Submitted:
10 May 2023
Posted:
10 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
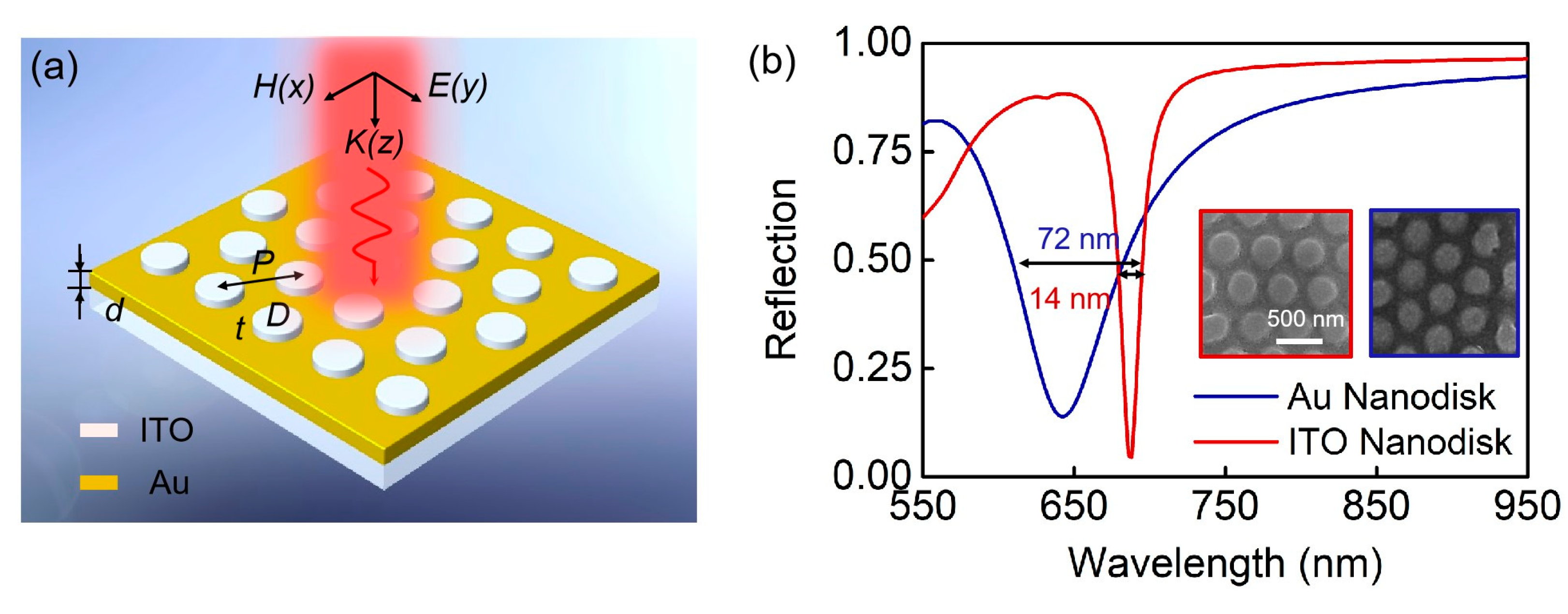
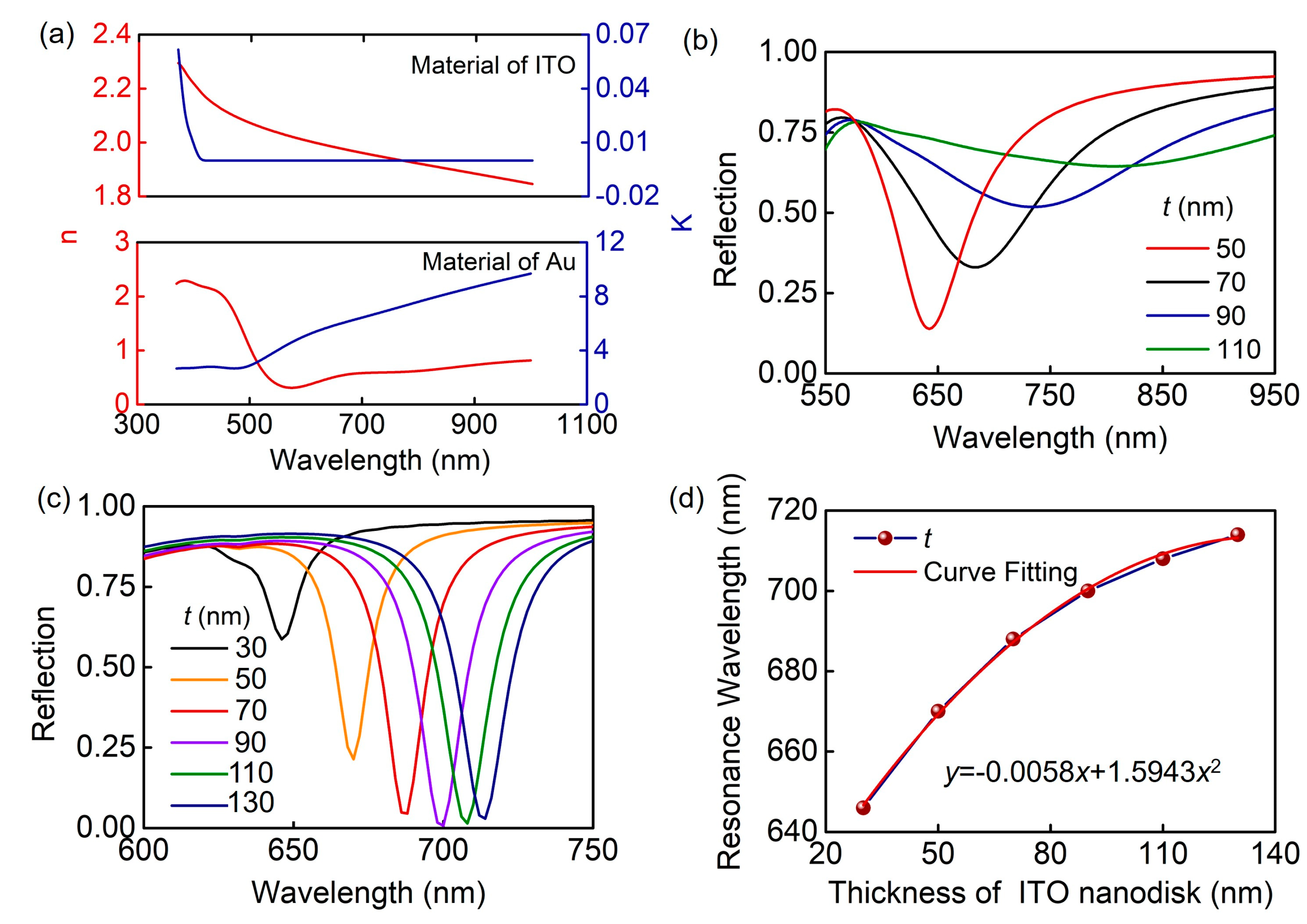
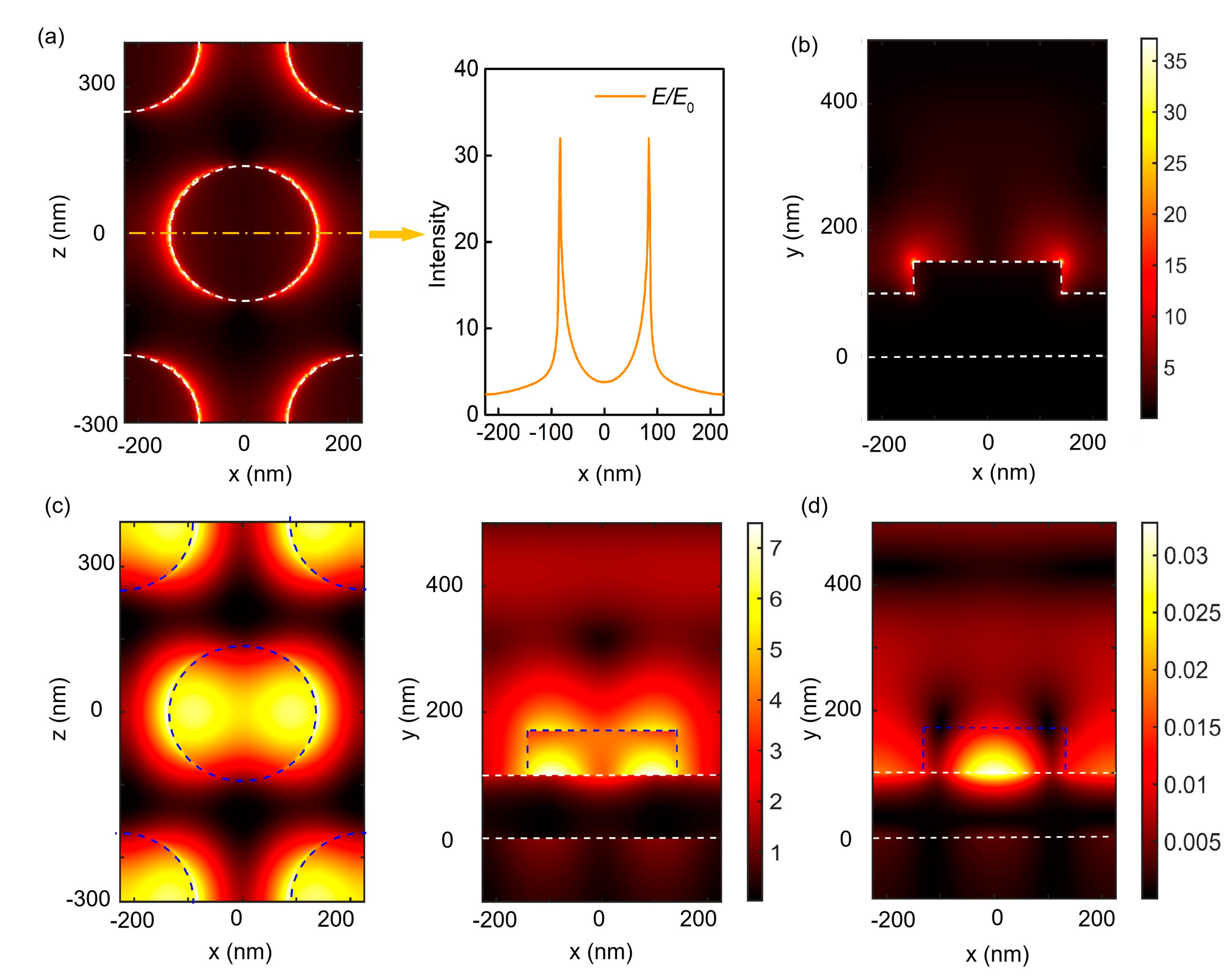
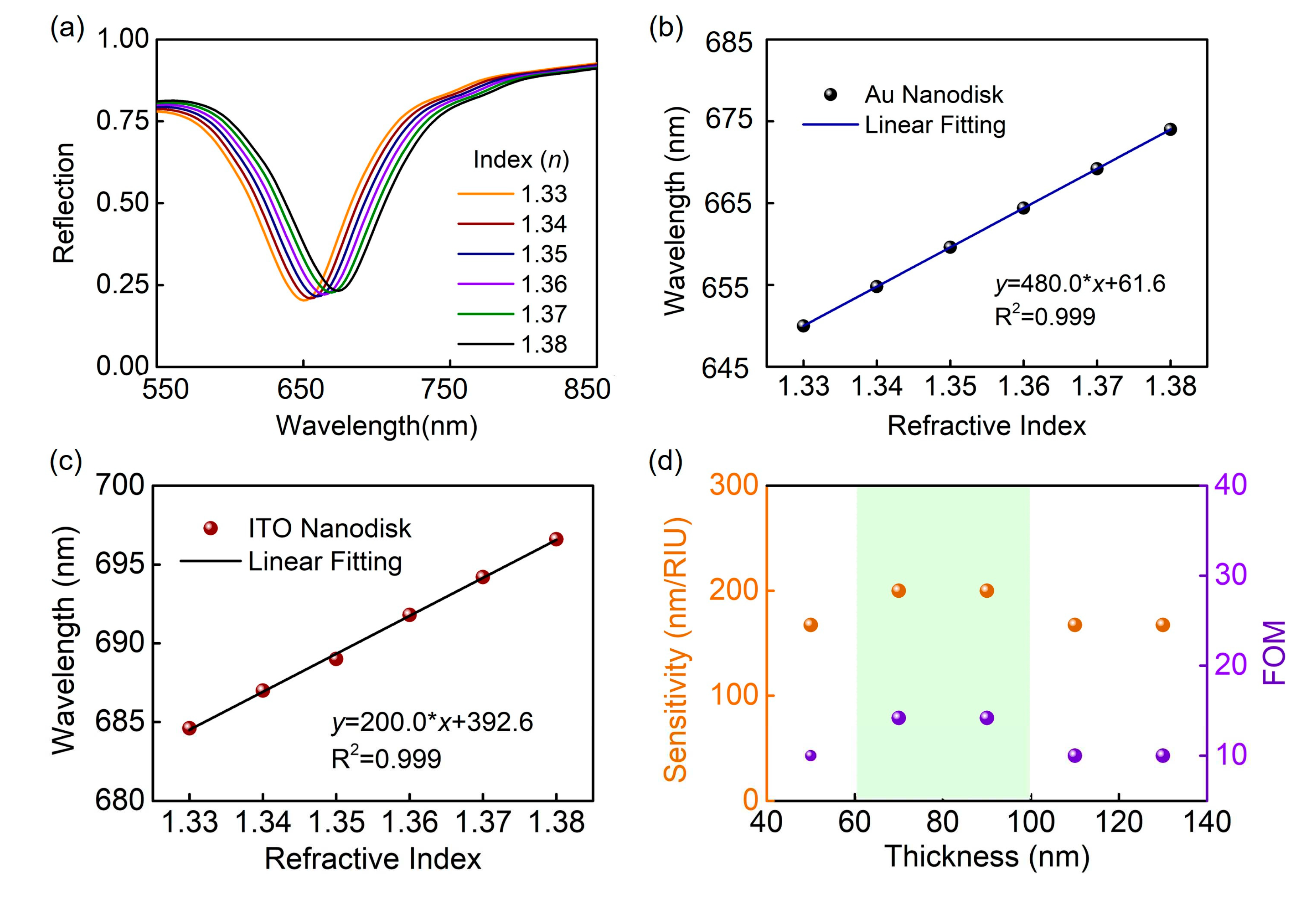
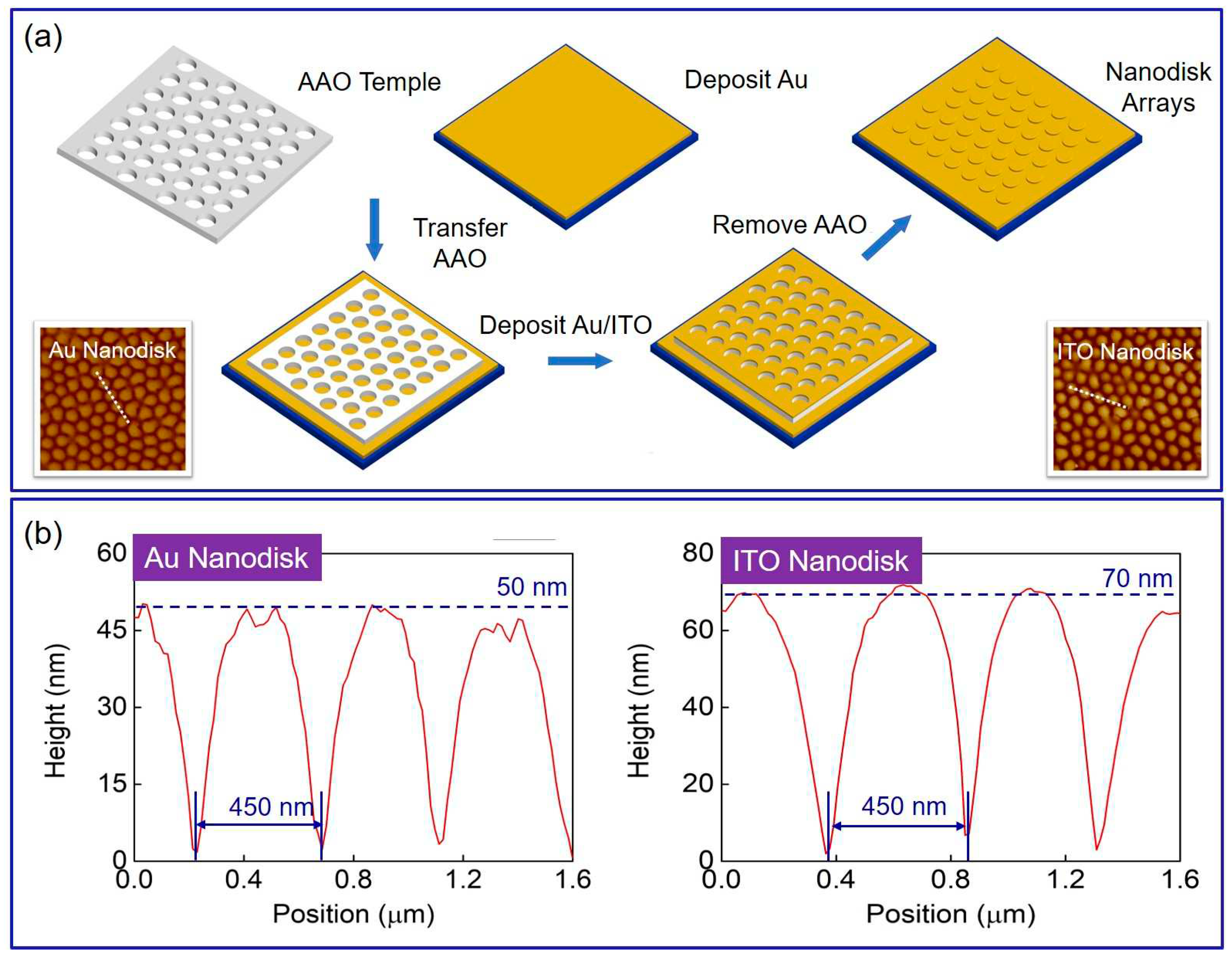
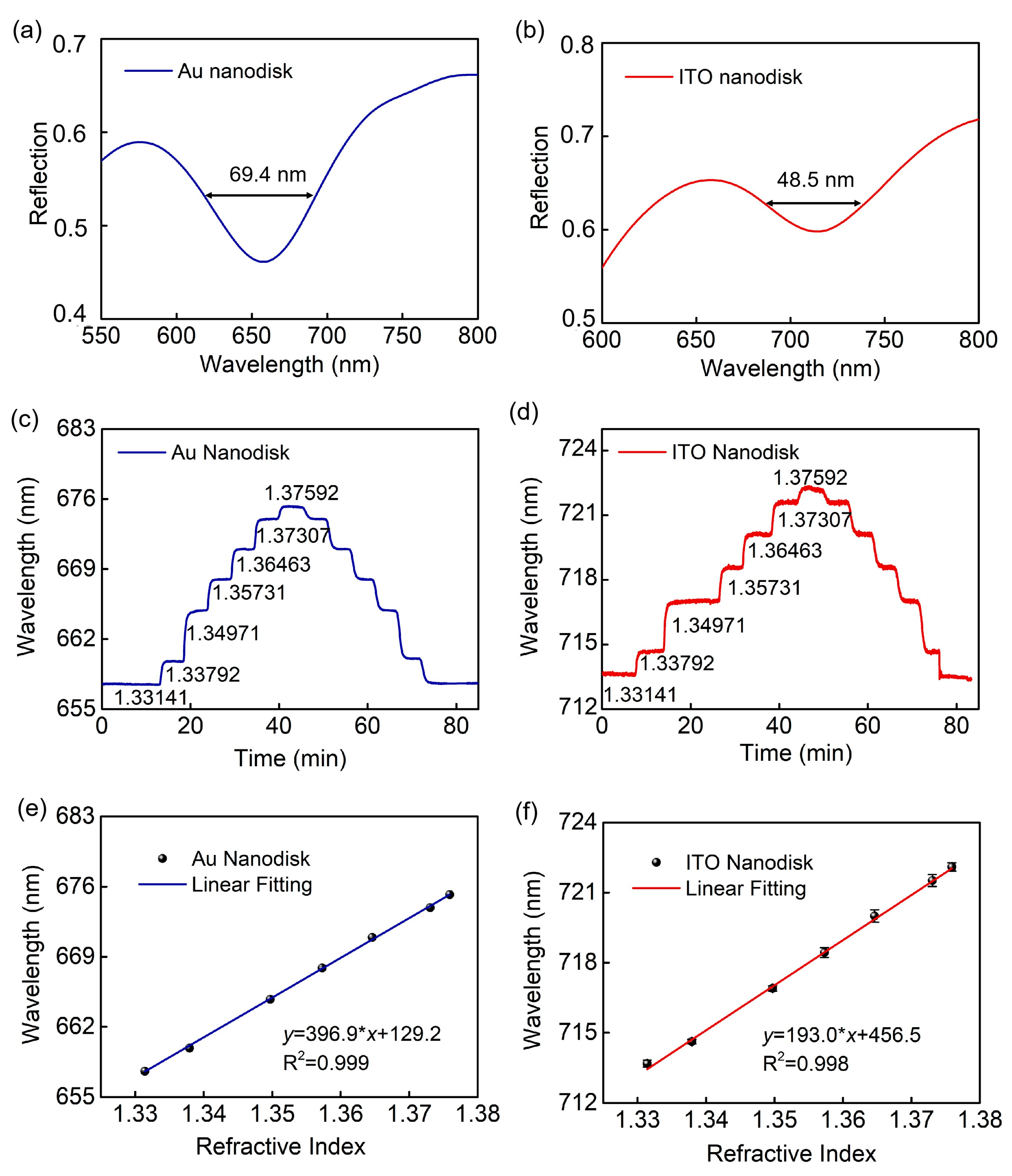
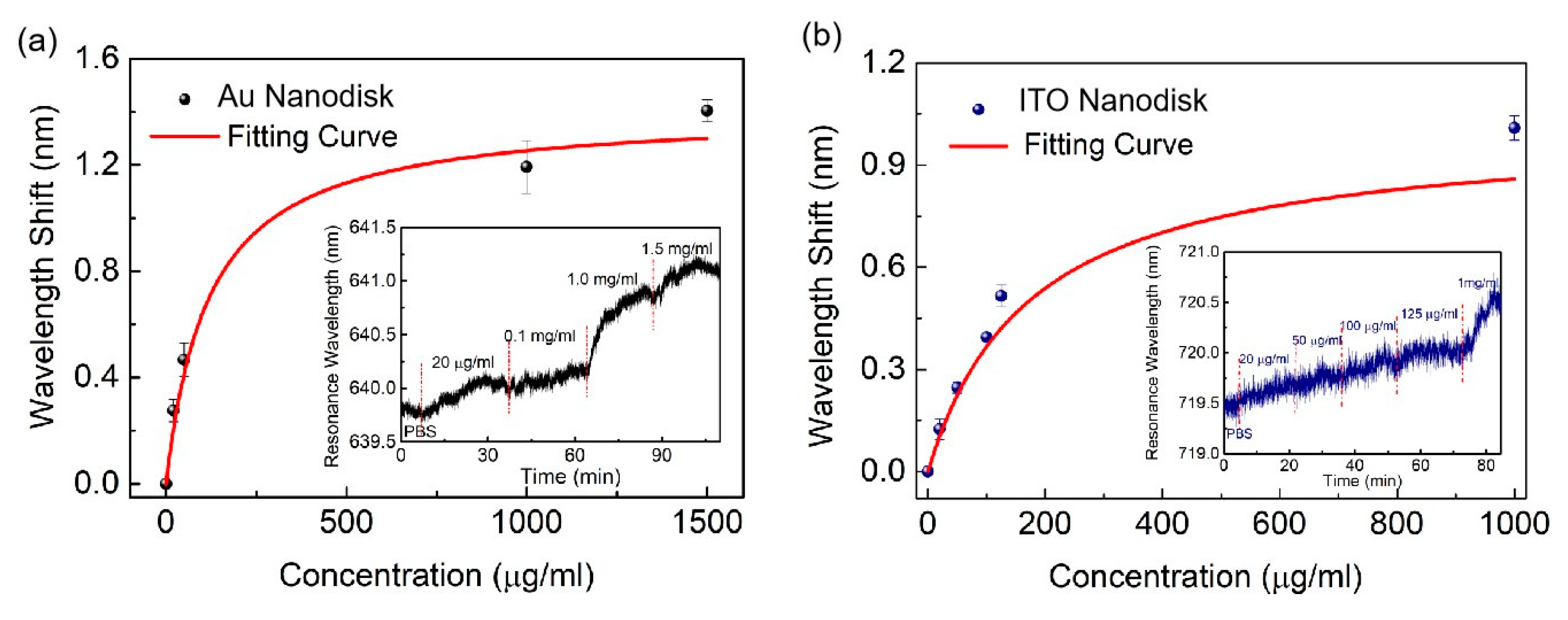
2. Results and Discussion
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yang, J. K.; Yeo S., P.; Qiu, C. W. Color generation via subwavelength plasmonic nanostructures. Nanoscale, 2015, 7, 6409–6419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Xiao, S.; Song, Q.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wang, S.; Yu, J.; Han, J.; Tsai, D. P. All-dielectric metasurface for high-performance structural color. Nat. Commun., 2020, 11, 1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.; Liao, Z. F.; Liu, Z. Q.; Liu, X. S.; Zhou, J.; Liu, G. Q.; Yi, Z.; Wang, J. Q. Recent progresses on metamaterials for optical absorption and sensing: a review. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys., 2021, 54, 113002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Besteiro, L. V.; Huang, Y. J.; Wu, J.; Fu, L.; Tan, H. H.; Jagadish, C.; Wiederrecht, G. P.; Govorov, A. O.; Wang, Z. M. Broadband metamaterial absorbers. Adv. Optical Mater., 2018, 7, 1800995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.; Yu, J.; Liu, W.; Yu, T.; Gao, P. Ultra-narrowband perfect absorption of monolayer two-dimensional materials enabled by all-dielectric subwavelength gratings. Opt. Express, 2020, 28, 38592–38602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, W.; Zhang, X.; Yan, M.; Zhao, L.; Ning, T.; Huo, Y. Low-threshold and controllable nanolaser based on quasi-BIC supported by an all-dielectric eccentric nanoring structure. Opt. Express, 2021, 29, 12634–12643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, W.; Xu, T.; Wang, H.; Zhang, C.; Deotare, P. B.; Agrawal, A.; Lezec, H. J. Surface plasmon polariton laser based on a metallic trench Fabry-Perot resonator. Sci. Adv., 2017, 3, 2375–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minopoli, A.; Acunzo, A.; Della, V. B.; Velotta, R. Nanostructured surfaces as plasmonic biosensors: a review. Adv. Mater. Interfaces, 2021, 9, 2101133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauriz, E.; Lechuga, L. M. Plasmonic biosensors for single-molecule biomedical analysis. Biosensors, 2021, 11, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A. K.; Pandey, A. K. Self-referenced plasmonic sensor with TiO2 grating on thin Au layer: simulated performance analysis in optical communication band. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B, 2019, 36, F25–F31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyoshi, K.; Tanaka, Y. Y.; Ishida, T.; Shimura, T.; Tatsuma, T. Plasmonic-diffractive hybrid sensors based on a gold nanoprism array. ACS Appl. Nano Mater., 2018, 1, 5994–5999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameen, A.; Hackett, L. P.; Seo, S.; Dar, F. K.; Gartia, M. R.; Goddard, L. L.; Liu, G. L. Plasmonic sensing of oncoproteins without resonance shift using 3D periodic nanocavity in nanocup arrays. Adv. Opt. Mater., 2017, 5, 1601051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C. W.; Wang, S. H.; Lo, S. C.; Yong, W. H.; Ho, Y. L.; Delaunay, J. J.; Tsai, W. S.; Wei, P. K. Sensitive Oligonucleotide Detection Using Resonant Coupling between Fano Resonance and Image Dipoles of Gold Nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2022; 14, 14012–14024. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y. H.; Liang, Z. Z.; Meng, D. J.; Qin, Z.; Fan, Y. D.; Shi, X. Y.; Smith, D. R.; Hou, E. Z. All-dielectric refractive index sensor based on Fano resonance with high sensitivity in the mid-infrared region. Results Phys., 2021, 24, 104129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B. Q.; Yu, P.; Wang, W. H.; Zhang, X. T.; Kuo, H. C.; Xu, H. X.; Wang, Z. M. High-Q Plasmonic Resonances: Fundamentals and Applications. Adv. Optical Mater., 2021, 9, 2001520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasani, S.; Curtin, K.; Wu, N. A review of 2D and 3D plasmonic nanostructure array patterns: fabrication, light management and sensing applications. Nanophotonics, 2019, 8, 2065–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Yao, X.; Liu, B.; Ren, B. Metallic plasmonic array structures: principles, fabrications, properties, and applications. Adv. Mater., 2021, 33, e2007988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Cui, W.; Li, L.; Yu, Z.; Peng, W.; Xu, T. Large-scale plasmonic nanodisk structures for a high sensitivity biosensing platform fabricated by transfer nanoprinting. Adv. Optical Mater., 2019, 7, 1801269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Chen, S.; Zhang, J.; Yao, X.; Zhong, J. h.; Lin, H. X.; Huang, T. X.; Yang, Z. L.; Zhu, J. F.; Liu, S.; Lienau, C.; Wang, L.; Ren, B. A Plasmonic Sensor Array with Ultrahigh Figures of Merit and Resonance Linewidths down to 3 nm. Adv. Mater. 2018; 30, 1706031. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, T. Nanoslit-microcavity-based narrow band absorber for sensing applications. Opt. Express, 2015, 23, 20715–20720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zheng, L.; Ma, P.; Zhong, Y.; Liu, B.; Chen, X.; Liu, H. Metasurface generated polarization insensitive Fano resonance for high-performance refractive index sensing. Opt. Express, 2019, 27, 13252–13262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Peng, C.; Qi, S. B.; Zhang, Q.; Tang, C. J.; Shen, X. Y.; Da, H. X.; Wang, L. H.; Park, G. S. Photonic microcavity-enhanced magnetic plasmon resonance of metamaterials for sensing applications. IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett., 2019, 31, 113–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, S. W.; Liang, Y. Z.; Yuan, H. Z.; Yu, L.; Liu, Q.; Peng, W. Ultranarrow linewidth coupling resonance in flexible plasmonic nanopillar array for enhanced biomolecule detection. Adv. Mater. Interfaces, 2022, 9, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Q.; Luo, J.; Wen, C. C.; Zhang, J. F.; Zhu, Z. H.; Qin, S. Q.; Yuan, X. D. ; Hybrid metal-graphene plasmonic sensor for multi-spectral sensing in both near- and mid-infrared ranges. Opt. Express, 2019, 27, 35914–35924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vala, M.; Ertsgaard, C. T.; Wittenberg, N. J.; Oh S., H. Plasmonic sensing on symmetric nanohole arrays supporting high-Q hybrid modes and reflection geometry. ACS Sens., 2019, 4, 3265–3274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spackova, B. , Wrobel P., Bockova M., Homola, J. Optical biosensors Based on plasmonic nanostructures: a review. Proc. IEEE, 2016, 104, 2380–2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conteduca, D.; Barth, I.; Pitruzzello, G.; Reardon, C. P.; Martins, E. R.; Krauss, T. F. Dielectric nanohole array metasurface for high-resolution near-field sensing and imaging. Nat. Commun., 2021, 12, 3293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yesilkoy, F.; Arvelo, E. R.; Jahani, Y.; Liu, M. K.; Tittl, A.; Cevher, V.; Kivshar, Y.; Altug, H. Ultrasensitive hyperspectral imaging and biodetection enabled by dielectric metasurfaces. Nat. Photonics, 2019, 13, 390–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruso, F.; Niikura, K.; Furlong, D. N.; Okahata, Y. 2. Assembly of alternating polyelectrolyte and protein multilayer films for immunosensing. Langmuir, 1997, 13, 3427–3433.
- Wang, G. L.; Shu, J. X.; Dong, Y. M.; Xu, X. M.; Li, Z. J. An ultrasensitive and universal photoelectrochemical immunoassay based on enzyme mimetics enhanced signal amplification. Biosens. Bioelectron, 2015, 66, 283–289.
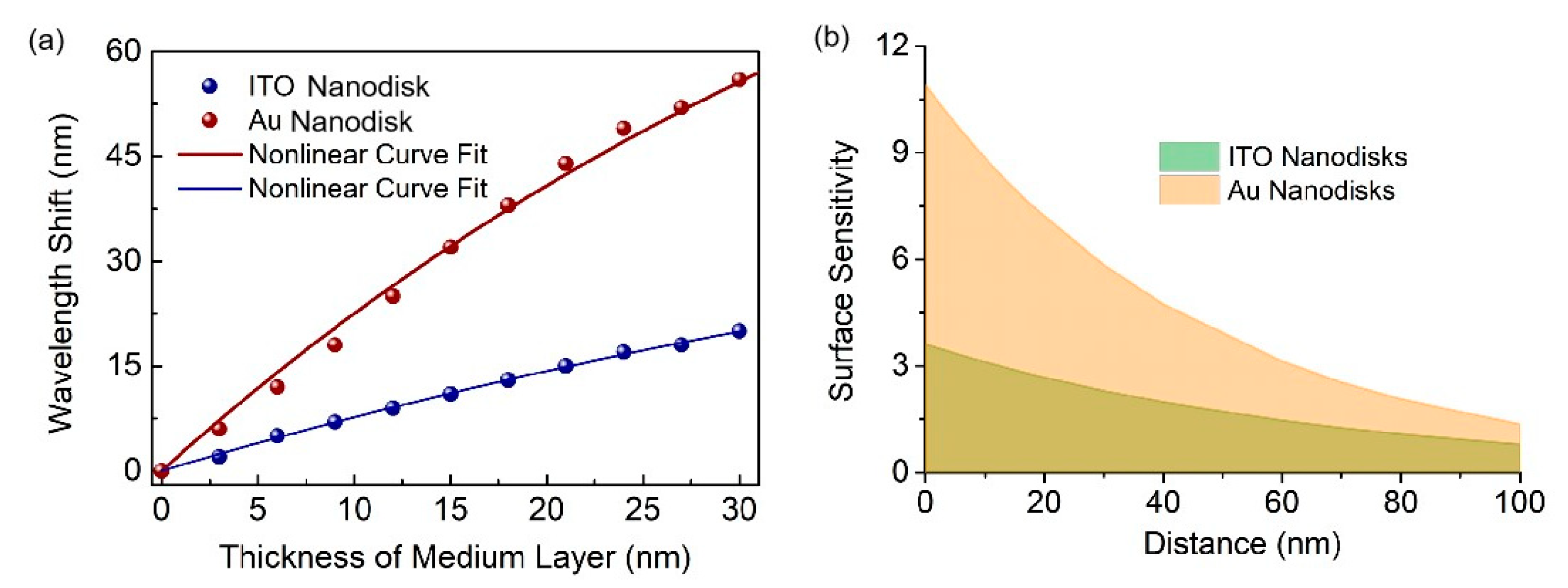
| Δλ∞ | ld | |
|---|---|---|
| Full-metal nanodisk arrays | 119.8 nm | 48.0 nm |
| ITO nanodisk arrays | 54.8 nm | 66.2 nm |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





