Childhood leukemia
Since the beginning of the radiation age, childhood leukemia has become a favourite indicator of radiation health effects. The disease increased from the 1920s in proportion to the mining of Uranium and production of Radium [
1]. It followed radiation exposure in Japan after the A-Bombs [
2,
3]. During the atmospheric testing fallout, the UK Medical Research Council [
4] maintained that the exposure was safe. Nevertheless, Strontium-90 increased in the milk and in children [
5,
6] and the USA and Soviet Union stopped the testing, Kennedy citing child leukemia as a reason. By 1960, Alice Stewart had reported significant levels of child leukemia in children who had been X-rayed
in utero, with an excess risk of about 40% for a 10mSv external dose (ERR of 40 per Sievert, similar to that reported for the LSS cohorts [
3,
7].) In 1983 the child leukemia cluster near the Sellafield nuclear plant in the UK brought the attention of the world to the possibility that “low doses” of internal radionuclide exposures could cause significant effects [
8,
9,
10,
11,
12].
The Sellafield cluster was dismissed as a radiation effect by the UK agencies in the 1980s and since. A 1993 court case was lost on the basis that the overall dose was too low [
8,
11,
12]. However, excess risks were soon found at most of the contaminated nuclear sites in Europe, though similarly dismissed [
10,
11]. The ERR in the case of the nuclear sites must have been greater than 1000 per Sievert if causal. But one early pointer to the involvement of internal exposures was a study in 1985 by Lyman et al. of an area of USA where phosphate deposits caused levels of Radium-226 to be high. Leukemia rates were found to be 50% higher in the high Radium area [
13].
Therefore, it is clear from the literature that the risk of child leukemia is significantly high for low internal doses, but for external doses, the risk factor per dose is lower by orders of magnitude. We have to reconcile two quite starkly opposing pieces of evidence. Relatively high external doses (e.g. obstetric X-rays [
7] the Japanese LSS [
3], ankylosing spondylitis [
14] are required to cause modest increases in child leukemia, and at the same time very small doses from internal radionuclides are reported to cause significantly larger effects. This is a puzzle, which it is proposed here might be resolved on the basis of a biological approach to causation.
The aim of this study is to re-examine the question of radiogenic child leukemia on the basis of two simple biologically plausible assumptions:
That internal exposure provides a much greater risk than external exposure because internal exposures cause much higher local cell-ionisation damage.
That there is a hump-backed or Weibull type dose response owing to the combination of mutation at low cell dose and killing at high or multi-hit cell ionisation damage.
What would these assumptions predict for child leukemia?
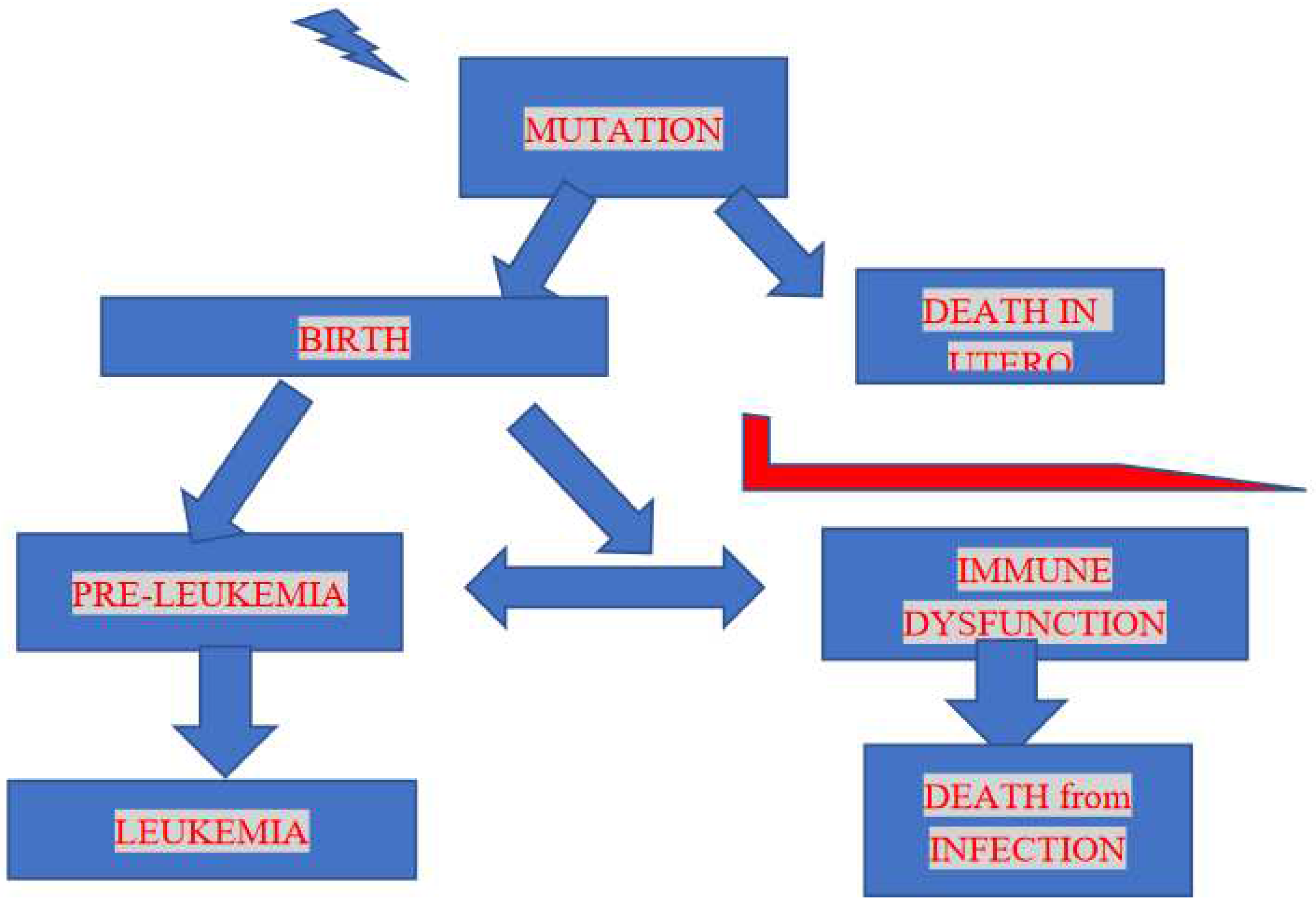
Figure 1 provides a flow chart which outlines the downstream possibilities from radiation damage to an individual which lead to leukemia in childhood and which represents the basis for the approach in this study and the interpretation of the results.
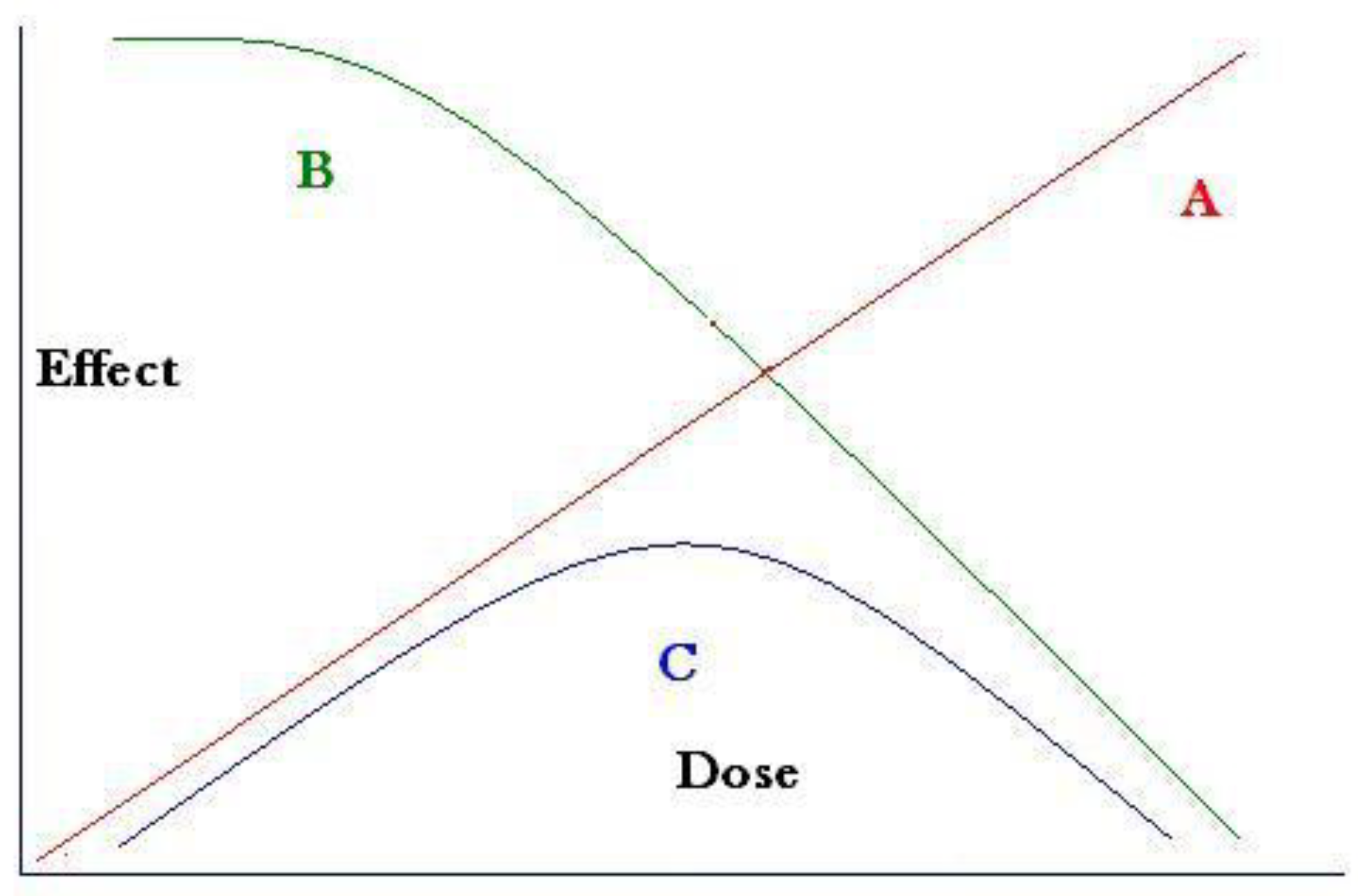
Since higher doses at the cell level would cause cell death (or sterilisation) the final leukemia yield would result from a combination of two opposing rates, mutation rate and pre-leukemia deaths, which could be expressed as foetal death or also pre-leukemia death due to a compromised immune system. The resulting dose-response would represent a failure type or Weibull distribution [
15] and appear like
Figure 2 where mutation is assumed to be linearly proportional to dose and cell death or cell sterilisation would follow the well-known radiation cell survival curve [
16]. This is a Weibull distribution due to stress-induced failure of the component (the child).
In the last 10 years, evidence has emerged that questions the validity of the radiation risk model which had been employed to provide answers to these questions. The focus has shifted to the hazard from internal radionuclide exposures. The problem is the risk model assumptions about anisotropy of ionisation at the cell level. Internal high local doses or multiple decays can certainly kill cells and cause greater mutation damage than the average doses calculated by current risk models, where energy is averaged over whole organs [
17].
External or internal exposure: scientific induction
The Scientific method is one of induction [
18]. That is, results from an experiment, or an investigation, are interpreted with logic [
19] as the primary source of any theory about the process being examined. From the Sellafield childhood leukemias from the 1980s onward, the approach of science has been “deductive”. That is, the assumption has been that, based on previous theories obtained from Japanese A-Bomb victim data, and exposures at high external doses like the “ankylosing spondylitis” epidemiology [
14], a 10-fold excess risk at doses which were thousands of times lower could not possibly be a cause [
9]. Arguments about mechanism are effectively deductive. So, if the result of an examination of the health effects of such a process clearly demonstrates an effect (like the effects at Sellafield) then an explanation must be provided and a mechanism sought.
Bradford-Hill, in his “Principles of Medical Statistics” provided a
caveat that knowledge of mechanism, although valuable, was not a necessary part of establishing causation because future research or thinking might provide such a missing piece of causation architecture [
20].
In April 1986 much of Europe was contaminated with a spectrum of radionuclides from the Chernobyl reactor explosion. This included Scotland and Wales where significant increases were found in infant leukemia 0-1 in a temporal cohort born in the period 01/07/86 to 31/12/87 [
21,
22]. This short period was chosen by researchers studying effects in Scotland, Greece, Germany, and Belarus [
21,
22,
23,
24,
25,
26]. The logic behind the choice of the period seems to have been based on “absorbed dose” for which external gamma ray exposures provided the largest value when calculated using the ICRP energy per unit mass approach [
17]. These higher levels of external gamma ray doses were associated with the rained out gamma-emitting nuclides Caesium-137 and Iodine 131. This peaked in the first few months and fell to low levels owing to dispersion of the radioactivity and the short half life of the Iodine. However, radioactive contamination of foodstuffs and milk persisted for several years and the internal contamination of parents of leukemia children from these sources remained at measurable levels for several years. In Wales sheep sale restrictions were only lifted in 2012, some 26 years after the event [
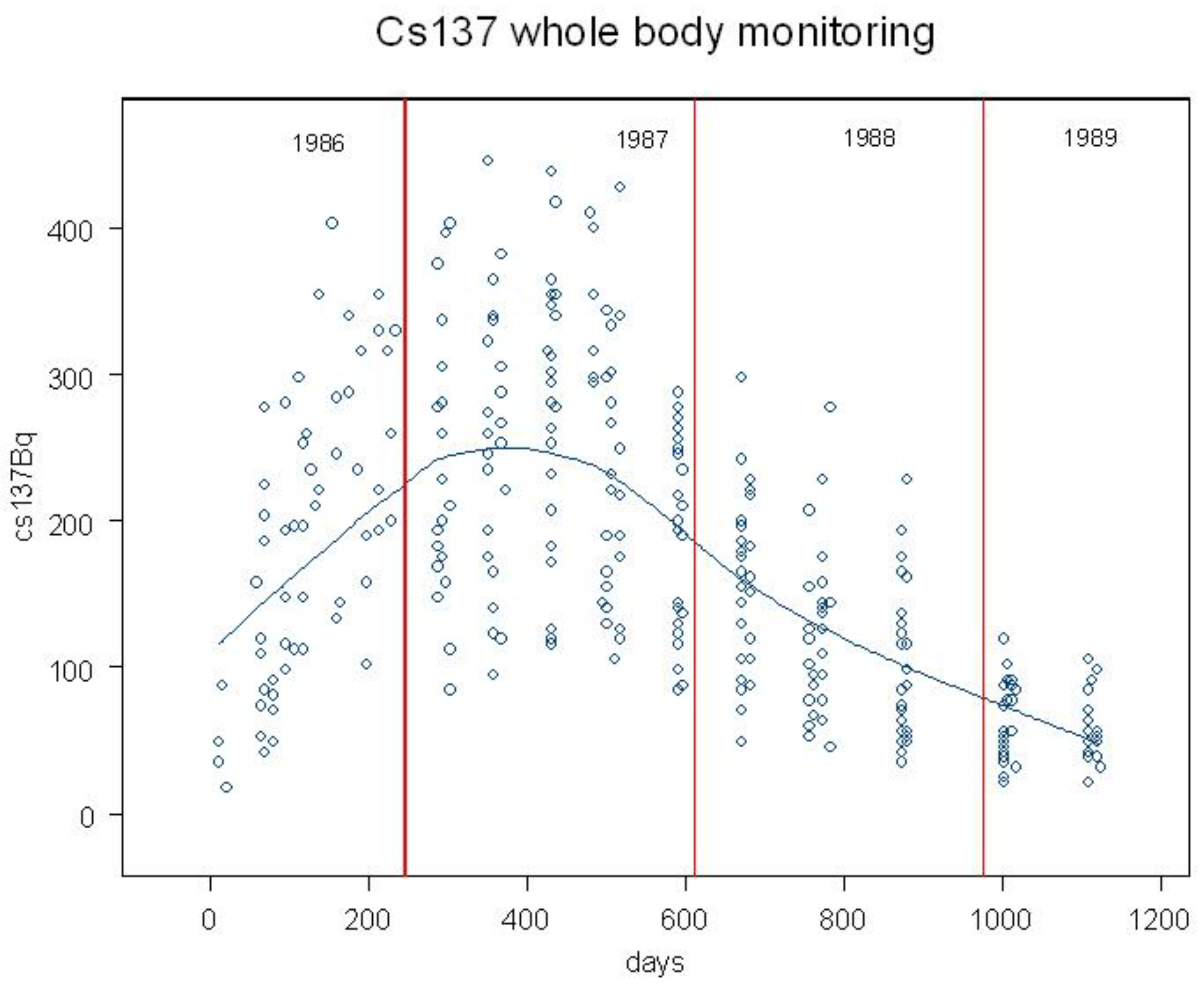
27]. Whole body monitoring for Chernobyl Cs-137 was carried out in England and showed a trend in internal contamination which persisted from 1986 to 1990 (
Figure 3) [
28]. It is a plausible assumption that in Wales and Scotland the trend in internal contamination was similar, though the magnitude of the contamination was clearly greater. It should be noted that although the contamination measured was from the radioactive Caesium 137 and 134, these may be indicators for the Uranium and other particles that formed the condensation nuclei for the rain clouds.
The origin of the data
The finding of significant excesses of infant leukemia after Chernobyl, along with similar evidence that the current radiation risk model may be unsafe, led in 2000 to the formation by the UK Environment Minister (The Rt Hon Michael Meacher MP) of the Committee Examining Radiation Risks from Internal Emitters (CERRIE), which met from 2001-2004 [
29,
30]. The 3-person epidemiological sub-committee, of which this author was a member, obtained comprehensive data on child leukemia in Scotland, Wales and England from the Oxford-based Childhood Cancer Research Group (CCRG). These data were unique. Child leukemia epidemiology has previously been aggregated to 5-year or 15-year age groups and by year of exposure. The CCRG data gave numbers by single year of birth and by age and sex, and were believed to be the most accurate available. CCRG also gave data for infant leukemia by shorter periods of exposure stratified by area of Chernobyl contamination in England and Wales but these data were only for ages 0-1 and were of no value in examining the older children 0-4. Here the 0-4 data are employed to obtain an Excess Relative Risk (ERR) for childhood leukemia from mainly internal exposure from Chernobyl contamination. The internal exposures were significant for at least four years after the event as material passed though the food chain. Because of the resolution available from the CCRG dataset it was possible, for the first time, to examine rates by single year of birth as well as single year of exposure. Scotland and Wales were chosen for the study since, although England data was available, there was much less (average) contamination of England by Chernobyl rainfall.
Method
The CCRG data employed here listed cases with leukemia by sex, year, single ages 0 to 9 and mid-year populations of Wales and Scotland from 1970 to 1997. Scotland and Wales were contaminated by Chernobyl in April 1986. Exposure periods were divided into exposed period A of 5 years following the deposition, 1986-1990, and two unexposed periods B: 1970 to 1985 and C: 1991 to 1994. On the basis of the findings at Sellafield and the Lyman et al 1985 results, this study begins with the assumption that internal exposures are critical and thus defines exposure periods based on published whole body Cs-137 monitoring results [
28] showing that Caesium-137 from Chernobyl was present in individuals in England for 1100 days after the accident [
Figure 3]. Since Scotland and Wales were more heavily contaminated,
in utero exposures will have occurred up to and including 1989 with effects in 1990. Since it is widely assumed that exposure
in utero is an initiating event [
31] the method examined leukemia risk by year of birth in ages 0-4. That is, for each year from 1970 to 1990 the birth cohorts were followed: e.g. age 0 in 1970, 1 in 1971, 2 in 1972 and so forth. However, year of exposure rate for 0-4y (e.g. ages 0-4 in 1970, 71, 72…) was also plotted to illustrate the difference between ways of approaching the problem epidemiologically. The raw data and the two methods of aggregating the data (year of birth and year of exposure) are presented and explained in Supplementary Table 1 and the raw dataset itself can be found online [
32].
Contingency Table Chi-squared analysis (Mantel Haenszel) were employed to test the difference between Exposed A versus Unexposed periods B and C, and also B+C combined [
33].
Results
Population and leukemia rates in the three periods are given in
Table 1 together with Relative Risk Ratios and statistical test results.
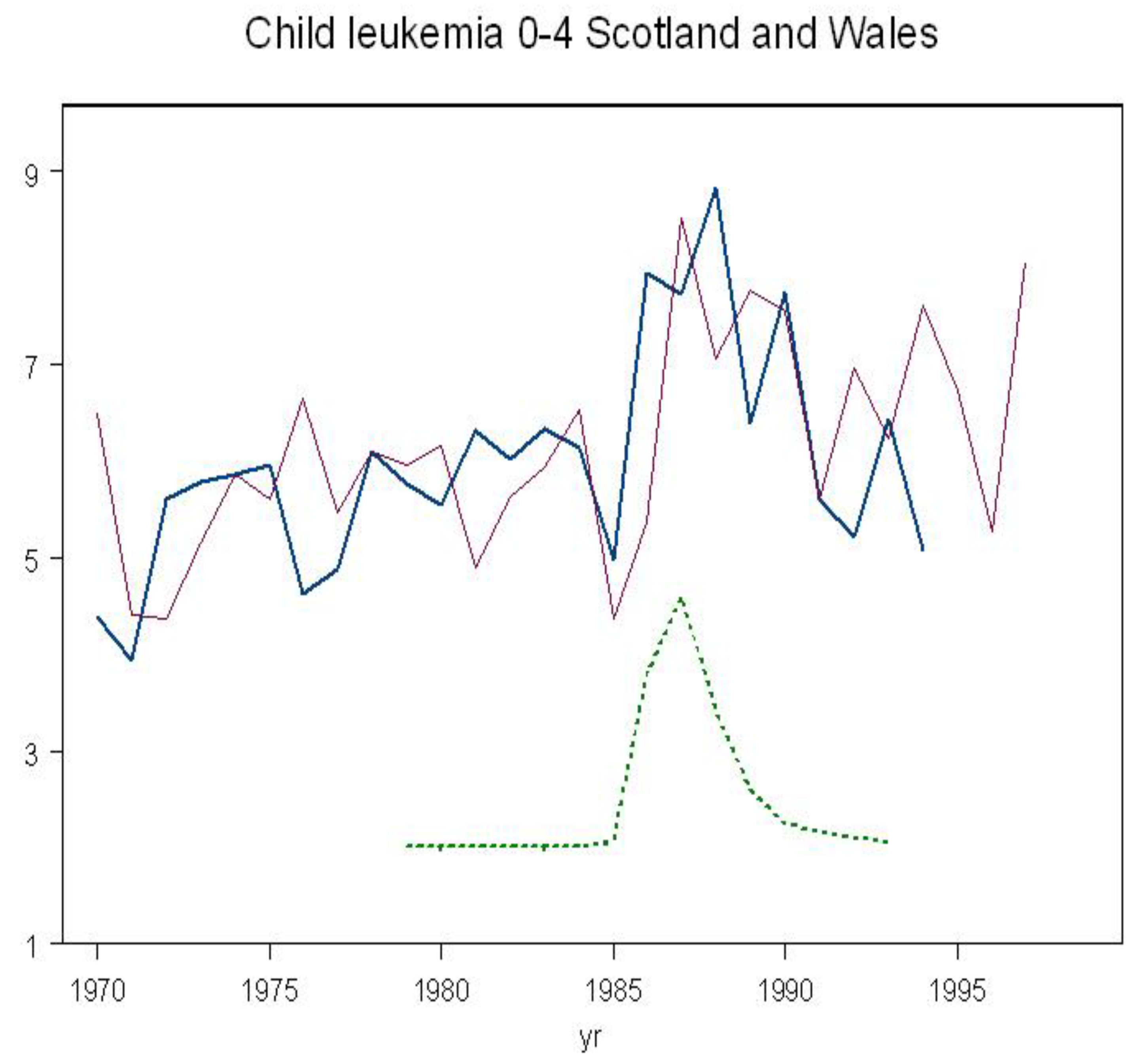
Rates are plotted in
Figure 4 together with the whole-body monitoring Caesium-137 trend. There was a significant increase in leukemia in Scotland and Wales corresponding to the exposure (
Table 1,
Figure 4). Estimated collective cumulative doses
in utero from Chernobyl contamination to the children followed from age 0-4, based on data published in the CERRIE report, was about 0.06mSv [
29]. This produced a statistically significant excess 41% risk. The ERR per Sievert is thus about 7000. This is capable of explaining the Sellafield cluster at an
in utero dose of about 1mSv.
Discussion
The results show that the Chernobyl fallout in Scotland and Wales caused significant increases in leukemia in those children aged 0-4 who were
in utero over the period of internal contamination. The effect is clear from the trend graph in
Figure 4. This finding parallels the Chernobyl infant leukemia findings reported by several different groups for Greece, Germany, Wales, Scotland and Belarus. In a separate analysis of year of exposure, an effect is also clear, as can be seen from the red line in
Figure 4.
This finding adds to the evidence that the current radiation risk model may be unsafe for internal exposures [
17,
34,
35].
The issue of post-Chernobyl effects was discussed in CERRIE. The majority report contained an annex which provided an analysis of infant leukemia and conceded the existence of a significant excess risk. However, the committee was divided on the issue of causation [
29,
30].
It should be clear that a significant excess risk at very low doses in 5 countries reported by 5 different researchers, had already philosophically falsified the ICRP model approach [
30] and had already supported a radiogenic explanation for the Sellafield cluster. This is why Mr Meacher set up the CERRIE. With regard to child leukemia 0-4 the CERRIE annex generally ignored it except for a reference to the ECLIS study, Parkin et al 1996 [
36]. Since this study was influential on the issue of Chernobyl and child leukemia, it will be addressed.
The ECLIS study
Parkin et al 1996 [
36] employed a pooled European and eastern European database of 0-14year-olds and employed multivariate logistic regression on absorbed dose to see if there was any increase in the period following the accident. The study began with some curious assumptions:
The leukemogenic effect of environmental radiation has a latency of 1 year. The report states: the cumulative dose due to the accident is a function of region and year. It is zero for all person years of observation before 1987; the dose in 1986 is zero because of the assumed latency of the dose effect of 1 year.
The dose is assumed to fall linearly throughout the first year following the accident and exponentially thereafter. In other words, the external dose predominates and exposures to internal nuclides in the four years after the accident are ignored.
Both these assumptions are questionable, and in the case of the first one would not predict any infant leukemia in 1986 or 1987 since the largest and immediate May 1986 dose from the prompt fallout is registered in the regression as zero. Accordingly, Parkin et al 1996 found no effect on infant leukemia even though five different groups were to report the effect. The 8-32 month follow up post-accident produced a small 1.07; p<0.01 effect in the 0-4 age group but this was dismissed because there was no linear increase with doses between countries.
By employing mathematical regression, the study assumes a linear or monotonic increase of child leukemic with dose. The bigger the dose, the greater the leukemia numbers. The arguments presented here suggest that the dose response involves a threshold and reversal due to death as a confounding effect (
Figure 3). Regression methods are unsafe if the true dose response is not linear (as regression requires) but biphasic or Weibull owing to death-before-leukemia expression [
17,
37,
38,
39,
40,
41]. The Exposed Cohort period employed by the infant leukemia studies was based on external exposure levels: 01/07/86 to 31/12/87. This period can be seen from
Figure 1 to split increased leukemia risk between the exposed and control groups so naturally by comparing exposed with exposed nothing was found. Other problems with the Parkin et al study were identified by Hoffman [
42].
There is another concern about child leukemia epidemiology. The age group 0-14 and 0-4 and the time periods of the studies relative to the external exposure single year spike (1986) identify individuals who were born before the exposures. Looking for leukemia in those aged 0-14 in 1987 examines rates in individuals who were born in 1973-1987, i.e. mostly before exposure. This is a criticism which applies to all analyses of leukemia rates by 5-year and to 15-year age groups. Looking at 0-15y child leukemias from Chernobyl would be to examine a cohort who were almost entirely unexposed in utero .
Pre-leukemia deaths and the dose response: a biological confounder
This study aims to examine and interpret radiogenic child leukemia on the basis of a new approach; one which has been outlined above and laid out schematically in
Figure 1 and
Figure 2.
If the critical issue in child leukemia epidemiology is that if the disease is initiated mainly before birth [
43] then spontaneous abortion (miscarriage) and pre-leukemia deaths from foetal exposures (e.g. infant and perinatal mortality) above a critical survival dose will cause the dose response to turn over (Fig2). Thus, higher doses will produce less effect than lower doses. This general problem with fetal developmental epidemiology was identified as early as 1987 by Selevan and LeMasters [
37] and was presented as the reason for undertaking this study. A similar dose response is seen in birth defects after Chernobyl arguably from the same reason [
43,
44].
But it is not only foetal death that can cause such an effect, nor is it possible to say that the leukemogenic effect of radiation operates
in utero exclusively which was the starting point basis for this study; indeed, it seems biologically implausible that this is entirely the case. And closer examination of the CCRG data in Supplementary
Table 1 reveals that children who were
in utero before the fallout exposure began had an excess risk of child leukemia. This observation raises a question over the theory that child leukemia is entirely an
in utero instigated phenomenon. The issue will be addressed elsewhere by examining data from the 5-9 year-olds.
There is evidence that child leukemia follows severe infection, which has resulted in the hypothesis that infection is a part-cause of the development of the condition [
44]. But this argument can be inverted: if serious infection occurs in pre-leukemic children due to immune dysfunction, the population of potential leukemia children will fall through what has been termed “mortality displacement” and the rate will also fall since susceptible individuals are lost to the study group by early deaths from other causes [17, 43,44]. This is shown in
Figure 1 where the flow chart removes potential child leukemia individuals before birth but also after birth.
The theoretical dose response resulting from these considerations can be described as a Weibull distribution and is shown schematically in
Figure 2 (blue line). Plotting the risk in Scotland and Wales against the internal exposure trend based on the Harwell whole body monitoring results trend shows a saturation and reversal of the rates exactly as predicted (
Figure 5)
The dose response for the infant leukemias is biphasic: in the high dose regions like Belarus the effect is lower than in the lower dose regions and the low dose regions conform to the Weibull type explanation provided here [
19,
20].
Chernobyl effects on foetal viability
If foetal irradiation caused effects on perinatal mortality and miscarriage there should be evidence of this. There is; but the studies showing this looked at the wrong indicators. In a study of perinatal mortality in the higher Chernobyl fallout regions of Wales and Scotland, Bentham [
45] reported that there was no persuasive evidence of any effect, looking for an increase in perinatal mortality (that is infant mortality plus stillbirth). But if there are no babies because they all fail in development, are not conceived in the first place, or miscarried, there will be a
reduction in infant mortality relative to a previous control period. Closer examination of Bentham’s numbers of cases reveals just that: a significant reduction in perinatal mortality in the period 28/06/1986 to 30/01/1987 i.e. beginning in the first trimester and ending suddenly 9 months later in February/ March when the perinatal mortality rate doubled. There were 47 perinatal deaths in children exposed
in utero for the 6 months after Chernobyl compared with 76 expected RR = 0.62; p = 0.0002. Thus, half the pregnancies which were later than 3 months in that post Chernobyl period failed to reach term. Bentham focused on perinatal mortality and although he commented on this remarkable, statistically significant and unusual effect, he believed that Chernobyl radiation could not be a cause.
There were other relevant studies of pregnancy outcomes after Chernobyl, in Germany [
46] Finland [
47] and Sweden [
48]. The Finland and Sweden results, like the Bentham study show statistically significant effects on foetal survival of the same kind as seen in Wales. Although (as with Bentham) the Finnish authors concluded that there were no significant Chernobyl effects, close examination of their graphs reveals a highly significant
reduction of stillbirth rate in 1986 in the higher dose areas compared with 1985 and 1987. In the high exposed group, there were 68 stillbirths in 1985 (rate 5.06 per 1000 births) and 70 in 1987 (rate 5.56) but only 49 (rate 3.7) in 1986 (p <0.004) [
40]. From 1987 on to 1991 (as the contamination increased in the exposed) induced abortions increased. A similar trend occurred in Sweden [
48]. In support of the fetal failure explanation of the reduction in stillbirth rates in Finland, the Swedish study showed a significant increase in reported miscarriages in areas with low exposure to Chernobyl fallout (5-29kBqm
-2) in pregnancies beginning after the accident.
The results therefore support the existence of confounding effects in radiogenic childhood leukemia due to death of the individuals
in utero or after birth, effects which cause a dose response which is predicted to saturate and fall at high internal doses. The results also identify a very large difference between external photon radiation and internal particulate or specific nuclide exposure. This is not the forum to rehearse the reasons for the internal external risk found here, though one thing could be stated. Cancer or leukemia begins with a mutation, and such a mutation begins with a single cell. The dilution of energy from radioactive particulates into whole organs, with mass of kilograms, which is the way in which Chernobyl exposures are dealt with by the ICRP model, results in calculated doses which are vanishingly small. This leads to the denials of causation seen in the risk agencies treatment of the Sellafield children and other instances of epidemiological finding [
12].
It is unsafe to assume that for the DNA in a single cell, ionisation density is the same thing as Absorbed Equivalent Dose, based on averaging energy to whole organ. This issue was the remit of CERRIE, and has been discussed elsewhere [17, 30, 49, 50].
Epidemiology without biology is unsafe. It is an error to assume that causation must be demonstrated by linear or at least monotonic increase in leukemia rate with dose, if at some critical dose, the end point falls due to confounding early death. Thus, regression methods, such as those employed by Parkin et al 1996 are methodologically questionable. The excess risk of 7000 Sv-1 found here for the level of dose calculated using the conventional risk model method supports the belief that the nuclear site child leukemias are also caused by radioactive contamination. It is unclear why CERRIE did not report the excess found here.
Epidemiology: cross-sectional or trend analysis?
If the condition is developmental in origin, and has a truncated or reversing dose-response, then using epidemiology based on linear trend with dose fails. However, it should be possible to investigate by direct comparison of rates across areas with high and low exposures, cross-sectional epidemiology. This was carried out by Bentham and Haynes in 1995 [
51]. They compared England and Wales child leukemia rates 0-4 over the period of the fallout. They defined low medium and high fallout areas before and after the peak testing based on rainfall. They found a significant excess 23% risk for the high rainfall area over the low rainfall area. The doses assumed were from the trend investigation by Darby et al [
52] which found little effect, for reasons which will be revisited below. The foetal dose differences between the low and high dose regions was shown by [
52] to be 0.2mSv. The ERR per Sievert here is thus 1150, which supports findings in the present study. A similar 1987 study in the USA by Archer et al [
53] examined States of the USA with high and low Strontium-90 levels from fallout and deaths from leukemia in 0-19 year-olds from 1949 to 1979. There was a distinct increase in the trend low-medium-high dose plotted against levels of Sr-90 in milk, food and bone [
53]. Archer assumed a very large and unlikely value of 5mSv for the Sr-90 dose differences. The peak effect in 1960-69 gave a 4% difference for leukemia deaths between the high and low Sr-90 States, though it should be pointed out that Archer was comparing 0-19y age group effects which are much smaller than 0-4y effects.
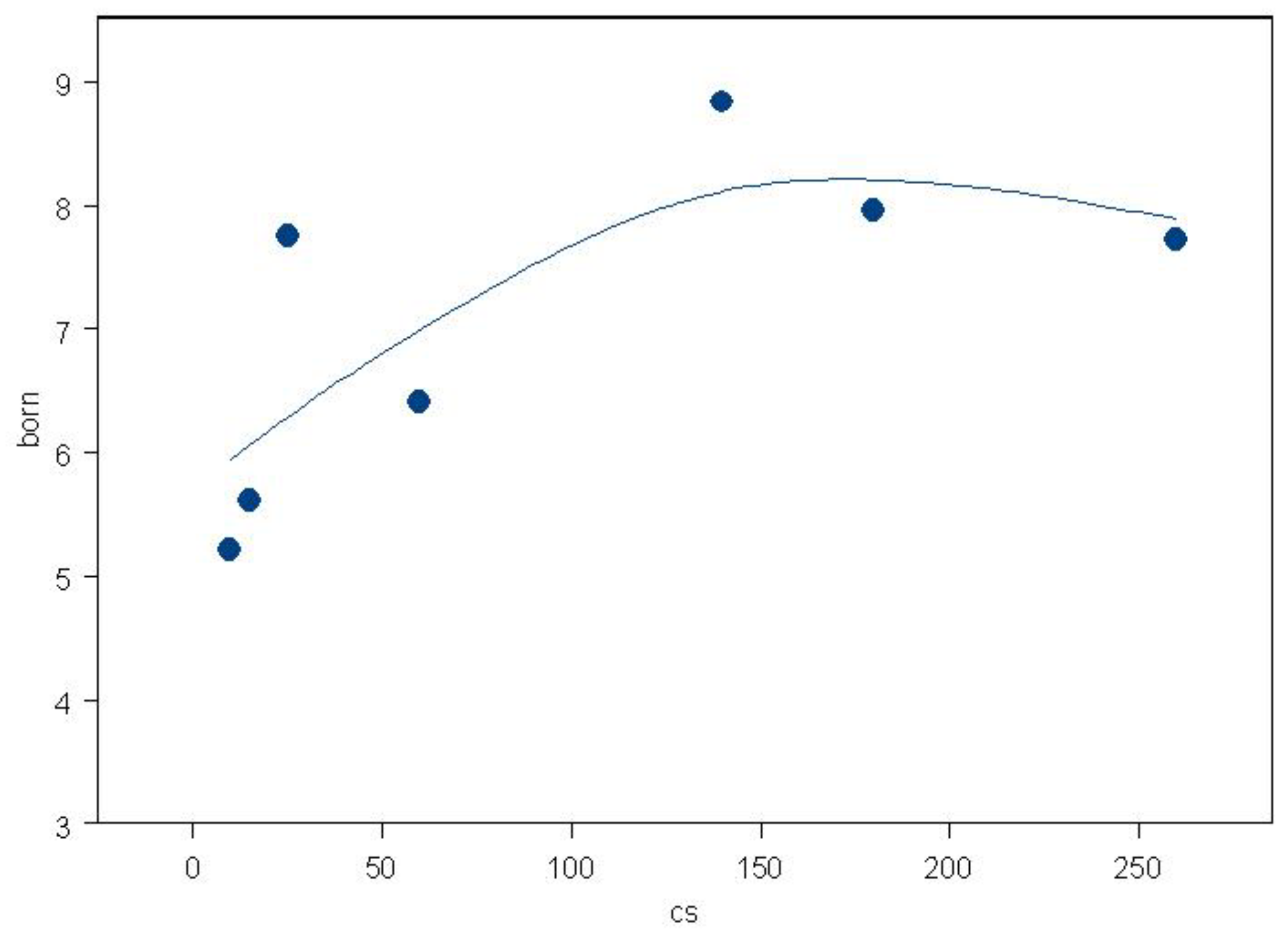
One recent study, which could possibly point to nanoparticle fallout inhalation exposures as the origin of the effect, employed the risk of child leukemia by distance from high voltage power lines. This issue of child leukemia near high voltage power lines has exercised the scientific community since the 1980s. Using data from the most recent updated power line case control study by the CCRG [
54] it was possible to show that the excess risk in children 0-4 living near high voltage power lines in England and Scotland clearly followed the trend in radioactive particles from the nuclear tests [
55]. The particles are concentrated near the power lines by corona ion production [
56]. The trend in dose was similar to that found in the present study and is shown in
Figure 6.
Other weapons fallout studies; looking at trend
Discussion of the issue would not be complete without addressing briefly studies of the effects of the atmospheric weapon testing fallout contamination peaking in 1959-63. In 1993, at the time of the Sellafield court case [
8,
9] Darby et al. published the Nordic Leukemia Study, which assembled child leukemia data from Sweden, Norway, Denmark, Finland and Iceland to construct a graph of rates in children 0-14 by calendar year of birth 1948-1982 [
52]. The trend graphs showed no obvious effect at the time of the peaks in fallout. However, the study did not make it explicit that the graphs spliced together data from Denmark from 1943 to the data from the other Nordic countries which began in 1959 when the main fallout also appeared (1959-1963). Removal of the Danish data from the trend graph shows a clear 30% increase in rates in the 0-4 age group, similar to the result found by Bentham and Haynes. Danish epidemiologists had earlier separately published reports on the increases in child leukemia over the period of the weapons fallout. In Hansen et al (1983) [
57], the authors stated:
An epidemiological study of the total population of patients with leukemia in Denmark 1943-1977 was performed. The material stemmed from the Danish National Cancer Registry and was believed to be complete. Over the 35-year period the incidence of acute leukemia increase threefold in the age group 0-9.
A similar report from Hakulinen et al 1986 showed the peak to be in the 0-4 year olds [
58]. At page 92 in this report Hakulinen wrote:
Hansen et al (1983) concluded that the increases in child leukemia may not be an artefact. They suggest environmental factors are involved. Ionising radiation is a well-known risk factor in child leukemia.
Darby et al 1993 failed to cite either of the earlier published Danish studies [
57,
58] a matter which was raised in the CERRIE committee but never resolved, even though Darby had been co-opted to the committee by the Chair [29, 30].
The issue of child leukemia following the weapons test fallout was later addressed by Wakeford et al 2010 in a similar way to the earlier Nordic Leukemia study [
59]. The authors examined data for “all leukemias 0-14 and 0-4” measured as mean rates plotted with data points centred on a “calendar year of diagnosis” which was a 5-year moving average. The interpretation of the results from the 10 different cancer registries is difficult. The results, plotted on different time axes for the different registries reportedly followed a displaced 5-year moving average based on year of diagnosis rather than year of birth. A 5-year age group and a 5-year moving average rate looked for an effect based on exposure year plotted against time; the result is a very highly averaged trend which, in any case, seems to be displaced to the left (earlier) on the time axis.
The explanation for a failure to see a big increase in a child leukemia trend during the peak weapons fallout in 1962-63 is, of course, the same as that provided earlier here: the children died before developing leukemia. The increases in infant mortality over the fallout period were first pointed out by Sternglass [
60] and then later by Whyte [
61]. The issue was discussed at some length in CERRIE but not resolved. There is a relevant discussion in Busby 2017 [
49] and in the CERRIE minority report [
30].
Summary and Conclusion; the biological explanation
The question raised by the profound differences between the child leukemias at very low internal dose shown by the nuclear site studies and conversely the high external dose studies like the “ankylosing spondylitis”, obstetric X-ray and Japanese LSS studies is addressed. It is first proposed that ionisation density or “dose” to the cell is the cause of the mutations that lead to child leukemia and that this is quite different from the “absorbed dose” computed at the organ level as energy per unit mass by the current ICRP risk model. Second, the linear no threshold assumption of the ICRP is confounded in child leukemia by death of the individual either in utero or in early childhood which results in an inverted bowl or Weibull-type of dose-response. The results of the study here support both these hypotheses and support the belief that very low doses of internal radiation can cause significant increases in child leukemia .
The biological explanation is therefore that this internal low dose effect is in reality a high local dose to the cell which saturates at higher doses due to deaths of pre-leukemic individuals either in utero or in in early childhood before diagnosis, so that epidemiology fails to find an effect which is nevertheless present but with a dose response confounded by a developmental block or failure of the individual.
This submission has by no means attempted to survey all the studies of childhood leukemia and radiation. This is a very large field. Sufficient citations have been included to make the case that there is an enigma relating to childhood leukemia at low dose and high dose as currently calculated. This leads to a re-examination of the biological basis for the epidemiological studies.
Finally, evidence provided here focuses on the increase in child leukemia 0-4 in Wales and Scotland after Chernobyl. Results reveal an unequivocal and statistically significant 41% excess risk at an internal dose of around 0.06mSv. The excess is in those children who were born between 1986 and 1990, a period when Chernobyl contamination persisted in the population as shown by whole body monitoring. The ERR found supports a risk coefficient of about 7000/Sv in the very low dose region in Scotland and Wales. Similar levels of risk can be shown in populations exposed to different levels of atmospheric test fallout and to nuclear site contamination.
Conflict of Interest
The author has no conflict of interest to report. The author is the Scientific Secretary of the European Committee on Radiation Risk, an independent NGO which has criticized the current radiation risk model.
References
- Proceedings of the British Nuclear Energy Society,4th International Conference. Health Effects of low dose radiation by Chris Busby “High Risks at Low doses.” Fig 2 p6 Keble College Oxford 2002. London: BNES.
- Kusano N. Atomic Bomb Injuries. Report for the Japanese Preparatory Committee for Le Congres Mondiale des Medecins pour Etudes des Conditions Actuelles de Vie. Tokyo: Tsukiji Shokan Co. 1953.
- Delongchamp R, Mabuchi K, Yoshimoto Y, Preston DL. Cancer mortality in atomic bomb survivors exposed in utero or as young children, October 1950- May 1992. Radiation Research 1997 147, 385-395.
- Doll R. The Hazards to Man of Nuclear and Allied Radiation, Medical Research Council CMMD1225 London: HMSO 1957.
- ARC (Agricultural Research Council), Letcombe Laboratory Annual Reports (London: HMSO).
- UKAEA Committee on the Monitoring of radioactivity from fallout. Assay of Strontium-90 in human bone in the UK. Reports No 1-19. Harwell, Oxfordshire: United Kingdom Atomic Energy Authority 1959-1970.
- Stewart, A. M., Webb, J. W., Giles, B. D., Hewitt, D. Malignant Disease in Childhood and Diagnostic Irradiation in Utero, Lancet, 1956 ii/447. [CrossRef]
- Elizabeth Reay and Vivien Hope vs. BNFL Queens Bench Division 1993 https://inis.iaea.org/search/search.aspx?orig_q=RN:26029165.
- Independent Advisory Group Investigation of the Possible Increased Incidence of Cancer in West Cumbria, `The Black Report', London: HMSO 1984.
- Beral, V, E. Roman, and M. Bobrow (eds.) Childhood Cancer and Nuclear Installations London: British Medical Journal. 1993.
- Baker PJ and Hoel DG. Meta analysis of standardised incidence and mortality rates of childhood cancer in proximity to nuclear facilities. European J Cancer Care. 2007 18(4) 429-30.
- COMARE Committee on Medical Aspects of Radiation in the Environment COMARE 14th Report. Further considerations of childhood leukemia around nuclear power plants in Great Britain. UK: Health Protection Agency 2011.
- Lyman GH, Lyman CG, Johnson W. Association of leukemia with Radium groundwater contamination. JAMA 1986 254(5) 621-626. [CrossRef]
- Darby SC, Doll R, Gill SK, Smith PG. Long term mortality after a single treatment course with X-rays in patients treated for ankylosing spondylitis. Br J Cancer 1987 55:179-190. [CrossRef]
- See https://www.weibull.com/basics/lifedata.htm for a description of this statistical distribution.
- Hall EJ. Radiobiology for the radiologist. 8th Edition Amsterdam. Wolters Kluwer 2018.
- Busby C. Ionizing radiation and cancer—the failure of the risk model. Cancer Treatment and Research Communications. 2022 31 100565. [CrossRef]
- Harre R. The Philosophies of Science. Oxford: University Press 1985.
- Mill JS. A system of logic London: Longmans Green. 1879.
- Bradford Hill A. Principles of Medical Statistics London: The Lancet 1949.
- Gibson B.E.S.; Eden O.B.; Barrett A.; Stiller C.A.; Draper GJ. Leukemia in young children in Scotland. The Lancet 1988 2, (corres), 630.
- Busby C.; Scott Cato M.; Increases in leukemia in infants in Wales and Scotland following Chernobyl Energy and Environment 2000 11 (2), 127-137. [CrossRef]
- Petridou E.; Trichopoulos N.; Dessypris N.; Flytzani V.; Haidas S.; Kalmanti M. Infant leukemia after in utero exposure to radiation from Chernobyl. Nature 1996, 382, 352-353. [CrossRef]
- Kaletsch U.; Michaelis J.; Burkart W.; Grosche B. Infant leukemia after the Chernobyl Accident. Nature 1997 387, 246. [CrossRef]
- Ivanov E.; Tolochko G.V.; Shuvaeva L.P.; Infant leukemia in Belarus after the Chernobyl accident. Radiat. Env. Biophys 1998 37, 53-5. [CrossRef]
- Busby C.C. Very Low Dose Fetal Exposure to Chernobyl Contamination Resulted in Increases in Infant Leukemia in Europe and Raises Questions about Current Radiation Risk Models. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.; 2009 6(12):3105-3114. http://www.mdpi.com/1660-4601/6/12/3105. [CrossRef]
- https://www.walesonline.co.uk/news/wales-news/how-chernobyl-made-welsh-sheep-16360676.
- Etherington G and Dorrian M-D Radiocaesium levels intakes and consequent doses in a group of adults living in Southern England. IAEA Document SM306/29 pp327-338. 1989.
- CERRIE Report of the Committee Examining Radiation Risk from Internal Emitters (CERRIE) Chilton, UK: National Radiological Protection Board. 2004.
- Busby CC, Bramhall R and Dorfman P. CERRIE Minority Report: Minority Report of the UK Department of Health/ Department of Environment (DEFRA) Committee Examining Radiation Risk from Internal Emitters. Aberystwyth: Sosiumi Press 2004.
- Greaves M. A causal mechanism for Childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Nature Reviews Cancer. 2018 18 471-484. [CrossRef]
- The CCRG CERRIE dataset employed here is downloadable from www.llrc.org and from www.academia.edu.
- Fliess JL Statistical methods for rates and proportions. 2nd Edn. New York: Wiley 1981.
- Busby Christopher. The Hiroshima A-Bomb Black Rain and the Lifespan Study; a Resolution of the Enigma, Cancer Investigation, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Busby C. Letter to the Editor on “The Hiroshima Nagasaki survivor studies. Discrepancies between results and general perception.” By Bernard R Jordan. Genetics. 2016 204(4) 1627-1629.
- Parkin DM et al. Childhood leukemia in Europe after Chernobyl: 5-year follow up. British Journal of Cancer 1996 37; 1006-1012. [CrossRef]
- Selevan SG Lemasters GK. The Dose Response fallacy in human reproductive studies. J Occup. Med. 1987 29(5) 451-454.
- Burlakova EB, Naiditch V. The effects of low dose radiation. New aspects of radiobiological research prompted by the Chernobyl disaster. Routledge: CRC Press 2004.
- Burlakova EB, Goloshchapov AN , Gorbunova NV et al . Mechanisms of biological action of low dose radiation in Burlakov EB Editor: Consequences of the Chernobyl Catastrophe for Human Health. Moscow: Scientific Council on Radiobiology, Russian Academy of Sciences. 1996.
- Busby Chris, Lengfelder Edmund, Pflugbeil Sebastian, Schmitz Feuerhake Inge The evidence of radiation effects in embryos and fetuses exposed by Chernobyl fallout and the question of dose response. Medicine, Conflict, Survival 2009 25(1) 18-39.
- Schmitz-Feuerhake, Busby C, Pflugbeil P Genetic Radiation Risks-A Neglected Topic in the Low Dose Debate. Environmental Health and Toxicology. 2016 31 Article ID e2016001. [CrossRef]
- Hoffman W Has fallout from the Chernobyl accident caused childhood leukemia in Europe? European Journal of Public Health 2002, 12. 72-76. [CrossRef]
- Greaves M. Infection, immune responses and the aetiology of childhood leukaemia. Nature Rev. Cancer 2006 6, 193–203. [CrossRef]
- Kaplan HS On the aetiology and pathogenesis of the leukemias: a review. Canc. Res. 1954 14. 535-548.
- Bentham, G. Chernobyl Fallout and Perinatal Mortality in England and Wales, Social Science Medicine 1991 33/4: 429-34. [CrossRef]
- Grosche B Epidemiologische Studien in Deutscheland nach Tschernobyl: eine kurtze Ubersicht. Strahlenachutzpraxis. 1996 1: 21-34.
- Auvinen A, Vahteristo M, Arvela H et al. Chernobyl fallout and outcome of pregnancy in Finland. Environmental Health Perspectives. 2001 109 (2) 179-185. [CrossRef]
- Eriksen A, Kallen B Pregnancy outcome in Sweden after the Chernobyl accident. Env Res, 1994 67; 149-159. [CrossRef]
- Busby C. Radiochemical Genotoxicity Risk and Absorbed Dose. Res Rep Toxi. 2017 Vol.1 No.1:1 https://www.imedpub.com/articles/radiochemical-genotoxicity-risk-and-absorbed-dose.php?aid=20305.
- Busby Christopher. Aspects of DNA Damage from Internal Radionuclides, New Research Directions in DNA Repair, Prof. Clark Chen (Ed.), ISBN: 978-953-51-1114-6, InTech, https://doi.org/10.5772/53942. (2013) Available from: http://www.intechopen.com/books/new-research-directions-in-dna-repair/aspects-of-dna-damage-from-internal-radionuclides. [CrossRef]
- Bentham G and R. Haynes. Childhood leukemia in Great Britain and fallout from nuclear weapons testing. Journal of Radiological Protection, 1995 15/1, 37-43. [CrossRef]
- Darby, S. C., Olsen, J. H., Doll, R., Thakrar, B., de Nully Brown, P., Storm, H. H., Barlow, L., Langmark, F., Teppo, L., and Tulinius, H. (1992), Trends in Childhood Leukemia in the Nordic Countries in Relation to Fallout from Nuclear Weapons Testing, British Medical Journal 1992 304: 1005-9. [CrossRef]
- Archer, V. E. Association of Nuclear Fallout with Leukemia in the United States Archives of Environmental Health, 1987 42: 263-71. [CrossRef]
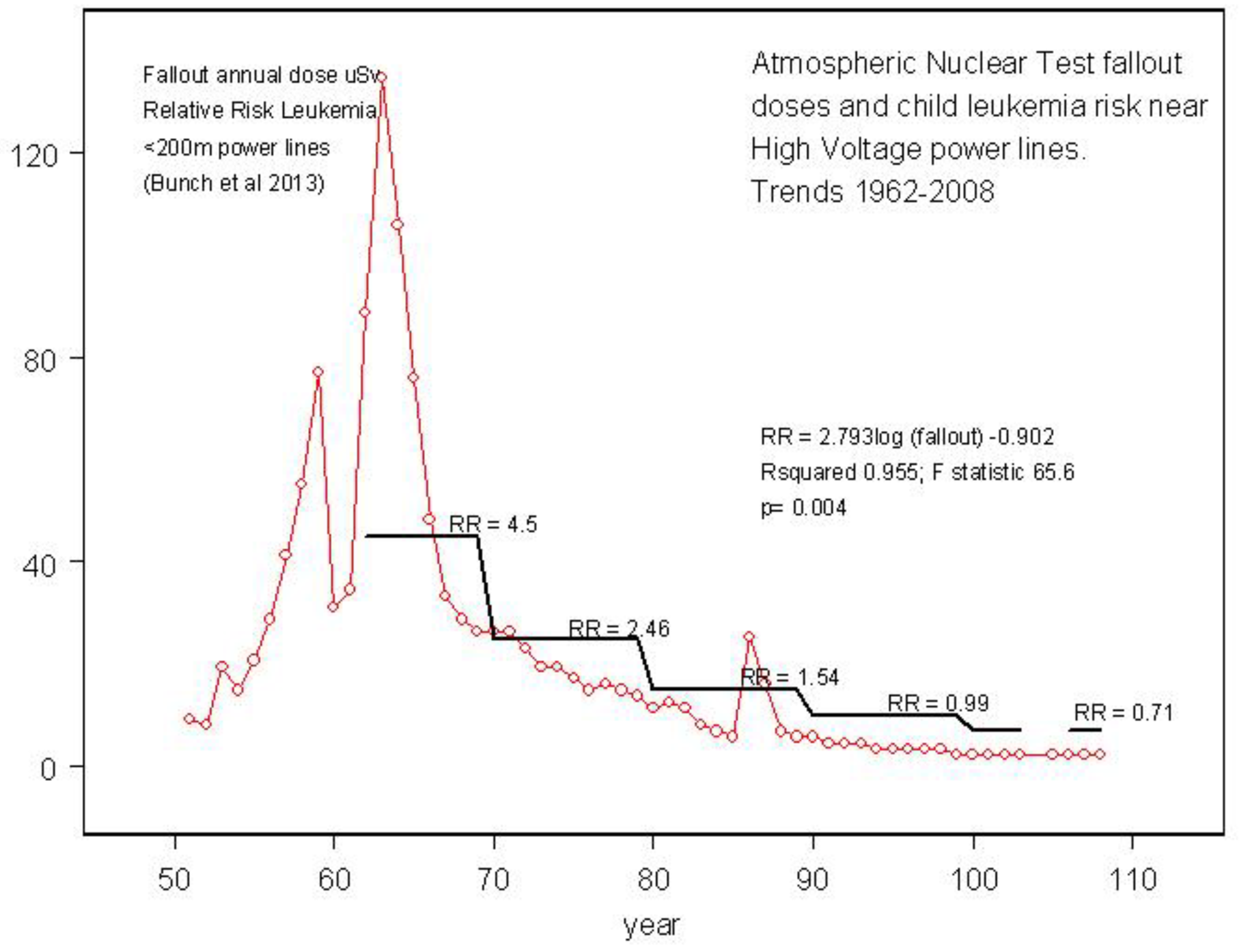
- Bunch KJ, Keegan TJ, Swanson J, Vincent TJ and Murphy MFG. Residential distance at birth from overhead high voltage power lines: childhood cancer in Britain 1962-2008. Br J Cancer 2014 110: 1402-1408. [CrossRef]
- Busby C. Childhood leukemia, atmospheric test fallout and high voltage power distribution lines. Pediatric Dimensions. 2017. [CrossRef]
- Fews AP, Henshaw D, Wilding RJ, Keitch PA. Corona ions from powerlines and increased exposure to pollutant aerosols. Int J Radiation Biol. 1999 75: 1523. [CrossRef]
- Hansen NE, Karle H, Jensen OM Trends in the incidence of leukemia in Denmark 1943-77. An epidemiologic study of 14000 patients. J. Natl. Can. Inst. 1983 71, 697-701.
- Hakulinen T, Andersen A, Malker B, Pukkala E, Schou G, and Tulinius H. Trends in cancer incidence in the Nordic countries. A collaborative study of the five Nordic cancer registries. Acta Pathol. Microbiol. Immunol. Scand Suppl. 1986 288, 1-151.
- Wakeford R, Darby S, Murphy FG. Temporal trends in childhood leukemia incidence following exposure to radioactive fallout from atmospheric nuclear weapons testing. Radiat. Envir. Biophys 2010. [CrossRef]
- Sternglass, E.J. Environmental Radiation and Human Health, in Proceedings of the Sixth Berkeley Symposium on Mathematical Statistics and Probability, ed. J. Neyman Berkeley, Calif.: University Press 1971.
- Whyte, R.K First Day Neonatal Mortality since 1935: A Re-examination of the Cross Hypothesis, British Medical Journal, 1992 304: 343-6. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).