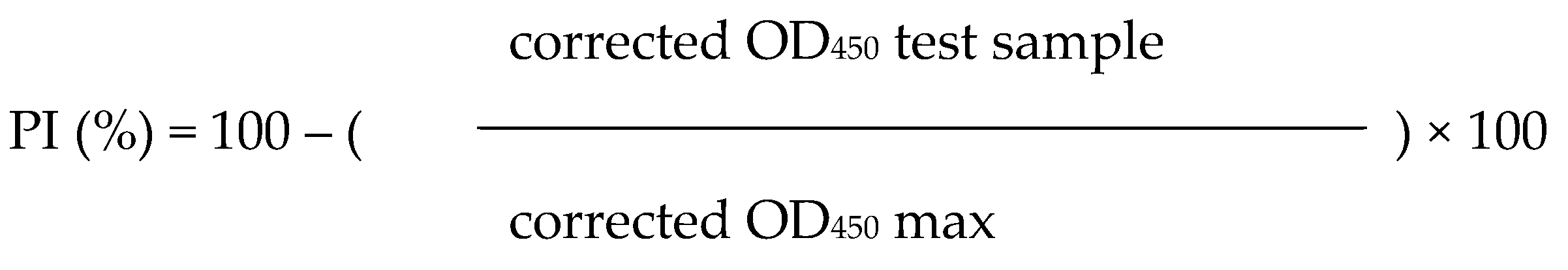1. Introduction
Foot-and-mouth disease (FMD) is a highly contagious disease that occurs in animals with split hooves, such as cattle, pigs, and goats [
1]. Foot-and-mouth disease virus (FMDV) belonging to the genus Picornaviridae and Aphthovirus has single-stranded positive RNA [
2]. FMDV is one of the viruses with high antigenic variability, existing 80 kinds of subtypes and seven major serotypes what are A, O, C, Asia1, SAT1, SAT2 and SAT3 [
3].
The highly contagious FMDV spreads rapidly through direct contact with infected animals and indirect contact through air and humans [
1,
4]. Infected live stocks fever and some of the following symptoms, they are blisters on the gums, tongue, and nose, loss of appetite, blisters spread all over the body, and symptoms of limping in the legs appear [
1,
5]. Transmission power, growth disorders, movement disorders, and lactation disorders lead to a decrease in productivity are all caused by FMDV, and also causing enormous economic damage to livestock farmers and the country [
6,
7].
In order to prevent FMDV, most countries in the world use the inactivated whole virus vaccine for FMD with immune adjuvant [
8]. To prevent FMDV, the Korean government is implementing a prevention policy through FMDV vaccination twice at an interval of one month. However, even if an FMD vaccine including an adjuvant is inoculated, an effective immune response does not occur in a short time, and it takes a long time for sufficient antibodies to be produced [
9]. In addition, the use of an oil-type immune adjuvant causes stress to livestock, and cartilage lesions such as granuloma, inflammation, and suppuration occur at the inoculation site, making it difficult to recover the status of a clean country with FMD [
8].
Zinc, which is essential for the growth, development and maintenance of the immune function, plays a role in regulating innate immunity and acquired immunity through proliferation and maturation of immune cells [
9]. In weaned piglets, if they do not receive sufficient zinc through feed, the immune system malfunctions, and diarrhea can lead to death [
10,
11]. This is because passive immunity is reduced in weaned piglets after lactation and active immunity is not sufficiently developed, resulting in lower resistance to pathogen infection [
12,
13].
Zinc-Aspartic acid (Zn-ASP), which is ionic and coordinated through atomic sharing with amino acids (AAs), has high bioavailability compared to inorganic minerals [
14]. Aspartic acid (ASP) is used as a precursor for synthesizing essential AAs such as lysine and methionine, and exhibits a stable-structure by binding to zinc through a carboxyl group or an amine group [
15]. Oral ingestion of Zn-ASP has been reported to improve the effect of immunity and productivity [
14]. However, there are no studies on the antibody formation promoting effect of vaccination after Zn-ASP administration, which enhances immune cell’s activity.
Therefore, the purpose of this study is to demonstrate the effectiveness of oral adjuvants through clinical trials in piglets, specifically, antibody titer and blood biochemical analysis was performed by FMD-vaccination after Zn-ASP administration to piglets. Through the results of these studies, the antibody positivity rate according to the number and period of vaccination was evaluated to confirm its applicability as an oral adjuvant to increase the antibody titer of the FMD vaccine.
2. Materials and Methods
This study was carried out with approval from the Korea Agriculture, Forestry and Livestock Quarantine Headquarters for veterinary medicine clinical trials. All animal experimental processes were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) of Gyeongsang National University, under approval number GNU-211013-P0084, and performed in compliance with the guidelines of the IACUC of Gyeongsang National University, Republic of Korea.
2.1. Test Farm, Test Group and Test Animals
A general breeding farm in Hapcheon, Gyeongsangnam-do was selected as a test farm, and 100 healthy piglets before and after 6 weeks of age were selected and identified by attaching a mark. The test animals were published in the test after going through an adaptation period in the experimental breeding facility for one week. The test group consisted of NC (negative control; unvaccinated and no additional added Zn-ASP in diet), PC (positive control; vaccination), ZA-0.1 (vaccination + 0.1% Zn-ASP intake), ZA-0.2 (vaccination + 0.2% Zn-ASP intake), and ZA-0.3 (vaccination + 0.3% Zn-ASP intake). Zn-ASP was administered in a mixture of 0.1%, 0.2%, and 0.3% in the feed according to the test group, and was administered for 10 weeks from 2 weeks before the primary FMD vaccine to 4 weeks after the secondary FMD vaccine. The feed was made to meet the nutrient recommendations of the National Research Council (NRC, 2012). The test feed was fed at a certain time, and water was freely ingested through an automatic feeder.
2.2. Vaccination
The FMD vaccine used in the test used inactivated purified bivalent foot-and-mouth disease vaccine Bioatogen [Careside, Korea]. According to the composition of the test group, piglets were inoculated by intramuscular injection of 2 mL each at 8 and 12 weeks of age.
2.3. Structural Protein (SP) Antibody Titer Measurement
In order to measure the antibody titer following foot-and-mouth disease vaccination, the blood of experimental pigs for each farm was collected and serum was separated before the first vaccination (8 weeks old), before the second vaccination (12 weeks old), after the second vaccination 4 weeks (16 weeks old), 8 weeks (20 weeks of age) and at the time of shipment (28 weeks of age).
For the antibody titer of the FMD vaccine in the serum, an LPB ELISA kit (Biogenesis-Bago S.A., Garin, Argentina) of Bioatogen FMD vaccine O type was used. Absorbance was measured at 450 nm wavelength according to the manufacturer's manual. The antibody titer was calculated by the following formula, and the antibody positivity rate was determined as positive when the percentage-inhibition (PI (%)) value was 50% or more.
2.4. Cellular Immune Marker (IFN-γ) Test
Serum IFN-γ concentration was measured using Nori Porcine IFN-γ ELISA kit (Genorise Scientific Inc., Glen Mills, PA, USA), and analyzed according to the manufacturer's instructions.
2.5. Serum Immunoglobulin (IgG, IgM, IgA) Measurement
The concentrations of IgG, IgM, and IgA in serum were measured using Porcine IgG ELISA kit (Koma Biotech, Seoul), Porcine IgM ELISA kit (Koma Biotech, Seoul), Porcine IgA ELISA kit (Koma Biotech, Seoul), respectively. Analysis was performed according to the manufacturer's instructions.
2.6. Hematological and Blood Biochemical Analysis
Blood collected from experimental pigs was analyzed for hematological indicators using an automatic blood analyzer (device name). Hematological analyzes include white blood cells (WBC), hemoglobin (Hb), hematocrit (HCT), lymphocytes (LYM), neutrophils (NEU), eosinophils (EOS), basophils (BAS), monocytes (MON), mean corpuscular volume (MCV), mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH), mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC), and platelets (PLT) were analyzed.
For blood biochemical analysis, Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP), Glucose (GLU), Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST), Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT), Blood urea Nitrogen (BUN), Creatinine (CREA), and Creatine Phosphokinase (CPK) were analyzed.
2.7. Statistical Analysis
Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation. The average value was statistically processed using Students’ t-test, ANOVA, or linear regression according to the characteristics of each test method, and was considered significant when p < 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Zn-ASP on FMD Vaccine Antibody Titer
The blood of experimental pigs was collected before vaccination (8 weeks of age), 4 weeks after primary vaccination (12 weeks of age), 4 weeks of secondary vaccination (16 weeks of age), 8 weeks (20 weeks of age), and before shipment (28 weeks of age). Blood was collected, and the antibody positivity rate was evaluated after measuring the antibody titer of the foot-and-mouth disease vaccine using the LPB ELISA kit (Biogenesis-Bago SA, Garin, Argentina) of Bioatogen FMD vaccine type O (
Table 1 and
Table 2). Co-administration of the foot-and-mouth disease vaccine and Zn-ASP increased the vaccine antibody titer, and when mixed with feed at doses of 0.2% and 0.3%, it increased statistically significantly compared to the positive control group (p<0.05). The antibody positivity rate in the Zn-ASP combination group was higher than that of the positive control group vaccinated only 4 weeks after the primary vaccination, and when 0.2% Zn-ASP was administered, the antibody positivity rate was 90%, which was 45% higher than that of the positive control group. After the second foot-and-mouth disease vaccination, all except the unvaccinated group showed an antibody positive rate of 100%.
3.2. Effect of Zn-ASP on Cellular Immune Markers (IFN-γ)
To confirm the effect of the combination prescription of the foot-and-mouth disease vaccine and Zn-ASP on cellular immune markers, IFN-γ was analyzed using an ELISA kit (Genorise Scientific Inc., Glen Mills, PA, USA) (
Table 3).
The combination of foot-and-mouth disease vaccine and Zn-ASP was confirmed to have an effect of increasing the concentration of IFN-γ in the blood. In particular, 4 weeks after the first dose and second dose of foot-and-mouth disease vaccine, the TRT3 and TRT2 group had the highest blood IFN-γ concentration, respectively. In addition, the TRT2 and TRT3 groups significantly up-regulated IFN-γ, a cellular immune marker, compared to the positive control group (p<0.05).
3.3. Effects of Zn-ASP on Humoral Immune Markers (IgG, IgM, IgA)
In order to confirm the efficacy of the combined prescription of the foot-and-mouth disease vaccine and Zn-ASP on humoral immune markers, IgG, IgM, and IgA were each administered using Porcine IgG ELISA kit (Koma Biotech, Seoul), Porcine IgM ELISA kit (Koma Biotech, Seoul), Porcine IgA ELISA kit (Koma Biotech, Seoul) was used for analysis (
Table 4). The concentrations of IgG, IgM, and IgA in blood increased with foot-and-mouth disease vaccination, and showed a tendency to decrease in the negative control group which was not administered with the vaccine or Zn-ASP. The combined treatment of the foot-and-mouth disease vaccine and Zn-ASP reduced the concentrations of IgG and IgM in the blood, but did not show a significant difference. On the other hand, the concentration of IgA was significantly increased in the TRT2 (p<0.05) and TRT3 (p<0.01) groups treated with the foot-and-mouth disease vaccine and Zn-ASP.
3.4. Effect of Zn-ASP on Hematological Indicators
Blood was collected from experimental pigs and hematological indicators were analyzed using an automatic blood analyzer (
Table 5). Regarding the hematologic parameters, the foot-and-mouth disease vaccine and the Zn-ASP combination did not show a statistically significant difference compared with the positive control group.
3.5. Effect of Zn-ASP on Blood Biochemical Markers
Blood biochemical parameters (alanine aminotransferase (ALT), serum aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alkaline phosphatase (ALP), blood urea nitrogen (BUN), creatine phosphokinase (CPK), creatinine, glucose) were analyzed using an automatic blood analyzer for serum obtained by centrifuging blood collected from experimental pigs before foot-and-mouth disease vaccination, 4 weeks after the first vaccination, and 4 weeks after the second vaccination, respectively (
Table 6).
The combined treatment of foot-and-mouth disease vaccine and Zn-ASP significantly reduced the concentrations of AST and CPK compared to the positive control group, and there was no statistically significant difference in other blood biochemical parameters.
4. Discussion
FMD vaccination for the prevention of foot-and-mouth disease uses an inactivated FMDV antigen, and is mixed with an oil-based adjuvant [
8]. However, when pigs are vaccinated with FMD inactivated antigen vaccine, foot-and-mouth disease antibodies are generated within 1 to 2 weeks, but they do not maintain long-term protection, so additional vaccinations and adjuvants are required [
16]. Accordingly, the antibody formation promoting effect by vaccination using Zn-ASP that induces T-cell immune response was confirmed.
In weaned pigs, the immunity transferred from the sow's milk is rapidly lost, causing diseases such as stunted growth and epidemic diarrhea, and the mortality rate is high [
10,
11]. For this reason, the pig industry mainly uses zinc to improve the immunity and growth rate of pigs and to alleviate the incidence of diarrhea. It has been reported that Zn-ASP coordinated with amino acids based on zinc affects the activation and proliferation of T cells and cytokine regulation [
17]. In addition, a previous study what we confirmed the effect of Zn-ASP administration to pigs to increase the zinc content in the blood and thus the growth rate [
14]. In this study, as a result of analyzing the antibody titer of the FMD structural protein in 6-week-old piglets after Zn-ASP administration and 4 weeks after the primary vaccination, 0.3% Zn-ASP administration improved the antibody titer by 7.3% compared to the positive control group, 0.2% Zn-ASP administration increased the antibody positive rate by 45% compared to the positive control group. In the antibody titer analysis result 4 weeks after the second vaccination, the Zn-ASP group showed a 3.81% improvement compared to the positive control group, and both the Zn-ASP group and the non-administration group showed a 100% antibody positive rate until shipment. The combined treatment of FMD vaccine and Zn-ASP significantly increased IFN-γ, a cellular immune marker. Zinc promotes the secretion of IFN-γ through T-cell activation, thereby promoting the production of antibodies in B-cells [
18]. It is thought that the improvement of IFN-γ in blood by Zn-ASP is due to T cell activity, and the activated T cell stimulates B cells to promote the production of antibodies against the inactivated FMDV antigen that has invaded the body [
19].
The mucous membrane is the site where the host first encounters FMDV, and the formation of mucosal immunity is very important to block the initial infection of FMD. However, the mucosal immune response is not effectively induced with the injection-type vaccine, and an effective immune response is exhibited by IgA, a cellular immune marker [
20]. According to Junhua Shen et. Al (2014), it was reported that zinc intake through the oral route promotes the production of mucosal IgA and activates the mucosal immune system [
21]. Similarly, in this study, a significant increase in blood IgA was shown by oral administration of Zn-ASP. This is thought to show effective defense against external pathogen invasion by activating mucosal immunity as well as promoting humoral immunity through co-administration of Zn-ASP with vaccine.
Zinc is found in all cells by binding to proteins such as serum albumin or intracellular metallothionein [
22]. No significant change was confirmed as a result of analysis of hematological indicators in the administration of Zn-ASP. On the other hand, as a result of blood biochemical analysis, Zn-ASP showed a significant decrease in AST and CPK. When the affected area is damaged, AST and CPK leaks into the blood and blood levels increase. Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) is an enzyme present in hepatocytes, and creatine phosphokinase (CPK) is an enzyme found in the skeletal muscle, myocardium, and brain, etc. [
23,
24]. However, it is judged that it is possible to develop a safe oral vaccine adjuvant since it did not affect the results of hematological and blood biochemical analysis by Zn-ASP administration.
5. Conclusions
As a result of this study, after oral administration of Zn-ASP to piglets, only one dose vaccination of the FMD vaccine with administration of Zn-ASP showed a 90% antibody positivity rate, and showed an effect of increasing the antibody positivity rate by 45% compared to the non-dosing group (only FMD vaccine, non- administration of Zn-ASP). This suggests that Zn-ASP can be used as an oral vaccine adjuvant, and further studies are needed on the mechanism of immune activation. If the Zn-ASP oral administration provides protection against FMDV with only one vaccination, inducing stress in pigs and reducing the occurrence of abnormal meat at the inoculation site caused by additional vaccination may be decreased to increase the economic feasibility of breeding farms.
Author Contributions
Y.-S.K., K.I.P. and H.-J.L. developed the study design and revised the manuscript. B.-R.L. and N.-H.K. participated in the study design, performed the experiments, and analyzed the data. B.-R.L. wrote the draft manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was carried out with the support of “Cooperative Research Program for Agriculture Science and Technology Development (Project No. SA-00016498)” Rural Development Administration, Republic of Korea.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was carried out with approval from the Korea Agriculture, Forestry and Livestock Quarantine Headquarters for veterinary medicine clinical trials and was established according to the ethical guidelines and approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) of Gyeongsang National University, Republic of Korea.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available upon request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Grubman, M.J.; Baxt, B. Foot-and-mouth disease. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2004, 17, 465–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, A.M.Q.; Brown, F.; Christian, P.; Hovi, T.; Hyypia, T.; Knowles, NJ.; Lemon, SM.; Minor, PD.; Palmenberg, A.C.; Skern, T.; Stanway, G. Picornaviridae. In Virus taxonomy: Classification and Nomenclature of Viruses; Seventh report of the international committee on taxonomy of viruses; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2000; pp. 657–673. [Google Scholar]
- Barnett, P.V.; Cox, S.J.; Aggarwal, N.; Gerber, H.; McCullough, K.C. Further studies on the early protective responses of pigs following immunization with high potency foot and mouth disease vaccine. Vaccine 2002, 20, 3197–3208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, M.; Murphy, C.M.; Zhang, Z.; Durand, S.; Esteves, I.; Doel, C.; Alexandersen, S. Influence of exposure intensity on the efficiency and speed of transmission of Foot-and-mouth disease. J. Comp. Pathol. 2009, 140, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, F.A.; Gibbs, J.E.P.; Horzinek, M.C.; Studdert, M.J. Veterinary Virology, Veterinary and Zoonotic Viral Disease, 3rd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1999; pp. 521–528. [Google Scholar]
- Jamal, S.M.; Belsham, G.J. Foot-and-mouth disease: Past, present and future. Vet. Res. 2013, 44, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, E.Y.; Jung, S.; Jeong, H.K.; Han, J.H.; Son, J.H. Effects of Foot-and-mouth Disease Vaccination Location and Injection Device on the Incidence of Site Lesions in Pork. Korean J. Food. Sci. Anim. Resour. 2018, 38, 498–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valtulini, S.; Macchi, C.; Ballanti, P.; Cherel, Y.; Laval, A.; Theaker, J. M.; Bak, M.; Ferretti, E.; Morvan, H. Aluminium hydroxide-induced granulomas in pigs. Vaccine 2005, 23, 3999–4004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.H. Requirements for improved vaccines against foot-and-mouth disease epidemics. Clin. Exp. Vaccine Res. 2013, 2, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonaventura, P.; Benedetti, G.; Albarède, F.; Miossec, P. Zinc and its role in immunity and inflammation. Autoimmun. Rev. 2015, 14, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelton, N.W.; Tokach, M.D.; Nelssen, J.L.; Goodband, R.D.; Dritz, S.S.; DeRouchey, J.M.; Hill, G.M. Effects of copper sulfate, tri-basic copper chloride, and zinc oxide on weanling pig performance. J. Anim. Sci. 2011, 89, 2440–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, H.J.; Park, Y.J.; Cho, J.H. Changes in Diarrhea Score, Nutrient Digestibility, Zinc Utilization, Intestinal Immune Profiles, and Fecal Microbiome in Weaned Piglets by Different Forms of Zinc. Animals 2021, 11, 1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brean, M.; Abraham, S.; Hebart, M.; Kirkwood, R.N. Influence of parity of birth and suckled sows on piglet nasal mucosal colonization with Haemophilus parasuis. Can. Vet. J. 2016, 57, 1281–1283. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jiao, Y.; Li, X.; Kim, I.H. Changes in growth performance, nutrient digestibility, immune blood profiles, fecal microbial and fecal gas emission of growing pigs in response to zinc aspartic acid chelate. Asian-Australas J. Anim. Sci. 2020, 33, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutierrez, E.; Miller, T.C.; Gonzalez-Redondo, J.R.; Holcombe, J.A. Characterization of immobilized poly-L-aspartate as a metal chelator. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1999, 33, 1664–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, L.L.; Grubman, M.J. Foot and mouth disease virus vaccines. Vaccine 2009, 27, D90–D94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schubert, C.; Guttek, K.; Grüngreiff, K.; Thielitz, A.; Bühling, F.; Reinhold, A.; Brocke, S.; Reinhold, D. Oral zinc aspartate treats experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Biometals 2014, 27, 1249–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonardo, K.; Bruna, P.F.; Bianca, A.; João, P.B. The role of interferon-gamma on immune and allergic responses. Memórias do Instituto Oswaldo Cruz 2005, 100, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Hojyo, S.; Fukada, T. Roles of Zinc Signaling in the Immune System. J. Immunol. Res. 2016, 6762343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, S.J.; Parida, S.; Voyce, C. Further evaluation of higher potency vaccines for early protection of cattle against FMDV direct contact challenge. Vaccine 2007, 25, 7687–7695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, A.; He, M.; Mao, L.; Zou, H.; Peng, Q.; Xue, B.; Wang, L.; et al. Coated zinc oxide improves intestinal immunity function and regulates microbiota composition in weaned piglets. Br. J. Nutr. 2014, 111, 2123–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roohani, N.; Hurrell, R.; Kelishadi, R.; Schulin, R. Zinc and its importance for human health: An integrative review. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2013, 18, 144–157. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, H.K.; Hall, W.D.; Hurst, J.W. Clinical Methods: The History, Physical, and Laboratory Examinations, 3rd ed.; 1990.
- Wallimann, T.; Hemmer, W. Creatine kinase in non-muscle tissues and cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 1994, 133–134, 193–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Table 1.
Effect of increasing foot-and-mouth disease virus vaccine structural protein antibody positive rates in piglets administered with zinc-aspartic acid.
Table 1.
Effect of increasing foot-and-mouth disease virus vaccine structural protein antibody positive rates in piglets administered with zinc-aspartic acid.
| Group |
FMD antibody titer (PI, %) |
Before vaccination
(8 weeks old) |
Primary vaccination |
Secondary
vaccination |
after 4 weeks
(12 weeks old) |
after 4 weeks
(16 weeks old) |
after 8 weeks
(20 weeks old) |
after 16 weeks (before shipment) |
| NC |
21.75±2.86 |
22.46±3.92 |
23.14±4.29 |
22.32±3.76 |
22.63±3.10 |
| PC |
22.10±3.75 |
51.42±4.05 |
65.27±4.86 |
70.67±4.97 |
66.94±4.25 |
| TRT1 |
21.90±3.66 |
52.25±3.60 |
66.38±3.41 |
72.48±4.40 |
67.61±3.72 |
| TRT2 |
22.51±3.86 |
54.36±3.81a
|
68.45±±4.36a
|
73.82±4.54a
|
69.12±4.56a
|
| TRT3 |
22.04±3.25 |
55.16±4.19a
|
69.04±5.10a
|
73.92±4.76a
|
69.49±4.65a
|
Table 2.
Antibody positivity by FMD vaccination.
Table 2.
Antibody positivity by FMD vaccination.
| Group |
FMD antibody positive rate (%) |
Before vaccination
(8 weeks old) |
Primary vaccination |
Secondary
vaccination |
after 4 weeks
(12 weeks old) |
after 4 weeks
(16 weeks old) |
after 8 weeks
(20 weeks old) |
after 16 weeks
(before shipment) |
| NC |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
| PC |
0 |
55 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
| TRT1 |
0 |
65 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
| TRT2 |
0 |
90 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
| TRT3 |
0 |
85 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
Table 3.
Effect of combination prescription of FMD vaccine and Zn-ASP on humoral immune indicator.
Table 3.
Effect of combination prescription of FMD vaccine and Zn-ASP on humoral immune indicator.
| Group |
IFN-γ con. (pg/ml) |
| Before vaccination |
Primary vaccination
after 4 weeks |
Secondary vaccination
after 4 weeks |
| NC |
85.8±6.3 |
88.3±9.0 |
91.1±7.4 |
| PC |
85.3±5.6 |
97.21±5.94 |
105.07±7.14 |
| TRT1 |
86.2±7.9 |
104.63±6.92 |
115.41±9.01 |
| TRT2 |
86.5±7.8 |
105.24±7.55a
|
118.45±9.82a
|
| TRT3 |
87.1±8.3 |
108.72±7.30b
|
117.32±8.67a
|
Table 4.
Effect of combination prescription of FMD vaccine and Zn-ASP on cellular immune indicators (IgG, IgM, IgA).
Table 4.
Effect of combination prescription of FMD vaccine and Zn-ASP on cellular immune indicators (IgG, IgM, IgA).
| Item |
Group |
Antibody con. (pg/ml) |
| Before vaccination |
Primary vaccination
after 4 weeks |
Secondary vaccination
after 4 weeks |
IgG
(mg/ml) |
NC |
21.73±1.03 |
20.80±0.72 |
20.21±1.02 |
| PC |
21.12±0.81 |
24.54±1.39 |
25.89±1.08 |
| TRT1 |
21.55±1.19 |
24.30±1.16 |
25.11±1.13 |
| TRT2 |
21.96±1.29 |
24.41±0.98 |
25.47±1.06 |
| TRT3 |
21.85±1.05 |
24.10±0.79 |
25.28±1.19 |
IgM
(mg/ml) |
NC |
2.48±0.14 |
2.14±0.09 |
1.62±0.07 |
| PC |
2.50±0.16 |
3.41±0.19 |
4.51±0.28 |
| TRT1 |
2.45±0.09 |
3.36±0.16 |
4.44±0.27 |
| TRT2 |
2.47±0.12 |
3.27±0.18 |
4.39±0.22 |
| TRT3 |
2.43±0.13 |
3.22±0.16 |
4.34±0.21 |
IgA
(mg/ml) |
NC |
0.73±0.05 |
0.58±0.04 |
0.47±0.06 |
| PC |
0.74±0.06 |
0.84±0.08 |
0.94±0.09 |
| TRT1 |
0.71±0.07 |
0.92±0.10 |
1.04±0.10 |
| TRT2 |
0.72±0.04 |
0.98±0.11a
|
1.10±0.14a
|
| TRT3 |
0.75±0.07 |
1.03±0.12b
|
1.16±0.12b
|
Table 5.
Effect of concomitant prescription of FMD vaccine and Zn-ASP on hematological indicators.
Table 5.
Effect of concomitant prescription of FMD vaccine and Zn-ASP on hematological indicators.
| Item |
Group |
before vaccination |
Primary vaccination
after 4 weeks |
Secondary vaccination after 4 weeks |
WBC
(×103/μL) |
NC |
14.91±1.16 |
14.84±1.04 |
14.87±1.37 |
| PC |
14.96±1.46 |
16.43±1.57 |
15.55±1.30 |
| TRT1 |
14.83±1.09 |
15.96±1.14 |
15.09±1.16 |
| TRT2 |
14.89±1.06 |
16.14±1.27 |
15.23±1.26 |
| TRT3 |
14.84±1.20 |
16.09±1.28 |
15.31±1.05 |
RBC
(×106/μL) |
NC |
6.82±0.50 |
6.87±0.51 |
6.84±0.62 |
| PC |
6.86±0.38 |
6.83±0.45 |
6.94±0.47 |
| TRT1 |
6.92±0.47 |
7.03±0.48 |
7.15±0.48 |
| TRT2 |
6.88±0.37 |
7.08±0.51 |
7.19±0.46 |
| TRT3 |
6.80±0.42 |
7.06±0.41 |
7.22±0.47 |
Hb
(g/dL) |
NC |
12.05±1.08 |
12.09±1.13 |
12.04±1.04 |
| PC |
12.01±0.81 |
11.93±1.20 |
12.28±1.32 |
| TRT1 |
12.06±1.39 |
12.16±0.89 |
12.34±1.03 |
| TRT2 |
12.09±1.25 |
12.22±1.00 |
12.37±1.25 |
| TRT3 |
12.02±0.99 |
12.27±0.90 |
12.44±1.09 |
| HCT(%) |
NC |
35.55±2.74 |
35.43±2.36 |
35.49±3.03 |
| PC |
35.35±2.24 |
35.73±2.62 |
35.91±2.21 |
| TRT1 |
35.26±2.69 |
35.68±2.48 |
35.82±2.41 |
| TRT2 |
35.49±2.33 |
35.78±2.77 |
35.98±3.46 |
| TRT3 |
35.33±2.44 |
35.71±2.08 |
35.91±2.44 |
| LYM(%) |
NC |
53.41±2.09 |
53.53±3.55 |
53.44±2.97 |
| PC |
53.67±3.22 |
56.85±3.33 |
57.15±2.74 |
| TRT1 |
53.57±3.37 |
54.75±3.20 |
55.23±4.09 |
| TRT2 |
53.36±4.51 |
55.16±3.52 |
55.62±3.68 |
| TRT3 |
53.21±4.12 |
55.35±3.60 |
55.99±3.16 |
| NEU(%) |
NC |
36.37±1.32 |
36.69±1.54 |
36.58±1.96 |
| PC |
36.64±1.97 |
42.73±2.05 |
40.51±1.87 |
| TRT1 |
36.56±1.77 |
41.85±1.88 |
38.93±1.71 |
| TRT2 |
36.34±1.98 |
41.42±2.24 |
38.56±2.18 |
| TRT3 |
36.19±1.03 |
41.18±2.09 |
38.21±2.06 |
| EOS(%) |
NC |
2.25±0.24 |
2.30±0.17 |
2.33±0.20 |
| PC |
2.28±0.20 |
3.95±0.23 |
3.82±0.19 |
| TRT1 |
2.21±0.22 |
3.84±0.21 |
3.71±0.23 |
| TRT2 |
2.27±0.17 |
3.92±0.23 |
3.77±0.22 |
| TRT3 |
2.34±0.19 |
3.78±0.22 |
3.65±0.18 |
| BAS(%) |
NC |
0.79±0.07 |
0.81±0.06 |
0.78±0.05 |
| PC |
0.81±0.05 |
1.24±0.10 |
1.17±0.09 |
| TRT1 |
0.83±0.06 |
1.21±0.12 |
1.09±0.08 |
| TRT2 |
0.80±0.06 |
1.19±0.08 |
1.15±0.06 |
| TRT3 |
0.82±0.04 |
1.23±0.11 |
1.16±0.10 |
| MON(%) |
NC |
3.50±0.26 |
3.59±0.37 |
3.54±0.21 |
| PC |
3.48±0.22 |
3.85±0.30 |
3.72±0.22 |
| TRT1 |
3.55±0.30 |
3.77±0.29 |
3.69±0.32 |
| TRT2 |
3.49±0.31 |
3.74±0.33 |
3.71±0.27 |
| TRT3 |
3.54±0.32 |
3.82±0.32 |
3.75±0.34 |
| MCV(fl) |
NC |
60.30±2.79 |
59.84±2.11 |
60.87±3.27 |
| PC |
60.79±3.03 |
59.45±2.86 |
60.35±3.06 |
| TRT1 |
60.42±2.10 |
59.60±2.32 |
60.46±2.01 |
| TRT2 |
60.63±3.75 |
59.46±2.58 |
60.30±2.51 |
| TRT3 |
60.28±2.68 |
59.37±2.88 |
60.37±2.93 |
| MCH(pg) |
NC |
18.32±0.92 |
18.63±0.82 |
18.47±0.77 |
| PC |
18.48±0.88 |
18.16±1.04 |
18.57±1.10 |
| TRT1 |
18.54±0.70 |
18.04±0.59 |
18.52±0.74 |
| TRT2 |
18.34±1.03 |
17.98±0.79 |
18.47±0.80 |
| TRT3 |
18.36±0.71 |
18.17±0.72 |
18.55±0.97 |
MCHC
(g/dL) |
NC |
32.12±0.92 |
32.29±0.85 |
32.20±0.96 |
| PC |
32.21±1.09 |
32.57±0.93 |
32.82±0.85 |
| TRT1 |
32.32±0.57 |
32.49±0.80 |
32.72±1.00 |
| TRT2 |
32.41±1.00 |
32.51±0.97 |
32.80±0.80 |
| TRT3 |
32.42±0.93 |
32.55±0.95 |
32.79±0.88 |
PLT
(×103/μL) |
NC |
352.0±23.9 |
349.2±21.7 |
353.1±19.9 |
| PC |
351.2±26.6 |
384.5±25.6 |
373.2±25.1 |
| TRT1 |
350.9±19.7 |
385.6±17.6 |
368.0±27.1 |
| TRT2 |
354.2±18.5 |
383.2±14.6 |
370.8±16.3 |
| TRT3 |
357.5±16.9 |
388.8±14.6 |
368.5±23.7 |
Table 6.
Effect of concomitant prescription of FMD vaccine and Zn-ASP on blood biochemical indicators.
Table 6.
Effect of concomitant prescription of FMD vaccine and Zn-ASP on blood biochemical indicators.
| Item |
Group |
before vaccination |
Primary vaccination
after 4 weeks |
Secondary vaccination after 4 weeks |
ALP
(U/L) |
NC |
237.0±12.3 |
236.7±9.35 |
238.2±12.2 |
| PC |
238.4±13.5 |
247.5±12.7 |
243.9±15.8 |
| TRT1 |
235.3±13.2 |
246.9±13.1 |
241.2±12.7 |
| TRT2 |
237.5±11.5 |
247.1±12.0 |
241.7±13.4 |
| TRT3 |
239.8±13.7 |
249.7±15.9 |
242.1±11.9 |
GLU
(mg/dL) |
NC |
124.4±11.6 |
125.3±8.0 |
123.6±10.4 |
| PC |
123.9±8.1 |
129.5±7.9 |
127.1±15.4 |
| TRT1 |
124.8±12.2 |
127.3±8.4 |
126.0±9.4 |
| TRT2 |
123.2±11.3 |
126.6±8.7 |
124.3±7.1 |
| TRT3 |
124.1±17.7 |
125.1±8.4 |
124.1±10.1 |
AST
(U/L) |
NC |
60.06±2.82 |
60.20±2.09 |
59.92±3.20 |
| PC |
60.25±2.38 |
72.14±3.45 |
68.43±3.03 |
| TRT1 |
59.96±3.09 |
67.03±2.76a
|
63.14±2.69b
|
| TRT2 |
60.19±2.07 |
65.47±3.73b
|
62.92±3.90a
|
| TRT3 |
60.10±2.93 |
64.36±2.72c
|
62.60±2.75b
|
ALT
(U/L) |
NC |
35.55±2.74 |
35.43±2.36 |
35.49±3.03 |
| PC |
35.35±2.24 |
35.73±2.62 |
35.91±2.21 |
| TRT1 |
35.26±2.69 |
35.68±2.48 |
35.82±2.41 |
| TRT2 |
35.49±2.33 |
35.78±2.77 |
35.98±3.46 |
| TRT3 |
35.33±2.44 |
35.71±2.08 |
35.91±2.44 |
BUN
(mg/dL) |
NC |
12.23±1.09 |
12.11±1.15 |
12.07±1.13 |
| PC |
12.17±1.14 |
12.50±1.53 |
12.32±1.17 |
| TRT1 |
12.24±0.93 |
12.38±1.30 |
12.19±1.44 |
| TRT2 |
12.31±1.29 |
12.40±0.87 |
55.62±3.68 |
| TRT3 |
53.21±4.12 |
12.34±1.39 |
55.99±3.16 |
CREA
(mg/dL) |
NC |
0.79±0.05 |
0.81±0.05 |
0.77±0.05 |
| PC |
0.77±0.04 |
0.85±1.00 |
0.81±0.07 |
| TRT1 |
0.78±0.05 |
0.83±0.07 |
0.80±0.06 |
| TRT2 |
0.79±0.05 |
0.80±0.05 |
0.79±0.08 |
| TRT3 |
0.78±0.04 |
0.79±0.07 |
0.78±0.06 |
CPK
(U/L) |
NC |
916.1±40.6 |
925.4±46.6 |
945.9±29.1 |
| PC |
917.8±41.9 |
1,170.9±45.9 |
1,245.1±43.6 |
| TRT1 |
913.1±33.5 |
1,117.2±44.7a
|
1,188.5±46.4a
|
| TRT2 |
920.5±42.9 |
1,030.1±43.7c
|
1,068.7±36.2c
|
| TRT3 |
918.0±42.5 |
1,018.6±40.3c
|
991.9±43.1c |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).