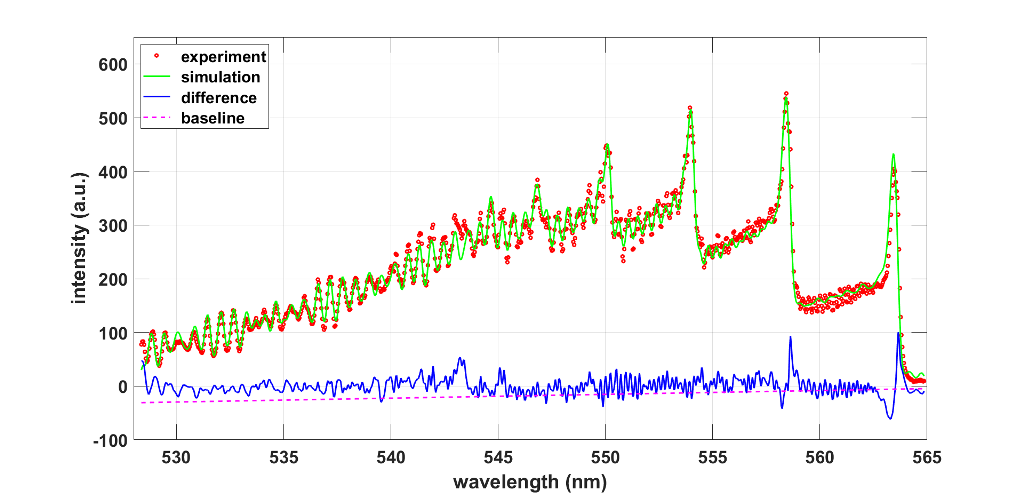
This article presents analysis of carbon Swan, C$_2$, laser-plasma emission records using line strength data, C$_2$-Swan-lsf, and the ExoMol astrophysical database. Line-strength data fitting of 0.25-nanometer spectral resolution ExoMol-computed spectra for a 6,000-Kelvin temperature C$_2$ Swan system, ${\rm d}\ ^3\,\Pi_{\rm g} \longrightarrow {\rm a} \ ^3\,\Pi_{\rm u}$, $\Delta {\rm v} = 0, \pm 1$, reveals a temperature of 5,640 Kelvin. The six per cent lower temperature is associated primarily with the accuracy of the transition wavelengths in the ExoMol vs. C$_2$-Swan-lsf data. The analysis of experiment data examines spectra that are recorded following laser-induced optical breakdown in carbon monoxide. The laser plasma data are recorded with 0.35-nm spectral resolution. The temperature inferences are elaborated when using non-linear fitting with both databases. The results show temperatures in excess of 6,000 Kelvin for the $\Delta {\rm v} = -1$ sequence, and for a time delay of 30\,$\upmu$s from laser plasma initiation. The accuracy of the C$_2$ Swan bands line strength data is of the order of 1 picometer. These line strength data are also utilized for analysis of laser-induced fluorescence experiments that employ a spectral resolution of 5.5 picometer, and a temperature of 2,716 Kelvin is inferred. Accurate C$_2$ databases show many applications in laboratory diagnosis and interpretation of astrophysical plasma records.