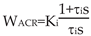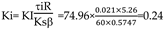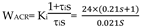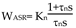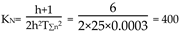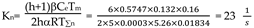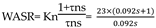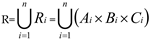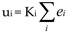1. Introduction
By the end of February 2020, there have been 85 million disabled people in China. It accounts for about 6.21% of the total population in China, among which there are 25 million patients with functional disabilities of upper and lower limbs, and the number of patients with physical disabilities and disabilities caused by congenital, disease, natural disasters and traffic accidents is increasing year by year. The number of seniors over the age of 60 is 241 million, and with the severity of aging, the size of the disabled seniors continues to expand. There are a large number of people with quadriplegia caused by spinal cord injury, cerebral palsy, stroke and other reasons in the world [
1]. Relevant research has been carried out in the field of smart wearable medical devices in order to help severely disabled people have a relatively independent ability to live and improve their quality of life. Among them, tongue-controlled aids can perform most of the work that requires the use of a personal computer. Due to high flexibility, tongue and mouth are chosen to perform assistive techniques to achieve more precise control of movement. For patients with severe disabilities who have lost their limbs, research has shown that tongue control aids are of attraction and applicabilityThe introduction should briefly place the study in a broad context and highlight why it is important. It should define the purpose of the work and its significance. The current state of the research field should be carefully reviewed and key publications cited. Please highlight controversial and diverging hypotheses when necessary. Finally, briefly mention the main aim of the work and highlight the principal conclusions. As far as possible, please keep the introduction comprehensible to scientists outside your particular field of research. References should be numbered in order of appearance and indicated by a numeral or numerals in square brackets—e.g., [
1] or [
2,
3], or [
4,
5,
6]. See the end of the document for further details on references.
1.1. Relevant Work
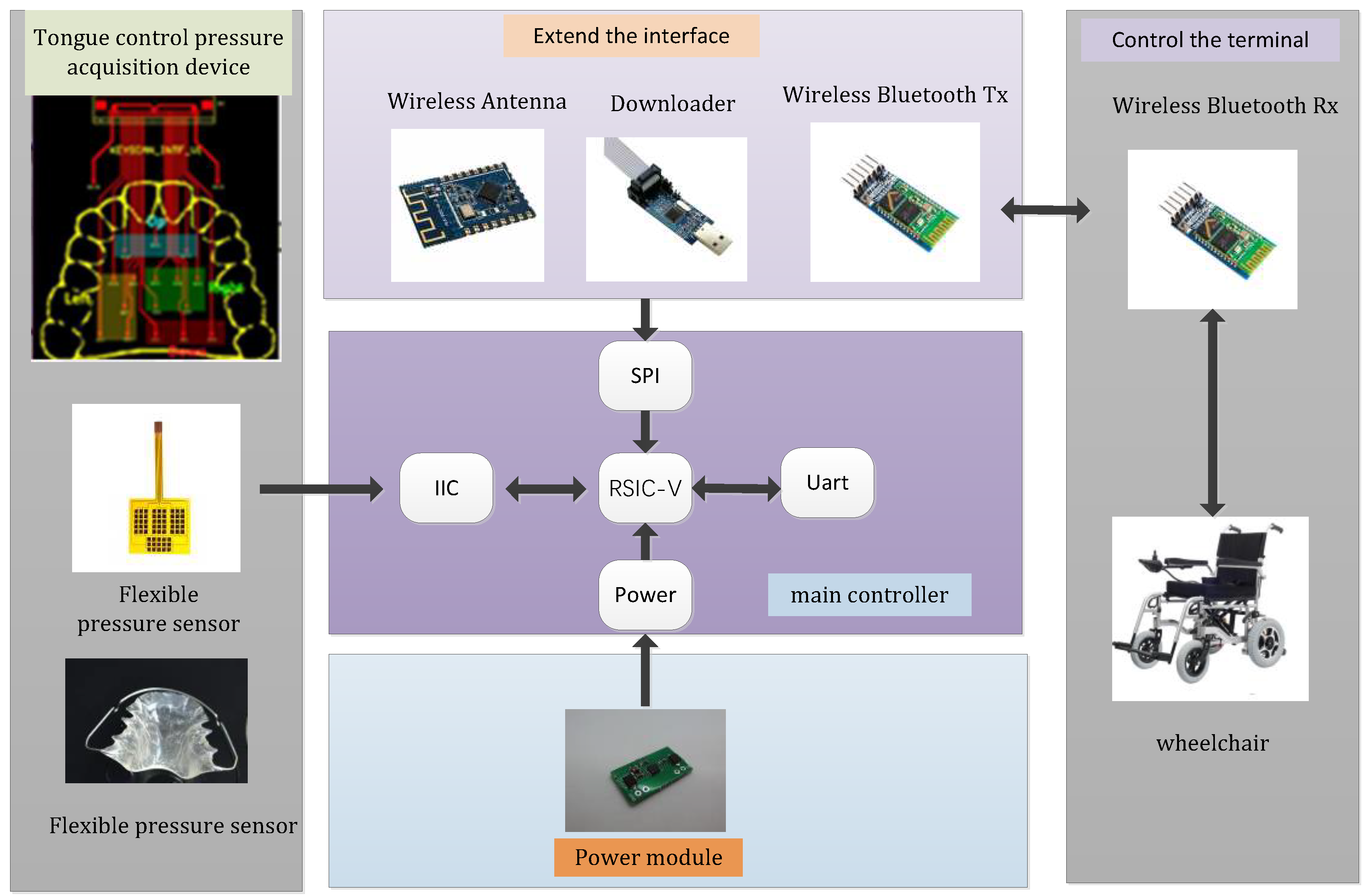
Currently popular tongue control research protocols include low-power independent system of tongue drive (iSTD) based on magnetic array, extraoral tongue drive system (ETDS), and joystick-controlled tongue control intelligent assistive device (STD) [2-4] . For iSTD systems, any bumps on a wheelchair of the patient may lead to misoperation of magnetic beads on the tongue and cause the control unit to emit misoperation signals, and ETDS and STD sometimes have similar problems. In addition, the above three methods only involve simple control of wheelchairs in the direction of up, down, left and right without optimizing the subsequent smoothing control of wheelchair's specific motion speed. To solve this problem, we propose a non-invasive intraoral stand-alone tongue control system based on RSIC-V edge computing by using Rocket processor as edge node decision-maker to obtain communication with low power consumption and low bandwidth while maintaining reasonable cost. By setting the pressure threshold and changing the amount of pressure, the wheelchair is controlled by closed-loop fuzzy PID, so as to avoid the malfunction of the control unit and optimize the users’ experience.The structure diagram of the non-invasive intraoral independent tongue control system based on RSIC-V edge computing is shown in
Figure 1 below.
2. System Hardware Architecture
2.1. Master Controller
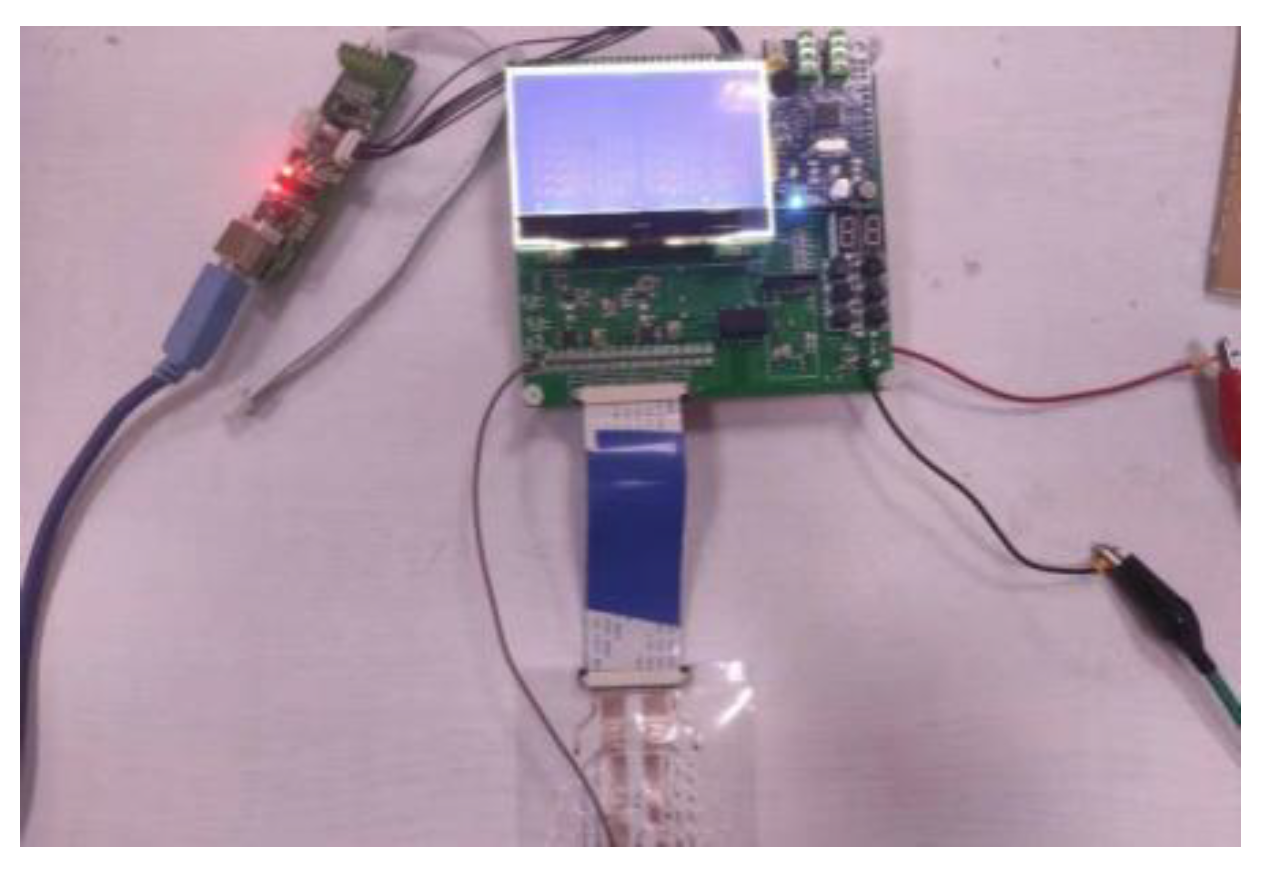
Due to the particularity of the oral environment, the master control chip placed in the oral cavity for monitoring the tongue muscle pressure needs to have the characteristics of stability, small size, light weight, low power consumption, and supporting for wireless communication to adapt to the particularity of the oral environment and provide an effective means to monitor tongue control devices. Consequently, the controller adopts the RSIC-V chip based on the Rocket kernel, and the characteristics of modularity make RISC-V have the characteristics of miniaturization and low energy consumption, which is crucial for embedded applications. The dynamic power of the Rocket kernel is 0.034mW/MHz, which is manufactured by TSMC 40GPLUS technology and its area is 0.14 mm2. In comparison, the Arm Cortex-A5 (32bit single-phase order) manufactured with the same process has a dynamic power of 0.08mW/MHz and an area of 0.27mm2. Running at the same frequency (>1GHz), the 64-bit Rocket scalar kernel consumes less power than the A5 kernel. To reduce power consumption, a power management unit is added to the SoC un the RSIC-V chip. If the SoC or a certain domain of the SoC is not used at certain times or in some applications, the power management unit will lower the voltage.
Figure 2.
RSIC-V System Board.
Figure 2.
RSIC-V System Board.
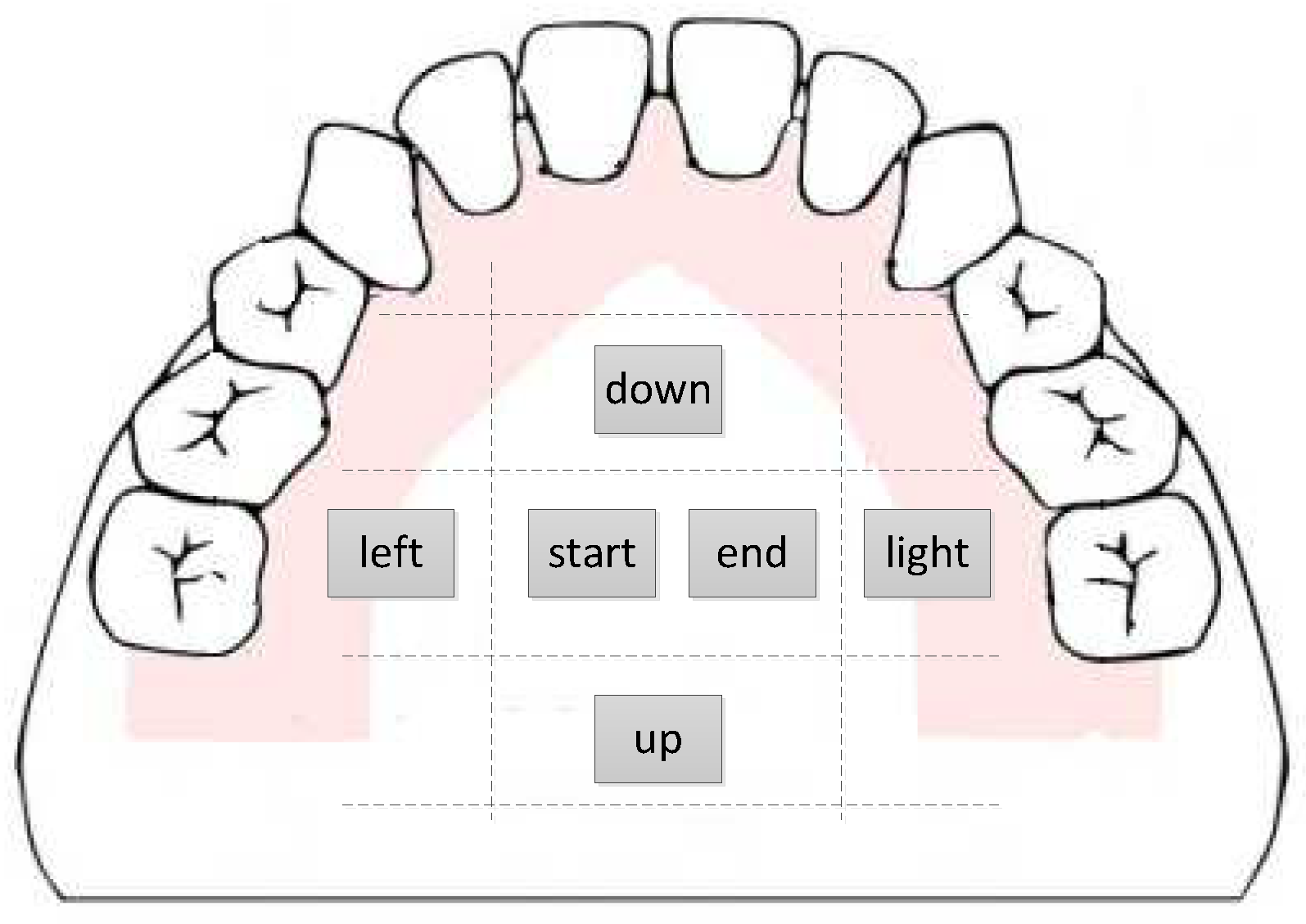
2.2. Pressure Sensor Array
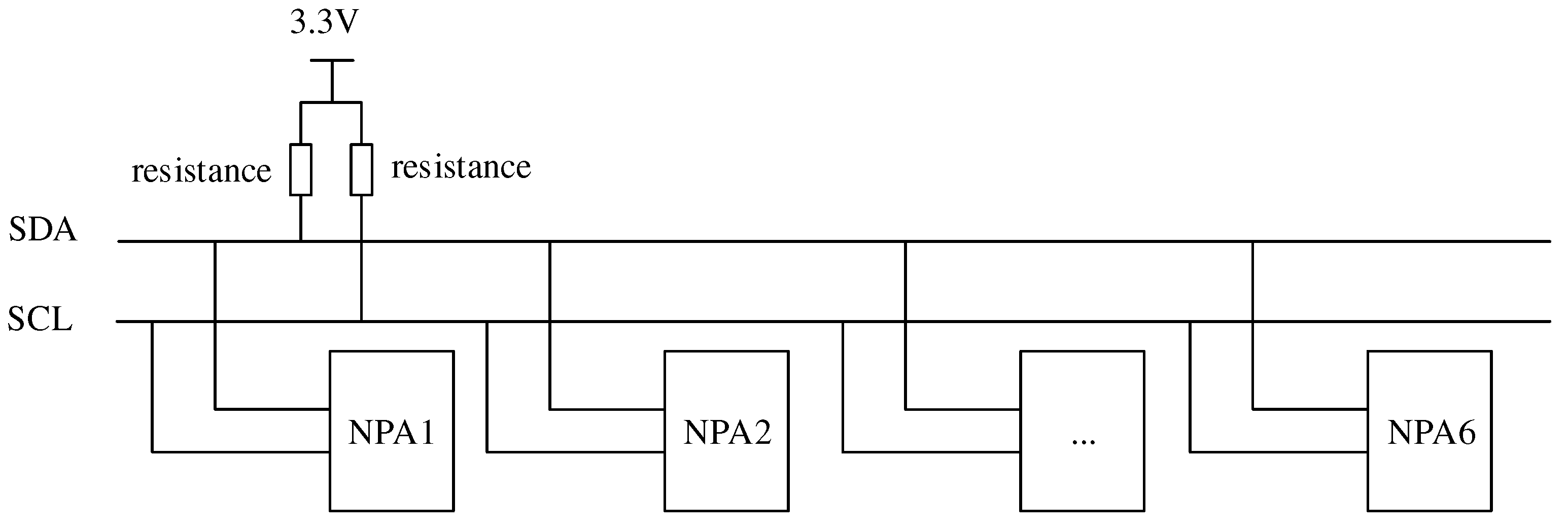
Compared with traditional pressure sensors, flexible thin-film pressure sensors are more suitable for closed and humid environments in the mouth. Thus we use a carbon nanotube-PDMS resistive pressure sensor array to integrate a signal conditioning circuit next to the pressure sensor bridge. Because this pressure sensor uses the inter-integrated circuit (I2C) communication protocol, all six sensors are connected to the same data and clock bus, as shown in
Figure 3. The I2C protocol specifies that the data and clock bus connect a pull-up resistor between the bus and the power supply, and Ohm 's Law is used to determine the minimum pull-up resistor required for the I2C connection. At this stage, there is no timing requirements; therefore, the minimum value of the pull-up resistor used is 4.7k. A 3.7V DTP301120 polymer Li-ion is used to power the electronics [7-10]. The carbon nanotube-PDMS resistance pressure sensor is shown in
Figure 3 and
Figure 4, and
Figure 5 shows the layout of the pressure sensor on the artificial palate film.
2.3. Wireless device
Compared with etds, the challenge of this method lies in embedding flexible pressure sensors in a wet oral environment, and the collected pressure signals generate specific action commands through the signal conditioning circuits, and finally the action commands are transmitted to the wheelchair side wireless receiver through a wireless communication module. In order to solve the problems of Tx antenna impedance and RF loss, Ali Jafari et al. put forward several ideas [
11]. Here, we used a custom-designed intraoral antenna to address this issue. Also, in previous iTDS and eTDS versions, raw magnetic sensor data had to be sent wirelessly to the Rx,and then processed and converted to tongue commands on a PC or smartphone. In this new design, an efficient tongue command detection algorithm processes raw data inside the tongue cavity and generates tongue commands directly in real time without relying on Rx processing power or software. By reducing the amount of data sent wirelessly to Rx, the intralingual pressure sensor data node is independent, and the power consumption of the system is reduced. Furthermore, by standardizing motion commands to match the standard format of Human Interface Devices (HIDs), they can be universally accepted as peripherals by most of today's computing devices [
12].
3. Experimental Methods
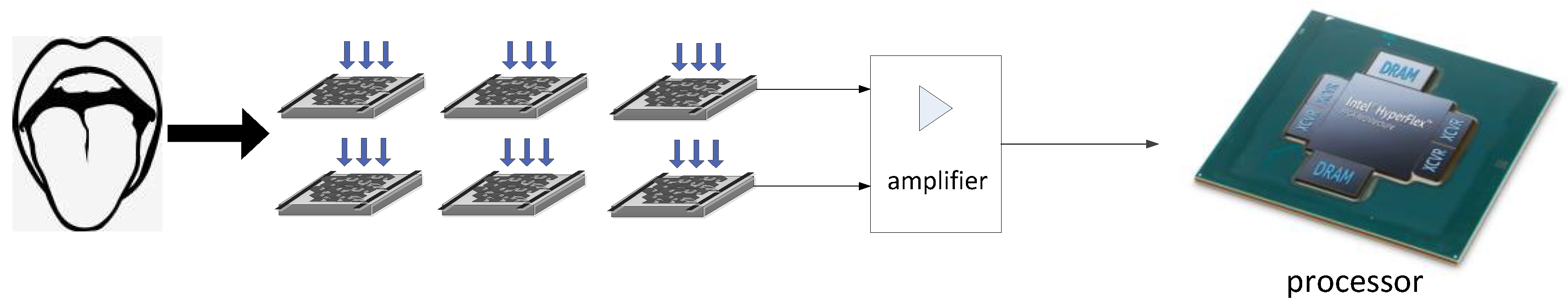
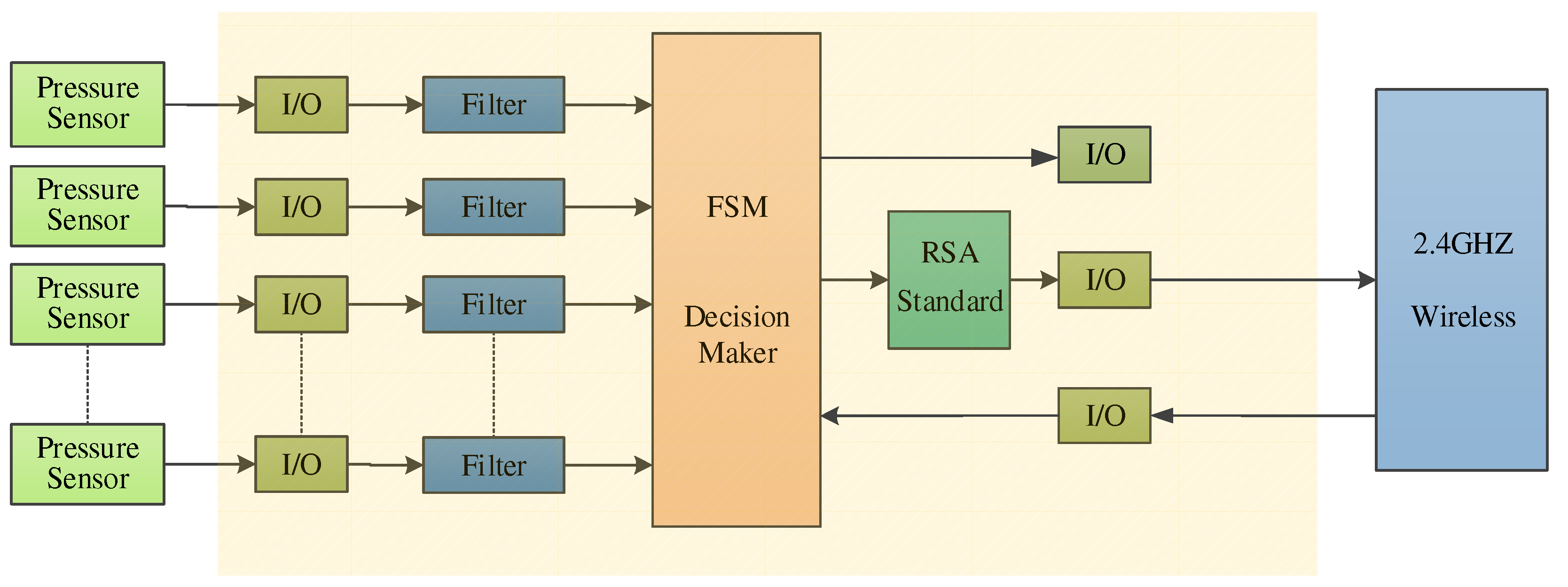
The system edge node is shown in
Figure 6 below, whose design consists of four parts: data acquisition part, data processing part, master controller, and wireless transmission. Pressure sensors are distributed on the edge to collect raw pressure data, which is subsequently transmitted to the RSIC-v processor in parallel through the signal conditioning circuit. Due to the parallel transmission mode, the number of pressure sensor nodes will not affect the system data transmission rate. The signal conditioning circuit is mainly composed of differential mode amplifier and filter. The third part is the finite state machine (FSM), which is a kind of computing model abstracted to study the computation process of finite memory and some language classes. A finite state automaton has a finite number of states, each of which can transmit to zero or more states, and the input string determines which transmission state is performed. This module converts pressure data into action instructions and it is also the decision-maker of the whole system, which processes all data from sensors and combines them with triggers from the cloud, and then the FSM determines the state of the environment around the node [
13]. For example, if the pressure signal is less than the set action threshold, then the decision-maker will judge it as invalid and the system does not issue any action commands. The AES encryptor is the third part of this edge Internet of Things, which guarantees the security of data transmission. All data from the FSM unit is encrypted before the nodes are transmitted to the cloud. In this paper, the 128-bit version of the RSA module is employed. The last part of the edge node is the wireless transceiver module, which transmits the encrypted output from the node to the cloud [
14]. The transceiver module can also send some defined information or instructions to the node from the cloud. In this paper, we use node 2.4GHZ high-gain antenna as the wireless transceiver module. The wireless sending nodes only need to transmit the modulated action command without transmitting a large amount of raw pressure data, which makes the system require low throughput.
3.1. System Software Process
The software architecture of the tongue control auxiliary device includes two modules: the software design of the intraoral stand-alone unit and the software design of the extraoral stand-alone unit. For the intraoral standalone unit, the communication mode between the CNT-PDMS pressure sensor array and the data processing unit is iic. Firstly, establish the communication between master and slave machines according to the device address and configure the wireless transmitter Rx. When the pressure sensor captures the pressure signal, the wireless transmitter can choose to send the original pressure data or send the action signal that has been processed by the data processing unit. Considering that if the original pressure data is sent, more resources and power consumption will be consumed, thus we choose to send the processed action signal directly through Rx. For the extraoral independent unit, communication with the intraoral independent unit needs to be established at first. When the wireless receiver Tx receives the action information, the master control chip transmits this action information to the wheelchair through Rx so as to control the movement of the wheelchair. The intracavitary independent unit software is shown in
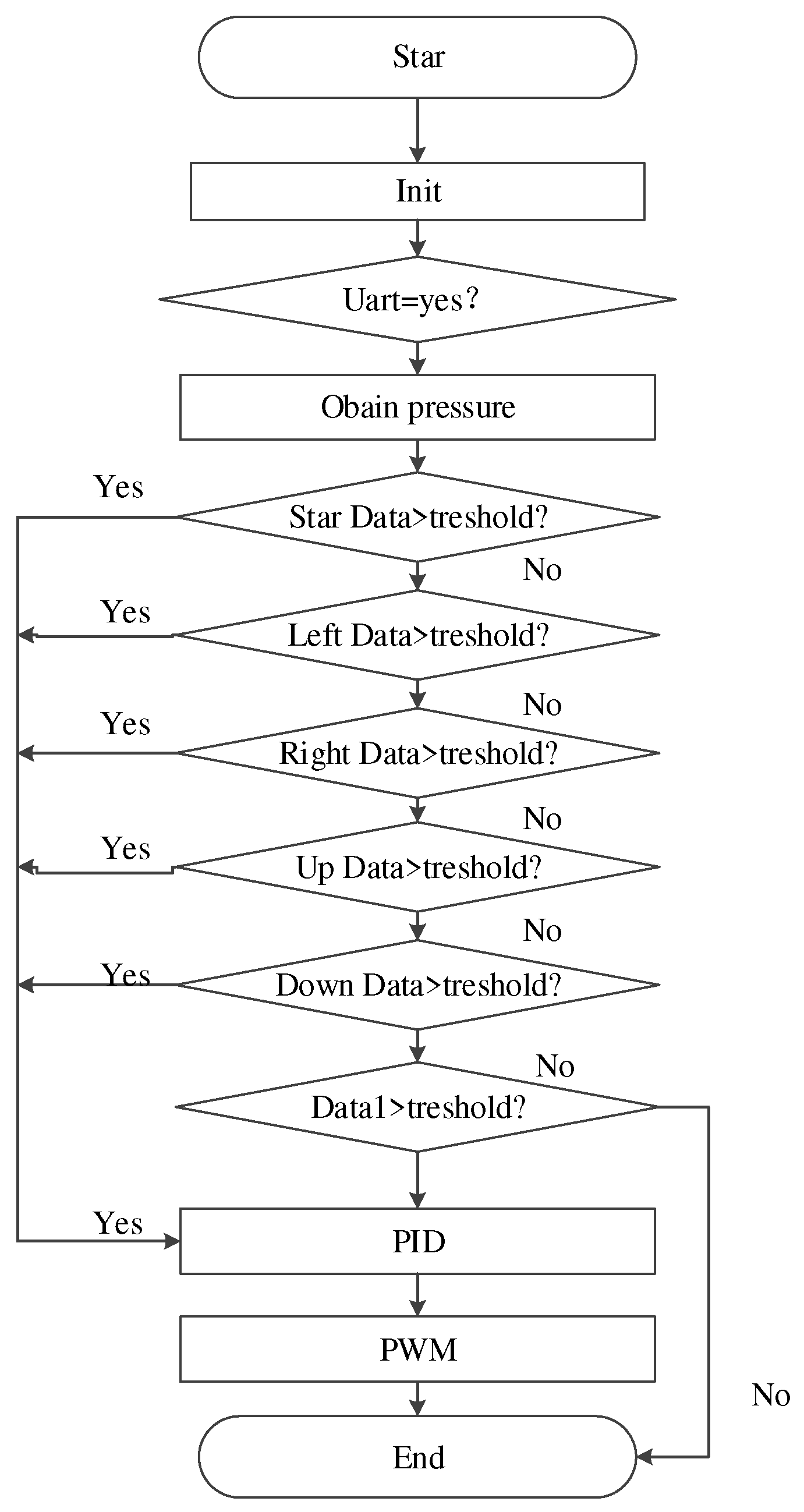
Figure 7 below. When the pressure sensor detects that the current pressure is larger than the set threshold, the pressure signal is employed to control the PWM of the wheelchair motor through adaptive fuzzy PID, so as to ensure the smooth movement of wheelchair and increase the comfortability of users.
3.2. Control Algorithm
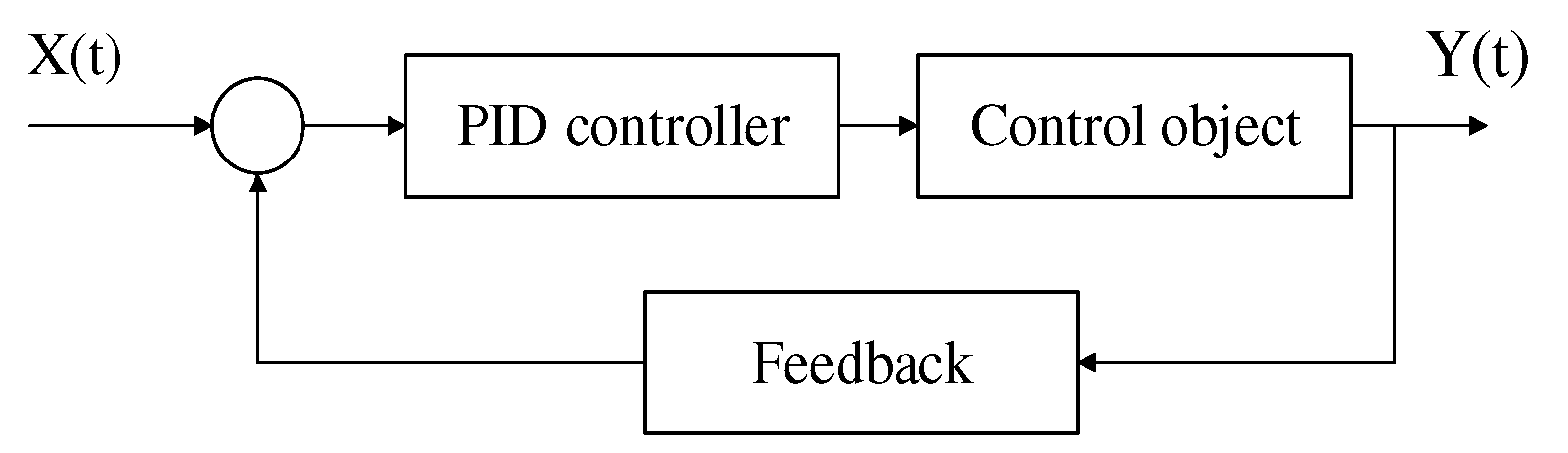
What is introduced above is mainly the information collection method adopted by the tongue control device. For a comprehensive control system, follow-up control methods should also be considered. In engineering practice, the most widely used regulator control law is PID control. When the structure and parameters of PID regulating controlled object cannot be fully mastered or there is no accurate mathematical model, the structure and parameters of system controller must be determined through experience and field debugging [
15]. In practice, there are also PI and PD controls in PID control. PID controller is a systematic error, which is controlled by proportional, integral and differential calculation of the control quantity. When the pressure of the tongue muscle touching the pressure sensor changes, the movement of the wheelchair is also approximately uniform or uniformly accelerated and decelerated accordingly, allowing the user to feel more comfortable during the movement. The flow chart of the traditional PID algorithm is shown in
Figure 8 below.
The specifications of the wheelchair DC motor are as follows: rated voltage U N = 2 4 V, rated current I N = 13 .7A, maximum speed nN = 75 0 r/min, allowable overload factor = 1.6, amplification factor of the thyristor triggered rectifier: Ks = 30, loop resistance R = 5.26 Ω , Electromagnetic time constant: Tl = 0.021s, PI type is selected for current regulator, and its transfer function is
ACR preemptive time constant: τ
i = Tl = 0.021s. The scale factor of ACR is
PI type is selected for current loop ASR regulator, and its transfer function is
Speed loop open loop gain:
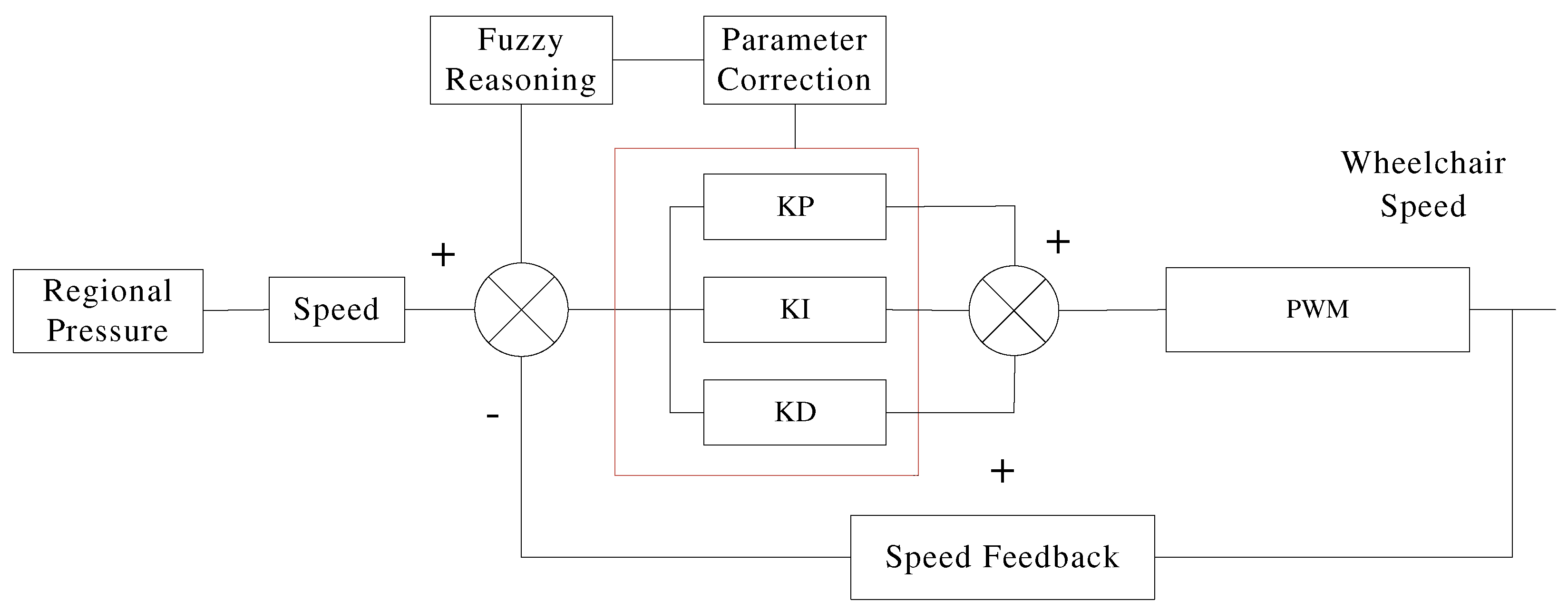
Intelligent wheelchair is a multi-variable, nonlinear, time-varying system, which requires high accuracy and robustness, while it is difficult for traditional PID controllers to achieve this goal. Fuzzy PID control can effectively solve the problem of nonlinearity and rapid changing, and minimize the influence of disturbance and parameter change. It does not rely on the precise mathematical model of the controlled object; besides it can overcome the influence of nonlinear factors, and has a strong robustness to the parameter changes of the controlled object. It does not need to establish a mathematical model. According to the input and output result data of the actual system and referring to the operating experience of field operators, the system can controlled in real time [
16]. Its fuzzy PID control flow chart is as shown in
Figure 9 below, and its wheelchair rotation speed can be obtained by the encoder.
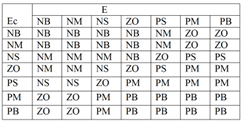
The adaptive fuzzy pid quantifies and fuzzifies the input quantity,which is the deviation E between the set output voltage and the feedback voltage of the motor and the deviation change rate Ec. Seven fuzzy control states are used to describe the speed deviation E in the motor speed regulation fuzzy controller system: Negative Big (NB), Negative Medium (NM), Negative Small (NS), Zero (ZO), Positive Small (PS), Medium (PM), and Positive Big (PB). The corresponding universe of fuzzy sets after discretization is as follow: E*={-6, -5, -4, -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6} . The fuzzy control rules of DC motors are summarized in
Table 1,with a total of 49 control rules [
17].
The fuzzy relation of the output control system is:
The parameters of PI controller are determined by engineering design method, and the output u i * of fuzzy PID controller obtained from the figure is:
3.3. Anti-misoperation Pressure Threshold Setting
We first averaged the simulated mis-touch tongue muscle pressure collected by 4 different experimenters using a carbon nanotube-PDMS pressure sensor (the simulated mis-touch tongue muscle pressure included the situation when the experimenters sit in a wheelchair and bump or they swallow saliva normally). For each experimenter, we measure three times for bumping on the wheelchair as well as normal swallowing of saliva respectively, and then collect the pressure under normal touch. Each experimenter normally touched the pressure sensor three times, and the experimental results are shown in
Table 1. According to the data in the table below, we can conclude that when the pressure is greater than 0.12N, the pressure signal is the action signal.
Table 2.
Normal Touch Pressure and Mis-touch Tongue Pressure Collection Form Currently.
Table 2.
Normal Touch Pressure and Mis-touch Tongue Pressure Collection Form Currently.
Number of experiments |
Pressure Data |
|
Object |
|
|
| |
A |
B |
C |
D |
1
2
3 |
Normal pressure
Swallowing saliva pressure
Bump pressure
Normal pressure
Swallowing saliva pressure
Bump pressure
Normal pressure
Swallowing saliva pressure
Bump pressure |
0.124
0.042
0.022
0.122
0.05
0.024
0.128
0.037
0.028
|
0.138
0.048
0.025
0.132
0.063
0.027
0.139
0.042
0.027
|
0.131
0.041
0.029
0.135
0.061
0.022
0.134
0.036
0.024
|
0.127
0.043
0.021
0.129
0.057
0.035
0.132
0.034
0.022
|
4. System Testing and Evaluation
In order to evaluate the performance of the device, an accelerated response time test and a central strike experiment are conducted. Besides, in order to test the performance of the system, six not-disabled subjects wear the system to perform two tasks for two different algorithm experiments: the speed response over time test, and a center click task [
18]. Three healthy men and three healthy women perform the experiment, none of whom has ever used a tongue machine interface device before the experiment. In addition, a 20-second calibration is performed at first use, after which the subjects perform the following tasks according to the test content respectively.
4.1. Speed Response Time Test
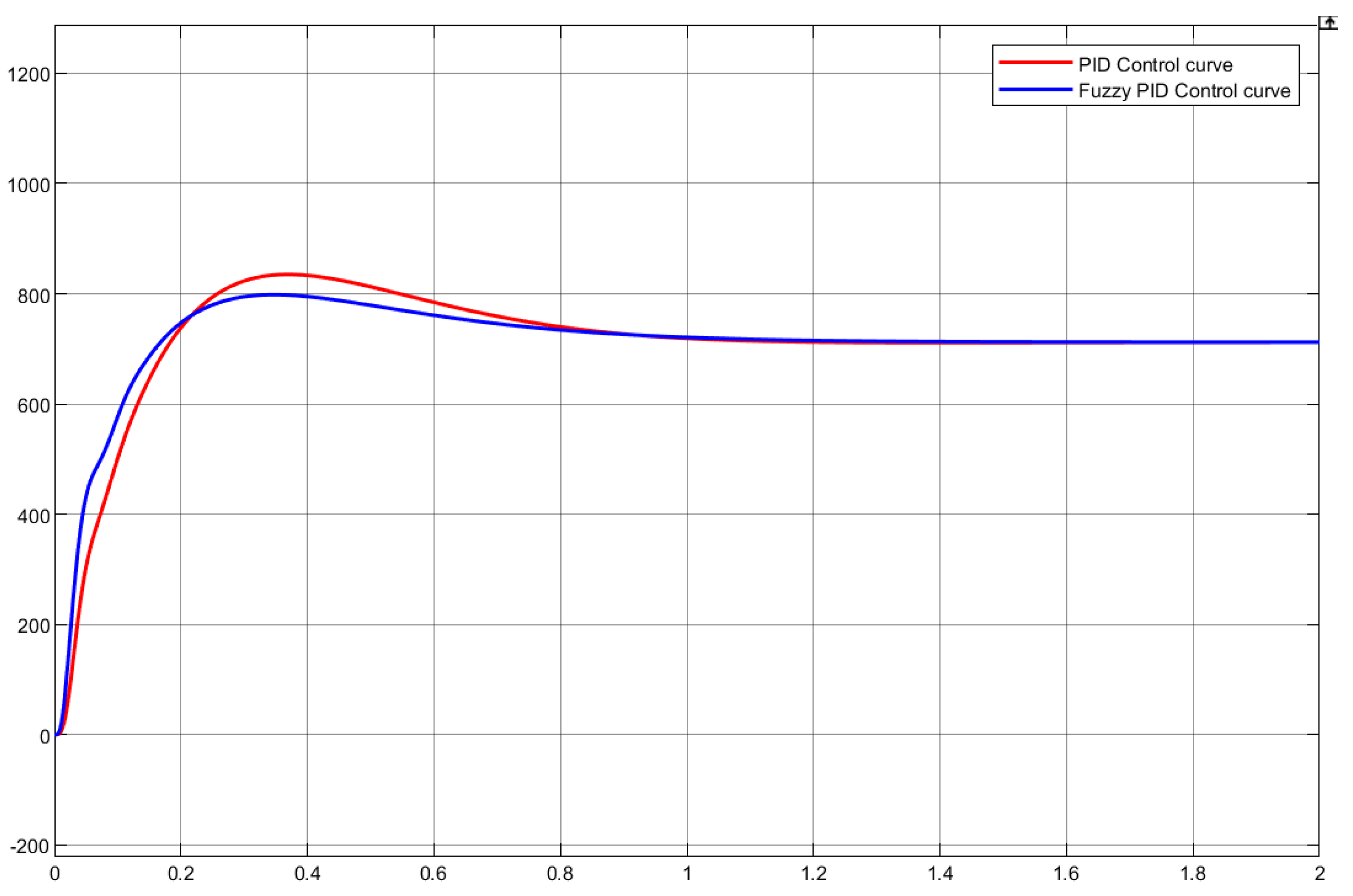
In this test, the response time of speed control command is detected, and the speed response curve of wheelchair acceleration with time is obtained by matlab simulation. When a DC motor with a set speed of 750 r/min reaches the steady state, the rise time of the traditional PID model is 0.14s and the adjustment time is 0.64 s, while the rise time of the adaptive fuzzy PID is 0.108s, and the adjustment time is 0.59s. Compared with the traditional PID, the adaptive fuzzy PID control algorithm is more stable in the robustness of this system.
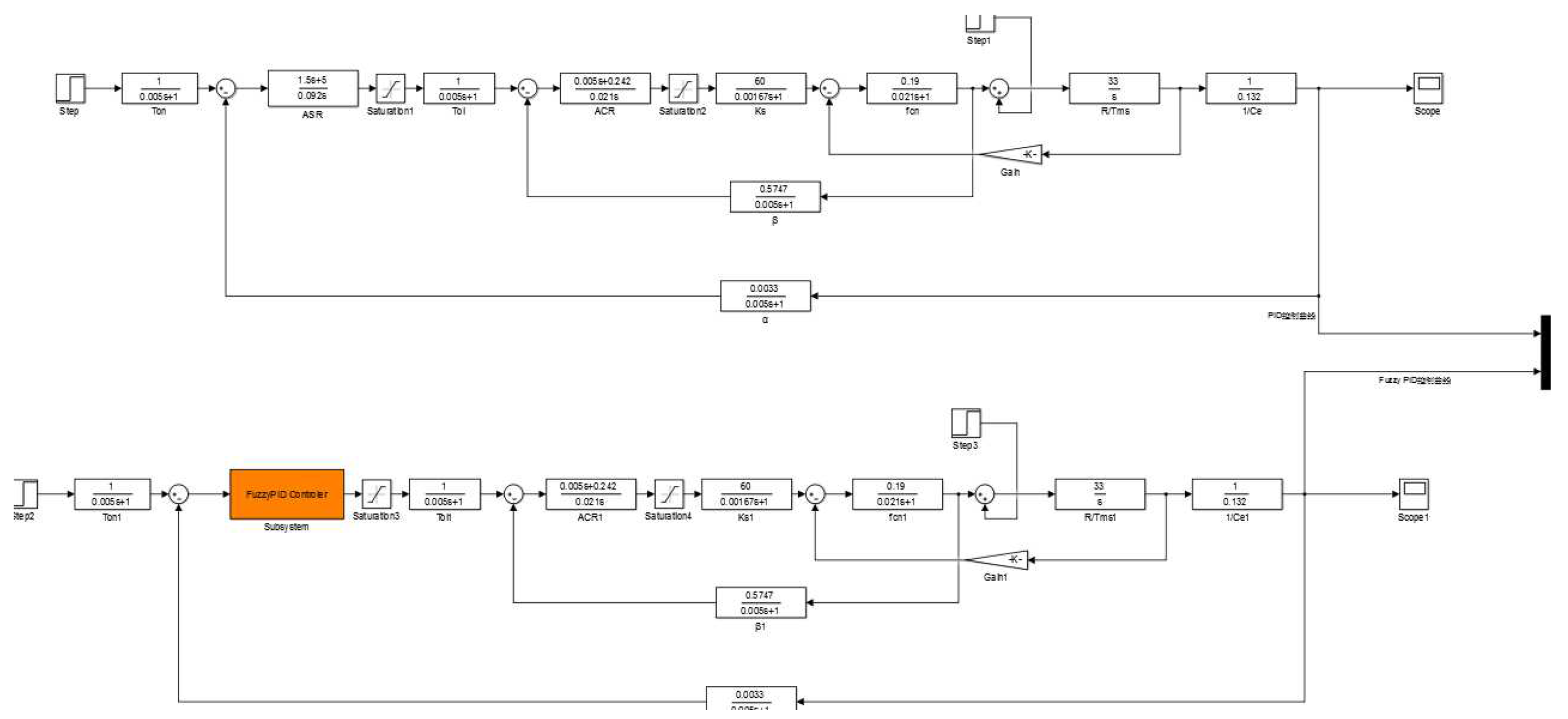
Figure 10 shows the siumlink model of PID and adaptive fuzzy PID, and
Figure 11 shows the simulation results.
The results show that compared with the PID control algorithm, by adopting the fuzzy adaptive PID control algorithm, the system may reduce the overshoot and the time to reach the set speed of the wheelchair during the acceleration process.
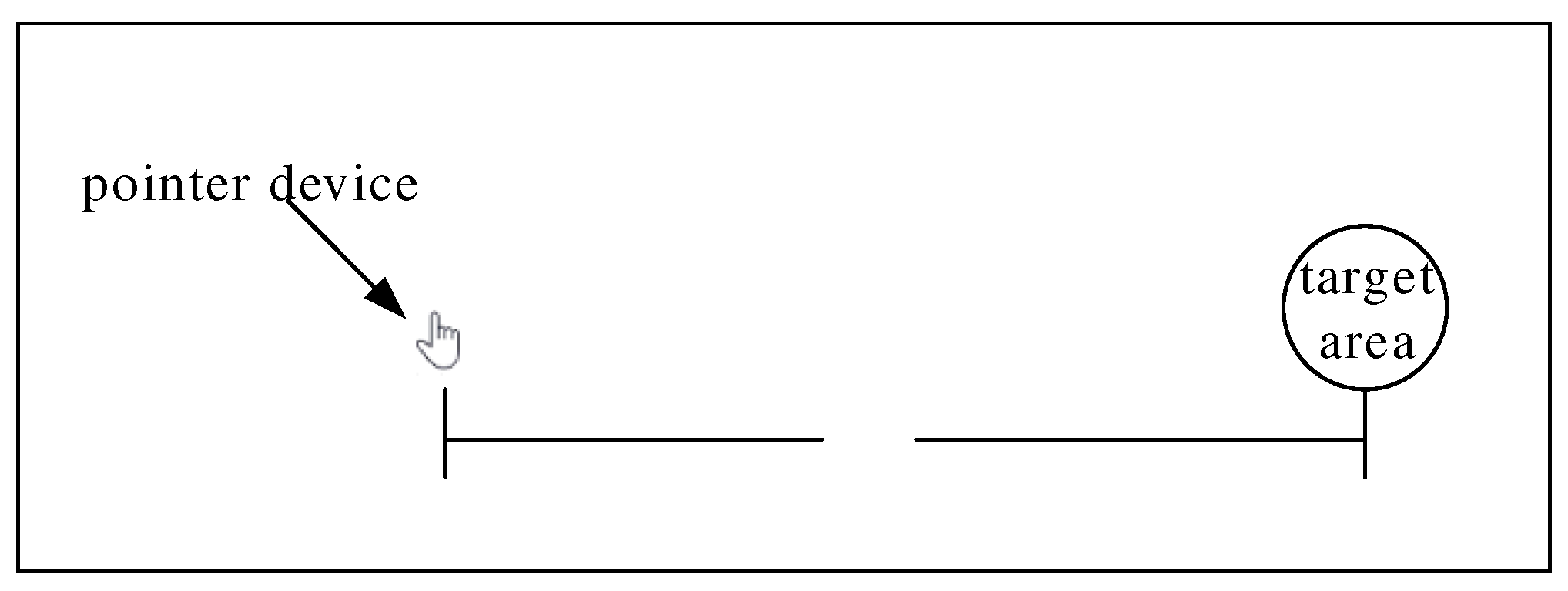
4.2. Center Click
The center click task evaluates tongue-controlled devices by speed and precision based on Fitts' law, which states the time to move a pointer to a target is related to the distance D between the current position of the pointer device and the target position and the size S of the target, as shown in
Figure 1 1. The expression formula is:
where a , b represent empirical parameters which are based on the physical characteristics of the pointer device, the subject, and the environment [
19].
Figure 1 1.
Schematic Diagram of Fitts‘ Law.
Figure 1 1.
Schematic Diagram of Fitts‘ Law.
According to the method described by Fanpeng Kong et al. [
20], two circular targets of different diameters are given randomly as 30 and 60 pixels respectively. The target appears only one at a time with various distances from the center. Subjects manually manipulated the cursor to move from the center to the target and click on the center of the target as possible as one could. A total of 32 circular targets were randomly presented according to the subjects' clicks. In this paper, throughput and reaction time are used as reference indexes.
Figure 1 2.
Center Click Task.
Figure 1 2.
Center Click Task.
In this paper, throughput is used to represent the information transfer rate from the system to laptop computer, which is in bits/s. The average throughput is given by the following equation [
15]:
Among them, ID represents the difficulty index under the same conditions; MT represents the mean movement time; m represents the target number of subjects; n represents the total number of subjects, and the difficulty index under the same conditions is calculated according to the Shannon’s formula:
wherein, D represents the distance from the pointer device, that is, the manual operation pointer, to the center of the circular target, and W represents the diameter of the circular target.
Response time refers to the time for the system to operate the cursor movement, represented by RT, and the unit is second.
The error rate refers to the proportion of subjects who fall outside the target range when they click on the target, expressed in ER.
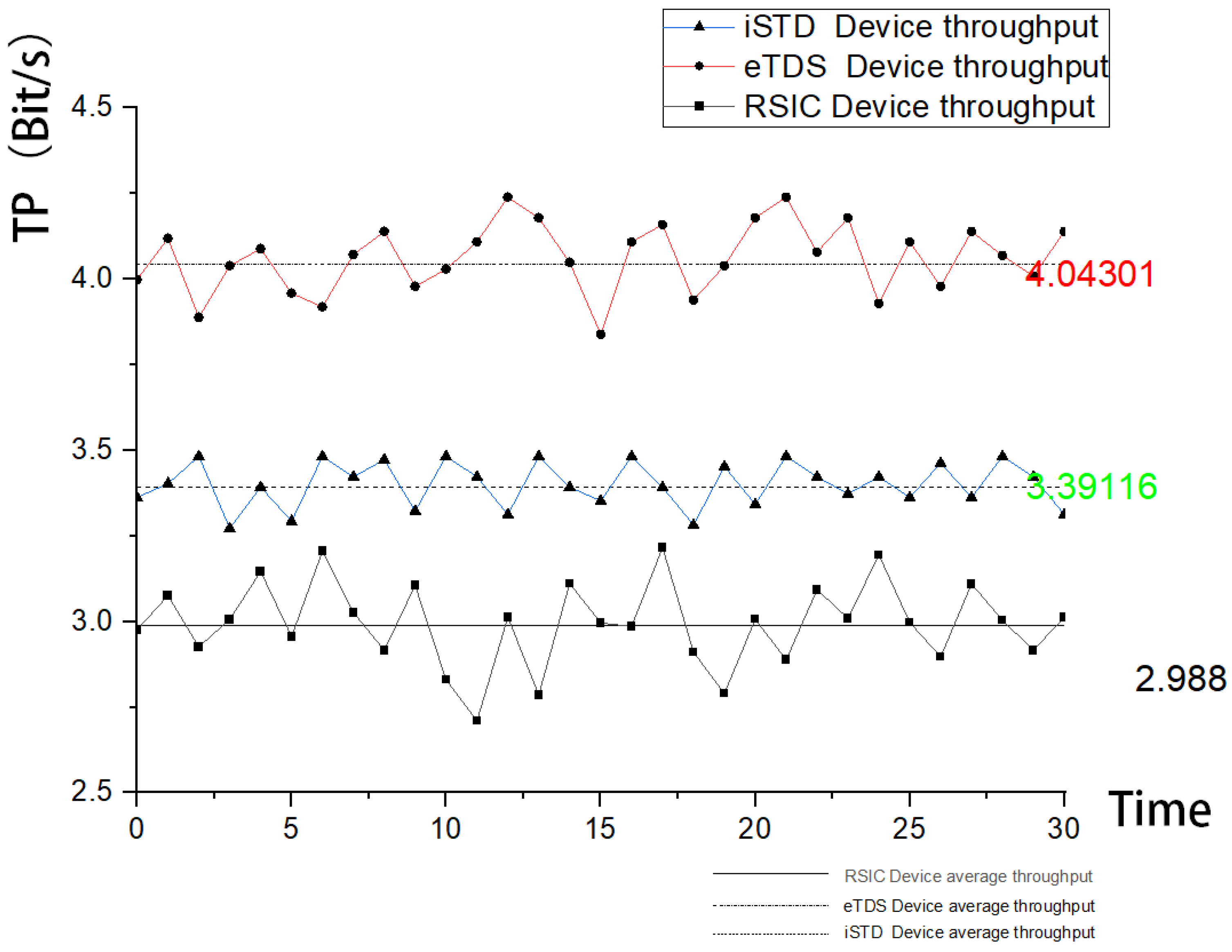
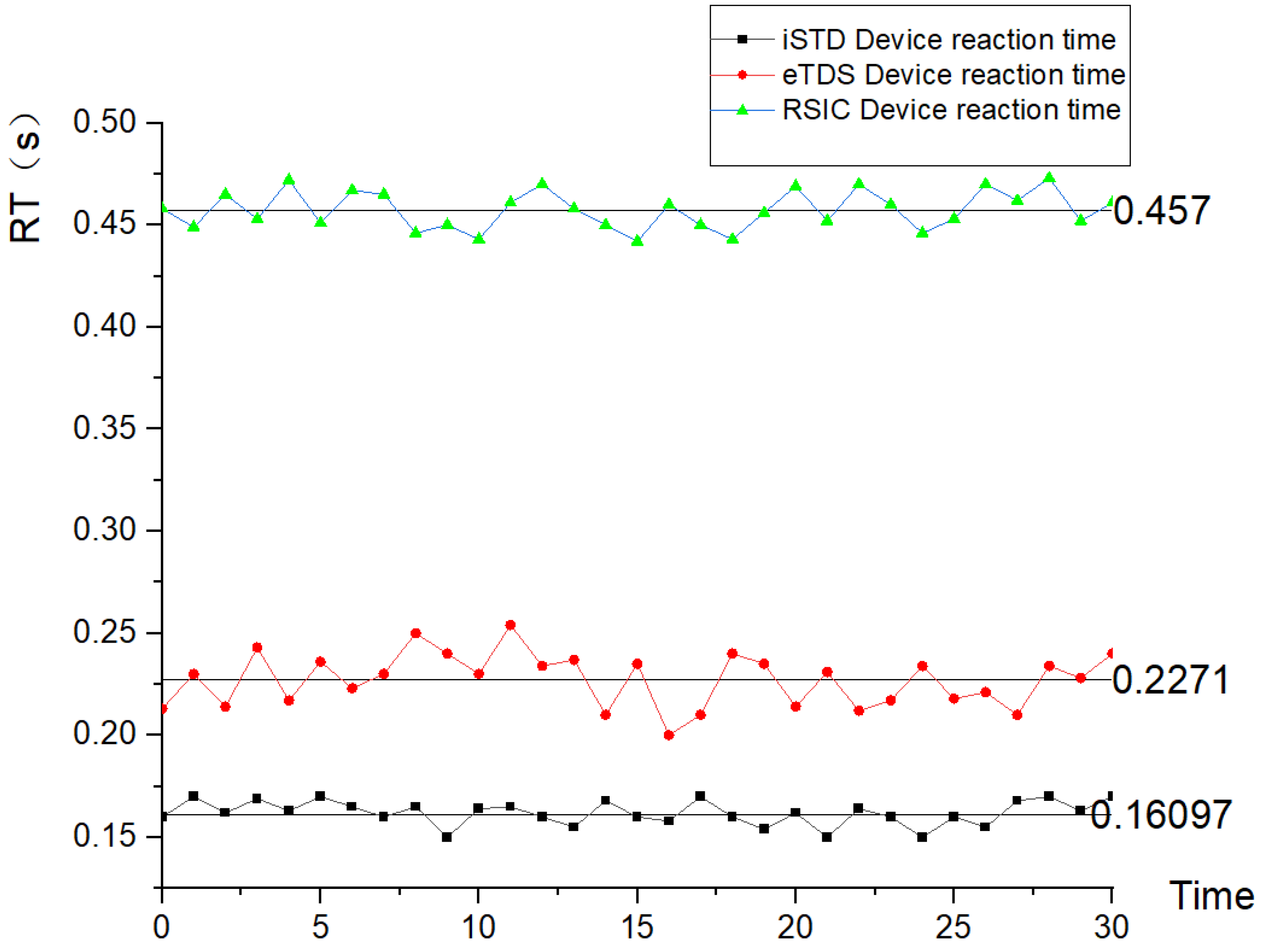
Subjects performed 30 tongue touch tasks using iSTD, eSTD, and RSIC-V edge-based tongue control device, respectively, and the analysis results are shown in
Figure 13 and
Figure 14 below.
From the above results, it can be observed that the throughput of tongue-controlled devices based on RSIC-V edge computing is less than that of iSTD devices and eTDS devices because the raw data of tongue-controlled devices based on RSIC-V edge computing has been processed on the sensor side and specific instructions have been generated, which greatly reduces the requirements for data transmission rate and thus reduces the loss of CPU occupancy and energy in data transmission; and the reaction time of tongue-controlled devices based on RSIC edge computing in the central click task averages to be 0.16S, which is faster than that of iSTD devices (0.457S) and eTDS (0.227s) devices.
4.3. Power Consumption Experiments and Analysis
The power consumption of the system is tested in the state of normal sending commands and standby as shown in
Table 3 below:
Compared with a low-power wearable standalone tongue drive system (sTDS) developed by Ali Jafari et al., the dynamic power is 4.451mw,which decreases by 18.8%, and the total power consumption is 4.471 mw, which decreases by 11.5%
5. Conclusions
In this paper, a non-intrusive intraoral stand-alone tongue control system based on RSIC-V edge computing is proposed. Patients can detect the pressure signal of tongue muscle touching the palate through a flexible carbon nanotube-PDMS pressure sensor array placed in the mouth, avoid the occurrence of false movement signal through the setting of pressure threshold, and perform adaptive fuzzy PID control on the wheelchair through the normal tongue touching pressure. It can accurately control the movement of the wheelchair, thus increasing the reliability of the device and imporve the user 's experience. After many system tests, it is proved that the tongue-controlled system control scheme studied in this paper is reasonable. The problem of tongue control miscontact is solved; the data transmission is reduced; and the power consumption is reduced by 11.5% compared with the sTDS system. On the whole, the tongue-driven system placed in the mouth can achieve better use results after reasonable training and practice.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the Jilin Provincial Department of Science and Technology(Grant/Awardi Number:No.YDZJ202303CGZH01.YDZJ202301ZYTS496), Jilin Provincial Department of Human Resources and Social Security (2022QN05), Changchun Science and Technology Bureau (21ZGM29) in this article.
References
- S. Kumar T., S. B. Arun, G. S. Jatadhara, A. Majumder and A. Dhar, "Design and Fabrication of Rehabilitation-based Exoskeleton for Paralytic Arm," 2020 International Conference on Smart Electronics and Communication (ICOSEC), Trichy, India, 2020, pp. 143-148. [CrossRef]
- Kong, F. , et al. "A Stand-Alone Intraoral Tongue-Controlled Computer Interface for People With Tetraplegia." IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Circuits and Systems (2019).
- Mohammadi, M. , et al. "A high-resolution tongue-based joystick to enable robot control for individuals with severe disabilities." 2019.
- IEEE 16th International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics (ICORR) IEEE, 2019.
- Dang, B. , et al. "Tongue driven wireless electronic communication device." 2017 IEEE Sensors Applications Symposium (SAS) IEEE,.
- Qui N M , Lin C H , Chen P . Design and Implementation of a 256-Bit RISC-V-Based Dynamically Scheduled Very Long Instruction Word on FPGA[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8:172996-173007. [CrossRef]
- Shea C , Mohsenin T . Heterogeneous Scheduling of Deep Neural Networks for Low-power Real-time Designs[J]. ACM Journal on Emerging Technologies in Computing Systems (JETC), 2019.
- Akhter F , Siddiquei H R , Alahi M , et al. Design, Fabrication, and Implementation of a Novel MWCNTs/PDMS Phosphate Sensor for Agricultural Applications[J]. 2022.
- Zhang, K. , et al. "Self-healing and stretchable PDMS-based bifunctional sensor enabled by synergistic dynamic interactions." Chemical Engineering Journal 412.36(2021):128734. [CrossRef]
- Trujilho, L. , O. Saotome , and J. Berg . "Dependable I2C Communication withFPGA." Brazilian Technology Symposium Springer, Cham,.
- Wu, H. , et al. "All-Inorganic Lead Free Double Perovskite Li-Battery Anode Material Hosting High Li+ Ion Concentrations." Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters 12.17(2021):4125-4129. [CrossRef]
- Md, Nazmus, Sahadat, et al. An Independent Tongue-Operated Assistive System for Both Access and Mobility[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2018.
- Barlow S M , Custead R , Lee J , et al. Wireless Sensing of Lower Lip and Thumb-Index Finger 'Ramp-and-Hold' Isometric Force Dynamics in a Small Cohort of Unilateral MCA Stroke: Discussion of Preliminary Findings[J]. Sensors, 2020, 20(4):1221. [CrossRef]
- Yadav R , Zhang W , Elgendy I A , et al. Smart Healthcare: RL-Based Task Offloading Scheme for Edge-Enable Sensor Networks[J]. IEEE sensors journal, 2021(21-22).
- Ferdian R , Aisuwarya R , Erlina T . Edge Computing for Internet of Things Based on FPGA[C]// 2020 International Conference on Information Technology Systems and Innovation (ICITSI). 2020.
- Zand J P , Sabouri J , Katebi J , et al. A new time-domain robust anti-windup PID control scheme for vibration suppression of building structure[J]. Engineering structures, 2021(Oct.1):244.
- Tunjung D , Prajitno P , Handoko D . Temperature and water level control system in water thermal mixing process using adaptive fuzzy PID controller[J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2021, 1816(1):012032-. [CrossRef]
- Aftab A , Luan X . A fuzzy-PID series feedback self-tuned adaptive control of reactor power using nonlinear multipoint kinetic model under reference tracking and disturbance rejection[J]. Annals of Nuclear Energy, 2022, 166:108696-. [CrossRef]
- Engwall O . Combining MRI, EMA and EPG measurements in a three-dimensional tongue model[J]. Speech Communication, 2003, 41( 2–3):303-329. [CrossRef]
- Kim J , Park H , Bruce J , et al. Qualitative assessment of Tongue Drive System by people with high-level spinal cord injury[J]. Journal of Rehabilitation Research & Development, 2014, 51(3):451-65. [CrossRef]
- Preliminary Assessment of a Novel Intraoral-Tongue Operated Assistive Technology with Computer Interface.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).