1. Introduction
Kidney transplantation (KT) is the treatment of choice for end-stage renal disease. The success of kidney transplantation depends on many factors, including the compatibility of the donor and recipient, the quality of the transplanted organ, and the immune response of the recipient. (1) Delayed graft function (DGF) and acute rejection (AR) are common complications following kidney transplantation, which can have a negative impact on the long-term outcome of the allograft. (2) The identification of biomarkers for the development of DGF and AR may help to guide post-transplant management and improve the long-term outcome of KT. (3) The perfusion fluid of donated organs contains a wealth of information about the immunologic and metabolic state of the organ and the extent of any damage that may have occurred due to ischemic insult or other insults. (4) The proportion of T lymphocyte (T-Li) has been suggested to play a role in the development of DGF and AR following deceased donor KT. (5) The mechanisms underlying this association are not fully understood, and recently many studies have investigated the possible way to selectively suppress the immune reaction of the body against the donor organ by modulating T-Li in the transplant organ to reduce the triggering of an immune response in the recipient, leading to DGF and AR. (6) In addition, studies of similar models of IR after KT have shown the associations between the proportion of donor T-Li and the deleterious potential of ischemia-reperfusion injuries following organ revascularization (7-12). We therefore conducted a retrospective and monocentric study to evaluate its impact after graft reperfusion during KT in adults.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Donor Cohort and Liver Perfusate Fraction Analysis
the cellular concentrations and phenotypes of T-Li, Natural Killer (NK), and NK-T were analyzed retrospectively in a consecutive series of liver perfusates (LPs) after surgical removal of whole livers on the bench previously collected from adult multi-organ donors after brain death (DBD), and compared with the demographic and pathological characteristics of the patients transplanted at our Institute with kidneys taken from the same donors, as elsewhere published. (13) The liver interstitial cells were purified from the perfusate by density gradient centrifugation and the phenotype was determined by flow cytometric investigation using the following immunological markers: CD3, CD4, CD8 and CD56.
In order to determine the relative percentage of T-Li, NK-T and NK subpopulations, cells were first gated according to their expression of CD3 to discriminate between T-Li (CD3+CD56-), NK-T (CD3+CD56+) and NK cells (CD3-CD56+). T-Li were then further classified according to the expression of surface CD4 (helper T cells, Th) or CD8 (cytotoxic T lymphocytes, CTLs). Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells (PBMC) were used as control. In details, perfusates were collected during the back-table surgical time after the procurement procedures for a series of multiorgan deceased donor LT for adult patients at IRRCS-ISMETT, from 2010 to 2020. The following deceased brain donor (DBD) conditions were excluded to render homogenous the entire study population: allergy or autoimmune disease, pregnancy or active breast-feeding, donors requiring systemic immunosuppressive drug at the time of procurement, history of malignancy and of human immunodeficiency virus positivity, donor who had previously received an organ transplant. A sample of donor peripheral blood was collected in BD Vacutainer® Blood Collection Tube containing K2 ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (Becton, Dickinson and Company, Plymouth, UK). All of the graft procurement were performed at the same standard setting of perfusion pressure and temperature, with identical surgical instruments, and skilled medical and nursing staff, and using the same procedure, except for administering two different organ preservation solutions after cross-clamp maneuver: University of Wisconsin (UW; ViaSpan, DuPont Pharmaceuticals, Wilmington, DE, USA) or Celsior solution (SangStat Medical Corporation, Fremont, CA, USA). During liver procurement, the aorta was clamped and the liver flushed in situ via the hepatic artery with up to 5 L of preservation solution, to exsanguinate the deceased donor (in-situ fraction). LP is collected via a vacuum-pump suction system, available in the operating room where graft is excised, directly into auto-transfusion reservoir (ATR40; Fresenius-Kabi) using a sterile tubing system connected to a sterile draining system made up of suction tube with a cannule. Before perfusate is collected, the autotransfusion reservoirs are filled with anticoagulant Acid-Citrate-Dextrose (ACD, B223011, Fresenius-Kabi) in a volume such to have a finale concentration of ACD 10%. Liver perfusate procurement is performed under sterile conditions. At the end of procurement, reservoirs are closed with appropriate sterile lids, placed in correspondence of the connectors for suction and drainage tubes. Lids are secured with hose clamps.
After excision, the liver is placed in a sterile Isolation Bag (Steri-Drape 1003, 3M) and transferred in ISMETT in a thermally insulated containers in ice, to guarantee a constant temperature of about 4°C. Once in the IRCCS/ISMETT operating room, the liver is perfused through the portal vein with a further 1 to 2 L of the preservation solution (ex-situ or back-table fraction), as above, and left in the 3M Isolation Bag until the organ was transplanted. After the liver is removed from the 3M bag for engraftment, the residual perfusate in the perfusate 3M Isolation Bag is aspirated in a new ATR40 reservoir. All reservoirs containing liver perfusate are kept at 4°C until processing. LPs were was collected in sterile reservoirs (ATR40 as Fresenius-Kabi, Italy) in the presence of 10% of anticoagulant citrate dextrose formula-A, and progressively numbered.
The reservoirs were then transferred to the Regenerative Medicine and Biomedical Technology Unit – IRCCS/ISMETT for cell isolation. Lymphocyte phenotypic characterization was performed on the ex-situ fraction. Under laminar hood, liver graft perfusates were transferred from the auto-transfusion reservoir into 250 ml conicals (Corning GmbH HQ, Wiesbaden, Germany) and centrifuged at 2000 rpm, 10°C, 10 minutes (Multifuge 4KR, Heraeus, DJB Labcare Ltd, Newport Pagnell, England).
Contaminating erythrocytes were lysed using ACK buffer (10-548E, Lonza, Euroclone S.p.a., Italy) for 5 minutes at room temperature, cells were washed 2x with Dulbecco′s phosphate buffered saline (PBS) (D8537, Sigma-Aldrich s.r.l, Milan, Italy), 2% Fetal Bovine Serum (FBS) (F7524, Sigma-Aldrich s.r.l, Milan, Italy) and cell number and vitality were obtained by Trypan Blue exclusion (17-942E, Lonza, Euroclone S.p.a., Italy). T-Li, NK, and NKT cells concentrations and phenotypes were analyzed.
2.2. Flow Cytometry Staining of Lymphocytes and Antibody
Aliquots of 1 × 106 isolated liver-derived cells and PBMC were stained for surface markers with a panel of pre-diluted fluorochrome-conjugated anti-human monoclonal antibodies: BD Multitest™ CD3/CD16+CD56/CD45/CD19 reagent (CD3-FITC (IgG2a, clone SK7); CD16-PE (IgG1, clone B73.1) and CD56-PE (IgG1, clone NCAM 16.2); CD45-PerCP (IgG1, clone 2D1); CD19-APC (IgG1, clone SJ25C1)), CD3-FITC (IgG2a, clone SK7); CD4-PE-Cy7 (IgG1, clone L200); CD8-APC-Cy7 (IgG1, clone SK1); CD56-AlexaFluor-700 (IgG1, clone B159); antiCD337/NKp30-AlexaFluor-647 (IgG1, clone p30-15); CD335/NKp46-PE-Cy7 (IgG1, clone 9E2/Nkp46); CD314/NKG2D-PerCP-Cy5.5 (IgG1, clone 1D11). These antibodies were purchased from BD Biosciences (Europe, dilution 1:10). CD3-PerCP (IgG2a, clone BW264/56); CD16-APC (IgM, clone VEP13); CD161-FITC (IgG2a, clone 191B8); CD336/NKp44-PE (IgG1, clone 2.29) were purchased from Miltenyi Biotec, (Bergisch Gladbach; Germany dilution 1:20). TCRVa7.2-PE (IgG1, clone 3C10) was purchased from Biolegend (Campoverde s.r.l., Milan, Italy, dilution 1:25). Samples were incubated for 30 minutes at room temperature in the dark, washed once with PBS/2% FBS and then analyzed by flow cytometry with FACSAria II dual-laser 8-colors cytometer (BD Biosciences, Europe). Acquired data were analyzed with FACSDiva software 6.1.3.
2.3. Recipient Cohort and Study Endpoints
All of KT recipients with kidney grafts procured from liver adult DBDs) and liver deceased after circulatory death (DCD) donors were initially included. We excluded patients who underwent dual KT and/or combined solid organ transplantation, and a recipient who underwent KT with a graft procured from a DBD affected with thrombotic micro-angiopathy, and recipients of a living donor transplant. Kidney with prolonged ischemia time (> 20 hours) as a result of extra-regional donors, while awaiting cross-match results and recipient preoperative dialysis, and DCD kidney were preserved at 4°C with hypothermic machine perfusion (HMP) (Kidney Assist® Organ Assist Product, Groningen, The Netherlands), with a fixed systolic perfusion pressure of 25 mmHg. (13) Duration of HMP, perfusion parameters, such as flow, renal resistance (RR) and pressure were recorded. The primary end points of this study were the incidence of delayed graft function (DGF) defined as acute kidney injury (AKI) needing dialysis within 1week of transplantation, (1) incidence of early graft loss (EGL) at 6 months after KT, overall and intensive care unit (ICU) length of stay, operating room readmission, hospital readmission (within 30 days), biopsy-proven acute cellular, humoral and vascular rejection episodes, and post-operative complications such as onset of secondary infection from Cytomegalovirus (CMV).
2.4. Statistical Analysis
The T-Li median value of flow cytometric results were used to divide the LP population in two subgroups (inferior vs. equal or superior of the median ranks). Significant differences among these groups were determined comparing continuous variables with the Student t test or the Wilcoxon rank-sum test, and categorical variables with the chi-square test or Fisher's exact test, as appropriate. Multiple logistic regression analysis was used to identify independent risk factors from those variables that were identified as statistically significant in group comparison tests: odds ratios (ORs) with the corresponding 95% confidence interval (95% CI) were calculated. Donor characteristics were were collected prospectively from electronic medical records. The following DBD variables were included in these analyses: age, gender, height, weight, body mass index (BMI), cause of death, ICU length of stay, macrovesicular steatosis, hemodynamic risk factors, including use of amine for more than 6 hours to sustain blood pressure for prolonged hypotension (systolic blood pressure < 60 mm Hg for more than 2 hours), cold ischemic time (CIT), natremia and donor liver function tests (aspartate aminotransferase – AST, alanine aminotransferase – ALT, gamma-glutamyl transferase – GGT, total bilirubin) before aortic cross clamp, viral serologic markers, donor bacterial infections, and history of diabetes or glucose intolerance. Early-Graft-Loss/Donor Risk-Index (EGL-DRI) was analyzed as semi-continuous variables to consider a multifactorial scoring system to identify livers at highest risk of early graft dysfunction and failure. (14)
Linear regression analysis were performed for semi-continuous variable, when significant univariate associations to the different percentage of cellular fractions were determined. Statistical significance was determined at p < 0.05. Data handling and analyses were done with SAS software version 9.4.
2.5. Ethical Validation
The study was conducted in accordance with the principles outlined in the Declaration of Helsinki of 1996 and the institutional research review board (IRRB) approved the protocol (protocol number IRRB/14/15).
3. Results
All livers were used for transplant purposes at ISMETT. Of the kidneys recovered (n = 84), 42 were transplanted by our center while the remaining 42 were assigned to other centers in Sicily. The LPs and the related clinical outcome of these kidney transplant recipients from 2010 to 2020, were analyzed. Donors’ and recipients’ characteristics are described in table 1. (
Table 1)
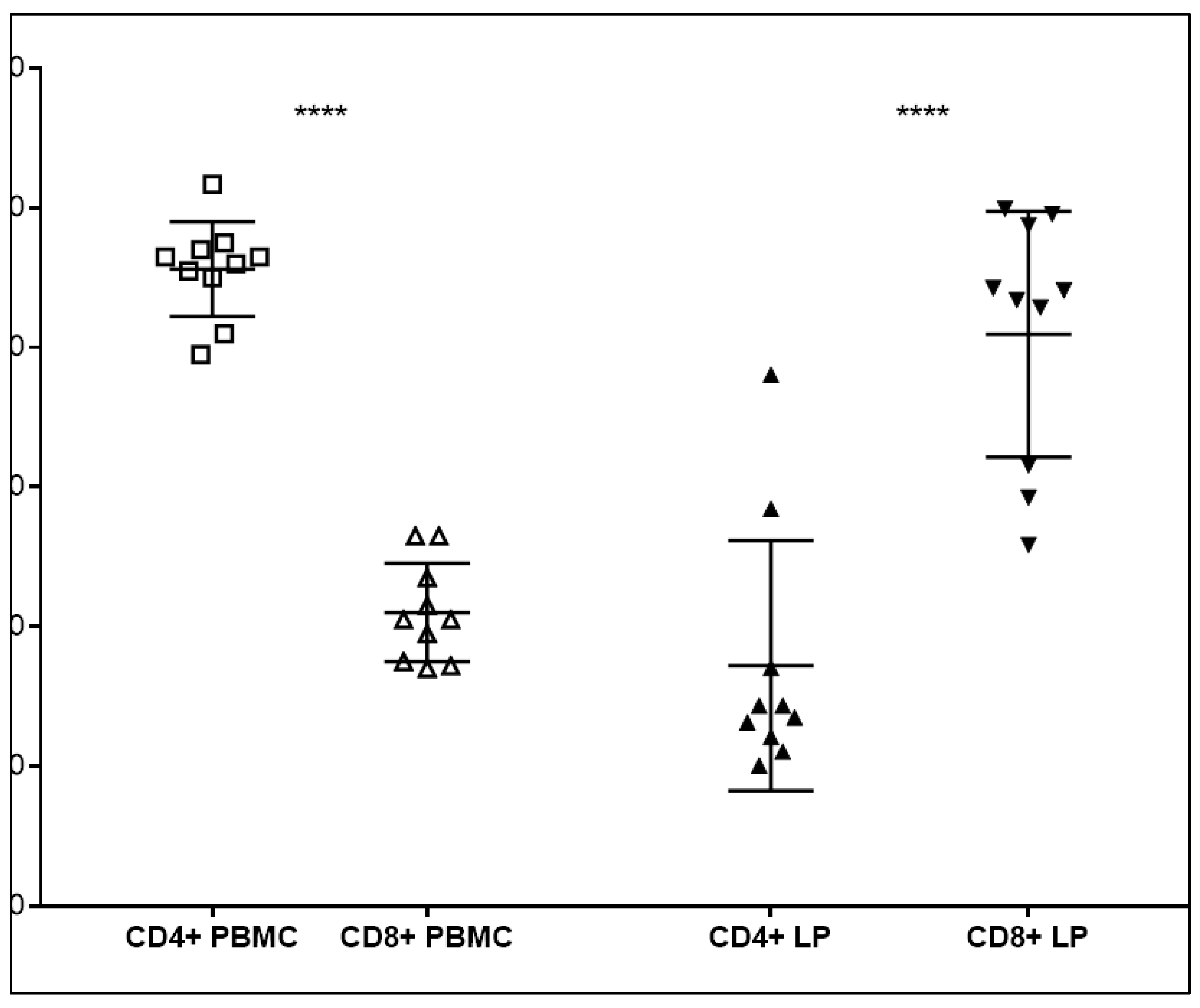
The proportion of CD8+ CTLs was significantly increased compared to CD4+ T helper cells in the LPs. By contrast, the opposite ratio was observed in matched PBMC. The median percentages of T-Li was 25.0%, based on the entire lymphocytic population obtained by cytofluorimetric analyses.
The LP specific pattern of T-Li, NK, and NKT cells were not influenced by the two different organ preservation solutions. Neither gender, nor a history of viral infection, diabetes or glucose intolerance, cardiac arrest, or amine infusion had any correlation with different lymphocyte proportions obtained from DBD liver perfusate. DBD LPs with CD3+CD56- T lymphocytes below 25% had a percent of CD8+ T-cells as high as 88.9% of total T-cells. CD8+ T cells percent of total T-cells in the perfusate was lower (64.7%) among DBDs with more than 25% of perfusate leucocytes were CD3+ T cells. A significant association between low T-cell proportion and cold ischemia time was found. Average cold ischemia time was 522 ± 443.6 min in DBD liver perfusate with T-cell percentage below 25% of total cells (T-test, p = 0.03). (
Table 2)
Ex-situ LPs were collected during the pre-transplantation albumin perfusion of a series of 46 DBD livers on the bench, with a mean CIT of 481 ± 122.8 min. and an average donor age of 52 ± 19.6 years. The DBDs were female in 24 cases and the main cause of death was a cerebro-vascular accident in 29 donors. The population of CD4+ T helper cells was significanlty higher in the PBMC of donors. By contrast, CD8+ cytotoxic T cells were highly represented in the backtable fraction of the liver perfusate of matched donors and significantly more abundant compared to CD4+ T cells (P<0.0001). (
Figure 1)
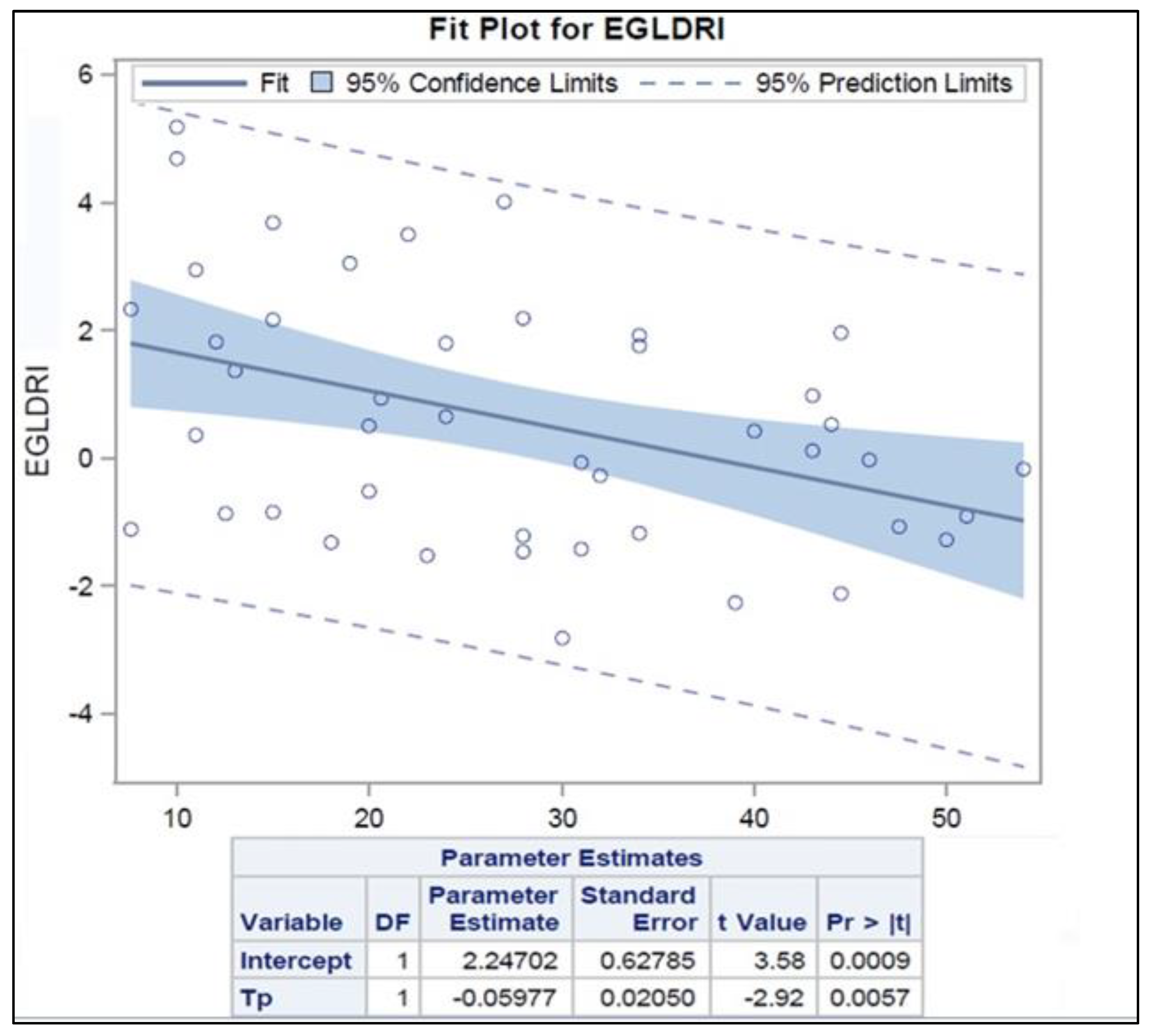
Percent T-Li number was significantly associated with cold ischemia time (p= 0.02), and EGL-DRI score (p = 0.01). Increasing the percentage of T-cell by one the EGL-DRI decreases by 0.06, (p-value = 0.006). (
Figure 2)
T-Li were significantly associated with the time in days of delayed functional recovery of transplanted kidneys (DGF) (p = 0.02), to onset of secondary infection from Cytomegalovirus (p = 0.03). On COX analysis, percent cell concentration of T-Li and time to DGF were significantly associated with an increased relative risk (HR) of organ survival (HR = 1.038, p = 0.04; and HR = 1.029, p = 0.01, respectively). The specificity of the NK and NK-T cell proportions were not associated with any relevant clinical outcomes in kidney transplant patients.
4. Discussion
Organ transplantation is a life-saving therapy for end-stage organ diseases. However, organ shortage remains a significant challenge in this field. Therefore, it is essential to optimize the use of available organs by ensuring their viability and function. (1) One of the ways to achieve this is through the use of organ perfusion. (16) The ultimate goal of organ perfusion is to maintain the organ viability and function by providing oxygen and nutrients to the cells while removing waste products. (17) This is particularly important in liver and/or kidney transplantation, where the organ is susceptible to ischemia-reperfusion injury, which can lead to primary non-function or DGF. The use of perfusion can reduce the risk of complications and improve the success rate of transplantation. (18)
The most common method of dynamic perfusion in liver transplantation is the use of HMP, which involves cooling the organ to 4°C and circulating a preservation solution through the blood vessels. HMP has been shown to improve organ function and reduce the risk of complications compared to cold storage. (19, 20) Another method of dynamic perfusion is normothermic machine perfusion (NMP), which involves perfusing the organ at body temperature. NMP has been shown to be effective in reducing ischemia-reperfusion injury and improving organ function. NMP can also be used to assess the viability of marginal organs and to repair them ex-vivo before transplantation. (21) Both HMP and NMP have been shown to be effective in preserving organ function and reducing the risk of ischemia-reperfusion injury. NMP has the additional advantage of allowing for ex-vivo repair of marginal organs. Further research is needed to optimize the use of organ perfusion in liver transplantation and to explore its potential applications in other types of organ transplantation. (22) During the transplantation process, the liver graft is exposed to a variety of pro-inflammatory stimuli, such as ischemia-reperfusion injury and release of damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs), which activate innate immune cells such as neutrophils and macrophages. These cells then produce pro-inflammatory cytokines and reactive oxygen species, leading to tissue damage and inflammation. This process can also affect the renal allograft, which is located near the liver and shares the same blood supply. In particular, activation of the innate immune system can cause early renal allograft injury, which is characterized by acute tubular necrosis and endothelial damage. This can lead to impaired renal function, longer hospital stays, and increased risk of graft loss. (23, 24)
Several studies have suggested that the presence of certain innate immune cells, such as neutrophils and monocytes, in the peripheral blood can serve as predictive biomarkers of early renal allograft injury. By monitoring these cells before and after transplantation, clinicians may be able to identify patients who are at increased risk of renal injury and provide them with more aggressive monitoring and treatment. In the liver reside a big number of immune cells, which maintain the homeostasis between tolerance and inflammation. Liver-resident immune cells infiltrating the sinusoids include professional antigen-presenting cells, myeloid cells, and innate and adaptive lymphocytes. There is evidence that ischemia reperfusion injury-associated inflammation is reduced in machine-perfused livers. However the role of MP on the activation state and function of the hepatic immune-cell repertoire is not clear yet. It remains to be assessed if liver-resident immune cells exert a pro-inflammatory destructive function on machine-perfused organs, or on the contrary mediate liver regeneration and counteract liver damage. Upon inflammation, hepatic NK cells, macrophages and neutrophils, induces the inflammatory cascade and further initiates the adaptive immune response mediated by T and B cells. However, immune cells resident in the liver have been shown to have a protective anti-inflammatory role for the liver, mediating liver regeneration. Neutrophils for example produce ROS and cytokines, perform formation of neutrophil extracellular traps (NET)osis, phagocytosis, proteolysis, and induce angiogenesis, which damage hepatocytes, enhance local inflammation and promote graft rejection. By contrast, neutrophils have been shown to participate in tissue regeneration by clearing necrotic debris. Likewise, NK cells have cytotoxic functions and are implicated in tissue damage by releasing pro-inflammatory cytokines like IFN-γ and TNF-α. However, there is also evidence that NK cell populations have immune-regulatory functions. NK cells also work against biliary epithelial cells and contribute to hinder fibrosis through killing of hepatic stellate cells. A high proportion of hepatic NK cells express the inhibitory receptor NKG2A by which depleted activated T cells and mediate tolerance induction after liver transplantation. The liver adaptive immune response is driven by CD4 and CD8 T cells. CD8 T recognize peptides from intracellular pathogens in the context of MHC I and produce cytokines, such as IFN-γ and TNF-α, and initiate cytotoxic reaction mediated by the release of further granule contents like perforin and granzyme and by triggering Fas-mediated apoptosis. It has been reported that human livers subjected to NMP have reduced numbers of pro-inflammatory cytokines IFN-γ CD8 T cells. CD4 and CD8 T cells are primarily involved in the pathogenesis of IRI. Recently, it was demonstrated that NMP significantly increased the proportion of T-Li in the perfusate throughout the course of perfusion thus suggesting that donor tissue T-Li are mobilized into the perfusate during perfusion. (13)
In deceased donor kidney transplantation, the proportion of donor T lymphocyte has been suggested to play a role in the development of DGF, AR, and allograft outcome. Studies have reported a significant association between a higher proportion of donor T lymphocyte and an increased risk of worse outcomes. The mechanisms underlying this association are not fully understood, but it is hypothesized that the presence of donor T lymphocyte in the transplant organ may trigger an immune response in the recipient, leading to DGF and AR. It is difficult to speculate on the impact of liver phenotype on graft survival as some immune populations might have a dual controversial impact on tissue integrity. However it appears clear how the immunological signature plays a fundamental role on the fitness and fate of immune organs, such as the liver, after transplantation. The possibility to mobilize before transplantation unwanted immune cells that might pose at risk graft survival represents a great challenge. Equally important is the method of organ perfusion to guarantee tissue preservation and cellular recovery. Shortage of donations had led to the use sub-optimal organs and identification of the best biomarkers of organ viability and function are subject of research in many laboratories. The possibility to identify the immunological signature of liver perfusate to define available organs to be transplanted would improve utilization of the pool of potential donor organs. In parallel, the identification of detrimental immune factors would permit development of organ treatment protocols prior to implantation to abrogate ischemia-reperfusion, and immunomodulation to prevent rejection. (25, 26)
Here we show that by using perfusion of the liver perfusate, it is possible to assess the quality of the organ and identify potential criticisms before transplantation, thereby reducing the risk of complications and improving the success rate of transplantation. The present study points to a new potential role of T-Li detected in the context of liver perfusate DBD, and could detect potential impacts in organ allocation, surgical recovering techniques and in the analysis of IRI pathophysiological events after kidney transplants from multi-organ DBDs. Our data are obtained by flow cytometry analysis of the phenotype of liver perfusate from deceased donors. Flow cytometry allows to obtain very rapidly detailed phenotyping of the cellular product from perfusion of the liver. A fast result would permit to routinely phenotype donor’s livers before organ allocation. Also, it would help determine the need for induction therapy, the development of personalized protocols for post-renal transplant immunotherapy and monitoring of rejection. However, here we describe a retrospective study which might suffer from selection bias for donor inclusion criteria. Additionally, it is difficult to predict how specific characteristics associated to DBD might influence the homing of donor T cells, thus suggesting that non-specific inflammatory signals related to brain death may alter adaptive immunity.
Accurate and, especially, early identification and monitoring of patients with increased risk for IRI and IRI-related clinical complications following KT is elementary to guide clinical decision-making and to select those patients who might benefit from novel prophylactic treatment. Some studies have provided insights on how innate immune cells like neutrophils, monocytes and NK cells were reliable prognostic markers for the detection and monitoring of IRI on different days in the postoperative course after KT and also for predicting IRI-associated early graft dysfunction and clinical complications. (22-28)
The resulting risk groups according to our proposed marker cutoff levels based on the quantitative and qualitative phenotyping of the population of CD8 T cells and on the CD4/CD8 ratio is a tool for risk stratification and better risk-adapted monitoring for perioperative complications following transplantation compared to established clinical and paraclinical criteria such as CIT, recipient characteristics (e.g., BMI) or special donor variables. In the light of this, the future treatment of IRI-induced organ damage may lie in targeting the inflammatory responses of IRI by aiming at pathways of both the innate and the adaptive immune system. This might also apply at different time points, during the process of graft and recipient conditioning before and during the transplantation, and in the early and late postoperative period. With these multimodal approaches, perhaps in combination with techniques already applied, such as ischemic or volatile anesthetic-induced preconditioning, we might succeed in the future to reduce the detrimental effects of IRI and thereby improve long-term graft outcome after kidney transplantation. This approach is particularly important in the context of organ transplantation, where the timely detection of organ damage can be critical for successful transplantation and patient outcomes. (28, 29) By using the perfusion fluid of donated organs as a kind of liquid biopsy, clinicians may be able to identify patients who are at increased risk of organ damage following transplantation and provide them with more aggressive monitoring and treatment, which can ultimately improve outcomes for transplant recipients and reduce the risk of graft loss. (17, 24)
5. Conclusion:
The proportion of donor T lymphocyte is a potential biomarker for the development of DGF and allograft outcome following deceased donor kidney transplantation. Studies have reported a significant association between a higher proportion of donor T lymphocyte and an increased risk of DGF and a worse allograft outcome. Further studies are needed to confirm these findings and to investigate the mechanisms underlying this association. The identification of biomarkers for the development of DGF may help to guide post-transplant management and improve the long-term outcome of KT.
Author Contribution
Duilio Pagano and Ester Badami have equally participated to conceptualization, design, supervision, methodology, data collection, analysis, interpretation and writing. Caterina Accardo, Giovanni Zito, Barbara Buscemi, Giandomenico Amico, Rosalia Busà, Sergio Li Petri, Fabrizio di Francesco, Sergio Calamia, Pasquale Bonsignore and Alessandro Tropea have participated to data collection, interpretation, review and editing. Fabio Tuzzolino has participated to statistical analysis. Ivan Vella, Salvatore Piazza, Paola Salis have participated to data collection, methodology, analysis of the data, review and editing. PierGiulio Conaldi and Salvatore Gruttadauria have participated to analysis and interpretation of the data, review and editing. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests. This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Abbreviations
ACD: Acid-Citrate-Dextrose; AKI: acute kidney injury; ALT: alanine amino transaminase; AP: alkaline phosphatase; AR: acute rejection; AST: aspartate amino transaminase; CI: confidence interval; CMV: Cytomegalovirus; CTL: cytotoxic T lymphocyte; DAMP: damage-associated molecular pattern; DBD: deceased brain donor; DGF: delayed graft function; DRI: donor risk index; EGL: early graft loss; FBS: Fetal Bovine Serum; GGT: gamma-glutamyl transferase; ICU: intensive care unit; IFN-γ: interferon gamma; IRI: ischemia-reperfusion injury; IRRB: institutional research review board; KT: kidney transplantation; LP: liver perfusate; NET: neutrophil extracellular traps; NK: Natural Killer; PBMC: peripheral blood mononuclear cells; PBS: phosphate buffered saline; RBC: packed red blood cells; Th: helper T cells; T-Li: T-lymphocytes; TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor alfa.
References
- Swanson KJ, Bhattarai M, Parajuli S. Delayed graft function: current status and future directions. Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2023, 28, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim WH, Johnson DW, Teixeira-Pinto A, Wong G. Association Between Duration of Delayed Graft Function, Acute Rejection, and Allograft Outcome After Deceased Donor Kidney Transplantation. Transplantation. 2019, 103, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morath C, Schmitt A, Kleist C, Daniel V, Opelz G, Süsal C, Ibrahim E, Kälble F, Speer C, Nusshag C, Pego da Silva L, Sommerer C, Wang L, Ni M, Hückelhoven-Krauss A, Czock D, Merle U, Mehrabi A, Sander A, Hackbusch M, Eckert C, Waldherr R, Schnitzler P, Müller-Tidow C, Hoheisel JD, Mustafa SA, Alhamdani MS, Bauer AS, Reiser J, Zeier M, Schmitt M, Schaier M, Terness P. Phase I trial of donor-derived modified immune cell infusion in kidney transplantation. J Clin Invest. 2020, 130, 2364–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Leur K, Dieterich M, Hesselink DA, Corneth OBJ, Dor FJMF, de Graav GN, Peeters AMA, Mulder A, Kimenai HJAN, Claas FHJ, Clahsen-van Groningen MC, van der Laan LJW, Hendriks RW, Baan CC. Characterization of donor and recipient CD8+ tissue-resident memory T cells in transplant nephrectomies. Sci Rep. 2019, 9, 5984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahn N, Sack U, Stehr S, Vöelker MT, Laudi S, Seehofer D, Atay S, Zgoura P, Viebahn R, Boldt A, Hau HM. The Role of Innate Immune Cells in the Prediction of Early Renal Allograft Injury Following Kidney Transplantation. J Clin Med. 2022, 11, 6148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayachandran R, Gumienny A, Bolinger B, Ruehl S, Lang MJ, Fucile G, Mazumder S, Tchang V, Woischnig AK, Stiess M, Kunz G, Claudi B, Schmaler M, Siegmund K, Li J, Dertschnig S, Holländer G, Medina E, Karrer U, Moshous D, Bumann D, Khanna N, Rossi SW, Pieters J. Disruption of Coronin 1 Signaling in T Cells Promotes Allograft Tolerance while Maintaining Anti-Pathogen Immunity. Immunity. 2019, 50, 152–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zito G, Miceli V, Carcione C, Busà R, Bulati M, Gallo A, Iannolo G, Pagano D, Conaldi PG. Human Amnion-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal/Stem Cells Pre-Conditioning Inhibits Inflammation and Apoptosis of Immune and Parenchymal Cells in an In Vitro Model of Liver Ischemia/Reperfusion. Cells. 2022, 11, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safinia N, Afzali B, Atalar K, Lombardi G, Lechler RI. T-cell alloimmunity and chronic allograft dysfunction. Kidney Int Suppl. 2010, 119, S2–S12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scandling JD, Busque S, Dejbakhsh-Jones S, Benike C, Millan MT, Shizuru JA, Hoppe RT, Lowsky R, Engleman EG, Strober S. Tolerance and chimerism after renal and hematopoietic-cell transplantation. N Engl J Med. 2008, 358, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noris M, Azzollini N, Mister M, Pezzotta A, Piccinini G, Casiraghi F, Cugini D, Perico N, Orisio S, Remuzzi G. Peripheral donor leukocytes prolong survival of rat renal allografts. Kidney Int. 1999, 56, 1101–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salgar SK, Shapiro R, Dodson F, Corry R, McCurry K, Zeevi A, Pham S, Abu-Elmagd K, Reyes J, Jordan M, Keenan R, Griffith B, Sesky T, Ostrowski L, Starzl TE, Fung JJ, Rao AS. Infusion of donor leukocytes to induce tolerance in organ allograft recipients. J Leukoc Biol. 1999, 66, 310–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Besouw NM, van der Mast BJ, de Kuiper P, Smak Gregoor PJ, Vaessen LM, IJzermans JN, van Gelder T, Weimar W. Donor-specific T-cell reactivity identifies kidney transplant patients in whom immunosuppressive therapy can be safely reduced. Transplantation. 2000, 70, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pagano D, Badami E, Conaldi PG, Seidita A, Tuzzolino F, Barbàra M, di Francesco F, Tropea A, Liotta R, Chiarello G, Luca A, Gruttadauria S. Liver Perfusate Natural Killer Cells From Deceased Brain Donors and Association With Acute Cellular Rejection After Liver Transplantation: A Time-to-Rejection Analysis. Transplantation. 2019, 103, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonsignore P, Pagano D, Piazza S, Ricotta C, di Francesco F, Cintorino D, Li Petri S, Canzonieri M, Tropea A, Calamia S, Checchini G, Salis P, Arcadipane A, Liotta R, Gruttadauria S. Crucial Role of Extended Criteria Donors in Deceased Donor Single Kidney Transplantation to Face Chronic Shortage in the Heart of the Mediterranean Basin: A Single-Center Experience. Transplant Proc. 2019, 51, 2868–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelico M, Nardi A, Romagnoli R, Marianelli T, Corradini SG, Tandoi F, Gavrila C, Salizzoni M, Pinna AD, Cillo U, Gridelli B, De Carlis LG, Colledan M, Gerunda GE, Costa AN, Strazzabosco M; Liver Match Study Investigators. A Bayesian methodology to improve prediction of early graft loss after liver transplantation derived from the liver match study. Dig Liver Dis. 2014, 46, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh N, Logan A, Schenk A, Bumgardner G, Brock G, El-Hinnawi A, Rajab A, Washburn K. Machine perfusion of kidney allografts affects early but not late graft function. Am J Surg. 2022, 223, 804–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhee, EP. Kidney-specific metabolomic profiling in machine perfusate. Kidney Int. 2023, 103, 661–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellini MI, Bonaccorsi Riani E, Giorgakis E, Kaisar ME, Patrono D, Weissenbacher A. Organ Reconditioning and Machine Perfusion in Transplantation. Transpl Int. 2023, 36, 11100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malinoski D, Saunders C, Swain S, Groat T, Wood PR, Reese J, Nelson R, Prinz J, Kishish K, Van De Walker C, Geraghty PJ, Broglio K, Niemann CU. Hypothermia or Machine Perfusion in Kidney Donors. N Engl J Med. 2023, 388, 418–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlegel A, Mueller M, Muller X, Eden J, Panconesi R, von Felten S, Steigmiller K, Sousa Da Silva RX, de Rougemont O, Mabrut JY, Lesurtel M, Cerisuelo MC, Heaton ND, Allard MA, Adam R, Monbaliu D, Jochmans I, Haring MPD, Porte RJ, Parente A, Muiesan P, Kron P, Attia M, Kollmann D, Berlakovich G, Rogiers X, Petterson K, Kranich AL, Amberg S, Müllhaupt B, Clavien PA, Dutkowski P. A multicenter randomized-controlled trial of hypothermic oxygenated perfusion (HOPE) for human liver grafts before transplantation. J Hepatol. 2023, 78, 783–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazilescu LI, Urbanellis P, Kim SJ, Goto T, Noguchi Y, Konvalinka A, Reichman TW, Sayed BA, Mucsi I, Lee JY, Robinson LA, Ghanekar A, Selzner M. Normothermic Ex Vivo Kidney Perfusion for Human Kidney Transplantation: First North American Results. Transplantation. 2022, 106, 1852–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mawad H, Pinard L, Medani S, Chagnon M, Boucquemont J, Turgeon J, Dieudé M, Hamelin K, Rimbaud AK, Belayachi A, Yang B, Collette S, Sénécal L, Foster BJ, Hébert MJ, Cardinal H. Hypothermic Perfusion Modifies the Association Between Anti-LG3 Antibodies and Delayed Graft Function in Kidney Recipients. Transpl Int. 2023, 36, 10749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu RX, Koyawala N, Thiessen-Philbrook HR, Doshi MD, Reese PP, Hall IE, Mohan S, Parikh CR. Untargeted metabolomics of perfusate and their association with hypothermic machine perfusion and allograft failure. Kidney Int. 2023, 103, 762–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peris A, Fulceri GE, Lazzeri C, Bonizzoli M, Li Marzi V, Serni S, Cirami L, Migliaccio ML. Delayed graft function and perfusion parameters of kidneys from uncontrolled donors after circulatory death. Perfusion. 2021, 36, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stringer D, Gardner L, Shaw O, Clarke B, Briggs D, Worthington J, Buckland M, Danzi G, Hilton R, Picton M, Thuraisingham R, Borrows R, Baker R, McCullough K, Stoves J, Phanish M, Shah S, Shiu KY, Walsh SB, Ahmed A, Ayub W, Hegarty J, Tinch-Taylor R, Georgiou E, Bidad N, Kılıç A, Moon Z, Horne R, McCrone P, Kelly J, Murphy C, Peacock J, Dorling A. Optimized immunosuppression to prevent graft failure in renal transplant recipients with HLA antibodies (OuTSMART): a randomised controlled trial. EClinicalMedicine. 2023, 56, 101819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brulé N, Canet E, Péré M, Feuillet F, Hourmant M, Asehnoune K, Rozec B, Duveau A, Dube L, Pierrot M, Humbert S, Tirot P, Boyer JM, Martin-Lefevre L, Labadie F, Robert R, Benard T, Kerforne T, Thierry A, Lesieur O, Vincent JF, Lesouhaitier M, Larmet R, Vigneau C, Goepp A, Bouju P, Quentin C, Egreteau PY, Huet O, Renault A, Le Meur Y, Venhard JC, Buchler M, Michel O, Voellmy MH, Herve F, Schnell D, Courte A, Glotz D, Amrouche L, Hazzan M, Kamar N, Moal V, Bourenne J, Le Quintrec-Donnette M, Morelon E, Boulain T, Grimbert P, Heng AE, Merville P, Garin A, Hiesse C, Fermier B, Mousson C, Guyot-Colosio C, Bouvier N, Rerolle JP, Durrbach A, Drouin S, Caillard S, Frimat L, Girerd S, Albano L, Rostaing L, Bertrand D, Hertig A, Westeel PF, Montini F, Delpierre E, Dorez D, Alamartine E, Ouisse C, Sebille V, Reignier J. Impact of targeted hypothermia in expanded-criteria organ donors on recipient kidney-graft function: study protocol for a multicentre randomised controlled trial (HYPOREME). BMJ Open. 2022, 12, e052845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morath C, Schmitt A, Schmitt M, Wang L, Kleist C, Opelz G, Süsal C, Tran TH, Scherer S, Schwenger V, Kemmner S, Fischereder M, Stangl M, Hauser IA, Sommerer C, Nusshag C, Kälble F, Speer C, Benning L, Bischofs C, Sauer S, Schubert ML, Kunz A, Hückelhoven-Krauss A, Neuber B, Mehrabi A, Schwab C, Waldherr R, Sander A, Büsch C, Czock D, Böhmig GA, Reiser J, Roers A, Müller-Tidow C, Terness P, Zeier M, Daniel V, Schaier M. Individualised immunosuppression with intravenously administered donor-derived modified immune cells compared with standard of care in living donor kidney transplantation (TOL-2 Study): protocol for a multicentre, open-label, phase II, randomised controlled trial. BMJ Open. 2022, 12, e066128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrosi G, Vizzini GB, Gruttadauria S, Gridelli B. Clinical applications of hepatocyte transplantation. World J Gastroenterol. 2009, 15, 2074–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruttadauria S, di Francesco F, Vizzini GB, Luca A, Spada M, Cintorino D, Li Petri S, Pietrosi G, Pagano D, Gridelli B. Early graft dysfunction following adult-to-adult living-related liver transplantation: predictive factors and outcomes. World J Gastroenterol. 2009, 15, 4556–4560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).