Submitted:
10 May 2023
Posted:
10 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Media and Other Reagents
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Testing the Ability of Lactobacilli Cells to Remove Cholesterol from Model Gastric Juice or Model Intestinal Juice
2.3.2. Testing the Ability of Lactobacilli Cells to Release Previously Bound Cholesterol under Conditions of Model Gastric Juice and Model Intestinal Juice
2.3.3. Testing the Ability of Lactobacilli Cells to Remove Cholesterol from Model Dairy Products under Conditions of Model Gastric Juice and Model Intestinal Juice
2.3.4. Determination of Cholesterol Content in Model Dairy Products Using Gas Chromatography Technology Combined with Mass Spectrometry
2.3.5. Determination of the Fatty Acid Profile of Lactobacilli Cells in MRS Broth with and without the Addition of Cholesterol Solution
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Testing the Ability of Lactobacilli Cells to Remove Cholesterol from Model Gastric Juice or Model Intestinal Juice
3.2. Testing the Ability of Lactobacilli Cells to Release Previously Bound Cholesterol under Conditions of Model Gastric Juice and Model Intestinal Juice
3.3. Testing the Ability of Lactobacilli Cells to Remove Cholesterol from Model Dairy Products under Conditions of Model Gastric Juice and Model Intestinal Juice
3.4. Survival of Lactic Acid Bacteria Cells under Model Conditions of the Digestive System
3.5. Determination of the Fatty Acid Profile of Lactobacilli Cells in MRS Broth without and with the Addition of Cholesterol Solution
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Albano, C.; Morandi, S.; Silvetti, T.; Casiraghi, M.C.; Manini, F.; Brasca, M. Lactic Acid Bacteria with Cholesterol-Lowering Properties for Dairy Applications: In Vitro and in Situ Activity. J. Dairy. Sci. 2018, 101, 10807–10818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liong, M.T.; Shah, N.P. Optimization of Cholesterol Removal by Probiotics in the Presence of Prebiotics by Using a Response Surface Method. Appl. Env. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 1745–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverman, M.G.; Ference, B.A.; Im, K.; Wiviott, S.D.; Giugliano, R.P.; Grundy, S.M.; Braunwald, E.; Sabatine, M.S. Association Between Lowering LDL-C and Cardiovascular Risk Reduction Among Different Therapeutic Interventions: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JAMA 2016, 316, 1289–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, T.K.; Pradhan, S.; Chakrabarti, S.; Mondal, K.C.; Ghosh, K. Current Status of Probiotic and Related Health Benefits. Appl. Food Res. 2022, 2, 100185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Park, S.; Lee, H.; Min, B.; Jung, S.; Park, S.; Kim, E.; Oh, S. Effect of Lactobacillus Acidophilus NS1 on Plasma Cholesterol Levels in Diet-Induced Obese Mice. J. Dairy. Sci. 2015, 98, 1492–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buck, L.M.; Gilliland, S.E. Comparisons of Freshly Isolated Strains of Lactobacillus Acidophilus of Human Intestinal Origin for Ability to Assimilate Cholesterol During Growth. J. Dairy. Sci. 1994, 77, 2925–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilliland, S.E.; Nelson, C.R.; Maxwell, C. Assimilation of Cholesterol by Lactobacillus Acidophilust. Appl. Env. Microbiol. 1985, 49, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziarno, M.; Zając, A. Fermented Dairy Products and Cholesterol Levels. Przem. Spoz. 2007, 61, 44–46 /abstract in English/. [Google Scholar]
- Rašić, J.L.; Vujičić, I.F.; Škrinjar, M.; Vulić, M. Assimilation of Cholesterol by Some Cultures of Lactic Acid Bacteria and Bifidobacteria. Biotechnol. Lett. 1992, 14, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, D.K.; Gilliland, S.E. Relationships Among Bile Tolerance, Bile Salt Deconjugation, and Assimilation of Cholesterol by Lactobacillus Acidophilus. J. Dairy. Sci. 1993, 76, 956–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahri, K.; Grill, J.P.; Schneider, F. Bifidobacteria Strain Behavior toward Cholesterol: Coprecipitation with Bile Salts and Assimilation. Curr. Microbiol. 1996, 33, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, D.O.; Kim, S.H.; Gilliland, S.E. Incorporation of Cholesterol into the Cellular Membrane of Lactobacillus Acidophilus ATCC 43121. J Dairy Sci 1997, 80, 3107–3113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brashears, M.M.; Gilliland, S.E.; Buck, L.M. Bile Salt Deconjugation and Cholesterol Removal from Media by Lactobacillus Casei. J. Dairy. Sci. 1998, 81, 2103–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grill, J.P.; Cayuela, C.; Antoine, J.M.; Schneider, F. Effects of Lactobacillus Amylovorus and Bifidobacterium Breve on Cholesterol. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2000, 154–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.-Y.; Chen, T. Reduction of Cholesterol by Lactobacillus Acidophilus in Culture Reduction of Cholesterol by Lactobacillus Acidophilus in Culture Broth Broth. J. Food Drug Anal. 2000, 8, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosono, A.; Otani, H.; Yasui, H.; Watanuki, M. Impact of Fermented Milk on Human Health: Cholesterol-Lowering and Immunomodulatory Properties of Fermented Milk. Anim. Sci. J. 2002, 73, 241–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosono, A.; Tono-Oka, T. Binding of Cholesterol with Lactic Acid Bacterial Cells. Milchwissenschaft 1995, 50, 556–560. [Google Scholar]
- Taranto, M.; Llano, D.G.D.; Rodríguez, A.; Hodalgo, A.P.D.R.; Valdez, G. Bile Tolerance and Cholesterol Reduction by Enterococcus Faecium, a Candidate Microorganism for the Use as a Dietary Adjunct in Milk Products. Milchwissenschaft 1996, 51, 383–385. [Google Scholar]
- Dambekodi, P.C.; Gilliland, S.E. Incorporation of Cholesterol into the Cellular Membrane of Bifidobacterium Longum. J. Dairy. Sci. 1998, 81, 1818–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimoto, H.; Ohmomo, S.; Okamoto, T. Cholesterol Removal from Media by Lactococci. J. Dairy. Sci. 2002, 85, 3182–3188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, V.C.; Peat, G. Serum Cholesterol and Bowel Flora in the Newborn. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1975, 28, 1351–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grunewald, K.K. Serum Cholesterol Levels in Rats Fed Skim Milk Fermented by Lactobacillus Acidophilus. J. Food Sci. 1982, 47, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rodas, B.Z.; Gilliland, S.E.; Maxwell, C. V. Hypocholesterolemic Action of Lactobacillus Acidophilus ATCC 43121 and Calcium in Swine with Hypercholesterolemia Induced by Diet. J Dairy Sci 1996, 79, 2121–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, J.W.; Gilliland, S.E. Effect of Fermented Milk (Yogurt) Containing Lactobacillus Acidophilus L1 on Serum Cholesterol in Hypercholesterolemic Humans. 2013, 18, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kießling, G.; Schneider, J.; Jahreis, G. Long-Term Consumption of Fermented Dairy Products over 6 Months Increases HDL Cholesterol. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2002, 56, 843–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, H.J.; Kim, S.Y.; Lee, W.K. Isolation of Cholesterol-Lowering Lactic Acid Bacteria from Human Intestine for Probiotic Use. J. Vet. Sci. 2004, 5, 391–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourens-Hattingh, A.; Viljoen, B.C. Yogurt as Probiotic Carrier Food. Int. Dairy. J. 2001, 11, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Wang, L.; Liu, F.; Li, B.; Tang, Y.; Yu, S.; Zhang, D.; Huo, G. Effect of Bile Salt Hydrolase-Active Lactobacillus Plantarum KLDS 1.0344 on Cholesterol Metabolism in Rats Fed a High-Cholesterol Diet. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 61, 103497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, N.P. Functional Cultures and Health Benefits. Int. Dairy. J. 2007, 17, 1262–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayyash, M.M.; Abdalla, A.K.; AlKalbani, N.S.; Baig, M.A.; Turner, M.S.; Liu, S.Q.; Shah, N.P. Invited Review: Characterization of New Probiotics from Dairy and Nondairy Products—Insights into Acid Tolerance, Bile Metabolism and Tolerance, and Adhesion Capability. J. Dairy. Sci. 2021, 104, 8363–8379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anandharaj, M.; Sivasankari, B. Isolation of Potential Probiotic Lactobacillus Oris HMI68 from Mother’s Milk with Cholesterol-Reducing Property. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2014, 118, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, X.; Chen, Y.; Menghebilige; Bao, Q. Selection of Potential Probiotic Lactobacilli for Cholesterol-Lowering Properties and Their Effect on Cholesterol Metabolism in Rats Fed a High-Lipid Diet. J. Dairy. Sci. 2012, 95, 1645–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziarno, M. Mechanisms of Cholesterol Lowering by Lactobacillus Bacteria. Żywienie Człowieka i Metabolizm 2004, 2, 10–18, /abstract in English/. [Google Scholar]
- Ziarno, M. Health-Promoting Properties of Lactobacilli. Przegląd Mlecz. 2004, 11, 4–10, /abstract in English/. [Google Scholar]
- Ziarno, M. Importance of Bile Salt Hydrolase Activity in Lactobacilli. Postępy Mikrobiol. 2004, 43, 285–296, /abstract in English/. [Google Scholar]
- Usman, P.; Hosono, A. Binding of Cholesterol to the Cells and Peptidoglycan of Lactobacillus Gasseri. Milchwissenschaft 1999, 54(9), 495–498. [Google Scholar]
- St-Onge, M.P.; Farnworth, E.R.; Jones, P.J.H. Consumption of Fermented and Nonfermented Dairy Products: Effects on Cholesterol Concentrations and Metabolism. Am J Clin Nutr 2000, 71, 674–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, D.I.A.; Gibson, G.R. Cholesterol Assimilation by Lactic Acid Bacteria and Bifidobacteria Isolated from the Human Gut. Appl. Env. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 4689–4693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pigeon, R.M.; Cuesta, E.P.; Gilliland, S.E. Binding of Free Bile Acids by Cells of Yogurt Starter Culture Bacteria. J. Dairy. Sci. 2002, 85, 2705–2710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liong, M.T.; Shah, N.P. Acid and Bile Tolerance and Cholesterol Removal Ability of Lactobacilli Strains. J. Dairy. Sci. 2005, 88, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liong, M.T.; Shah, N.P. Bile Salt Deconjugation Ability, Bile Salt Hydrolase Activity and Cholesterol Co-Precipitation Ability of Lactobacilli Strains. Int. Dairy. J. 2005, 15, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liong, M.T.; Shah, N.P. Bile Salt Deconjugation and BSH Activity of Five Bifidobacterial Strains and Their Cholesterol Co-Precipitating Properties. Food Res. Int. 2005, 38, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziarno, M. Significance of Bile Salt Hydrolase Activity in Bacteria of the Genus Bifidobacterium. Biotechnologia 2005, 2, 183–195, /abstract in English/. [Google Scholar]
- Anandharaj, M.; Sivasankari, B.; Santhanakaruppu, R.; Manimaran, M.; Rani, R.P.; Sivakumar, S. Determining the Probiotic Potential of Cholesterol-Reducing Lactobacillus and Weissella Strains Isolated from Gherkins (Fermented Cucumber) and South Indian Fermented Koozh. Res. Microbiol. 2015, 166, 428–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabuchi, M.; Tamura, A.; Yamada, N.; Ishida, T.; Hosoda, M.; Hosono, A. Hypocholesterolemic Effects of Viable and Heat-Sterilized Cells of Lactobacillus GG in Rats Fed a High-Cholesterol Diet. Milchwissenschaft 2004, 59(5), 249–253. [Google Scholar]
- Ishimwe, N.; Daliri, E.B.; Lee, B.H.; Fang, F.; Du, G. The Perspective on Cholesterol-Lowering Mechanisms of Probiotics. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2015, 59, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayyash, M.; Abushelaibi, A.; Al-Mahadin, S.; Enan, M.; El-Tarabily, K.; Shah, N. In-Vitro Investigation into Probiotic Characterisation of Streptococcus and Enterococcus Isolated from Camel Milk. LWT 2018, 87, 478–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaver, F.A.M.; Van der Meer, R. The Assumed Assimilation of Cholesterol by Lactobacilli and Bifidobacterium Bifidum Is Due to Their Bile Salt-Deconjugating Activity. Appl. Env. Microbiol. 1993, 59, 1120–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taranto, M.P.; Fernandez Murga, M.L.; Lorca, G.; De Valdez, G.F. Bile Salts and Cholesterol Induce Changes in the Lipid Cell Membrane of Lactobacillus Reuteri. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2003, 95, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.B.; Lew, L.C.; Yeo, S.K.; Parvathy, S.N.; Liong, M.T. Probiotics and the BSH-Related Cholesterol Lowering Mechanism: A Jekyll and Hyde Scenario. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2014, 35, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maske, B.L.; de Melo Pereira, G. V.; da, S. Vale, A.; de Carvalho Neto, D.P.; Karp, S.G.; Viesser, J.A.; De Dea Lindner, J.; Pagnoncelli, M.G.; Soccol, V.T.; Soccol, C.R. A Review on Enzyme-Producing Lactobacilli Associated with the Human Digestive Process: From Metabolism to Application. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2021, 149, 109836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sridevi, N.; Vishwe, P.; Prabhune, A. Hypocholesteremic Effect of Bile Salt Hydrolase from Lactobacillus Buchneri ATCC 4005. Food Res. Int. 2009, 42, 516–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.L.; Martoni, C.J.; Parent, M.; Prakash, S. Cholesterol-Lowering Efficacy of a Microencapsulated Bile Salt Hydrolase-Active Lactobacillus Reuteri NCIMB 30242 Yoghurt Formulation in Hypercholesterolaemic Adults. British Journal of Nutrition 2012. [CrossRef]
- Pereira, D.I.A.; McCartney, A.L.; Gibson, G.R. An in Vitro Study of the Probiotic Potential of a Bile-Salt-Hydrolyzing Lactobacillus Fermentum Strain, and Determination of Its Cholesterol-Lowering Properties. Appl. Env. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 4743–4752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakajima, H.; Suzuki, Y.; Hirota, T. Cholesterol Lowering Activity of Ropy Fermented Milk. J. Food Sci. 1992, 57, 1327–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vuyst, L.; De Vin, F.; Vaningelgem, F.; Degeest, B. Recent Developments in the Biosynthesis and Applications of Heteropolysaccharides from Lactic Acid Bacteria. Int. Dairy. J. 2001, 11, 687–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clavel, T.; Carlin, F.; Lairon, D.; Nguyen-The, C.; Schmitt, P. Survival of Bacillus Cereus Spores and Vegetative Cells in Acid Media Simulating Human Stomach. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2004, 97, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marteau, P.; Minekus, M.; Havenaar, R.; Huis In’t Veld, J.H.J. Survival of Lactic Acid Bacteria in a Dynamic Model of the Stomach and Small Intestine: Validation and the Effects of Bile. J. Dairy. Sci. 1997, 80, 1031–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletouris, D.J.; Botsoglou, N.A.; Psomas, I.E.; Mantis, A.I. Rapid Determination of Cholesterol in Milk and Milk Products by Direct Saponification and Capillary Gas Chromatography. J. Dairy. Sci. 1998, 81, 2833–2840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buyer, J.S. Rapid Sample Processing and Fast Gas Chromatography for Identification of Bacteria by Fatty Acid Analysis. J. Microbiol. Methods 2002, 51, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidd Haack, S.; Garchow, H.; Odelson, D.A.; Forney, L.J.; Klug, M.J. Accuracy, Reproducibility, and Interpretation of Fatty Acid Methyl Ester Profiles of Model Bacterial Communities. Appl. Env. Microbiol. 1994, 60, 2483–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kankaanpää, P.; Yang, B.; Kallio, H.; Isolauri, E.; Salminen, S. Effects of Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids in Growth Medium on Lipid Composition and on Physicochemical Surface Properties of Lactobacilli. Appl. Env. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brondz, I. Development of Fatty Acid Analysis by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography, Gas Chromatography, and Related Techniques. Anal. Chim. Acta 2002, 465, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christie, W.W.; Dobson, G.; Adlof, R.O. A Practical Guide to the Isolation, Analysis and Identification of Conjugated Linoleic Acid. Lipids 2007, 42, 1073–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montanari, C.; Sado Kamdem, S.L.; Serrazanetti, D.I.; Etoa, F.X.; Guerzoni, M.E. Synthesis of Cyclopropane Fatty Acids in Lactobacillus Helveticus and Lactobacillus Sanfranciscensis and Their Cellular Fatty Acids Changes Following Short Term Acid and Cold Stresses. Food Microbiol. 2010, 27, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, L.U.; Jenkins, D.J.A.; Reichert, R. The Effect of Fermented and Unfermented Milks on Serum Cholesterol. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1982, 36, 1106–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaspers, D.A.; Massey, L.K.; Luedecke, L.O. Effect of Consuming Yogurts Prepared with Three Culture Strains on Human Serum Lipoproteins. J. Food Sci. 1984, 49, 1178–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.Y.; Ayres, J.W.; Winkler, W.; Sandine, W.E. Lactobacillus Effects on Cholesterol: In Vitro and In Vivo Results. J. Dairy. Sci. 1989, 72, 2885–2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNamara, D.J.; Lowell, A.E.; Sabb, J.E. Effect of Yogurt Intake on Plasma Lipid and Lipoprotein Levels in Normolipidemic Males. Atherosclerosis 1989, 79, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, E.A.; Chang, H.C. Cholesterol-Lowering Effects of a Putative Probiotic Strain Lactobacillus Plantarum EM Isolated from Kimchi. LWT - Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 62, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooi, L.-G.; Liong, M.-T. Cholesterol-Lowering Effects of Probiotics and Prebiotics: A Review of in Vivo and in Vitro Findings. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2010, 11, 2499–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lye, H.S.; Rusul, G.; Liong, M.T. Removal of Cholesterol by Lactobacilli via Incorporation and Conversion to Coprostanol. J. Dairy. Sci. 2010, 93, 1383–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.K.; El-Nezami, H.; Haskard, C.A.; Gratz, S.; Puong, K.Y.; Salminen, S.; Mykkänen, H. Kinetics of Adsorption and Desorption of Aflatoxin B1 by Viable and Nonviable Bacteria. J. Food Prot. 2003, 66, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miremadi, F.; Ayyash, M.; Sherkat, F.; Stojanovska, L. Cholesterol Reduction Mechanisms and Fatty Acid Composition of Cellular Membranes of Probiotic Lactobacilli and Bifidobacteria. J. Funct. Foods 2014, 9, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Nezami, H.; Kankaanpaa, P.; Salminen, S.; Ahokas, J. Ability of Dairy Strains of Lactic Acid Bacteria to Bind a Common Food Carcinogen, Aflatoxin B1. Food and Chemical Toxicology 1998, 36, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aloǧlu, H.; Öner, Z. Assimilation of Cholesterol in Broth, Cream, and Butter by Probiotic Bacteria. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2006, 108, 709–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, H.; Doesburg, K.; Iwasaki, T.; Mierau, I. Screening of Lactic Acid Bacteria for Bile Salt Hydrolase Activity. J. Dairy. Sci. 1999, 82, 2530–2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taranto, M.P.; Sesma, F.; Pesce De Ruiz Holgado, A.; De Valdez, G.F. Bile Salts Hydrolase Plays a Key Role on Cholesterol Removal by Lactobacillus Reuteri. Biotechnol. Lett. 1997, 19, 845–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liong, M.T.; Shah, N.P. Bile Salt Deconjugation Ability, Bile Salt Hydrolase Activity and Cholesterol Co-Precipitation Ability of Lactobacilli Strains. Int. Dairy. J. 2005, 15, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Qiu, L.; Xu, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhan, H.; Tao, X.; Shah, N.P.; Wei, H. Beneficial Effects of Probiotic Cholesterol-Lowering Strain of Enterococcus Faecium WEFA23 from Infants on Diet-Induced Metabolic Syndrome in Rats. J. Dairy. Sci. 2017, 100, 1618–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roobab, U.; Batool, Z.; Manzoor, M.F.; Shabbir, M.A.; Khan, M.R.; Aadil, R.M. Sources, Formulations, Advanced Delivery and Health Benefits of Probiotics. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2020, 32, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinderola, C.G.; Reinheimer, J.A. Lactic Acid Starter and Probiotic Bacteria: A Comparative “in Vitro” Study of Probiotic Characteristics and Biological Barrier Resistance. Food Res. Int. 2003, 36, 895–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kailasapathy, K.; Chin, J. Survival and Therapeutic Potential of Probiotic Organisms with Reference to Lactobacillus Acidophilus and Bifidobacterium Spp. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2000, 78, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elli, M.; Callegari, M.L.; Ferrari, S.; Bessi, E.; Cattivelli, D.; Soldi, S.; Morelli, L.; Feuillerat, N.G.; Antoine, J.M. Survival of Yogurt Bacteria in the Human Gut. Appl. Env. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 5113–5117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lye, H.S.; Rusul, G.; Liong, M.T. Removal of Cholesterol by Lactobacilli via Incorporation and Conversion to Coprostanol. J. Dairy. Sci. 2010, 93, 1383–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boudreau, A.; Arul, J. Cholesterol Reduction and Fat Fractionation Technologies for Milk Fat: An Overview. J. Dairy. Sci. 1993, 76, 1772–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benito, M.J.; Serradilla, M.J.; Ruiz-Moyano, S.; Martín, A.; Pérez-Nevado, F.; Córdoba, M.G. Rapid Differentiation of Lactic Acid Bacteria from Autochthonous Fermentation of Iberian Dry-Fermented Sausages. Meat Sci. 2008, 80, 656–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirabunyanon, M.; Hongwittayakorn, P. Potential Probiotic Lactic Acid Bacteria of Human Origin Induce Antiproliferation of Colon Cancer Cells via Synergic Actions in Adhesion to Cancer Cells and Short-Chain Fatty Acid Bioproduction. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2013, 169, 511–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glatz, J.F.C.; Luiken, J.J.F.P. Fatty Acids in Cell Signaling: Historical Perspective and Future Outlook. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2015, 92, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partanen, L.; Marttinen, N.; Alatossava, T. Fats and Fatty Acids as Growth Factors for Lactobacillus Delbrueckii. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2001, 24, 500–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcoran, B.M.; Stanton, C.; Fitzgerald, G.F.; Ross, R.P. Growth of Probiotic Lactobacilli in the Presence of Oleic Acid Enhances Subsequent Survival in Gastric Juice. Microbiology 2007, 153, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
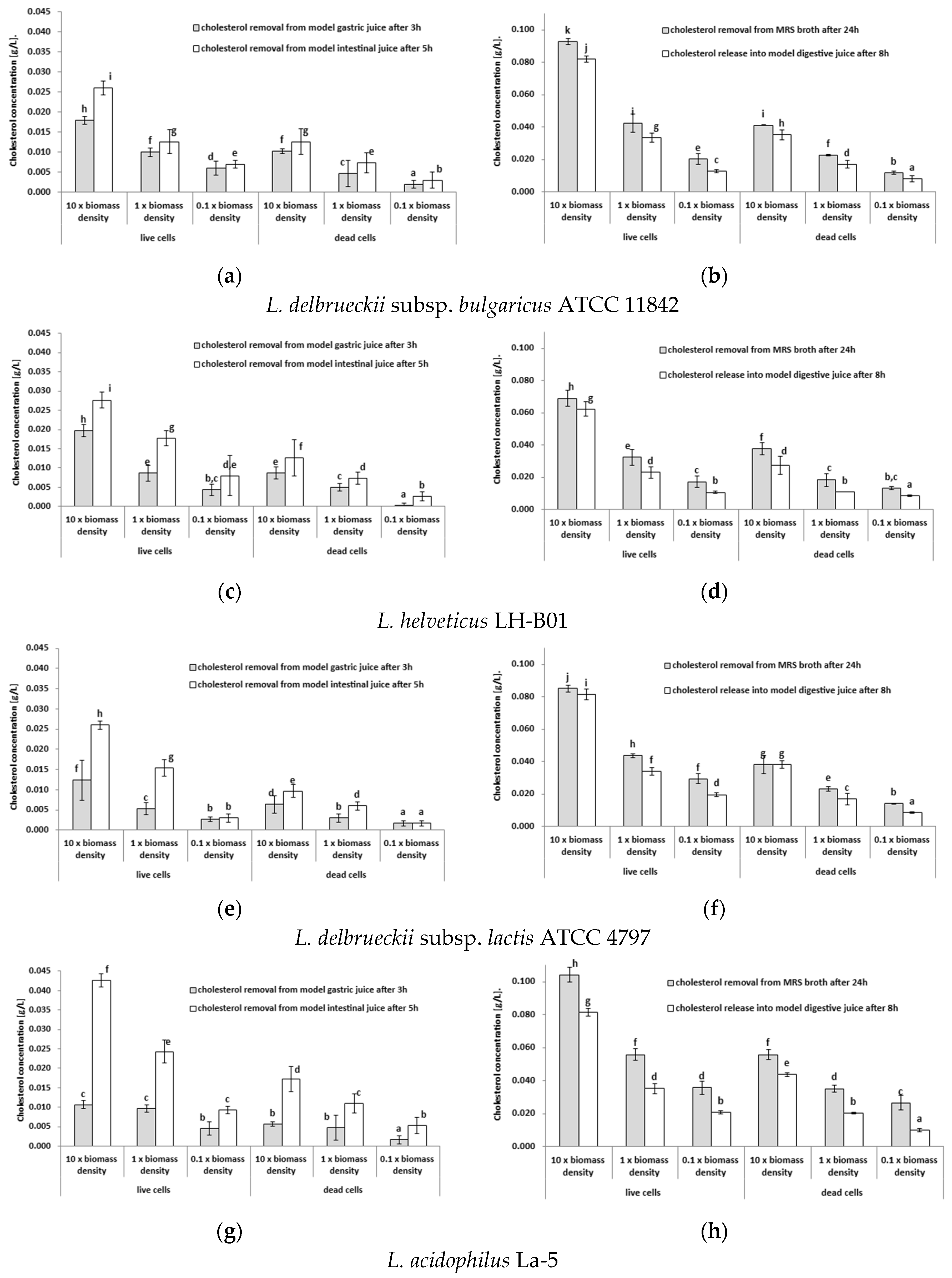
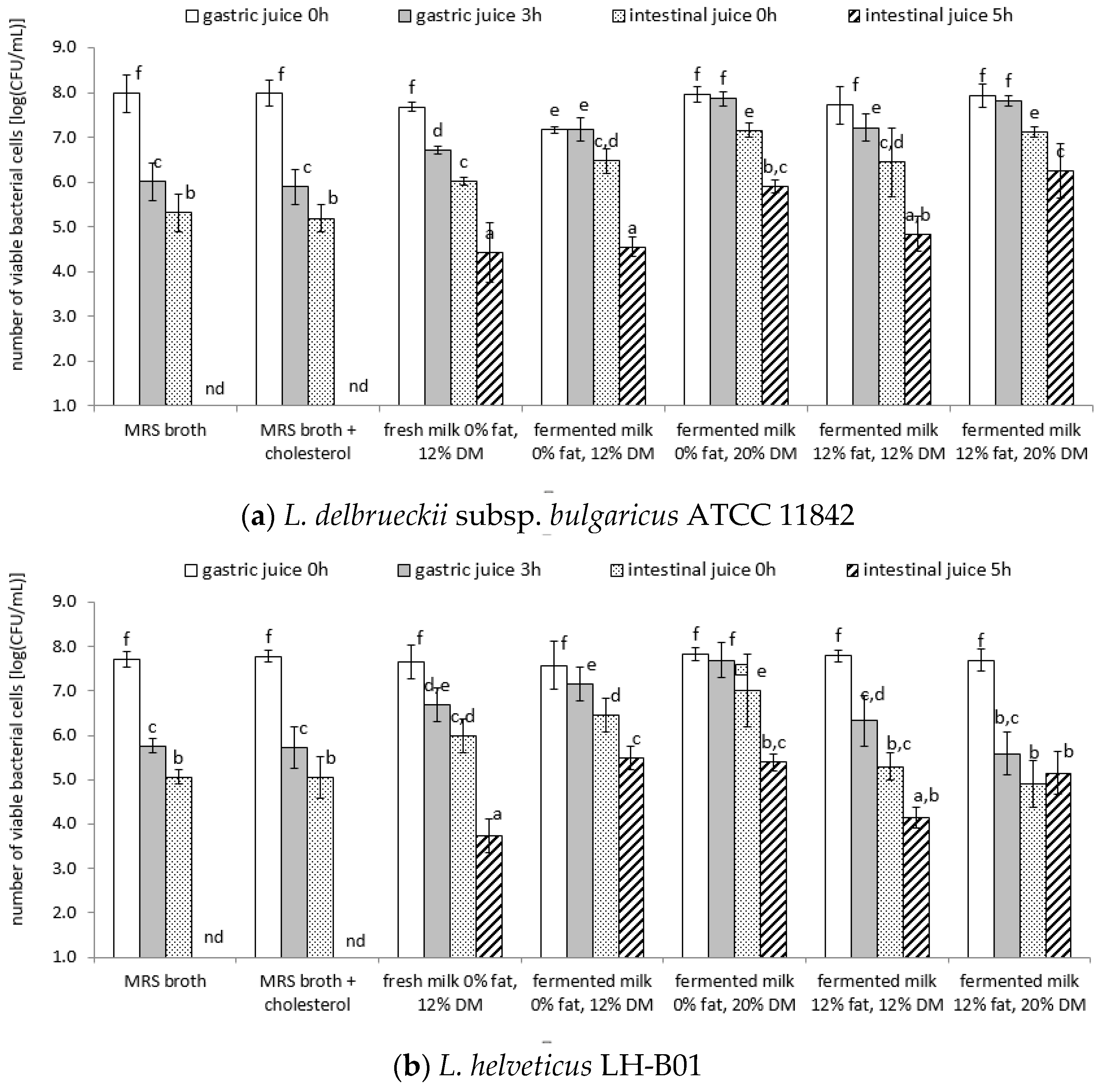
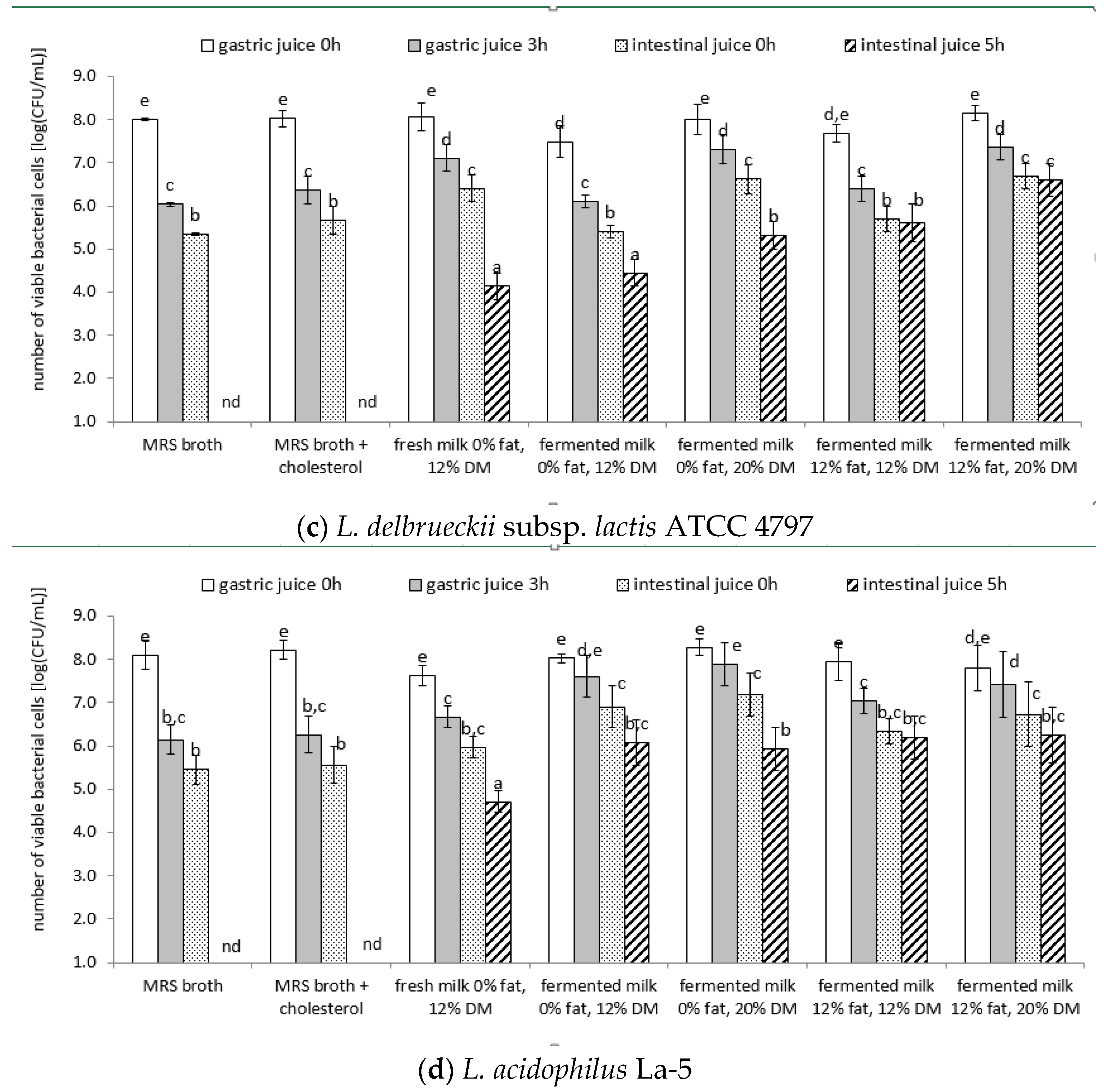
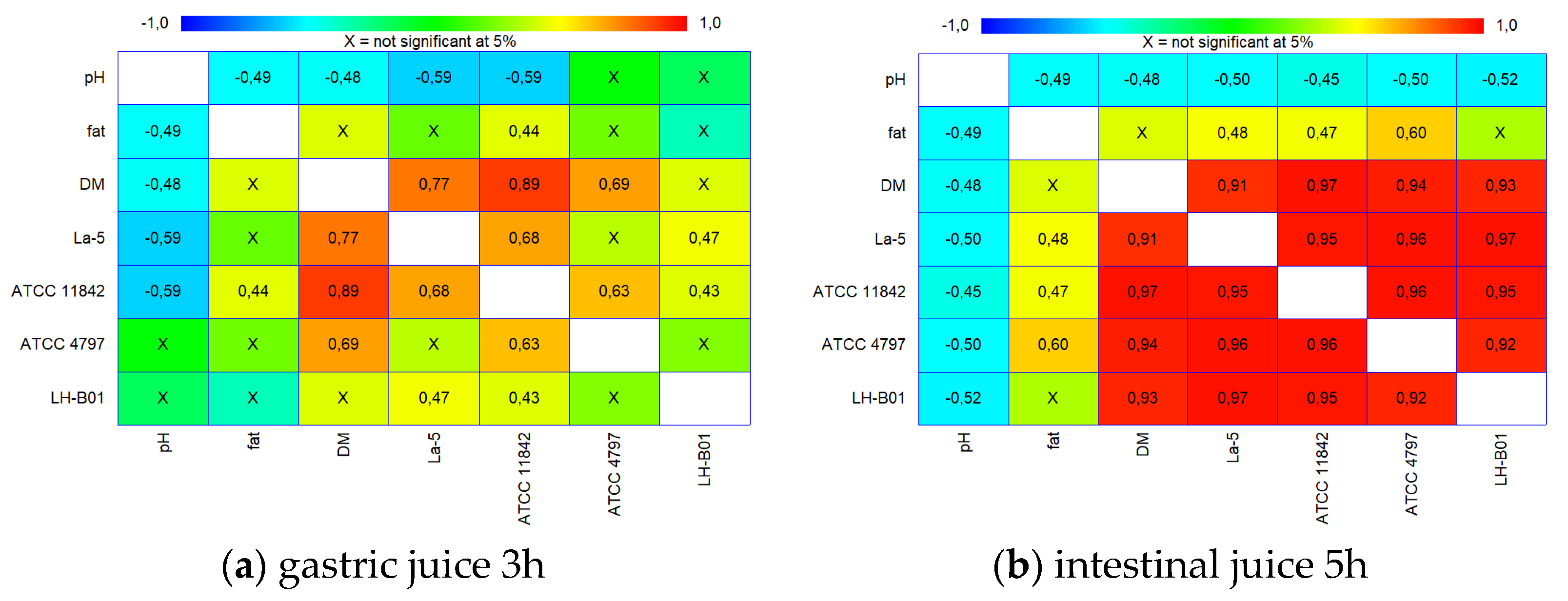
| Strain | Product | Directly after Preparation | After 1 Week of Cold Storage |
After 4 Weeks of Cold Storage |
Model Gastric Juice after 3 Hours | Model Duodenal Fluid after 5h |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L. delbrueckii subsp. Bulgaricus ATCC 11842 | MRS broth | 0.0 a ±0.00 | 0.0 a ±0.00 | 0.0 a ±0.00 | 0.0 a ±0.00 | 0.0 a ±0.00 |
| MRS broth + cholesterol | 0.7 b ±0.01 | 0.7 b ±0.04 | 0.7 b ±0.02 | 0.7 b ±0.03 | 0.7 b ±0.03 | |
| fresh milk 0,05% fat, 12% DM | 1.7 c ±0.04 | 1.6 c ±0.02 | 1.6 c ±0.04 | 1.7 c ±0.05 | 1.6 c ±0.05 | |
| fermented milk 0,05% fat, 12% DM | 1.7 c ±0.04 | 1.6 c ±0.02 | 1.6 c ±0.04 | 1.7 c ±0.05 | 1.6 c ±0.05 | |
| fermented milk 0,05% fat, 20% DM | 1.6 c ±0.04 | 1.5 c ±0.02 | 1.5 c ±0.04 | 1.6 c ±0.05 | 1.5 c ±0.05 | |
| fermented milk 12% fat, 12% DM | 40.6 e ±1.07 | 39.4 e ±0.41 | 38.5 e ±1.02 | 40.5 e ±1.13 | 39.0 e ±1.13 | |
| fermented milk 12% fat, 20% DM | 37.5 d ±0.99 | 36.5 d ±0.38 | 35.6 d ±0.95 | 37.4 d ±0.97 | 36.0 d ±0.97 | |
| L. helveticus LH-B01 | MRS broth | 0.0 a ±0.00 | 0.0 a ±0.00 | 0.0 a ±0.00 | 0.0 a ±0.00 | 0.0 a ±0.00 |
| MRS broth + cholesterol | 0.7 b ±0.02 | 0.7 c ±0.02 | 0.7 c ±0.02 | 0.6 b ±0.02 | 0.6 b ±0.02 | |
| fresh milk 0,05% fat, 12% DM | 1.6 c ±0.04 | 1.6 c ±0.06 | 1.6 c ±0.01 | 1.6 c ±0.05 | 1.6 c ±0.05 | |
| fermented milk 0,05% fat, 12% DM | 1.6 c ±0.04 | 1.6 c ±0.06 | 1.6 c ±0.01 | 1.6 c ±0.05 | 1.5 c ±0.05 | |
| fermented milk 0,05% fat, 20% DM | 1.5 c ±0.04 | 1.5 c ±0.05 | 1.5 c ±0.01 | 1.5 c ±0.04 | 1.4 c ±0.04 | |
| fermented milk 12% fat, 12% DM | 39.3 e ±0.93 | 38.1 e ±1.39 | 39.1 e ±0.23 | 39.3 e ±1.15 | 37.2 e ±1.15 | |
| fermented milk 12% fat, 20% DM | 36.4 d ±0.85 | 35.3 d ±1.28 | 36.2 d ±0.22 | 36.4 d ±1.09 | 34.5 d ±1.09 | |
| L. delbrueckii subsp. Lactis ATCC 4797 | MRS broth | 0.0 a ±0.00 | 0.0 a ±0.00 | 0.0 a ±0.00 | 0.0 a ±0.00 | 0.0 a ±0.00 |
| MRS broth + cholesterol | 0.6 b ±0.03 | 0.7 b ±0.01 | 0.7 b ±0.02 | 0.6 b ±0.01 | 0.6 b ±0.01 | |
| fresh milk 0,05% fat, 12% DM | 1.6 c ±0.01 | 1.6 c ±0.02 | 1.6 c ±0.01 | 1.6 c ±0.05 | 1.5 c ±0.05 | |
| fermented milk 0,05% fat, 12% DM | 1.6 c ±0.01 | 1.6 c ±0.02 | 1.6 c ±0.01 | 1.6 c ±0.05 | 1.5 c ±0.04 | |
| fermented milk 0,05% fat, 20% DM | 1.5 c ±0.01 | 1.5 c ±0.02 | 1.5 c ±0.01 | 1.5 c ±0.04 | 1.4 c ±0.04 | |
| fermented milk 12% fat, 12% DM | 37.9 e ±0.29 | 38.6 e ±0.56 | 38.0 e ±0.25 | 37.9 e ±1.01 | 36.5 e ±1.01 | |
| fermented milk 12% fat, 20% DM | 35.1 d ±0.27 | 35.8 d ±0.51 | 35.1 d ±0.24 | 35.1 d ±1.02 | 33.8 d ±1.02 | |
| L. acidophilus La-5 | MRS broth | 0.0 a ±0.00 | 0.0 a ±0.00 | 0.0 a ±0.00 | 0.0 a ±0.00 | 0.0 a ±0.00 |
| MRS broth + cholesterol | 0.6 b ±0.03 | 0.7 b ±0.01 | 0.7 b ±0.03 | 0.6 b ±0.02 | 0.6 b ±0.02 | |
| fresh milk 0,05% fat, 12% DM | 1.6 c ±0.06 | 1.6 c ±0.03 | 1.6 c ±0.02 | 1.6 c ±0.04 | 1.5 c ±0.05 | |
| fermented milk 0,05% fat, 12% DM | 1.6 c ±0.06 | 1.6 c ±0.03 | 1.6 c ±0.02 | 1.6 c ±0.05 | 1.5 c ±0.06 | |
| fermented milk 0,05% fat, 20% DM | 1.5 c ±0.05 | 1.5 c ±0.02 | 1.5 c ±0.02 | 1.5 c ±0.05 | 1.4 c ±0.05 | |
| fermented milk 12% fat, 12% DM | 38.6 e ±1.32 | 38.8 e ±0.64 | 38.5 e ±0.51 | 38.6 e ±1.05 | 36.6 e ±1.05 | |
| fermented milk 12% fat, 20% DM | 35.8 d ±1.23 | 35.9 d ±0.59 | 35.7 d ±0.48 | 35.7 d ±1.07 | 33.9 d ±1.07 |
| Fatty acid | L. delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus ATCC 11842 | L. helveticus LH-B01 | L. delbrueckii subsp. lactis ATCC 4797 | L. acidophilus La-5 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MRS broth | MRS broth + chol |
MRS broth | MRS broth + chol |
MRS broth | MRS broth + chol |
MRS broth | MRS broth + chol |
||
| C10:0 | caproic / decanoic | 0.0009 a,b ±0.0006 | 0.0002 a,b ±0.0002 | 0.0003 a ±0.0001 | 0.0005 a ±0.0002 | 0.0005 a,b ±0.0002 | 0.0015 a,b ±0.0009 | 0,0017 b ±0,0006 | 0,0008 b ±0,0002 |
| C12:0 | lauric / dodecanoic | 0.0047 ±0.0019 | 0.0012 ±0.0000 | 0.0118 ±0.0025 | 0.0269 ±0.0011 | 0.0044 ±0.0003 | 0.0131 ±0.0021 | 0,0100 ±0,0018 | 0,0051 ±0,0001 |
| C14:0 | myristic / tetradecanoic | 0.0081 ±0.0020 | 0.0041 ±0.0002 | 0.0038 ±0.0017 | 0.0032 ±0.0005 | 0.0026 ±0.0006 | 0.0076 ±0.0019 | 0,0285 ±0,0029 | 0,0156 ±0,0025 |
| 15:0,iso | iso-13-methyltetradecanoic | 0.0036 a,b ±0.0012 | 0.0009 a,b ±0.0001 | 0.0118 b ±0.0024 | 0.0267 b ±0.0040 | 0.0001 a ±0.0000 | 0.0002 a ±0.0001 | 0,0002 a ±0,0001 | 0,0001 a ±0,0000 |
| 15:0,anteiso | anteiso-12-methyltetradecanoic | 0.0003 ±0.0002 | 0.0001 ±0.0001 | 0.0006 ±0.0009 | 0.0014 ±0.0012 | 0.0002 ±0.0001 | 0.0007 ±0.0004 | 0,0008 ±0,0003 | 0,0004 ±0,0001 |
| C15:0 | pentadecanoic | 0.0001 ±0.0001 | 0.0000 ±0.0000 | 0.0005 ±0.0007 | 0.0011 ±0.0010 | 0.0001 ±0.0000 | 0.0004 ±0.0002 | 0,0004 ±0,0002 | 0,0002 ±0,0000 |
| C16:0 | palmitic / hexadecanoic | 0.0243 ±0.0049 | 0.0210 ±0.0068 | 0.0148 ±0.0038 | 0.0182 ±0.0027 | 0.0142 ±0.0013 | 0.0360 ±0.0016 | 0,0913 ±0,0037 | 0,0483 ±0,0050 |
| C16:1,trans-9 | palmitelaidic / trans-9-hexadecenoic | 0.0200 b ±0.0023 | 0.0194 b ±0.0086 | 0.0112 b ±0.0025 | 0.0253 b ±0.0018 | 0.0002 a ±0.0000 | 0.0005 a ±0.0003 | 0,0005 a ±0,0002 | 0,0003 a ±0,0001 |
| C16:1,cis-9 | palmitoleic / cis-9-hexadecenoic | 0.0954 b ±0.0185 | 0.0031 b ±0.0000 | 0.0031 b ±0.0013 | 0.0000 a ±0.0000 | 0.0006 a ±0.0001 | 0.0000 a ±0.0000 | 0,0065 b ±0,0012 | 0,0044 b ±0,0004 |
| C12:0,2OH | 2-hydroxydodecanoic | 0.0003 ±0.0002 | 0.0001 ±0.0001 | 0.0008 ±0.0002 | 0.0018 ±0.0006 | 0.0001 ±0.0000 | 0.0004 ±0.0002 | 0,0005 ±0,0002 | 0,0003 ±0,0001 |
| cycC17:0,cis-9,10 | cis-9,10-methylenehexadecanoic | 0.0049 b ±0.0010 | 0.0048 b ±0.0016 | 0.0000 a ±0.0000 | 0.0000 a ±0.0000 | 0.0001 a ±0.0000 | 0.0003 a ±0.0002 | 0,0000 a ±0,0000 | 0,0000 a ±0,0000 |
| C18:0 | stearic / octadecanoic | 0.0030 ±0.0008 | 0.0054 ±0.0010 | 0.0029 ±0.0005 | 0.0067 ±0.0014 | 0.0024 ±0.0004 | 0.0082 ±0.0027 | 0,0296 ±0,0025 | 0,0138 ±0,0014 |
| C18:1 | octadecenoic | 0.0010 ±0.0006 | 0.0003 ±0.0002 | 0.0009 ±0.0004 | 0.0021 ±0.0009 | 0.0000 ±0.0000 | 0.0000 ±0.0000 | 0,0013 ±0,0005 | 0,0006 ±0,0001 |
| C18:1,trans-6 | petroselaidic / trans-6-octadecenoic | 0.0000 a ±0.0000 | 0.0000 a ±0.0000 | 0.0007 b ±0.0010 | 0.0015 b ±0.0004 | 0.0000 a ±0.0000 | 0.0000 a ±0.0000 | 0,0001 a ±0,0000 | 0,0000 a ±0,0000 |
| C18:1,trans-9 | elaidic / trans-9-octa-decenoic | 0.0002 ±0.0001 | 0.0005 ±0.0004 | 0.0000 ±0.0001 | 0.0018 ±0.0008 | 0.0000 ±0.0000 | 0.0000 ±0.0000 | 0,0000 ±0,0000 | 0,0000 ±0,0000 |
| C18:1,trans-11 | trans-vaccenic / trans-11-octadecenoic | 0.0012 ±0.0007 | 0.0003 ±0.0003 | 0.0020 ±0.0019 | 0.0044 ±0.0010 | 0.0007 ±0.0002 | 0.0020 ±0.0003 | 0,0024 ±0,0009 | 0,0012 ±0,0002 |
| C18:1,cis-6 | petroselinic / cis-6-octadecenoic | 0.0004 a ±0.0003 | 0.0005 a ±0.0005 | 0.0063 b ±0.0014 | 0.0144 b ±0.0029 | 0.0000 a ±0.0000 | 0.0000 a ±0.0000 | 0,0004 a ±0,0002 | 0,0002 a ±0,0000 |
| C18:1,cis-9 | oleic / cis-9-octadecenoic | 0.1324 a,b ±0.0011 | 0.0624 a ±0.0000 | 0.0327 a ±0.0022 | 0.0584 a ±0.0016 | 0.0545 a ±0.0007 | 0.1142 a,b ±0.0072 | 0,1270 b ±0,0047 | 0,0625 a ±0,0059 |
| C18:1,cis-11 | cis-vaccenic / cis-11-octadecenoic | 0.0179 ±0.0010 | 0.1600 ±0.0047 | 0.0574 ±0.0049 | 0.1302 ±0.0071 | 0.0025 ±0.0000 | 0.0075 ±0.0002 | 0,0059 ±0,0013 | 0,0030 ±0,0006 |
| C18:2,trans-9,trans-12 | linoelaidic / trans-9,trans-12-octadecadienoic |
0.0008 b ±0.0005 | 0.0002 a,b ±0.0002 | 0.0000 a ±0.0000 | 0.0000 a ±0.0000 | 0.0000 a ±0.0000 | 0.0001 a ±0.0001 | 0,0000 a ±0,0000 | 0,0000 a ±0,0000 |
| C18:2,cis-9,cis-12 | linoleic / cis-9,cis12-octadecadienoic | 0.0005 a ±0.0003 | 0.0184 b ±0.0000 | 0.0000 a ±0.0000 | 0.0038 a,b ±0.0019 | 0.0000 a ±0.0000 | 0.0080 b ±0.0026 | 0,0043 a,b ±0,0010 | 0,0000 a ±0,0000 |
| cycC19:0,cis-9,10 | dihydrosterculic / cis-9,10-methyleneoctadecanoic |
0.0632 b ±0.0087 | 0.0108 b ±0.0000 | 0.0070 a ±0.0015 | 0.0000 a ±0.0000 | 0.0078 a ±0.0012 | 0.0068 a ±0.0007 | 0,0413 b ±0,0020 | 0,0053 a ±0,0015 |
| cycC19:0,cis-10,11 | lactobacillic / cis-11,12-methyleneoctadecanoic |
0.0087 a ±0.0013 | 0.0022 a ±0.0009 | 0.0600 b ±0.0017 | 0.1361 b ±0.0023 | 0.0000 a ±0.0000 | 0.0000 a ±0.0000 | 0,0018 a7 ±0,0007 | 0,0009 a ±0,0002 |
| 18:2,cis-9,trans-11 | conjugated octadecadienoic | 0.0058 ±0.0015 | 0.0015 ±0.0003 | 0.0069 ±0.0002 | 0.0156 ±0.0021 | 0.0015 ±0.0005 | 0.0045 ±0.0018 | 0,0057 ±0,0012 | 0,0029 ±0,0006 |
| C18:2, CLA_1 | conjugated octadecadienoic | 0.0005 ±0.0003 | 0.0001 ±0.0001 | 0.0007 ±0.0010 | 0.0015 ±0.0004 | 0.0002 ±0.0001 | 0.0007 ±0.0004 | 0,0005 ±0,0002 | 0,0003 ±0,0000 |
| 18:2,trans-10,cis-12 | conjugated octadecadienoic | 0.0031 ±0.0019 | 0.0008 ±0.0007 | 0.0074 ±0.0009 | 0.0167 ±0.0011 | 0.0023 ±0.0007 | 0.0070 ±0.0023 | 0,0062 ±0,0014 | 0,0032 ±0,0006 |
| C18:2, CLA_2 | conjugated octadecadienoic | 0.0004 ±0.0002 | 0.0001 ±0.0000 | 0.0007 ±0.0001 | 0.0015 ±0.0004 | 0.0002 ±0.0001 | 0.0006 ±0.0002 | 0,0006 ±0,0002 | 0,0003 ±0,0001 |
| C18:2, CLA_3 | conjugated octadecadienoic | 0.0001 ±0.0000 | 0.0000 ±0.0000 | 0.0006 ±0.0009 | 0.0014 ±0.0002 | 0.0002 ±0.0001 | 0.0005 ±0.0003 | 0,0006 ±0,0002 | 0,0003 ±0,0001 |
| C18:2, CLA_4 | conjugated octadecadienoic | 0.0034 ±0.0011 | 0.0009 ±0.0008 | 0.0067 ±0.0018 | 0.0151 ±0.0036 | 0.0016 ±0.0005 | 0.0049 ±0.0010 | 0,0049 ±0,0009 | 0,0025 ±0,0005 |
| fatty acid | acid name | RT [min] * | ECL | EI * |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C11:0 | undecanoic | 15.466 | 11.000 | 74,87,143,157,200 |
| C12:0 | lauric / dodecanoic | 17.655 | 12.000 | 74,87,143,214 |
| C13:0 | tridecanoic | 19.751 | 13.000 | 74,87,143,185,228 |
| C14:0 | myristic / tetradecanoic | 21.757 | 14.000 | 74,87,143,199,242 |
| C10:0,2OH | 2-hydroxydecanoic | 22.658 | 14.481 | 69,83,143,228 |
| C15:0,iso | iso-13-methyltetradecanoic | 22.777 | 14.542 | 74,87,143,213,256 |
| C15:0,anteiso | anteiso-12-methyltetradecanoic | 23.084 | 14.701 | 74,87,143,213,256 |
| C15:0 | pentadecanoic | 23.673 | 15.000 | 74,87,143,213,256 |
| C16:0,iso | iso-14-methylpentadecanoic | 24.647 | 15.541 | 74,87,143,227,270 |
| C16:0 | palmitic / hexadecanoic | 25.505 | 16.000 | 74,87,143,227,270 |
| C17:0,iso | iso-15-methylhexadecanoic | 26.442 | 16.541 | 74,87,143,241,284 |
| C16:1,cis-9 | palmitoleic / hexadecenoic | 26.485 | 16.565 | 69,83,96,152,236 |
| C12:0,2OH | 2-hydroxydodecanoic | 26.636 | 16.653 | 69,83,97,171,230 |
| C17:0 | heptadecanoic | 27.255 | 17.000 | 74,87,143,241,284 |
| cycC17:0,cis-9,10 | cis-9,10-methylenehexadecanoic | 27.965 | 17.432 | 69,74, 83,97,250 |
| C18:0 | stearic / octadecanoic | 28.934 | 18.000 | 74,87,143,255,298 |
| C12:0,3OH | 3-hydroxydodecanoic | 29.175 | 18.159 | 71,74,83,103 |
| C18:1,trans-9 | elaidic / octadecenoic | 29.492 | 18.351 | 69,74,83,97,123,264 |
| C18:1,cis-9 | oleic / octadecenoic | 29.705 | 18.486 | 69,74,83,97,123,264 |
| C14:0,2OH | 2-hydroxytetradecanoic | 30.221 | 18.797 | 69,83,97,199 |
| C19:0 | nonadecanoic | 30.545 | 19.000 | 74,87,143,312 |
| C18:2,cis-9,cis-12 | linoleic / cis-9,cis12-octadecadienoic | 31.015 | 19.307 | 97,81,95,123,294 |
| cycC19:0,cis-9,10 | dihydrosterculic / cis-9,10-methylene-octadecanoic | 31.122 | 19.376 | 69,74,83,97,123,278 |
| C20:0 | eicosanic | 32.086 | 20.000 | 74,87,143,326 |
| C14:0,3-OH | 3-hydroxytetradecanoic | 32.592 | 20.318 | 71,74,103 |
| C16:0,2-OH | 2-hydroxyhexadecanoic | 33.475 | 20.864 | 69,83,97,227 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





