1. Introduction
Complex networks have developed rapidly over the past two decades [
1]. There are many real-world systems that can be modeled as complex networks, with a large number of nodes and edges. The study of networks can help us understand corresponding complex systems. For example, social networks can help us understand the ways in which humans interact and how information spreads in society; transportation networks can help us study the flow and congestion of traffic in cities. The controllability of a network is a crucial factor, as control networks are designed to serve people [
2,
3]. In this context, controllability refers to the ability of a dynamical network to be guided by external inputs from any initial state to any desired target state within a finite duration of time under an admissible control input.
Recently, failures and attacks on complex networks haven become more frequent and severe on complex networks [
4,
5]. When failures and attacks occur, it is removed in the form of node or edge removals. During node removals, the the target node and the edges previously connected to the node will be removed, while during edge removals, only the target edges will be disconnected. Network attacks are typically categorized into two types: random and malicious, random attacks refer to the uniform random selection of attack targets, while malicious attacks choose the most effective targets to attack. Malicious attacks typically have a better effect than random attacks, but they also consume more time. During malicious attacks, the most destructive target is selected for attacking, such target choices usually based on centrality of nodes. For example, the node with the highest degree is attacked firstly or the edge with the highest betweenness is preferentially removed. Beside degree and betweenness, commonly-used measures of node importance include closeness [
6], Katz centrality [
7], neighborhood similarity [
8], branch weighting [
9], structural holes [
10], and so on. Many attack models have also been proposed, the hierarchical structure of a directed network enables the random upstream (or downstream) attack to the network controllability, which results in a more destructive attack strategy than random attacks [
11]. The module-based attack strategy [
12,
13] aims at attacking the nodes with inter-community edges that are crucial to maintain the connectivity among communities.
In addition, nodes can be categorized as critical or non-critical based on their impact on network controllability when removed. Removing critical nodes can significantly reduce network controllability [
14], so they should be protected during network construction to enhance controllability robustness. Bridges, a type of edge in networks, can also be targeted for removal to decrease network controllability [
15]. Many deep learning and optimization methods can be used to find such hidden pattern and key roles of networks, the proposed Finder framework, which employs reinforcement learning, offers a unified approach for identifying a group of nodes that can destroy network function to the greatest extent after removals [
16]; the deep learning models were used to predicting network robustness [
17,
18,
19,
20]; evolutionary algorithms are utilized for network attacks [
21,
22].
The research on network attacks aims to enhance the robustness of networks from the perspective of attackers, enabling them to better withstand attacks. One effective approach to improving the controllability robustness of networks is to protect bridges, as they play a critical role in network connectivity. protecting critical nodes and edges during network construction is also a viable strategy for enhancing controllability robustness [
14]. Studies have shown that 3-ring and 4-ring structures in networks are beneficial to controllability robustness [
23], which suggests that networks with random triangle and random quadrilateral structures tend to exhibit good controllability robustness.
The structural controllability of the network can be evaluated by identifying the maximum matching of the network to determine the minimum number of external control inputs required as driver nodes [
4]. However, this approach is only suitable for directed networks and is challenging to apply to large-scale networks. To address this issue, the exact controllability framework was proposed, which can be utilized for all large-scale sparse networks [
24].
Controllability robustness can be measured using two approaches:
A priori measure and
A posteriori measure. The
A priori measure calculates network features in a single calculation, while the
A posteriori measure simulates the change in network controllability curve under attack. Although the
A posteriori measure is more accurate, it can be computationally expensive, especially for large-scale networks. Recently, deep learning has emerged as a promising approach to measure network robustness accurately and efficiently, providing a less time-consuming alternative to simulation-based methods [
17,
19,
20,
25,
26].
Overall, this paper presents an attack strategy for undirected network controllability. The main contributions are:
- 1)
A novel attack strategy is proposed, which can effectively disrupt the controllability of undirected networks.
- 2)
The impact of removing nodes with degree 1 and 2 on network controllability is analyzed, revealing that nodes with low degree are not beneficial to the robustness of network controllability.
- 3)
The findings provide valuable insights for identifying key nodes and designing networks with improved controllability robustness in future research.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows,
Section 2 introduces the preliminary concepts of controllability and controllability robustness;
Section 3 detailed illustrates the proposed attack model LNNA;
Section 4 demonstrates the experimental results on synthetic and real-world networks;
Section 5 concludes this paper.
2. Network Controllability and Controllability Robustness
The robustness of network controllability is mainly concerned with the change in controllability when the network is attacked. Controllability robustness reflects the ability of the network to resist attacks, from the perspective of attackers, which also can be the evaluation index of attack performance, namely, the worse the robustness, the better the attack model. Network controllability is measured by the density of driver nodes
,
where
represents the number of driver nodes required to maintain network controllability and
N represents the total number of network nodes. The minimum value of
is
, and the maximum value is 1. A smaller value of
indicates better network controllability, while a larger value of
indicates worse network controllability. According to the minimum-inputs theorem [
4], for directed networks,
can be obtained by the number of unmatched nodes for a directed network:
where
is the size of maximum matching. As for exact controllability [
24],
is calculated by:
where
is the rank of the adjacency matrix
A. For node-removal attacks, the controllability robustness of the network can be measured by the controllability curve, which is calculated as follows:
where
the number of driver nodes needed to maintain network controllability after removing a total of
i nodes,
N is the size of the original network,
is calculated by using the exact controllability framework as Eq. (
3), which applies to large and sparse undirected networks,
records the changes in network controllability after each node is removed. The overall measure of controllability robustness can be obtained by averaging controllability curves as follows:
where
is the structural controllability of the remaining network after
i nodes are removed. The network controllability robustness can be evaluated by
, a smaller
indicates better controllability robustness, while a larger
indicates worse controllability robustness. For an attack model, a better controllability robustness indicates a worse attack performance.
3. Leaf Node Neighbor-Based Attack Strategy
The removal of different nodes in networks has different impacts on the controllability of networks. Leaf nodes, which are the nodes with a degree of 1, are most likely as a driver node in the network. If the only neighbor of a leaf node is removed, the leaf node will become an isolated node and the number of connected components of the network will increase. Further more, if the neighbor of a leaf node, which is connected to many leaf nodes, after it is attacked, all the leaf nodes connected to it will become drive nodes. Therefore, the neighbor of a leaf node are important for controllability attacks, and the number of leaf nodes connected by that neighbor node is also an important reference. The above ideas are applied to the following attack strategy design, the following subsections detailed analyze the impacts of removing leaf node neighbor on network controllability.
3.1. Leaf Node Neighbor-Based Attack Strategy
As neighbors of leaf nodes can be removed to reduce the controllability of a network, a leaf node neighbor-based attack (LNNA) strategy is proposed. Before proposing the algorithm, there are two necessary concepts,
k-neighbor node and
k-neighbor degree, are pre-defined, where
k-neighbor node is a neighbor of a node with degree
k, and
k-neighbor degree for a node, is the number of neighbors with degree
k. The proposed LNNA is based on the above concepts and detailed described in Algorithm 1.
|
Algorithm 1:Leaf Node Neighbor-based Attack Strategy |
-
Input:
a network G with N nodes -
Output:
index t of target node to be attacked - 1:
- 2:
- 3:
// get node degrees and neighbors - 4:
for to N do
- 5:
- 6:
if then
- 7:
- 8:
- 9:
end if
- 10:
end for - 11:
ifthen
- 12:
// get the nodes and their neighbors with smallest degree k, generally, k equals to 1 - 13:
- 14:
- 15:
- 16:
for do
- 17:
if then
- 18:
- 19:
- 20:
end if
- 21:
end for
- 22:
- 23:
for to do
- 24:
for do
- 25:
if in then
- 26:
- 27:
end if
- 28:
end for
- 29:
end for
- 30:
- 31:
else - 32:
- 33:
end ifreturnt
|
As shown in Algorithm 1, LNNA usually starts from the neighboring node of leaf nodes, i.e., 1-neighbors. When attacking the 1-neighbors, the attack target is determined based on the number of leaf nodes connected to these nodes, i.e., the 1-neighbor degree. The node with the highest 1-neighbor degree among the 1-neighbors will be attacked. When there are no leaf nodes in the network, LNNN will choose nodes to attack from the 2-neighbors. Similarly, the node with the highest 2-neighbor degree among the 2-neighbors will be selected as the target. This process continues recursively.
In terms of time complexity, for each attack, finding neighbors of each node is
,
N is the number of nodes; finding and getting the smallest
k-neighbors is
; getting
k-neighbor degrees is
,
K is the number of
k-neighbors,
; thus, the total time complexity is
. For typical malicious attack methods, namely degree- (DEG), betweenness- (BET), closeness- (CLO) based attacks, the time complexity comparison is listed in
Table 1. For degree-based attack, getting degree of each node is
, similar to finding neighbors of each node; for betweenness-based attack, getting betweenness of each node is
when using Floyd-Warshall algrithm; for closeness-based attack, computing time of closeness is
,
M is the number of edges.
3.2. Influence of Leaf Node Neighbor Failures
An algorithm that targets the neighbors of low-degree nodes (i.e. leaf nodes) with a node attack has been developed in sub
Section 3.1. In this subsection, we also provide a mathematical proof detailing why attacking the neighbors of leaf nodes is effective and leads to an increase in the number of driver nodes.
Theorem 1. Let be the adjacency matrix of a network, and be the adjacency matrix after removing a node . , if the following condition holds: is the only neighbor of a leaf node .
Proof. The adjacency matrix
and
can be represented as follow:
As the permutation invariance of adjacency matrix, the first row (column) of
represents
, the last row (column) of
represents
; it is clear that,
Theorem 2. Let be the number of driver nodes in a network, and be the number of driver nodes on the network after removing a leaf node neighbor. , if the following condition holds: .
Proof. If
, then,
. Therefore, the following equation holds,
Theorem 3. Let be the number of driver nodes in a network, and be the number of driver nodes on the network after removing a leaf node neighbor. , if the following condition holds: .
Proof. If
, then
, the following equation holds,
According to Theorem 1, 2, and 3, removing the neighbor of a leaf node from the network increases or maintains the total number of driver nodes. From Eq.
1 and
4, we can find that, the more driver nodes there are, the worse controllability the network has.
4. Experimental Studies
LNNA is applied to three kinds of synthetic networks, and real networks. In order to verify its effectiveness, the performance of LNNA was compared with feature-based attacks such as degree-, betweenness-, and closeness-based attacks. The main focus of this paper is to investigate the impact of attacking nodes with the lowest degree, excluding isolated nodes, on network controllability. Specifically, the study explores the effects of removing neighbor of leaf nodes on network controllability.
The three synthetic networks are Erdös-Rényi (ER) random-graph [
27], Generic scale-free (SF) network [
28], and Newman-Watts small-world (SW) network [
29]. The real-world networks are
econ-mahindas and
soc-wiki-Vote, all networks are undirected. The number of nodes are
and
, the average degree
, and 10 respectively. In order to reduce the influence of randomness, 30 random instances are generated for each network.
4.1. Results on Synthetic Networks for Different Average Degrees
Liu et al. [
4] suggested that controlling sparse heterogeneous networks can be challenging and that such networks tend to have poor network controllability and robustness. Conversely, dense homogeneous networks are easier to control and have better network controllability and robustness. Moreover, networks with higher average degrees have more redundant edges, which help maintain the core structure of the network and make it less susceptible to destruction, resulting in better network controllability and robustness.
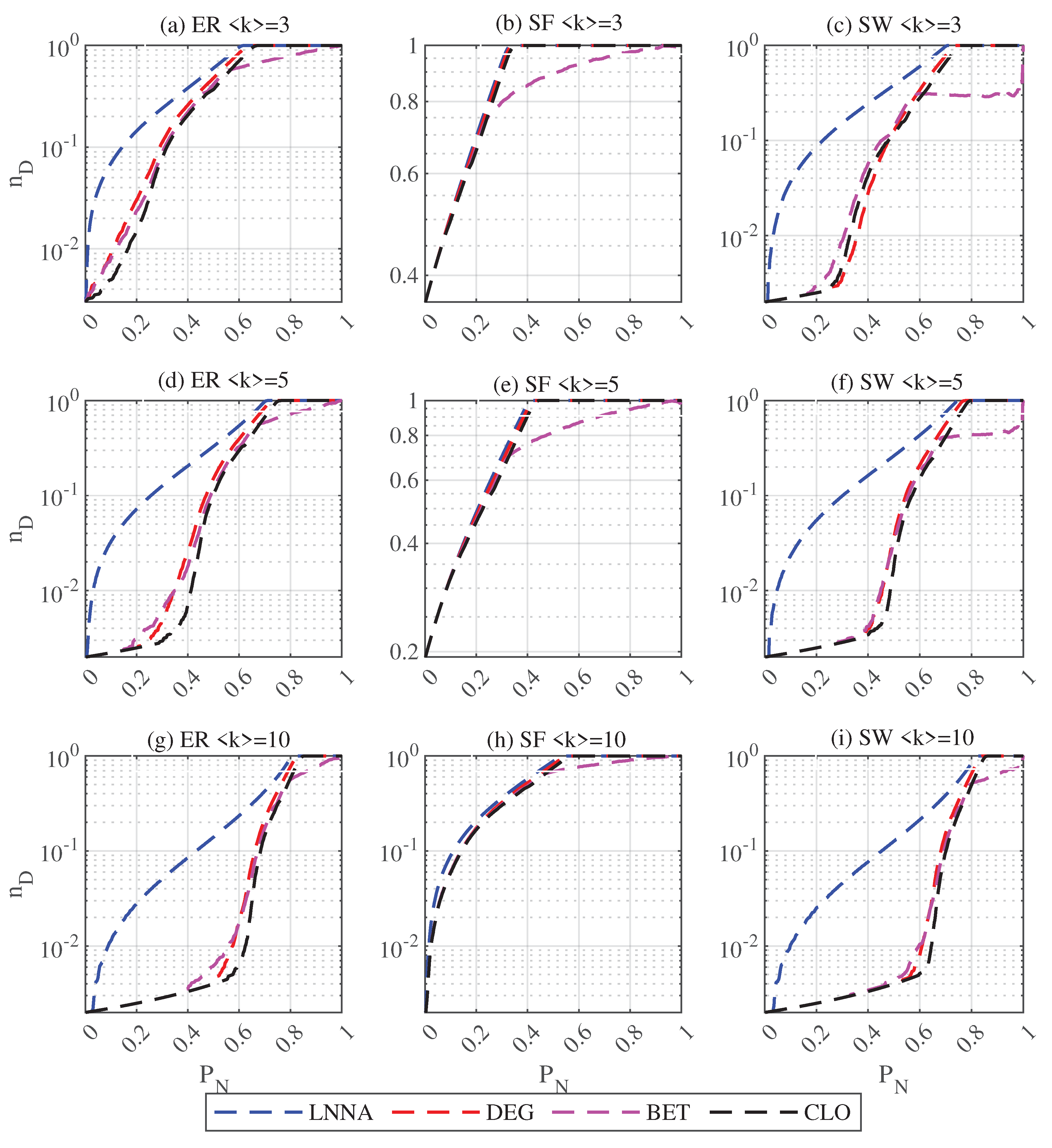
As shown in Fig.
Figure 1, for ER and SW networks with an average degree of 3, LNNA can effectively disrupt network controllability from the beginning of attacks. When the average degree is 5, for the degree- (DEG), betweenness- (BET), closeness- (CLO) based attacks on ER networks, the controllability of ER networks begins to decrease significantly after about 20% of nodes are removed, and for the SW networks, the threshold proportion is 40%. However, LNNA can significantly reduce the controllability of networks from the beginning of the attacks. For SF networks, there is no significant difference between different attacks, since the topology of SF networks makes the network robust on controllability, and nodes that can disrupt the network controllability are easy to be found. When
, for ER networks, the three feature-based attacks rapidly reduce the controllability of the network when more than 40% of the nodes are removed. For SW networks, the ratio is around 50%. For SF networks, LNNA is slightly better than other attacks, because with the increase of average degree, the network controllability robustness is improved. Over all, as shown in
Table 2, LNNA has the best attack effect on the three synthetic networks with different average degrees, the best results are bold.
4.2. Results on Synthetic Networks for Different Network Sizes
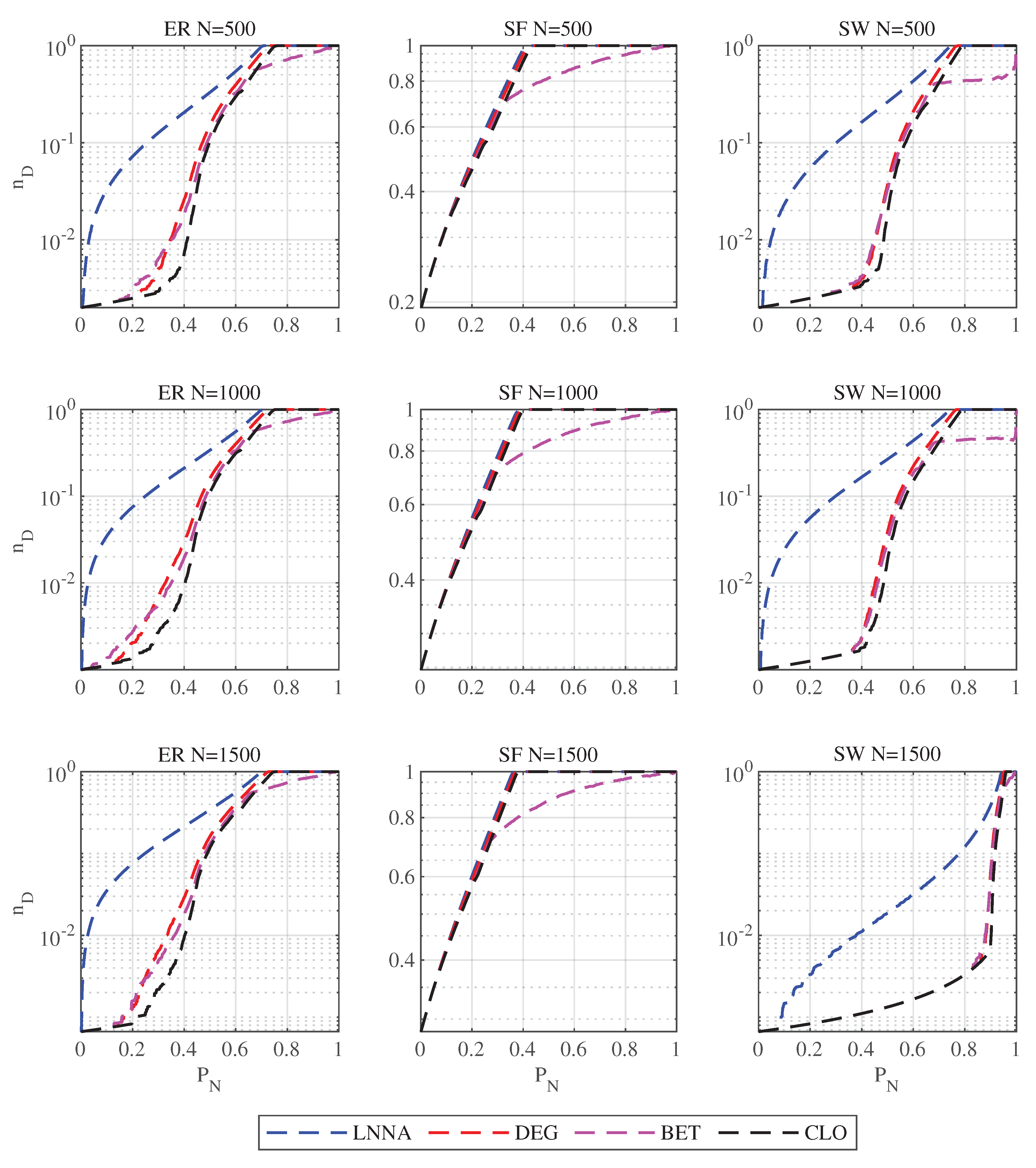
The size of a network is typically defined as the number of nodes in the network. Large-scale networks tend to be more complex and may exhibit a variety of structures, and the controllability robustness of networks can vary across different scales. Moreover, in terms of attack strategies, networks with more nodes require higher computational costs relative to smaller networks. As shown in Fig.
Figure 2, the effect of different attacks on the three synthetic networks is similar when the average degree is 5, regardless of network size (i.e., 500, 1000, or 1500 nodes). However, LNNA shows better attack performance on ER and SW networks compared to other attack methods, while no significant difference is observed in SF networks.
Table 3 also shows that when the average degree is 5, LNNA performs the best on the three networks with 500, 1000, and 1500 nodes.
4.3. Results on Real-World Networks
LNNA is Applied to two real-world networks, called
econ-mahindas and
soc-wiki-Vote [
30]. The information of networks is shown in
Table 4.
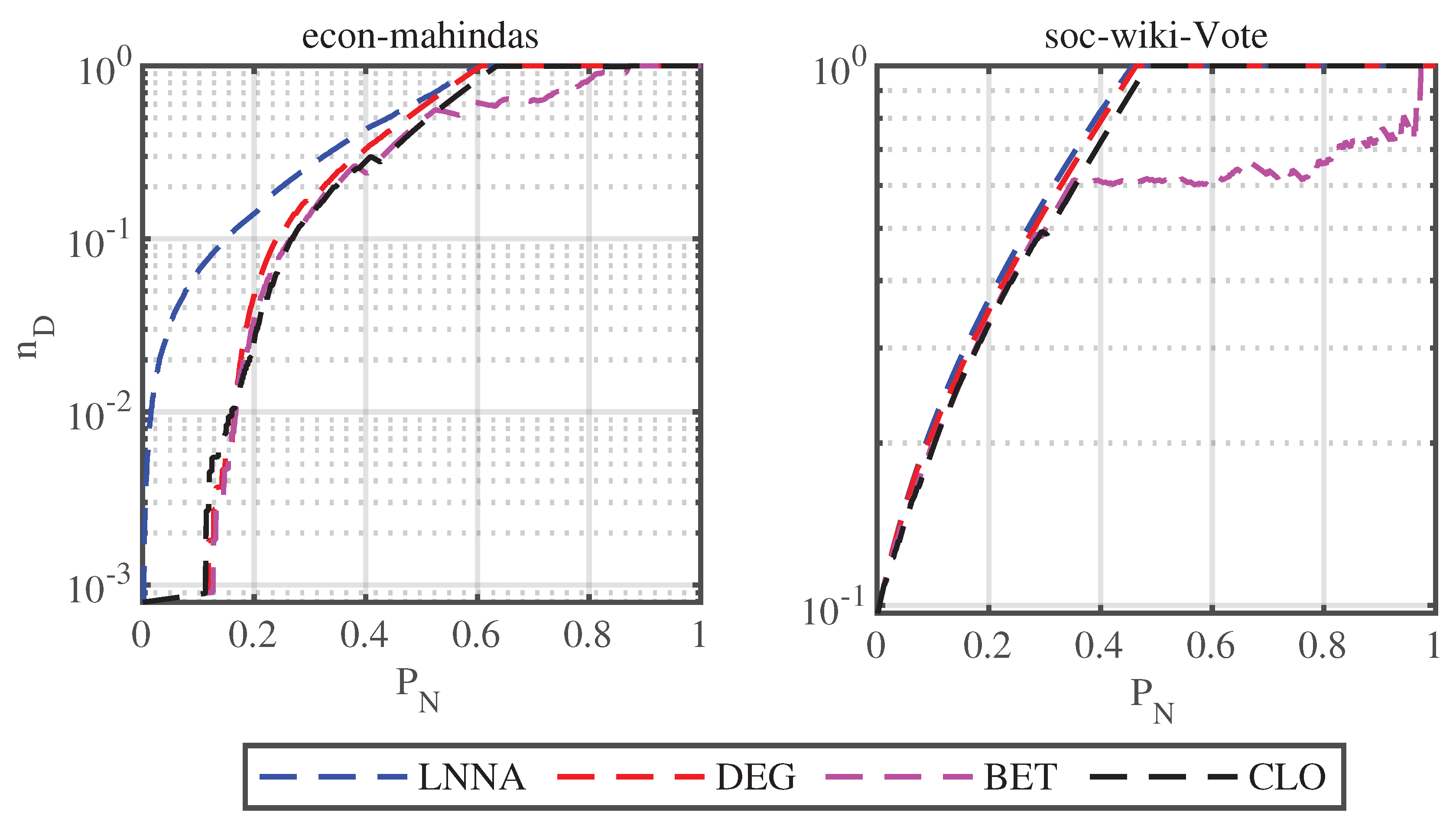
As shown in Fig.
Figure 3, for the
econ-mahindas network, the attack effect of LNNA is obviously better than that of other attack strategies. For the
soc-wiki-Vote network, the attack effect of LNNA is slightly better than other strategies, but there is no significant difference. These results are consistent with those obtained on synthetic networks. Furthermore, for networks with good controllability robustness, LNNA is more destructive to the network controllability.
4.4. Attack Process Discussion
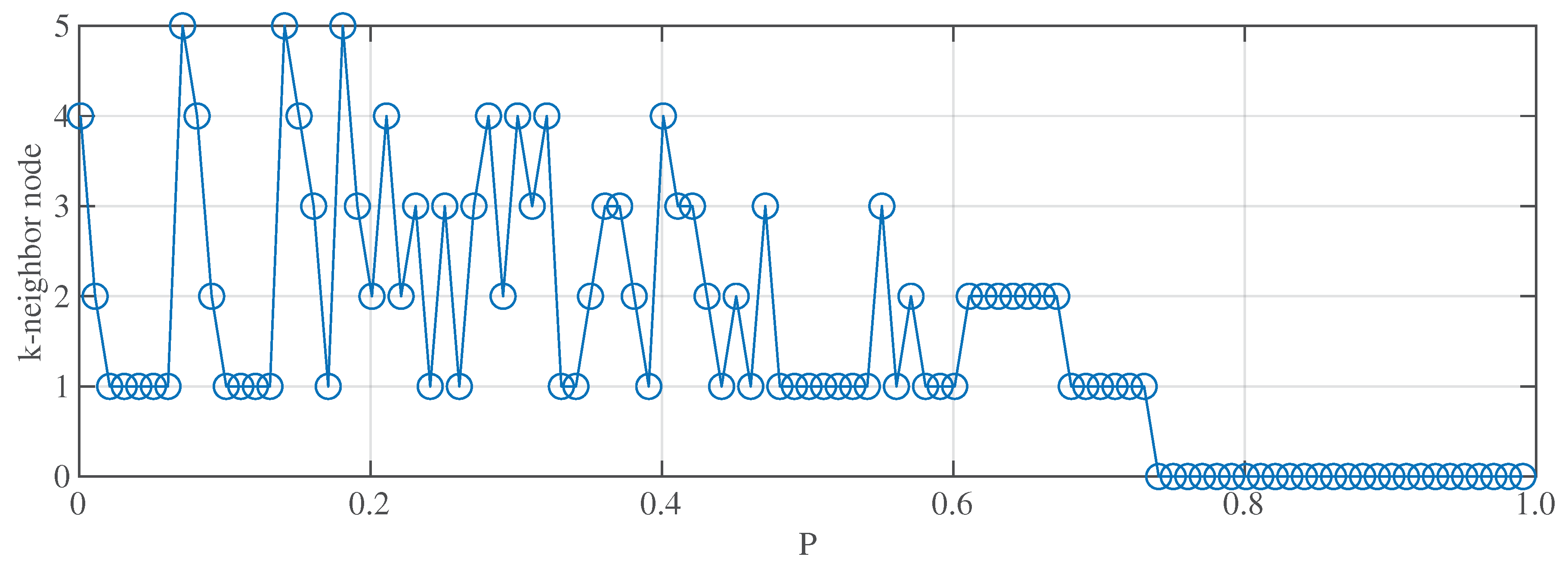
Figure 4 illustrates what types of the selected nodes during the LNNA. When approximately 70% of the nodes are removed, only isolated nodes remain in the network.
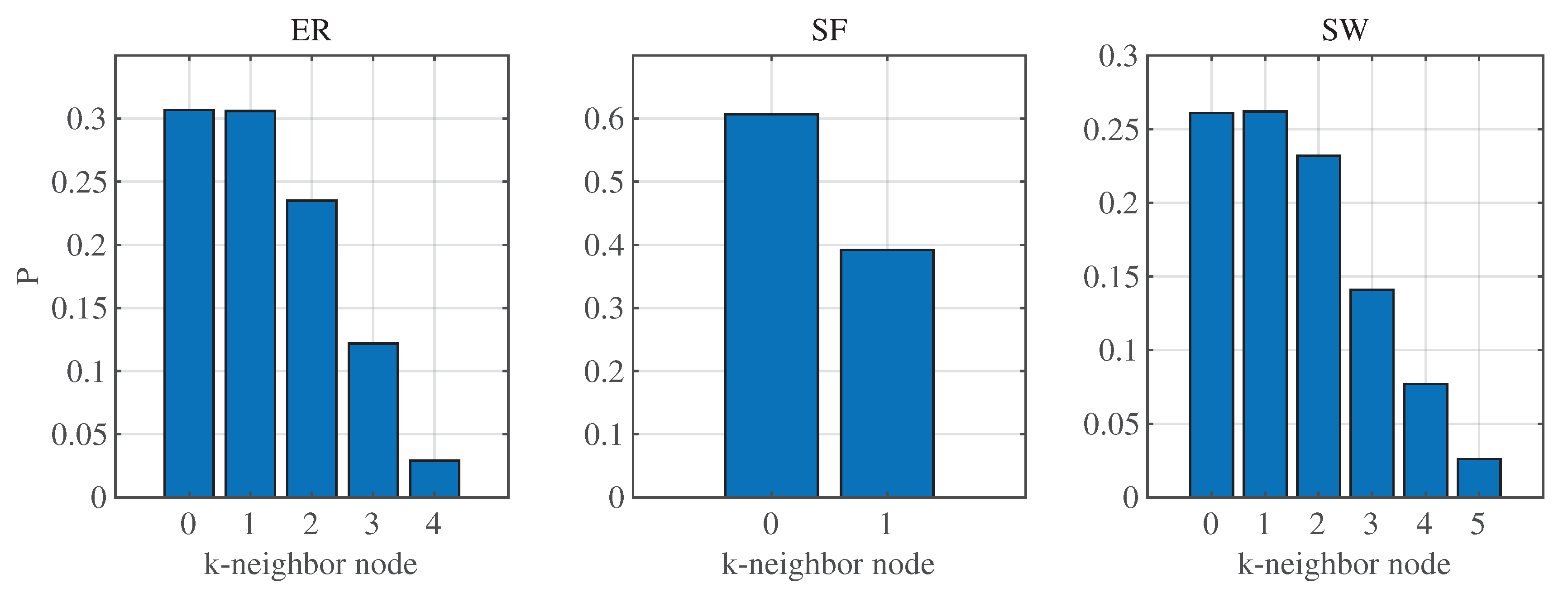
Figure 5 illustrates the proportion of different nodes removed by different networks under LNNA. It can be observed that the proportion of nodes decreases as the
k of
k-neighbor increases. Apart from isolated nodes, the largest proportion is 1-neighbor nodes, which refers to the neighbor of a leaf node. When a
k-neighbor node is attacked, a (
)-neighbor node is generated. In the case of ER and SW networks, 1-neighbor nodes account for approximately 30% and 25% respectively, and the damage to network controllability is significant. For the SF network, it can be seen that the attacked nodes are 1-neighbor nodes, accounting for about 40%. Subsequently, only isolated nodes remain in the network, indicating that the SF network is vulnerable to attack.
5. Conclusions
In order to investigate the controllability robustness of networks from the perspective of attacks, this paper mainly examines the destructive impact of the neighbor nodes of a node with low degree on network controllability. It proposes the attack strategy of leaf node neighbors and introduces the concept of k-neighbor nodes and k-neighbor degrees. This attack strategy prioritizes attacking the neighbor node of a node with the lowest degree, except for isolated nodes. In a network, if the k-neighbor nodes are attacked, the ()-neighbor nodes will be generated, and this process continues until 1-neighbor nodes appears, which is then to be attacked. Simulated experiments on synthetic and real-world networks demonstrate that the proposed LNNA performs better than degree-, betweenness-, and closeness-based attacks. This suggests that the presence of low-degree nodes in networks is not conducive to network controllability robustness. In the future, when designing networks with good controllability robustness, it is advisable to make the network more homogeneous.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, software, investigation, methodology, writing—original draft preparation, C.W., Z.Y.; formal analysis, visualization, S.X.; investigation, project administration and supervision, J.L.; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (number 62002249) and in part by the Open Project Program of the State Key Lab of CADCG (A2112), Zhejiang University.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (number 62002249) and in part by the Open Project Program of the State Key Lab of CADCG (A2112), Zhejiang University. The author would like to acknowledge the tutor and students for their valuable feedback on the draft to improve the flow and quality of the work.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Chen, G.; Wang, X.; Li, X. Fundamentals of Complex Networks: Models, Structures and Dynamics, 2 ed.; John Wiley & Sons, 2014.
- Menichetti, G.; Dall’Asta, L.; Bianconi, G. Network Controllability Is Determined by the Density of Low In-Degree and Out-Degree Nodes. Physical Review Letters 2014, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, T. Controllability Analysis for a Networked Dynamic System With Autonomous Subsystems. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control 2017, 62, 3408–3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.Y.; Slotine, J.J.; Barabási, A.L. Controllability of Complex Networks. Nature 2011, 473, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.D.; Lao, S.Y.; Hou, L.L.; Bai, L. Optimization of robustness of network controllability against malicious attacks. Chinese Physics B 2014, 23, 118902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgatti, S.P. Centrality and network flow. Social Networks 2005, 27, 55–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, L. A new status index derived from sociometric analysis. Psychometrika 1953, 18, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi-Run, R.; Song-Yang, L.; Jun-De, W.; Liang, B.; and, C.L.D. Node importance measurement based on neighborhood similarity in complex network. Acta Physica Sinica 2017, 66, 038902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šimon, M.; Luptáková, I.D.; Huraj, L.; Hosťovecký, M.; Pospíchal, J. Combined Heuristic Attack Strategy on Complex Networks. Mathematical Problems in Engineering 2017, 2017, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; An, S. Critical Nodes Identification in Complex Networks. Symmetry 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.Y.; Slotine, J.J.; Barabási, A.L. Control Centrality and Hierarchical Structure in Complex Networks. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Cunha, B.R.; González-Avella, J.C.; Gonçalves, S. Fast Fragmentation of Networks Using Module-Based Attacks. PLOS ONE 2015, 10, e0142824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shai, S.; Kenett, D.Y.; Kenett, Y.N.; Faust, M.; Dobson, S.; Havlin, S. Critical tipping point distinguishing two types of transitions in modular network structures. Physical Review E 2015, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, Y.; Wang, L.; Chen, G. A Framework of Hierarchical Attacks to Network Controllability. Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation 2021, 98, 105780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhao, G.; Kong, Z.; Zhao, Y. Controllability and Optimization of Complex Networks Based on Bridges. Complexity 2020, 2020, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Zeng, L.; Sun, Y.; Liu, Y.Y. Finding key players in complex networks through deep reinforcement learning. Nature Machine Intelligence 2020, 2, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, Y.; He, Y.; Wang, L.; Tsang, K.F.; Chen, G. Knowledge-Based Prediction of Network Controllability Robustness. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Lou, Y.; Wu, R.; Liu, W.; Li, J. CNN-based Prediction of Network Robustness With Missing Edges. 2022 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN). IEEE, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Lou, Y.; He, Y.; Wang, L.; Chen, G. Predicting Network Controllability Robustness: A Convolutional Neural Network Approach. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics 2022, 52, 4052–4063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Y.; Wu, R.; Li, J.; Wang, L.; Li, X.; Chen, G. A Learning Convolutional Neural Network Approach for Network Robustness Prediction. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics. [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Wu, J.; Qi, M.; Tan, Y. Optimal disintegration strategy in spatial networks with disintegration circle model. Chaos: An Interdisciplinary Journal of Nonlinear Science 2019, 29, 061102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventresca, M. Global search algorithms using a combinatorial unranking-based problem representation for the critical node detection problem. Computers & Operations Research 2012, 39, 2763–2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Y.; Wang, L.; Chen, G. Toward Stronger Robustness of Network Controllability: A Snapback Network Model. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers 2018, 65, 2983–2991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.Z.; Zhao, C.; Di, Z.R.; Wang, W.X.; Lai, Y.C. Exact Controllability of Complex Networks. Nature Communications 2013, 4, 2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, Y.; Wu, R.; Li, J.; Wang, L.; Chen, G. A Convolutional Neural Network Approach to Predicting Network Connectedness Robustness. IEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering 2021, 8, 3209–3219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Y.; Wu, R.; Li, J.; Wang, L.; Tang, C.B.; Chen, G. Classification-based prediction of network connectivity robustness. Neural Networks 2023, 157, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erdös, P.; Rényi, A. On the Strength of Connectedness of a Random Graph. Acta Mathematica Hungarica 1964, 12, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, K.I.; Kahng, B.; Kim, D. Universal Behavior of Load Distribution in Scale-free Networks. Physical Review Letters 2001, 87, 278701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, M.E.; Watts, D.J. Renormalization Group Analysis of the Small-world Network Model. Physics Letters A 1999, 263, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, R.; Ahmed, N. The Network Data Repository with Interactive Graph Analytics and Visualization. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Association for the Advancement of Artificial Intelligence (AAAI), 2015, Vol. 29. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).