1. Introduction
After years of exploration practice in continental fault basin in eastern China, a set of continental petroleum geology theories represented by “continental petroleum generation theory” and “source control theory” are formed. From exploration of anticline reservoirs in the early days to subtle reservoirs exploration at present, the theory of oil/gas generation and distribution in continental fault basin in China has been developed as follows: the “source control theory” is proposed after the discovery of Daqing oilfield (1960s~1970s). Based on exploration achievements of continental fault basin represented by Bohai bay basin, the “composite oil/gas accumulation zone theory” is formed (1980s). “Accumulation of petroleum in oil-bearing belt” theory is concluded by geologists of Shengli Oilfield during exploration process in Dongying Sag (1990s). In the study of formation and distribution characteristics of subtle reservoir in Erlian basin, “Complementarity” Feature (2003), “Theory of Advantage” Feature (2005) and the concept of “Multi-factor Controlling and Key Factor Entrapping”(2006) are proposed. Not only are these new understandings and concepts function as important guidelines in oil and gas exploration of continental fault basin in China, but also greatly enrich the Continental Petroleum Generation Theory[1-4]. Practice is the basis of innovation, and the development of new theory will cause further improvement in oil and gas reserves. Based on geological theories and technique researches, combining with years of related working experiences, the writer proposed “one” + “three” accumulation model, in which fractures acts as ties and with the trinity of lithosome, effective source rock and effective reservoir physical properties, for the formation of lithologic reservoir in continental fault basin.
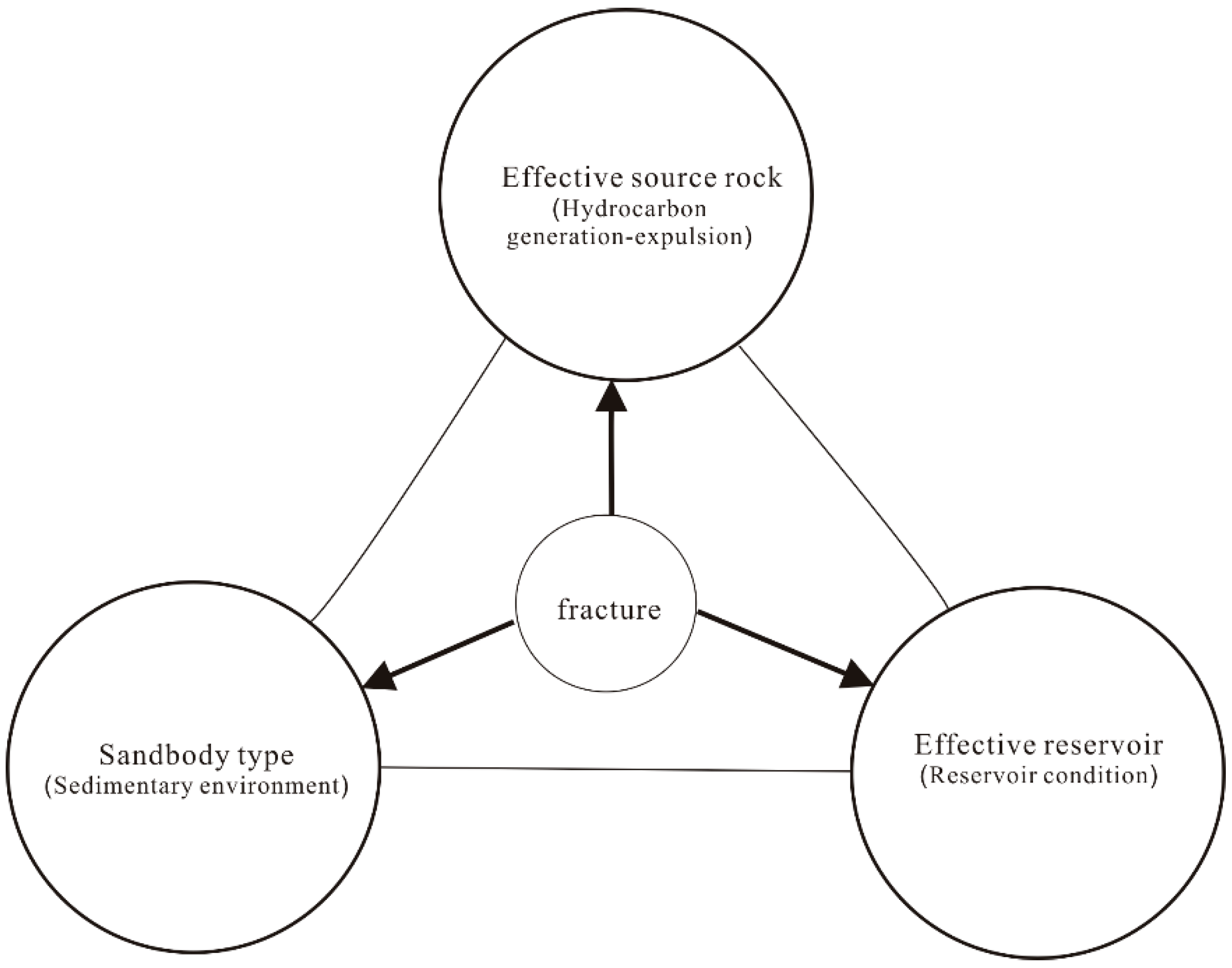
2. Connotation of “1” + “3” hydrocarbon accumulation model
There must be one factor in domain among all factors that influence the development of a thing. Likely, in the 6 controllers of “source, reservoir, cap, migration, trap and preservation”, there lies in one key factor that controlling the others. Research is taken on the controlling factors and accumulation process of lithologic reservoir of Nantun Formation in Tanan Sag of continental fault basin, and results indicate that fractures and its combination mode are in control of reservoir distribution, and are close related to source rock development position and trap distribution as well. By recovering fault development and the processes of hydrocarbon generation, migration, accumulation and dissipation, comparison and analysis are taken in both time and space domain. The results showing evident correlation in development degree, time synchronism and spatial matching between fault development and hydrocarbon accumulation: either mutual growth or decline, or consistent with each other, the batter matching in time-space, the richer hydrocarbon is accumulated
[5-9]. Allocation of sand type, effective source rock and effective reservoir is optimized under the effect of fractures, and coupled hydrocarbon reservoir with these three elements. Thus, the writer builds up the “1”+“3”hydrocarbon accumulation model for lithologic reservoir in continental fault basin (
Figure 1). Here, “1” represents fracture set, while “3” represents sand type, effective source rock and effective reservoir.
2.1. Connotation of “1”
“1” refers specially to fracture set in this paper. Fracture combination morphology is the reflection of fault kinematic characteristics. Different types of fracture have different motions, which will cause different fault complex. Continental fault basin is caused by extension and subsidence of costal continental area after collision and subduction of oceanic plates. Asymmetric “half-graben structure” is formed in continental fault basin due to the special genetic mechanism of the basin [10-11]. Fault screened reservoirs take a great proportion in eastern China and over 90% reservoirs are fault controlled or related [12-15]. Through study it is concluded that fracture set mainly has four effects in the hydrocarbon accumulation of continental fault basin.
Figure 1.
“1”+“3” hydrocarbon accumulation model of lithologic reservoir in continental fault basin.
Figure 1.
“1”+“3” hydrocarbon accumulation model of lithologic reservoir in continental fault basin.
(1) Bridge function—Fractures are functioned as bridge in the construction of spatial allocation of lithologic body, source rock and reservoir physical property.
Practices in hydrocarbon exploration proved that fractures are very important in hydrocarbon accumulation. There is no doubt they act as barriers and channels in hydrocarbon accumulation and migration respectively. However, the role that fracture plays in hydrocarbon accumulation has been studied limited within one basin or sag, with no consideration of the influences that may caused by different spatial allocation of these fractures in the basin or sag. The spatial relationship between fracture, source rock and reservoir is different when fracture’s position changes in the basin or sag [
16]. Although fracture still controls petroleum accumulation and reservoir formation, it works in different way and the effect varies obviously.
(2)Properties of sand control, hydrocarbon control and reservoir quality control——Syngenetic fractures are very developed in ①continental downfaulted lake basin. These syndepositional fractures and their allocations generate the characters of “gully source control, fault-break sand control” in basining. Fractures are in control of sand body spatial distribution. The configuration in plane controls sand disperse system through conducting, confining, separating and adjusting activities. ②fracture can affect source rock in two aspects, one of which is source rock spatial distribution. Downfaulted lake basin is features by deep depression, high division degree, diversity depositional systems and types. Generally, several depocenters are contemporaneously developed due to regional tectonic elevating movement. Depocenter of a lake basin often shifts obviously in different geological periods and results in many hydrocarbon generation centers, which are consist of different layer systems, complementary in spatial distribution and characterized by “overlapped and connected sandbodies”. A good environment for “Sag-wide Oil-Bearing” is created this way and sources for hydrocarbon generation in different zones and various traps are also provided, thus a foundation for complementary hydrocarbon distribution is laid. The other aspect is that source rocks may form a low-mature reservoir [
17] under the effects of fractures in low-mature stage before major oil generation period. Compared to mature source rock, it is often hard for low mature source rock to reach hydrocarbon expulsion threshold of oil saturation. However, as long as fractures are developed in the area, it is possible for primary migration and generation of a productive reservoir. ③control in physical properties presents as improvements in reservoir permeability caused by micro fracture or “reservoir petrophysical fracture”. Usually they control the distribution of high permeability zones, and the reservoir physical fault system that consists of these fractures is in control of “dessert” area distribution in basin [
18].
(3)Conducting effect —fault zones act as major channels for hydrocarbon migration in continental fault basin, in which synsedimentary faults are well developed. The conducting system mainly presents as tridimensional fault complex that differ in scale or property. There is one thing in common that one or more inherited regional faults must exist to provide channels, thus oil and gas can migrate along these fractures from source bed on the bottom to reservoir bed on the top, and finally form a petroleum accumulation. Distribution of deep fractures and secondary fractures, especially those developed inside a lake basin with the extension ranges from several km to tens of km, are always in control of the orientation of sags or subsags, as well as formation development degree and sedimentary facies distribution. What’s more, a set of similar secondary faults and minor faults are derived, constructing combinations and relative conducting networks in “fault-steeped type”, “ladder-shaped”, “grid-type” and “chair-type” in space [
19].
(4)Sealing effect—Fault sealing is the major determinant of hydrocarbon enrichment degree in a fault screened reservoir. It is commonly accepted that fractures are in main control of reservoir formation and destruction. People like Jones (1974), Price (1980) and Weker (1975) consider that faults are conductor in oil and gas migration [
20], whereas some people claim faults are functioned as barriers [
21] (Rerkkins, 1961, Smith, 1980, Fowler1971). Others have the idea that faults play both roles of channel and barrier [
22] (Seebarger, 1981; Chapmaw, 1981, Hooker, 1991, Losh and others 1999). Break up of a sealing fault is good for further petroleum migration and accumulation, and fault sealing is the primary cause of variation in oil and gas aboundance in fault trap. Therefore, fault sealing analysis is highlighted in the study of fractures influence on hydrocarbon migration and reservoir accumulation. It is considered that as long as the time of unsealing and sealing is clear, the hydrocarbon enrichment degree in this fault trap can be evaluated.
2.2. Connotation of “3”
“3” here refers to the three fundamental geological elements of “sandstone type”, “effective source rock” and “effective reservoir”.
(1) Sandstone type is influenced by sedimentary environment and lithofacies paleogeography. Sedimentary environment controls reservoir distribution and development, and also has great effect on reservoir lithology and physical property [
23]. Structure factors and depositional environment affect petroleum accumulation and reservoir formation. Controlled by sedimentation in certain geological conditions, hydrocarbon accumulation is relatively rich only in traps with specific sand type. Although lithologic reservoir may develop in many sedimentary environments [
24] (river channel, delta, coastal sand bar, various kinds of turbidite fan), hydrocarbon potential are not the same in different sandbody formed in different sedimentary environments. During primary hydrocarbon expulsion, oil and gas mainly migrate upward or laterally toward basin margin. Reservoir itself is good pathway without the influence of fault. Reservoirs themselves are good channel for hydrocarbon migration without the affects of faults, for that oil and gas enter into reservoirs directly from source rocks through sandbodies, it means turbidite sandstones surrounded by source rocks enjoyed advantaged superiority for hydrocarbon accumulation
[25 ] 。
(2)As source rock is buried deeper, abundant hydrocarbon is generated by thermal evolution. Only when it reaches threshold depth, and after various hydrocarbon involved actions such as self-adsorption, interstitial water solution, oil dissolution (gas) and capillary sealing have taken place, will free oil and gas begin massive migration or expulsion. Traps that surrounded or contacted by source rock, or communicated by fault are qualified to form reservoirs. As buried depth increases, hydrocarbon generation-expulsion intensity grows and the trap is more petroliferous.
(3) Sand body poro-perm character and grain size sorting property (differential) are also controlling factors of oil and gas charging in litohlogical trap. Only when sand body porosity and permeability reach critical value, can the sand body be able to keep hydrocarbon coming from outside. Better physical property means the trap is more potential. Through experiment researchers find that sand body with big grain size is petroliferous, while small grain size may indicate no oil or gas accumulation.Experiment on reservoir formation of lithologic sand body also proves oil and gas can not be accumulated to form lithological reservoir unless grain size of sand body reaches certain level [
24].
Type of sand body indicates sedimentary environment. Burier depth and hydrocarbon expulsion intensity are employed to describe hydrocarbon generation and expulsion conditions of wall rock. Physical properties show accumulation conditions of this sand body. The trap is qualified for accumulation when all these three elements are in certain conditions, and better conditions are, more hydrocarbon potential the trap is.
3. Effects of fracture set-sandbody type-effective source rock-effective reservoir on lithologic reservoir
3.1. Sandstone-mudstone combination optimization and lithologic reservoir distribution controlled by fracture set
Configration of sand type, effective source rock and effective reservoir is optimized under the effect of fractures, and coupled reservoir with these three elements. Tanan sag is a typical continental downfaulted lake basin with syngenetic fractures greatly developed. These synsedimentary faults and their configuration have caused basining features of “gully source control, fault-break sand control” of Tanan sag. Fractures are in control of sandbody spitial distribution; moreover, micro fractures have greatly improved physical properties of low porosity and permeability reservoir. On the hanging wall and foot wall, dark mudstone and sandstone are connected within hydrocarbon expulsion threshold, thus a “three in one” configuration is formed among lithosome, source rock and reservoir.
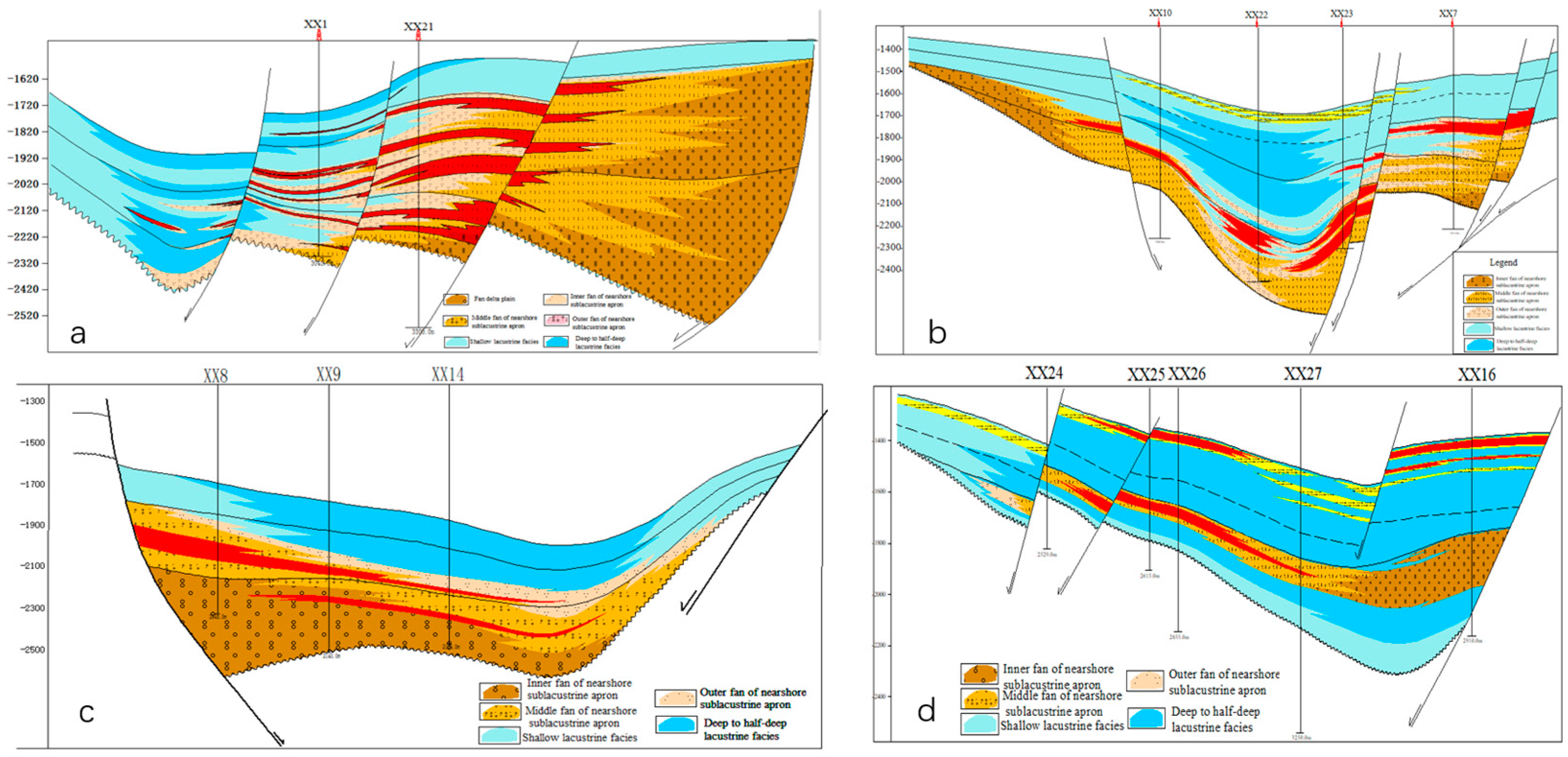
Based on known reservoir type, distribution and reservoir-forming features, combined with informations like geologic configuration of subsags and fault slope type in Tamtsag exploration area, 4 hydrocarbon accumulation modes in Tanan sag are concluded as follows: terrace fault steep-slope break mode, terrace fault gentle-slope break mode, fault scrap steep-slope break mode, intrabasinal slope break mode (
Figure 2). As is shown in these pictures, lithologic reservoirs all developed along fractures in different tectonic units of Tanan sag. Sandstone-mudstone contact relationships are different in different positions of fracture. Thus a lithologic reservoir is likely to form under such conditions: Basin shape is controlled by first order fault on basin margin, while spatial distribution of sand rock and source rock are controlled by syndepositional fault, sand disperse system is conducted, confined, separated or adjusted by fractures developed in accommodation zones and transfer zones, distal sublacustrine fan or subaqueous turbidite fan, which are developed on the thrown side of fault exists on the slope break of basin, are fully contacted with sublacustrine dark mudstone.
Figure 2.
Typical reservoir forming modes in Tanan sag (a, b, c, d are in represent of terrace fault steep-slope break mode, terrace fault gentle-slope break mode, fault scrap steep-slope break mode, intrabasinal slope break mode respectively).
Figure 2.
Typical reservoir forming modes in Tanan sag (a, b, c, d are in represent of terrace fault steep-slope break mode, terrace fault gentle-slope break mode, fault scrap steep-slope break mode, intrabasinal slope break mode respectively).
3.2. Lithologic reservoir distribution controlled by sand body type
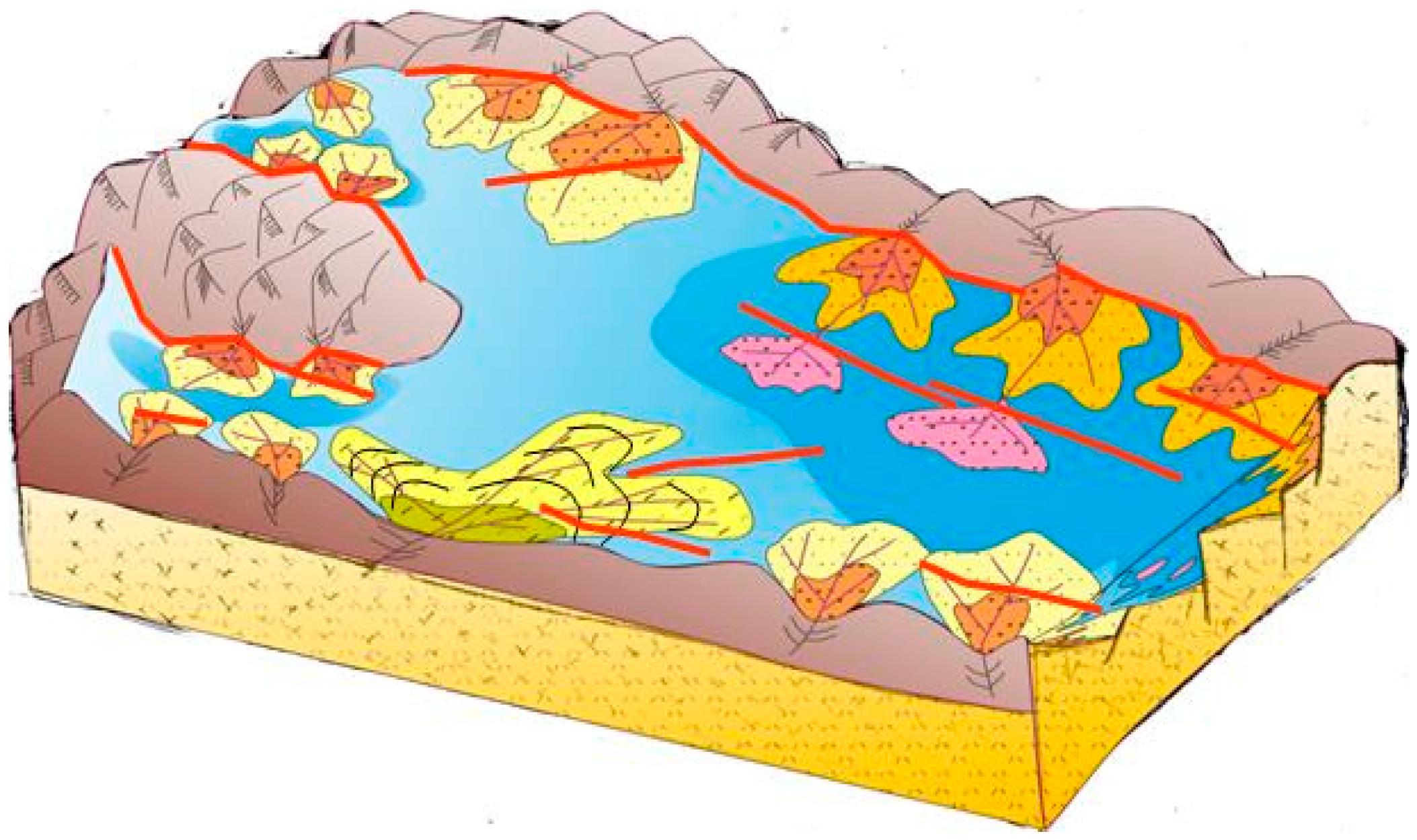
(1) Sand-control effects of basin margin gully and fault slope
Paleostructural and paleogeomorphologic features are in direct control of sequence development. As a key tectonic unit, sedimentary slope controls the development of main stratigraphic sequences in basin, and sequence types that generated on slopes with different paleogeomorphologic features varies greatly. As the most typical paleogeomorphologic units, “gully” and “fault-slope zone” are in control of favorable reservoir sandbody distribution. Researches on sequence stratigraphy in Tanan sag indicate that only the position of fan is determined by basin margin gully, while its scale and thickness are determined by sandbody types that controlled by different syndepositional structure fault-slopes. Thus the type of lithologic reservoir is further controlled. (
Figure 3).
Figure 3.
Paleostructure background and sedimentation model, Nantun formation of Tanan sag.
Figure 3.
Paleostructure background and sedimentation model, Nantun formation of Tanan sag.
Basin margin gully at steep or gentle slope in Tanan sag are lake inlets of rivers. Parallel (terrace fault) slope break zone, cross fault slope break zone, brush fault slope break zone and comb fault slope break zone are in control of sandbody thickness, and their strikes influence sandbody distribution. Thick lowstand sandbodies are developed in major structural slope break zones of sag, besides, excellent lake transgression source rocks and highstand source rocks are also developed in this area. These high-quality source rocks developed on lowstand sandbodies can be functioned as cap rocks as well as hydrocarbon generator, and make up a good combination of “source, reservoir and cap”. Meanwhile, active slope-break fractures can serve as conducting system for hydrocarbon migration and communicate source bed with sandbodies, which are developed at both sides of the slope-break. Slope-break fracture acts as reservoir cap during its stable period, therefore, a hydrocarbon enriched zone of lithologic reservoir is developed at where structural slope break zones, lowstand sandbodies and lake transgression source rocks are effectively configurated at Tanan sag.
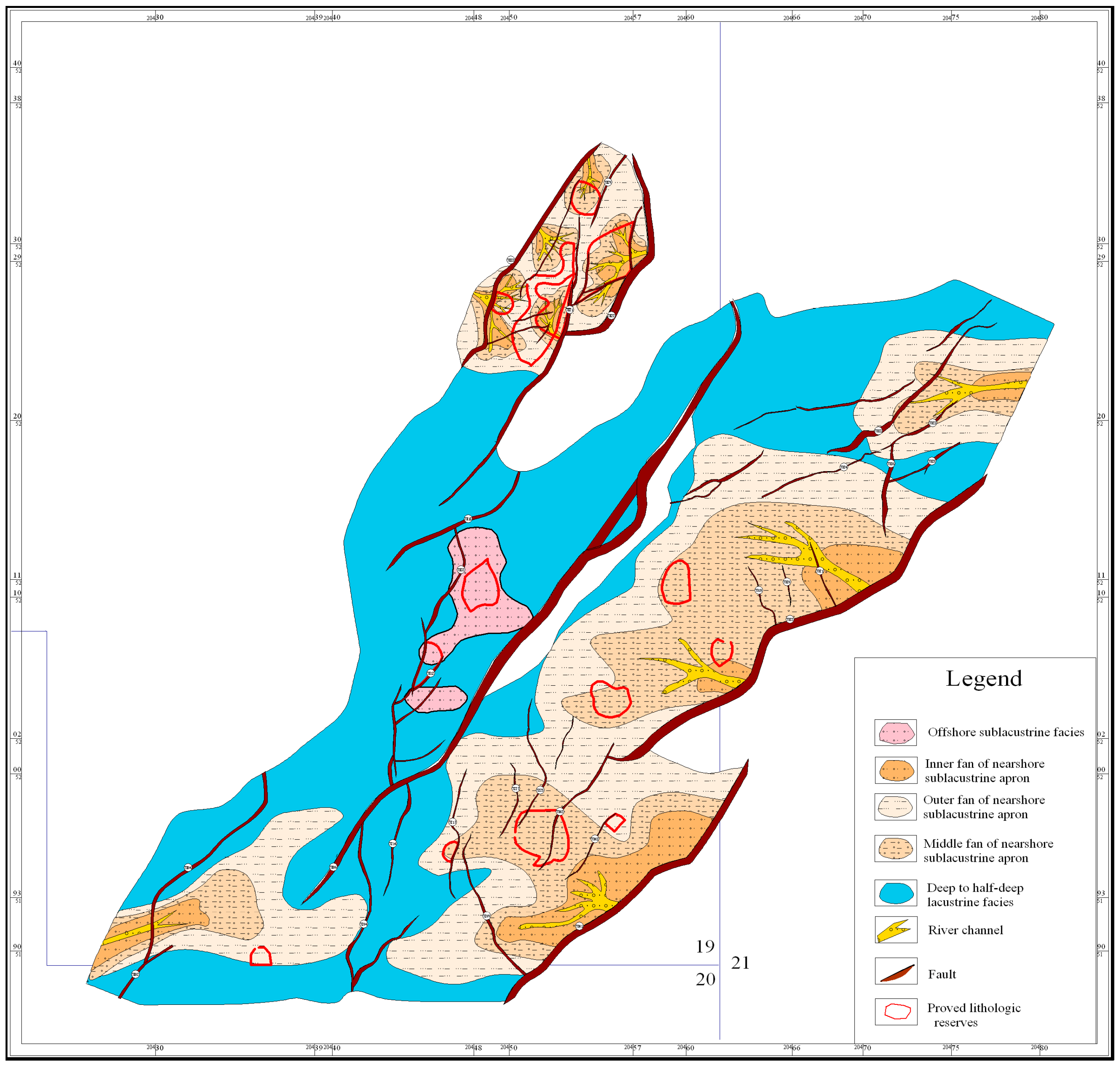
(2) Effects of sandstone type on lithologic reservoir
For lithologic reservoirs and structural-lithologic reservoirs of Nantun formation of Tanan sag, sandbodies are mostly developed in places like nearshore subaqueous middle-fan, distal subaqueous fan, fan-delta front and delta front, which are controlled by boundary faults and sag-controlled faults. (
Figure 4) Rock types are mainly glutenite, fine sandstone and siltstone. It has been found through exploration and development that sandbody distribution is controlled by sedimentary facies. Lithologic sandbodies are developed with good hydrocarbon potential in places like nearshore subaqueous middle-fan of steep slope zone, fan-delta front of gental slope zone and delta front, followed by nearshore outer-fan and distal subaqueous fan. (
Table 1)
Figure 4.
Overlay map of sedimentary facies, sag-controlled faults and lithologic reservoir distribution.
Figure 4.
Overlay map of sedimentary facies, sag-controlled faults and lithologic reservoir distribution.
Table 1.
Major sedimentary microfacies and rock types in Tamtsag exploration area.
Table 1.
Major sedimentary microfacies and rock types in Tamtsag exploration area.
| Block |
Structural type |
Oil-bearig area |
Number of wells |
Reservoir thickness |
Reservoir lithology |
Sedimentary facies |
Hydrocarbon filling degree |
| km2 |
|
m |
% |
| XX1 |
Lithologic reservoir |
7.33 |
4 |
30 |
Glutenite, siltstone |
nearshore subaqueous middle-fan |
24.43 |
| XX2 |
Lithologic reservoir |
2.32 |
3 |
96 |
Siltstone, grit stone, glutenite |
nearshore subaqueous middle-fan |
2.42 |
| XX3 |
Lithologic reservoir |
3.12 |
2 |
200 |
Fine sandstone, siltstone, glutenite |
nearshore subaqueous middle-fan |
1.56 |
| XX4 |
Lithologic reservoir |
1.09 |
1 |
15 |
Fine sandstone, siltstone |
nearshore subaqueous outer-fan |
7.27 |
| XX5 |
Lithologic reservoir |
3.32 |
3 |
80 |
Siltstone, fine sandstone |
nearshore subaqueous middle-fan |
4.15 |
| XX6 |
Structural-lithologic
reservoir |
1.32 |
1 |
400 |
Glutenite, fine sandstone |
nearshore subaqueous middle-fan |
0.30 |
| XX7 |
Structural-lithologic
reservoir |
7.26 |
6 |
60 |
Fine sandstone |
nearshore subaqueous middle-fan |
9.44 |
| XX8 |
Structural-lithologic
reservoir |
4.72 |
5 |
50 |
Siltstone |
nearshore subaqueous outer-fan |
7.59 |
| XX9 |
Structural-lithologic
reservoir |
11.38 |
10 |
150 |
Glutenite, fine sandstone |
nearshore subaqueous middle-fan |
3.92 |
| XX10 |
Structural-lithologic
reservoir |
0.98 |
1 |
25 |
Glutenite, fine sandstone |
nearshore subaqueous inner/middle-fan |
1.50 |
| XX11 |
Structural-lithologic
reservoir |
0.6 |
1 |
40 |
Siltstone |
nearshore subaqueous outer-fan |
2.76 |
| XX12 |
Structural-lithologic
reservoir |
1.93 |
1 |
70 |
Fine sandstone |
distal subaqueous fan |
3.97 |
| XX13 |
Structural-lithologic
reservoir |
3.97 |
21 |
100 |
Siltstone, fine sandstone |
distal subaqueous fan |
1.33 |
| XX14 |
Structural-lithologic
reservoir |
0.6 |
1 |
45 |
Fine sandstone, glutenite |
nearshore subaqueous middle-fan |
0.33 |
3.3. Lithologic reservoir size controlled by effective source rock
Judging from current research results, the distribution of effective source rock is apparently related to lithologic reservoir formation. 4 types of position relationship between effective source rock and lithologic reservoir can be concluded as follows: (1) lithologic reservoir inside source rock (2) lithologic reservoir outside source rock (3) lithologic reservoir over source rock (4) lithologic reservoir under source rock
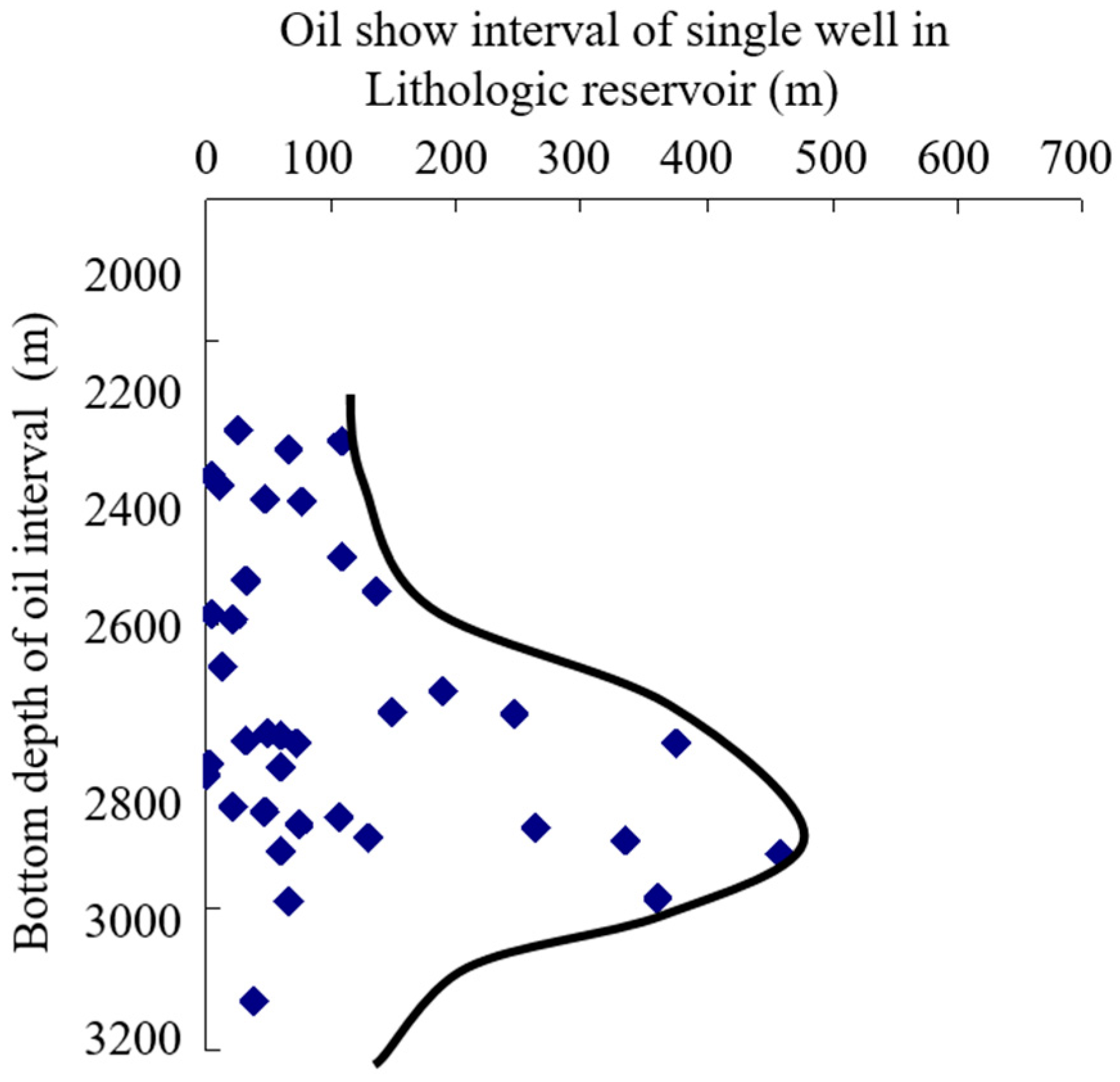
As source rock is buried deeper, abundant hydrocarbon is generated by thermal evolution. Only when it reaches threshold depth, and after various hydrocarbon involved actions such as self-adsorption, interstitial water solution, oil dissolution (gas) and capillary sealing have taken place, will free oil and gas begin massive migration or expulsion. With the increase in hydrocarbon generation and expulsion intensity, the trap is more petroliferous near oil and gas generation-expulsion centre. In Tanan sag, oil-bearing characters in vertical and horizontal are controlled by effective source rocks and hydrocarbon expulsion peak. (
Figure 5 and
Figure 7) Hydrocarbon expulsion threshold depth is around 2500m in Nantun formation of Tanan sag (
Figure 6) and hydrocarbon expulsion peak appears between 2600~3000m, thus lithologic reservoir of Tanan sag are mainly developed at depth ranges from 2500m to 3000m. As burial depth increases, oil shows interval of this productive lithologic reservoir first increases and then decreases (
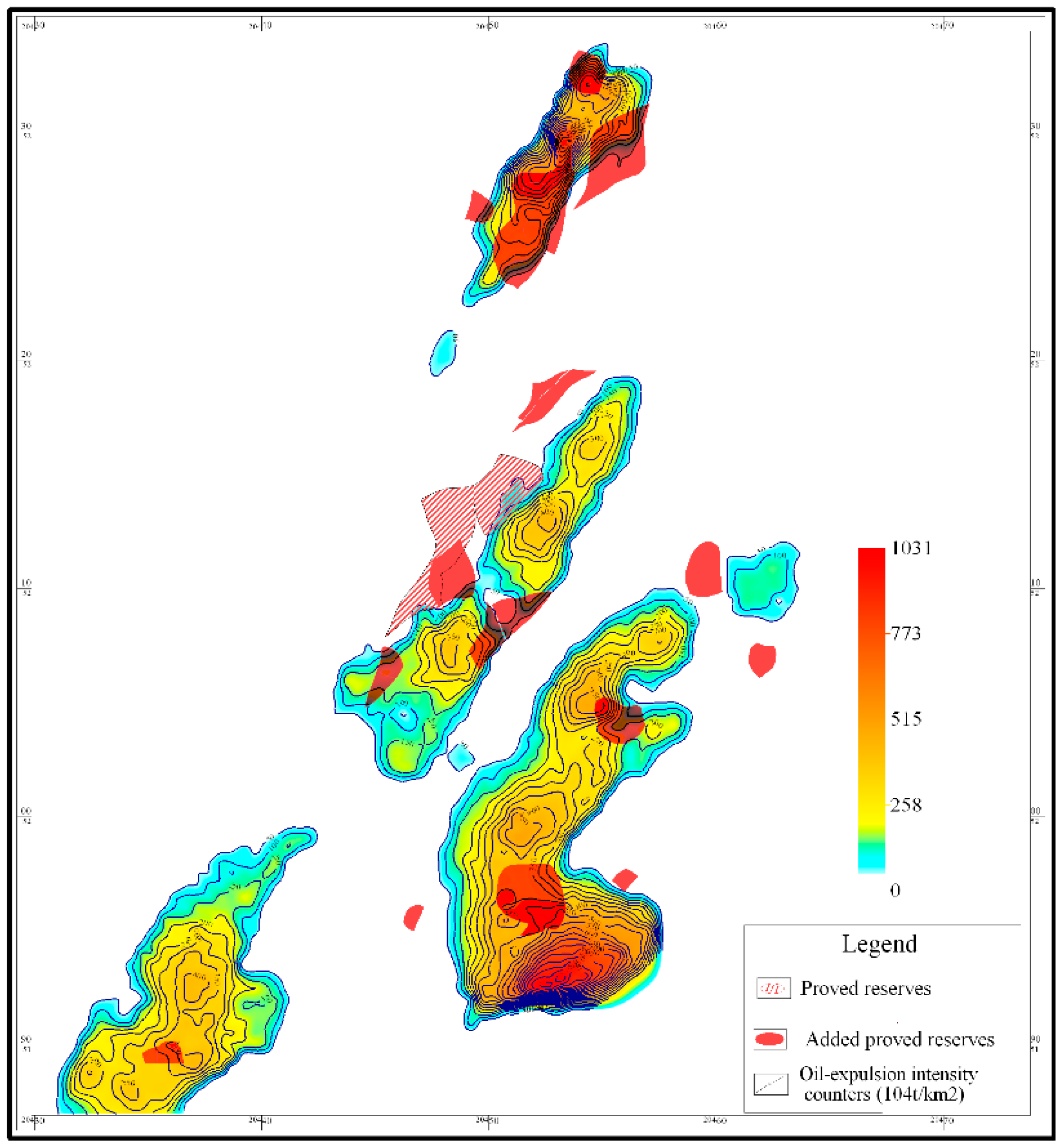
Figure 5). Judging from positions between traps and expulsion counters of effective source rocks, all isolated sandstone lithologic reservoirs are discovered within hydrocarbon expulsion scope or on the hydrocarbon expulsion boundary of effective source rocks, for example, lithologic reservoirs and structural-lithologic reservoirs in XX2、XX10、XX7、XX8 and XX9 blocks in north trough of west subsag and XX3、XX5、XX1 and XX11 blocks in east subsag, as well as lithologic reservoirs in XX4 block in south trough of middle subsag (
Figure 7). However, structural reservoirs in XX15, XX16, XX17 and XX18 blocks, which are conducted by fractures in the highstand of Nantun formation, are exceptions in this case. Traps that formed in the center and surrounded by source rocks in Nantun formation are more petroliferous than those laterally connected with source rocks. The closer to the center, the more oil and gas are accumulated in the trap (
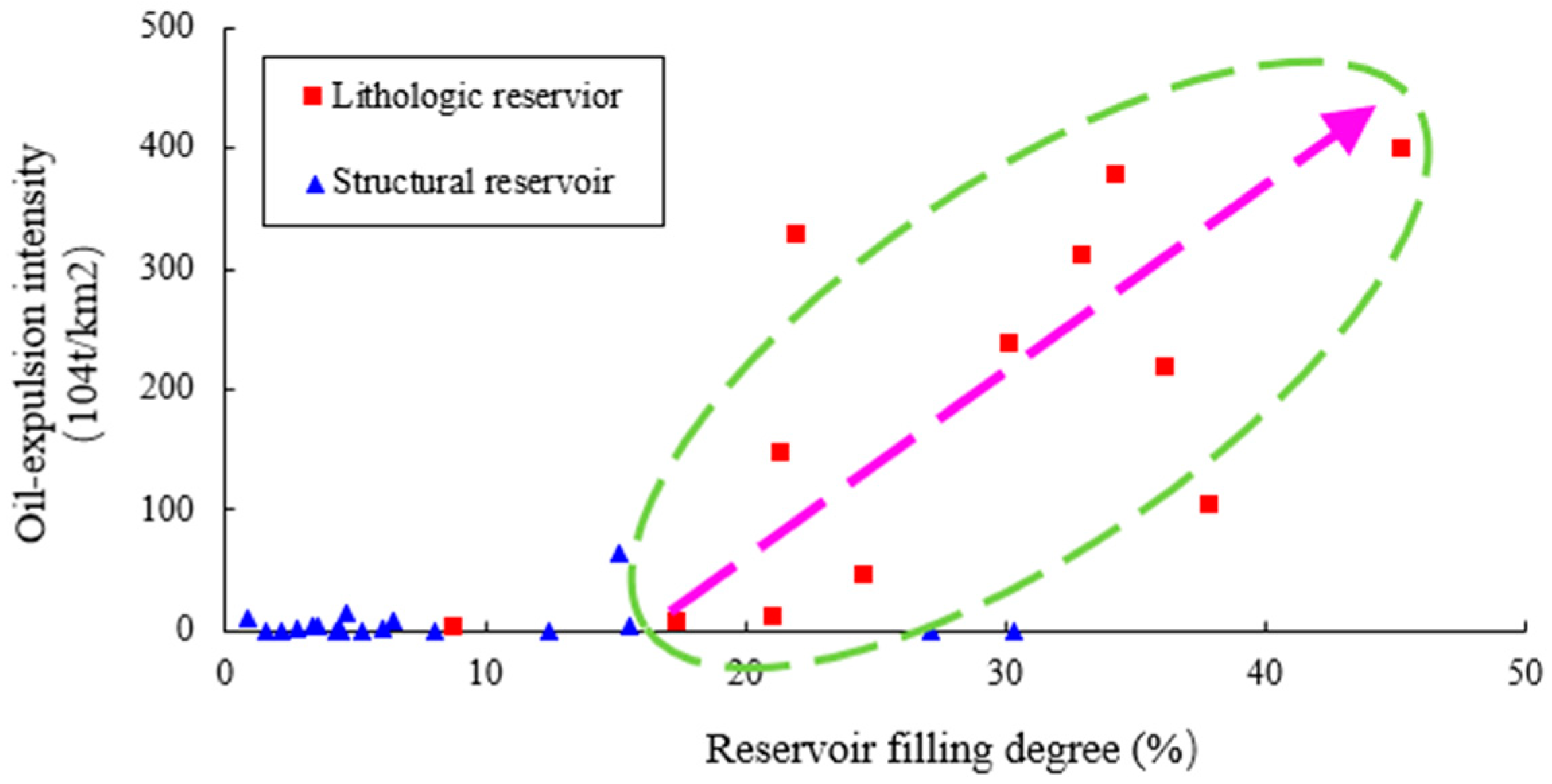
Figure 8). In other words, lithologic reservoir is usually high-quality where hydrocarbon expulsion is intensive, and vice versa.
Figure 8 shows the relationship between trap filling degree and hydrocarbon expulsion intensity in lithologic reservoir and structural reservoir. Judging from this picture, trap filling degree is closely related to expulsion intensity in lithologic reservoir, yet it is less affected by oil abundance in structural reservoir in Nantun formation. It means hydrocarbon has to migrate a long way before accumulate in a structural trap, while lithologic traps are usually close to the oil sources.
Figure 5.
Relationship between oil show interval and depth in lithologic reservoir in Nantun formation of Tanan sag.
Figure 5.
Relationship between oil show interval and depth in lithologic reservoir in Nantun formation of Tanan sag.
Figure 6.
Hydrocarbon- expulsion threshold of source rock in Nantun formation of Tanan.
Figure 6.
Hydrocarbon- expulsion threshold of source rock in Nantun formation of Tanan.
Figure 7.
Overlay maps of oil-expulsion intensity and oil-bearing area (1P) in Nantun formation of Tanan sag.
Figure 7.
Overlay maps of oil-expulsion intensity and oil-bearing area (1P) in Nantun formation of Tanan sag.
Figure 8.
Relationship between trap filling degree and hydrocarbon expulsion intensity in Tanan sag.
Figure 8.
Relationship between trap filling degree and hydrocarbon expulsion intensity in Tanan sag.
3.4. Hydrocarbon enrichment degree controlled by effective reservoir
(1)Impacts of reservoir physical property on lithologic reservoir accumulation
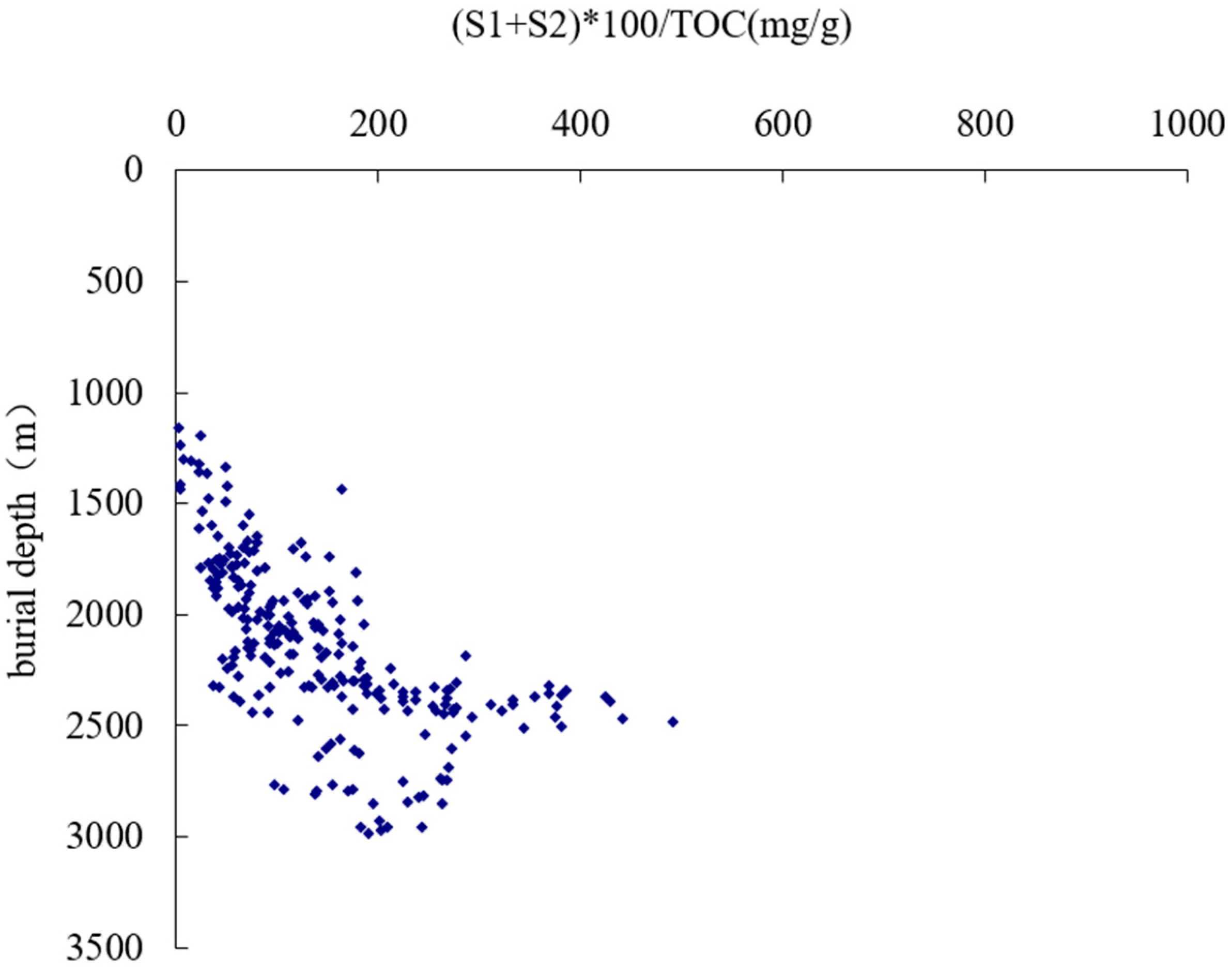
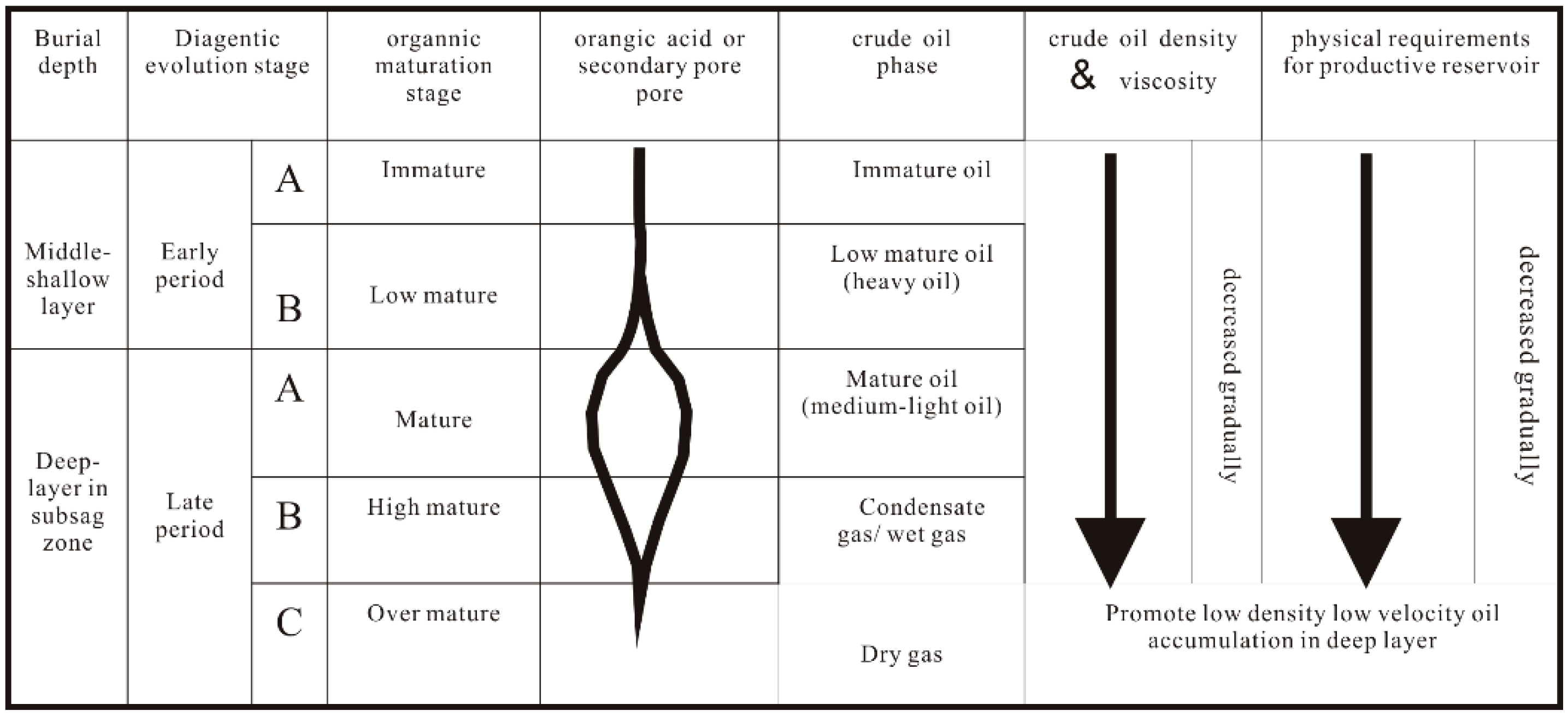
In addition to exterior sedimentary conditions and resource rocks, gas and oil in lithologic reservoirs are also controlled by reservoirs conditions of the sand rocks themselves. In the process of burial compaction, pore throat radiuses between rock particles decrease as the burial depth increases. Compactions between sand rocks and mud stones differ from each other under the same burial conditions. Compaction for mud stones is greater than that of sand rocks, resulting in different throat radiuses. Due to the different radiuses, the difference between pore throat capillary pressures becomes one of the causes of lens reservoirs. In the deep trough zones, because of deep burial depth, high temperature and great pressure, organics are highly evolved and the phase state of crude oil changes with the evolution. As the burial depth increases in trough zones, crude oil changes from medium oil into light oil and eventually become condensate gas, and phase state of oil transmits from single state into gas-oil mixed state and eventually becomes gas. For example, the reservoir revealed at 2896-2905m by the XX1 Well in Tanan Sag of Tamtsag Basin is nearly condensate gas reservoir, with a density of crude oil of 0.76g/cm. Besides, for the same Tanan Sag, revealed by wells such as XX19, XX20 and so on, the oil and gas phase state at the burial depth has evolved into gas-oil mixed state. As a result of the changes in crude oil and phase states, oil density and viscosity of the deep buried tight layers decreases, physical properties of the layers are suitable for the low density and viscosity gas and oil to form industrial reservoirs (
Figure 9). These lead to a broadened enrichment and accumulation of oil and gas in trough zones.
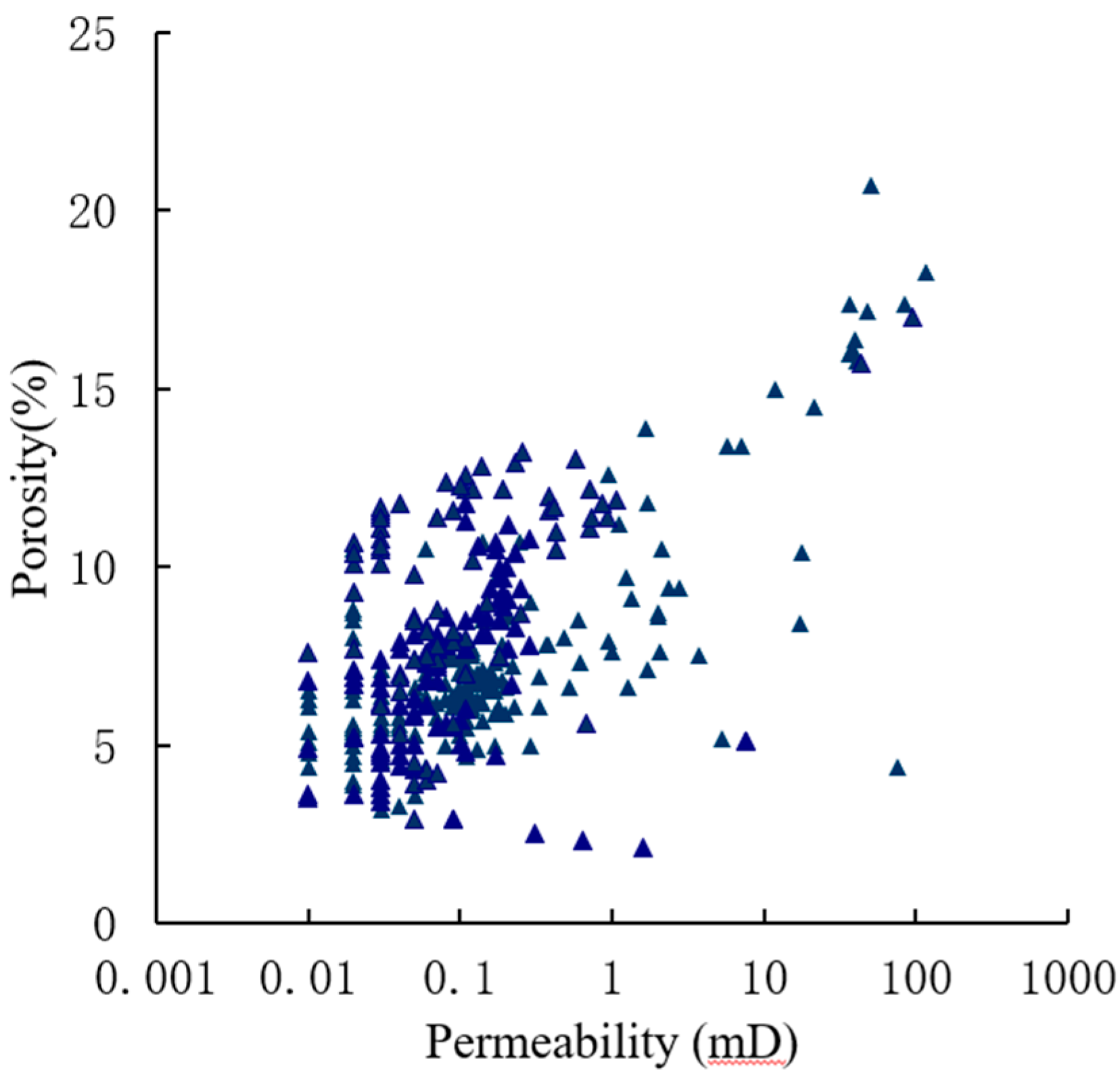
Burial depth of the industrial reservoir in Tanan Sag is between 1600m and 3200m and average porosity at 3200m is about 5%. Statistics between porosity and permeability show that, under the current fracturing technology, gas and oil of the lithologic reservoir accumulate in sand bodies with porosity higher than 4.5% and permeability higher than 0.01mD (
Figure 10). It is generally concluded from the data of unbroken cores that, under the current fracturing technology, the low limits of porosity and permeability for lithologic reservoir is 5% and 0.01mD. oil bearing and space filling factor increases with the physical properties of the reservoir. It is obvious in
Figure 10 that, for the NanTun groups in Tanan Sag, average oil saturation is in direction proportion to average porosity. Consequently, better physical properties of the sands are suitable for the hydrocarbon expulsion, accumulation and reservoir formation of exterior resource rocks into the sands
Figure 9.
Diagenetic evolution, hydrocarbon phase change and their requirements for reservoir quality (by Luo Qun, 2010).
Figure 9.
Diagenetic evolution, hydrocarbon phase change and their requirements for reservoir quality (by Luo Qun, 2010).
Figure 10.
Poro-perm relationship in lithologic reservoir in Nantun formation of Tanan sag.
Figure 10.
Poro-perm relationship in lithologic reservoir in Nantun formation of Tanan sag.
(2) Impacts of reservoir shale content on lithologic reservoir accumulation
Certain minerals in the reservoir react with water to cause lattice expansion, dispersion or fragment, resulting in blocked pores, throats and decreased permeability. They are called water sensitive minerals and have great capacity of cation exchange. Clays are normal water sensitive minerals and the typical of them are smectit and illite-smectite. Apart from them, kaolinite, illite and chlorite are also strongly water sensitive. Due to the strong hydratability of sodium ion and weak gravitational force between crystal layers, crystal layers of smectite hydrate and expand with outer water molecules. The expanded smectite further disperse and migrate with flow liquid, causing water sensitivity damage and velocity sensitivity damage to the oil layers. These eventually lead to hard reservior development and have certain influence on the research on distribution of lithologic reservoirs.
Researches have been taken on lithologic reservoirs in Tanan sag, where tuffaceous sandstones (conglomerates) are well developed, and the results show relatively high water sensitive and acid sensitive degrees in this area, which are strong evidences that strong correlation exist between reservoir sensitivity and rock type. Argillaceous fractions like clay minerals are responsible for the reservoir sensitivity in Tanan sag. Positive correlation exists between clay mineral and reservoir water/velocity sensitive damages.
Nantun formation of Tanan sag mainly formed in the early-middle time of peak period of rifting, nearshore subaqeous fans are major sedimentary system in this area, dominating by turbidite deposit. Thus reservoirs are poorly sorted with relatively high shale content.
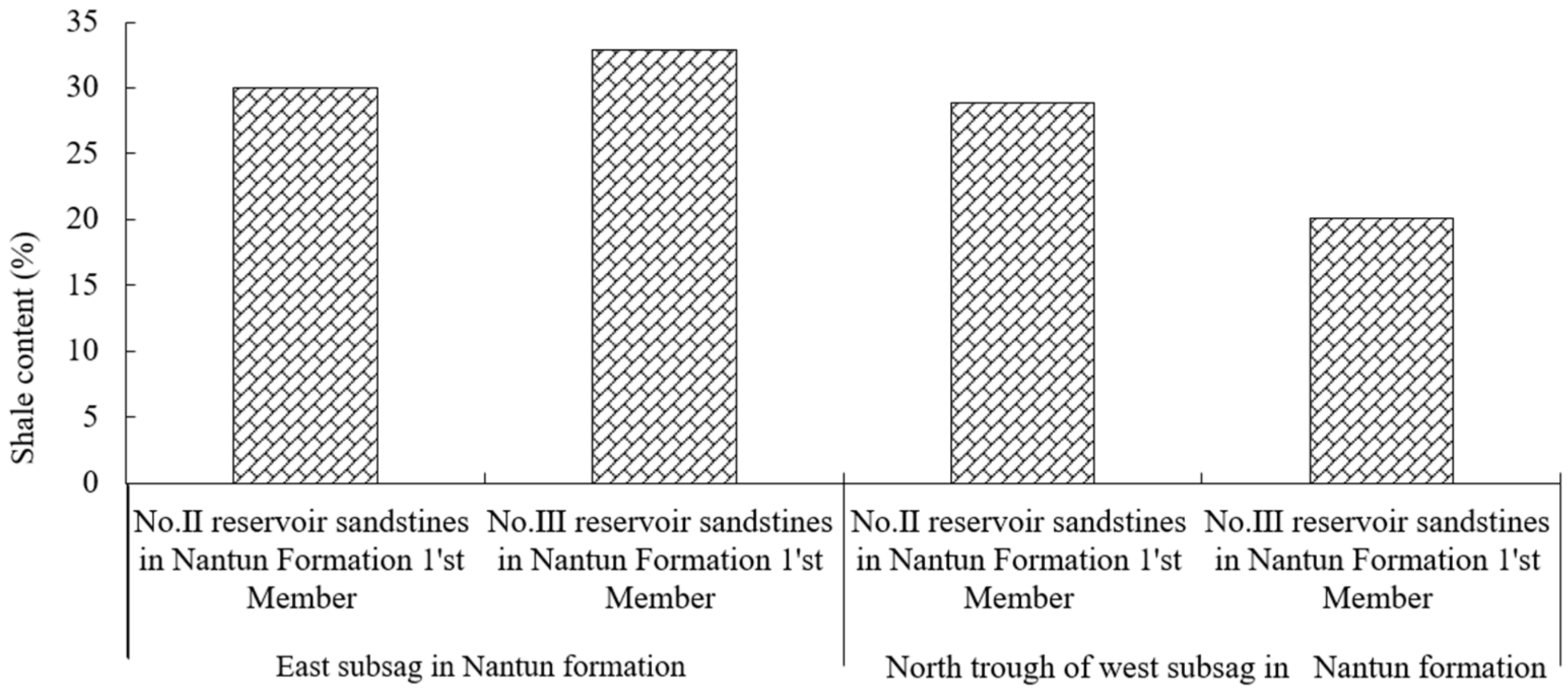
Figure 11 is average shale content histrogram of reservoir in lowstand of north trough of east/west subsag of Nantun formation. Overall shale content in reservoirs of Nantun formation of Tanan sag is relatively high, with an average value of 32.8%. Large scale of conglomerate are developed in lowstand sandbodies in north trough of west subsag, with relatively low shale content of 20% in average, which is main reason for Subsag-wide Oil-Bearing in this area. However, in east subsag where source rock and reservoir bed are both developed, high shale content may result in water sensitive during fracture treatment, and finally cause difficulties in production.
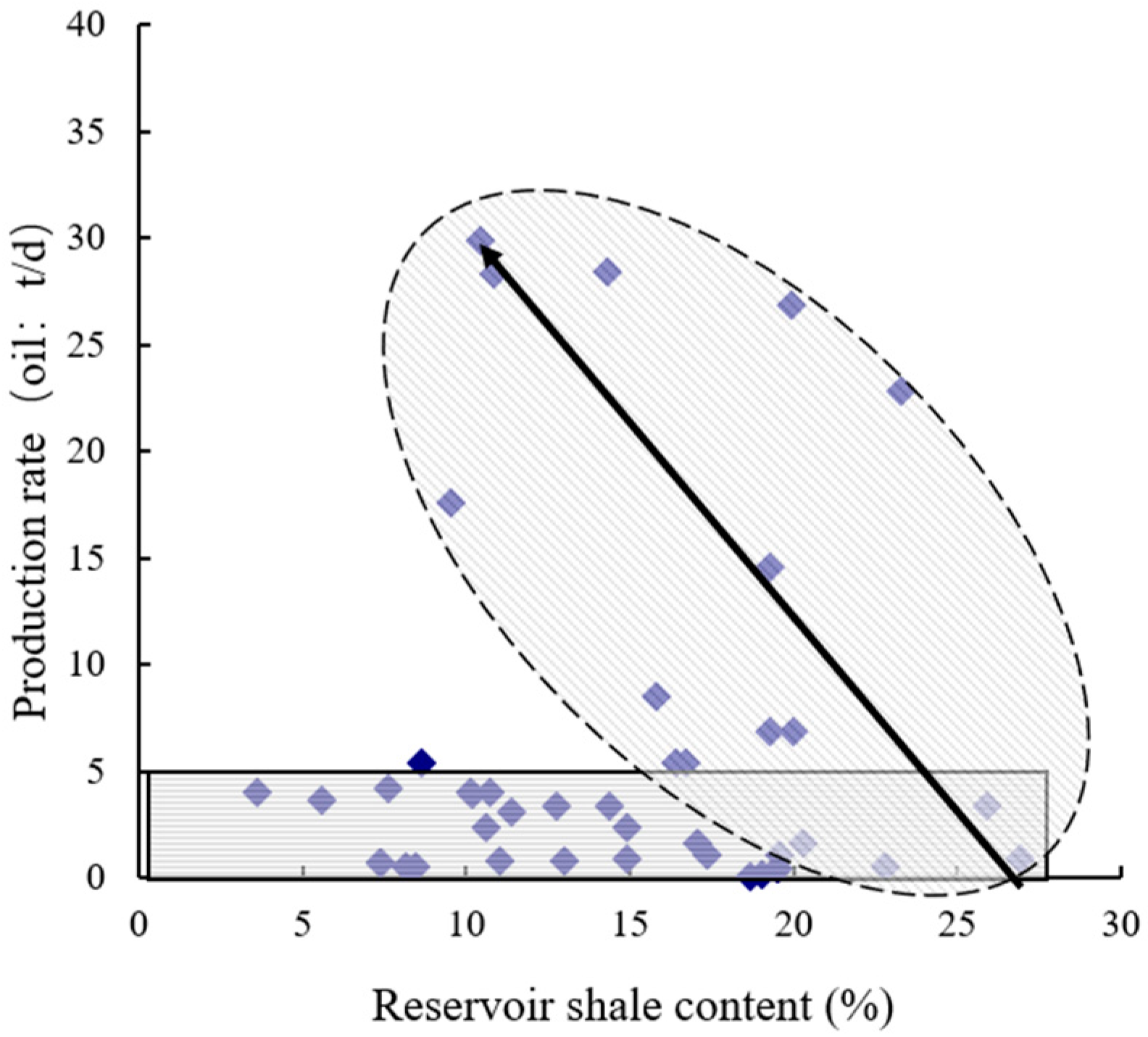
Figure 12 shows relationship between shale content and reservoir output in Nantun formation of Tanan sag. When production rate is over 5t/d, there is a negative relation between production rate and shale content, which indicates that reservoir output is strongly constrained by shale content.
Figure 11.
Average shale content histrogram of reservoir in Nantun formation of Tanan sag.
Figure 11.
Average shale content histrogram of reservoir in Nantun formation of Tanan sag.
Figure 12.
Relationship between shale content and reservoir output in Nantun formation of Tanan sag.
Figure 12.
Relationship between shale content and reservoir output in Nantun formation of Tanan sag.
4. Conclusions
(1)The “1”+ “3” lithologic reservoir model in continental fault basin is based on analysis of key factors in lithologic reservoir formation and reservoir forming process. Fractures and their combinations not only control reservoir distribution, but also close related to source rock development and lithologic trap distribution. When time-space relationship between fault development and reservoir formation process is good, oil and gas accumulation is abundant. Under the effect of fractures, the best spatial relationship is made up among sandbodies, dark mudstones and effective reservoirs and coupled hydrocarbon reservoir. As a typical continental downfaulted lake basin, Tanan sag has many contemporaneous fractures and the “gully source control, fault-break sand control” basining characters, which are determined by synsedimentary fractures and their configurations. Fractures are in control of sandbody distribution. On the hanging wall and foot wall, dark mudstone and sandstone are connected within hydrocarbon expulsion threshold, thus a “three in one” configuration is formed among lithosome, source rock and reservoir.
(2)Structural factors and sedimentary environment of lithologic reservoir can influence hydrocarbon accumulation and reservoir formation. Affected by sedimentary actions, abundant hydrocarbons only accumulate in traps formed by certain sandbody type under particular geological conditions. Lower parts of various slope break zones, nearshore subaqueous fans, fan delta sandbodies and turbidite sandbodies in Tanan sag have good chances in forming lithologic traps.
(3)With the increase in depth, enough hydrocarbon generate in source rock under thermal evolution. Hydrocarbon generation and expulsion are more intensive when it comes to the depth threshold and critical conditions of hydrocarbon supplying are met. Traps that surrounded or contacted by source rock, or communicated by fault are qualified to form reservoirs. As buried depth increases, hydrocarbon generation-expulsion intensity grows and the trap is more petroliferous.
(4)Hydrocarbon accumulation and reservoir formation are also controlled by sandbody accumulation conditions. When it meets the critical conditions of hydrocarbon generation and concrete oil and gas are charged in, better physical properties of sandbody always indicate more hydrocarbon accumulation in the trap..
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Exploration and Development Research Instutute ,PetroChina Daqing Oilfield Company, China.
References
- Liu, Z.; Chen, Y.P.; Zhao, Y., Hao, Q., Xu, X.M., Chang, M. Distribution and controlling factors of hydrocarbon reservoirs in continental fault basins [J] . Lithologic Reservoirs, 2007, 19(2) :121- 127. (in Chinese).
- Li, P.L. Zonary distribution of hydrocarbon in oil enriched rifted basins and exploration direction in the Huimin sag [J]. Petroleum Experimental Geology, 2001 (02). (in Chinese).
- Zhang, Y.F. Modelling Experiments of Lithologic Reservoirs Formation in Source Rocks and Its Accumulation Mechanism Analysis [J]. Laboratory Research and Exploration, 2001 (02). (in Chinese).
- Zhao, W.Z., He, D.F., Chi, Y.L., Lei, Z.Y., Qu, H. Major characteristics and exploration technology of muti-source petroleum systems in China [J]. Journal of Petroleum, 2001 (01). (in Chinese).
- Di, L.J. Controlling of petrophysical fractures on extra-low permeability oil and gas reservoirs in Ordos Basin [J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development,2006,33( 6) : 667-670. (in Chinese).
- Luo, Q. Concept , principle , model and significance of the fault controlling hydrocarbon theory [J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2010,37(3):316-328. (in Chinese).
- Tong, C.G. Some characteristics of petroleum geology of the rift systemin eastern China [J]. Acta Petroleum Sinica,1980,1(4):44-49. (in Chinese).
- Luo,Z.L., Liu, S.G. Plate tectonics and petroliferous basins in China [M]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences Press,1989,15-54. (in Chinese).
- Zhang,J.F., Lan, C.L. Fractures and faults distribution and its effect on gas enrichment areas in Ordos Basin [J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2006,33(2):172-177. (in Chinese).
- Dong, Y.X., Wang, Z.C., Zheng, H.J., Xu, A.N. Control of strike-slip faulting on reservoir formation of oil and gas in Nanpusag [J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development,2008,35(4):424-430. (in Chinese).
- Li, J.M. Fault system and its control on oil-water relationship of development block in Haita basin [D], Northeast Petroleum University, 2010,49-50. (in Chinese).
- Gu, S.S., Xu, W. Discussion on the article of “Application of fault control hydrocarbon theory to realize a greatbreakthrough of petroleum exploration in Qaidam Basin” [J]. Acta Petrol Sinica,2003,24(6):107-108. (in Chinese).
- Luo, Q. Fault controlling hydrocarbon theory and it’s application in Baitang depression in Bohai Gulf Coastal Basin and Qaidam Basin [D], PetroChina Research Institute of Petroleum Exploration and Development,2001,9-11. (in Chinese).
- Wang, Z.C., Zhao, W.Z., Li, Z.Y., Jiang X.F., Li, J. Role of basement faults in gas accumulation of Xujiahe Formation, Sichuan Basin [J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development,2008,35(5):541-547. (in Chinese). [CrossRef]
- Fu, G., Lei, L. Research on Differences of Controlling of Fault to Oil Accumulation in and outside Oil Source Area [J]. Geological review, 2010,56(5): 719-725. (in Chinese).
- Hooper E, Fluid migration along growth fault in compacting sediments, Journal of Petroleum gevlogg,1991,14(2): 160-190.
- Zhou, H.Y., Lu, J.F. Faults: A key factor for expelling low mature oil. [J]. Journal of Jian han Petroleum Institute ,1998 ,20 (2) :33~27. (in Chinese).
- Lingjun Di. Controlling of petrophysical fractures on extra-low permeability oil and gas reservoirs in Ordos Basin. [J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development,2006,33( 6) : 667-670. (in Chinese).
- Yi, S.W. ExPloration Theory and Practice of Lithologic and StratigraPhic Reservoirs in Erlian Basin[D]. Chengdu University of Technology, 2006,53. (in Chinese).
- Hooper E, Fluid migration along growth fault in compacting sediments. [J]. Journal of Petroleum gevlogg,1991,14(2):P160-190.
- Wang, J.Q. The chimney effects of hydrocarbon activity. [J]. Experimental petroleum Geology,1997,19(3):193-199. (in Chinese).
- Zeng, J.H., Jin, Z.J. Physical modeling of secondary oil migration and accumulation [M]. Petroleum Industry Press, 2000. 121-179. (in Chinese).
- Chen, D.X., Pang, X.Q., Weng, Q.P., Jiang Z.X., Zhang J. Discussion and preliminary application of ternary genetic mechanism of lithologic reservoir [J] . Oil & Gas Geology, 2003, 24(3) : 228-232. (in Chinese).
- Симнoвич. В. В. None-Anticline Reserviors [M].1986.
- Zhao, C.L., Zhang, S.W., Yuan, J . Depositional Reservoir and Hydrocarbon of Shengli oil Region [M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press,1999:95-96. (in Chinese).
- Hao, F., Zou, H.Y., Jiang, J.Q. Dynamics of petroleum accumulation and its advances [J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2000,7(3):11-21. (in Chinese).
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).