Submitted:
06 May 2023
Posted:
09 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Preparation of plasmids
2.2. Antibodies
2.3. Cell lines
2.4. Development of hybridomas
2.5. Purification of EMab-300
2.6. Flow cytometric analysis
2.7. Determination of dissociation constant (KD) by flow cytometry
3. Results
3.1. Development of anti-mEGFR mAbs by the CBIS method
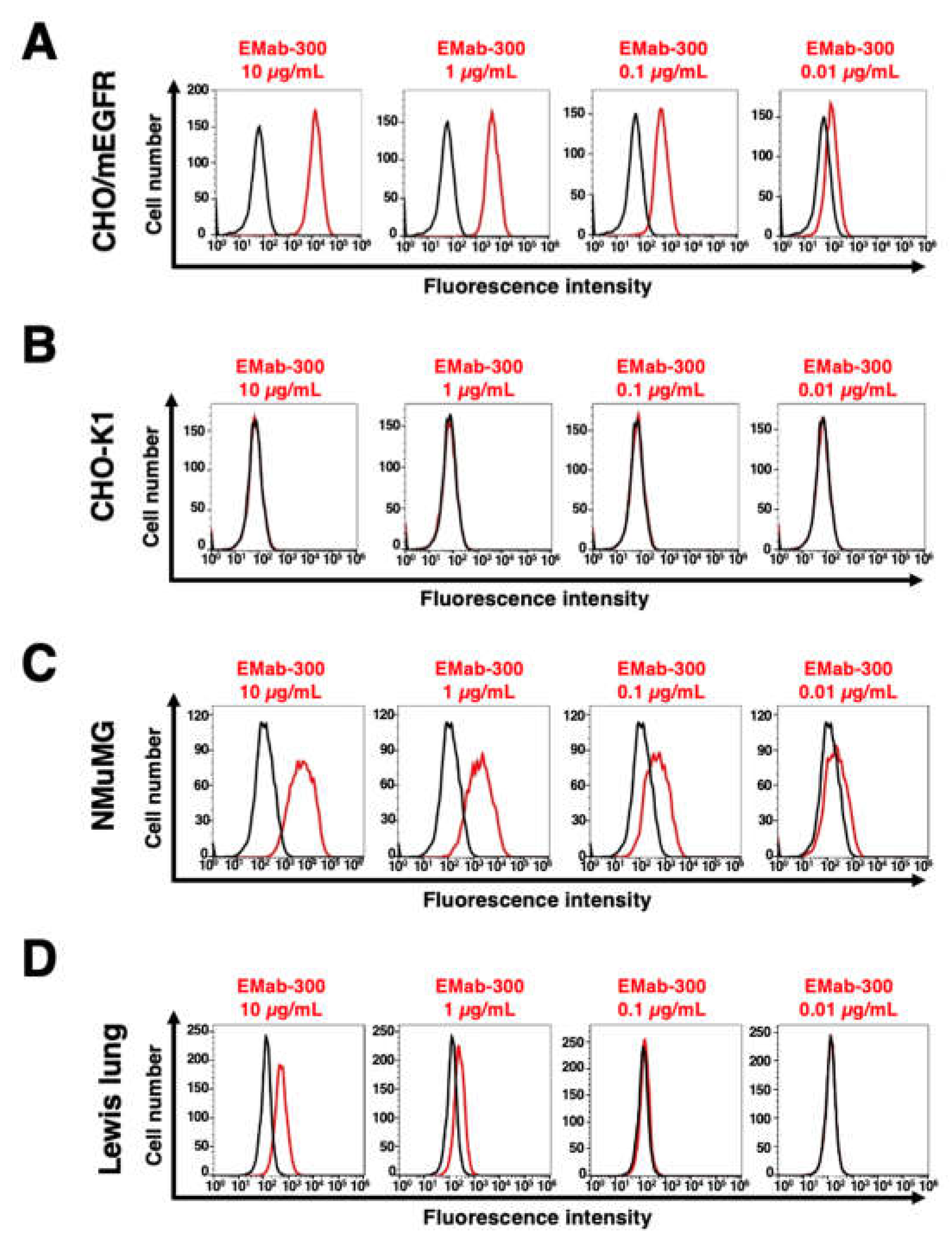
3.2. Flow cytometric analysis using EMab-300
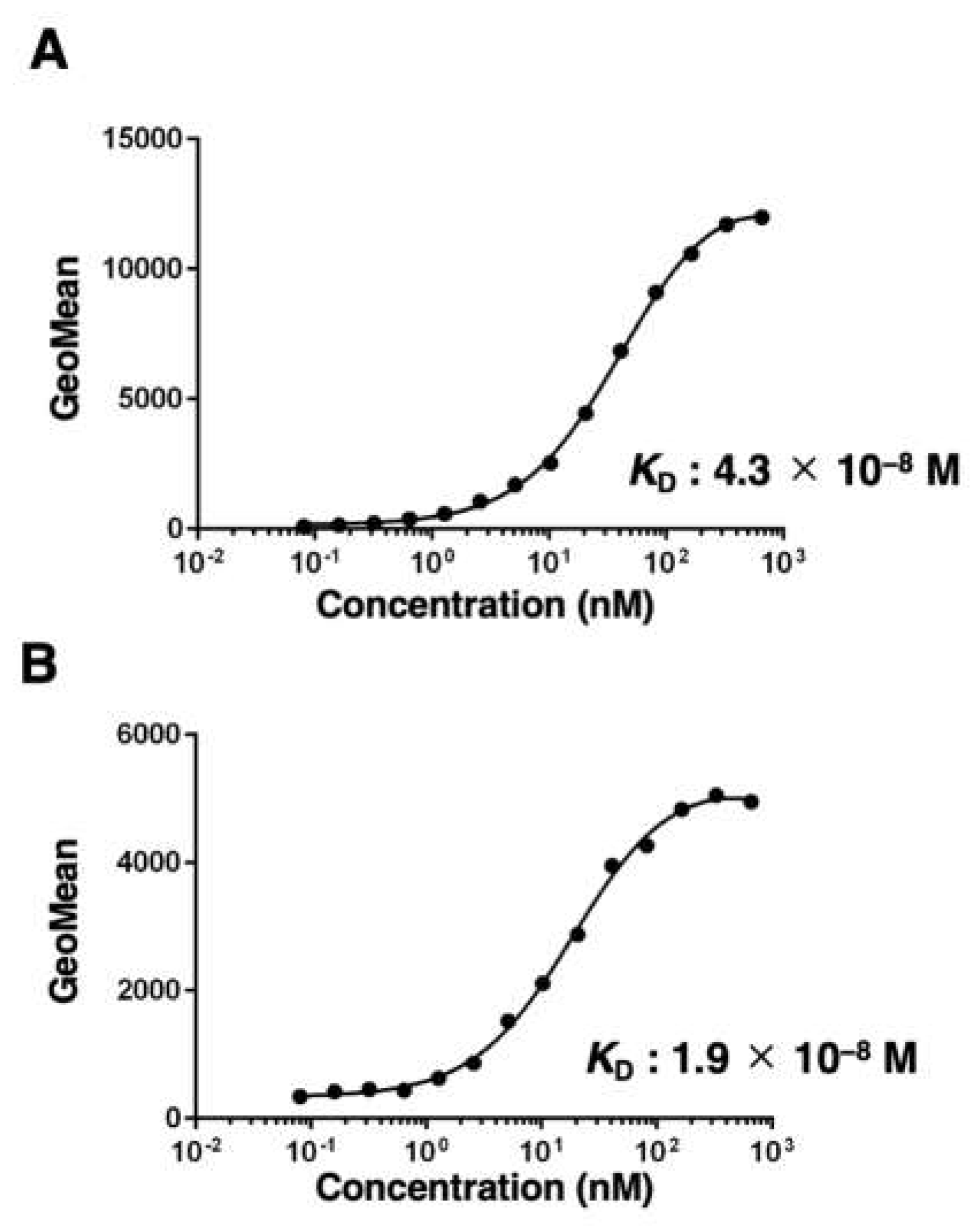
3.3. Kinetic analysis of EMab-300 using flow cytometry
4. Discussion
References
- Zandi, R.; Larsen, A.B.; Andersen, P.; Stockhausen, M.T.; Poulsen, H.S. Mechanisms for oncogenic activation of the epidermal growth factor receptor. Cell Signal 2007, 19, 2013–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, A.J.; Sequist, L.V.; Lin, J.J. Third-generation EGFR and ALK inhibitors: mechanisms of resistance and management. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2022, 19, 499–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D. Hallmarks of Cancer: New Dimensions. Cancer Discov 2022, 12, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsao, L.C.; Force, J.; Hartman, Z.C. Mechanisms of Therapeutic Antitumor Monoclonal Antibodies. Cancer Res 2021, 81, 4641–4651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubair, T.; Bandyopadhyay, D. Small Molecule EGFR Inhibitors as Anti-Cancer Agents: Discovery, Mechanisms of Action, and Opportunities. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Schmitz, K.R.; Jeffrey, P.D.; Wiltzius, J.J.; Kussie, P.; Ferguson, K.M. Structural basis for inhibition of the epidermal growth factor receptor by cetuximab. Cancer Cell 2005, 7, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonker, D.J.; O’Callaghan, C.J.; Karapetis, C.S.; Zalcberg, J.R.; Tu, D.; Au, H.J.; Berry, S.R.; Krahn, M.; Price, T.; Simes, R.J.; et al. Cetuximab for the treatment of colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med 2007, 357, 2040–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonner, J.A.; Harari, P.M.; Giralt, J.; Cohen, R.B.; Jones, C.U.; Sur, R.K.; Raben, D.; Baselga, J.; Spencer, S.A.; Zhu, J.; et al. Radiotherapy plus cetuximab for locoregionally advanced head and neck cancer: 5-year survival data from a phase 3 randomised trial, and relation between cetuximab-induced rash and survival. Lancet Oncol 2010, 11, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohishi, T.; Kaneko, M.K.; Yoshida, Y.; Takashima, A.; Kato, Y.; Kawada, M. Current Targeted Therapy for Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardelli, A.; Jänne, P.A. The road to resistance: EGFR mutation and cetuximab. Nat Med 2012, 18, 199–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeVita, V.T., Jr.; Chu, E. A history of cancer chemotherapy. Cancer Res 2008, 68, 8643–8653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Day, C.P.; Merlino, G.; Van Dyke, T. Preclinical mouse cancer models: a maze of opportunities and challenges. Cell 2015, 163, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, R.M.; Trivedi, S.; Concha-Benavente, F.; Gibson, S.P.; Reeder, C.; Ferrone, S.; Ferris, R.L. CD137 Stimulation Enhances Cetuximab-Induced Natural Killer: Dendritic Cell Priming of Antitumor T-Cell Immunity in Patients with Head and Neck Cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2017, 23, 707–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubach, J.; Hubo, M.; Amendt, C.; Stroh, C.; Jonuleit, H. IgG1 anti-epidermal growth factor receptor antibodies induce CD8-dependent antitumor activity. Int J Cancer 2015, 136, 821–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itai, S.; Fujii, Y.; Kaneko, M.K.; Yamada, S.; Nakamura, T.; Yanaka, M.; Saidoh, N.; Chang, Y.W.; Handa, S.; Takahashi, M.; et al. H(2)Mab-77 is a Sensitive and Specific Anti-HER2 Monoclonal Antibody Against Breast Cancer. Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother 2017, 36, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asano, T.; Ohishi, T.; Takei, J.; Nakamura, T.; Nanamiya, R.; Hosono, H.; Tanaka, T.; Sano, M.; Harada, H.; Kawada, M.; et al. Anti-HER3 monoclonal antibody exerts antitumor activity in a mouse model of colorectal adenocarcinoma. Oncol Rep 2021, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Suzuki, H.; Asano, T.; Tanaka, T.; Suzuki, H.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y. Development of a Novel Anti-EpCAM Monoclonal Antibody for Various Applications. Antibodies (Basel) 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, M.K.; Ohishi, T.; Takei, J.; Sano, M.; Nakamura, T.; Hosono, H.; Yanaka, M.; Asano, T.; Sayama, Y.; Harada, H.; et al. Anti-EpCAM monoclonal antibody exerts antitumor activity against oral squamous cell carcinomas. Oncol Rep 2020, 44, 2517–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayama, Y.; Kaneko, M.K.; Takei, J.; Hosono, H.; Sano, M.; Asano, T.; Kato, Y. Establishment of a novel anti-TROP2 monoclonal antibody TrMab-29 for immunohistochemical analysis. Biochem Biophys Rep 2021, 25, 100902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Ohishi, T.; Asano, T.; Takei, J.; Nanamiya, R.; Hosono, H.; Sano, M.; Harada, H.; Kawada, M.; Kaneko, M.K.; et al. An anti-TROP2 monoclonal antibody TrMab-6 exerts antitumor activity in breast cancer mouse xenograft models. Oncol Rep 2021, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, S.; Itai, S.; Nakamura, T.; Yanaka, M.; Chang, Y.W.; Suzuki, H.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y. Monoclonal Antibody L(1)Mab-13 Detected Human PD-L1 in Lung Cancers. Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother 2018, 37, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, S.; Itai, S.; Nakamura, T.; Yanaka, M.; Saidoh, N.; Chang, Y.W.; Handa, S.; Harada, H.; Kagawa, Y.; Ichii, O.; et al. PMab-52: Specific and Sensitive Monoclonal Antibody Against Cat Podoplanin for Immunohistochemistry. Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother 2017, 36, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furusawa, Y.; Kaneko, M.K.; Nakamura, T.; Itai, S.; Fukui, M.; Harada, H.; Yamada, S.; Kato, Y. Establishment of a Monoclonal Antibody PMab-231 for Tiger Podoplanin. Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother 2019, 38, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furusawa, Y.; Takei, J.; Sayama, Y.; Yamada, S.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y. Development of an anti-bear podoplanin monoclonal antibody PMab-247 for immunohistochemical analysis. Biochem Biophys Rep 2019, 18, 100644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furusawa, Y.; Yamada, S.; Itai, S.; Nakamura, T.; Takei, J.; Sano, M.; Harada, H.; Fukui, M.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y. Establishment of a monoclonal antibody PMab-233 for immunohistochemical analysis against Tasmanian devil podoplanin. Biochem Biophys Rep 2019, 18, 100631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goto, N.; Suzuki, H.; Tanaka, T.; Asano, T.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y. Development of a Monoclonal Antibody PMab-292 Against Ferret Podoplanin. Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother 2022, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furusawa, Y.; Yamada, S.; Itai, S.; Sano, M.; Nakamura, T.; Yanaka, M.; Handa, S.; Mizuno, T.; Maeda, K.; Fukui, M.; et al. Establishment of Monoclonal Antibody PMab-202 Against Horse Podoplanin. Monoclon. Antib. Immunodiagn. Immunother. 2018, 37, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, Y.; Yamada, S.; Furusawa, Y.; Itai, S.; Nakamura, T.; Yanaka, M.; Sano, M.; Harada, H.; Fukui, M.; Kaneko, M.K. PMab-213: a monoclonal antibody for immunohistochemical analysis against pig podoplanin. Monoclon. Antib. Immunodiagn. Immunother. 2019, 38, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furusawa, Y.; Yamada, S.; Nakamura, T.; Sano, M.; Sayama, Y.; Itai, S.; Takei, J.; Harada, H.; Fukui, M.; Kaneko, M.K.; et al. PMab-235: A monoclonal antibody for immunohistochemical analysis against goat podoplanin. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, Y.; Furusawa, Y.; Yamada, S.; Itai, S.; Takei, J.; Sano, M.; Kaneko, M.K. Establishment of a monoclonal antibody PMab-225 against alpaca podoplanin for immunohistochemical analyses. Biochem Biophys Rep 2019, 18, 100633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, Y.; Furusawa, Y.; Itai, S.; Takei, J.; Nakamura, T.; Sano, M.; Harada, H.; Yamada, S.; Kaneko, M.K. Establishment of an Anticetacean Podoplanin Monoclonal Antibody PMab-237 for Immunohistochemical Analysis. Monoclon. Antib. Immunodiagn. Immunother. 2019, 38, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, Y.; Furusawa, Y.; Sano, M.; Takei, J.; Nakamura, T.; Yanaka, M.; Okamoto, S.; Handa, S.; Komatsu, Y.; Asano, T.; et al. Development of an Anti-Sheep Podoplanin Monoclonal Antibody PMab-256 for Immunohistochemical Analysis of Lymphatic Endothelial Cells. Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother 2020, 39, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, T.; Asano, T.; Sano, M.; Takei, J.; Hosono, H.; Nanamiya, R.; Nakamura, T.; Yanaka, M.; Harada, H.; Fukui, M.; et al. Development of Monoclonal Antibody PMab-269 Against California Sea Lion Podoplanin. Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother 2021, 40, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, S.; Kaneko, M.K.; Sayama, Y.; Asano, T.; Sano, M.; Yanaka, M.; Nakamura, T.; Okamoto, S.; Handa, S.; Komatsu, Y.; et al. Development of Novel Mouse Monoclonal Antibodies Against Human CD19. Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother 2020, 39, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furusawa, Y.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y. Establishment of C(20)Mab-11, a novel anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody, for the detection of B cells. Oncol Lett 2020, 20, 1961–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furusawa, Y.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y. Establishment of an Anti-CD20 Monoclonal Antibody (C(20)Mab-60) for Immunohistochemical Analyses. Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother 2020, 39, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawara, M.; Suzuki, H.; Goto, N.; Tanaka, T.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y. A Novel Anti-CD44 Variant 9 Monoclonal Antibody C44Mab-1 was Developed for Immunohistochemical Analyses Against Colorectal Cancers Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2023, 45, 3658–3673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, Y.; Suzuki, H.; Tanaka, T.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y. Development of a Novel Anti-CD44 variant 5 Monoclonal Antibody C44Mab-3 for Multiple Applications against Pancreatic Carcinomas. Antibodies 2023, 12, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ejima, R.; Suzuki, H.; Tanaka, T.; Asano, T.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y. Development of a Novel Anti-CD44 Variant 6 Monoclonal Antibody C(44)Mab-9 for Multiple Applications against Colorectal Carcinomas. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, S.; Itai, S.; Nakamura, T.; Yanaka, M.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y. Detection of high CD44 expression in oral cancers using the novel monoclonal antibody, C(44)Mab-5. Biochem Biophys Rep 2018, 14, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itai, S.; Fujii, Y.; Nakamura, T.; Chang, Y.W.; Yanaka, M.; Saidoh, N.; Handa, S.; Suzuki, H.; Harada, H.; Yamada, S.; et al. Establishment of CMab-43, a Sensitive and Specific Anti-CD133 Monoclonal Antibody, for Immunohistochemistry. Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother 2017, 36, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asano, T.; Nanamiya, R.; Tanaka, T.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y. Development of Antihuman Killer Cell Lectin-Like Receptor Subfamily G Member 1 Monoclonal Antibodies for Flow Cytometry. Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother 2021, 40, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanamiya, R.; Takei, J.; Asano, T.; Tanaka, T.; Sano, M.; Nakamura, T.; Yanaka, M.; Hosono, H.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y. Development of Anti-Human CC Chemokine Receptor 9 Monoclonal Antibodies for Flow Cytometry. Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother 2021, 40, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takei, J.; Asano, T.; Nanamiya, R.; Nakamura, T.; Yanaka, M.; Hosono, H.; Tanaka, T.; Sano, M.; Kaneko, M.K.; Harada, H.; et al. Development of Anti-human T Cell Immunoreceptor with Ig and ITIM Domains (TIGIT) Monoclonal Antibodies for Flow Cytometry. Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother 2021, 40, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asano, T.; Nanamiya, R.; Takei, J.; Nakamura, T.; Yanaka, M.; Hosono, H.; Tanaka, T.; Sano, M.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y. Development of Anti-Mouse CC Chemokine Receptor 3 Monoclonal Antibodies for Flow Cytometry. Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother 2021, 40, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, T.; Nanamiya, R.; Takei, J.; Nakamura, T.; Yanaka, M.; Hosono, H.; Sano, M.; Asano, T.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y. Development of Anti-Mouse CC Chemokine Receptor 8 Monoclonal Antibodies for Flow Cytometry. Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother 2021, 40, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, R.; Oi, R.; Akashi, S.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y.; Nogi, T. Application of the NZ-1 Fab as a crystallization chaperone for PA tag-inserted target proteins. Protein Sci 2019, 28, 823–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, Y.; Matsunaga, Y.; Arimori, T.; Kitago, Y.; Ogasawara, S.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y.; Takagi, J. Tailored placement of a turn-forming PA tag into the structured domain of a protein to probe its conformational state. J Cell Sci 2016, 129, 1512–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, Y.; Kaneko, M.; Neyazaki, M.; Nogi, T.; Kato, Y.; Takagi, J. PA tag: a versatile protein tagging system using a super high affinity antibody against a dodecapeptide derived from human podoplanin. Protein Expr Purif 2014, 95, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, Y.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y. MAP Tag: A Novel Tagging System for Protein Purification and Detection. Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother 2016, 35, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakasa, A.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y.; Takagi, J.; Arimori, T. Site-specific epitope insertion into recombinant proteins using the MAP tag system. J Biochem 2020, 168, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, Y.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kuno, A.; Uchiyama, N.; Amano, K.; Chiba, Y.; Hasegawa, Y.; Hirabayashi, J.; Narimatsu, H.; Mishima, K.; et al. Inhibition of tumor cell-induced platelet aggregation using a novel anti-podoplanin antibody reacting with its platelet-aggregation-stimulating domain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2006, 349, 1301–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalise, L.; Kato, A.; Ohno, M.; Maeda, S.; Yamamichi, A.; Kuramitsu, S.; Shiina, S.; Takahashi, H.; Ozone, S.; Yamaguchi, J.; et al. Efficacy of cancer-specific anti-podoplanin CAR-T cells and oncolytic herpes virus G47Delta combination therapy against glioblastoma. Mol Ther Oncolytics 2022, 26, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishikawa, A.; Waseda, M.; Ishii, T.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y.; Kaneko, S. Improved anti-solid tumor response by humanized anti-podoplanin chimeric antigen receptor transduced human cytotoxic T cells in an animal model. Genes Cells 2022, 27, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura-Sakaguchi, R.; Aruga, R.; Hirose, M.; Ekimoto, T.; Miyake, T.; Hizukuri, Y.; Oi, R.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y.; Akiyama, Y.; et al. Moving toward generalizable NZ-1 labeling for 3D structure determination with optimized epitope-tag insertion. Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol 2021, 77, 645–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaneko, M.K.; Ohishi, T.; Nakamura, T.; Inoue, H.; Takei, J.; Sano, M.; Asano, T.; Sayama, Y.; Hosono, H.; Suzuki, H.; et al. Development of Core-Fucose-Deficient Humanized and Chimeric Anti-Human Podoplanin Antibodies. Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother 2020, 39, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, S.; Kaneko, M.K.; Tsuchihashi, Y.; Izumi, T.; Ogasawara, S.; Okada, N.; Sato, C.; Tobiume, M.; Otsuka, K.; Miyamoto, L.; et al. Antitumor effect of novel anti-podoplanin antibody NZ-12 against malignant pleural mesothelioma in an orthotopic xenograft model. Cancer Sci 2016, 107, 1198–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, M.K.; Abe, S.; Ogasawara, S.; Fujii, Y.; Yamada, S.; Murata, T.; Uchida, H.; Tahara, H.; Nishioka, Y.; Kato, Y. Chimeric Anti-Human Podoplanin Antibody NZ-12 of Lambda Light Chain Exerts Higher Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity and Complement-Dependent Cytotoxicity Compared with NZ-8 of Kappa Light Chain. Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother 2017, 36, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, A.; Ohta, M.; Kato, Y.; Inada, S.; Kato, T.; Nakata, S.; Yatabe, Y.; Goto, M.; Kaneda, N.; Kurita, K.; et al. A Real-Time Near-Infrared Fluorescence Imaging Method for the Detection of Oral Cancers in Mice Using an Indocyanine Green-Labeled Podoplanin Antibody. Technol Cancer Res Treat 2018, 17, 1533033818767936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiina, S.; Ohno, M.; Ohka, F.; Kuramitsu, S.; Yamamichi, A.; Kato, A.; Motomura, K.; Tanahashi, K.; Yamamoto, T.; Watanabe, R.; et al. CAR T Cells Targeting Podoplanin Reduce Orthotopic Glioblastomas in Mouse Brains. Cancer Immunol Res 2016, 4, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuwata, T.; Yoneda, K.; Mori, M.; Kanayama, M.; Kuroda, K.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y.; Tanaka, F. Detection of Circulating Tumor Cells (CTCs) in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma (MPM) with the “Universal” CTC-Chip and An Anti-Podoplanin Antibody NZ-1.2. Cells 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishinaga, Y.; Sato, K.; Yasui, H.; Taki, S.; Takahashi, K.; Shimizu, M.; Endo, R.; Koike, C.; Kuramoto, N.; Nakamura, S.; et al. Targeted Phototherapy for Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma: Near-Infrared Photoimmunotherapy Targeting Podoplanin. Cells 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, Y.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kunita, A.; Ito, H.; Kameyama, A.; Ogasawara, S.; Matsuura, N.; Hasegawa, Y.; Suzuki-Inoue, K.; Inoue, O.; et al. Molecular analysis of the pathophysiological binding of the platelet aggregation-inducing factor podoplanin to the C-type lectin-like receptor CLEC-2. Cancer Sci 2008, 99, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, Y.; Vaidyanathan, G.; Kaneko, M.K.; Mishima, K.; Srivastava, N.; Chandramohan, V.; Pegram, C.; Keir, S.T.; Kuan, C.T.; Bigner, D.D.; et al. Evaluation of anti-podoplanin rat monoclonal antibody NZ-1 for targeting malignant gliomas. Nucl Med Biol 2010, 37, 785–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, S.; Rapraeger, A. Altered structure of the hybrid cell surface proteoglycan of mammary epithelial cells in response to transforming growth factor-beta. J Cell Biol 1988, 107, 1959–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer-Schaller, N.; Cardner, M.; Diepenbruck, M.; Saxena, M.; Tiede, S.; Lüönd, F.; Ivanek, R.; Beerenwinkel, N.; Christofori, G. A Hierarchical Regulatory Landscape during the Multiple Stages of EMT. Dev Cell 2019, 48, 539–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Antin, P.; Berx, G.; Blanpain, C.; Brabletz, T.; Bronner, M.; Campbell, K.; Cano, A.; Casanova, J.; Christofori, G.; et al. Guidelines and definitions for research on epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2020, 21, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okita, Y.; Kimura, M.; Xie, R.; Chen, C.; Shen, L.T.; Kojima, Y.; Suzuki, H.; Muratani, M.; Saitoh, M.; Semba, K.; et al. The transcription factor MAFK induces EMT and malignant progression of triple-negative breast cancer cells through its target GPNMB. Sci Signal 2017, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellar, A.; Egan, C.; Morris, D. Preclinical Murine Models for Lung Cancer: Clinical Trial Applications. Biomed Res Int 2015, 2015, 621324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, M.; Lin, D.; Yan, N.; Li, H.; Li, J.; Huang, Z. Oxaliplatin facilitates tumor-infiltration of T cells and natural-killer cells for enhanced tumor immunotherapy in lung cancer model. Anticancer Drugs 2022, 33, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canon, J.; Rex, K.; Saiki, A.Y.; Mohr, C.; Cooke, K.; Bagal, D.; Gaida, K.; Holt, T.; Knutson, C.G.; Koppada, N.; et al. The clinical KRAS(G12C) inhibitor AMG 510 drives anti-tumour immunity. Nature 2019, 575, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Suzuki, H.; Ohishi, T.; Asano, T.; Tanaka, T.; Yanaka, M.; Nakamura, T.; Yoshikawa, T.; Kawada, M.; Kaneko, M.K.; et al. Antitumor activities of a defucosylated anti-EpCAM monoclonal antibody in colorectal carcinoma xenograft models. Int J Mol Med 2023, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanamiya, R.; Takei, J.; Ohishi, T.; Asano, T.; Tanaka, T.; Sano, M.; Nakamura, T.; Yanaka, M.; Handa, S.; Tateyama, N.; et al. Defucosylated Anti-Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Monoclonal Antibody (134-mG(2a)-f) Exerts Antitumor Activities in Mouse Xenograft Models of Canine Osteosarcoma. Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother 2022, 41, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawabata, H.; Suzuki, H.; Ohishi, T.; Kawada, M.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y. A Defucosylated Mouse Anti-CD10 Monoclonal Antibody (31-mG(2a)-f) Exerts Antitumor Activity in a Mouse Xenograft Model of CD10-Overexpressed Tumors. Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother 2022, 41, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawabata, H.; Ohishi, T.; Suzuki, H.; Asano, T.; Kawada, M.; Suzuki, H.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y. A Defucosylated Mouse Anti-CD10 Monoclonal Antibody (31-mG(2a)-f) Exerts Antitumor Activity in a Mouse Xenograft Model of Renal Cell Cancers. Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asano, T.; Tanaka, T.; Suzuki, H.; Li, G.; Ohishi, T.; Kawada, M.; Yoshikawa, T.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y. A Defucosylated Anti-EpCAM Monoclonal Antibody (EpMab-37-mG(2a)-f) Exerts Antitumor Activity in Xenograft Model. Antibodies (Basel) 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tateyama, N.; Nanamiya, R.; Ohishi, T.; Takei, J.; Nakamura, T.; Yanaka, M.; Hosono, H.; Saito, M.; Asano, T.; Tanaka, T.; et al. Defucosylated Anti-Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Monoclonal Antibody 134-mG(2a)-f Exerts Antitumor Activities in Mouse Xenograft Models of Dog Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Overexpressed Cells. Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother 2021, 40, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takei, J.; Ohishi, T.; Kaneko, M.K.; Harada, H.; Kawada, M.; Kato, Y. A defucosylated anti-PD-L1 monoclonal antibody 13-mG(2a)-f exerts antitumor effects in mouse xenograft models of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Biochem Biophys Rep 2020, 24, 100801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takei, J.; Kaneko, M.K.; Ohishi, T.; Hosono, H.; Nakamura, T.; Yanaka, M.; Sano, M.; Asano, T.; Sayama, Y.; Kawada, M.; et al. A defucosylated antiCD44 monoclonal antibody 5mG2af exerts antitumor effects in mouse xenograft models of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Rep 2020, 44, 1949–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asano, T.; Kaneko, M.K.; Takei, J.; Tateyama, N.; Kato, Y. Epitope Mapping of the Anti-CD44 Monoclonal Antibody (C44Mab-46) Using the REMAP Method. Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother 2021, 40, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sano, M.; Kaneko, M.K.; Aasano, T.; Kato, Y. Epitope Mapping of an Antihuman EGFR Monoclonal Antibody (EMab-134) Using the REMAP Method. Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother 2021, 40, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asano, T.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y. Development of a Novel Epitope Mapping System: RIEDL Insertion for Epitope Mapping Method. Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother 2021, 40, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanamiya, R.; Sano, M.; Asano, T.; Yanaka, M.; Nakamura, T.; Saito, M.; Tanaka, T.; Hosono, H.; Tateyama, N.; Kaneko, M.K.; et al. Epitope Mapping of an Anti-Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Monoclonal Antibody (EMab-51) Using the RIEDL Insertion for Epitope Mapping Method. Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother 2021, 40, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




