Submitted:
05 May 2023
Posted:
09 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
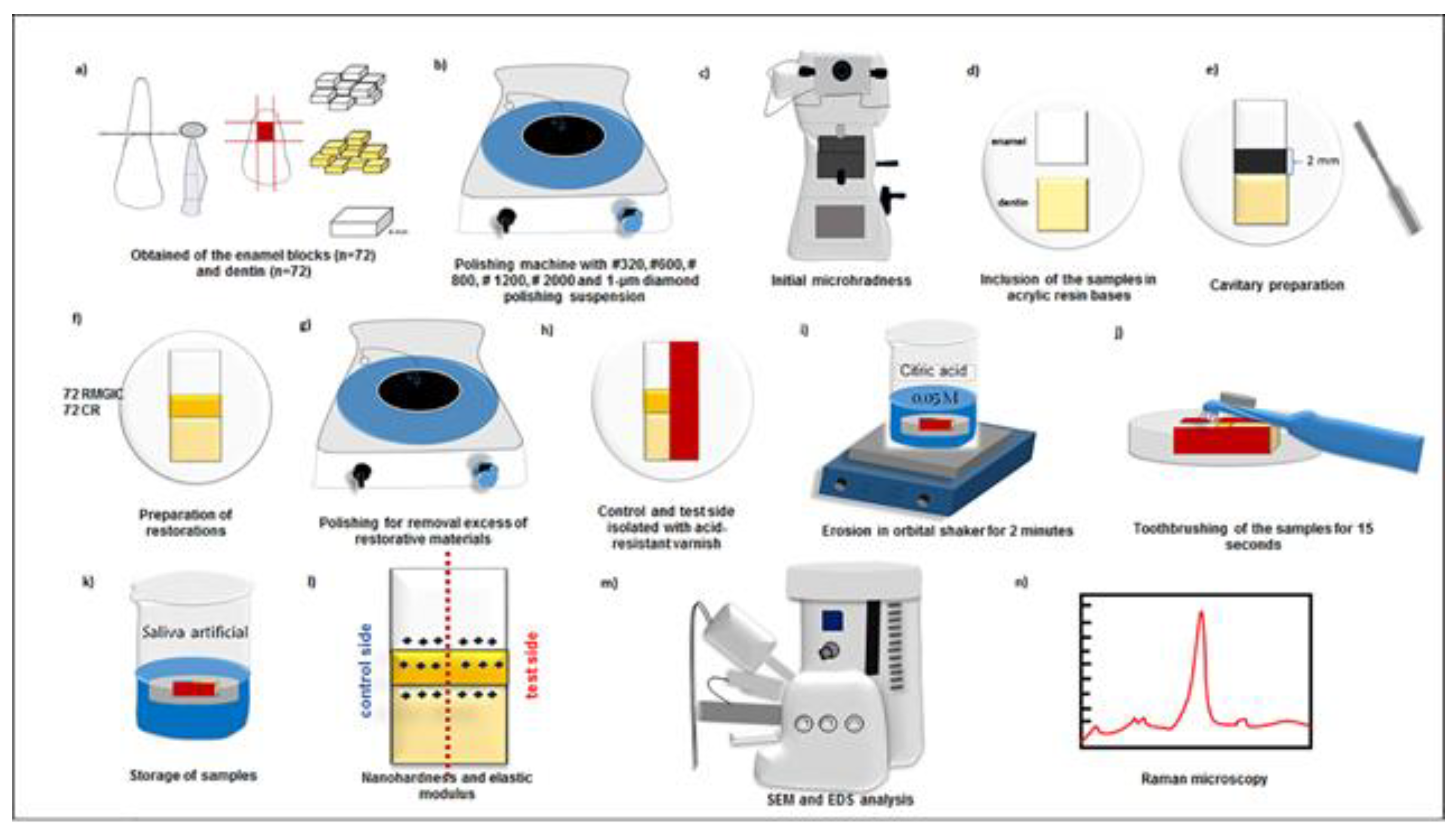
2.1. Experimental design
2.2. Specimen preparation
2.3. Restorative procedures
2.4. Erosion-abrasion cycling
2.5. Analyses of the nanohardness (H) and elastic modulus (Er)
2.6. Analyses of energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM)
2.7. Analysis of micro-Raman spectroscopy
2.8. Statistical analysis
3. Results
3.1. Nanomechanical properties (H and Er)
3.2. Energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS)
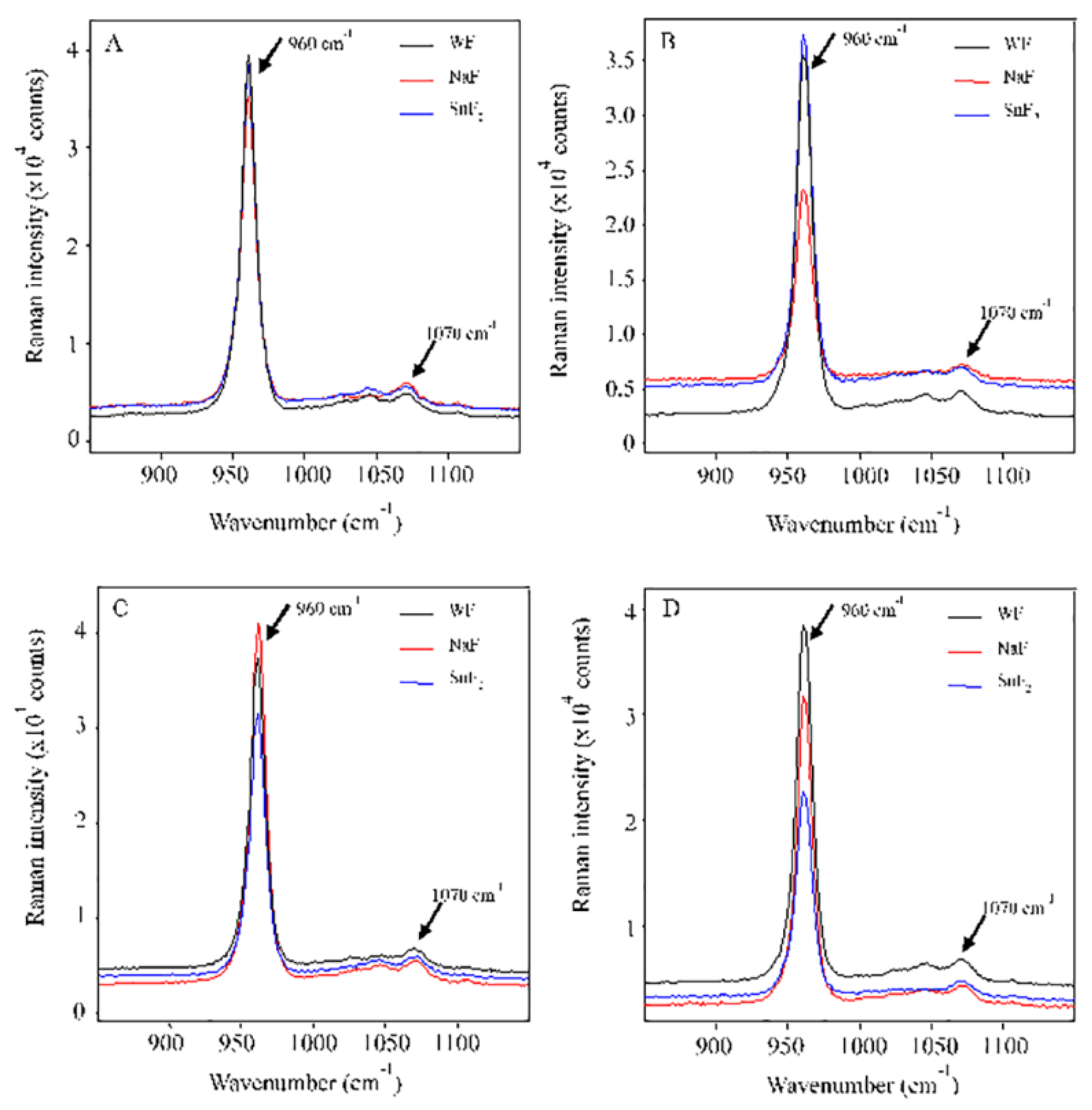
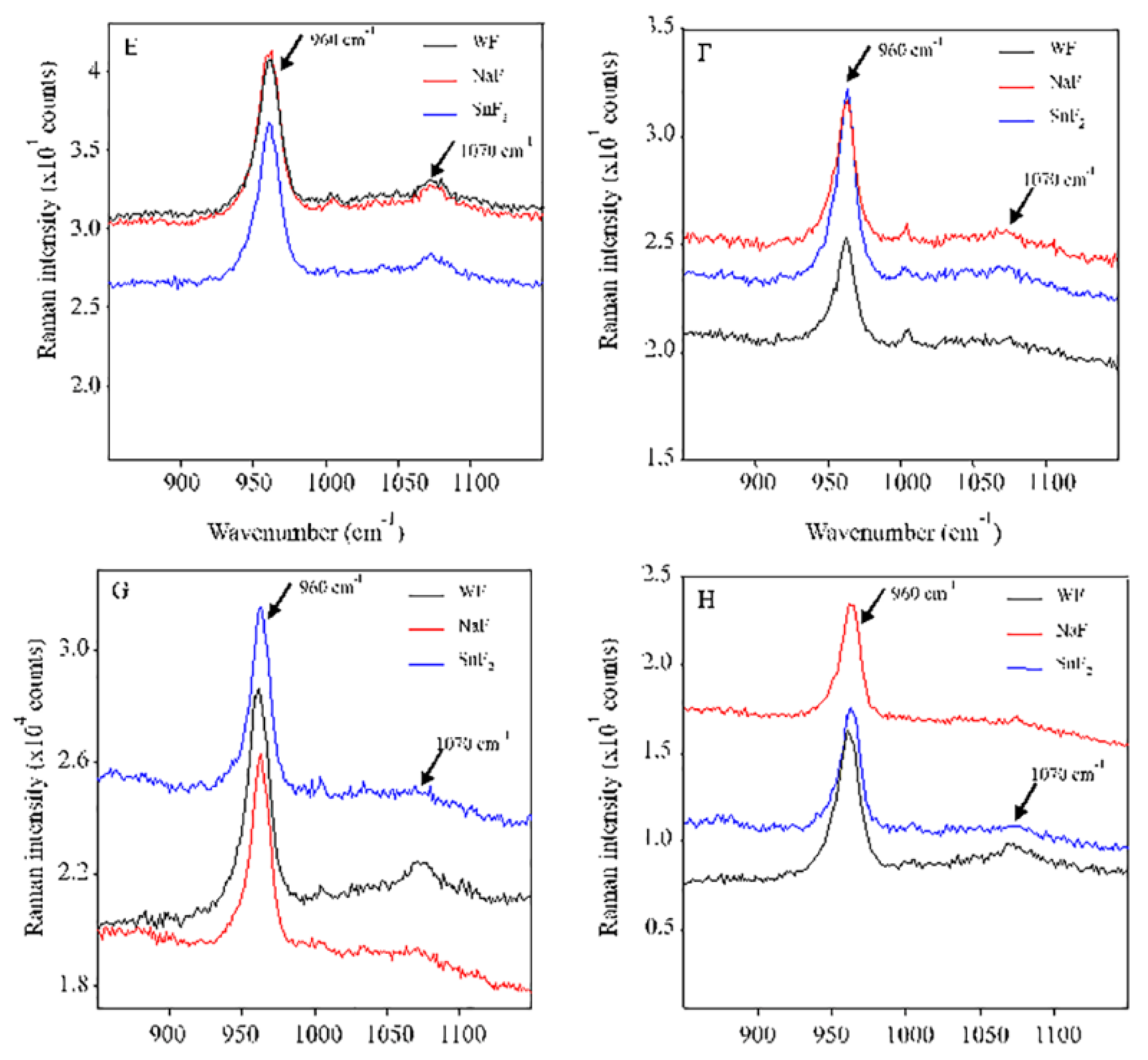
3.3. Analysis of micro-Raman spectroscopy
3.4. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM)
4. Discussion
Conflict of Interest
References
- Coupal, I. , Sołtysiak A. Dental erosion in archaeological human remains: A critical review of literature and proposal of a differential diagnosis protocol. Arch Oral Biol 2017, 84, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho TS, Colon P, Ganss C, Huysmans MC, Lussi A, Schlueter N, Schmalz G, Shellis RP, Tveit AB, Wiegand A. Consensus report of the European federation of conservative dentistry: Erosive tooth wear-diagnosis and management. Clin Oral Investig 2015, 19, 1557–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlueter N, Glatzki J, Klimek J, Ganss C. Erosive-abrasive tissue loss in dentine under simulated bulimic conditions. Arch Oral Biol 2012, 57, 1176–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganss C, Lussi A, Schlueter N. The histological features and physical properties of eroded dental hard tissues. Monogr Oral Sci 2014, 25, 99–107. [Google Scholar]
- Lussi A, Buzalaf MAR, Duangthip D, Anttonen V, Ganss C, João-Souza SH, Baumann T, Carvalho TS. The use of fluoride for the prevention of dental erosion and erosive tooth wear in children and adolescents. Eur Arch Paediatr Dent 2019, 20, 517–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlueter N, Lussi A, Tolle A, Ganss C. Effects of erosion protocol design on erosion/abrasion study outcome and on active agent (NaF and SnF2) efficacy. Caries Res 2016, 50, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moda MD, Briso ALF, Oliveira RP, Pini NIP, Gonçalves DFM, Santos PHD, Fagundes TC. Effects of different toothpastes on the prevention of erosion in composite resin and glass ionomer cement enamel and dentin restorations. J Appl Oral Sci, 2020, 28, e20200493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dündar, A. , Şengün A., Başlak C, Kuş M. Effects of citric acid modified with fluoride, nano-hydroxyapatite and casein on eroded enamel. Arch Oral Biol, 2018, 93, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganss C, Möllers M, & Schlueter N. Do abrasives play a role in toothpaste efficacy against erosion/abrasion? Caries Res 2017, 51, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pini NI, Lima DA, Lovadino JR, Ganss C, Schlueter, N. In vitro efficacy of experimental chitosan-containing solutions as anti-erosive agents in enamel. Caries Res 2016, 50, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kielbassa AM, Gillmann L, Zantner C, Meyer-Lueckel H, Hellwig E, Schulte-Mönting J. (). Profilometric and microradiographic studies on the effects of toothpaste and acidic gel abrasivity on sound and demineralized bovine dental enamel. Caries Res 2005, 39, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lussi A, Schlueter N, Rakhmatullina E, Ganss C. Dental erosion: an overview with emphasis on chemicaland histopathological aspects. Caries Res 2011, 45, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlueter N, Jaeggi T, Lussi A. Is dental erosion really a problem? Adv Dent Res, 2012, 24, 68–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alghilan MA, Cook NB, Platt JA, Eckert GJ, Hara AT. Susceptibility of restorations and adjacent enamel/dentine to erosion under different salivary flow conditions. J Dent 2015, 43, 1476–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viana Í, Alania Y, Feitosa S, Borges AB, Braga RR, Scaramucci, T. Bioactive materials subjected to erosion/abrasion and their influence on dental tissues. Oper Dent, 2020, 45, E114–E123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honório HM, Rios D, Francisconi LF, Magalhães AC, Machado MA, Buzalaf MA. Effect of prolonged erosive pH cycling on different restorative materials. J Oral Rehabil, 2008, 35, 947–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza BM, Comar LP, Vertuan M, Fernandes-Neto C, Buzalaf MA, Magalhães AC. Effect of an experimental paste with hydroxyapatite nanoparticles and fluoride on dental demineralisation and remineralisation in situ. Caries Res, 2015, 49, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz NV, Pessan JP, Manarelli MM, Souza MD, Delbem AC. In vitro effect of low-fluoride toothpastes containing sodium trimetaphosphate on enamel erosion. Arch Oral Biol, 2015, 60, 1231–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strazzi-Sahyon HB, Chimanski A, Yoshimura HN, Dos Santos PH. Effect of previous photoactivation of the adhesive system on the color stability and mechanical properties of resin components in ceramic laminate veneer luting. J Prosthet Dent 2018, 120, 631.e1–631.e6. [Google Scholar]
- Dos Santos PH, Karol S, Bedran-Russo AKB. Long-term nano-mechanical properties of biomodified dentin–resin interface components. J Biomech, 2011, 44, 1691–1694.
- Wiegand A, Schneider S, Sener B, Roos M. , Attin T. Stability against brushing abrasion and the erosion-protective effect of different fluoride compounds. Caries Res 2014, 48, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furini LN, Feitosa E, Alessio P, Shimabukuro MH, Riul Jr A, Constantino CJ. Tuning the nanostructure of DODAB/nickel tetrasulfonated phthalocyanine bilayers in LbL films. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl, 2013, 33, 2937–2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toledano M, Cabello I, Osorio E, Aguilera FS, Medina-Castillo AL, Toledano-Osorio M, Osorio R. Zn-containing polymer nanogels promote cervical dentin remineralization. Clin Oral Investig, 2019, 23, 1197–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlueter N, Hara A, Shellis RP, Ganss C. Methods for the measurement and characterization of erosion in enamel and dentine. Caries Res, 2011, 45, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basting RT, Leme, AA, Bridi EC, Amaral FL, França FM, Turssi CP, Bedran-Russo, AK. Nanomechanical properties, SEM, and EDS microanalysis of dentin treated with 2.5% titanium tetrafluoride, before and after an erosive challenge. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater, 2015, 103, 783–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves DFM, Briso ALF, Pini NIP, Moda MD, Parpinelli de Oliveira R, Santos PHD, Fagundes TC. Effects of dentifrices on mechanical resistance of dentin and restorative materials after erosion and abrasion. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater 2019, 97, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medeiros MI, Carlo HL, Lacerda-Santos R, Lima BA, Souza FB, Rodrigues JA, Carvalho FG. Thickness and nanomechanical properties of protective layer formed by TiF4 varnish on enamel after erosion. Braz Oral Res, 2016, 30, e75err. [Google Scholar]
- Cadenaro M, Antoniolli F, Sauro S, Tay FR, Di Lenarda R, Prati C, Biasotto M. , Contardo L, Breschi L. Degree of conversion and permeability of dental adhesives. Eur J Oral Sci, 2005, 113, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki TY, Gomes-Filho JE, Gallego J, Pavan S, Dos Santos PH, Fraga-Briso AL. Mechanical properties of components of the bonding interface in different regions of radicular dentin surfaces. J Prosthet Dent 2015, 113, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur S, Makkar S, Kumar R, Pasricha S, Gupta, P. Comparative evaluation of surface properties of enamel and different esthetic restorative materials under erosive and abrasive challenges: An in vitro study. Indian J Dent 2015, 6, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajewski VE, Pfeifer CS, Fróes-Salgado NR, Boaro LC, Braga RR. Monomers used in resin composites: Degree of conversion, mechanical properties and water sorption/solubility. Braz Dent J 2012, 23, 508–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rolim FG, Sá AF, Silva-Filho GW, Brandim AS, Vale GC. Effect of high-fluoride dentifrice on enamel erosion adjacent to restorations in vitro. Oper Dent 2016, 41, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira-Junior, WF, Ferraz LN, Pini N, Ambrosano G, Aguiar F, Tabchoury C, Lima D. Effect of toothpaste use against mineral loss promoted by dental bleaching. Oper Dent, 2018, 43, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bezerra SJC, João-Souza SH, Aoki IV, Borges AB, Hara AT, Scaramucci T. Anti-Erosive effect of solutions containing sodium fluoride, stannous chloride, and selected film-forming polymers. Caries Res 2019, 53, 305–313. [CrossRef]
- Guler S, Unal M. The evaluation of color and surface roughness changes in resin based restorative materials with different contents after waiting in various liquids: An SEM and AFM study. Microsc Res Tech, 2018, 81, 1422–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osorio R, Toledano-Osorio M, Osorio E, Aguilera FS, Padilla-Mondéjar S, Toledano, M. Zinc and silica are active components to efficiently treat in vitro simulated eroded dentin. Clin Oral Investig, 2018, 22, 2859–2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganss C, Schlueter N, Klimek J. Retention of KOH-soluble fluoride on enamel and dentine under erosive conditions - A comparison of in vitro and in situ results. Arch Oral Biol 2007, 52, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Material. | Application mode | Composition | Manufacturer |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Adper Single Bond 2 (Adhesive system) |
Apply one layer of adhesive, wait for 20 s, air stream for 5 s, and polymerize for 10 s | Bis-GMA, HEMA, dimethacrylates, ethanol, water, a novel photoinitiator system and a methacrylate functional copolymer of polyacrylic and polyitaconic acids | 3M ESPE, St. Paul, MN, USA. |
|
Filtek Z350 XT (color A2B) Batch: 672912 |
Apply increments of 2 mm and polymerize for 20 s each | Bis-GMA, UDMA, Bis-EMA, TEGDMA, PEGDMA, Zirconia and agglomerates of silica, camphorquinone | 3M ESPE, St. Paul, MN, USA. |
|
Fuji II LC (color A3) Batch: 17051316 |
GC conditioner was applied for 20 s, rinsed and dried for 10 s. 1 level scoop of powder to 2 drops of liquid was dispensed and mixed for 15-20 s. The mixture was transferred to the centrix syringe | Powder: fluor-amino-silicate glass. Liquid: aqueous solution of polycarboxylic acid, TEGDMA and HEMA | GC, Tokyo, Japan. |
|
Curaprox Enzycal Zero (RDA-60)* Batch: 442MHDEXP1121 |
Fluoride-free Toothpaste (WF) |
Water, Sorbitol, Hydrated Silica, Glycerin, Steareth-20, Titanium Dioxide (Cl 77891), Flavor, Sodium Phosphate, Carrageenan, Sodium Chloride, Citric Acid, Sodium Benzoate, Potassium Thiocyanate, Glucose Oxidase, Amyloglucosidase, Lactoperoxidase | Trybol, Neuhausen am Rheinfall, Swiss. |
|
Colgate Total 12 (RDA-70/80)* Batch: 6184BR121R |
Sodium Fluoride Toothpaste (NaF) |
Sodium Fluoride (1450 ppm as NaF) Water, Triclosan, Sorbitol, Silica, Sodium Lauryl Sulfate, PMV / MA Copolymer, Sodium Hydroxide, Saccharin Sodium, Titanium Dioxide |
Colgate-Palmolive, São Bernardo do Campo, SP, Brazil. |
|
Crest Pro-Health (RDA-155)* Batch: 6039GF |
Stannous Fluoride Toothpaste (SnF2) |
Stannous fluoride (1100 ppm F as SnF2) Glycerin, Hydrated Silica, Sodium Hexametaphosphate, Propylene Glycol, PEG 6, Water, Zinc Lactate, Trisodium Phosphate, Sodium Lauryl Sulfate, Sodium Lauryl Sulfate, Carrageenan, Sodium Saccharin, Xanthan Gum, Blue 1 |
Procter & Gamble, Cincinnati, OH, USA. |
| Factors | ERMGIC-C | ECR-C | RMGIC-C | CR-C | DRMGIC-C | DCR-C |
| WF | 2.97 (0.45) Aa | 2.66 (0.40) Ab | 0.47 (0.20) Ab | 0.69 (0.12) Aa | 0.68 (0.15) Aa | 0.63 (0.10) Aa |
| NaF | 2.89 (0.73) Aa | 2.96 (0.43) Aa | 0.41 (0.19) Ab | 0.67 (0.17) Aa | 0.59 (0.12) Ba | 0.61 (0.15) Aa |
| SnF2 | 3.09 (0.83) Aa | 2.98 (0.63) Aa | 0.49 (0.21) Ab | 0.70 (0.21) Aa | 0.65 (0.13) Aba | 0.67 (0.15) Aa |
| Factors | ERMGIC-E | ECR-E | RMGIC-E | CR-E | DRMGIC-E | DCR-E |
| WF | 0.51 (0.17) Aa* | 0.55 (0.22) Aa* | 0.29 (0.09) Ab* | 0.64 (0.08) Aa | 0.05 (0.02) Aa* | 0.10 (0.05) Aa* |
| NaF | 0.52 (0.24) Aa* | 0.50 (0.30) Aa* | 0.34 (0.16) Ab | 0.65 (0.18) Aa | 0.08 (0.04) Aa* | 0.06 (0.02) Aa* |
| SnF2 | 0.27 (0.07) Aa* | 0.23 (0.06) Aa* | 0.25 (0.14) Ab* | 0.63 (0.11) Aa | 0.08 (0.03) Aa* | 0.07 (0.02) Aa* |
| Upper case letters compare toothpastes in each control or eroded side. Lowercase letters compare surfaces separately (p < 0.05). *Statistical difference among the control and eroded surfaces. SD, standard deviation; H, nanohardness; GPa, gigapascal. | ||||||
| Factors | ERMGIC-C | ECR-C | RMGIC-C | CR-C | DRMGIC-C | DCR-C |
| WF | 79.92 (7.45) Aa | 64.74 (7.14) Bb | 12.99 (3.38) Aa | 13.60 (1.56) Aa | 21.34 (3.56) Aa | 18.70 (2.53) Aa |
| NaF | 76.25 (14.51) Ba | 82.37 (8.08) Aa | 13.50 (3.07) Aa | 13.31 (2.15) Aa | 18.62 (2.97) Aa | 18.26 (2.57) Aa |
| SnF2 | 87.73 (14.86) Aa | 75.22 (8.68) Aa | 14.71 (4.26) Aa | 14.26 (2.15) Aa | 19.08 (3.90) Aa | 19.70 (3.23) Aa |
| Factors | ERMGIC-E | ECR-E | RMGIC-E | CR-E | DRMGIC-E | DCR-E |
| WF | 30.23 (8.63) Aa* | 17.08 (8.22) Bb* | 10.18 (2.37) Ab* | 13.45 (1.51) Aa | 1.54 (0.40) Aa* | 2.65 (0.84) Aa* |
| NaF | 34.52 (12.91) Aa* | 34.59 (8.83) Aa* | 10.38 (3.55) Ab* | 13.52 (2.11) Aa | 1.97 (0.61) Aa* | 2.06 (0.79) Aa* |
| SnF2 | 20.72 (9.90) Ba* | 19.33 (3.26) Ba* | 6.47 (1.14) Bb* | 13.62 (1.50) Aa | 2.36 (0.66) Aa* | 1.99 (0.40) Aa* |
| Upper case letters compare toothpastes in each control or eroded side. Lowercase letters compare surfaces separately (p < 0.05). *Statistical difference among the control and eroded surfaces. SD, standard deviation; Er, elastic modulus; GPa, gigapascal | ||||||
| Factors | ERMGIC-C | ERMGIC –E | ECR-C | ECR-E |
| WF | 1.80 (0.10) Aa | 1.78 (0.12) Aa | 1.79 (0.10) Aa | 1.80 (0.12) Aa |
| NaF | 1.75 (0.14) Aa | 1.78 (0.16) Aa | 1.80 (0.10) Aa | 1.87 (0.08) Aa |
| SnF2 | 1.81 (0.02) Aa | 1.71 (0.09) Aa | 1.75 (0.12) Aa | 1.77 (0.09) Aa |
| Upper case letters compare toothpastes in each surface. Lowercase letters compare surfaces in each toothpaste (p < 0.05). SD, standard deviation. | ||||
| Factors | DRMGIC-C | DRMGIC –E | DCR-C | DCR-E |
| WF | 1.74 (0.08) Aa | 0.53 (0.83) Ab | 1.71 (0.09) Aa | 0.62 (0.96) Bb |
| NaF | 1.68 (0.08) Aa | 1.12 (0.87) Aa | 1.95 (0.35) Aa | 1.77 (0.12) Aa |
| SnF2 | 1.70 (0.08) Aa | 0.53 (0.81) Aa | 1.74 (0.10) Aa | 1.22 (0.95) ABab |
| Upper case letters compare toothpastes in each surface. Lowercase letters compare surfaces in each toothpaste (p < 0.05). SD, standard deviation. | ||||
| Factors | ERMGIC-C | ERMGIC –E | ECR-C | ECR-E |
| WF | 0.06 (0.08) Aa | 0.04 (0.01) Aa | 0.04 (0.01) Aa | 0.04 (0.01) Aa |
| NaF | 0.05 (0.01) Aa | 0.05 (0.02) Aa | 0.03 (0.01) Aa | 0.04 (0.01) Aa |
| SnF2 | 0.04 (0.02) Aa | 0.08 (0.13) Aa | 0.04 (0.01) Aa | 0.04 (0.02) Aa |
| Upper case letters compare toothpastes in each surface. Lowercase letters compare surfaces in each toothpaste (p < 0.05). SD, standard deviation. | ||||
| Factors | DRMGIC-C | DRMGIC –E | DCR-C | DCR-E |
| WF | 0.33 (0.20) Bb | 0.35 (0.05) Aab | 0.42 (0.07) Aa | 0.29 (0.04) Ab |
| NaF | 0.42 (0.06) Aa | 0.36 (0.08) Aab | 0.39 (0.04) Aa | 0.26 (0.08) Ab |
| SnF2 | 0.45 (0.07) Aa | 0.31 (0.08) Ab | 0.42 (0.06) Aa | 0.25 (0.09) Ab |
| Upper case letters compare toothpastes in each surface. Lowercase letters compare surfaces in each toothpaste (p < 0.05). SD, standard deviation. | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




