1. Introduction
Wireless sensor networks (WSNs) encounter issues when deployed to support applications requiring mobility support, such as disaster and earthquake recovery, combat field surveillance, monitoring animals, and applications to enforce the law. As a result, to ensure reliable communication, dependable connectivity of the network, low energy usage, and prolonged network life span for these applications, a dynamic and adaptive WSN network with mobility support is required [
1]. Consequently, these networks must preserve fault tolerance and self-organizing capabilities to operate properly [
2,
3,
4,
5].
Therefore, it is vital to provide energy-efficient systems throughout the whole protocol stack variances in mobility play a major role and directly impact the scalability and energy efficiency of WSNs. Thus, performance deterioration and unpredictably broken links result from needing to provide a reliable mobility model [
1,
6,
7].
Various mobility models were proposed in the literature and are considered good candidates to be used in ad-hoc networks. However, when using them in WSNs, they provide low QoS parameters and increase energy consumption because of how they behave in these networks. To elaborate, the random waypoint mobility model performs reasonably when used in ad-hoc networks. However, it is not a suitable choice in WSNs because of its poor choice of velocity and uniform distribution [
8,
9,
10].
On the other hand, the nomadic community mobility model was introduced to address the drawbacks of the random waypoint mobility model. Because nodes move randomly from one site to another, this model is appropriate for applications supporting military operations and mobile communications in conferences. Furthermore, based on the collective motion of the group, a reference point for each point is determined. This approach consumes much energy to discover or pinpoint the location of a single node [
11,
12].
Consequently, a geographic-based circular mobility model was introduced to handle sink node mobility. This model collects data by traveling over a circular, static point-based track. The condition that nodes stay stationary eight or sixteen times during each cycle is a significant drawback in this model. Therefore, a wind mobility model based on eight directions was proposed in [
13] to extend the network lifetime. This paradigm is depicted for sink nodes, although nodes in this model only support group mobility. As a result, to determine the position of one node, a group of nodes moves and consume energy [
14]. Thus, the wind mobility model must provide high performance for the network due to the additional pause time, the speed of nodes, and their interdependencies [
15].
Additionally, processing, sensing, and communication are the three subsystems of sensor nodes. Also, the communication subsystem is the main source of energy consumption because the distance between the source and destination nodes determines how much energy is used to convey a message. [
16,
17]. Thus, multi-hop communication can reduce the distance required in transmission, which comes at the expense of increasing the delay compared to single-hop communication [
16,
18].
A mobile and energy-rich sink node or nodes have been introduced to solve this issue. In this method, the mobile sink moves randomly or follows a predetermined mobility model to gather data from stationary sensor nodes and transmit it to the base station. Additionally, using a mobile sink increases the performance of WSNs in a variety of ways, including decreasing the distance needed for a stationary node to transmit data, lowering the number of intermediary nodes, increasing network throughput, and providing coverage for remote areas [
2]
This paper proposes a sink mobility model using a single, energy-rich mobile sink node to collect data from stationary sensor nodes. The proposed model is based on creating a Bipartite graph of the WSN. After that, a sink node mobility path is acquired from the properties of the Bipartite graph. Also, this work proposes combining single-hop and multi-hop routing to achieve good network performance.
The following will be the order of this paper's remaining sections: A concise explanation of the bipartite graph is provided in
Section 2.
Section 3 follows with a literature review of existing models. In
Section 4, the proposed mobility model is then explained. Additionally,
Section 5 discusses the performance indicators and simulated scenarios used to investigate the proposed work's effectiveness—additionally,
Section 6 discusses the simulation's outcomes. Finally,
Section 7 presents final observations and ideas for further research.
2. Bipartite Graph Overview
Nowadays, WSNs are playing a major role in numerous applications, including military, environment, and disaster monitoring applications, to name a few. Consequently, it is very important to consume sensor nodes wisely with limited resources to better control the phenomenon being studied and prolong the network lifetime [
8]. According to [
9], a bipartite graph is considered a simple graph where the vertices of a graph are divided into two disjoint sets. Say it in another way, consider a graph denoted by
G, and the vertices of G are denoted by
V (G). A bipartite graph is constructed by dividing the vertices of G into two disjoint sets, namely V
1 and V
2, with the following properties:
Consider a vertex v where , then v cannot be adjacent to vertices in V1. On the contrary, it can be adjacent to vertices that belong to V2.
Consider a vertex v where, then v cannot be adjacent to vertices in V2. On the contrary, it can be adjacent to vertices that belong to V1.
, there is no intersection between V1 and V2.
, the union of V1 and V2 will result in all the vertices of the graph G.
As a result, when creating a bipartite graph for a randomly deployed WSN, sensor nodes will be divided into two sets. Hence, deploying a mobile sink to move and collect data from one set is possible. After that, when finishing all the nodes in the set, the mobile sink will move and start collecting data from the other set. Also, the nodes in one set are adjacent to nodes in the other set, which can benefit the mobile sink when gathering data from static nodes.
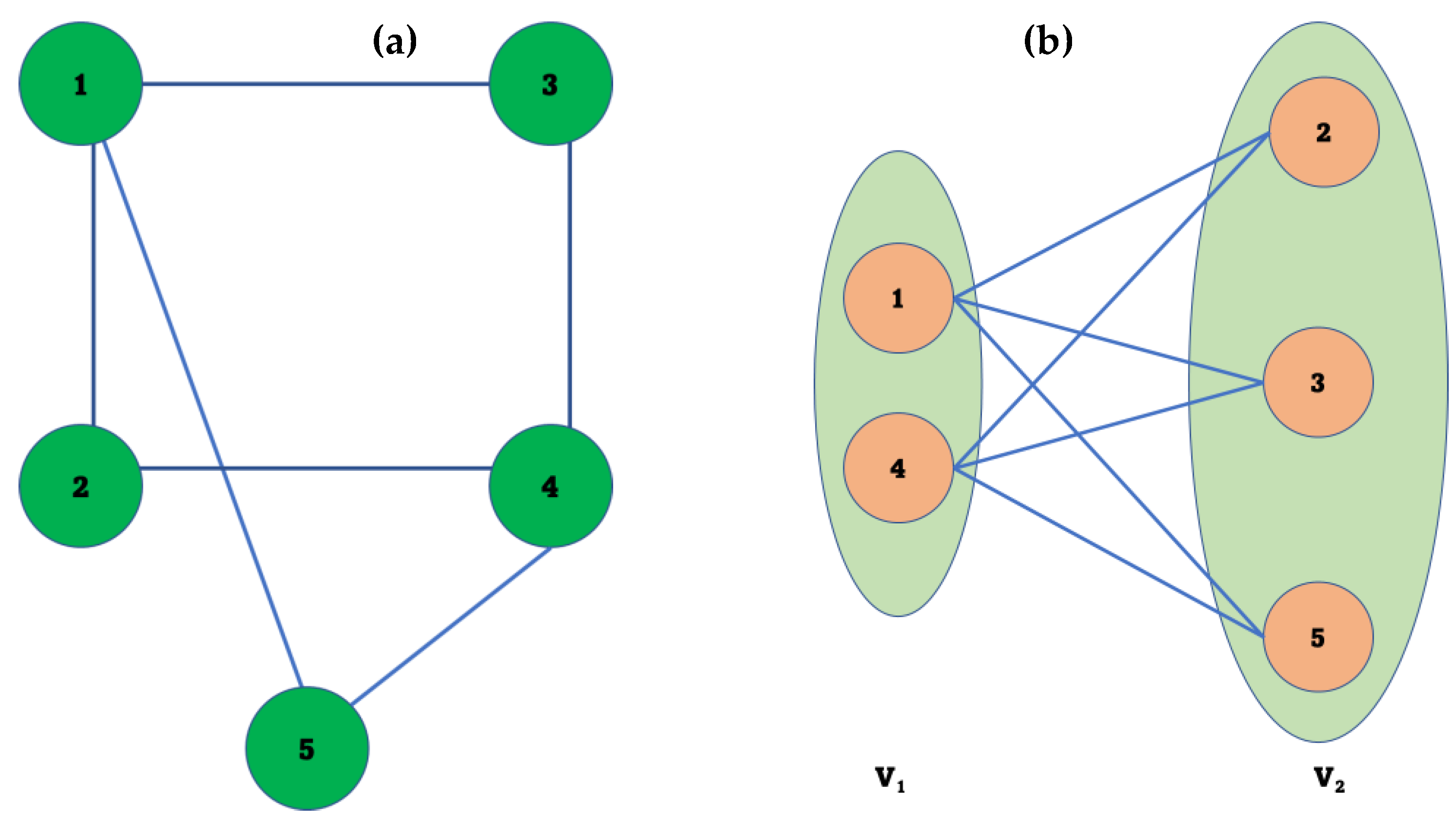
For example, the graph shown in
Figure 1a represents a graph of 5 nodes labeled by numbers from 1 to 5. To check whether the given graph is bipartite, we need to apply the definition of a bipartite graph. In other words, we need to check if the nodes in the given graph can be partitioned into two disjoint sets, V
1 and V
2, with the abovementioned properties.
Figure 1b shows that the nodes or vertices of the graph shown in
Figure 1a can be divided into two disjoint sets denoted by V
1 and V
2 in the figure. Furthermore, it can be seen that the nodes that are part of the set named V
1 are not neighbors or adjacent to each other. However, each node in V
1 is a neighbor or adjacent to nodes in V
2.
To elaborate, in
Figure 1b, node one and node 4 are members of V1. Form
Figure 1a shows that these nodes are not neighbours. On the other hand, node 1, for example, is a neighbor of node 1, node three, and node five, which are members of the other set denoted by V2, as shown in
Figure 1b.
As a result, it can be concluded that the graph shown in
Figure 1 is bipartite because all the nodes or vertices of that graph were divided into two disjoint sets where the nodes in each set are not neighbors or adjacent. Still, at the same time, every node in one set is adjacent to nodes in the other set.
Thus, using a bipartite graph might help to improve the performance of the WSN in two folds: (1). The mobile sink will visit smaller nodes, i.e., not all the nodes in the network in each round. (2). The proposed model will help stationary sensor nodes mix between multi-hop and single-hop communication depending on which set is being visited and to which set the stationary sensor node belongs.
3. Mobility Models
Several research papers have suggested algorithms or models to support mobility in WSNs. According to [
19], the capacity of nodes in WSNs to relocate themselves upon deployment is referred to as node mobility. As a result, there are two primary categories of sensor node mobility algorithms or models. The first is the usage of mobile sinks or sinks that can receive data from stationary sensor nodes while moving, whereas the second is based on providing all sensor nodes the capacity to move. Because it is more pertinent to the proposed mobility model, we will focus our review in this paper on studies that supply a single mobile sink that moves to collect data from stationary sensor nodes and send them to the base station.
The study proposed in [
20] introduced a data-gathering method based on path planning to reduce distances traveled by the mobile sink and reduce the communication range. An inner center path planning algorithm was used to shorten the distance a mobile sink had to travel. The movement path back propagation problem was also considered by presenting a back-routing algorithm. Therefore, the proposed scheme must enable the mobile sink to make adaptive judgments to move adequately.
In addition, the research presented in [
21] suggested addressing the relay selection problem to decrease energy use and increase the lifespan of WSNs. As a result, the k-means method was used in the proposed study to partition the network into clusters. A movable sink-based cluster head selection technique was suggested to increase energy usage inside the cluster. The mobile sink node will function as a cluster head close to stationary sensor nodes to gather data and reduce energy consumption for static sensor nodes and the cluster head.
The authors of the research presented in [
22] were written by writers who developed a sink mobility model derived from Korhonen’s self-organization map (SOM). Their study establishes the mobile sink's movement path using Korhonen SOM. The mobile sink thus moves during movement times and stops during pause periods. The mobile sink will remain in its present location during the stop periods for a fixed period, after which it will begin migrating to a new site determined using the Korhonen SOM, and so on, until topology changes are brought on by energy depletion take place. As a result, a new Korhonen SOM calculation of the mobility path will be performed.
To further improve the operation of environmental monitoring and anomaly search in WSNs, a collaborative approach was presented in [
23]. The proposed method is composed mostly of two components. Based on a weighted Gaussian coverage strategy, the first focus is collaboratively installing the static sensor nodes. The second section, on the other hand, focuses on path planning for the mobile sink and is based on modifying an active monitoring and anomaly search system that uses a Markov decision process model. The major objective is quickly identifying environmental irregularities so that the mobile mode can respond appropriately based on a cumulative reward function.
Another study that divides the network into zones to enhance wireless sensor network performance and extend their lifetime is proposed in [
24]. The mobile sink will travel close to the heavily loaded zone. It's important to note that a fuzzy logic system is used to select the strongly loaded zone to address any uncertainties that may arise when making this choice.
Similarly, an adaptive mobile routing method concerned with identifying burst traffic is proposed in [
25]. Additionally, the algorithm relies on splitting the network's clusters into two groups, and the proposed network architecture is based on having two mobile sinks. After that, each sensor node will be in charge of one group and communicate with the cluster heads. Additionally, the mobile sink will visit the cluster heads within the group specifically. The mobile sink will, however, disregard the sequence in which the cluster heads are visited and move close to the heavily loaded cluster head if a traffic burst is detected.
An ant colony optimization-based end-to-end data-gathering technique was also presented in [
26]. The proposed method is based on building a data forwarding tree and arbitrarily choosing data gathering points. As a result, the mobile sink's route is estimated and described.
A sink mobility model using a genetic algorithms model is presented in [
27]. The mobility model uses genetic algorithms to determine the direction the mobile sink should take when moving. After that, using single-hop routing, the mobile sink will travel to the nodes that are a part of the computed path to gather data from them via single-hop routing. On the other hand, multi-hop routing is used by nodes, not members of the mobile sink movement path, to forward packets to the mobile sink. Additionally, the portable sink's movement is split into pause and movement periods to facilitate data communication and reduce changes in routing paths. To elaborate, the mobile sink migrates to new locations that are calculated using the proposed algorithm during the movement phase instead of the pause period, during which it remains in the current location.
Furthermore, a model based on creating mobile pathways for the mobile sink to decrease latency and energy usage was proposed in [
28]. Choosing a meeting location, designing a trajectory, collecting data, and transmitting data are the four stages of the algorithm's operation.
In [
29], a mobile sink-based geographic routing scheme was developed. This study used two mobile sinks to gather information from sensor nodes in cells or geographic regions. As a result, each cell's sensor nodes collect data and send it to the mobile sink. It's important to note that single-hop and multi-hop routing can connect sensor nodes to the mobile sink.
4. Proposed Mobility Model
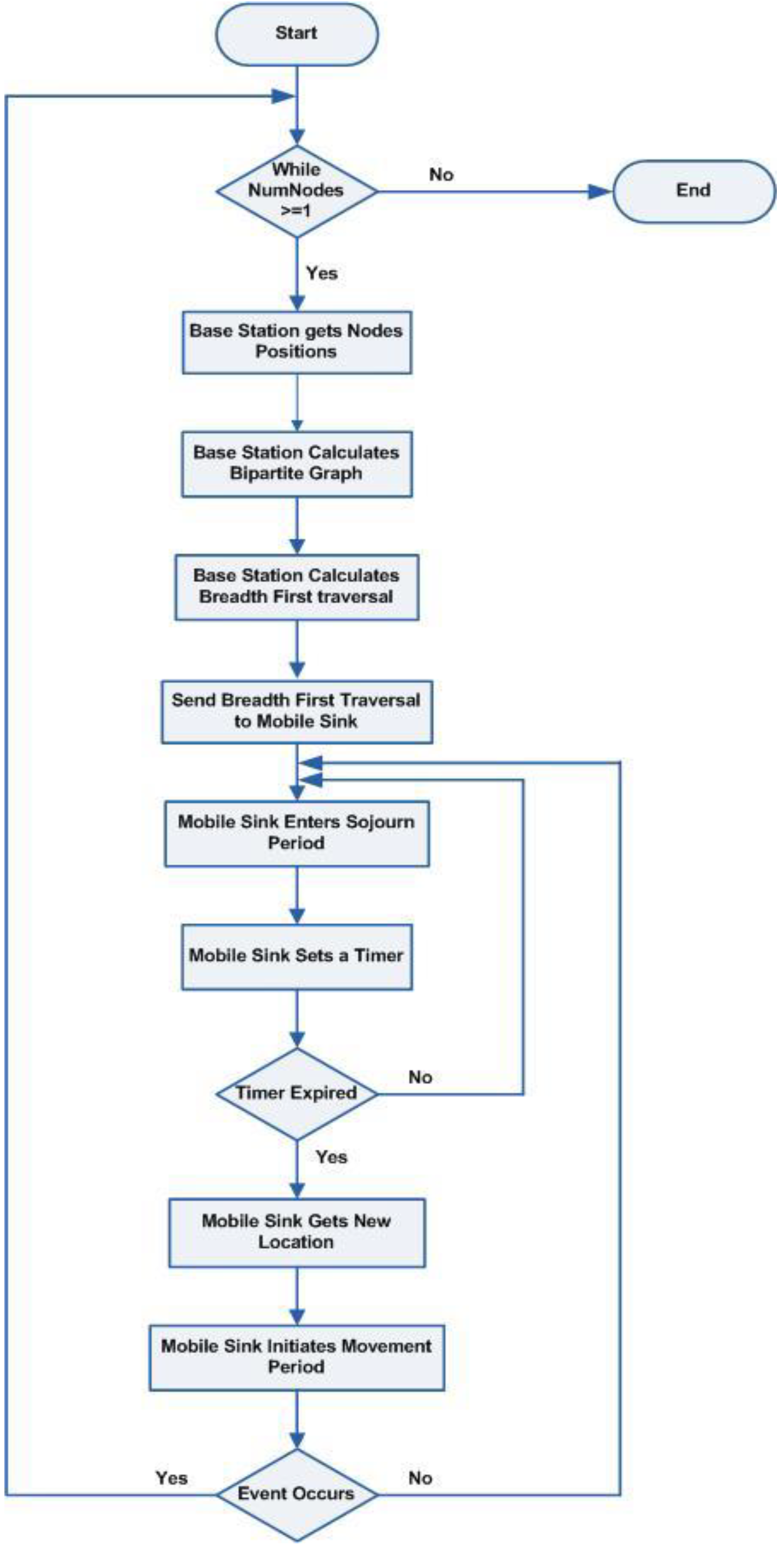
The work proposed in this paper relies on randomly deployed WSNs made up of N stationary sensor nodes and one additional node that can move to serve as a mobile sink node. Following network deployment, the base station receives the locations of the mobile sink and the stationary sensor nodes. Consequently, the base station calculates a bipartite graph, and the stationary sensor nodes are grouped into two disjoint sets, as explained in
Section 2. Worth noting that the mobile sink is not included in this calculation because it is supposed to visit stationary sensor nodes and collect information.
To clarify, a bipartite graph is derived by the base station using the locations of the static sensor nodes as a point of reference and the neighborhood data of the static sensor nodes. Thus, the stationary sensor nodes are grouped into two disjoint sets. Also, the based station will calculate the breadth-first traversal for the nodes in each subset based on the Euclidean distance between the static sensor nodes within each set. After that, based on the locations of the stationary sensor nodes, the mobile sink will choose one of the sets to start visiting stationary sensor nodes that are members of that set. In other words, the mobile sink will choose the nearest node to it and start visiting it; thus, it selects the set with the nearest member nodes to the mobile sink.
Consequently, the mobile sink will deal with the nodes in the selected set as a subgraph. The stationary sensor nodes within the set are visited according to the breadth-first traversal algorithm calculated based on the Euclidean distance between the nodes that are members of the selected set.
After visiting all the nodes in the first set, the mobile sink node will start moving towards the nearest member of the other set, and the static sensor nodes within that set are visited according to the breadth-first algorithm that is calculated based on the Euclidean distance between the nodes that are a member of the new set. This process continues until a recalculation of the bipartite graph is triggered or required based on changes in the topology of the WSN that might occur because of the death of static sensor nodes caused by energy depletion.
Worth noting that when the mobile sink is visiting stationary sensor nodes in one set, it will be within the range of communication of other stationary sensor nodes that are members of the other set but are neighbors of the node being visited; thus, these neighbor nodes can send data to the mobile sink before being visited. Consequently, we can ensure that the nodes will not suffer from buffer overflow and that the sensed information will promptly be communicated to the mobile sink.
Furthermore, the mobile sink's movement will follow the breadth traversal of the nodes in the selected set and is divided into sojourn periods and Movement periods. In the sojourn period, the mobile sink will pause in its current location for a specific period. After that, it will begin moving toward a new location at a set pace. When the mobile sink arrives at the new location, the sojourn period begins again and stays in the new place for the same period. A flowchart of the mobility model suggested in this paper is shown in
Figure 2.
Consider the networks shown in
Figure 1a that were processed to deduce the bipartite graph in
Figure 1b. Based on the Euclidian distance, the mobile sink will choose the nearest node to it to start its journey. For example, the mobile sink selected node one, which belongs to V
1, as the starting node of its journey. As a result, the mobile sink must visit all the nodes in V
1 based on the breadth-first traversal algorithm. After visiting all the nodes in V
1, the mobile sink will move to the nearest node in V
2 and will visit all the nodes of V
2 using the breadth-first traversal algorithm. Thus, the mobile sink will keep switching between the nodes of the two sets.
It is worth noting that when the mobile sink visits node 1 in V1, it will be a neighbor of some or all the nodes in V2. In this case, the mobile sink neighbors’ nodes 2, three, and five from V2. As a result, data can be collected from the nodes being visited, their neighbors who are members of the other set, and so on. After pausing for a specified period at node 1, the mobile sink will move towards another node in V1, node 4. Thus, it will be a neighbor to nodes 2, three, and node 5. Therefore, the mobile sink will be able to collect information from node four and its neighbors. Upon visiting all the nodes in V1, the mobile sink will move to the nearest node in V2. For example, the mobile sink will visit node 5 in V2, a neighbor to node one, and node four from V1. When the mobile sink arrives at the new location, i.e., near node 5, the mobile sink can collect information from node 5, node one, and node 4 using single-hop communication.
Consequently, by adopting this approach, the mobile sink will be able to visit nodes that are not neighbors to each other and collect data from the neighbors of the node being visited. Also, it can be observed that static sensor nodes will have multiple chances to report their data to the mobile sink, especially when having multiple neighbors. As a result, up-to-date data will be collected from sensor nodes promptly. The chances of sensor nodes suffering from buffer overflow are reduced because static sensor nodes do not have to store the collected information for long waiting to be visited by the mobile sink.
5. Simulation
5.1. Simulation Scenarios
Several simulation scenarios were run on the NS-2 simulator to examine the performance of the proposed sink mobility model. The Ad hoc On-Demand Distance Vector (AODV) routing protocol conveys messages to their intended recipients. Static sensor nodes provide traffic at a steady bit rate (CBR). In addition, the effectiveness of the proposed mobility model was examined in networks consisting of 26, 51, 76, and 101 randomly distributed nodes in a grid of 1000 * 1000. Additionally, each network consists of N nodes numbered from 0 to n-2 representing static sensor nodes for each network size. One additional energy-rich node serves as a mobility sink in the network, marked by n-1. To further explain, the stationary sensor nodes in the network of 26 nodes are numbered from 0 to 24. A different node with the number 25 represents an energy-rich mobile sink node that will move between the stationary sensor nodes per the mobility model proposed in this work. Additionally, for each network size, the performance of the suggested model was examined for mobile sink speeds of 5, 10, 15, and 20 m/s. In
Table 1, the simulation parameters are displayed.
5.2. Performance Metrics
The metrics used to analyze the network's performance while utilizing the proposed mobility model include average end-to-end delay, packet delivery ratio, and throughput. The average end-to-end delay is the time a packet takes from its starting point to its ending point. By averaging the amount of time needed to send each packet between each source and each destination within the network, the average end-to-end delay for the entire network may be determined [
30]. The average end-to-end delay is calculated using Equation (1).
In Equation (1) and Represent the received the transmitted copy of a packet, respectively, and N is the total number of received packets.
As stated in Equation (2), the ratio of successfully received packets to all packets transmitted is used to calculate the packet delivery rate. [
31,
32].
Where: P
rs is the total number of successfully received packets, and present is the overall number of sent packets. The total number of correctly received packets throughout a certain period is the definition of throughput, the third performance metric considered. As a result, in our simulation, throughput is computed as stated in equation 3 by dividing the total number of packets successfully received by the total simulation time [
30,
31].
6. Simulation Results
This part shows and discusses the results of applying the simulation scenarios in
Section 5.1. Each scenario was executed ten times to produce more detailed findings. The results of the ten runs for each example were averaged to acquire the simulation results.
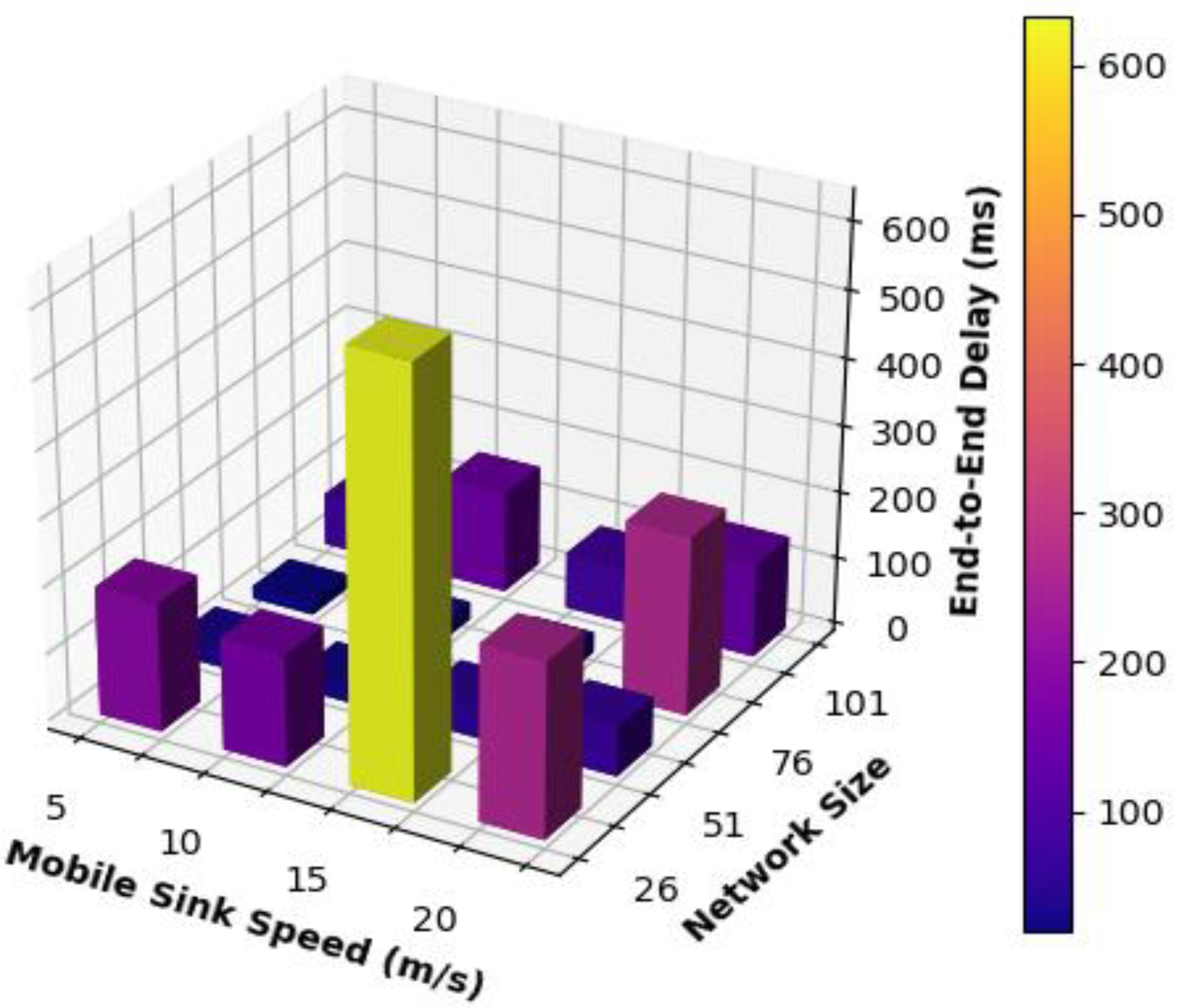
Figure 3 displays the average end-to-end delay results for various network sizes and mobile sink movement speeds. Network networks with 51 and 76 nodes achieved the best overall results regarding the end-to-end delay, especially when the mobile sink speed was equal to 5, 10, and 15 m/s. The reason behind such behavior is that these speeds are considered as low or moderate speeds of the mobile sink, which results in extensive multi-hop communication through long routes, which is the primary factor affecting the end-to-end delay results obtained for this case.
For other networks sizes, it can be seen that the proposed mobility model obtained low and consistent end-to-end delay results, especially when increasing the speed of the mobile sink to be equal to 5, 10, and 15 m/s which can be regarding the frequent use of single-hop communication because the mobile sink is moving at moderate speeds and visits static sensor nodes frequently. The network consisting of 26 nodes was an exception when the mobile sink speed was increased to 15 m/s. As it is clear from
Figure 3, the performance of this network increased dramatically because the network size is small and the speed of the mobile sink is relatively high, which may cause frequent changes and updates to the routing paths. Thus, multi-hop communication is used more frequently, and packets must go through extra and unnecessary hops to be delivered to the mobile sink.
On the other hand, when increasing the speed of the mobile sink to 20 m/s, these networks obtained higher end-to-end delay results because 20 m/s is considered a high speed and may cause frequent changes in the routing paths used to convey messages to the mobile sink. As a result, a packet may go through unnecessary hops to be delivered to the mobile sink.
For other network sizes, better results were obtained because the changes in the routing path did not affect all the nodes in the network. Hence, packets did not need to wander around or circulate through the network and go through some unnecessary and replicated intermediate nodes. Consequently, packets went through fewer hops until delivered to the mobile sink. As a result, smaller results for end-to-end delay were obtained.
Furthermore,
Figure 3 shows that networks comprising 26 and 101 nodes obtained the worst performance compared to all other networks. This can be regarded as the frequent use of multi-hop routing for the packets to be delivered to their destination. To put it in another way, the path to be adopted by the mobile sink is relatively short. As a result, the motion of the mobile sink will affect the routing paths for most of the static sensor nodes. Thus, packets sent from static sensor nodes will go through multiple hops, and some of these hops result from the changes or updates to the routing path. Therefore, those packets might have been routed more than once from the same node to adapt to changes in the routing path until they are delivered to the mobile sink.
Furthermore,
Table 2 compares the results obtained for the average end-to-end delay for different network sizes and speeds of the mobile sink. It can be observed that medium-size networks, namely 51 and 76 node networks, performed better than other networks, especially when the mobile sink was moving according to low speed and moderate speeds equal to 5, 10, and 15 m/s. Also, it can be observed that the 51 nodes network obtained more consistent results than those obtained for 76 nodes for all speeds of the mobile sink. As a result, the mobility model proposed in this paper is more suitable for use with medium-sized networks when we aim to achieve low end-to-end delay.
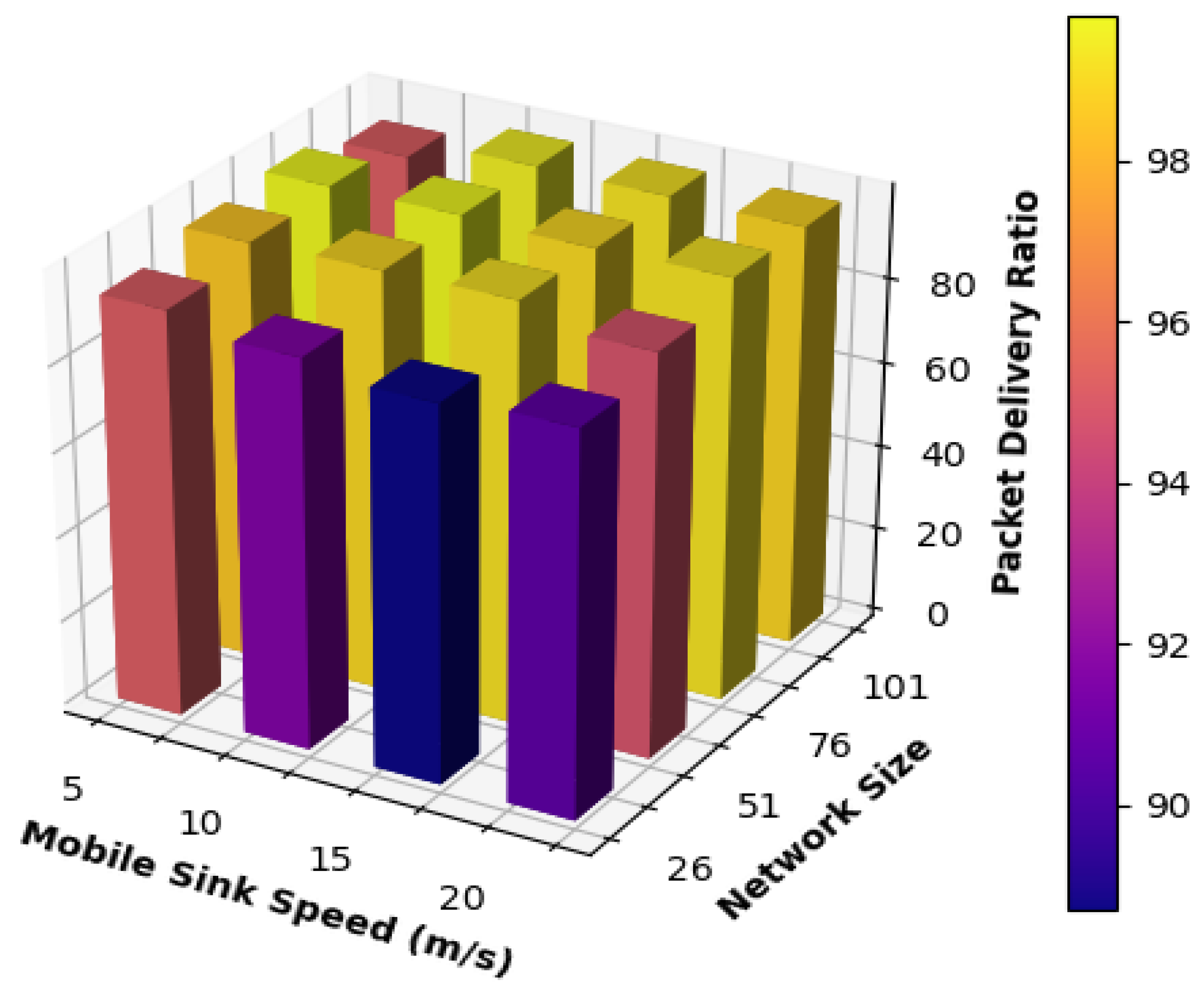
The results acquired for the packet delivery ratio are shown in
Figure 4. The figure shows that the proposed mobility model obtained highly stable performance under all network sizes. The networks with 51 nodes and 76 nodes achieved the highest performance results regarding packet delivery ratio when the mobile sink speed was equal to 5, 10, and 15 m/s, consistent with the results from
Figure 4.
To elaborate, since this network acquired the best results for the end-to-end delay, this will result in obtaining the highest results for packet delivery ratio due to the same reason discussed when explaining the results of
Figure 1.(b). Additionally, from
Figure 4, it can be observed that the increase in the velocity of the mobile sink to 20 m/s has affected the performance of all networks and caused a slight decrease in the performance of all networks. Thus, for small network sizes, when moving the mobile sink at high speed, frequent and rapid changes in the routing paths will take place and cause a decrease in performance. Also, the mobile sink will be moving at high speed; completing data transmission between the mobile sink and the static sensor nodes will be challenging.
Also, it can be observed that the performance of the network consisting of 101 kept increasing when the speed of the mobile sink was increased because the higher the speed of the mobile sink, the more frequently static sensor nodes are visited; thus, data can be transmitted to the mobile sink via single hop promptly and static sensor nodes do not suffer from buffer overflow which results from storing sensed information for long periods waiting to get visiting by the mobile sink.
On the other hand, for small network sizes, the mobile sink's anticipated mobility path is smaller than that in medium- and large-sized networks. As a result, increasing the speed of the mobile sink to 20 m/s will affect static sensor nodes and their neighbors. Thus, these nodes will not have enough time to deliver packets to the mobile sink, and packets must be routed via multi-hop routing to be delivered to the destination. Also, packets will go through unnecessary and extra hops to adapt to the frequent changes in the routing path to be delivered to the mobile sink.
Table 3 summarizes the result obtained for packet delivery ratio and compares the results achieved by each network using different mobile sink speeds. The table shows that all networks achieved high-performance results in terms of packet delivery ratio except the network consisting of 26 nodes.
Table 3 shows that 26 nodes' network performance was lower than the performance of all other networks for all the different speeds used for the mobile sink. As a result, it can be concluded that all the speeds used for the mobile sink caused frequent updates to the routing paths. Thus, packets kept circulating in the network until they got dropped. This case was made even worse when the movement speed of the mobile sink was increased because the static sensor nodes did not have enough time to communicate with the mobile sink and deliver their packets using single-hop communication.
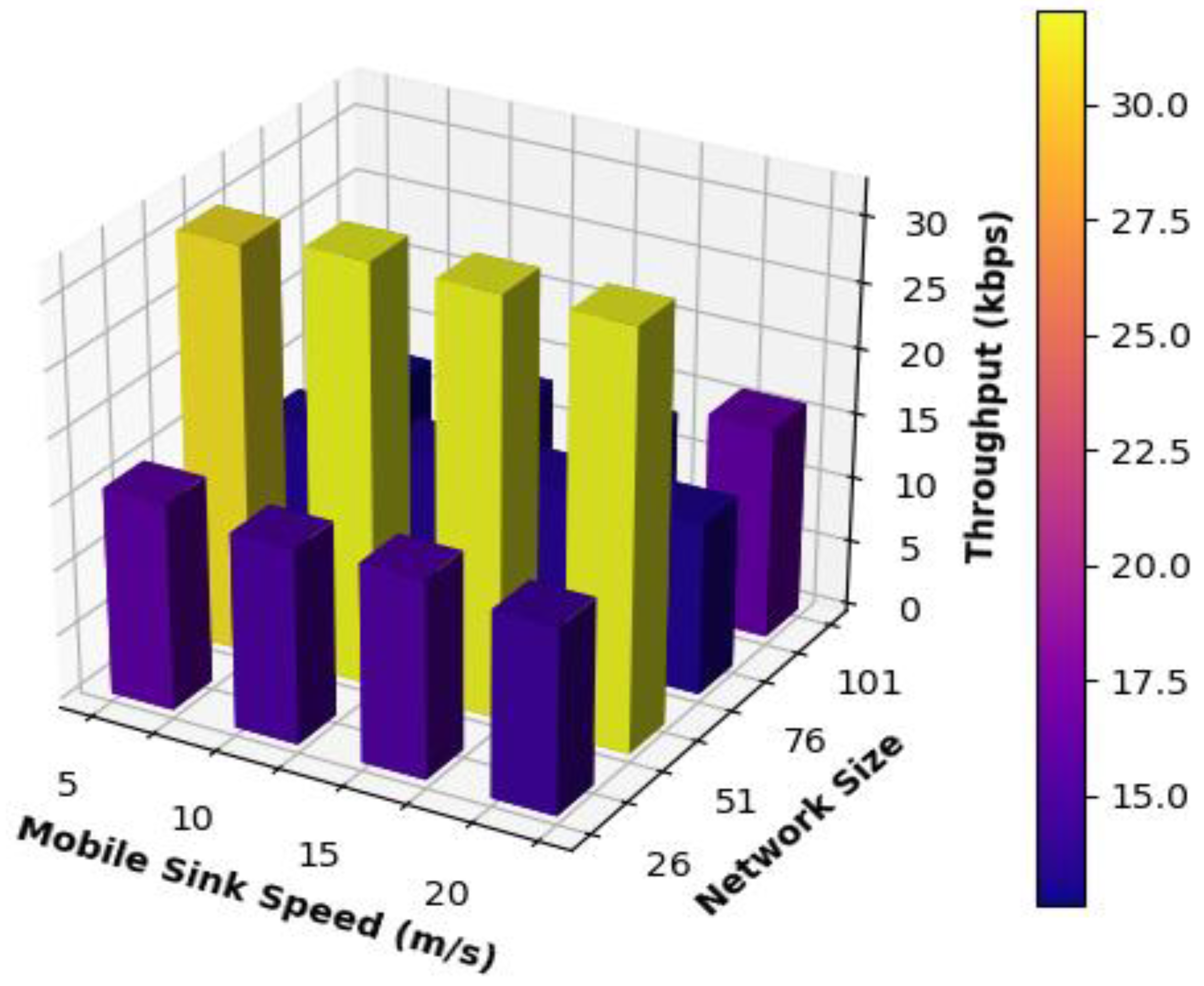
Figure 5 shows the results obtained for network throughput when the mobile sink moved following the suggested mobility model at various speeds and with varying network sizes.
From
Figure 5, it can be seen that the proposed mobility obtained high and stable results for all network sizes under the speed of 10 and 15 m/s of the mobile sink because the mobile sink is moving at moderate speeds, which reduced the number of updates and the changes that may occur to the routing paths. Additionally, static sensor nodes will have a reasonable amount of time to communicate with the mobile sink and deliver data successfully. The performance of the network consisting of 51 nodes was the best and the most stable in all cases because the length of the routing paths was moderate; as a result, the packet did not have to go through many hops to be delivered. Also, the length of the movement path adopted by the mobile sink was moderate; as a result, static sensor nodes did not need to update their routing tables frequently; as a result, higher performance results were achieved.
For all other cases of mobile sink speeds, the performance of different network sizes was almost stable but was lower than that of 51 nodes networks. This can be regarded as one of two reasons; First, the speed at which the mobile sink moves may not be suitable for the size of the network. Say it in another way; high speeds may not be suitable for small networks, and low speeds may not be suitable for large networks because the network may get congested, and packets get dropped. Second, for large networks routing and low speeds, the routing paths may be very long, which might cause congestion in some parts of the network and results in dropping packet. On the contrary, small networks operating under high speeds of the mobile sink packet may get dropped because of frequent changes in the topology and the routing paths, which results in consuming a large amount of the bandwidth to update the paths, affecting the network performance and increases the number of dropped packets. Additionally, many packets may go through unnecessary hops to be delivered. Thus, the time to live timer or counter of the packet expires. As a result, it gets dropped.
Table 4 summarizes the results obtained for the network throughput and compares the results achieved by each network using different mobile sink speeds. From
Table 4, it is clear that the network consisting of 51 nodes outperformed all other networks under all the different speeds used for the mobile sink. Consequently, for all other networks, using the different speeds of the mobile sink may have caused frequent updates to the routing paths, or the movement path adopted by the mobile sink was very long. As a result, static sensor nodes may have suffered from buffer overflow, and packets were dropped, affecting these networks' performance.
7. Conclusions
A sink mobility model that is built on creating a bipartite graph of the current network was presented in this paper. Then, the proposed mobility model was addressed after the concept of a bipartite graph was introduced. Additionally, the NS-2 simulator was adopted to run several scenarios to examine the performance and effectiveness of the mobility model presented in this research. Furthermore, the end-to-end delay, packet delivery ratio, and throughput were used to analyze the performance of the mobility model. Because the network with 51 nodes offered stable and respectable performance, the results demonstrate that the proposed mobility model performed better and is appropriate for use in medium-sized networks with moderate mobile sink speeds. Future research can expand on the work provided in this paper to measure additional performance indicators like energy efficiency, routing overhead, and jitters. Additionally, the effectiveness of the suggested mobility model can be investigated when employing routing protocols other than AODV.
References
- Al-Rahayfeh A, Razaque A, Jararweh Y, Almiani M. Location-Based Lattice Mobility Model for Wireless Sensor Networks. Sensors (Basel) 2018, 18, 4096. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivasan, J. Wu, Track: A novel connected dominating set based sink mobility model for wsns, in 2008 Proceedings of 17th International Conference on Computer Communications and Networks, IEEE, 2008, pp. 1–8.
- X. Sun, Y. Yang, M. Ma, Minimum connected dominating set algorithms for ad hoc sensor networks. Sensors 2019, 19, 1919. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sikora, E. Niewiadomska-Szynkiewicz, Mobility model for self-configuring mobile sensor network, in The Fifth International Conference on Sensor Technologies and Applications, SENSORCOMM, Vol. 11, 2011, pp. 97–102.
- Sardouk, R. Rahim-Amoud, L. Merghem-Boulahia, D. Ga¨ıti, Data aggregation scheme for a multi-application wsn, in IFIP/IEEE International Conference on Management of Multimedia Networks and Services, Springer, 2009, pp.183–188.
- Razaque, A.; Elleithy, K.M. Energy-Efficient Boarder Node Medium Access Control Protocol for Wireless Sensor Networks. Sensors 2014, 14, 5074–5117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Akyildiz, I.F. Effects of different mobility models on traffic patterns in wireless sensor networks. In Proceedings of the Global Telecommunications Conference (GLOBECOM 2010), Miami, FL, USA, 6–10 December 2010; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, J.; Liu, M.; Noble, B. Random waypoint considered harmful. In Proceedings of the INFOCOM 2003 Twenty-Second Annual Joint Conference of the IEEE Computer and Communications, San Francisco, CA, USA, 30 March–3 April 2003; pp. 1312–1321. [Google Scholar]
- Salvatore, J. Bipartite graphs and problem-solving. The University of Chicago. 2007 Aug 8:8.
- Navidi, W.; Camp, T. Stationary distributions for the random waypoint mobility model. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2004, 3, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premi, M.G.; Shaji, K. Impact of Mobility Models on MMS Routing in Wireless Sensor Networks. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2011, 22, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabour, F.C.; Giancoli, E.; Pedroza, A. Mobility support for wireless sensor networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer and Electrical Engineering, Phuket, Thailand, 6–10 July 2008; pp. 630–634. [Google Scholar]
- Premi, M.G.; Shaji, K. Impact of Mobility Models on MMS Routing in Wireless Sensor Networks. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2011, 22, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabour, F.C.; Giancoli, E.; Pedroza, A. Mobility support for wireless sensor networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer and Electrical Engineering, Phuket, Thailand, 6–10 July 2008; pp. 630–634. [Google Scholar]
- Camp, T.; Boleng, J.; Davies, V. A survey of mobility models for ad hoc network research. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2002, 2, 483–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A. Taleb, A comparative study of mobility models for wireless sensor networks, J. Comput. Sci. 2018, 14, 1279–292. [CrossRef]
- S. Aslam, F. Farooq, S. Sarwar, Power consumption in wireless sensor networks, in Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Frontiers of Information Technology, 2009, pp. 1–9.
- M. Al-Razgan, T. Alfakih, Wireless sensor network architecture based on mobile edge computing, Security and Communication Networks 2022.
- Z. N. Jwair, M. A. Abdlhusein, Some dominating results of the topological graph, International Journal of Nonlinear Analysis and Applications.
- N. Temene, C. Sergiou, C. Georgiou, V. Vassiliou, A survey on mobility in wireless sensor networks. Ad Hoc Networks 2022, 125, 102726. [CrossRef]
- J.-Y. Chang, J.-T. Jeng, Y.-H. Sheu, Z. Jian, W.-Y. Chang, et al., An efficient data collection path planning scheme for wireless sensor networks with mobile sinks, EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking 2020 (1) (2020) 1–23.
- A. Taleb, Sink mobility model for wireless sensor networks using Kohonen self-organizing map. Int. J. Commun. Netw. Inf. Secur. 2021, 13, 62–67.
- Y. Guo, Z. Xu, J. Saleh, Collaborative allocation and optimization of path planning for static and mobile sensors in hybrid sensor networks for environment monitoring and anomaly search, Sensors 2021, 21, 7867. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasanth, S. Pavalarajan, Zone-based sink mobility in wireless sensor networks. Sensor Review 2019, 39, 874–880. [Google Scholar]
- S. YALC¸IN, E. ERDEM, Performance analysis of burst traffic awareness-based mobile sink routing technique for wireless sensor networks. Gazi University Journal of Science 35, 506–522. [CrossRef]
- X. Wu, Z. Chen, Y. Zhong, H. Zhu, P. Zhang, End-to-end data collection strategy using the mobile sink in wireless sensor networks. Int. J. Distrib. Sens. Netw. 2022, 18, 15501329221077932.
- Abu Taleb, Sink mobility model for wireless sensor networks using genetic algorithm, J. Theor. Appl. Inf. Technol. 2021, 99, 540–551.
- Alsaafin, A. M. Khedr, Z. Al Aghbari, Distributed trajectory design for data gathering using the mobile sink in wireless sensor networks. AEU-Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2018, 96, 1–12. [CrossRef]
- M. Naghibi, H. Barati, Egrpm: Energy efficient geographic routing protocol based on the mobile sink in wireless sensor networks. Sustain. Comput. : Inform. Syst. 2020, 25, 100377.
- M. Amnai, Y. Fakhri, J. Abouchabaka, et al., Impact of mobility on delay-throughput performance in multi-service mobile ad-hoc networks. Int’l J. Commun. Netw. Syst. Sci. 2011, 4, 395.
- M. Karyakarte, A. Tavildar, R. Khanna, Effect of mobility models on the performance of mobile wireless sensor networks. Int J Comput Netw Wirel Mob Commun (IJCNWMC) 2013, 3, 137–148.
- L. Guezouli, K. Barka, S. Bouam, A. Zidani, Implementation and optimization of rwp mobility model in wsns under tossing simulator, Int. J. Commun. Netw. Inf. Secur. 2017, 9, 1.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).