Submitted:
10 May 2023
Posted:
10 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Nanoparticles
2.2. Microalgae Cultures and Exposure Protocol
2.3. Flow Cytometry Measurement
2.4. Microscopy
2.5. Statistical Analysis
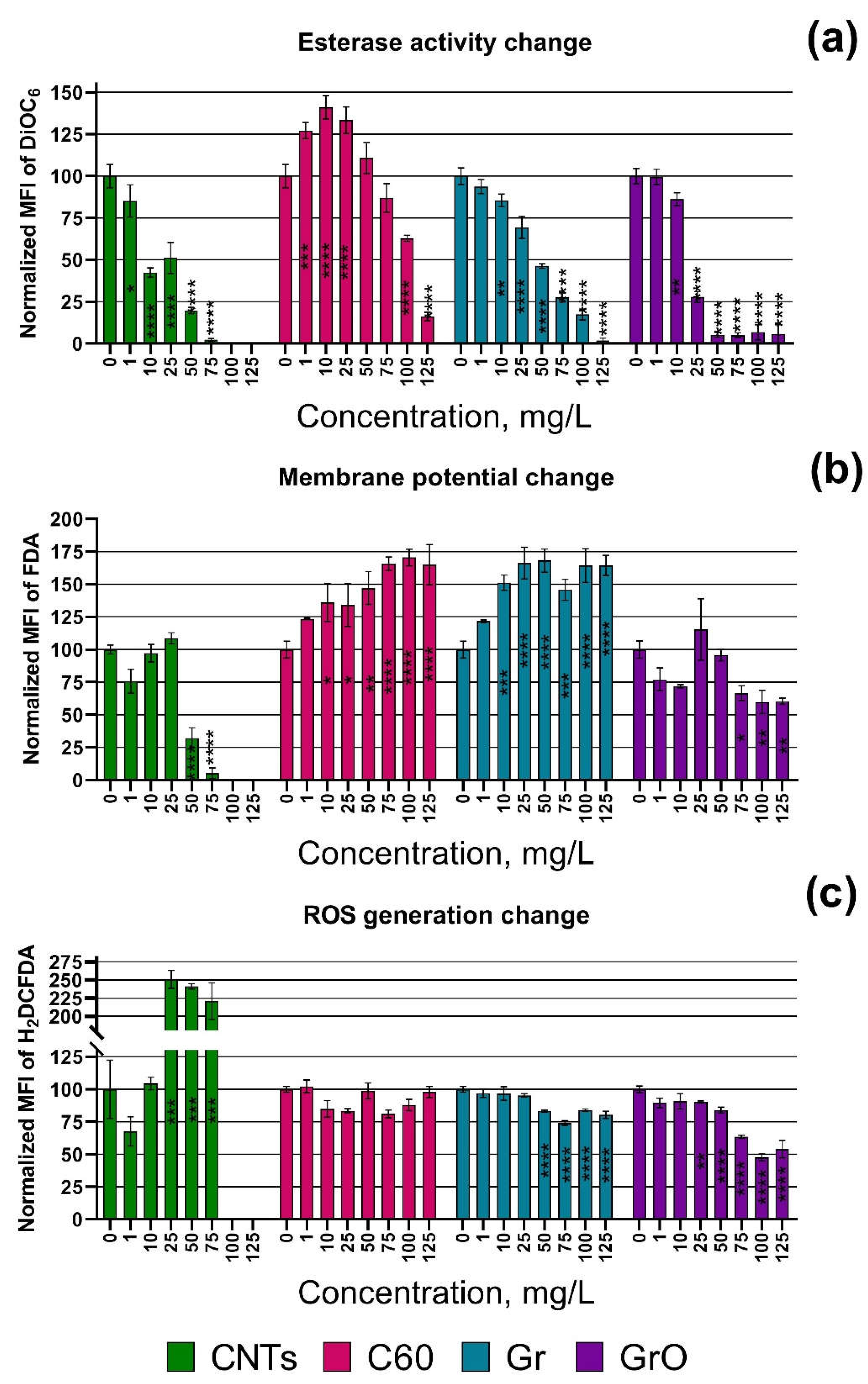
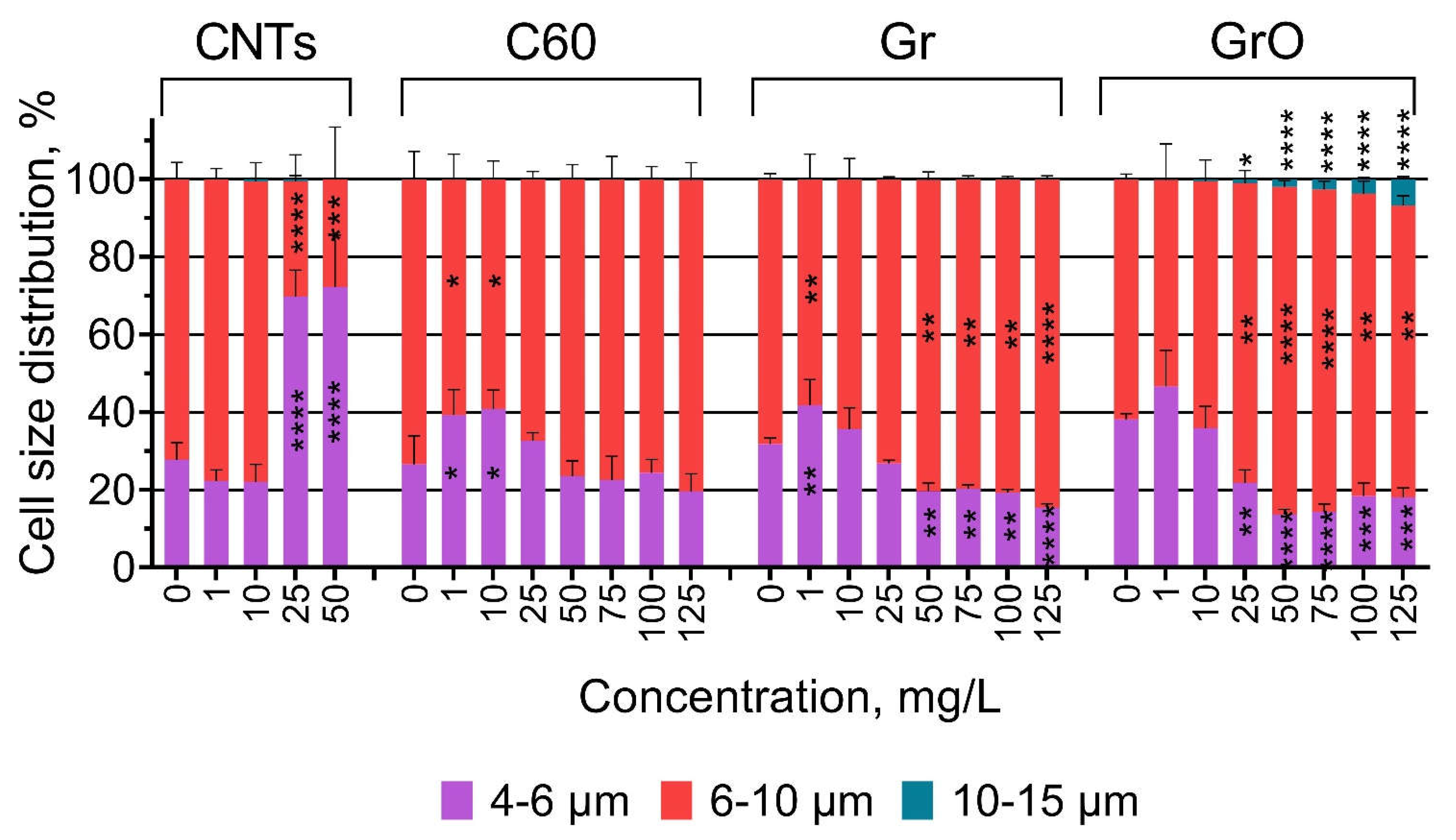
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jordan, C.C.; Kaiser, I.; Moore, V.C. 2013 nanotechnology patent literature review: Graphitic carbon-based nanotechnology and energy applications are on the rise. Nanotech. L. & Bus. 2014, 11, 111. [Google Scholar]
- Debnath, S.K.; Srivastava, R. Drug Delivery With Carbon-Based Nanomaterials as Versatile Nanocarriers: Progress and Prospects. Front. Nanotechnol. 2021, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.-N. , Carbon-Based Nanomaterials for Energy Conversion and Storage: Applications in Electrochemical Catalysis. Vol. 325. 2022: Springer Nature.
- Mishra, R. ; J Militky, Nanotechnology in textiles: theory and application. 2018: Woodhead Publishing.
- Freixa, A.; Acuña, V.; Sanchís, J.; Farré, M.; Barceló, D.; Sabater, S. Ecotoxicological effects of carbon based nanomaterials in aquatic organisms. Sci. Total. Environ. 2018, 619-620, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, Y.; Gong, C.; Liu, B.; Wei, G. Production, structural design, functional control, and broad applications of carbon nanofiber-based nanomaterials: A comprehensive review. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 402, 126189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiti, D.; Tong, X.; Mou, X.; Yang, K. Carbon-Based Nanomaterials for Biomedical Applications: A Recent Study. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 9, 1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eivazzadeh-Keihan, R.; Noruzi, E.B.; Chidar, E.; Jafari, M.; Davoodi, F.; Kashtiaray, A.; Gorab, M.G.; Hashemi, S.M.; Javanshir, S.; Cohan, R.A.; et al. Applications of carbon-based conductive nanomaterials in biosensors. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 442, 136183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makvandi, P.; Ghomi, M.; Padil, V.V.T.; Shalchy, F.; Ashrafizadeh, M.; Askarinejad, S.; Pourreza, N.; Zarrabi, A.; Zare, E.N.; Kooti, M.; et al. Biofabricated Nanostructures and Their Composites in Regenerative Medicine. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2020, 3, 6210–6238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Chen, J.; Qiao, S.; Zhang, W. Carbon-Based Nanomaterials for Bone and Cartilage Regeneration: A Review. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 7, 4718–4735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yogeswari, B.; Khan, I.; Kumar, M.S.; Vijayanandam, N.; Devarani, P.A.; Anandaram, H.; Chaturvedi, A.; Misganaw, W. Role of Carbon-Based Nanomaterials in Enhancing the Performance of Energy Storage Devices: Design Small and Store Big. J. Nanomater. 2022, 2022, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.-Y.; Ye, Y.-W.; Guo, X.; Cheng, F. Design and synthesis of carbon-based nanomaterials for electrochemical energy storage. New Carbon Mater. 2022, 37, 59–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Gu, W.; Zhou, L.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Lei, J. Recent advances in MOF-derived carbon-based nanomaterials for environmental applications in adsorption and catalytic degradation. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 427, 131503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.C.; Rodrigues, D.F. Carbon-based nanomaterials for removal of chemical and biological contaminants from water: A review of mechanisms and applications. Carbon 2015, 91, 122–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, C.E.D.; Almeida, J.C.; Lopes, C.B.; Trindade, T.; Vale, C.; Pereira, E. Recovery of Rare Earth Elements by Carbon-Based Nanomaterials—A Review. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iftekhar, S.; Heidari, G.; Amanat, N.; Zare, E.N.; Asif, M.B.; Hassanpour, M.; Lehto, V.P.; Sillanpaa, M. Porous materials for the recovery of rare earth elements, platinum group metals, and other valuable metals: a review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2022, 20, 3697–3746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marchi, L.; Pretti, C.; Gabriel, B.; Marques, P.A.; Freitas, R.; Neto, V. An overview of graphene materials: Properties, applications and toxicity on aquatic environments. Sci. Total. Environ. 2018, 631-632, 1440–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, S.-H.; An, Y.-J. Size- and shape-dependent toxicity of silver nanomaterials in green alga Chlorococcum infusionum. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 168, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleh, T.A. Nanomaterials: Classification, properties, and environmental toxicities. Environmental Technology & Innovation 2020, 20, 101067. [Google Scholar]
- Czarnecka, J.; Wiśniewski, M.; Forbot, N.; Bolibok, P.; Terzyk, A.P.; Roszek, K. Cytotoxic or Not? Disclosing the Toxic Nature of Carbonaceous Nanomaterials through Nano–Bio Interactions. Materials 2020, 13, 2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pikula, K.; Johari, S.A.; Golokhvast, K. Colloidal Behavior and Biodegradation of Engineered Carbon-Based Nanomaterials in Aquatic Environment. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 4149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, R.J.; Harrison, S.; Keller, V.; Kuenen, J.; Lofts, S.; Praetorius, A.; Svendsen, C.; Vermeulen, L.C.; van Wijnen, J. Models for assessing engineered nanomaterial fate and behaviour in the aquatic environment. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2018, 36, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasyukova, I.A.; Zakharova, O.V.; Chaika, V.V.; Pikula, K.S.; Golokhvast, K.S.; Gusev, A.A. Toxic Effect of Metal-Based Nanomaterials on Representatives of Marine Ecosystems: A Review. Nanobiotechnology Rep. 2021, 16, 138–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhotra, N.; Villaflores, O.B.; Audira, G.; Siregar, P.; Lee, J.-S.; Ger, T.-R.; Hsiao, C.-D. Toxicity Studies on Graphene-Based Nanomaterials in Aquatic Organisms: Current Understanding. Molecules 2020, 25, 3618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Cheng, S.H. Influence of carbon nanotube length on toxicity to zebrafish embryos. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 3731–3739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrence, J.R.; Waiser, M.J.; Swerhone, G.D.W.; Roy, J.; Tumber, V.; Paule, A.; Hitchcock, A.P.; Dynes, J.J.; Korber, D.R. Effects of fullerene (C60), multi-wall carbon nanotubes (MWCNT), single wall carbon nanotubes (SWCNT) and hydroxyl and carboxyl modified single wall carbon nanotubes on riverine microbial communities. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 10090–10102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kavosi, A.; Noei, S.H.G.; Madani, S.; Khalighfard, S.; Khodayari, S.; Khodayari, H.; Mirzaei, M.; Kalhori, M.R.; Yavarian, M.; Alizadeh, A.M.; et al. RETRACTED ARTICLE: The toxicity and therapeutic effects of single-and multi-wall carbon nanotubes on mice breast cancer. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwok, K.W.; Leung, K.M.; Flahaut, E.; Cheng, J.; Cheng, S.H. Chronic toxicity of double-walled carbon nanotubes to three marine organisms: influence of different dispersion methods. Nanomedicine 2010, 5, 951–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, N.; Izumi, H.; Morimoto, Y. Review of toxicity studies of carbon nanotubes. J. Occup. Heal. 2017, 59, 394–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guérard, M.; Baum, M.; Bitsch, A.; Eisenbrand, G.; Elhajouji, A.; Epe, B.; Habermeyer, M.; Kaina, B.; Martus, H.; Pfuhler, S.; et al. Assessment of mechanisms driving non-linear dose–response relationships in genotoxicity testing. Mutat. Res. Mol. Mech. Mutagen. 2015, 763, 181–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, I.R.; Ives, J.A.; Wayne, B.J. Nonlinear Effects of Nanoparticles: Biological Variability from Hormetic Doses, Small Particle Sizes, and Dynamic Adaptive Interactions. Dose-Response 2013, 12, 202–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Forman, H.J.; Ge, Y.; Lunec, J. Multi-walled carbon nanotubes: A cytotoxicity study in relation to functionalization, dose and dispersion. Toxicol. Vitr. 2017, 42, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasidharan, A.; Panchakarla, L.S.; Chandran, P.; Menon, D.; Nair, S.; Rao, C.N.R.; Koyakutty, M. Differential nano-bio interactions and toxicity effects of pristine versus functionalized graphene. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 2461–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Wang, X.; Ji, Z.; Sun, B.; Zhang, H.; Chang, C.H.; Lin, S.; Meng, H.; Liao, Y.-P.; Wang, M.; et al. Surface Charge and Cellular Processing of Covalently Functionalized Multiwall Carbon Nanotubes Determine Pulmonary Toxicity. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 2352–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figarol, A.; Pourchez, J.; Boudard, D.; Forest, V.; Tulliani, J.-M.; Lecompte, J.-P.; Cottier, M.; Bernache-Assollant, D.; Grosseau, P. Biological response to purification and acid functionalization of carbon nanotubes. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2014, 16, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshehri, R.; Ilyas, A.M.; Hasan, A.; Arnaout, A.; Ahmed, F.; Memic, A. Carbon Nanotubes in Biomedical Applications: Factors, Mechanisms, and Remedies of Toxicity. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 8149–8167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, B.; Xu, Z.; Guo, W.; Li, Q. Impact of Natural Organic Matter on the Physicochemical Properties of Aqueous C60 Nanoparticles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 2853–2859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanphere, J.D.; Rogers, B.; Luth, C.; Bolster, C.H.; Walker, S.L. Stability and Transport of Graphene Oxide Nanoparticles in Groundwater and Surface Water. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2014, 31, 350–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Cao, X.; Wang, Z.; Dai, Y.; Xing, B. Mechanistic understanding toward the toxicity of graphene-family materials to freshwater algae. Water Res. 2017, 111, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pikula, K.; Chaika, V.; Zakharenko, A.; Markina, Z.; Vedyagin, A.; Kuznetsov, V.; Gusev, A.; Park, S.; Golokhvast, K. Comparison of the Level and Mechanisms of Toxicity of Carbon Nanotubes, Carbon Nanofibers, and Silicon Nanotubes in Bioassay with Four Marine Microalgae. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwab, F.; Bucheli, T.D.; Lukhele, L.P.; Magrez, A.; Nowack, B.; Sigg, L.; Knauer, K. Are carbon nanotube effects on green algae caused by shading and agglomeration? Environmental science & technology 2011, 45, 6136–6144. [Google Scholar]
- Verneuil, L.; Silvestre, J.; Mouchet, F.; Flahaut, E.; Boutonnet, J.C.; Bourdiol, F.; Bortolamiol, T.; Baqué, D.; Gauthier, L.; Pinelli, E. Multi-walled carbon nanotubes, natural organic matter, and the benthic diatom Nitzschia palea:“A sticky story”. Nanotoxicology 2015, 9, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garacci, M.; Barret, M.; Mouchet, F.; Sarrieu, C.; Lonchambon, P.; Flahaut, E.; Gauthier, L.; Silvestre, J.; Pinelli, E. Few Layer Graphene sticking by biofilm of freshwater diatom Nitzschia palea as a mitigation to its ecotoxicity. Carbon 2017, 113, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pikula, K.; Kirichenko, K.; Chernousov, V.; Parshin, S.; Masyutin, A.; Parshina, Y.; Pogodaev, A.; Gridasov, A.; Tsatsakis, A.; Golokhvast, K. The Impact of Metal-Based Nanoparticles Produced by Different Types of Underwater Welding on Marine Microalgae. Toxics 2023, 11, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, T.M.; Rennison, D.; Cervin, G.; Pavia, H.; Hellio, C.; Foulon, V.; Brimble, M.A.; Cahill, P.; Svenson, J. Towards eco-friendly marine antifouling biocides–Nature inspired tetrasubstituted 2, 5-diketopiperazines. Science of The Total Environment 2022, 812, 152487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ankit; Bauddh, K. ; Korstad, J. Phycoremediation: Use of Algae to Sequester Heavy Metals. Hydrobiology 2022, 1, 288–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlova, T.Y.; Stonik, I.V.; Shevchenko, O.G. Flora of planktonic microalgae of Amursky Bay, Sea of Japan. Russ. J. Mar. Biol. 2009, 35, 60–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markina, Z.V.; Orlova, T.Y.; Vasyanovich, Y.A.; Vardavas, A.I.; Stivaktakis, P.D.; Vardavas, C.I.; Kokkinakis, M.N.; Rezaee, R.; Ozcagli, E.; Golokhvast, K.S. Porphyridium purpureum microalga physiological and ultrastructural changes under copper intoxication. Toxicol. Rep. 2021, 8, 988–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pikula, K.S.; Chernyshev, V.V.; Zakharenko, A.M.; Chaika, V.V.; Waissi, G.; Hai, L.H.; Hien, T.T.; Tsatsakis, A.M.; Golokhvast, K.S. Toxicity assessment of particulate matter emitted from different types of vehicles on marine microalgae. Environ. Res. 2019, 179, 108785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aizdaicher, N.A.; Stonik, I.V.; Boroda, A.V. The development of Porphyridium purpureum (Bory de Saint-Vincent) Drew et Ross, 1965 (Rhodophyta) from Amursky Bay, Sea of Japan, in a laboratory culture. Russ. J. Mar. Biol. 2014, 40, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schornstein, K.L.; Scott, J. Ultrastructure of cell division in the unicellular red alga Porphyridium purpureum. Can. J. Bot. 1982, 60, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillard, R.R.; Ryther, J.H. Studies of marine planktonic diatoms: I. Cyclotella nana Hustedt, and Detonula confervacea (Cleve) Gran. Canadian journal of microbiology 1962, 8, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thines, R.; Mubarak, N.; Nizamuddin, S.; Sahu, J.; Abdullah, E.; Ganesan, P. Application potential of carbon nanomaterials in water and wastewater treatment: A review. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2017, 72, 116–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinzmann, M.; Jaworski, S.; Kutwin, M.; Jagiełło, J.; Koziński, R.; Wierzbicki, M.; Grodzik, M.; Lipińska, L.; Sawosz, E.; Chwalibog, A. Nanoparticles containing allotropes of carbon have genotoxic effects on glioblastomamultiforme cells. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 2409–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharisov, B.I. ; OV Kharissova, Carbon Allotropes in the Environment and Their Toxicity. Carbon Allotropes: Metal-Complex Chemistry, Properties and Applications, 2019: p. 639-652.
- Nel, A.E.; Mädler, L.; Velegol, D.; Xia, T.; Hoek, E.M.V.; Somasundaran, P.; Klaessig, F.; Castranova, V.; Thompson, M. Understanding biophysicochemical interactions at the nano–bio interface. Nat. Mater. 2009, 8, 543–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.; Huo, P.; Zhang, R.; Liu, B. Antibacterial Properties of Graphene-Based Nanomaterials. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, V.C.; Jachak, A.; Hurt, R.H.; Kane, A.B. Biological Interactions of Graphene-Family Nanomaterials: An Interdisciplinary Review. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2011, 25, 15–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.; Zhang, W. Measurement of the surface hydrophobicity of engineered nanoparticles using an atomic force microscope. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 24434–24443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pogodin, S.; Slater, N.K.H.; Baulin, V.A. Surface Patterning of Carbon Nanotubes Can Enhance Their Penetration through a Phospholipid Bilayer. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 1141–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Meng, T.; Guo, X.; Yang, R.; Si, X.; Zhou, J. Humic acid alleviates the ecotoxicity of graphene-family materials on the freshwater microalgae Scenedesmus obliquus. Chemosphere 2018, 197, 749–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazeem, L.J.; Bououdina, M.; Dewailly, E.; Slomianny, C.; Barras, A.; Coffinier, Y.; Szunerits, S.; Boukherroub, R. Toxicity effect of graphene oxide on growth and photosynthetic pigment of the marine alga Picochlorum sp. during different growth stages. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 24, 4144–4152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Z.; Ji, J.; Yang, K.; Lin, D.; Wu, F. Systematic and Quantitative Investigation of the Mechanism of Carbon Nanotubes’ Toxicity toward Algae. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 8458–8466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Lu, K.; Mu, L.; Kang, J.; Zhou, Q. Interactions between graphene oxide and plant cells: Regulation of cell morphology, uptake, organelle damage, oxidative effects and metabolic disorders. Carbon 2014, 80, 665–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.K.; Moon, J.-Y.; Lee, Y.-C. Microalgal ecotoxicity of nanoparticles: An updated review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 201, 110781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, C.; Li, Y.; Yin, J.-J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, C. The contributions of metal impurities and tube structure to the toxicity of carbon nanotube materials. NPG Asia Mater. 2012, 4, e32–e32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonardo, T.; Farhi, E.; Boisson, A.M.; Vial, J.; Cloetens, P.; Bohic, S.; Rivasseau, C. Determination of elemental distribution in green micro-algae using synchrotron radiation nano X-ray fluorescence (SR-nXRF) and electron microscopy techniques–subcellular localization and quantitative imaging of silver and cobalt uptake by Coccomyxa actinabiotis. Metallomics 2014, 6, 316–329. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liang, S.X.T.; Wong, L.S.; Dhanapal, A.C.T.A.; Djearamane, S. Toxicity of Metals and Metallic Nanoparticles on Nutritional Properties of Microalgae. Water, Air, Soil Pollut. 2020, 231, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameri, M.; Baron-Sola, A.; Khavari-Nejad, R.A.; Soltani, N.; Najafi, F.; Bagheri, A.; Martinez, F.; Hernández, L.E. Aluminium triggers oxidative stress and antioxidant response in the microalgae Scenedesmus sp. J. Plant Physiol. 2020, 246-247, 153114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenfield, M.A.; van Dam, J.W.; Harford, A.J.; Parry, D.; Streten, C.; Gibb, K.; van Dam, R.A. Aluminium, gallium, and molybdenum toxicity to the tropical marine microalga Isochrysis galbana. Environmental toxicology and chemistry 2015, 34, 1833–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruces, E.; Barrios, A.C.; Cahue, Y.P.; Januszewski, B.; Gilbertson, L.M.; Perreault, F. Similar toxicity mechanisms between graphene oxide and oxidized multi-walled carbon nanotubes in Microcystis aeruginosa. Chemosphere 2020, 265, 129137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Giri, S.; Wadhwa, G.; Pulimi, M.; Anand, S.; Chandrasekaran, N.; Johari, S.A.; Rai, P.K.; Mukherjee, A. Comparative ecotoxicity of graphene, functionalized multi-walled CNTs, and their mixture in freshwater microalgae, Scenedesmus obliquus: analyzing the role of oxidative stress. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 2023, 30, 70246–70259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neagu, M.; Piperigkou, Z.; Karamanou, K.; Engin, A.B.; Docea, A.O.; Constantin, C.; Negrei, C.; Nikitovic, D.; Tsatsakis, A. Protein bio-corona: critical issue in immune nanotoxicology. Arch. Toxicol. 2016, 91, 1031–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Hevia, L.; Saramiforoshani, M.; Monge, J.; Iturrioz-Rodríguez, N.; Padín-González, E.; González, F.; González-Legarreta, L.; González, J.; Fanarraga, M.L. The unpredictable carbon nanotube biocorona and a functionalization method to prevent protein biofouling. J. Nanobiotechnology 2021, 19, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braccia, C.; Castagnola, V.; Vázquez, E.; González, V.J.; Loiacono, F.; Benfenati, F.; Armirotti, A. The lipid composition of few layers graphene and graphene oxide biomolecular corona. Carbon 2021, 185, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
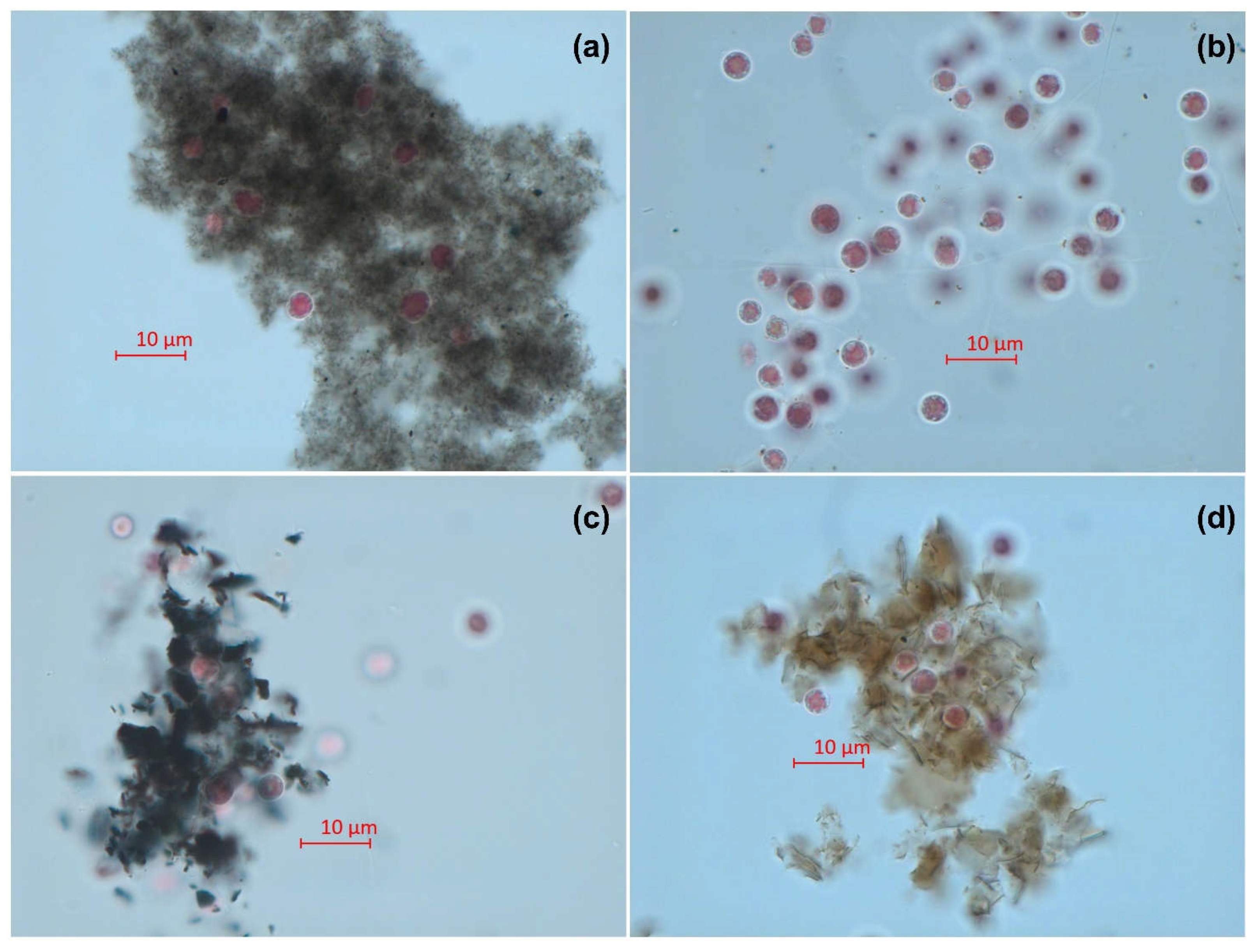

| Sample | Size | Purity | Synthesis or manufacturer information |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNTs | Diameter: 6-13 nm; Length: 2.5-20 µm |
> 98% (main trace metals: Al - 10000 ppm, Co – 2652 ppm) | Batch Number: MKCM1457; Sigma Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA |
| C60 | Diameter: 0.8 nm | > 95.5% (oxide C60) | Batch Number: 120722; Modern Synthesis Technology (MST), Saint-Petersburg, Russia |
| Gr | Thickness: 3-10 nm; Diameter: 0.5-10 µm |
> 99% | Type #1, CAS#: 1034343-98-0; Modern Synthesis Technology (MST), Saint-Petersburg, Russia |
| GrO | Diameter:10-100 µm | Carbon: 46%; Oxygen: 49%; Hydrogen: 2,5%; Sulfur: 2,5% | CAS#: 1034343-98-0; Modern Synthesis Technology (MST), Saint-Petersburg, Russia |
| Endpoint | Fluorescent Dye or Registered Parameter | Duration of microalgae exposure before the measurement | Dye concentration / Duration of Staining * | Emission Channel / Band Width, nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Growth inhibition | PI | 96 h | 20 µM/20 min | 610/20 |
| Size | Forward scatter intensity (size calibration kit F13838 by Molecular Probes, USA) | 96 h | – | FSC |
| Esterase activity | FDA | 24 h | 100 µM/20 min | 525/40 |
| Membrane potential | DiOC6 | 24 h | 5 µM/20 min | 525/40 |
| ROS generation | H2DCFDA | 24 h | 100 µM/40 min | 525/40 |
| Descriptor | CNTs | C60 | Gr | GrO |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Growth rate inhibition, 96 h | ||||
| NOEL. mg/L | <1 | 50 | 10 | <1 |
| EC10. mg/L | 0.49 (0.4396–0.5494) | 24.10 (10.24–67.41) | 15.55 (9.479–22.97) | 8.60 (7.727–9.553) |
| EC50. mg/L | 2.08 (1.935–2.251) | >131.0 | 94.88 (83.68–108.5) | 23.37 (21.84–24.98) |
| Esterase activity inhibition, 24 h | ||||
| NOEL. mg/L | <1 | <1 | 1 | 1 |
| EC10. mg/L | 1.01 (0.36–2.43) | 57.12 (41.60–73.18) | 14.48 (10.09–19.88) | 8.44 (6.84–10.45) |
| EC50. mg/L | 8.182 (5.014–12.44) | 93.17 (83.68–102.6) | 44.73 (38.82–50.92) | 18.28 (16.67–20.02) |
| Membrane potential change, 24 h | ||||
| NOEL. mg/L | 25inh | 1sti | <1sti | 125n/a |
| EC10. mg/L | 38.68 (26.24–50.00)inh | <1sti | <1sti | n/a |
| EC50. mg/L | 46.55 (39.39–49.55)inh | 17.40 (6.76–32.61)sti | 5.61 (1.16–12.69)sti | n/a |
| ROS generation change, 24 h | ||||
| NOEL. mg/L | 10sti | 125n/a | 25inh | 25inh |
| EC10. mg/L | 10.82 (n/a) | n/a | 27.90 (13.80–43.82)inh | 25.54 (13.64–37.77)inh |
| EC50. mg/L | 14.66 (n/a) | n/a | >125inh | 123.20 (106.30–153.00)inh |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





