Submitted:
06 May 2023
Posted:
08 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- We constructed a skeleton graph for Large Scale SLR with selected 27 key points among the whole body key points. The main purpose of this graph is to construct a unified graph to dynamically optimize the nodes and edges based on the different actions. Due to the minimum number of the skeleton key points being selected among the whole body, the computational complexity can be solved to increase the model’s efficiency.
- We extracted the hybrid feature by combining the Graph-based SL-GDN and Generale Neural network features from the multiple streams. After concatenating the feature, we used a classification module to refine the concatenated feature and prediction.
- To evaluate the model, we used three large-scale datasets with four modalities: joint, joint, bone and bone. Our model generated a high performance compared to the existing system.
2. Related Work
3. Dataset
3.1. AUTSL Dataset
3.2. CSL Dataset
3.3. WLASL Dataset
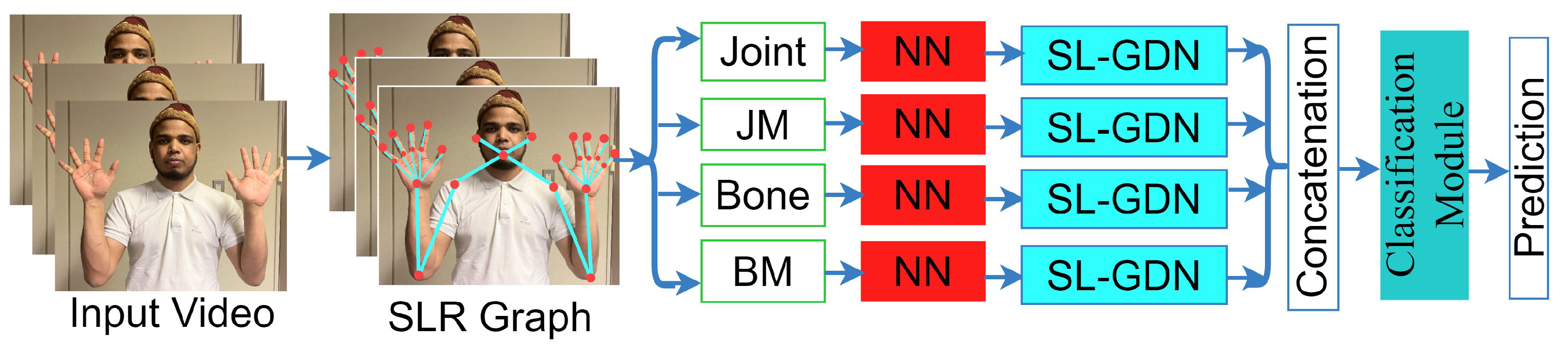
4. Proposed Methodology
4.1. Key points Selection and Graph Construction
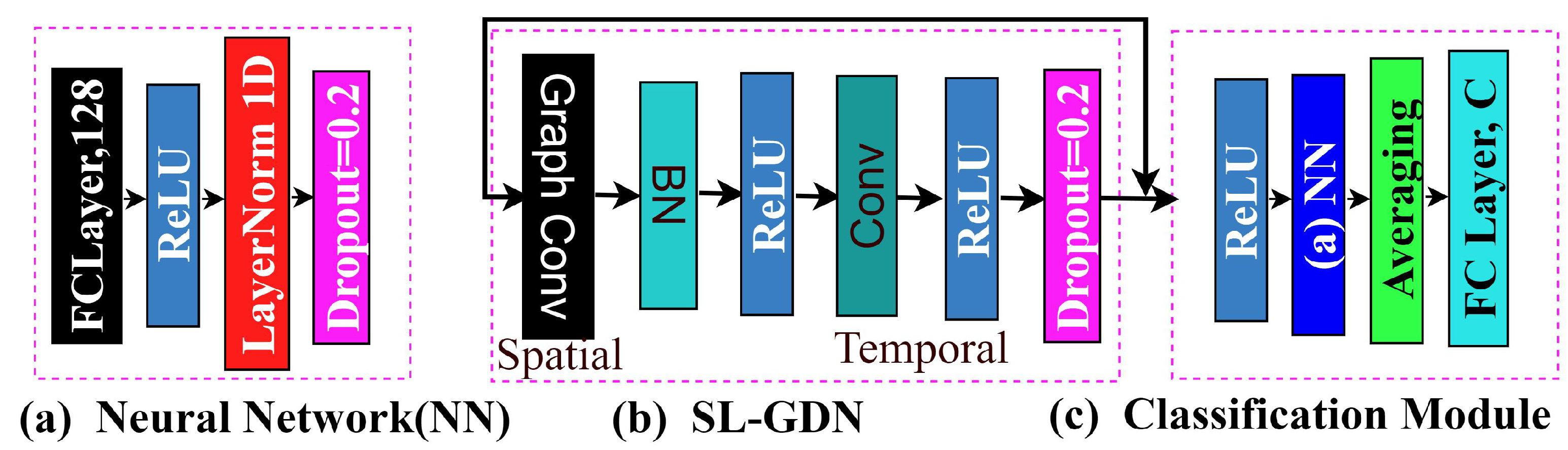
4.2. Neural Network (NN)
4.3. Graph Convolution
4.4. SL-GDN Architecture Block
4.5. Four-stream Approach
4.6. Classification Module
5. Experimental result
5.1. Environmental Setting
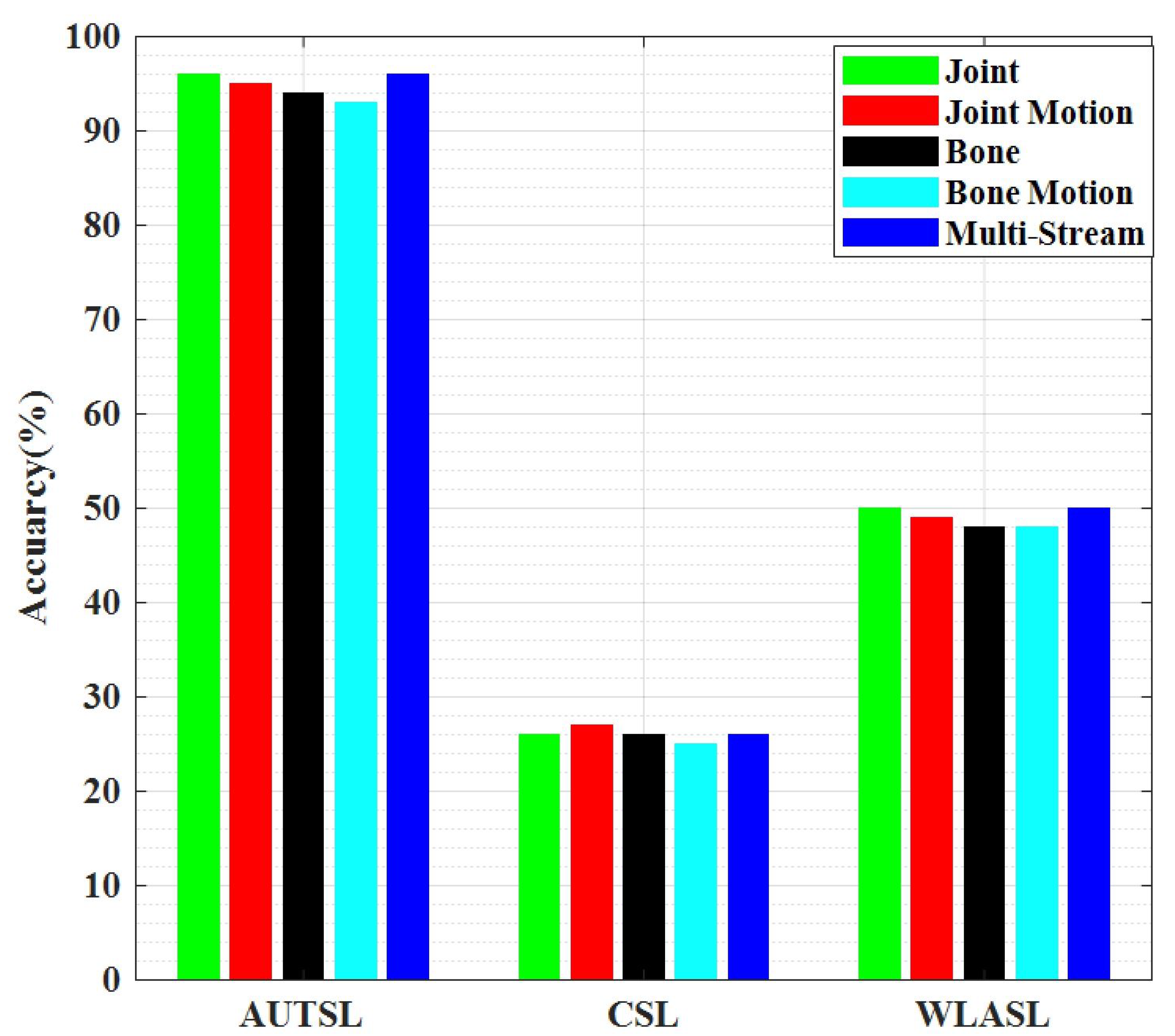
5.2. Performance Accuracy with the Three dataset
5.3. State of the art comparison of the proposed model with AUTSL Dataset
5.4. State of the art comparison of the proposed model with CSL Dataset
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Miah, A.S.M.; Hasan, M.A.M.; Shin, J. Dynamic Hand Gesture Recognition using Multi-Branch Attention Based Graph and General Deep Learning Model. IEEE Access 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miah, A.S.M.; Hasan, M.A.M.; Shin, J.; Okuyama, Y.; Tomioka, Y. Multistage Spatial Attention-Based Neural Network for Hand Gesture Recognition. Computers 2023, 12, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miah, A.S.M.; Shin, J.; Hasan, M.A.M.; Rahim, M.A. BenSignNet: Bengali Sign Language Alphabet Recognition Using Concatenated Segmentation and Convolutional Neural Network. Applied Sciences 2022, 12, 3933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miah, Abu Saleh Musa, S.J.; Hasan, M.A.M.; Rahim, M.A.; Okuyama, Y. Rotation, Translation And Scale Invariant Sign Word Recognition Using Deep Learning. Computer Systems Science and Engineering, 44.
- Miah, A.S.M.; Shin, J.; Islam, M.M.; Molla, M.K.I.; others. Natural Human Emotion Recognition Based on Various Mixed Reality (MR) Games and Electroencephalography (EEG) Signals. 2022 IEEE 5th Eurasian Conference on Educational Innovation (ECEI). IEEE, 2022, pp. 408–411.
- Miah, A.S.M.; Mouly, M.A.; Debnath, C.; Shin, J.; Sadakatul Bari, S. Event-Related Potential Classification Based on EEG Data Using xDWAN with MDM and KNN. International Conference on Computing Science, Communication and Security. Springer, 2021, pp. 112–126.
- Emmorey, K. Language, cognition, and the brain: Insights from sign language research; Psychology Press, 2001.
- Jiang, S.; Sun, B.; Wang, L.; Bai, Y.; Li, K.; Fu, Y. Skeleton aware multi-modal sign language recognition. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2021, pp. 3413–3423.
- Yang, Q. Chinese sign language recognition based on video sequence appearance modeling. 2010 5th IEEE Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications. IEEE, 2010, pp. 1537–1542.
- Valli, C.; Lucas, C. Linguistics of American sign language: An introduction; Gallaudet University Press, 2000.
- Mindess, A. Reading between the signs: Intercultural communication for sign language interpreters; Nicholas Brealey, 2014.
- Shin, J.; Musa Miah, A.S.; Hasan, M.A.M.; Hirooka, K.; Suzuki, K.; Lee, H.S.; Jang, S.W. Korean Sign Language Recognition Using Transformer-Based Deep Neural Network. Applied Sciences 2023, 13, 3029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miah, A.S.M.; Shin, J.; Hasan, M.A.M.; Molla, M.K.I.; Okuyama, Y.; Tomioka, Y. Movie Oriented Positive Negative Emotion Classification from EEG Signal using Wavelet transformation and Machine learning Approaches. 2022 IEEE 15th International Symposium on Embedded Multicore/Many-core Systems-on-Chip (MCSoC). IEEE, 2022, pp. 26–31.
- Miah, A.S.M.; Rahim, M.A.; Shin, J. Motor-imagery classification using Riemannian geometry with median absolute deviation. Electronics 2020, 9, 1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miah, A.S.M.; Islam, M.R.; Molla, M.K.I. Motor imagery classification using subband tangent space mapping. 2017 20th International Conference of Computer and Information Technology (ICCIT). IEEE, 2017, pp. 1–5.
- Lowe, D.G. Object recognition from local scale-invariant features. Proceedings of the seventh IEEE international conference on computer vision. Ieee, 1999, Vol. 2, pp. 1150–1157.
- Zhu, Q.; Yeh, M.C.; Cheng, K.T.; Avidan, S. Fast human detection using a cascade of histograms of oriented gradients. 2006 IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR’06). IEEE, 2006, Vol. 2, pp. 1491–1498.
- Dardas, N.H.; Georganas, N.D. Real-time hand gesture detection and recognition using bag-of-features and support vector machine techniques. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and measurement 2011, 60, 3592–3607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memiş, A.; Albayrak, S. A Kinect based sign language recognition system using spatio-temporal features. Sixth International Conference on Machine Vision (ICMV 2013). SPIE, 2013, Vol. 9067, pp. 179–183.
- Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, W.; Feng, B. Deep attention network for joint hand gesture localization and recognition using static RGB-D images. Information Sciences 2018, 441, 66–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, K.M.; Tan, A.W.C.; Lee, C.P.; Tan, S.C. Isolated sign language recognition using convolutional neural network hand modelling and hand energy image. Multimedia Tools and Applications 2019, 78, 19917–19944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, B.; Del Rio, A.M.; Keane, J.; Michaux, J.; Brentari, D.; Shakhnarovich, G.; Livescu, K. American sign language fingerspelling recognition in the wild. 2018 IEEE Spoken Language Technology Workshop (SLT). IEEE, 2018, pp. 145–152.
- Li, D.; Rodriguez, C.; Yu, X.; Li, H. Word-level deep sign language recognition from video: A new large-scale dataset and methods comparison. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF winter conference on applications of computer vision, 2020, pp. 1459–1469.
- Pigou, L.; Van Den Oord, A.; Dieleman, S.; Van Herreweghe, M.; Dambre, J. Beyond temporal pooling: Recurrence and temporal convolutions for gesture recognition in video. International Journal of Computer Vision 2018, 126, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sincan, O.M.; Tur, A.O.; Keles, H.Y. Isolated sign language recognition with multi-scale features using LSTM. 2019 27th signal processing and communications applications conference (SIU). IEEE, 2019, pp. 1–4.
- Tur, A.O.; Keles, H.Y. Isolated sign recognition with a siamese neural network of RGB and depth streams. IEEE EUROCON 2019-18th International Conference on Smart Technologies. IEEE, 2019, pp. 1–6.
- Huang, J.; Zhou, W.; Li, H.; Li, W. Attention-based 3D-CNNs for large-vocabulary sign language recognition. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology 2018, 29, 2822–2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, Q.; Li, H.; Li, W. Video-based sign language recognition without temporal segmentation. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2018, Vol. 32.
- Cheng, K.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, C.; Shi, L.; Cheng, J.; Lu, H. Decoupling gcn with dropgraph module for skeleton-based action recognition. Computer Vision–ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, August 23–28, 2020, Proceedings, Part XXIV 16. Springer, 2020, pp. 536–553.
- Shi, L.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, J.; Lu, H. Skeleton-based action recognition with multi-stream adaptive graph convolutional networks. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing 2020, 29, 9532–9545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.F.; Zhang, Z.; Shan, C.; Wang, L. Stronger, faster and more explainable: A convolutional graph baseline for skeleton-based action recognition. proceedings of the 28th ACM international conference on multimedia, 2020, pp. 1625–1633.
- Wang, H.; Wang, L. Modeling temporal dynamics and spatial configurations of actions using two-stream recurrent neural networks. Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2017, pp. 499–508.
- Yan, S.; Xiong, Y.; Lin, D. Spatial, temporal graph convolutional networks for skeleton-based action recognition. Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, 2018, Vol. 32.
- Oberweger, M.; Lepetit, V. Deepprior++: Improving fast and accurate 3d hand pose estimation. Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision Workshops, 2017, pp. 585–594.
- Shin, J.; Matsuoka, A.; Hasan, M.A.M.; Srizon, A.Y. American sign language alphabet recognition by extracting feature from hand pose estimation. Sensors 2021, 21, 5856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, S.; Xu, L.; Xu, J.; Wang, C.; Liu, W.; Qian, C.; Ouyang, W.; Luo, P. Whole-body human pose estimation in the wild. Computer Vision–ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, August 23–28–28, 2020, Proceedings, Part IX 16. Springer, 2020, pp. 196–214.
- Xiao, Q.; Qin, M.; Yin, Y. Skeleton-based Chinese sign language recognition and generation for bidirectional communication between deaf and hearing people. Neural networks 2020, 125, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mejía-Peréz, K.; Córdova-Esparza, D.M.; Terven, J.; Herrera-Navarro, A.M.; García-Ramírez, T.; Ramírez-Pedraza, A. Automatic recognition of Mexican Sign Language using a depth camera and recurrent neural networks. Applied Sciences 2022, 12, 5523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahim, M.A.; Miah, A.S.M.; Sayeed, A.; Shin, J. Hand gesture recognition based on optimal segmentation in human-computer interaction. 2020 3rd IEEE International Conference on Knowledge Innovation and Invention (ICKII). IEEE, 2020, pp. 163–166.
- Cai, Z.; Wang, L.; Peng, X.; Qiao, Y. Multi-view super vector for action recognition. Proceedings of the IEEE conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2014, pp. 596–603.
- Neverova, N.; Wolf, C.; Taylor, G.; Nebout, F. Moddrop: adaptive multi-modal gesture recognition. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 2015, 38, 1692–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, J.; Zhou, W.; Li, H. Iterative alignment network for continuous sign language recognition. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2019, pp. 4165–4174.
- Koller, O.; Zargaran, S.; Ney, H.; Bowden, R. Deep sign: Enabling robust statistical continuous sign language recognition via hybrid CNN-HMMs. International Journal of Computer Vision 2018, 126, 1311–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venugopalan, S.; Rohrbach, M.; Donahue, J.; Mooney, R.; Darrell, T.; Saenko, K. Sequence to sequence-video to text. Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, 2015, pp. 4534–4542.
- Cui, R.; Liu, H.; Zhang, C. A deep neural framework for continuous sign language recognition by iterative training. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia 2019, 21, 1880–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Zhou, W.; Li, H.; Wang, M. Hierarchical LSTM for sign language translation. Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, 2018, Vol. 32.
- Parelli, M.; Papadimitriou, K.; Potamianos, G.; Pavlakos, G.; Maragos, P. Exploiting 3D Hand Pose Estimation in Deep Learning-Based Sign Language Recognition from RGB Videos. Computer Vision – ECCV 2020 Workshops; Bartoli, A., Fusiello, A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2020; pp. 249–263. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, J.; Jiang, N.; Han, X.; Jia, K.; Lu, J. JOLO-GCN: Mining Joint-Centered Light-Weight Information for Skeleton-Based Action Recognition. 2021, pp. 2734–2743. [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Chen, S.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tian, Q. Actional-structural graph convolutional networks for skeleton-based action recognition. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2019, pp. 3595–3603.
- Li, S.; Li, W.; Cook, C.; Zhu, C.; Gao, Y. Independently recurrent neural network (indrnn): Building a longer and deeper rnn. Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2018, pp. 5457–5466.
- Shi, L.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, J.; Lu, H. Two-stream adaptive graph convolutional networks for skeleton-based action recognition. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2019, pp. 12026–12035.
- de Amorim, C.C.; Macêdo, D.; Zanchettin, C. Spatial-temporal graph convolutional networks for sign language recognition. Artificial Neural Networks and Machine Learning–ICANN 2019: Workshop and Special Sessions: 28th International Conference on Artificial Neural Networks, Munich, Germany, September 17–19, 2019, Proceedings 28. Springer, 2019, pp. 646–657.
- hen, Y.; Zuo, R.; Wei, F.; Wu, Y.; Liu, S.; Mak, B. Two-Stream Network for Sign Language Recognition and Translation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2211.01367 2022.
- Sincan, O.M.; Keles, H.Y. Autsl: A large scale multi-modal turkish sign language dataset and baseline methods. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 181340–181355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagliari, D.; Pinto, L. Calibration of kinect for xbox one and comparison between the two generations of microsoft sensors. Sensors 2015, 15, 27569–27589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Shahroudy, A.; Xu, D.; Wang, G. Spatio-temporal lstm with trust gates for 3d human action recognition. Computer Vision–ECCV 2016: 14th European Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, October 11-14, 2016, Proceedings, Part III 14. Springer, 2016, pp. 816–833.
- Paszke, A.; Gross, S.; Massa, F.; Lerer, A.; Bradbury, J.; Chanan, G.; Killeen, T.; Lin, Z.; Gimelshein, N.; Antiga, L.; others. Pytorch: An imperative style, high-performance deep learning library. Advances in neural information processing systems 2019, 32. [Google Scholar]
- Tock, K. Google CoLaboratory as a platform for Python coding with students. RTSRE Proceedings 2019, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Gollapudi, S. Learn computer vision using OpenCV; Springer, 2019.
- Dozat, T. Incorporating nesterov momentum into adam 2016.


| Dataset Name | Language Name | Year | Signes | Subjects | Total Sample | Sample Sign |
| WLASL [53] | Amercian | 2020 | 2000 | 119 | 21089 | 10.5 |
| AUTSL [54] | Turkish | 2020 | 226 | 43 | 38336 | 169.6 |
| CSL [23] | Chines | 2019 | 500 | 50 | 125000 | 250 |
| Stream | AUTSL | CSL | WLASL |
| Joint | 96.00 | 88.70 | 50.00 |
| Joint Motion | 95.00 | 87.00 | 49.00 |
| Bone | 94.00 | 86.00 | 48.00 |
| Bone Motion | 93.00 | 86.50 | 48.00 |
| Multi-Stream | 96.00 | 89.45 | 50.00 |
| Dataset Types | Method Name | Performance |
| RGB+Depth | CNN+FPM+LSTM+Attention [54] | 83.93 |
| Skeleton Joint | Jiang[8] | 95.02 |
| Skeleton Joint Motion | Jiang [8] | 94.70 |
| Skeleton Bone | Jiang [8] | 93.10 |
| Skeleton Bone Motion | Jiang [8] | 92.49 |
| Skeleton Multi-Stream | Jiang [8] | 95.45 |
| Skeleton Joint | Proposed Model | 96.00 |
| Skeleton Joint Motion | Proposed Model | 95.00 |
| Skeleton Bone | Proposed Model | 94.00 |
| Skeleton Bone Motion | Proposed Model | 93.00 |
| Skeleton Multi-Stream | Proposed Model | 96.45 |
| Dataset Name | Dataset Types | Methodology | Performance [%] |
| CSL | RGB-D+Skeleton | 3D-CNN [27] | 88.70 |
| Proposed Model | Skeleton | SL-GDN | 89.45 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





