Submitted:
23 September 2023
Posted:
25 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
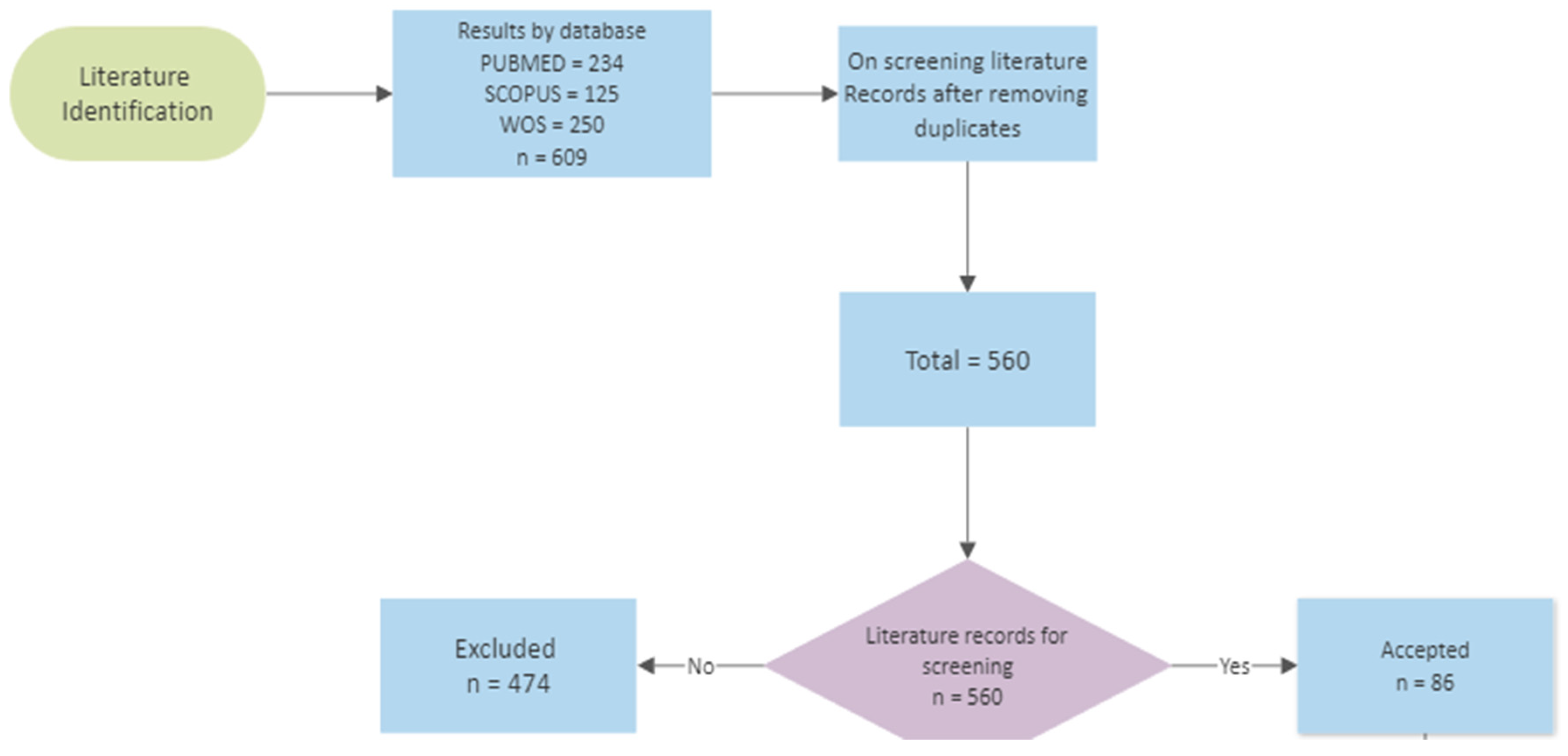
2. Methodology and Search Strategy
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Brief History of Androgen Receptor (AR)
3.2. AR Family Members
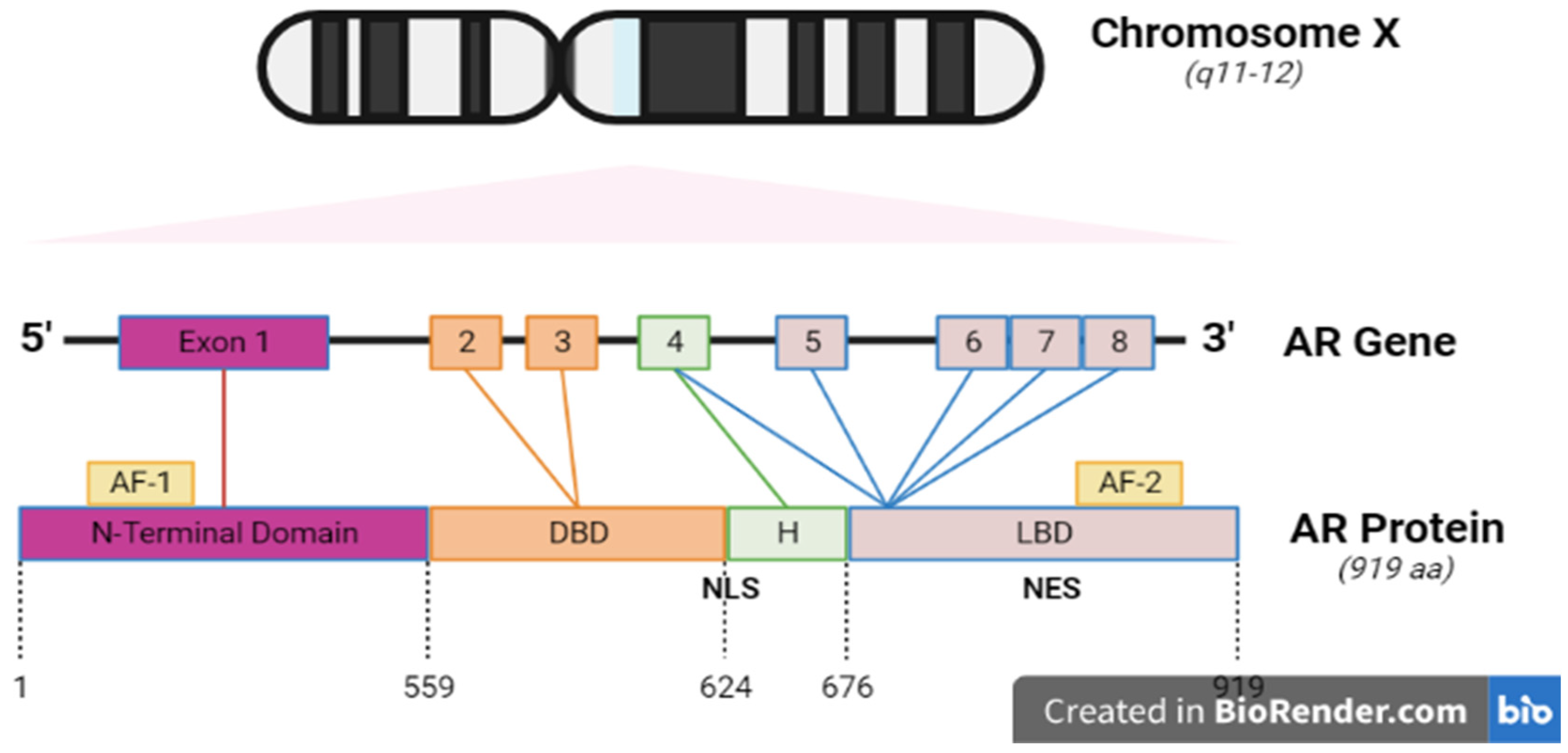
3.3. AR Structure
3.4.1. The NH2-terminal domain
3.4.2. The Central DNA-binding domain and hinge region
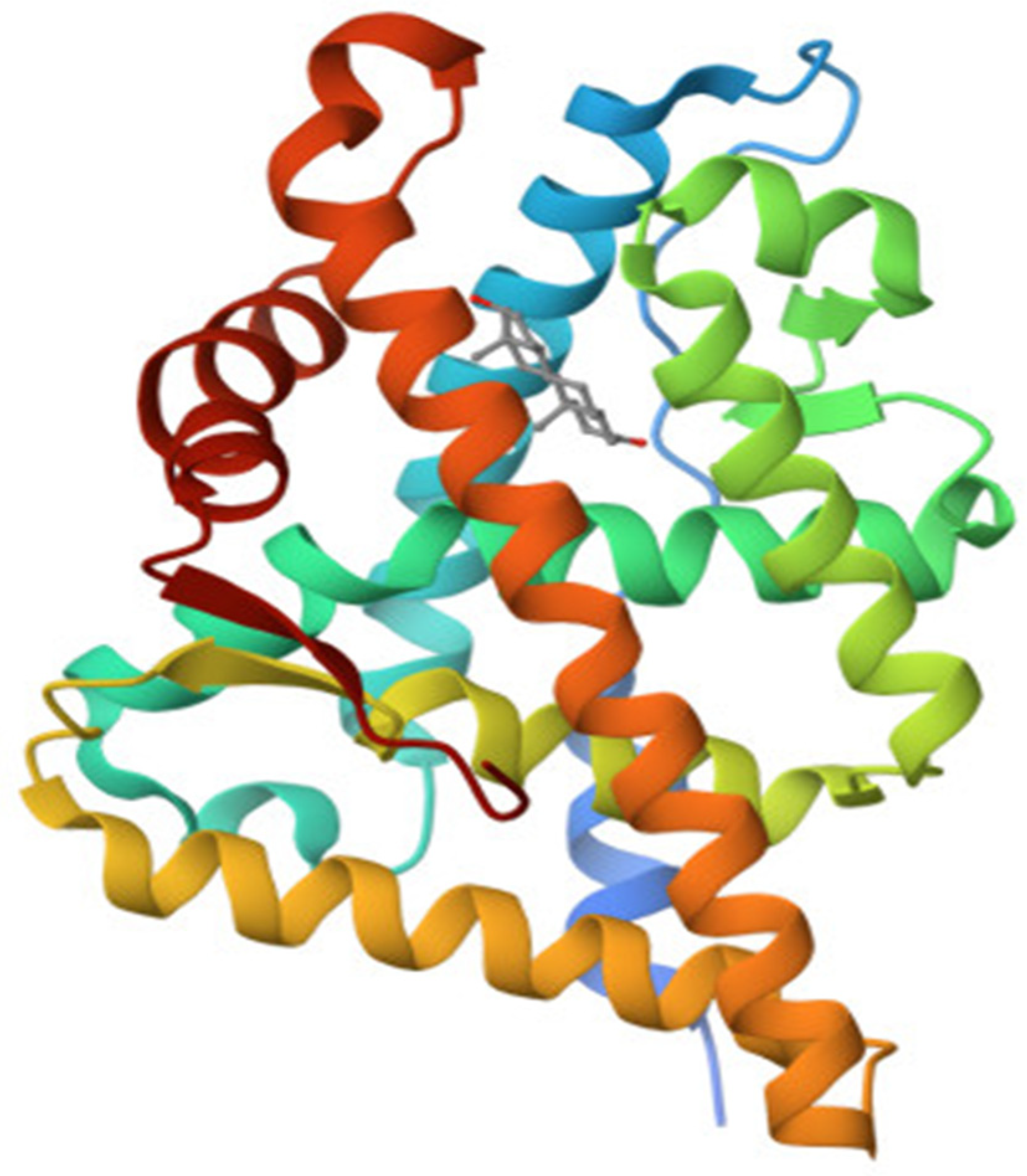
3.4.3. The Ligand Binding Domain
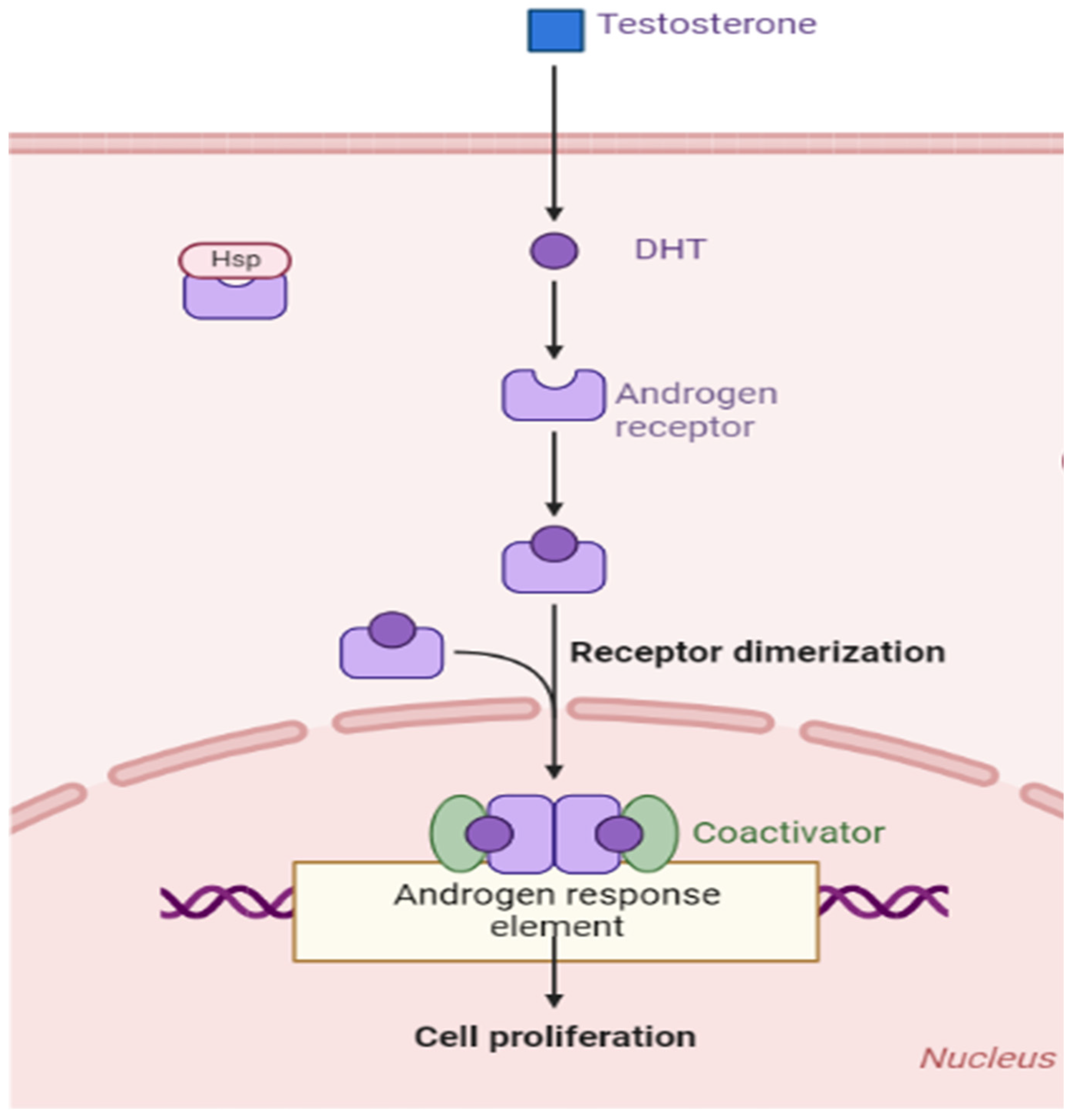
4. Physiological Role of AR and Signal Tranduction
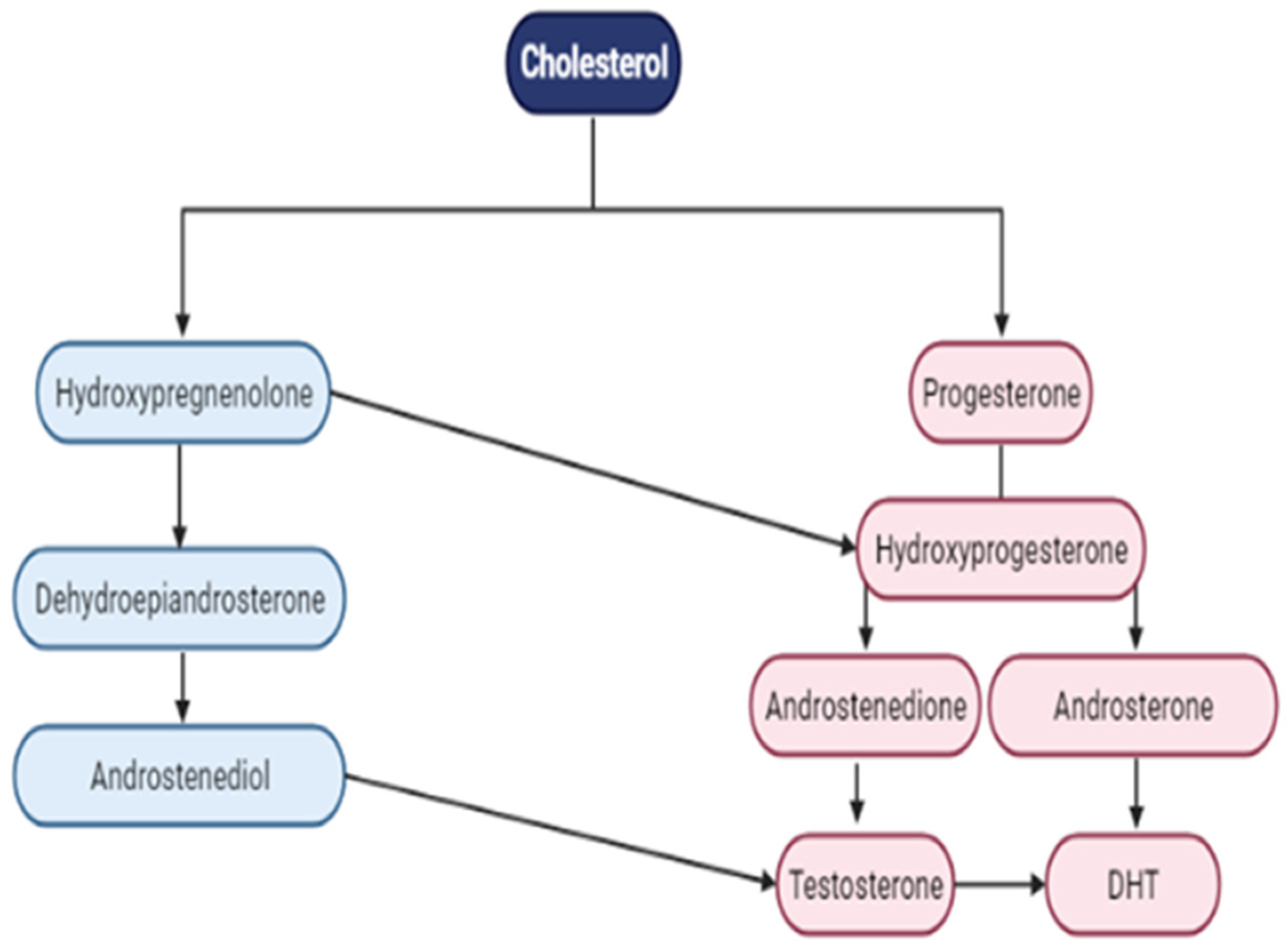
4.2. AR Ligand—Androgens
4.3. Prostate Cancer Susceptibility and AR
4.4. Role of Androgen Receptor in PCa
4.5. Prostate Cancer Progression to a Castration-Resistant State

4.6. Crosstalk between AR and other pathways
4.7. Targeting AR in Prostate cancer
4.7.1. Emerging Therapies Targeting AR
4.7.2. Androgen Deprivation Therapy (ADT)
4.7.3. Androgen Receptor Signaling Inhibitors (ARSIs)
4.7.4. Combinational Therapies
5. Conclusions and future directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chu, J.J. & Mehrzad, R. (2023) The biology of cancer. In: The Link Between Obesity and Cancer. Elsevier. pp. 35–45. [CrossRef]
- Ha, H., Kwon, H., Lim, T., Jang, J., Park, S.-K. & Byun, Y. (2021) Inhibitors of prostate-specific membrane antigen in the di-agnosis and therapy of metastatic prostate cancer – a review of patent literature. Expert Opinion on Therapeutic Patents. 31 (6), 525–547. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellinger, J.; Alajati, A.; Kubatka, P.; Giordano, F.A.; Ritter, M.; Costigliola, V.; Golubnitschaja, O. Prostate cancer treatment costs increase more rapidly than for any other cancer—how to reverse the trend? EPMA J. 2022, 13, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawla, P. Epidemiology of Prostate Cancer. World J. Oncol. 2019, 10, 63–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nevedomskaya, E.; Baumgart, S.J.; Haendler, B. Recent Advances in Prostate Cancer Treatment and Drug Discovery. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Lu, B.; He, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Du, L. Prostate Cancer Incidence and Mortality: Global Status and Temporal Trends in 89 Countries From 2000 to 2019. Front. Public Heal. 2022, 10, 811044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osadchuk, L.V.; Osadchuk, A.V. Role of CAG and GGC Polymorphism of the Androgen Receptor Gene in Male Fertility. Russ. J. Genet. 2022, 58, 247–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badal, S.; Aiken, W.; Morrison, B.; Valentine, H.; Bryan, S.; Gachii, A.; Ragin, C. Disparities in prostate cancer incidence and mortality rates: Solvable or not? Prostate 2020, 80, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Fu, C.; Song, X.; Grimm, R.; von Busch, H.; Benkert, T.; Kamen, A.; Lou, B.; Huisman, H.; Tong, A.; et al. Automated deep-learning system in the assessment of MRI-visible prostate cancer: comparison of advanced zoomed diffusion-weighted imaging and conventional technique. Cancer Imaging 2023, 23, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Sun, G.; Zhu, S.; Dai, J.; Chen, J.; Zhang, M.; Ni, Y.; Zhang, H.; Shen, P.; Zhao, X.; et al. Circulating tumour DNA reveals genetic traits of patients with intraductal carcinoma of the prostate. BJU Int. 2022, 129, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Hooker, E.; Yu, E.-J.; Wu, H.; Cunha, G.R.; Sun, Z. An Indispensable Role of Androgen Receptor in Wnt Responsive Cells During Prostate Development, Maturation, and Regeneration. STEM CELLS 2018, 36, 891–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzar, N.; Ganguly, P.; Khan, U.K.; Ateeq, B. Transcription networks rewire gene repertoire to coordinate cellular reprograming in prostate cancer. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2023, 89, 76–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Perez, M.P.; Perez-Navarro, E.; Alonso-Gordoa, T.; Conteduca, V.; Font, A.; Vázquez-Estévez, S.; González-Del-Alba, A.; Wetterskog, D.; Antonarakis, E.S.; Mellado, B.; et al. A correlative biomarker study and integrative prognostic model in chemotherapy-naïve metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer treated with enzalutamide. Prostate 2023, 83, 376–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, I.D. (2022) Triplet therapy for prostate cancer. The Lancet. 399 (1 0336), 1670–1671. [CrossRef]
- Crawford, E.D.; Schellhammer, P.F.; McLeod, D.G.; Moul, J.W.; Higano, C.S.; Shore, N.; Denis, L.; Iversen, P.; Eisenberger, M.A.; Labrie, F. Androgen Receptor Targeted Treatments of Prostate Cancer: 35 Years of Progress with Antiandrogens. J. Urol. 2018, 200, 956–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidemann, W.; Hanke, H. Cardiovascular Effects of Androgens. Cardiovasc. Drug Rev. 2002, 20, 175–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, P.M.; Garabedian, M.J.; Kirshenbaum, K. Targeting the Androgen Receptor with Steroid Conjugates. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 8224–8237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendelsohn, M.E.; Karas, R.H.; Yamamoto, Y.; Brady, M.P.; Lu, Z.P.; Maziasz, P.J.; Liu, C.T.; Pint, B.A.; More, K.L.; Meyer, H.M.; et al. Molecular and Cellular Basis of Cardiovascular Gender Differences. Science 2005, 308, 1583–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.; Saltzman, A.; Yeh, S.; Young, W.; Keller, E.; Lee, H.-J.; Wang, C.; Mizokami, A. Androgen Receptor: An Overview. Crit. Rev. Eukaryot. Gene Expr. 1995, 5, 97–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainwaring, W.I.P. A SOLUBLE ANDROGEN RECEPTOR IN THE CYTOPLASM OF RAT PROSTATE. J. Endocrinol. 1969, 45, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, F. The antiandrogen cyproterone acetate: discovery, chemistry, basic pharmacology, clinical use and tool in basic research*. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 1994, 102, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, A.H.; Zoubeidi, A. Targeting androgen receptor signaling: a historical perspective. Endocrine-Related Cancer 2021, 28, T11–T18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willems, A.; De Gendt, K.; Deboel, L.; Swinnen, J.V.; Verhoeven, G. The development of an inducible androgen receptor knockout model in mouse to study the post-meiotic effects of androgens on germ cell development. Spermatogenesis 2011, 1, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senapati, D.; Kumari, S.; Heemers, H.V. Androgen receptor co-regulation in prostate cancer. Asian J. Urol. 2020, 7, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davey, R.A.; Grossmann, M. Androgen Receptor Structure, Function and Biology: From Bench to Bedside. Clin. Biochem. Rev. 2016, 37, 3–15. [Google Scholar]
- Wetendorf, M.; DeMayo, F.J. The progesterone receptor regulates implantation, decidualization, and glandular development via a complex paracrine signaling network. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2012, 357, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akison, L.; Robker, R. The Critical Roles of Progesterone Receptor (PGR) in Ovulation, Oocyte Developmental Competence and Oviductal Transport in Mammalian Reproduction. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2012, 47, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cable, J.K. & Grider, M.H. (2023) Physiology, Progesterone. In: StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL), StatPearls Publishing. p. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK558960/.
- Timmermans, S.; Souffriau, J.; Libert, C. A General Introduction to Glucocorticoid Biology. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolaides, N.C., Chrousos, G. & Kino, T. (2000) Glucocorticoid Receptor. In: K.R. Feingold, B. Anawalt, M.R. Blackman, A. Boyce, G. Chrousos, et al. (eds.). Endotext. South Dartmouth (MA), MDText.com, Inc. p. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK279171/.
- Aurilio, G.; Cimadamore, A.; Mazzucchelli, R.; Lopez-Beltran, A.; Verri, E.; Scarpelli, M.; Massari, F.; Cheng, L.; Santoni, M.; Montironi, R. Androgen Receptor Signaling Pathway in Prostate Cancer: From Genetics to Clinical Applications. Cells 2020, 9, 2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidula, N.; Yau, C.; Wolf, D.; Rugo, H.S. Androgen receptor gene expression in primary breast cancer. npj Breast Cancer 2019, 5, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tindall, D.J.; Lonergan, P.E. Androgen receptor signaling in prostate cancer development and progression. J. Carcinog. 2011, 10, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamroze, A.; Chatta, G.; Tang, D.G. Androgen receptor (AR) heterogeneity in prostate cancer and therapy resistance. Cancer Lett. 2021, 518, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messner, E.A.; Steele, T.M.; Tsamouri, M.M.; Hejazi, N.; Gao, A.C.; Mudryj, M.; Ghosh, P.M. The Androgen Receptor in Prostate Cancer: Effect of Structure, Ligands and Spliced Variants on Therapy. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crona, D.J.; Whang, Y.E. Androgen Receptor-Dependent and -Independent Mechanisms Involved in Prostate Cancer Therapy Resistance. Cancers 2017, 9, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaffer, P.L.; Jivan, A.; Dollins, D.E.; Claessens, F.; Gewirth, D.T. Structural basis of androgen receptor binding to selective androgen response elements. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2004, 101, 4758–4763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemany, M. The Roles of Androgens in Humans: Biology, Metabolic Regulation and Health. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaffer, P.L.; McDonnell, D.P.; Gewirth, D.T. Characterization of Transcriptional Activation and DNA-Binding Functions in the Hinge Region of the Vitamin D Receptor. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 2678–2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, F.; Leblanc, E.; Cavga, A.D.; Huang, C.-C.F.; Flory, M.R.; Zhang, F.; Chang, M.E.K.; Morin, H.; Lallous, N.; Singh, K.; et al. Development of an Androgen Receptor Inhibitor Targeting the N-Terminal Domain of Androgen Receptor for Treatment of Castration Resistant Prostate Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 3488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Kharraz, S.; Dubois, V.; E van Royen, M.; Houtsmuller, A.B.; Pavlova, E.; Atanassova, N.; Nguyen, T.; Voet, A.; Eerlings, R.; Handle, F.; et al. The androgen receptor depends on ligand-binding domain dimerization for transcriptional activation. Embo Rep. 2021, 22, e52764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estébanez-Perpiñá, E.; Arnold, L.A.; Nguyen, P.; Rodrigues, E.D.; Mar, E.; Bateman, R.; Pallai, P.; Shokat, K.M.; Baxter, J.D.; Guy, R.K.; et al. A surface on the androgen receptor that allosterically regulates coactivator binding. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2007, 104, 16074–16079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westaby, D.; Maza, M.d.L.D.F.d.L.; Paschalis, A.; Jimenez-Vacas, J.M.; Welti, J.; de Bono, J.; Sharp, A. A New Old Target: Androgen Receptor Signaling and Advanced Prostate Cancer. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2022, 62, 131–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, A.; Raj, R.; Allison, D.B.; Myint, Z.W. Androgen Receptor Signaling in Prostate Cancer and Therapeutic Strategies. Cancers 2021, 13, 5417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Q.; He, B. Androgen Receptor Signaling in the Development of Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurung, P., Yetiskul, E. & Jialal, I. (2021) Physiology, male reproductive system. In: StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publish-ing. p.
- Carpenter, V.; Saleh, T.; Lee, S.M.; Murray, G.; Reed, J.; Souers, A.; Faber, A.C.; Harada, H.; Gewirtz, D.A. Androgen-deprivation induced senescence in prostate cancer cells is permissive for the development of castration-resistance but susceptible to senolytic therapy. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2021, 193, 114765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, P.E. (2013) Chapter 8. Male Reproductive System. In: Endocrine Physiology. 4th edition. New York, NY, The McGraw-Hill Companies. p. accessmedicine.mhmedical.com/content.aspx?aid=57307916.
- Mbemi, A.; Khanna, S.; Njiki, S.; Yedjou, C.G.; Tchounwou, P.B. Impact of Gene–Environment Interactions on Cancer Development. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Heal. 2020, 17, 8089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oladoyinbo, C.A., Akinbule, O.O., Bolajoko, O.O., Aheto, J.M., Faruk, M., Bassey, I.E., Odedina, F., Ogunlana, O.O., Ogun-sanya, M., Suleiman, A.M., Obialor, S. & Gali, R. (2020) Risk Factors for Prostate Cancer in West African Men: The Prostate Cancer Transatlantic Consortium (CaPTC) Cohort Study. Cancer Health Disparities. 4. Available online: https://www.companyofscientists.com.
- Vietri, M.T.; D’elia, G.; Caliendo, G.; Resse, M.; Casamassimi, A.; Passariello, L.; Albanese, L.; Cioffi, M.; Molinari, A.M. Hereditary Prostate Cancer: Genes Related, Target Therapy and Prevention. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foley, G.R.; Marthick, J.R.; Ostrander, E.A.; Stanford, J.L.; Dickinson, J.L.; FitzGerald, L.M. Association of a novel BRCA2 mutation with prostate cancer risk further supports germline genetic testing. Eur. J. Cancer 2023, 180, 155–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.R. , Woods-Burnham, L. A. ( 2021) Genetic contributions to prostate cancer disparities in men of West African descent. Frontiers in oncology. 11, 770500.
- A Rey, R. The Role of Androgen Signaling in Male Sexual Development at Puberty. Endocrinology 2021, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.H.; Kim, E.; Jung, Y.J.; Kim, H.-M.; Park, M.S.; Kim, J.K.; Lee, H.; Oh, J.J.; Lee, S.; Hong, S.K.; et al. Polygenic risk score for tumor aggressiveness and early-onset prostate cancer in Asians. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsing, A.W., Gao, Y.-T., Wu, G., Wang, X., Deng, J., Chen, Y.-L., Sesterhenn, I.A., Mostofi, F.K., Benichou, J. & Chang, C. (2000) Polymorphic CAG and GGN repeat lengths in the androgen receptor gene and prostate cancer risk: a popula-tion-based case-control study in China. Cancer research. 60 (18), 5111–5116.
- Allemailem, K.S., Almatroudi, A., Alrumaihi, F., Makki Almansour, N., Aldakheel, F.M., Rather, R.A., Afroze, D. & Rah, B. (2021) Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in prostate cancer: its implications in diagnostics and therapeutics. Ameri-can Journal of Translational Research. 13 (4), 3868–3889.
- Ratajczak, W.; Lubkowski, M.; Lubkowska, A. Heat Shock Proteins in Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia and Prostate Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takayama, K. (2018) The Biological Role of Androgen Receptor in Prostate Cancer Progression. In: M. Estrada (ed.). Advanc-es in Testosterone Action. IntechOpen. p. [CrossRef]
- Fujita, K.; Nonomura, N. Role of Androgen Receptor in Prostate Cancer: A Review. World J. Men’s Heal. 2019, 37, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Student, S.; Hejmo, T.; Poterała-Hejmo, A.; Leśniak, A.; Bułdak, R. Anti-androgen hormonal therapy for cancer and other diseases. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 866, 172783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tortorella, E.; Giantulli, S.; Sciarra, A.; Silvestri, I. AR and PI3K/AKT in Prostate Cancer: A Tale of Two Interconnected Pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonthier, K.; Poluri, R.T.K.; Audet-Walsh. Functional genomic studies reveal the androgen receptor as a master regulator of cellular energy metabolism in prostate cancer. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2019, 191, 105367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michmerhuizen, A.R.; Spratt, D.E.; Pierce, L.J.; Speers, C.W. ARe we there yet? Understanding androgen receptor signaling in breast cancer. npj Breast Cancer 2020, 6, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisano, C.; Tucci, M.; Di Stefano, R.F.; Turco, F.; Scagliotti, G.V.; Di Maio, M.; Buttigliero, C. Interactions between androgen receptor signaling and other molecular pathways in prostate cancer progression: Current and future clinical implications. Crit. Rev. Oncol. 2021, 157, 103185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khurana, N.; Sikka, S.C. Interplay Between SOX9, Wnt/β-Catenin and Androgen Receptor Signaling in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, D. Unravelling the molecular mechanisms of prostate cancer evolution from genotype to phenotype. Crit. Rev. Oncol. 2021, 163, 103370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, A.; Burleson, M. SPOP and cancer: a systematic review. Am J Cancer Res 2020, 10, 704–726. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Song, Y.; Ye, M.; Dai, X.; Zhu, X.; Wei, W. The diverse roles of SPOP in prostate cancer and kidney cancer. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2020, 17, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, J.E.; La, M.; Oh, K.H.; Oh, Y.M.; Kim, G.R.; Seol, J.H.; Baek, S.H.; Chiba, T.; Tanaka, K.; Bang, O.S.; et al. BTB Domain-containing Speckle-type POZ Protein (SPOP) Serves as an Adaptor of Daxx for Ubiquitination by Cul3-based Ubiquitin Ligase. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 12664–12672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Munoz I, Lund AH, Van Der Stoop P, Boutsma E, Muijrers I, Verhoeven E, Nusinow DA, Panning B, Marahrens Y & Van Lohuizen M (2005) Stable X chromosome inactivation involves the PRC1 polycomb complex and requires histone MACROH2A1 and the CULLIN3/SPOP ubiquitin E3 ligase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102, 7635–7640.
- Blattner, M.; Liu, D.; Robinson, B.D.; Huang, D.; Poliakov, A.; Gao, D.; Nataraj, S.; Deonarine, L.D.; Augello, M.A.; Sailer, V.; et al. SPOP Mutation Drives Prostate Tumorigenesis In Vivo through Coordinate Regulation of PI3K/mTOR and AR Signaling. Cancer Cell 2017, 31, 436–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernasocchi, T.; Theurillat, J.-P.P. SPOP-mutant prostate cancer: Translating fundamental biology into patient care. Cancer Lett. 2021, 529, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Severson, T.; Qiu, X.; Alshalalfa, M.; Sjöström, M.; Quigley, D.; Bergman, A.; Long, H.; Feng, F.; Freedman, M.L.; Zwart, W.; et al. Androgen receptor reprogramming demarcates prognostic, context-dependent gene sets in primary and metastatic prostate cancer. Clin. Epigenetics 2022, 14, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negri, A.; Marozzi, M.; Trisciuoglio, D.; Rotili, D.; Mai, A.; Rizzi, F. Simultaneous administration of EZH2 and BET inhibitors inhibits proliferation and clonogenic ability of metastatic prostate cancer cells. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2023, 38, 2163242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westaby, D.; Maza, M.d.L.D.F.d.L.; Paschalis, A.; Jimenez-Vacas, J.M.; Welti, J.; de Bono, J.; Sharp, A. A New Old Target: Androgen Receptor Signaling and Advanced Prostate Cancer. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2022, 62, 131–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekenwaneze CC, Zakari S, Amadi EC, Ogunlana OO. Recent Advances in Immunotherapy for Prostate Cancer Treatment. Presented at: Annual Conference of the Nigerian Society for Microbiology - NSM-OTA; July 2023; Covenant University, Ota, Ogun State, Nigeria. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/372915334_Recent_Advances_in_Immunotherapy_for_Prostate_Cancer_Treatment.
- Iheagwam FN, Iheagwam OT, Odiba JK, Ogunlana OO, Chinedu SN. Cancer and Glucose Metabolism: A Review on Warburg Mechanisms. TJNPR [Internet]. 2022 May 1 [cited 2023 Aug 6];6(5):661-7. Available online: https://tjnpr.org/index.php/home/article/view/42.
- Alabi, B.R.; Liu, S.; Stoyanova, T. Current and emerging therapies for neuroendocrine prostate cancer. Pharmacol. Ther. 2022, 238, 108255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Kharraz, S.; Dubois, V.; E van Royen, M.; Houtsmuller, A.B.; Pavlova, E.; Atanassova, N.; Nguyen, T.; Voet, A.; Eerlings, R.; Handle, F.; et al. The androgen receptor depends on ligand-binding domain dimerization for transcriptional activation. Embo Rep. 2021, 22, e52764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Xing, Z.; Sah, R.K.; Hu, J.; Hu, H. Androgen Metabolism and Response in Prostate Cancer Anti-Androgen Therapy Resistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, R. Therapeutic targeting of the androgen receptor (AR) and AR variants in prostate cancer. Asian J. Urol. 2020, 7, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crook JM, Iweala E, Popoola A, Jibrin P, Faruk M, Sowumi A, Fatiregun O, Blaise N, Oladoyinbo C, Okoye I, Salako AA, Omonisi A, Bassey IE, Adeniji K, Asura NH, Kaninjing E, Kukoyi O, Fathi P, Enuka R, Toye O, CaPTC Investigators, Odedina F. Vitamin C prediction of cancer diagnosis in men of African ancestry in Nigeria, Cameroon, and the United States: An analysis of the CaPTC prostate cancer study [abstract]. In: Proceedings of the 15th AACR Conference on the Science of Cancer Health Disparities in Racial/Ethnic Minorities and the Medically Underserved; 2022 Sep 16-19; Philadelphia, PA. Philadelphia (PA): AACR; Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2022;31(1 Suppl):Abstract nr C068.
- Otero J, Iweala E, Popoola A, Jibrin P, Faruk M, Sowumi A, Fatiregun O, Blaise N, Oladoyinbo C, Okoye I, Salako AA, Omonisi A, Bassey IE, Adenji K, Asura NH, Kaninjing E, Kukoyi O, Fathi P, Enuka R, Toye O, Crook J, Odedina F. Influence of access to care on cancer diagnoses in the CaPTC Prostate Cancer Familial Cohort Study of African Ancestry in Nigeria, Cameroon, and the United States [abstract]. In: Proceedings of the 15th AACR Conference on the Science of Cancer Health Disparities in Racial/Ethnic Minorities and the Medically Underserved; 2022 Sep 16-19; Philadelphia, PA. Philadelphia (PA): AACR; Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2022;31(1 Suppl):Abstract nr B072.
- Thomas, C.; Lamoureux, F.; Crafter, C.; Davies, B.R.; Beraldi, E.; Fazli, L.; Kim, S.; Thaper, D.; Gleave, M.E.; Zoubeidi, A. Synergistic Targeting of PI3K/AKT Pathway and Androgen Receptor Axis Significantly Delays Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer ProgressionIn Vivo. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2013, 12, 2342–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toren, P.; Kim, S.; Cordonnier, T.; Crafter, C.; Davies, B.R.; Fazli, L.; Gleave, M.E.; Zoubeidi, A. Combination AZD5363 with Enzalutamide Significantly Delays Enzalutamide-resistant Prostate Cancer in Preclinical Models. Eur. Urol. 2015, 67, 986–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Target | Agent | Phase | Administration | Condition | I.D on Clinicaltrial.gov |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AKT | AZD5363 | III | Docetaxel | mCRPC | NCT05348577 |
| MK2206 | II | Bicalutamide | High-Risk of Progression | NCT01251861 | |
| Capiversertib | II | Abiraterone acetate | High Risk Localized PCa | NCT05593497 | |
| PI3K | AZD8186 | I | Docetaxel | mPCa with PTEN Mut | NCT03218826 |
| GSK2636771 | I | Enzalutamide | PTEN(-) mCRPC Mut | NCT02215096 | |
| mTOR | Sepanisertib | II | Monotherapy | CRPC | NCT02091531 |
| Everolimus | I | + standard radiation therapy | PCa with rising PSA | NCT01548807 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





