Submitted:
03 May 2023
Posted:
04 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Computational Details
2.1. Molecular Properties
2.2. Reactivity Indexes
2.3. Enzymatic Interactions
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Derivatives and Properties
3.2. pKa and Antioxidant Activity
3.3. Polygenic Activity
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aborode, A.T.; Pustake, M.; Awuah, W.A.; Alwerdani, M.; Shah, P.; Yarlagadda, R.; Ahmad, S.; Silva Correia, I.F.; Chandra, A.; Nansubuga, E.P.; Abdul-Rahman, T.; Mehta, A.; Ali, O.; Amaka, S.O.; Zuñiga, Y.M.H.; Shkodina, A.D.; Inya, O.C.; Shen, B.; Alexiou, A. , Targeting Oxidative Stress Mechanisms to Treat Alzheimer's and Parkinson's Disease: A Critical Review. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 7934442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allan Butterfield, D.; Boyd-Kimball, D. , Mitochondrial oxidative and nitrosative stress and Alzheimer disease. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anwar, M.M. , Oxidative stress-A direct bridge to central nervous system homeostatic dysfunction and Alzheimer's disease. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2022, 40, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beura, S.K.; Dhapola, R.; Panigrahi, A.R.; Yadav, P.; Reddy, D.H.; Singh, S.K. , Redefining oxidative stress in Alzheimer's disease: Targeting platelet reactive oxygen species for novel therapeutic options. Life Sci. 2022, 306, 120855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, V.; Sharma, S. , Role of mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress and autophagy in progression of Alzheimer's disease. J. Neurol. Sci. 2021, 421, 117253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butterfield, D.A.; Halliwell, B. , Oxidative stress, dysfunctional glucose metabolism and Alzheimer disease. Nature Reviews Neuroscience 2019, 20, 148–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassidy, L.; Fernandez, F.; Johnson, J.B.; Naiker, M.; Owoola, A.G.; Broszczak, D.A. , Oxidative stress in alzheimer's disease: A review on emergent natural polyphenolic therapeutics. Complement. Ther. Med. 2020, 49, 102294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheignon, C.; Tomas, M.; Bonnefont-Rousselot, D.; Faller, P.; Hureau, C.; Collin, F. , Oxidative stress and the amyloid beta peptide in Alzheimer's disease. Redox Biol. 2018, 14, 450–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cioffi, F.; Adam, R.H.I.; Bansal, R.; Broersen, K. , A review of oxidative stress products and related genes in early alzheimer's disease. J. Alzheimer's Dis. 2021, 83, 977–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cioffi, F.; Adam, R.H.I.; Broersen, K. , Molecular Mechanisms and Genetics of Oxidative Stress in Alzheimer's Disease. J. Alzheimer's Dis. 2019, 72, 981–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionescu-Tucker, A.; Cotman, C.W. , Emerging roles of oxidative stress in brain aging and Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2021, 107, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juszczyk, G.; Mikulska, J.; Kasperek, K.; Pietrzak, D.; Mrozek, W.; Herbet, M. , Chronic stress and oxidative stress as common factors of the pathogenesis of depression and alzheimer’s disease; the role of antioxidants in prevention and treatment. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowalska, M.; Wize, K.; Prendecki, M.; Lianeri, M.; Kozubski, W.; Dorszewska, J. , Genetic variants and oxidative stress in alzheimer’s disease. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2020, 17, 208–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misrani, A.; Tabassum, S.; Yang, L. , Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Oxidative Stress in Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 13, 617588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rummel, N.G.; Butterfield, D.A. , Altered Metabolism in Alzheimer Disease Brain: Role of Oxidative Stress. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2022, 36, 1289–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shabbir, U.; Tyagi, A.; Elahi, F.; Aloo, S.O.; Oh, D.H. , The potential role of polyphenols in oxidative stress and inflammation induced by gut microbiota in alzheimer’s disease. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, C.; Kim, S.R. , Linking oxidative stress and proteinopathy in alzheimer’s disease. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simunkova, M.; Alwasel, S.H.; Alhazza, I.M.; Jomova, K.; Kollar, V.; Rusko, M.; Valko, M. , Management of oxidative stress and other pathologies in Alzheimer’s disease. Arch. Toxicol. 2019, 93, 2491–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchekalarova, J.; Tzoneva, R. , Oxidative Stress and Aging as Risk Factors for Alzheimer’s Disease and Parkinson’s Disease: The Role of the Antioxidant Melatonin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z. , Iron and oxidizing species in oxidative stress and Alzheimer's disease. Aging Med. 2019, 2, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.H.; Chen, C.M. , The role of oxidative stress in Parkinson’s disease. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dionísio, P.A.; Amaral, J.D.; Rodrigues, C.M.P. , Oxidative stress and regulated cell death in Parkinson's disease. Ageing Res. Rev. 2021, 67, 101263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorszewska, J.; Kowalska, M.; Prendecki, M.; Piekut, T.; Kozłowska, J.; Kozubski, W. , Oxidative stress factors in Parkinson's disease. Neural Regen. Res. 2021, 16, 1383–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.D.; Zhao, X.; Li, Y.; Li, G.R.; Liu, X.L. , Damage to dopaminergic neurons by oxidative stress in Parkinson's disease (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 41, 1817–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanzadeh, K.; Rahimmi, A. , Oxidative stress and neuroinflammation in the story of Parkinson’s disease: Could targeting these pathways write a good ending? J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 234, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hor, S.L.; Teoh, S.L.; Lim, W.L. , Plant polyphenols as neuroprotective agents in parkinson’s disease targeting oxidative stress. Curr. Drug Targets 2020, 21, 458–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monzani, E.; Nicolis, S.; Dell'Acqua, S.; Capucciati, A.; Bacchella, C.; Zucca, F.A.; Mosharov, E.V.; Sulzer, D.; Zecca, L.; Casella, L. , Dopamine, Oxidative Stress and Protein–Quinone Modifications in Parkinson's and Other Neurodegenerative Diseases. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. Engl. 2019, 58, 6512–6527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Percário, S.; Da Silva Barbosa, A.; Varela, E.L.P.; Gomes, A.R.Q.; Ferreira, M.E.S.; De Nazaré Araújo Moreira, T.; Dolabela, M.F. , Oxidative Stress in Parkinson's Disease: Potential Benefits of Antioxidant Supplementation. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 2360872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puspita, L.; Chung, S.Y.; Shim, J.W. , Oxidative stress and cellular pathologies in Parkinson's disease. Mol. Brain 2017, 10, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyatha, S.; Kim, H.; Lee, D.; Kim, K. , Association between Heavy Metal Exposure and Parkinson’s Disease: A Review of the Mechanisms Related to Oxidative Stress. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizor, A.; Pajarillo, E.; Johnson, J.; Aschner, M.; Lee, E. , Astrocytic oxidative/nitrosative stress contributes to parkinson’s disease pathogenesis: The dual role of reactive astrocytes. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trist, B.G.; Hare, D.J.; Double, K.L. , Oxidative stress in the aging substantia nigra and the etiology of Parkinson's disease. Aging Cell 2019, 18, e13031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallée, A.; Lecarpentier, Y.; Guillevin, R.; Vallée, J.N. , Circadian rhythms, Neuroinflammation and Oxidative Stress in the Story of Parkinson's Disease. Cells 2020, 9, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Z.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Liu, Q.; Cheng, Y. , Oxidative Stress in Parkinson's Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2018, 11, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adhikari, R.; Shiwakoti, S.; Ko, J.Y.; Dhakal, B.; Park, S.H.; Choi, I.J.; Kim, H.J.; Oak, M.H. , Oxidative Stress in Calcific Aortic Valve Stenosis: Protective Role of Natural Antioxidants. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amponsah-Offeh, M.; Diaba-Nuhoho, P.; Speier, S.; Morawietz, H. , Oxidative Stress, Antioxidants and Hypertension. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baboo, K.; Chen, Z.Y.; Zhang, X.M. , Role of oxidative stress and antioxidant therapies in endometriosis. Reprod. Dev. Med. 2019, 3, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berríos-Cárcamo, P.; Quezada, M.; Quintanilla, M.E.; Morales, P.; Ezquer, M.; Herrera-Marschitz, M.; Israel, Y.; Ezquer, F. , Oxidative stress and neuroinflammation as a pivot in drug abuse. A focus on the therapeutic potential of antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agents and biomolecules. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, H.S. , A Synopsis of the Associations of Oxidative Stress, ROS, and Antioxidants with Diabetes Mellitus. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouyahya, A.; Menyiy, N.E.; Oumeslakht, L.; Allam, A.E.; Balahbib, A.; Rauf, A.; Muhammad, N.; Kuznetsova, E.; Derkho, M.; Thiruvengadam, M.; Shariati, M.A.; Omari, N.E. , Preclinical and clinical antioxidant effects of natural compounds against oxidative stress-induced epigenetic instability in tumor cells. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, M.N.; Colone, M.; Gambioli, R.; Stringaro, A.; Unfer, V. , Oxidative stress and male fertility: Role of antioxidants and inositols. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, L.; Du, C.; Song, P.; Chen, T.; Rui, S.; Armstrong, D.G.; Deng, W. , The Role of Oxidative Stress and Antioxidants in Diabetic Wound Healing. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 8852759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Zhang, N.J.; Zhang, L.J. , Oxidative stress in leukemia and antioxidant treatment. Chin. Med. J. 2021, 134, 1897–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engwa, G.A.; Nweke, F.N.; Nkeh-Chungag, B.N. , Free Radicals, Oxidative Stress-Related Diseases and Antioxidant Supplementation. Altern. Ther. Health Med. 2022, 28, 144–128. [Google Scholar]
- Forman, H.J.; Zhang, H. , Targeting oxidative stress in disease: promise and limitations of antioxidant therapy. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 689–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, A.R.Q.; Cunha, N.; Varela, E.L.P.; Brígido, H.P.C.; Vale, V.V.; Dolabela, M.F.; de Carvalho, E.P.; Percário, S. , Oxidative Stress in Malaria: Potential Benefits of Antioxidant Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, M.; Lee, D.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, T.H. , Oxidative stress and antioxidant pathway in allergic rhinitis. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, T.Y.; Wu, S.B.; Kau, H.C.; Tsai, C.C. , The role of oxidative stress and therapeutic potential of antioxidants in graves’ ophthalmopathy. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsueh, Y.J.; Chen, Y.N.; Tsao, Y.T.; Cheng, C.M.; Wu, W.C.; Chen, H.C. , The Pathomechanism, Antioxidant Biomarkers, and Treatment of Oxidative Stress-Related Eye Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Dong, D.; Xia, M.; Yang, Y.; Wang, J.; Su, J.; Sun, L.; Yu, H. , Oxidative stress and antioxidant capacity: Development and prospects. New J. Chem. 2020, 44, 11405–11419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, T.; Murtaza, G.; Metwally, E.; Kalhoro, D.H.; Kalhoro, M.S.; Rahu, B.A.; Sahito, R.G.A.; Yin, Y.; Yang, H.; Chughtai, M.I.; Tan, B. , The Role of Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant Balance in Pregnancy. Mediators Inflamm. 2021, 2021, 9962860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iakovou, E.; Kourti, M. , A Comprehensive Overview of the Complex Role of Oxidative Stress in Aging, The Contributing Environmental Stressors and Emerging Antioxidant Therapeutic Interventions. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 827900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishimoto-Urata, M.; Urata, S.; Fujimoto, C.; Yamasoba, T. , Role of Oxidative Stress and Antioxidants in Acquired Inner Ear Disorders. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, H.; Bhardwaj, K.; Nepovimova, E.; Kuča, K.; Dhanjal, D.S.; Bhardwaj, S.; Bhatia, S.K.; Verma, R.; Kumar, D. , Antioxidant functionalized nanoparticles: A combat against oxidative stress. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Saxena, J.; Srivastava, V.K.; Kaushik, S.; Singh, H.; Abo-El-Sooud, K.; Abdel-Daim, M.M.; Jyoti, A.; Saluja, R. , The Interplay of Oxidative Stress and ROS Scavenging: Antioxidants as a Therapeutic Potential in Sepsis. Vaccines 2022, 10, 1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Li, Y.; Wang, R.; Ren, F.; Wang, X. , Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant Nanotherapeutic Approaches for Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Biomedicines 2021, 10, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macvanin, M.T.; Gluvic, Z.; Zafirovic, S.; Gao, X.; Essack, M.; Isenovic, E.R. , The protective role of nutritional antioxidants against oxidative stress in thyroid disorders. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 2023, 13, 1092837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcucci, G.; Domazetovic, V.; Nediani, C.; Ruzzolini, J.; Favre, C.; Brandi, M.L. , Oxidative Stress and Natural Antioxidants in Osteoporosis: Novel Preventive and Therapeutic Approaches. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meli, R.; Monnolo, A.; Annunziata, C.; Pirozzi, C.; Ferrante, M.C. , Oxidative stress and BPA toxicity: An antioxidant approach for male and female reproductive dysfunction. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meulmeester, F.L.; Luo, J.; Martens, L.G.; Mills, K.; van Heemst, D.; Noordam, R. , Antioxidant Supplementation in Oxidative Stress-Related Diseases: What Have We Learned from Studies on Alpha-Tocopherol? Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandi, S.; Ahmed, S.; Saxena, A.K. , Exploring the Role of Antioxidants to Combat Oxidative Stress in Malaria Parasites. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2022, 22, 2029–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nantachai, G.; Vasupanrajit, A.; Tunvirachaisakul, C.; Solmi, M.; Maes, M. , Oxidative stress and antioxidant defenses in mild cognitive impairment: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ageing Res. Rev. 2022, 79, 101639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olufunmilayo, E.O.; Gerke-Duncan, M.B.; Holsinger, R.M.D. , Oxidative Stress and Antioxidants in Neurodegenerative Disorders. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisoschi, A.M.; Pop, A.; Iordache, F.; Stanca, L.; Predoi, G.; Serban, A.I. , Oxidative stress mitigation by antioxidants - An overview on their chemistry and influences on health status. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 209, 112891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poznyak, A.V.; Grechko, A.V.; Orekhova, V.A.; Chegodaev, Y.S.; Wu, W.K.; Orekhov, A.N. , Oxidative stress and antioxidants in atherosclerosis development and treatment. Biology 2020, 9, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajoka, M.S.R.; Thirumdas, R.; Mehwish, H.M.; Umair, M.; Khurshid, M.; Hayat, H.F.; Phimolsiripol, Y.; Pallarés, N.; Martí-Quijal, F.J.; Barba, F.J. , Role of food antioxidants in modulating gut microbial communities: Novel understandings in intestinal oxidative stress damage and their impact on host health. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, K.; Gautam, P. , A Review on Antioxidants as Therapeutic in Use of Oxidative Stress and Neurodegenerative Disease. Int. J. Pharm. Qual. Assur. 2022, 13, 77–82. [Google Scholar]
- Rivas-Arancibia, S.; Hernández-Orozco, E.; Rodríguez-Martínez, E.; Valdés-Fuentes, M.; Cornejo-Trejo, V.; Pérez-Pacheco, N.; Dorado-Martínez, C.; Zequeida-Carmona, D.; Espinosa-Caleti, I. , Ozone Pollution, Oxidative Stress, Regulatory T Cells and Antioxidants. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shohag, S.; Akhter, S.; Islam, S.; Sarker, T.; Sifat, M.K.; Rahman, M.M.; Islam, M.R.; Sharma, R. , Perspectives on the Molecular Mediators of Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant Strategies in the Context of Neuroprotection and Neurolongevity: An Extensive Review. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 7743705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taherkhani, S.; Valaei, K.; Arazi, H.; Suzuki, K. , An overview of physical exercise and antioxidant supplementation influences on skeletal muscle oxidative stress. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, J.; Shin, J.M.; Park, J.; Han, M.; Kim, T.H. , Oxidative Stress and Antioxidants in Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tain, Y.L.; Hsu, C.N. , Oxidative Stress-Induced Hypertension of Developmental Origins: Preventive Aspects of Antioxidant Therapy. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theofanous, T.; Kourti, M. , Abrogating Oxidative Stress as a Therapeutic Strategy Against Parkinson’s Disease: A Mini Review of the Recent Advances on Natural Therapeutic Antioxidant and Neuroprotective Agents. Med. Chem. 2022, 18, 772–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsermpini, E.E.; Plemenitaš Ilješ, A.; Dolžan, V. , Alcohol-Induced Oxidative Stress and the Role of Antioxidants in Alcohol Use Disorder: A Systematic Review. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varesi, A.; Chirumbolo, S.; Campagnoli, L.I.M.; Pierella, E.; Piccini, G.B.; Carrara, A.; Ricevuti, G.; Scassellati, C.; Bonvicini, C.; Pascale, A. , The Role of Antioxidants in the Interplay between Oxidative Stress and Senescence. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vona, R.; Sposi, N.M.; Mattia, L.; Gambardella, L.; Straface, E.; Pietraforte, D. , Sickle cell disease: Role of oxidative stress and antioxidant therapy. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Kang, P.M. , Oxidative stress and antioxidant treatments in cardiovascular diseases. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xing, Y.; Miao, C.; Zhao, Y.; Chang, X.; Zhang, Q. , The Role of Oxidative Stress and Natural Antioxidants in Ovarian Aging. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 11, 617843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Guan, Q.W.; Chen, F.H.; Xia, Q.X.; Yin, X.X.; Zhou, H.H.; Mao, X.Y. , Antioxidants targeting mitochondrial oxidative stress: Promising neuroprotectants for epilepsy. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 6687185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, M.S.; Quarta, A.; Marradi, M.; Ragusa, A. , Recent developments in the reduction of oxidative stress through antioxidant polymeric formulations. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzman-Lopez, E.G.; Reina, M.; Perez-Gonzalez, A.; Francisco-Marquez, M.; Hernandez-Ayala, L.F.; Castañeda-Arriaga, R.; Galano, A. , CADMA-Chem: A Computational Protocol Based on Chemical Properties Aimed to Design Multifunctional Antioxidants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-González, A.; Castañeda-Arriaga, R.; Guzmán-López, E.G.; Hernández-Ayala, L.F.; Galano, A. , Chalcone Derivatives with a High Potential as Multifunctional Antioxidant Neuroprotectors. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 38254–38268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reina, M.; Guzmán-López, E.G.; Galano, A. , Computational design of rasagiline derivatives: Searching for enhanced antioxidant capability. Int. J. Quantum Chem. 2023, 123, e27011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.S.; Khalid, M.; Kamal, M.A.; Younis, K. , Study of Nutraceuticals and Phytochemicals for the Management of Alzheimer's Disease: A Review. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2021, 19, 1884–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachheti, R.K.; Worku, L.A.; Gonfa, Y.H.; Zebeaman, M.; Deepti; Pandey, D. P.; Bachheti, A., Prevention and Treatment of Cardiovascular Diseases with Plant Phytochemicals: A Review. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2022, 2022, 5741198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakrim, S.; Aboulaghras, S.; El Menyiy, N.; El Omari, N.; Assaggaf, H.; Lee, L.H.; Montesano, D.; Gallo, M.; Zengin, G.; AlDhaheri, Y.; Bouyahya, A. , Phytochemical Compounds and Nanoparticles as Phytochemical Delivery Systems for Alzheimer’s Disease Management. Molecules 2022, 27, 9043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balakrishnan, R.; Azam, S.; Cho, D.Y.; Su-Kim, I.; Choi, D.K. , Natural Phytochemicals as Novel Therapeutic Strategies to Prevent and Treat Parkinson's Disease: Current Knowledge and Future Perspectives. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 6680935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behl, T.; Rana, T.; Sehgal, A.; Makeen, H.A.; Albratty, M.; Alhazmi, H.A.; Meraya, A.M.; Bhatia, S.; Sachdeva, M. , Phytochemicals targeting nitric oxide signaling in neurodegenerative diseases. Nitric Oxide - Biol. Chem. 2023, 130, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bungau, S.; Vesa, C.M.; Abid, A.; Behl, T.; Tit, D.M.; Purza, A.L.; Pasca, B.; Todan, L.M.; Endres, L. , Withaferin a—a promising phytochemical compound with multiple results in dermatological diseases. Molecules 2021, 26, 2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Chen, Q.; Sun, P. , Natural phytochemicals that affect autophagy in the treatment of oral diseases and infections: A review. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 970596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dsouza, V.L.; Shivakumar, A.B.; Kulal, N.; Gangadharan, G.; Kumar, D.; Kabekkodu, S.P. , Phytochemical based Modulation of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Alzheimer's Disease. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2022, 22, 1880–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eilam, Y.; Pintel, N.; Khattib, H.; Shagug, N.; Taha, R.; Avni, D. , Regulation of Cholesterol Metabolism by Phytochemicals Derived from Algae and Edible Mushrooms in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forni, C.; Facchiano, F.; Bartoli, M.; Pieretti, S.; Facchiano, A.; D'Arcangelo, D.; Norelli, S.; Valle, G.; Nisini, R.; Beninati, S.; Tabolacci, C.; Jadeja, R.N. , Beneficial role of phytochemicals on oxidative stress and age-related diseases. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 8748253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesan, K.; Quiles, J.L.; Daglia, M.; Xiao, J.; Xu, B. , Dietary phytochemicals modulate intestinal epithelial barrier dysfunction and autoimmune diseases. Food Front. 2021, 2, 357–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.J.; Lv, C.H.; Chen, Z.; Shi, M.; Zeng, C.X.; Hou, D.X.; Qin, S. , The Regulatory Effect of Phytochemicals on Chronic Diseases by Targeting Nrf2-ARE Signaling Pathway. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossen, I.; Hua, W.; Ting, L.; Mehmood, A.; Jingyi, S.; Duoxia, X.; Yanping, C.; Hongqing, W.; Zhipeng, G.; Kaiqi, Z.; Fang, Y.; Junsong, X. , Phytochemicals and inflammatory bowel disease: a review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 1321–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, S.U.; Ahmed, M.B.; Ahsan, H.; Lee, Y.S. , Recent molecular mechanisms and beneficial effects of phytochemicals and plant-based whole foods in reducing ldl-c and preventing cardiovascular disease. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, V.; Lee, H.J. , Pharmacological Activities of Mogrol: Potential Phytochemical against Different Diseases. Life 2023, 13, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurindo, L.F.; de Maio, M.C.; Minniti, G.; de Góes Corrêa, N.; Barbalho, S.M.; Quesada, K.; Guiguer, E.L.; Sloan, K.P.; Detregiachi, C.R.P.; Araújo, A.C.; de Alvares Goulart, R. , Effects of Medicinal Plants and Phytochemicals in Nrf2 Pathways during Inflammatory Bowel Diseases and Related Colorectal Cancer: A Comprehensive Review. Metabolites 2023, 13, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Li, A.; Liu, R.; Yang, H.; Xia, X. , The Phytochemical Potential for Brain Disease Therapy and the Possible Nanodelivery Solutions for Brain Access. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 936054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naoi, M.; Maruyama, W.; Shamoto-Nagai, M. , Disease-modifying treatment of Parkinson’s disease by phytochemicals: targeting multiple pathogenic factors. J. Neural Transm. 2022, 129, 737–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nistor, M.; Pop, R.; Daescu, A.; Pintea, A.; Socaciu, C.; Rugina, D. , Anthocyanins as Key Phytochemicals Acting for the Prevention of Metabolic Diseases: An Overview. Molecules 2022, 27, 4254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.A.; Rahman, M.H.; Biswas, P.; Hossain, M.S.; Islam, R.; Hannan, M.A.; Uddin, M.J.; Rhim, H. , Potential therapeutic role of phytochemicals to mitigate mitochondrial dysfunctions in Alzheimer’s disease. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Naura, A.S. , Potential of phytochemicals as immune-regulatory compounds in atopic diseases: A review. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2020, 173, 113790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirsath, N.R.; Goswami, A.K. , Natural phytochemicals and their therapeutic role in management of several diseases: A review. Curr. Tradit. Med. 2020, 6, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subedi, L.; Lee, S.E.; Madiha, S.; Gaire, B.P.; Jin, M.; Yumnam, S.; Kim, S.Y. , Phytochemicals against TNFα-mediated neuroinflammatory diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, S.; Li, Q.; Lang, W.; Li, W.; Jiang, X.; Wan, Z.; Chen, J.; Wang, H. , Epigallocatechin-3-gallate: A phytochemical as a promising drug candidate for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 977521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Lu, B. , The effects of phytochemicals on circadian rhythm and related diseases. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 882–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.H.; Tao, G.; Yang, L.; Wu, X.; Liu, J.W.; Dagher, F.; Ou, S.Y.; Song, Y.; Huang, J.Q. , Dietary phytochemical and metabolic disease prevention: Focus on plant proteins. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1089487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahedipour, F.; Hosseini, S.; Henney, N.; Barreto, G.; Sahebkar, A. , Phytochemicals as inhibitors of tumor necrosis factor alpha and neuroinflammatory responses in neurodegenerative diseases. Neural Regen. Res. 2022, 17, 1675–1684. [Google Scholar]
- Bahadori, M.B.; Kirkan, B.; Sarikurkcu, C. , Phenolic ingredients and therapeutic potential of Stachys cretica subsp. smyrnaea for the management of oxidative stress, Alzheimer's disease, hyperglycemia, and melasma. Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 127, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakat, A.Z.; Bassuiny, R.I.; Abdel-Aty, A.M.; Mohamed, S.A. , Diabetic complications and oxidative stress: The role of phenolic-rich extracts of saw palmetto and date palm seeds. J. Food Biochem. 2020, 44, e13416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callcott, E.T.; Blanchard, C.L.; Oli, P.; Santhakumar, A.B. , Pigmented Rice-Derived Phenolic Compounds Reduce Biomarkers of Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2018, 62, 1800840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carballeda Sangiao, N.; Chamorro, S.; de Pascual-Teresa, S.; Goya, L. , Aqueous extract of cocoa phenolic compounds protects differentiated neuroblastoma sh-sy5y cells from oxidative stress. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castaneda-Arriaga, R.; Pérez-González, A.; Reina, M.; Alvarez-Idaboy, J.R.; Galano, A. , Comprehensive Investigation of the Antioxidant and Pro-oxidant Effects of Phenolic Compounds: A Double-Edged Sword in the Context of Oxidative Stress? J. Phys. Chem. B 2018, 122, 6198–6214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabbia, D.; Carpi, S.; Sarcognato, S.; Zanotto, I.; Sayaf, K.; Colognesi, M.; Polini, B.; Digiacomo, M.; Macchia, M.; Nieri, P.; Carrara, M.; Cazzagon, N.; Russo, F.P.; Guido, M.; De Martin, S. , The phenolic compounds tyrosol and hydroxytyrosol counteract liver fibrogenesis via the transcriptional modulation of NADPH oxidases and oxidative stress-related miRNAs. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 157, 114014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanafy, D.M.; Burrows, G.E.; Prenzler, P.D.; Hill, R.A. , Potential role of phenolic extracts of mentha in managing oxidative stress and alzheimer’s disease. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Tong, C.; Zhou, J.; Gao, C.; Olatunji, O.J. , Protective Effects of Shorea roxburghii Phenolic Extract on Nephrotoxicity Induced by Cyclophosphamide: Impact on Oxidative Stress, Biochemical and Histopathological Alterations. Chem. Biodivers. 2022, 19, e202200053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsinas, N.; Rodríguez-Rojo, S.; Enríquez-De-salamanca, A. , Olive pomace phenolic compounds and extracts can inhibit inflammatory-and oxidative-related diseases of human ocular surface epithelium. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruk, J.; Aboul-Enein, B.H.; Duchnik, E.; Marchlewicz, M. , Antioxidative properties of phenolic compounds and their effect on oxidative stress induced by severe physical exercise. J. Physiol. Sci. 2022, 72, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lion, Q.; Pichette, A.; Mihoub, M.; Mshvildadze, V.; Legault, J. , Phenolic extract from aralia nudicaulis L. rhizomes inhibits cellular oxidative stresses. Molecules 2021, 26, 4458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Guo, H.; DaSilva, N.A.; Li, D.; Zhang, K.; Wan, Y.; Gao, X.H.; Chen, H.D.; Seeram, N.P.; Ma, H. , Pomegranate (Punica granatum) phenolics ameliorate hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress and cytotoxicity in human keratinocytes. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 54, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oršolić, N.; Kunštić, M.; Kukolj, M.; Odeh, D.; Ančić, D. , Natural phenolic acid, product of the honey bee, for the control of oxidative stress, peritoneal angiogenesis, and tumor growth in mice. Molecules 2020, 25, 5583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramli, I.; Posadino, A.M.; Zerizer, S.; Spissu, Y.; Barberis, A.; Djeghim, H.; Azara, E.; Bensouici, C.; Kabouche, Z.; Rebbas, K.; D'Hallewin, G.; Sechi, L.A.; Pintus, G. , Low concentrations of Ambrosia maritima L. phenolic extract protect endothelial cells from oxidative cell death induced by H2O2 and sera from Crohn's disease patients. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 300, 115722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Y.; Sun-Waterhouse, D.; Ouyang, F.; Tan, X.; Li, D.; Xu, L.; Li, B.; Wang, Y.; Li, F. , Apple phenolic extracts ameliorate lead-induced cognitive impairment and depression- and anxiety-like behavior in mice by abating oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis via the miR-22-3p/SIRT1 axis. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 2647–2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, R.; Dua, T.K.; Das, S.; De Feo, V.; Dewanjee, S. , Wheat phenolics suppress doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity via inhibition of oxidative stress, MAP kinase activation, NF-κB pathway, PI3K/Akt/mTOR impairment, and cardiac apoptosis. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 125, 503–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Medina, A.; Redondo-Puente, M.; Dupak, R.; Bravo-Clemente, L.; Goya, L.; Sarriá, B. , Colonic Coffee Phenols Metabolites, Dihydrocaffeic, Dihydroferulic, and Hydroxyhippuric Acids Protect Hepatic Cells from TNF-α-Induced Inflammation and Oxidative Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winarsi, H.; Septiana, A.T. , Improving oxidative stress and inflammation status of obese women with metabolic syndrome using phenolic-rich red kidney bean sprout milk yogurt. Int. Food Res. J. 2022, 29, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yener, I.; Kocakaya, S.O.; Ertas, A.; Erhan, B.; Kaplaner, E.; Oral, E.V.; Yilmaz-Ozden, T.; Yilmaz, M.A.; Ozturk, M.; Kolak, U. , Selective in vitro and in silico enzymes inhibitory activities of phenolic acids and flavonoids of food plants: Relations with oxidative stress. Food Chem. 2020, 327, 127045–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Pruthi, V. , Potential applications of ferulic acid from natural sources. Biotechnol. Rep. 2014, 4, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- León-Carmona, J.R.; Alvarez-Idaboy, J.R.; Galano, A. , On the peroxyl scavenging activity of hydroxycinnamic acid derivatives: Mechanisms, kinetics, and importance of the acid-base equilibrium. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2012, 14, 12534–12543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Chen, D.; Yu, B.; Huang, Z. , Dietary ferulic acid supplementation improves intestinal antioxidant capacity and intestinal barrier function in weaned piglets. Anim. Biotechnol. 2022, 33, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, H.; Dye, L.; Mackie, A. , The impact of processing on the release and antioxidant capacity of ferulic acid from wheat: A systematic review. Food Res. Int. 2023, 164, 112371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horbury, M.D.; Baker, L.A.; Quan, W.D.; Greenough, S.E.; Stavros, V.G. , Photodynamics of potent antioxidants: Ferulic and caffeic acids. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 17691–17697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, H.J.; Lee, S.R.; Yoon, J.G.; Moon, H.R.; Zhang, J.; Park, E.; Yoon, S.I.; Cho, J.A. , Ferulic Acid as a Protective Antioxidant of Human Intestinal Epithelial Cells. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itagaki, S.; Kurokawa, T.; Nakata, C.; Saito, Y.; Oikawa, S.; Kobayashi, M.; Hirano, T.; Iseki, K. , In vitro and in vivo antioxidant properties of ferulic acid: A comparative study with other natural oxidation inhibitors. Food Chem. 2009, 114, 466–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, Â.C. O.; Dias, E.R.; Reis, I.M.A.; Carneiro, K.O.; Pinheiro, A.M.; Nascimento, A.S.; Silva, S.M.P.C.; Carvalho, C.A.L.; Mendonça, A.V.R.; Vieira, I.J.C.; Braz Filho, R.; Branco, A. , Ferulic acid as major antioxidant phenolic compound of the Tetragonisca angustula honey collected in Vera Cruz-Itaparica Island, Bahia, Brazil. Braz. J. Biol. 2022, 84, e253599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rampelotto, C.R.; Pereira, V.G.; da Silva Silveira, L.; Rossato, A.; Machado, A.K.; Sagrillo, M.R.; Gündel, A.; Burger, M.E.; Schaffazick, S.R.; de Bona da Silva, C. , Ferulic acid-loaded nanocapsules: Evaluation of mucosal interaction, safety and antioxidant activity in human mononucleated cells. Toxicol. In Vitro 2022, 78, 105259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, M.; Sudheer, A.R.; Menon, V.P. , Ferulic acid: Therapeutic potential through its antioxidant property. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2007, 40, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, D.H.; Nhung, N.T.A.; Dao, D.Q. , Iron ions chelation-based antioxidant potential vs. pro-oxidant risk of ferulic acid: A DFT study in aqueous phase. Comput. Theor. Chem. 2020, 1185, 112905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagle, S.; Sim, H.J.; Bhattarai, G.; Choi, K.C.; Kook, S.H.; Lee, J.C.; Jeon, Y.M. , Supplemental ferulic acid inhibits total body irradiation-mediated bone marrow damage, bone mass loss, stem cell senescence, and hematopoietic defect in mice by enhancing antioxidant defense systems. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildiztugay, E.; Ozfidan-Konakci, C.; Karahan, H.; Kucukoduk, M.; Turkan, I. , Ferulic acid confers tolerance against excess boron by regulating ROS levels and inducing antioxidant system in wheat leaves (Triticum aestivum). Environ. Exp. Bot. 2019, 161, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zduńska, K.; Dana, A.; Kolodziejczak, A.; Rotsztejn, H. , Antioxidant properties of ferulic acid and its possible application. Skin Pharmacol. Physiol. 2018, 31, 332–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, S.M.; Ravuri, H.G.; Pradhan, R.K.; Narra, S.; Kumar, J.M.; Kuncha, M.; Kanjilal, S.; Sistla, R. , Ferulic acid protects lipopolysaccharide-induced acute kidney injury by suppressing inflammatory events and upregulating antioxidant defenses in Balb/c mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 100, 304–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Z.N.; Wu, W.J.; Sun, C.Z.; Liu, H.F.; Chen, W.B.; Zhan, Q.P.; Lei, Z.G.; Xin, X.; Ma, J.J.; Yao, K.; Min, T.; Zhang, M.M.; Wu, H. , Antioxidant and Anti-inflammatory Capacity of Ferulic Acid Released from Wheat Bran by Solid-state Fermentation of Aspergillus niger. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2019, 32, 11–21. [Google Scholar]
- Amani, F.; Rezaei, A.; Kharazmi, M.S.; Jafari, S.M. , Loading ferulic acid into β-cyclodextrin nanosponges; antibacterial activity, controlled release and application in pomegranate juice as a copigment agent. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Aspects 2022, 649, 129454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, A.; Ferreira, C.; Saavedra, M.J.; Simões, M. , Antibacterial activity and mode of action of ferulic and gallic acids against pathogenic bacteria. Microb. Drug Resist. 2013, 19, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ordoñez, R.; Atarés, L.; Chiralt, A. , Antibacterial properties of cinnamic and ferulic acids incorporated to starch and PLA monolayer and multilayer films. Food Control 2022, 136, 108878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Q.B.; Shi, H.C.; Li, P.; Sheng, S.; Wu, F.A. , Antibacterial Activity of Ferulic Acid Ester against Ralstonia solanacearum and Its Synergy with Essential Oils. Sustainability (Switzerland) 2022, 14, 16348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonopoulou, I.; Sapountzaki, E.; Rova, U.; Christakopoulos, P. , Ferulic Acid From Plant Biomass: A Phytochemical With Promising Antiviral Properties. Front. Nutr. 2022, 8, 777576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.H.; Park, J.K.; Kim, K.M.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, S. , In vitro and in vivo antithrombotic and cytotoxicity effects of ferulic acid. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2018, 32, 22004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Q.; Ma, Z.C.; Huang, H.; Wang, Y.G.; Tan, H.L.; Xiao, C.R.; Liang, Q.D.; Zhang, H.T.; Gao, Y. , Antithrombotic activities of ferulic acid via intracellular cyclic nucleotide signaling. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 777, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zduńska-Pęciak, K.; Kołodziejczak, A.; Rotsztejn, H. , Two superior antioxidants: Ferulic acid and ascorbic acid in reducing signs of photoaging—A split-face comparative study. Dermatol. Ther. 2022, 35, e15254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuda, T.; Kuroda, T.; Kono, M.; Hyoguchi, M.; Tanaka, M.; Matsui, T. , Augmentation of ferulic acid-induced vasorelaxation with aging and its structure importance in thoracic aorta of spontaneously hypertensive rats. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 2015, 388, 1113–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Qu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Huo, L.; Gao, J.; Gao, W. , Ferulic acid ameliorates memory impairment in d-galactose-induced aging mouse model. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 67, 806–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, N.; Kumar, S.; Abbat, S.; Nikhil, K.; Sondhi, S.M.; Bharatam, P.V.; Roy, P.; Pruthi, V. , Ferulic acid amide derivatives as anticancer and antioxidant agents: synthesis, thermal, biological and computational studies. Med. Chem. Res. 2016, 25, 1175–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ani, G.; Tanya, T.Y.; Reneta, T. , Antitumor and apoptogenic effects of ferulic acid on cervical carcinoma cells. Res. J. Biotechnol. 2021, 16, 6–11. [Google Scholar]
- Bakholdina, L.A.; Markova, A.A.; Khlebnikov, A.I.; Sevodin, V.P. , Cytotoxicity of New Ferulic-Acid Derivatives on Human Colon Carcinoma (HCT116) Cells. Pharm. Chem. J. 2019, 53, 516–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Tang, J.; Wang, R. , Ferulic Acid Mitigates Growth and Invasion of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma through Inducing Ferroptotic Cell Death. Dis. Markers 2022, 2022, 4607966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, K.; Wu, H.; Fan, J.; Zhang, L.; Li, H.; Guo, H.; Yang, R.; Li, Z. , The Mixture of Ferulic Acid and P-Coumaric Acid Suppresses Colorectal Cancer through lncRNA 495810/PKM2 Mediated Aerobic Glycolysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damasceno, S.S.; Dantas, B.B.; Ribeiro-Filho, J.; Araújo, D.A.M.; Da Costa, J.G.M. , Chemical properties of caffeic and ferulic acids in biological system: Implications in cancer therapy. A review. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2017, 23, 3015–3023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodurga, Y.; Eroğlu, C.; Seçme, M.; Elmas, L.; Avcı, Ç.B.; Şatıroğlu-Tufan, N.L. , Anti-proliferative and anti-invasive effects of ferulic acid in TT medullary thyroid cancer cells interacting with URG4/URGCP. Tumor Biol. 2016, 37, 1933–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Gogary, R.I.; Nasr, M.; Rahsed, L.A.; Hamzawy, M.A. , Ferulic acid nanocapsules as a promising treatment modality for colorectal cancer: Preparation and in vitro/in vivo appraisal. Life Sci. 2022, 298, 120500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElKhazendar, M.; Chalak, J.; El-Huneidi, W.; Vinod, A.; Abdel-Rahman, W.M.; Abu-Gharbieh, E. , Antiproliferative and proapoptotic activities of ferulic acid in breast and liver cancer cell lines. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2019, 18, 2571–2576. [Google Scholar]
- Eroğlu, C.; Seçme, M.; Bağcı, G.; Dodurga, Y. , Assessment of the anticancer mechanism of ferulic acid via cell cycle and apoptotic pathways in human prostate cancer cell lines. Tumor Biol. 2015, 36, 9437–9446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahrioğlu, U.; Dodurga, Y.; Elmas, L.; Seçme, M. , Ferulic acid decreases cell viability and colony formation while inhibiting migration of MIA PaCa-2 human pancreatic cancer cells in vitro. Gene 2016, 576, 476–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Yu, H.; Guo, W.; Kong, Y.; Gu; Li, Q. ; Yang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y., The anticancer effects of ferulic acid is associated with induction of cell cycle arrest and autophagy in cervical cancer cells. Cancer Cell Int. 2018, 18, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.; Singh, A.K.; Loka, M.; Pandey, A.K.; Bishayee, A. , Ferulic acid-mediated modulation of apoptotic signaling pathways in cancer. In Adv. Protein Chem. Struct. Biol., 2021; Vol. 125, pp 215-257.
- Luo, L.; Zhu, S.; Tong, Y.; Peng, S. , Ferulic acid induces apoptosis of HeLa and caski cervical carcinoma cells by down-regulating the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt signaling pathway. Med. Sci. Monit. 2020, 26, e920095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Lin, D.; Jiang, R.; Li, H.; Wan, J.; Li, H. , Ferulic acid exerts antitumor activity and inhibits metastasis in breast cancer cells by regulating epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 36, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.A.; Sernia, C.; Brown, L. , Ferulic acid improves cardiovascular and kidney structure and function in hypertensive rats. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2013, 61, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Chen, L.; Song, M.; Fang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Coffie, J.W.; Zhang, L.; Ma, L.; Wang, Q.; Yang, W.; Fang, L.; Wang, S.; Gao, X.; Wang, H. , Ferulic acid protects cardiomyocytes from TNF-α/cycloheximide-induced apoptosis by regulating autophagy. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2020, 43, 863–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monceaux, K.; Gressette, M.; Karoui, A.; Pires Da Silva, J.; Piquereau, J.; Ventura-Clapier, R.; Garnier, A.; Mericskay, M.; Lemaire, C. , Ferulic Acid, Pterostilbene, and Tyrosol Protect the Heart from ER-Stress-Induced Injury by Activating SIRT1-Dependent Deacetylation of eIF2α. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neto-Neves, E.M.; Filho, C.D.S.M.B.; Dejani, N.N.; de Sousa, D.P. , Ferulic acid and cardiovascular health: Therapeutic and preventive potential. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2021, 21, 1625–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandi, A.; Raghu, M.H.; Chandrashekar, N.; Kalappan, V.M. , Cardioprotective effects of Ferulic acid against various drugs and toxic agents. Beni-Suef Univ. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2022, 11, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salau, V.F.; Erukainure, O.L.; Olofinsan, K.A.; Msomi, N.Z.; Ijomone, O.K.; Islam, M.S. , Ferulic acid mitigates diabetic cardiomyopathy via modulation of metabolic abnormalities in cardiac tissues of diabetic rats. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2023, 37, 44–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.X.; Zhao, D.S.; Wang, J.; Zhou, H.; Wang, L.; Mao, J.L.; He, J.X. , The treatment of cardiovascular diseases: A review of ferulic acid and its derivatives. Pharmazie 2021, 76, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ren, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, R.; Li, Y.; Yang, Z.; Yang, H. , Ferulic acid exerts neuroprotective effects against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion-induced injury via antioxidant and anti-apoptotic mechanisms in vitro and in vivo. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 40, 1444–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Giacomo, S.; Percaccio, E.; Gullì, M.; Romano, A.; Vitalone, A.; Mazzanti, G.; Gaetani, S.; Di Sotto, A. , Recent Advances in the Neuroprotective Properties of Ferulic Acid in Alzheimer’s Disease: A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, X.; Huang, R. , Ferulic acid: An extraordinarily neuroprotective phenolic acid with anti-depressive properties. Phytomedicine 2022, 105, 154355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanzadeh, P.; Arbabi, E.; Atyabi, F.; Dinarvand, R. , Ferulic acid, a phenolic compound with therapeutic effects in neuropsychiatric disorders, stimulates the production of nerve growth factor and endocannabinoids in rat brain. Physiol. Pharmacol. (Iran) 2017, 21, 279–294. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.; Nie, Y.; Huang, C.; Zhu, G.; Zhang, X.; Hu, C.; Li, Z.; Gao, Y.; Ma, Z. , Ferulic acid produces neuroprotection against radiation-induced neuroinflammation by affecting NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Int. J. Radia. Biol. 2022, 98, 1442–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.M.; Shen, J.D.; Xu, L.P.; Li, H.B.; Li, Y.C.; Yi, L.T. , Ferulic acid inhibits neuro-inflammation in mice exposed to chronic unpredictable mild stress. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2017, 45, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, T.; Wu, Q.; Wei, J.; Tang, Y.; He, Y.N.; He, C.L.; Chen, X.; Yu, L.; Yu, C.L.; Law, B.Y.; Wu, J.M.; Qin, D.L.; Wu, A.G.; Zhou, X.G. , Ferulic Acid Exerts Neuroprotective Effects via Autophagy Induction in C. elegans and Cellular Models of Parkinson’s Disease. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 3723567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojha, S.; Javed, H.; Azimullah, S.; Khair, S.B.A.; Haque, M.E. , Neuroprotective potential of ferulic acid in the rotenone model of Parkinson’s disease. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2015, 9, 5499–5510. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Arthur, R.; Upadhayay, S.; Kumar, P. , Ferulic acid ameliorates neurodegeneration via the Nrf2/ARE signalling pathway: A Review. Pharmacol. Res. - Modern Chinese Med. 2022, 5, 100190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapliyal, S.; Singh, T.; Handu, S.; Bisht, M.; Kumari, P.; Arya, P.; Srivastava, P.; Gandham, R. , A Review on Potential Footprints of Ferulic Acid for Treatment of Neurological Disorders. Neurochem. Res. 2021, 46, 1043–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, C.L.; Lu, R.G.; Zhu, J.F.; Huang, H.M.; Liu, X.; Li, Q.F.; Mo, Y.Y.; Zhu, H.J.; Chin, B.; Wu, J.X.; Liu, X.W.; Cheng, B.; Ruan, J.X.; Liang, Y.H.; Song, H.; Guo, H.W.; Su, Z.H.; Zheng, H. , The study of neuroprotective effect of ferulic acid based on cell metabolomics. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 864, 172694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.A. , Anti-hypertensive Effect of Cereal Antioxidant Ferulic Acid and Its Mechanism of Action. Front. Nutr. 2019, 6, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ardiansyah; Ohsaki, Y. ; Shirakawa, H.; Koseki, T.; Komai, M., Novel effects of a single administration of ferulic acid on the regulation of blood pressure and the hepatic lipid metabolic profile in stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Bassossy, H.; Badawy, D.; Neamatallah, T.; Fahmy, A. , Ferulic acid, a natural polyphenol, alleviates insulin resistance and hypertension in fructose fed rats: Effect on endothelial-dependent relaxation. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2016, 254, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, A.; Yamamoto, M.; Jokura, H.; Fujii, A.; Tokimitsu, I.; Hase, T.; Saito, I. , Ferulic Acid Restores Endothelium-Dependent Vasodilation in Aortas of Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Am. J. Hypertens. 2007, 20, 508–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenzi, J.; Rodrigues, A.F.; Rós, A.S.; de Castro, B.B.; de Lima, D.D.; Magro, D.D.D.; Zeni, A.L.B. , Ferulic acid chronic treatment exerts antidepressant-like effect: role of antioxidant defense system. Metab. Brain Dis. 2015, 30, 1453–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Lin, D.; Zhang, C.; Li, G.; Zhang, N.; Ruan, L.; Yan, Q.; Li, J.; Yu, X.; Xie, X.; Pang, C.; Cao, L.; Pan, J.; Xu, Y. , Antidepressant-like effects of ferulic acid: involvement of serotonergic and norepinergic systems. Metab. Brain Dis. 2015, 30, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, L.; Zhou, X.; Tao, G.; Hao, W.; Wang, L.; Lan, Z.; Song, Y.; Wu, M.; Huang, J.Q. , Ferulic acid and feruloylated oligosaccharides alleviate anxiety and depression symptom via regulating gut microbiome and microbial metabolism. Food Res. Int. 2022, 162, 111887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, K.; Iwata, N.; Ferdousi, F.; Isoda, H. , Antidepressant-Like Effect of Ferulic Acid via Promotion of Energy Metabolism Activity. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2019, 63, e1900327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, T.; Kaur, T.; Goel, R.K. , Ferulic Acid Supplementation for Management of Depression in Epilepsy. Neurochem. Res. 2017, 42, 2940–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Cheng, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yue, Y.; Li, Y.; Xia, S.; Li, Y.; Deng, H.; Zhang, J.; Cao, Y. , Ferulic acid improves depressive-like behavior in prenatally-stressed offspring rats via anti-inflammatory activity and HPA axis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, D.N.; Prasanna, N.; Sabina, E.P.; Rasool, M.K. , Hepatoprotective and antioxidant potential of ferulic acid against acetaminophen-induced liver damage in mice. Comp. Clin. Path. 2013, 22, 1177–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmat, M.A.; Osman, A.; Hassan, R.E.; Hagag, S.A.; El-maghraby, T.K. , Hepatoprotective effect of ferulic acid and/or low doses of γ-irradiation against cisplatin-induced liver injury in rats. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2022, 41, 9603271221136205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerin, F.; Erman, H.; Erboga, M.; Sener, U.; Yilmaz, A.; Seyhan, H.; Gurel, A. , The Effects of Ferulic Acid Against Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Formaldehyde-Induced Hepatotoxicity. Inflammation 2016, 39, 1377–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, R.M.; Anwar, M.M.; Farghaly, H.S.; Kandeil, M.A. , Gallic acid and ferulic acid protect the liver from thioacetamide-induced fibrosis in rats via differential expression of miR-21, miR-30 and miR-200 and impact on TGF-β1/Smad3 signaling. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2020, 324, 109098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Li, M.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, F.; Gong, L.; Han, L.; Wang, M. , Ferulic Acid Prevents Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Promoting Fatty Acid Oxidation and Energy Expenditure in C57BL/6 Mice Fed a High-Fat Diet. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Chen, K.; Lv, L.; Wu, S.; Guo, Z. , Ferulic acid ameliorates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and modulates the gut microbiota composition in high-fat diet fed ApoE −/− mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 113, 108753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoud, A.M.; Hussein, O.E.; Hozayen, W.G.; Bin-Jumah, M.; Abd El-Twab, S.M. , Ferulic acid prevents oxidative stress, inflammation, and liver injury via upregulation of Nrf2/HO-1 signaling in methotrexate-induced rats. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 7910–7921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roghani, M.; Kalantari, H.; Khodayar, M.J.; Khorsandi, L.; Kalantar, M.; Goudarzi, M.; Kalantar, H. , Alleviation of liver dysfunction, oxidative stress and inflammation underlies the protective effect of ferulic acid in methotrexate-induced hepatotoxicity. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2020, 14, 1933–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tawfik, M.S.; Saif-Elnasr, M.; Elkady, A.A.; Alkady, M.M.; Hawas, A.M. , Protective role of ferulic acid against the damaging effect induced by electromagnetic waves on rat liver and intestine tissues. Int. J. Radiat. Res. 2018, 16, 421–430. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Xue, X.; Fan, G.; Gu, Y.; Zhou, F.; Zheng, Q.; Liu, R.; Li, Y.; Ma, B.; Li, S.; Huang, G.; Ma, L.; Li, X. , Ferulic Acid Ameliorates Hepatic Inflammation and Fibrotic Liver Injury by Inhibiting PTP1B Activity and Subsequent Promoting AMPK Phosphorylation. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 754976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Zhou, F.; Fan, G.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Xue, X.; Lyu, X.; Lin, S.; Li, X. , Ferulic acid ameliorates acetaminophen-induced acute liver injury by promoting AMPK-mediated protective autophagy. IUBMB Life 2022, 74, 880–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Song, Q.; Zhou, L.; Yang, W.; Wu, X.; Qian, Q.; Chai, H.; Han, Q.; Pan, H.; Dou, X.; Li, S. , Ferulic acid alleviates lipotoxicity-induced hepatocellular death through the SIRT1-regulated autophagy pathway and independently of AMPK and Akt in AML-12 hepatocytes. Nutr. Metab. 2021, 18, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bairagi, U.; Mittal, P.; Singh, J.; Mishra, B. , Preparation, characterization, and in vivo evaluation of nano formulations of ferulic acid in diabetic wound healing. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2018, 44, 1783–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Chowdhury, S.; Sarkar, P.; Sil, P.C. , Ameliorative role of ferulic acid against diabetes associated oxidative stress induced spleen damage. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 118, 272–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Bai, L.; Ma, H.; Guo, H. , Ferulic acid alleviates diabetic cardiomyopathy in mice via decreasing blood glucose, reducing inflammation and down-regulating TLR-4/NF-κB pathway. Lat. Am. J. Pharm. 2021, 40, 1445–1450. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Wu, J.; Xu, F.; Chu, C.; Li, X.; Shi, X.; Zheng, W.; Wang, Z.; Jia, Y.; Xiao, W. , Use of Ferulic Acid in the Management of Diabetes Mellitus and Its Complications. Molecules 2022, 27, 6010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panwar, R.; Raghuwanshi, N.; Srivastava, A.K.; Sharma, A.K.; Pruthi, V. , In-vivo sustained release of nanoencapsulated ferulic acid and its impact in induced diabetes. Mater. Sci. Eng., C 2018, 92, 381–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salau, V.F.; Erukainure, O.L.; Olofinsan, K.O.; Bharuth, V.; Ijomone, O.M.; Islam, M.S. , Ferulic acid improves glucose homeostasis by modulation of key diabetogenic activities and restoration of pancreatic architecture in diabetic rats. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2023, 37, 324–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Gao, J.; Li, H. , Ferulic acid confers protection on islet β cells and placental tissues of rats with gestational diabetes mellitus. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2020, 66, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanvand, A.; Kharazmkia, A.; Mir, S.; Khorramabadi, R.M.; Darabi, S. , Ameliorative effect of ferulic acid on gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity in a rat model; role of antioxidant effects. J. Ren. Inj. Prev. 2018, 7, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeyemi, O.S.; Atolani, O.; Banerjee, P.; Arolasafe, G.; Preissner, R.; Etukudoh, P.; Ibraheem, O. , Computational and experimental validation of antioxidant properties of synthesized bioactive ferulic acid derivatives. Int. J. Food Prop. 2018, 21, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeyemi, O.S.; Awakan, O.J.; Atolani, O.; Iyeye, C.O.; Oweibo, O.O.; Adejumo, O.J.; Ibrahim, A.; Batiha, G.E.S. , New ferulic acid derivatives protect against carbon tetrachloride-induced liver injury in rats. Open Biochem. J. 2019, 13, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bautista-Aguilera, O.M.; Alonso, J.M.; Catto, M.; Iriepa, I.; Knez, D.; Gobec, S.; Marco-Contelles, J. , N-Hydroxy-N-Propargylamide Derivatives of Ferulic Acid: Inhibitors of Cholinesterases and Monoamine Oxidases. Molecules 2022, 27, 7437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgohain, R.; Handique, J.G.; Guha, A.K.; Pratihar, S. , A theoretical study on antioxidant activity of ferulic acid and its ester derivatives. J. Theor. Comput. Chem. 2016, 15, 1650028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, M.Y.; Xiao, M.W.; Xu, L.J.; Chen, Y.; Liu, A.L.; Ye, J.; Hu, A.X. , Bioassay of ferulic acid derivatives as influenza neuraminidase inhibitors. Arch. Pharm. 2020, 353, e1900174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Paiva, L.B.; Goldbeck, R.; dos Santos, W.D.; Squina, F.M. , Ferulic acid and derivatives: Molecules with potential application in the pharmaceutical field. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 49, 395–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drăgan, M.; Stan, C.D.; Iacob, A.; Profire, L. , Assessment of in vitro antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of new azetidin-2-one derivatives of ferulic acid. Farmacia 2016, 64, 717–721. [Google Scholar]
- Drăgan, M.; Stan, C.D.; Iacob, A.T.; Dragostin, O.M.; Boancă, M.; Lupuşoru, C.E.; Zamfir, C.L.; Profire, L. , Biological evaluation of azetidine-2-one derivatives of ferulic acid as promising anti-inflammatory agents. Processes 2020, 8, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekowati, J.; Diyah, N.W.; Nofianti, K.A.; Hamid, I.S. ; Siswandono, Molecular docking of ferulic acid derivatives on P2Y12 receptor and their ADMET prediction. J. Math. Fundam. Sci. 2018, 50, 203–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-García, L.; Sandoval-Lira, J.; Rosete-Luna, S.; Niño-Medina, G.; Sanchez, M. , Theoretical study of ferulic acid dimer derivatives: bond dissociation enthalpy, spin density, and HOMO-LUMO analysis. Struct. Chem. 2018, 29, 1265–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.S.; Yan, J.J.; Li, H.M.; Sultan, M.T.; Yu, J.; Lee, H.S.; Shin, K.J.; Song, D.K. , Protective effects of a dimeric derivative of ferulic acid in animal models of Alzheimer's disease. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 782, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatkar, A.; Nanda, A.; Kumar, P.; Narasimhan, B. , Synthesis and antimicrobial evaluation of ferulic acid derivatives. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2015, 41, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikugawa, M.; Tsutsuki, H.; Ida, T.; Nakajima, H.; Ihara, H.; Sakamoto, T. , Water-soluble ferulic acid derivatives improve amyloid-β-induced neuronal cell death and dysmnesia through inhibition of amyloid-β aggregation. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2016, 80, 547–553A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolaj, I.; Wang, Y.; Ye, K.; Meek, A.; Liyanage, S.I.; Santos, C.; Weaver, D.F. , Ferulic acid amide derivatives with varying inhibition of amyloid-β oligomerization and fibrillization. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2021, 43, 116247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, N.; Goel, N.; Chand Yadav, T.; Pruthi, V. , Quantum chemical, ADMET and molecular docking studies of ferulic acid amide derivatives with a novel anticancer drug target. Med. Chem. Res. 2017, 26, 1822–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, J.S.; Zeng, R.F.; Jiang, X.Y.; Hou, J.W.; Liu, Y.; Hu, Z.H.; Li, H.X.; Li, Y.; Xie, S.S.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, T. , Design, synthesis and evaluation of novel ferulic acid derivatives as multi-target-directed ligands for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 94, 103413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Rui, Y.X.; Guo, S.D.; Luan, F.; Liu, R.; Zeng, N. , Ferulic acid: A review of its pharmacology, pharmacokinetics and derivatives. Life Sci. 2021, 284, 119921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Li, N.; Tang, Y.; Li, B.; Liu, L.; Zhang, X.; Fu, H.; Duan, J.A. , Biological activity evaluation and structure-activity relationships analysis of ferulic acid and caffeic acid derivatives for anticancer. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 6085–6088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Xi, X.; Liu, Q.; Huang, P.; Li, J.; Lin, Q. , Research progress on the physiological activity and application of ferulic acid and its derivatives. J. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2018, 37, 449–454. [Google Scholar]
- Malik, S.A.; Ali, K.F.; Dawood, A.H. , Synthesis, Characterization, and Preliminary Evaluation of Ferulic Acid Derivatives Containing Heterocyclic Moiety. J. Med. Chem. Sci. 2023, 6, 1444–1456. [Google Scholar]
- Montaser, A.; Huttunen, J.; Ibrahim, S.A.; Huttunen, K.M. , Astrocyte-Targeted Transporter-Utilizing Derivatives of Ferulic Acid Can Have Multifunctional Effects Ameliorating Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in the Brain. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 3528148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquereau, S.; Galais, M.; Bellefroid, M.; Pachón Angona, I.; Morot-Bizot, S.; Ismaili, L.; Van Lint, C.; Herbein, G. , Ferulic acid derivatives block coronaviruses HCoV-229E and SARS-CoV-2 replication in vitro. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 20309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phadke, A.V.; Tayade, A.A.; Khambete, M.P. , Therapeutic potential of ferulic acid and its derivatives in Alzheimer’s disease—A systematic review. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2021, 98, 713–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinheiro, P.; Santiago, G.; Da Silva, F.; De Araujo, A.; De Oliveira, C.; Freitas, P.; Rocha, J.; De Araujo Neto, J.; Da Silva, M.; Tintino, S.; De Menezes, I.; Coutinho, H.; Da Costa, J. , Antibacterial activity and inhibition against Staphylococcus aureus NorA efflux pump by ferulic acid and its esterified derivatives. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2021, 11, 405–413. [Google Scholar]
- Pinheiro, P.G.; Santiago, G.M.P.; da Silva, F.E.F.; de Araújo, A.C.J.; de Oliveira, C.R.T.; Freitas, P.R.; Rocha, J.E.; Neto, J.B.D.A.; da Silva, M.M.C.; Tintino, S.R.; Siyadatpanah, A.; Norouzi, R.; Dashti, S.; Wilairatana, P.; Coutinho, H.D.M.; da Costa, J.G.M. , Ferulic acid derivatives inhibiting Staphylococcus aureus tetK and MsrA efflux pumps. Biotechnol. Rep. 2022, 34, e00717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sang, Z.; Pan, W.; Wang, K.; Ma, Q.; Yu, L.; Yang, Y.; Bai, P.; Leng, C.; Xu, Q.; Li, X.; Tan, Z.; Liu, W. , Design, synthesis and evaluation of novel ferulic acid-O-alkylamine derivatives as potential multifunctional agents for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 130, 379–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sang, Z.; Wang, K.; Han, X.; Cao, M.; Tan, Z.; Liu, W. , Design, Synthesis, and Evaluation of Novel Ferulic Acid Derivatives as Multi-Target-Directed Ligands for the Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2019, 10, 1008–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senthil, R.; Sakthivel, M.; Usha, S. , Structure-based drug design of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma inhibitors: ferulic acid and derivatives. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2021, 39, 1295–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serafim, T.L.; Carvalho, F.S.; Marques, M.P.M.; Calheiros, R.; Silva, T.; Garrido, J.; Milhazes, N.; Borges, F.; Roleira, F.; Silva, E.T.; Holy, J.; Oliveira, P.J. , Lipophilic caffeic and ferulic acid derivatives presenting cytotoxicity against human breast cancer cells. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2011, 24, 763–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Chen, X.; Qiang, S.; Su, J.; Li, J. , Anti-oxidation and anti-inflammatory potency evaluation of ferulic acid derivatives obtained through virtual screening. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Guo, D.; Tang, Y.; Qi, M.; Fang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chai, Y.; Cao, Y.; Lv, D. , A multi-omics study of the anti-cancer effect of a ferulic acid derivative FA-30. Mol. Omics 2022, 18, 805–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Yang, L.; Huang, K.; Li, X.; Hao, X.; Stöckigt, J.; Zhao, Y. , Preparation of ferulic acid derivatives and evaluation of their xanthine oxidase inhibition activity. Nat. Prod. Res. 2007, 21 (3), 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xie, D.; Gan, X.; Zeng, S.; Zhang, A.; Yin, L.; Song, B.; Jin, L.; Hu, D. , Synthesis, antiviral activity, and molecular docking study of trans-ferulic acid derivatives containing acylhydrazone moiety. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 4096–4100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Yin, W.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, H.; Li, Y.; Tian, J.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, Y. , Design and synthesis of the ring-opened derivative of 3-n-butylphthalide-ferulic acid-glucose trihybrids as potential anti-ischemic agents. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2020, 31, 1881–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Shi, Y.G.; Zheng, X.L.; Dang, Y.L.; Zhu, C.M.; Zhang, R.R.; Fu, Y.Y.; Zhou, T.Y.; Li, J.H. , Lipophilic ferulic acid derivatives protect PC12 cells against oxidative damage: Via modulating β-amyloid aggregation and activating Nrf2 enzymes. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 4707–4718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Chen, J.; Pan, J.; Zhao, L.; Liu, D.; Zhang, A.; Chen, J.; Hu, D.; Song, B. , Design, synthesis, antiviral bioactivity and three-dimensional quantitative structure–activity relationship study of novel ferulic acid ester derivatives containing quinazoline moiety. Pest Manage. Sci. 2017, 73, 2079–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Liu, Y.; Sun, J.; Zheng, L. , Synthesis of mitochondria-targeted ferulic acid amide derivatives with antioxidant, anti-inflammatory activities and inducing mitophagy. Bioorg. Chem. 2022, 127, 106037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, T.; Wang, Z.; Lan, S.; Gan, X. , Design, synthesis, antiviral activity, and mechanisms of novel ferulic acid derivatives containing amide moiety. Bioorg. Chem. 2022, 128, 106054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, T.; Wang, Z.; Liu, D.; Zeng, H.; Liang, J.; Hu, D.; Gan, X. , Ferulic acid derivatives with piperazine moiety as potential antiviral agents. Pest Manage. Sci. 2022, 78, 1749–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, S.J.; Zhang, P.X.; Zhu, Y.; Li, N.G.; Chen, Y.Y.; Li, J.J.; Zhang, S.; Jin, R.Y.; Yan, H.; Shi, X.Q.; Tang, Y.P.; Duan, J.A. , A ferulic acid derivative FXS-3 inhibits proliferation and metastasis of human lung cancer A549 cells via positive JNK signaling pathway and negative ERK/p38, AKt/mTOR and MEK/ERK signaling pathways. Molecules 2019, 24, 2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.X.; Lin, H.; Qu, C.; Tang, Y.P.; Li, N.G.; Kai, J.; Shang, G.; Li, B.; Zhang, L.; Yan, H.; Liu, P.; Duan, J.A. , Design, synthesis, and in vitro antiplatelet aggregation activities of ferulic acid derivatives. J. Chem. 2015, 2015, 376527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, H.; Fu, X.; Chang, X.; Ding, Z.; Yu, Y.; Xu, H.; Wang, R.; Shan, Y.; Ding, S. , The ester derivatives of ferulic acid exhibit strong inhibitory effect on the growth of Alternaria alternata in vitro and in vivo. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2023, 196, 112158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellerito, C.; Emanuele, S.; Ferrante, F.; Celesia, A.; Giuliano, M.; Fiore, T. , Tributyltin(IV) ferulate, a novel synthetic ferulic acid derivative, induces autophagic cell death in colon cancer cells: From chemical synthesis to biochemical effects. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2020, 205, 110999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Peng, Q.; Liu, J.; Alolga, R.N.; Zhou, W. , A novel ferulic acid derivative attenuates myocardial cell hypoxia reoxygenation injury through a succinate dehydrogenase dependent antioxidant mechanism. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 856, 172417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, X.; Zhang, W.; Lan, S.; Hu, D. , Novel Cyclized Derivatives of Ferulic Acid as Potential Antiviral Agents through Activation of Photosynthesis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 1369–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, K.C.; Oliveira, G.L.S.; Islam, M.T.; Junior, A.L.G.; De Sousa, D.P.; Freitas, R.M. , Anticonvulsant and behavioral effects observed in mice following treatment with an ester derivative of ferulic acid: Isopentyl ferulate. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2015, 242, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marucci, G.; Buccioni, M.; Ben, D.D.; Lambertucci, C.; Volpini, R.; Amenta, F. , Efficacy of acetylcholinesterase inhibitors in Alzheimer's disease. Neuropharmacology 2021, 190, 108352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreta, M.P.G.; Burgos-Alonso, N.; Torrecilla, M.; Marco-Contelles, J.; Bruzos-Cidón, C. , Efficacy of acetylcholinesterase inhibitors on cognitive function in alzheimer’s disease. Review of reviews. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.S.; Al Mamun, A.; Kabir, M.T.; Ashraf, G.M.; Bin-Jumah, M.N.; Abdel-Daim, M.M. , Multi-Target Drug Candidates for Multifactorial Alzheimer’s Disease: AChE and NMDAR as Molecular Targets. Mol. Neurobiol. 2021, 58, 281–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finberg, J.P.M. , Inhibitors of MAO-B and COMT: their effects on brain dopamine levels and uses in Parkinson’s disease. J. Neural Transm. 2019, 126, 433–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jost, W.H. , A critical appraisal of MAO-B inhibitors in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. J. Neural Transm. 2022, 129, 723–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özdemir, Z.; Alagöz, M.A.; Bahçecioğlu, Ö.F.; Gök, S. , Monoamine oxidase-B (MAO-B) inhibitors in the treatment of alzheimer’s and parkinson’s disease. Curr. Med. Chem. 2021, 28, 6045–6065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parambi, D.G.T. , Treatment of parkinson’s disease by MAO-B inhibitors, new therapies and future challenges - A mini-review. Comb. Chem. High Throughput Screening 2020, 23, 847–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, T. , Catechol-O-methyltransferase inhibitors in Parkinson's disease. Drugs 2015, 75, 157–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamagoe, K.; Tsuji, H.; Ishii, K.; Tamaoka, A. , Remarkable clinical responses of non-fluctuating Parkinson’s disease (PD) after alternating catechol O-methyltransferase inhibitors: case series switching from entacapone 200 ~ 300 mg/day to opicapone 25 mg/day. Neurol. Sci. 2021, 42, 4813–4814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabbri, M.; Ferreira, J.J.; Rascol, O. , COMT Inhibitors in the Management of Parkinson’s Disease. CNS Drugs 2022, 36, 261–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- St. Onge, E.; Vanderhoof, M.; Miller, S., Opicapone (Ongentys): A New COMT Inhibitor for the Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease. Ann. Pharmacother. 2021, 55, 1159–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calculation of molecular properties and bioactivity score. https://www.molinspiration.com/cgibin/ properties (2021).
- Drug Likeness Tool (DruLiTo 1). http://www.niper.gov.in/pi_dev_tools/DruLiToWeb/DruLiTo_index.html (February 8, 2020).
- Lipinski, C.A.; Lombardo, F.; Dominy, B.W.; Feeney, P.J. , Experimental and computational approaches to estimate solubility and permeability in drug discovery and development settings. Adv. Drug Delivery Rev. 2001, 46, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghose, A.K.; Viswanadhan, V.N.; Wendoloski, J.J. , A Knowledge-Based Approach in Designing Combinatorial or Medicinal Chemistry Libraries for Drug Discovery. 1. A Qualitative and Quantitative Characterization of Known Drug Databases. J. Comb. Chem. 1999, 1, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veber, D.F.; Johnson, S.R.; Cheng, H.Y.; Smith, B.R.; Ward, K.W.; Kopple, K.D. , Molecular Properties That Influence the Oral Bioavailability of Drug Candidates. J. Med. Chem. 2002, 45, 2615–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boda, K.; Seidel, T.; Gasteiger, J. , Structure and reaction based evaluation of synthetic accessibility. J. Comput.-Aided Mol. Des. 2007, 21, 311–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnet, P. , Is chemical synthetic accessibility computationally predictable for drug and lead-like molecules? A comparative assessment between medicinal and computational chemists. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 54, 679–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Tropsha, A.; Fourches, D.; Varnek, A.; Papa, E.; Gramatica, P.; Öberg, T.; Dao, P.; Cherkasov, A.; Tetko, I.V. , Combinatorial QSAR Modeling of Chemical Toxicants Tested against Tetrahymena pyriformis. J. Chem. Inf. Mode. 2008, 48, 766–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Petersson, G.A.; Nakatsuji, H.; Li, X.; Caricato, M.; Marenich, A.V.; Bloino, J.; Janesko, B.G.; Gomperts, R.; Mennucci, B.; Hratchian, H.P.; Ortiz, J.V.; Izmaylov, A.F.; Sonnenberg, J.L. ; Williams; Ding, F.; Lipparini, F.; Egidi, F.; Goings, J.; Peng, B.; Petrone, A.; Henderson, T.; Ranasinghe, D.; Zakrzewski, V.G.; Gao, J.; Rega, N.; Zheng, G.; Liang, W.; Hada, M.; Ehara, M.; Toyota, K.; Fukuda, R.; Hasegawa, J.; Ishida, M.; Nakajima, T.; Honda, Y.; Kitao, O.; Nakai, H.; Vreven, T.; Throssell, K.; Montgomery Jr., J.A.; Peralta, J.E.; Ogliaro, F.; Bearpark, M.J.; Heyd, J.J.; Brothers, E.N.; Kudin, K.N.; Staroverov, V.N.; Keith, T.A.; Kobayashi, R.; Normand, J.; Raghavachari, K.; Rendell, A.P.; Burant, J.C.; Iyengar, S.S.; Tomasi, J.; Cossi, M.; Millam, J.M.; Klene, M.; Adamo, C.; Cammi, R.; Ochterski, J.W.; Martin, R.L.; Morokuma, K.; Farkas, O.; Foresman, J.B.; Fox, D.J. Gaussian 16 Rev. C.01 Wallingford, CT, 2016.
- Marenich, A.V.; Cramer, C.J.; Truhlar, D.G. , Universal solvation model based on solute electron density and on a continuum model of the solvent defined by the bulk dielectric constant and atomic surface tensions. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 6378–6396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Schultz, N.E.; Truhlar, D.G. , Design of Density Functionals by Combining the Method of Constraint Satisfaction with Parametrization for Thermochemistry, Thermochemical Kinetics, and Noncovalent Interactions. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2006, 2, 364–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W. h.; Lei, P.; Liu, Q.; Hu, J.; Gunn, A.P.; Chen, M. s.; Rui, Y. f.; Su, X. y.; Xie, Z. p.; Zhao, Y.F. , Sequestration of Copper from β-Amyloid Promotes Selective Lysis by Cyclen-Hybrid Cleavage Agents. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 31657–31664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milenković, D.; Dorović, J.; Jeremić, S.; Dimitrić Marković, J.M.; Avdović, E.H.; Marković, Z. , Free Radical Scavenging Potency of Dihydroxybenzoic Acids. J. Chem. 2017, 2017, 5936239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amić, A.; Marković, Z.; Dimitrić Marković, J.M.; Lučić, B.; Stepanić, V.; Amić, D. , The 2H+/2e- free radical scavenging mechanisms of uric acid: Thermodynamics of N-H bond cleavage. Comput. Theor. Chem. 2016, 1077, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorović, J.; Marković, J.M.D.; Stepanić, V.; Begović, N.; Amić, D.; Marković, Z. , Influence of different free radicals on scavenging potency of gallic acid. J. Mol. Model. 2014, 20, 2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marković, Z.; Crossed, D.; Signorović, J.; Dekić, M.; Radulović, M.; Marković, S.; Ilić, M. , DFT study of free radical scavenging activity of erodiol. Chem. Pap. 2013, 67, 1453–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galano, A.; Alvarez-Idaboy, J.R.; Francisco-Márquez, M. , Physicochemical Insights on the Free Radical Scavenging Activity of Sesamol: Importance of the Acid/Base Equilibrium. J. Phys. Chem. B 2011, 115, 13101–13109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, J.V. , Toward an Exact One-Electron Picture of Chemical Bonding. In Advances in Quantum Chemistry, Academic Press Inc.: 1999; Vol. 35, pp 33-52.
- Ortiz, J.V. , Electron propagator theory: an approach to prediction and interpretation in quantum chemistry. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev.: Comput. Mol. Sci. 2013, 3, 123–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-González, A.; Galano, A.; Ortiz, J.V. , Vertical ionization energies of free radicals and electron detachment energies of their anions: a comparison of direct and indirect methods versus experiment. J. Phys. Chem. A 2014, 118, 6125–6131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz, J.V. , The Electron Propagator Picture of Molecular Electronic Structure. In Computational Chemistry: Reviews of Current Trends, WORLD SCIENTIFIC: 1997; Vol. Volume 2, pp 1-61.
- Marvin, 23.4.0; Chemaxon Ltd.: 2023.
- Ellermann, M.; Lerner, C.; Burgy, G.; Ehler, A.; Bissantz, C.; Jakob-Roetne, R.; Paulini, R.; Allemann, O.; Tissot, H.; Grünstein, D.; Stihle, M.; Diederich, F.; Rudolph, M.G. , Catechol-O-methyltransferase in complex with substituted 3́-deoxyribose bisubstrate inhibitors. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D. Biol. Crystallogr. 2012, 68, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binda, C.; Wang, J.; Pisani, L.; Caccia, C.; Carotti, A.; Salvati, P.; Edmondson, D.E.; Mattevi, A. , Structures of human monoamine oxidase B complexes with selective noncovalent inhibitors: Safinamide and coumarin analogs. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 5848–5852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, J.; Rudolph, M.J.; Burshteyn, F.; Cassidy, M.S.; Gary, E.N.; Love, J.; Franklin, M.C.; Height, J.J. , Structures of human acetylcholinesterase in complex with pharmacologically important ligands. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 10282–10286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šali, A.; Blundell, T.L. , Comparative protein modelling by satisfaction of spatial restraints. J. Mol. Biol. 1993, 234, 779–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- BIOVIA. https://www.3ds.com/products-services/biovia/ (02/2023),.
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. , AutoDock Vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System, 2.0; Schrödinger, LLC: 2015.
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Couch, G.S.; Greenblatt, D.M.; Meng, E.C.; Ferrin, T.E. , UCSF Chimera--a visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1605–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reina, M.; Guzmán-López, E.G.; Romeo, I.; Marino, T.; Russo, N.; Galano, A. , Computationally designed: P -coumaric acid analogs: Searching for neuroprotective antioxidants. New J. Chem. 2021, 45, 14369–14380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-González, L.M.; Alvarez-Idaboy, J.R.; Galano, A. , Computationally Designed Sesamol Derivatives Proposed as Potent Antioxidants. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 9566–9575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reina, M.; Castañeda-Arriaga, R.; Pérez-González, A.; Guzmán-López, E.G.; Tan, D.X.; Reiter, R.; Galano, A. , A computer-assisted systematic search for melatonin derivatives with high potential as antioxidants. Melatonin Res. 2018, 1, 27–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleeson, M.P.; Hersey, A.; Montanari, D.; Overington, J. , Probing the links between in vitro potency, ADMET and physicochemical parameters. Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery 2011, 10, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, H.; Mashinson, V.; Woolman, T.; Zha, M. , Understanding the molecular properties and metabolism of top prescribed drugs. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2013, 13, 1290–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiss, L.E.; Soares-Da-Silva, P. , Medicinal chemistry of catechol O -methyltransferase (COMT) inhibitors and their therapeutic utility. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 8692–8717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafferman, A.; Kronman, C.; Flashner, Y.; Leitner, M.; Grosfeld, H.; Ordentlich, A.; Gozes, Y.; Cohen, S.; Ariel, N.; Barak, D.; Harel, M.; Silman, I.; Sussman, J.L.; Velan, B. , Mutagenesis of human acetylcholinesterase. Identification of residues involved in catalytic activity and in polypeptide folding. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 17640–17648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felder, C.E.; Botti, S.A.; Lifson, S.; Silman, I.; Sussman, J.L. , External and internal electrostatic potentials of cholinesterase models. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 1997, 15, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edmondson, D.E.; Mattevi, A.; Binda, C.; Li, M.; Hubálek, F. , Structure and mechanism of monoamine oxidase. Curr. Med. Chem. 2004, 11, 1983–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massey, V.; Ghisla, S.; Kieschke, K. , Studies on the reaction mechanism of lactate oxidase. Formation of two covalent flavin-substrate adducts on reaction with glycollate. J. Biol. Chem. 1980, 255, 2796–2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korn, A.; Eichler, H.G.; Fischbach, R.; Gasic, S. , Moclobemide, a new reversible MAO inhibitor - interaction with tyramine and tricyclic antidepressants in healthy volunteers and depressive patients. Psychopharmacology 1986, 88, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fowler, J.S.; Logan, J.; Azzaro, A.J.; Fielding, R.M.; Zhu, W.; Poshusta, A.K.; Burch, D.; Brand, B.; Free, J.; Asgharnejad, M.; Wang, G.J.; Telang, F.; Hubbard, B.; Jayne, M.; King, P.; Carter, P.; Carter, S.; Xu, Y.; Shea, C.; Muench, L.; Alexoff, D.; Shumay, E.; Schueller, M.; Warner, D.; Apelskog-Torres, K. , Reversible inhibitors of monoamine oxidase-A (RIMAs): Robust, reversible inhibition of human brain MAO-A by CX157. Neuropsychopharmacology 2010, 35, 623–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Liu, H.; Wu, B. , Structure-based drug design of catechol-O-methyltransferase inhibitors for CNS disorders. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2014, 77, 410–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
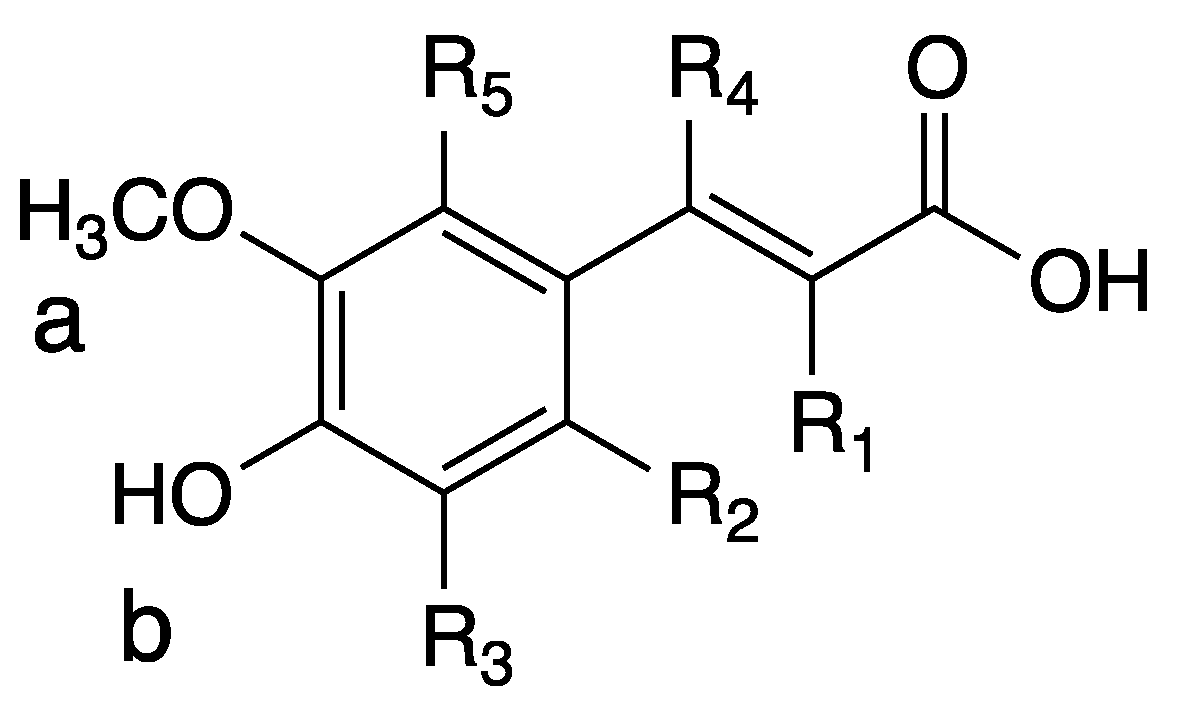
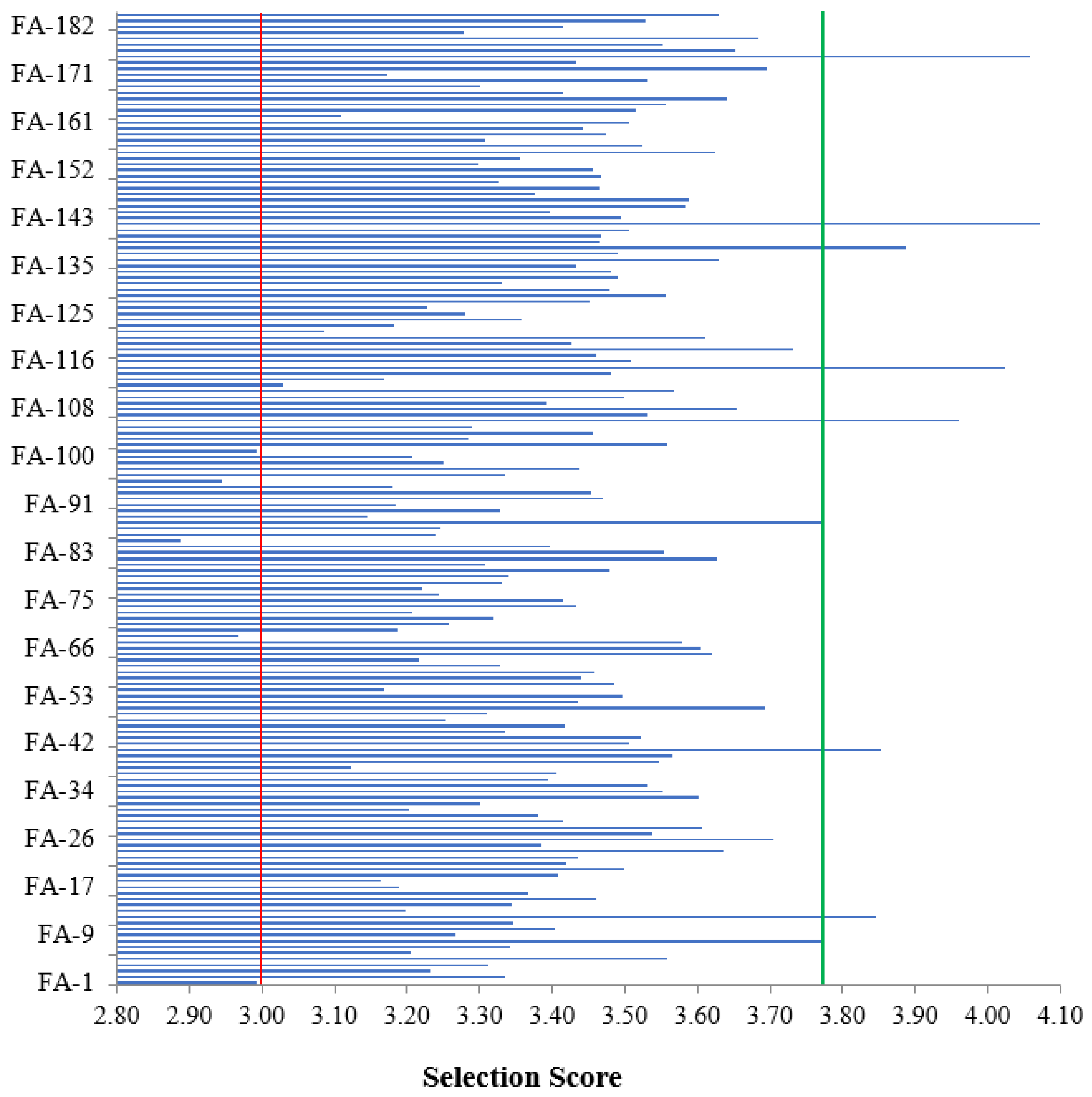
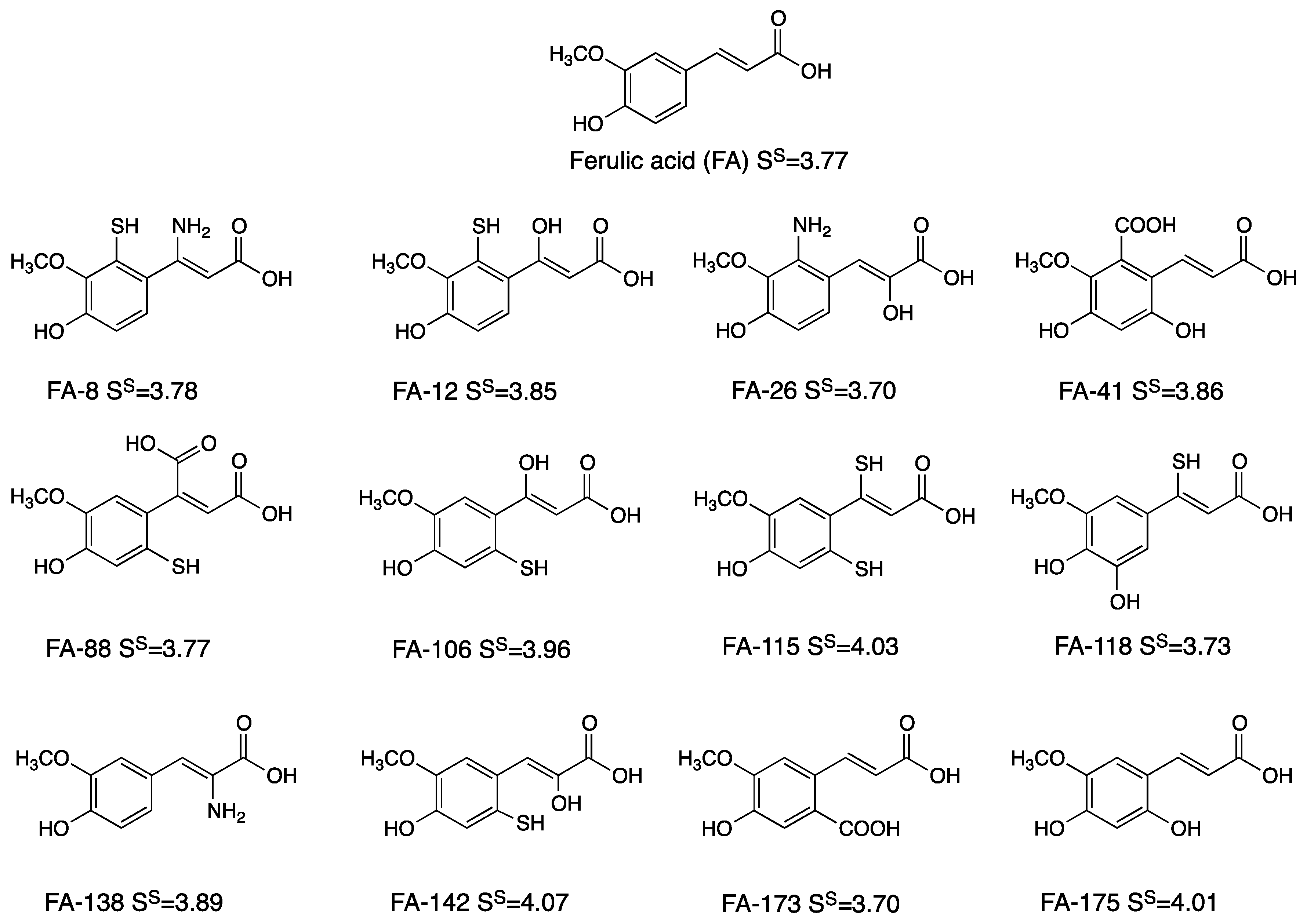
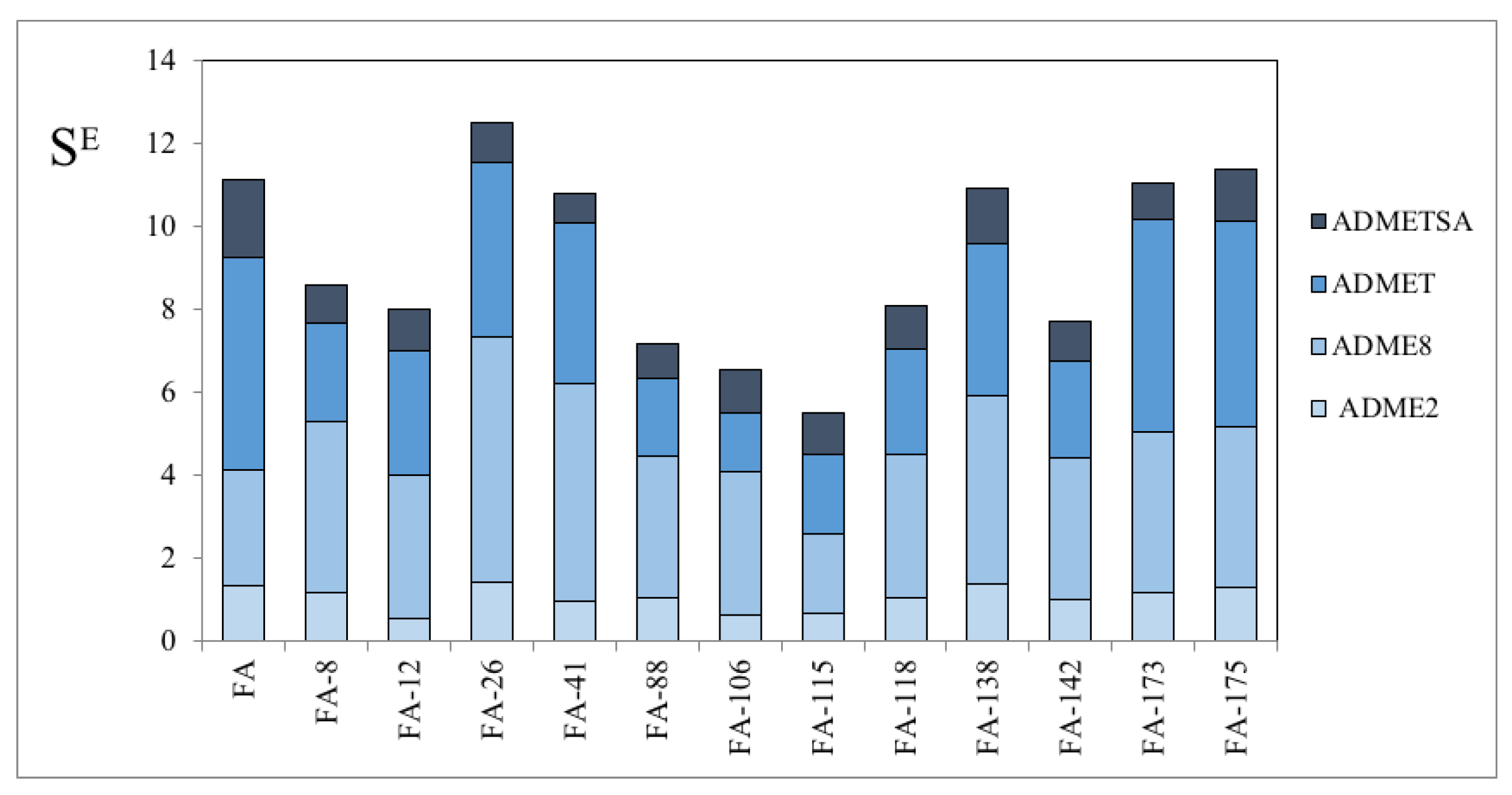
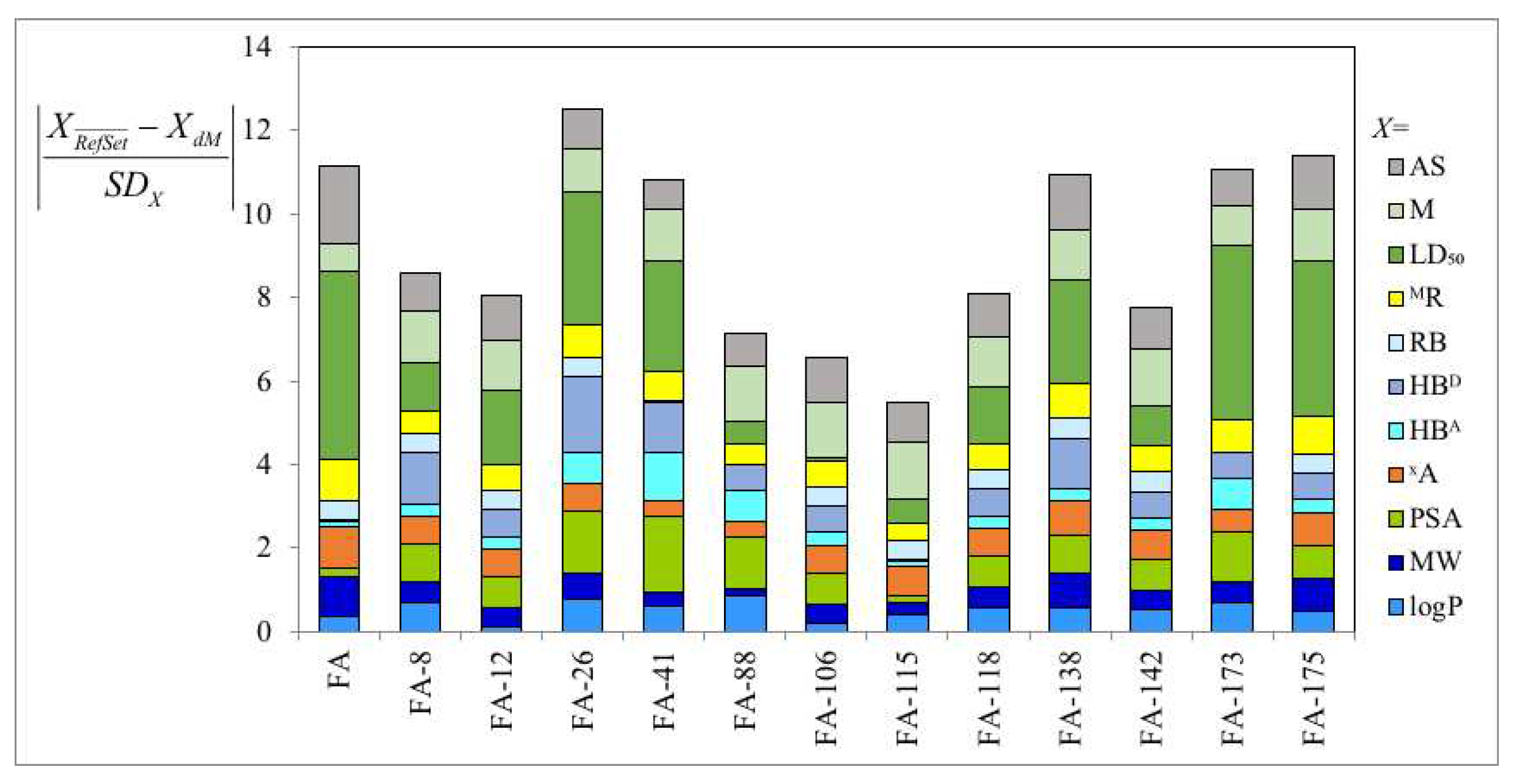
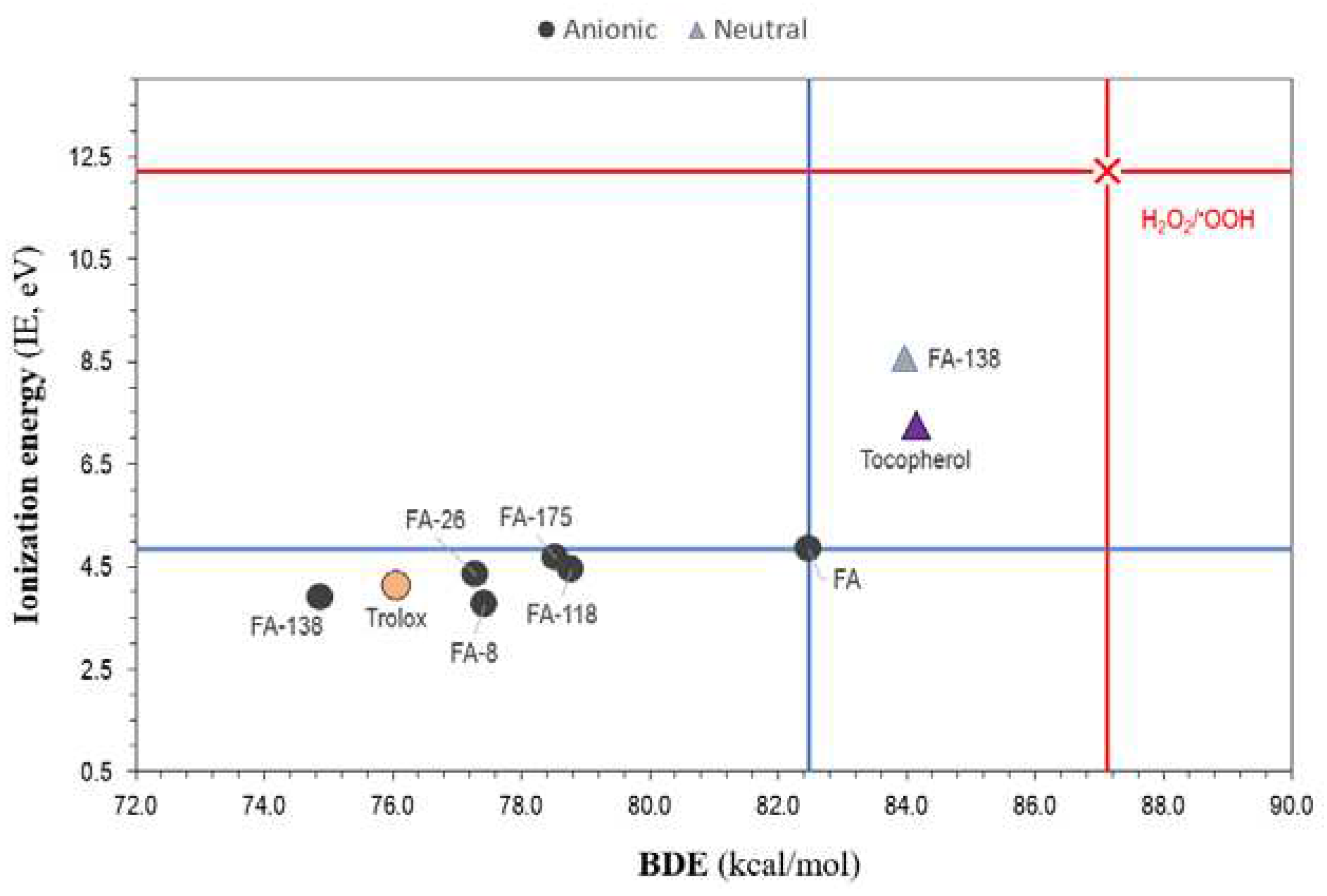
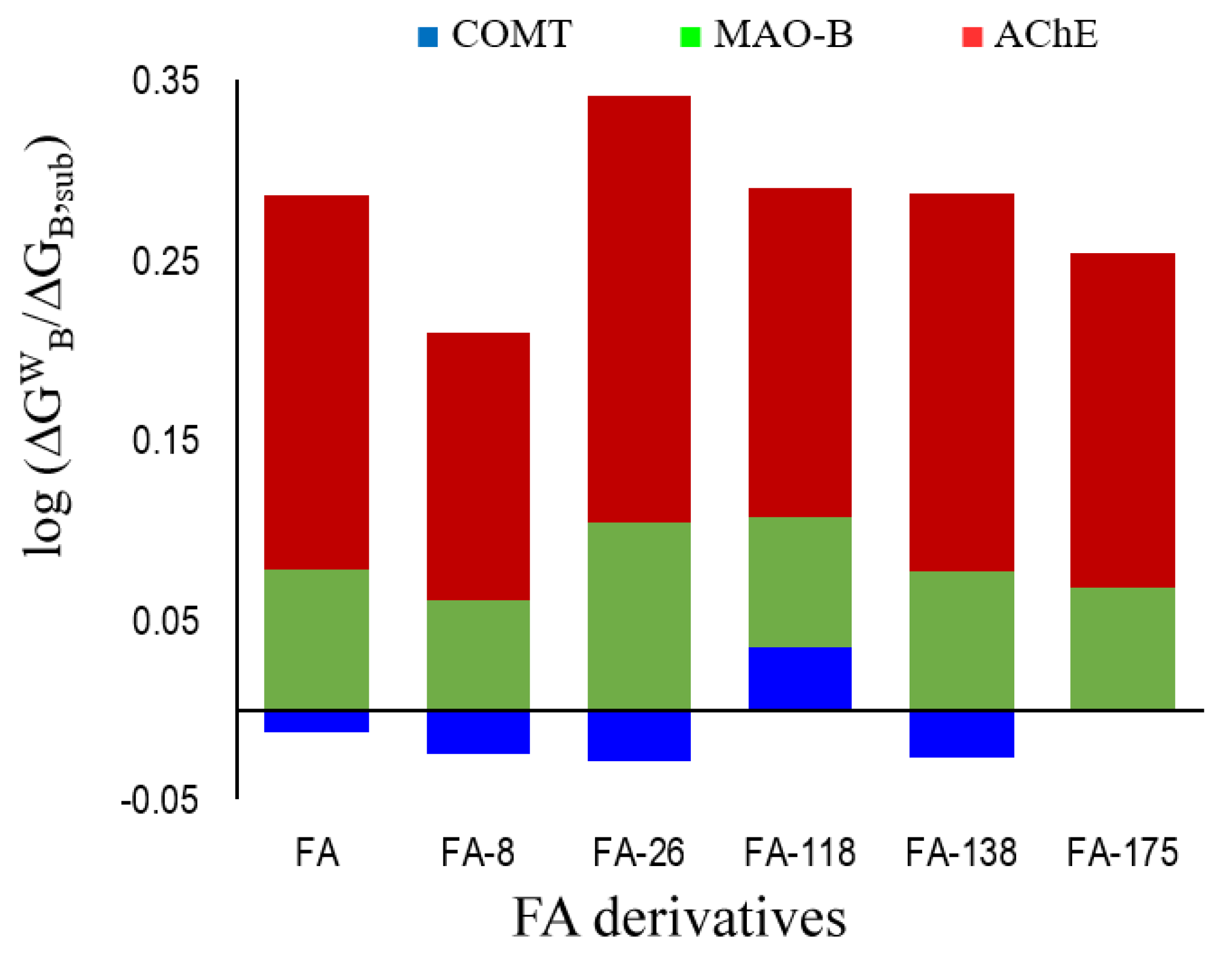
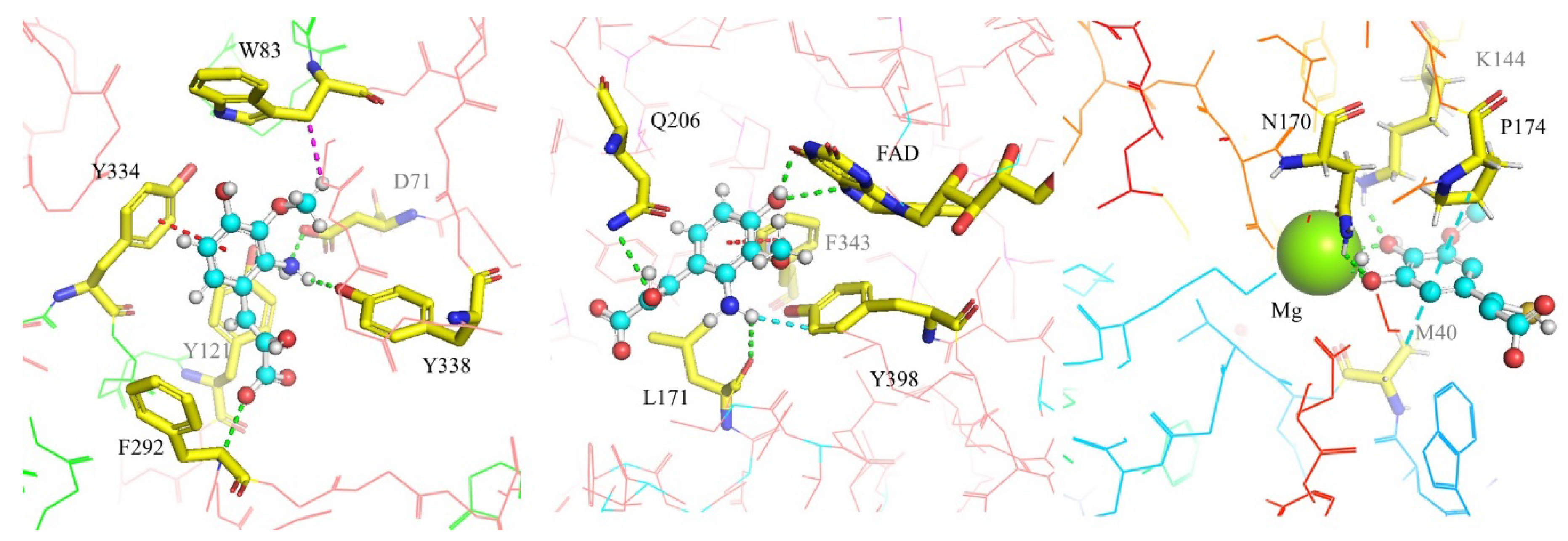
| Functionalization | Bioactivity | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| 3-n-butylphthalide + glucose | Anti-ischemic. | [252] |
| Alkyl esters | β-amyloid aggregation inhibition. | [253] |
| Amide | Antiviral | [256] |
| Amide | Antioxidant, inflammatory, mitophagy enhancing. | [255] |
| Amide | β-amyloid oligomerization and fibrillization inhibition. | [232] |
| Amide | Antioxidant, anticancer. | [156] |
| Amide + pyrazole | Antioxidant, and myocardial cell hypoxia reoxygenation. | [262] |
| Amino acid | Anti-inflammatory, antioxidant. | [239] |
| Aniline | Antimicrobial. | [230] |
| Azetidine-2-one | Anti-inflammatory, antioxidant. | [225, 226] |
| Benzyl, and phenylethyl esters | Anticancer. | [158] |
| Benzylamino, and carbamyl | β-amyloid aggregation inhibition, antioxidant, AChE inhibition. | [234] |
| Cyclized | Antiviral. | [263] |
| Different rings | Improvement of scopolamine-induced memory deficit in mice. | [245] |
| Dimer | Neuroprotection. | [229] |
| Dimethylthiazol + diphenyltetrazolium bromide | Anticancer. | [258] |
| Ester | Antibacterial. | [242, 243] |
| Ester | Antifungal. | [260] |
| Ester | Antithrombotic. | [259] |
| Ester | Anticancer. | [236] |
| Ester | Xanthine oxidase inhibition. | [250] |
| Ester, and amide | Anticancer. | [247] |
| Ester and amide | Antioxidant. | [219] |
| Glycerol, and diglycerol | β-amyloid aggregation inhibition. | [231] |
| Heterocyclic | Anticancer. | [238] |
| Isopentyl | Anticonvulsant. | [264] |
| N-Hydroxy-N-Propargylamide | Free radical scavenging, AChE inhibition, Cu(II) quelation. | [221] |
| O-alkylamines | Antioxidant, butyrylcholinesterase inhibition. | [244] |
| OH + OMe group + amide | Neuraminidase inhibition. | [223] |
| Phthalate, and maleate | Hepatoprotection. | [220] |
| Piperazine | Antiviral. | [257] |
| Tributyltin(IV) | Anticancer. | [261] |
| pKa1 | pKa2 | pKa3 | pKa4 | Mf(+1) | Mf(0) | Mf(-1) | Mf(-2) | Mf(-3) | Mf(-4) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FA | 4.0 | 10.0 | - | - | - | 4×10-4 | 0.997 | 0.003 | - | - |
| FA-8 | 3.1 | 4.4 | 5.8 | 10.8 | <10-4 | 0.023 | 0.976 | 4×10-4 | - | - |
| FA-12 | 3.7 | 5.6 | 10.3 | 11.3 | - | <10-4 | 0.015 | 0.984 | 0.001 | <10-4 |
| FA-26 | 2.5 | 3.9 | 10.1 | 11.8 | <10-4 | 3×10-4 | 0.998 | 0.002 | <10-4 | - |
| FA-41 | 2.7 | 4.4 | 9.7 | 11.1 | - | <10-4 | 0.001 | 0.994 | 0.005 | <10-4 |
| FA-88 | 1.9 | 5.2 | 5.9 | 10.5 | - | <10-4 | 2×10-4 | 0.033 | 0.966 | 0.001 |
| FA-106 | 3.7 | 5.7 | 10.3 | 11.2 | - | <10-4 | 0.019 | 0.980 | 0.001 | <10-4 |
| FA-115 | 3.8 | 5.8 | 8.6 | 10.9 | - | <10-4 | 0.023 | 0.918 | 0.059 | <10-4 |
| FA-118 | 3.6 | 8.5 | 9.5 | 13.0 | - | 1×10-4 | 0.921 | 0.078 | 0.001 | <10-4 |
| FA-138 | 4.0 | 7.6 | 9.9 | - | 2×10-4 | 0.596 | 0.403 | 0.001 | - | - |
| FA-142 | 3.1 | 5.8 | 10.4 | 12.2 | - | <10-4 | 0.022 | 0.977 | 0.001 | <10-4 |
| FA-173 | 3.6 | 4.2 | 10.0 | - | - | <10-4 | 0.001 | 0.997 | 0.003 | - |
| FA-175 | 3.8 | 9.6 | 11.0 | - | - | 3×10-4 | 0.994 | 0.006 | <10-4 | - |
| IE | EA | BDE | BDE-site* | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| q= 1 | ||||
| FA-138 | 11.64 | 3.54 | 89.30 | b (OH) |
| q= 0 | ||||
| FA | 8.36 | -0.28 | 85.15 | b (OH) |
| FA-8 | 8.75 | -0.13 | 80.24 | R5 (SH) |
| FA-26 | 8.35 | 0.34 | 83.06 | R1 (OH) |
| FA-118 | 8.31 | -0.95 | 80.18 | b (OH) |
| FA-138 | 8.58 | 0.29 | 83.97 | b (OH) |
| FA-175 | 8.12 | -0.23 | 80.09 | R2 (OH) |
| q= -1 | ||||
| FA | 4.85 | -2.95 | 82.48 | b (OH) |
| FA-8 | 3.75 | -2.95 | 77.44 | R5 (SH) |
| FA-26 | 4.33 | -3.12 | 77.29 | R1 (OH) |
| FA-118 | 4.43 | -2.98 | 78.79 | b (OH) |
| FA-138 | 3.89 | -3.11 | 74.88 | b (OH) |
| FA-175 | 4.66 | -3.05 | 78.54 | b (OH) |
| q= -2 | ||||
| FA | -0.06 | -6.00 | 96.96 | a (OCH3) |
| FA-8 | 0.20 | -5.58 | 82.04 | b (OH) |
| FA-26 | -0.34 | -6.04 | 71.30 | b (OH) |
| FA-118 | -1.09 | -4.97 | 74.87 | b (OH) |
| FA-138 | -0.55 | -5.77 | 97.02 | a (OCH3) |
| FA-175 | -0.31 | -5.32 | 75.90 | b (OH) |
| q= -3 | ||||
| FA-118 | -3.78 | -7.59 | 71.01 | b (OH) |
| Compound | DGBW (kcal/mol) | SP | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| COMT | MAO-B | AChE | ||
| Ferulic Acid | -5.28 | -7.19 | -7.37 | 3.78 |
| FA-9 | -5.14 | -6.91 | -6.43 | 3.50 |
| FA-26 | -5.09 | -7.63 | -7.88 | 3.93 |
| FA-118 | -5.90 | -7.09 | -6.95 | 3.79 |
| FA-138 | -5.12 | -7.17 | -7.40 | 3.76 |
| FA-175 | -5.42 | -7.02 | -7.01 | 3.70 |
| DGB, dopa= -5.44 kcal/mol in COMT; DGB, pea= -6.01 kcal/mol in MAO-B; DGB, ACh= 4.56 kcal/mol in AChE. For natural substrates SP=3.00 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





