Submitted:
29 April 2023
Posted:
30 April 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
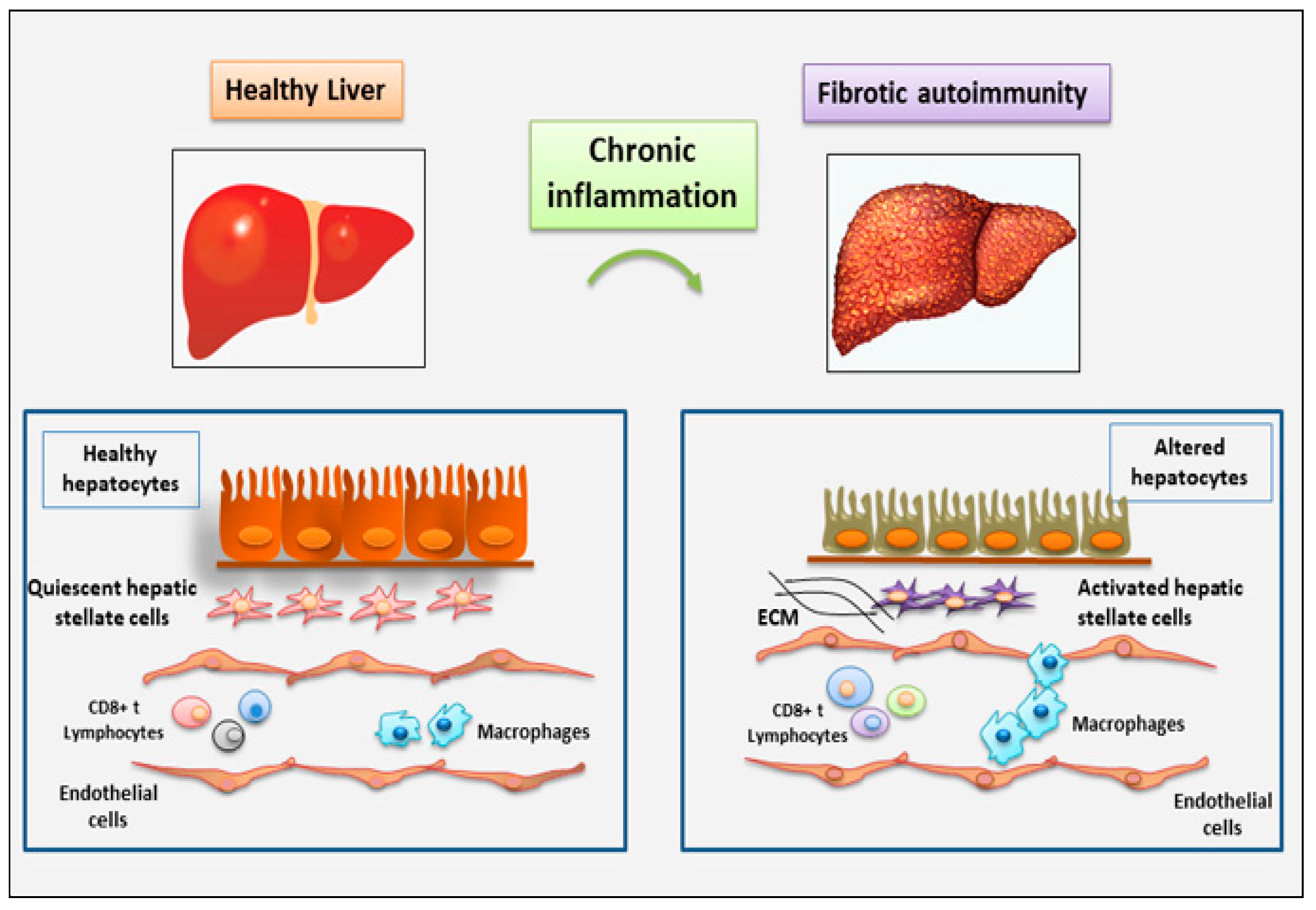
2. The role of immune and non-immune inflammatory cells in fibrotic autoimmune diseases: new discoveries
2.1. Current understanding of the involvement of immune cells in fibrotic autoimmune diseases
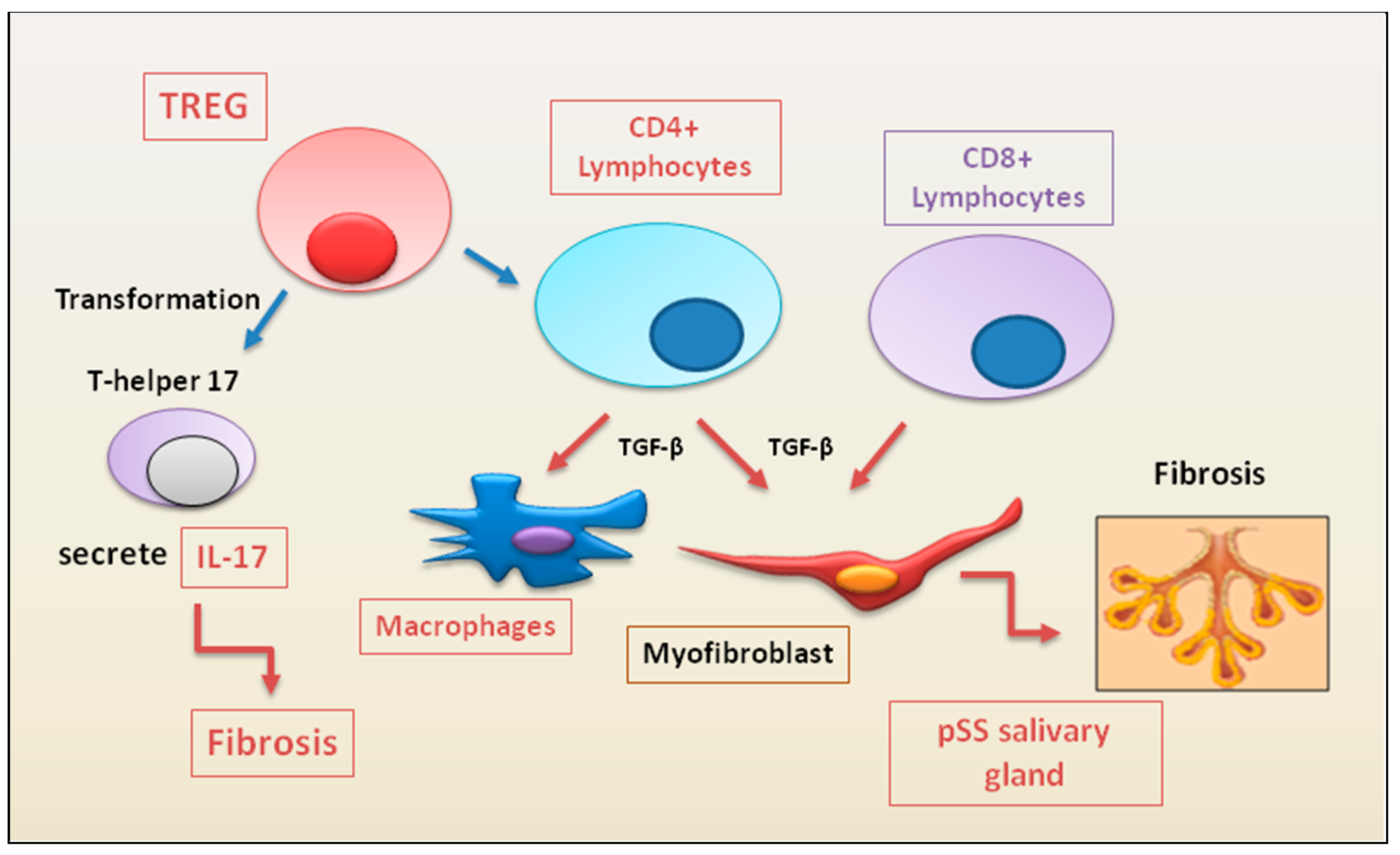
2.1.1. Update on the correlated pro-fibrotic role of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells
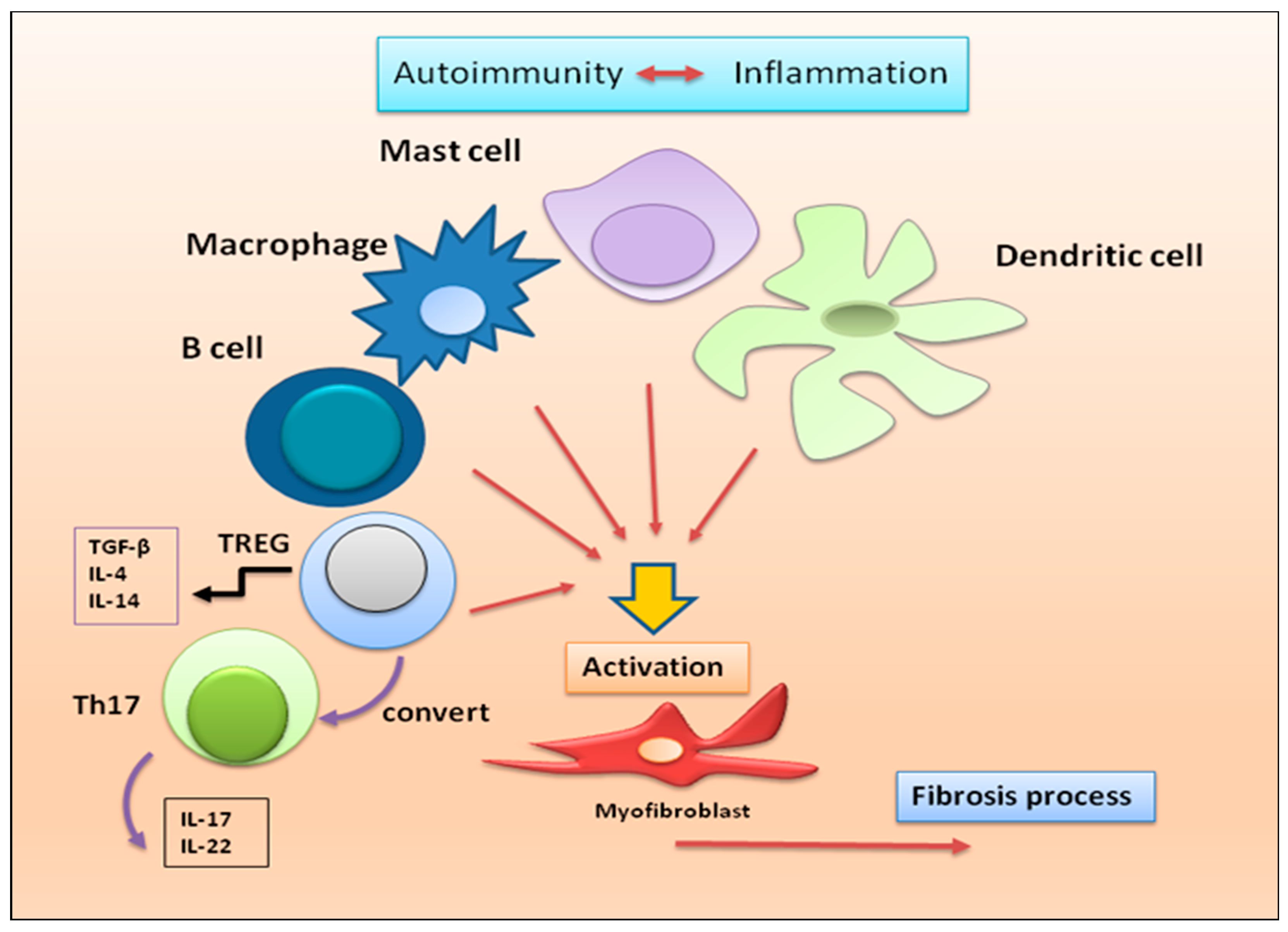
2.1.2. Autoimmune Treg pro-fibrotic role
2.1.3. Macrophages, dendritic cells, mast cells
2.2. Non-immune cells in fibrotic autoimmune diseases
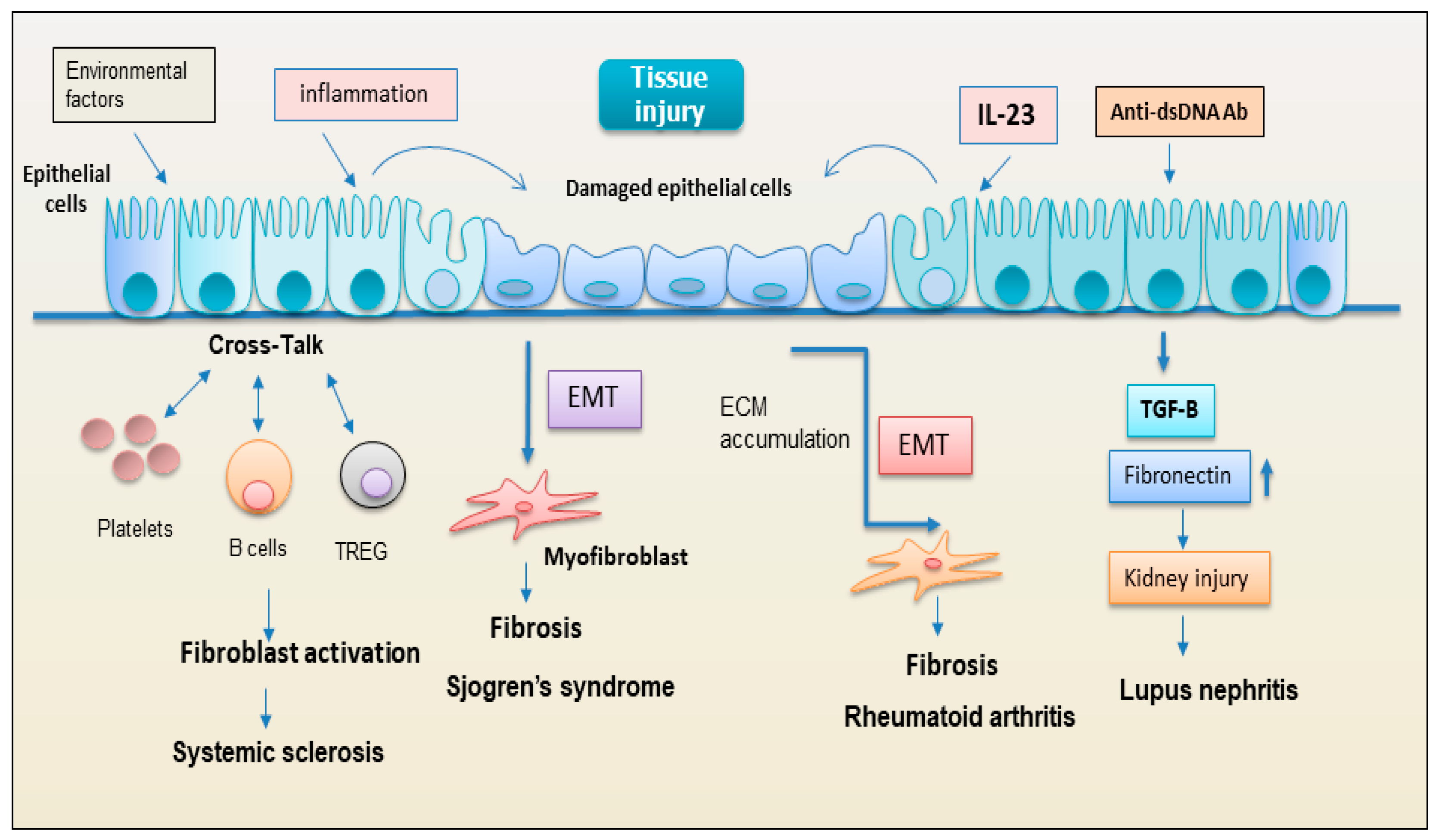
2.2.1. Epithelial cells
2.2.2. EMT: new player regulating the interplay between the immunity and fibrosis
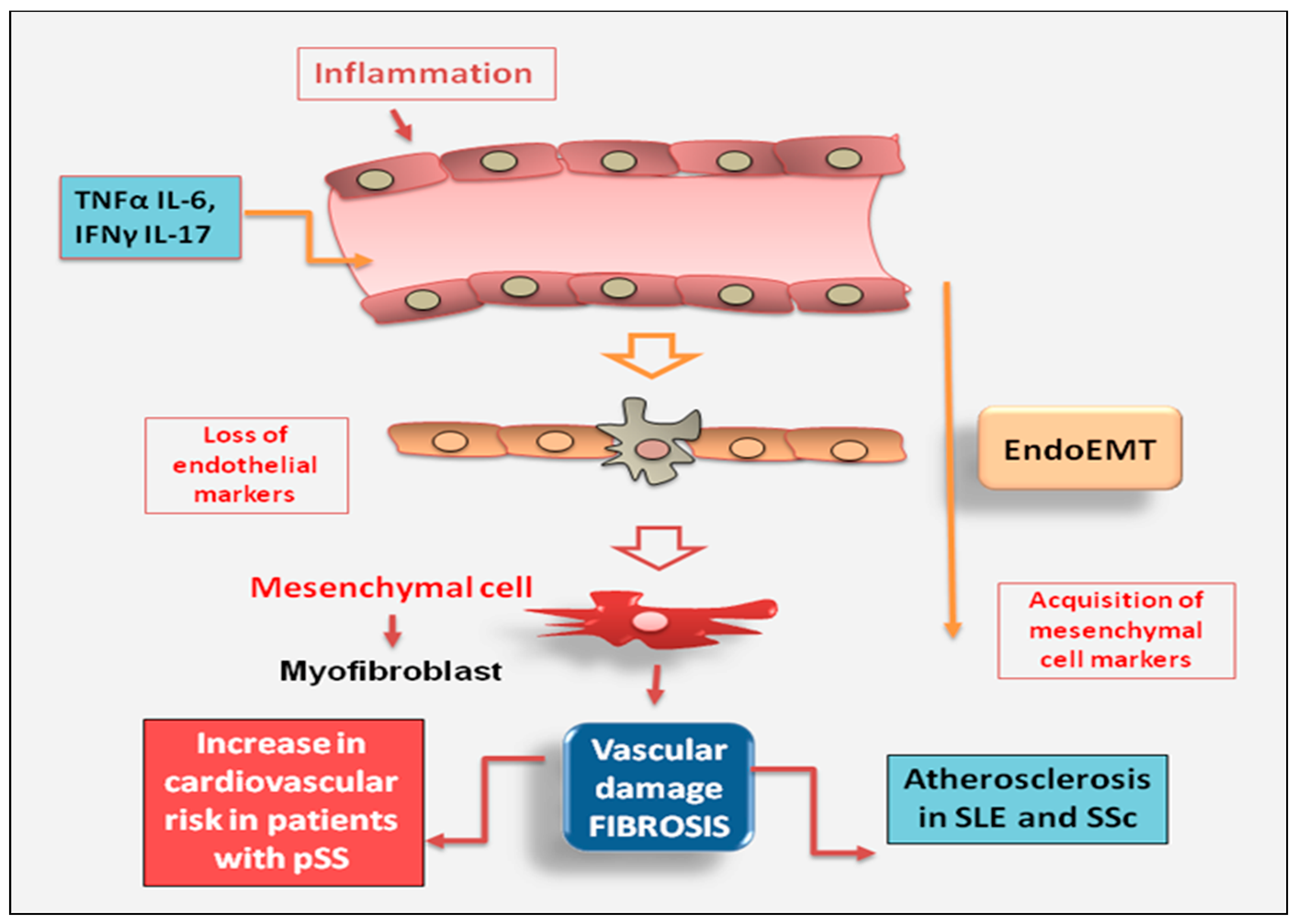
2.2.3. Endothelial cell
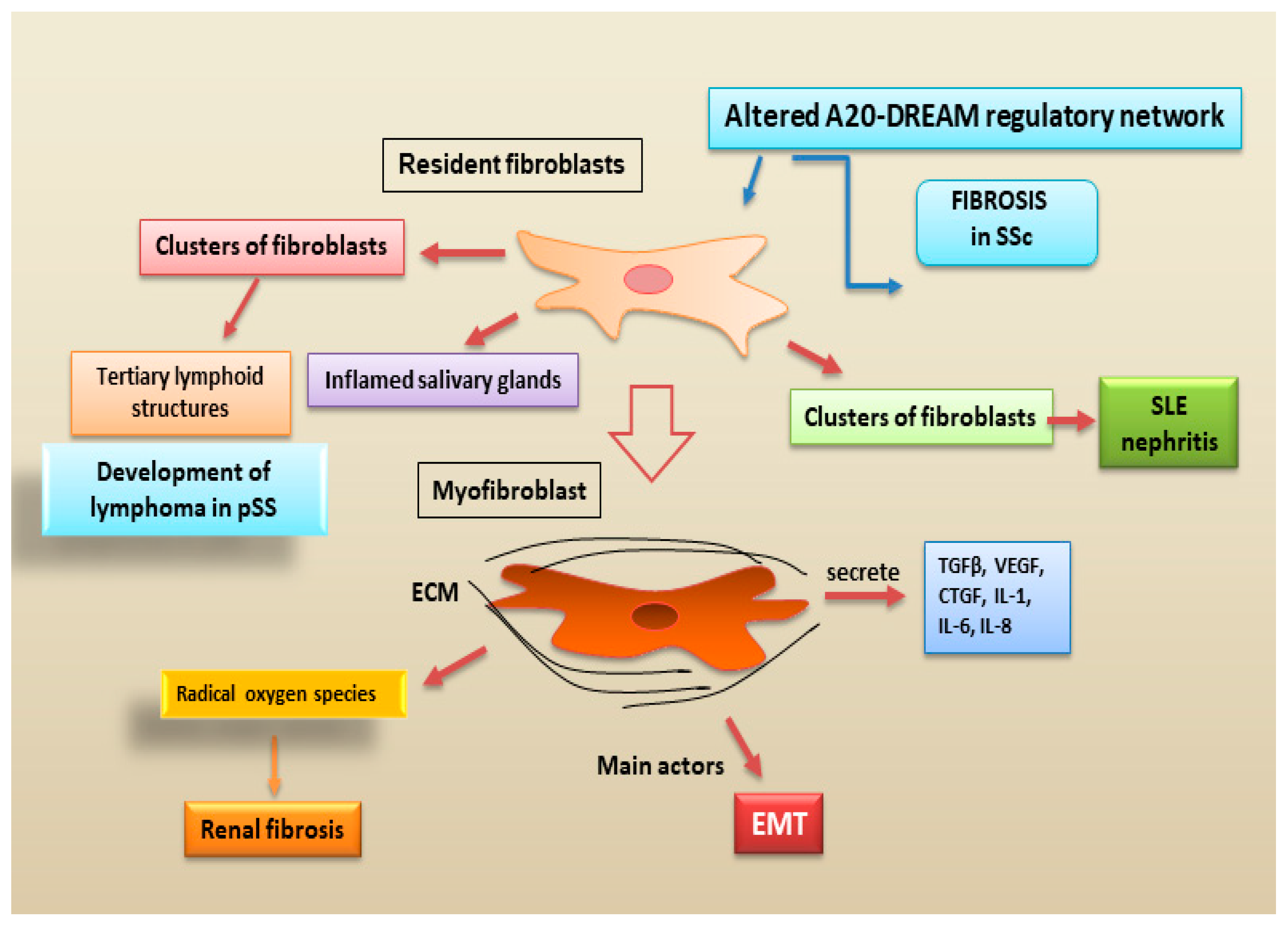
2.2.4. Fibroblasts
2.3. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Duan, L.; Rao, X.; Sigdel, K.R. Regulation of Inflammation in Autoimmune Disease. J. Immunol. Res. 2019, 2019, 7403796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frizinsky, S.; Haj-Yahia, S.; Machnes Maayan, D.; Lifshitz, Y.; Maoz-Segal, R.; Offengenden, I.; Kidon, M.; Agmon-Levin, N. The innate immune perspective of autoimmune and autoinflammatory conditions. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2019, 58, vi1–vi8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, Y.; Wei, X.; Ye, T.; Hang, L.; Mou, L.; Su, J. Interrelation Between Fibroblasts and T Cells in Fibrosing Interstitial Lung Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 747335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, X.; Liu, H.; Huang, G.; Dai, S.S. The emerging role of neutrophils in autoimmune-associated disorders: Effector, predictor, and therapeutic targets. Med. Comm. 2021, 2, 402–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, S.M.; Kim, W.U. Targeted Immunotherapy for Autoimmune Disease. Immune Netw. 2022, 22, e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Distler, J.H.W.; Gyorfi, A.H.; Ramanujam, M.; Whitfield, M.L.; Konigshoff, M.; Lafyatis, R. Shared and distinct mechanisms of fibrosis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2019, 15, 705–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, S. T Cells in Fibrosis and Fibrotic Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Chen, J.; Sun, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zou, D. New insights into fibrosis from the ECM degradation perspective: The macrophage-MMP-ECM interaction. Cell Biosci. 2022, 12, 117. [Google Scholar]
- Raphael, I.; Joern, R.R.; Forsthuber, T.G. Memory CD4+ T Cells in Immunity and Autoimmune Diseases. Cells. 2020, 9, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Q.; Luo, Y.; Chang, C.; Wu, H.; Ding, Y.; Xiao, R. The Emerging Epigenetic Role of CD8+T Cells in Autoimmune Diseases: A Systematic Review. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuschiotti, P. Current perspectives on the role of CD8+ T cells in systemic sclerosis. Immunol. Lett. 2018, 195, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, N.; Chen, H.; Perugino, C.A.; Maehara, T.; Munemura, R.; Yokomizo, S.; Sameshima, J.; Diefenbach, T.J.; Premo, K.R.; Chinju, A.; et al. Cytotoxic CD8+ T cells may be drivers of tissue destruction in Sjögren's syndrome. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 15427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shima, Y. Cytokines Involved in the Pathogenesis of SSc and Problems in the Devel-opment of Anti-Cytokine Therapy. Cells. 2021, 10, 1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzi, E.; Tabib, T.; Papazoglou, A.; Sembrat, J.; Trejo Bittar, H.E.; Rojas, M.; Lafyatis, R. Disparate Interferon Signaling and Shared Aberrant Basaloid Cells in Single-Cell Profiling of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis and Systemic Sclerosis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 595811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakkas, L.I.; Bogdanos, D.P. The Role of T Cells in SSc: An Update. Immuno 2022, 2, 534–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Wang, M.; Zhang, J.; Feng, X.; Liu, Z.; Cheng, Z. Association between tubulointerstitial CD8+T cells and renal prognosis in lupus nephritis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 99, 107877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vuerich, M.; Wang, N.; Kalbasi, A.; Graham, J.J.; Longhi, M.S. Dysfunctional Immune Regulation in Autoimmune Hepatitis: From Pathogenesis to Novel Therapies. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 746436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Covelli, C.; Sacchi, D.; Sarcognato, S.; Cazzagon, N.; Grillo, F.; Baciorri, F.; Fanni, D.; Cacciatore, M.; Maffeis, V.; Guido, M. Pathology of autoimmune hepatitis. Pathologica 2021, 113, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidotti, L.G.; Inverso, D.; Sironi, L.; Di Lucia, P.; Fioravanti, J.; Ganzer, L.; Fiocchi, A.; Vacca, M.; Aiolfi, R.; Sammicheli, S.; et al. Immunosurveillance of the liver by intravascular effector CD8(+) T. Cell 2015, 161, 486–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safadi, R.; Ohta, M.; Alvarez, C.E.; Fiel, M.I.; Bansal, M.; Mehal, W.Z.; Friedman, S.L. Immune stimulation of hepatic fibrogenesis by CD8 cells and attenuation by transgenic interleukin-10 from hepatocytes. Gastroenterology 2004, 127, 870–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novobrantseva, T.I.; Majeau, G.R.; Amatucci, A.; Kogan, S.; Brenner, I.; Casola, S.; Shlomchik, M.J.; Koteliansky, V.; Hochman, P.S.; Ibraghimov, A. Attenuated liver fibrosis in the absence of B cells. J. Clin. Invest. 2005, 115, 3072–3082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Xiang, Z.; Wu, B. T cells and liver fibrosis. Port Hypertens Cirrhos. 2022, 1, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Yang, J.; Tian, J.; Wang, S. CD8+ T Lymphocytes: Crucial Players in Sjögren's Syndrome. Front. Immunol. 2021, 11, 602823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chihaby, N.; Orliaguet, M.; Le Pottier, L.; Pers, J.O.; Boisramé, S. Treatment of Sjögren's Syndrome with Mesenchymal Stem Cells: A Systematic Review. Int J Mol Sci. 2021, 22, 10474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joachims, M.L.; Leehan, K.M.; Lawrence, C.; Pelikan, R.C.; Moore, J.S.; Pan, Z.; Rasmussen, A.; Radfar, L.; Lewis, D.M.; Grundahl, K.M.; et al. Single-cell analysis of glandular T cell receptors in Sjögren's syndrome. JCI Insight 2016, e85609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mingueneau, M.; Boudaoud, S.; Haskett, S.; Reynolds, T.L.; Nocturne, G.; Norton, E.; Zhang, X.; Constant, M.; Park, D.; Wang, W.; et al. Cytometry by time-of-flight immunophenotyping identifies a blood Sjögren's signature correlating with disease activity and glandular inflammation. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016, 137, 1809–1821.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tasaki, S.; Suzuki, K.; Nishikawa, A.; Kassai, Y.; Takiguchi, M.; Kurisu, R.; Okuzono, Y.; Miyazaki, T.; Takeshita, M.; Yoshimoto, K.; et al. Multiomic disease signatures converge to cytotoxic CD8 T cells in primary Sjögren's syndrome. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017, 76, 1458–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldeira-Dantas, S.; Furmanak, T.; Smith, C.; Quinn, M.; Teos, L.Y.; Ertel, A.; Kurup, D.; Tandon, M.; Alevizos, I.; Snyder, C.M. The Chemokine Receptor CXCR3 Promotes CD8+ T Cell Accumulation in Uninfected Salivary Glands but Is Not Necessary after Murine Cytomegalovirus Infection. J Immunol. 2018, 200, 1133–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verstappen, G.M.; Kroese, F.G.M.; Bootsma, H. T cells in primary Sjögren’s syndrome: Targets for early intervention. Rheumatology 2021, 60, 3088–3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, D.; Min, B. Tissue Resident Foxp3+ Regulatory T Cells: Sentinels and Saboteurs in Health and Disease. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 865593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendeeran, A.; Tenbrock, K. Regulatory T cell function in autoimmune disease. J. Transl Autoimmun. 2021, 4, 100130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, M.; Hao, Z.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, S.; Luo, J.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, C.; Liu, X.; Wu, X.; et al. Short-term and low-dose IL-2 therapy restores the Th17/Treg balance in the peripheral blood of patients with primary Sjogren’s syndrome. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 77, 1838–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frantz, C.; Auffray, C.; Avouac, J.; Allanore, Y. Regulatory T Cells in Systemic Sclerosis. Front Immunol. 2018, 9, 2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, S.; Nagafuchi, Y.; Shoda, H.; Fujio, K. The Pathophysiological Roles of Regulatory T Cells in the Early Phase of SSc. Front Immunol. 2022, 13, 900638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vignali, D.A.; Collison, L.W.; Workman, C.J. How regulatory T cells work. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008, 8, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, K.G.; Dawson, N.A.J.; Huang, Q.; Dunne, J.V.; Levings, M.K.; Broady, R. Regulatory T cells produce profibrotic cytokines in the skin of patients with systemic sclerosis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015, 135, 946–955.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keindl, M.; Davies, R.; Bergum, B.; Brun, J.G.; Hammenfors, D.; Jonsson, R.; Lyssenko, V.; Appel, S. Impaired activation of STAT5 upon IL-2 stimulation in Tregs and elevated sIL-2R in Sjögren's syndrome. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2022, 24, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchida, K. Recent progress on the Roles of Regulatory T Cells in IgG4-Related Disease. Immuno 2022, 2, 430–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.J.; Qian, Q.F.; Zhou, J.R.; Sun, D.L.; Duan, Y.F.; Zhu, X.; Sartorius, K.; Lu, Y.J. Regulatory T cells (Tregs) in liver fibrosis. Cell Death Discov. 2023, 9, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ormandy, L.A.; Hillemann, T.; Wedemeyer, H.; Manns, M.P.; Greten, T.F.; Korangy, F. Increased populations of regulatory T cells in peripheral blood of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 2457–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Adwi, Y.; Westra, J.; van Goor, H.; Burgess, J.K.; Denton, C.P.; Mulder, D.J. Macrophages as determinants and regulators of fibrosis in systemic sclerosis. Rheumatology 2023, 535–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, E.A.; Devitt, A.; Johnson, J.R. Macrophages: The Good, the Bad, and the Gluttony. Front Immunol. 2021, 12, 708186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoeft, K.; Schaefer, G.J.L.; Kim, H.; Schumacher, D.; Bleckwehl, T.; Long, Q.; Klinkhammer, B.M.; Peisker, F.; Koch, L.; Nagai, J.; et al. Platelet-instructed SPP1+ macrophages drive myofibroblast activation in fibrosis in a CXCL4-dependent manner. Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 112131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, D.; Chai, J.; Wang, H.; Fu, L.; Peng, S.; Ni, X. Hepatic macrophages: Key players in the development and progression of liver fibrosis. Liver Int. 2021, 41, 2279–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choreño-Parra, J.A.; Cervantes-Rosete, D.; Jiménez-Alvarez, L.A.; Ramírez-Martínez, G.; Márquez-García, J.E.; Cruz-Lagunas, A.; Magaña-Sanchez, A.Y.; Lima, G.; López-Maldonado, H.; Gaytán-Guzmán, E.; et al. Dendritic cells drive profibrotic inflammation and aberrant T cell polarization in systemic sclerosis. Rheumatology 2022, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conti, P.; Stellin, L.; Caraffa, A.; Gallenga, C.E.; Ross, R.; Kritas, S.K.; Frydas, I.; Younes, A.; Di Emidio, P.; Ronconi, G. Advances in Mast Cell Activation by IL-1 and IL-33 in Sjogren’s Syndrome: Promising Inhibitory Effect of IL-37. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leehan, K.M.; Pezant, N.P.; Rasmussen, A.; Grundahl, K.; Moore, J.S.; Radfar, L.; Lewis, D.M.; Stone, D.U.; Lessard, C.J.; Rhodus, N.L.; et al. Minor salivary gland fibrosis in Sjogren’s syndrome is elevated, associated with focus score and not solely a consequence of aging. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2018, 36, 80–88. [Google Scholar]
- Lamouille, S.; Xu, J.; Derynck, R. Molecular mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2014, 15, 178–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sisto, M.; Ribatti, D.; Lisi, S. Sjögren’s Syndrome-Related Organs Fibrosis: Hypotheses and Realities. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wynn, T.A.; Ramalingam, T.R. Mechanisms of fibrosis: Therapeutic translation for fibrotic disease. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 1028–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendt, M.K.; Allington, T.M.; Schiemann, W.P. Mechanisms of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition by TGF-beta. Future Oncol. 2009, 5, 1145–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuppe, C.; Ibrahim, M.M.; Kranz, J.; Zhang, X.; Ziegler, S.; Perales-Patón, J.; Jansen, J.; Reimer, K.C.; Smith, J.R.; Dobie, R.; et al. Decoding myofibroblast origins in human kidney fibrosis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2021, 589, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sisto, M.; Ribatti, D.; Lisi, S. Organ Fibrosis and Autoimmunity: The Role of Inflammation in TGFβ-Dependent EMT. Biomolecules. 2021, 11, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sisto, M.; Ribatti, D.; Lisi, S. Molecular Mechanisms Linking Inflammation to Autoimmunity in Sjögren's Syndrome: Identification of New Targets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asano, Y.; Takahashi, T.; Saigusa, R. Systemic sclerosis: Is the epithelium a missing piece of the pathogenic puzzle? J. Dermatol. Sci. 2019, 94, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.; Healy, H.; Kassianos, A.J. The Emerging Role of Renal Tubular Epithelial Cells in the Immunological Pathophysiology of Lupus Nephritis. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 578952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Ortega, M.; Rayego-Mateos, S.; Lamas, S.; Ortiz, A.; Rodrigues-Diez, R.R. Targeting the progression of chronic kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2020, 16, 269–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yung, S.; Ng, C.Y.; Ho, S.K.; Cheung, K.F.; Chan, K.W.; Zhang, Q. Anti-dsDNA antibody induces soluble fibronectin secretion by proximal renal tubular epithelial cells and downstream increase of TGF-beta1 and collagen synthesis. J. Autoimmun. 2015, 58, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, S.; Lau, J.; Roden, A.C.; Matteson, E.L.; Sun, J.; Luo, F.; Tschumperlin, D.J.; Vassallo, R. IL-23 amplifies the epithelial-mesenchymal transition of mechanically conditioned alveolar epithelial cells in rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease through mTOR/S6 signaling. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2021, 321, L1006–L1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Gregorio, J.; Robuffo, I.; Spalletta, S.; Giambuzzi, G.; De Iuliis, V.; Toniato, E.; Martinotti, S.; Conti, P.; Flati, V. The Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition as a Possible Therapeutic Target in Fibrotic Disorders. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 607483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Poe, D.; Yang, Y.; Hyatt, T.; Xing, J. Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition proceeds through directional destabilization of multidimensional attractor. Elife. 2022, 11, e74866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Novoa, J.M.; Nieto, M.A. Inflammation and EMT: An alliance towards organ fibrosis and cancer progression. EMBO Mol. Med. 2009, 1, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marconi, G.D.; Fonticoli, L.; Rajan, T.S.; Pierdomenico, S.D.; Trubiani, O.; Pizzicannella, J.; Diomede, F. Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT): The Type-2 EMT in Wound Healing, Tissue Regeneration and Organ Fibrosis. Cells. 2021, 10, 1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Dai, F.; Feng, L.; Zou, H.; Feng, L.; Xu, M. Communication Between Epithelial-Mesenchymal Plasticity and Cancer Stem Cells: New Insights Into Cancer Progression. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 617597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovisa, S. Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in Fibrosis: Concepts and Targeting Strategies. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 737570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.K.; Sheppard, D.; Chapman, H.A. TGF-β1 signaling and tissue fibrosis. Perspect. Biol. 2018, 10, a022293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.O.; Wan, Y.Y.; Sanjabi, S.; Robertson, A.K.; Flavell, R.A. Transforming growth factor-beta regulation of immune responses. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2006, 24, 99–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabregat, I.; Moreno-Càceres, J.; Sánchez, A.; Dewidar, B.; Giannelli, G.; Ten Dijke, P. IT-LIVER Consortium. TGF-β signalling and liver disease. FEBS J. 2016, 283, 2219–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis, B.C.; Borok, Z. TGF-β-induced EMT: Mechanisms and implications for fibrotic lung disease. Am. J. Physiol. 2007, 293, L525–L534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.E. Non-Smad pathways in TGF-beta signaling. Cell Res. 2009, 19, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, S.A. Role of endothelial to mesenchymal transition in the pathogenesis of the vascular alterations in systemic sclerosis. ISRN Rheumatol 2013, 2013, 835948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebmeier, S.; Horsley, V. Origin of fibrosing cells in systemic sclerosis. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol 2015, 27, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Benedetto, P.; Ruscitti, P.; Berardicurti, O.; Vomero, M.; Navarini, L.; Dolo, V.; Cipriani, P.; Giacomelli, R. Endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition in systemic sclerosis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2021, 205, 12–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moschetti, L.; Piantoni, S.; Vizzardi, E.; Sciatti, E.; Riccardi, M.; Franceschini, F.; Cavazzana, I. Endothelial Dysfunction in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Systemic Sclerosis: A Common Trigger for Different Microvascular Diseases. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 849086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Łuczak, A.; Małecki, R.; Kulus, M.; Madej, M.; Szahidewicz-Krupska, E.; Doroszko, A. Cardiovascular Risk and Endothelial Dysfunction in Primary Sjogren Syndrome Is Related to the Disease Activity. Nutrients. 2021, 13, 2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, M.; Miossec, P. Effects of Interleukin 17 on the cardiovascular system. Autoimmun Rev. 2017, 16, 984–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostmans, Y.; Cutolo, M.; Giddelo, C.; Decuman, S.; Melsens, K.; Declercq, H.; Vandecasteele, E.; De Keyser, F.; Distler, O.; Gutermuth, J.; et al. The role of endothelial cells in the vasculopathy of systemic sclerosis: A systematic review. Autoimmun. Rev. 2017, 16, 774–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plikus, M.V.; Wang, X.; Sinha, S.; Forte, E.; Thompson, S.M.; Herzog, E.L.; Driskell, R.R.; Rosenthal, N.; Biernaskie, J.; Horsley, V. Fibroblasts: Origins, definitions, and functions in health and disease. Cell. 2021, 184, 3852–3872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeBleu, V.S.; Taduri, G.; O’Connell, J.; Teng, Y.; Cooke, V.G.; Woda, C.; Sugimoto, H.; Kalluri, R. Origin and Function of Myofibroblasts in Kidney Fibrosis. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 1047–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, K.; Korsunsky, I.; Marshall, J.L.; Gao, A.; Watts, G.F.M.; Major, T.; Croft, A.P.; Watts, J.; Blazar, P.E.; Lange, J.K.; et al. Notch signalling drives synovial fibroblast identity and arthritis pathology. Nature. 2020, 582, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, T.J. Insights into the role of fibroblasts in human autoimmune diseases. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2005, 141, 388–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Bale, S.; Wei, J.; Yalavarthi, B.; Bhattacharyya, D.; Yan, J.J.; Abdala-Valencia, H.; Xu, D.; Sun, H.; Marangoni, R.G.; et al. Fibroblast A20 governs fibrosis susceptibility and its repression by DREAM promotes fibrosis in multiple organs. Nat.Commun. 2022, 13, 6358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onuora, S. Fibroblast A20 and its suppressor DREAM regulate fibrosis in SSc. Nat Rev Rheumatol, 2023, 19, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, K. Fibroblasts in Sjögren’s Syndrome, Fibroblasts-Advances in Inflammation, Autoimmunity and Cancer. FROM THE EDITED VOLUME Fibroblasts Edited by Mojca Frank Bertoncelj and Katja Lakota, Published: July 16th, 2021.
- Lee, B.; Lee, S.H.; Shin, K. Crosstalk between fibroblasts and T cells in immune networks. Front.Immunol. 2023, 13, 1103823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciascia, S.; Cozzi, M.; Barinotti, A.; Radin, M.; Cecchi, I.; Fenoglio, R.; Mancardi, D.; Wilson Jones, G.; Rossi, D.; Roccatello, D. RenalFibrosis in Lupus Nephritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tai, Y.; Woods, E.L.; Dally, J.; Kong, D.; Steadman, R.; Moseley, R.; Midgley, A.C. Myofibroblasts: Function, Formation, and Scope of Molecular Therapies for Skin Fibrosis. Biomolecules. 2021, 11, 1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabib, T.; Morse, C.; Wang, T.; Chen, W.; Lafyatis, R. SFRP2/DPP4 and FMO1/LSP1 Define Major Fibroblast Populations in Human Skin. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2018, 138, 802–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Caam, A.; Vonk, M.; van den Hoogen, F.; van Lent, P.; van der Kraan, P. Unraveling SSc Pathophysiology; The Myofibroblast. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falke, L.L.; Gholizadeh, S.; Goldschmeding, R.; Kok, R.J.; Nguyen, T.Q. Diverse Origins of the Myofibroblast—Implications for Kidney Fibrosis. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2015, 11, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schunk, S.J.; Floege, J.; Fliser, D.; Speer, T. WNT-β-Catenin Signalling—A Versatile Player in Kidney Injury and Repair. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2021, 17, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




