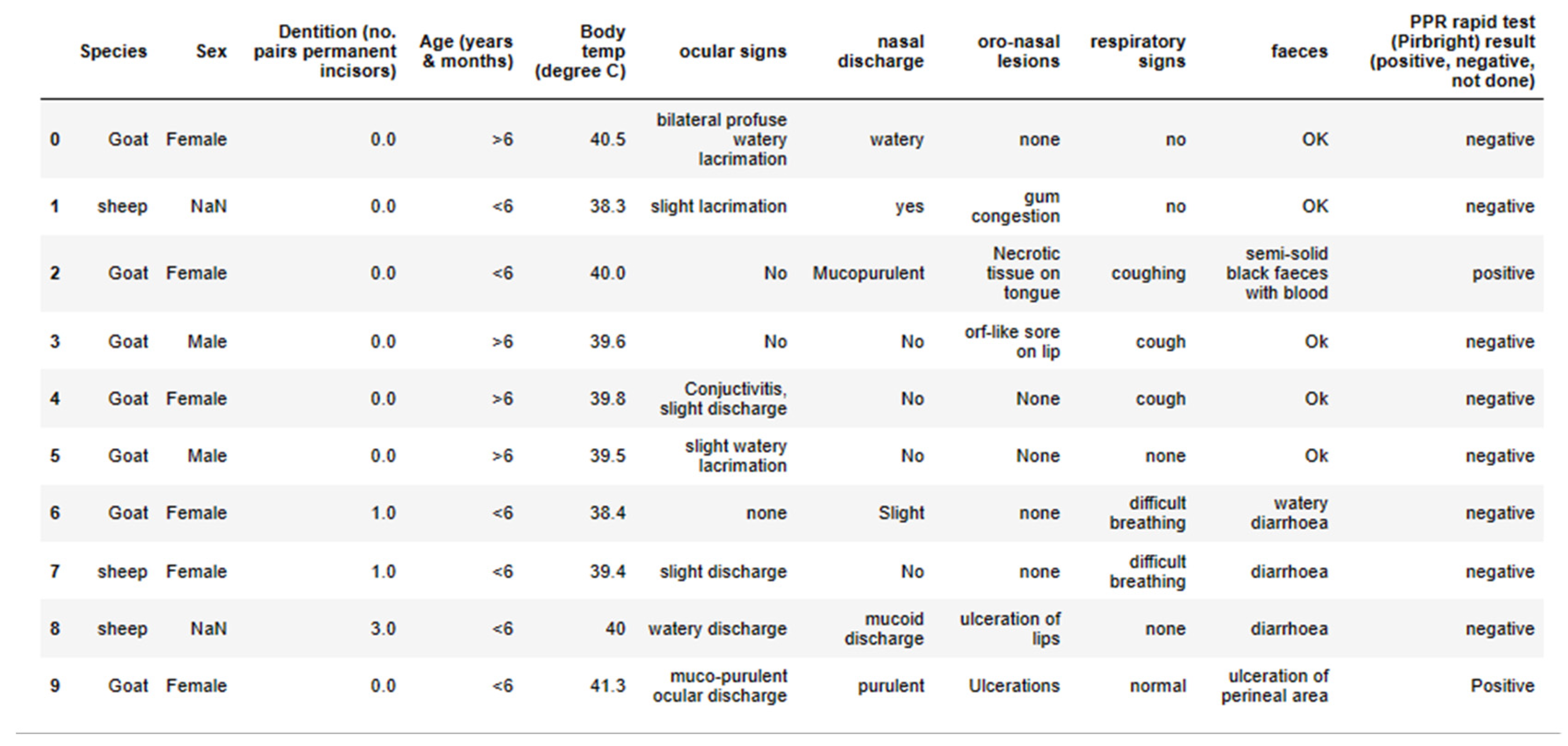
The dataset consisted of the following features: temp (Temperature), oral_discharge (Discharge from the mouth), diarreah (State of the feaces), difficult_breathing (State of breathing), Age, eye_discharge (Discharge from the eye), oral_nasal_lession (Wound in the nose and mouth area), animal, sex and result (Rapid Test Result). In this dataset, the target feature was result (rapid test result) because we wanted to predict whether the PPR is suspected in the ruminant or not. The first 10 entries of the dataset can be seen in the table in the
Figure 1.
The result feature had 12 positives, 2 not done and the rest 147 were negatives. With guidance from the PPR expert, to avoid data imbalance, 12 positive cases and 12 negative cases were selected as the primary dataset to synthesize more data. The dataset was then mapped to 0s and 1s for each column to obtain a binary dataset.
3.2. Synthesis using CTGAN
CTGAN was implemented in this work due to its ability to generate data that is statistically similar to the original data. CTGAN was used to train a dataset of 24 real-world examples with 10 features, including categorical variables. Three thousand (3000) epochs were used and the dataset was divided into training and validation sets. Early stopping was used to prevent overfitting where the training was stopped when the validation loss did not improve for 10 epochs.
4. Results and Discussions
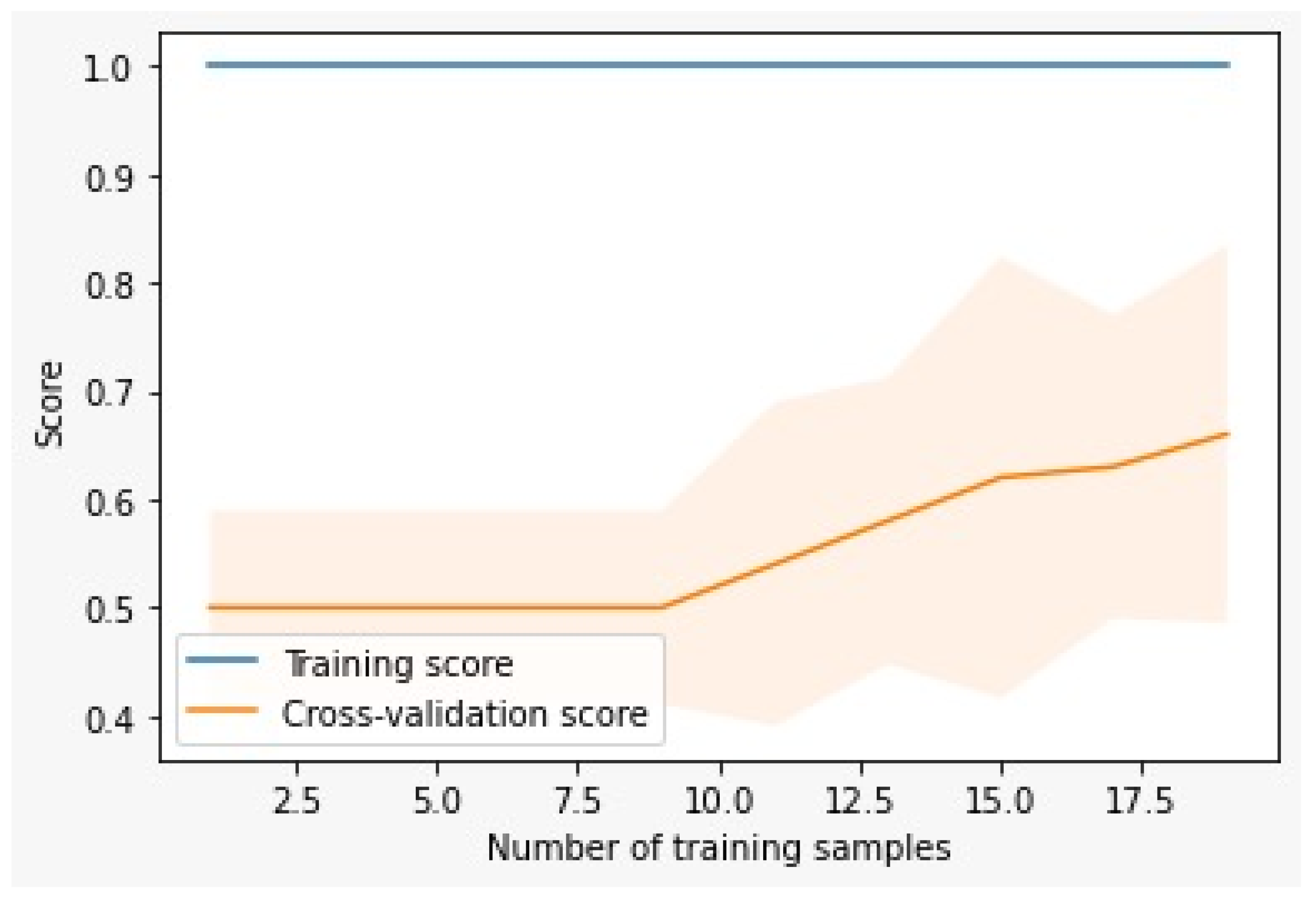
Initially the Random Forest model when trained with the few data resulted to overfitting. The results as seen in
Figure 2 showed that the training score was 100% while the cross-validation score reached 66%. When the model was trained with few data the model showed perfect performance on the training data but it could not generalize well to new or unseen data.
Since our challenge was on data availability, to reduce overfitting the solution was to increase the training data by performing data synthesis on the available data by using the conditional tabular generative adversarial network.
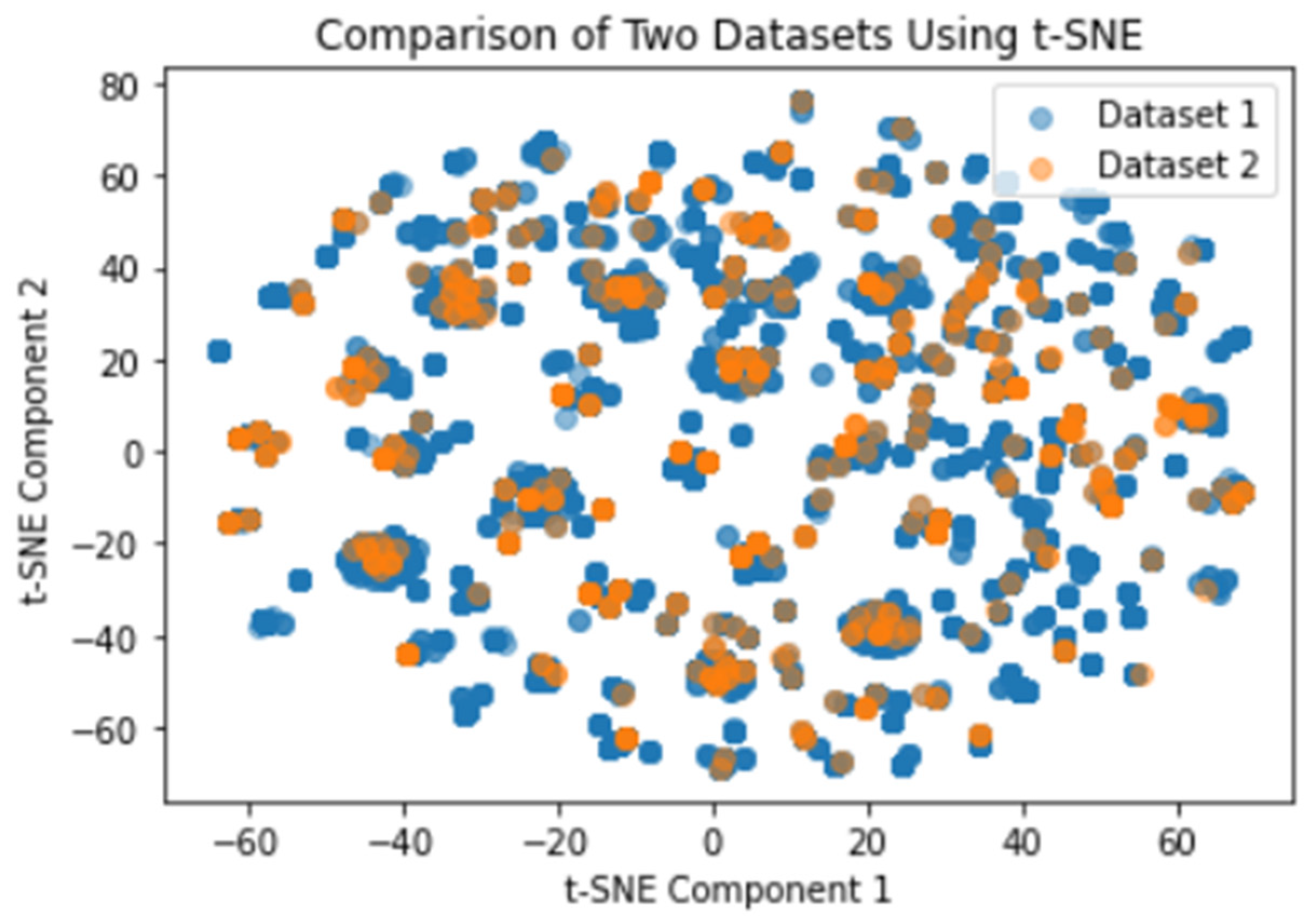
The generated data resulted to 21167 observations. The synthetic dataset was compared with the original dataset to check for correlation. The results as seen in
Figure 3 showed that the synthetic dataset maintained similar statistical features to the original dataset.
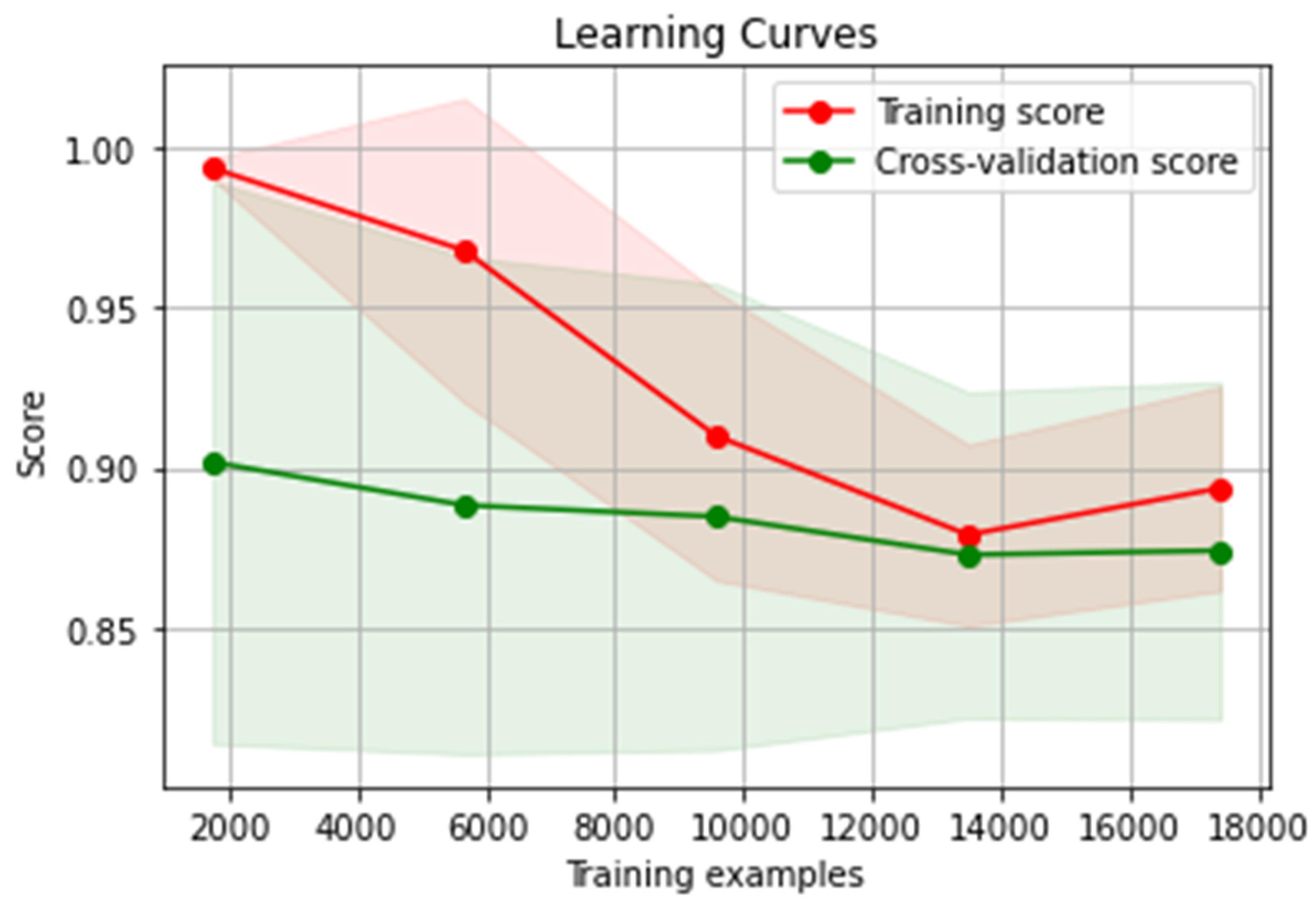
After adding the synthetic data to the model, the training score became 89% and the cross-validation score became 87.5% as shown in
Figure 4.
Similar to Bakhshipour, et al., this study aimed to synthesize data to enhance the availability of data in a domain that faces the challenge of data scarcity. While Bakhshipour, et al., (2020) shows the GRU layers being optimized for best performance of a GAN model in generating synthetic time-series data, increasing the epochs in this current study during training increased the model performance to attain higher training score. This hyperparameter is best to be considered as it also allows for better generalization of data and improved convergence of data.
It is essential for the statistical properties of the synthetic and the real-world data to match. The evaluation process of GAN models is not a straightforward. Zheng, et al., used Euclidean distance, cosine similarity and Pearson corelation coefficient as evaluation metrics, Bakhshipour, et al., used the Jensen-Shannon Divergence and Xu, et al., used likelihood fitness metric. This current study, a comparison was made using t-SNE.
5. Conclusion
In this work, CTGAN has proven to be a reliable method for data synthesis. This method has enabled the generation of adequate amount of data to train the model for predicting the Pestes des Petits Ruminant (PPR) in sheep and goats. This data can further be used to predict and propose surveillance mechanisms for the disease, especially in developing countries. In future, this dataset will be used to train predictive models for the PPR disease and compare performance of different algorithms on the same.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.G.N., N.N, and T.L.; methodology, D.G.N & T.L.; software, T.L & N.N.; validation, D. G. N., N.N., N.M. & R.S; formal analysis, T.L., D.G.N. & N.N; investigation, D.G.N.; resources, D.G.N; data curation, T.L; writing—original draft preparation, N.N.; writing—review and editing, D.G.N.; visualization, N.N. & T.L.; supervision, D.G.N. & N.M., R.S.; project administration, R.S.; funding acquisition, D.G.N., N.M. & R.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was carried out with the aid of a grant from the Artificial Intelligence for Development in Africa Program, a program funded by the Canada’s International Development Research Centre, Ottawa, Canada and the Swedish International Development Cooperation Agency, grant number 109704-001/002.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Alpaydin, E. (2010). Introduction to machine learning (2nd ed.). Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
- Arjovsky, M., Chintala, S., & Bottou, L. (2017). Wasserstein GAN. ArXiv. [CrossRef]
- Ates, C., Karwan, F., Okraschevski, M., Koch, R., & Bauer, H. (2023). Conditional Generative Adversarial Networks for modelling fuel sprays. Energy and AI. [CrossRef]
- Bakhshipour, A. E., Koochali, A., Dittmer, U., Haghighi, A., Ahmad, S., & Dengel, A. (2022). A BAYESIAN GENERATIVE ADVERSARIAL NETWORK (GAN) TO GENERATE SYNTHETIC TIME-SERIES DATA, APPLICATION IN COMBINED SEWER FLOW PREDICTION. 2nd International Joint Conference on Water Distribution Systems Analysis & Computing and Control in the Water Industry. Spain.
- Engelmann, J., & Lessmann, S. (2021). Conditional Wasserstein GAN-based oversampling of tabular data for imbalanced learning. Expert Systems with Applications. [CrossRef]
- Giacomo, A., & David, K. (2021). Generating Tabular Data using Generative Adversarial Networks with Differential Privacy. CONFERENCE OF EUROPEAN STATISTICIANS. Poland.
- Goodfellow, I., & Pouget-Abadie, J. (2014). Generative adversarial nets. Advances in neural information processing systems.
- Goodfellow, I., Pouget-Abadie, J., Mirza, M., Xu, B., Warde-Farley, D., Ozair, S., . . . Bengio, Y. (2020). Generative Adversarial Networks. Communications of the ACM. [CrossRef]
- Hastie, T., Tibshirani, R., & Friedman, J. (2009). The elements of statistical learning: Data mining, inference, and prediction (2nd ed.). New York: Springer. [CrossRef]
- Kingma, D. P., & Welling, M. (2013). Auto-encoding variational Bayes. [CrossRef]
- Mdetele, D. P., Komba, E., Seth, M. D., Misinzo, G., Kock, R., & Jones, B. A. (2021). Review of Peste des Petits Ruminants Occurrence and Spread in Tanzania. Animals (Basel). [CrossRef]
- Mduma, N., Kalegele, K., & Machuve, D. ( 2019). An Ensemble Predictive Model Based Prototype for Student Drop-out in Secondary Schools. Journal of Information Systems Engineering & Management. [CrossRef]
- Mihaylova, L., & Hussain, Z. (2021). Generating Synthetic Data for Time-Series Analysis Using Generative Adversarial Networks. Journal of Data Science.
- Mirza, M., & Osindero, S. (2014). Conditional Generative Adversarial Nets. ArXiv. [CrossRef]
- Nyambo, D., Luhanga, E., Yonah, Z., & Mujibi, F. (2019). Application of Multiple Unsupervised Models to Validate Clusters Robustness in Characterizing Smallholder Dairy Farmers. The Scientifc World Journa. [CrossRef]
- Wang, W., Liu, H., Guo, J., & Wang, J. (2021). Using synthetic data to improve the prediction of COVID-19 progression. Journal of Biomedical Informatics.
- Xu, L., Skoularidou, M., Cuesta-Infante, A., & Veeramachaneni, K. (2019). Modeling Tabular Data using Conditional GAN. Arxiv. [CrossRef]
- Yu, F., Wang, L., Fang, X., & Zhang, Y. (2020). The Defense of Adversarial Example with Conditional Generative Adversarial Networks. Security and Communication Networks. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J., Park, T., Isola, P., & Efros, A. A. (2017). Unpaired Image-to-Image Translation using Cycle-Consistent Adversarial Networks. . ArXiv. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).