1. Introduction
Atmospheric ice particles, which generally appearing in cirrus clouds, are an important component in atmospheric research such as remote sensing and radiation transfer. They are observed at altitudes of 7-10 km with hexagonal shape and size of 10-1000 µm in general. The density of particles in cirrus clouds is low in comparison with other types of clouds, but they have hardly predictable scattering properties because of the specific geometry of particles. These properties are actively studied within international projects and different methods are used: in-situ aircraft measurements, remote sensing from ground and space, etc. A huge amount of work has been done to study the properties of clouds, at the same time, many features of the light scattering problem for ice particles are still poorly studied [
1,
2,
3,
4,
5,
6,
7,
8,
9,
10,
11,
12,
13,
14].
There are direct and remote methods for studying cirrus clouds. Direct measurements include contact measurements from aircraft [
15], remote studies include monitoring of the atmosphere by lidar networks and photometers. Since direct methods are limited in time and financial resources, in practice, remote methods are more useful. For interpretation of lidar data, it is necessary to solve the inverse problem of light scattering for monochromatic laser radiation. However, one needs a database of light scattering matrices and corresponding microphysical properties of cloud particles [
15,
16,
17,
18,
19,
20,
21]. For solving this problem numerical methods are usually used [
22,
23,
24,
25,
26,
27].
Cirrus cloud particles can be distinguished by microphysical structure in two types: single particles (hexagonal columns, plates, bullet etc.) and aggregates consisting of several particles. According to data of in-situ measurements atmospheric ice aggregates take a significant part of particles in cirrus clouds [
28,
29]. However, the proper information about their scattering properties are absent in existed databases. In general crystals in clouds are arbitrarily oriented. And it is expected that light scattering of aggregates consisting of the same crystals and light scattering of single crystal are similar in particular cloud. In this case, it is possible to calculate the light scattering matrix for aggregates using dependency of light scattering matrix elements on number of particles in aggregates. But if particles in aggregate are compactly packed then the direction of scattering light might be changed. And the distribution of light from a single particle might be different from distribution for an aggregate.
The purpose of the research is to define the dependency of scattering matrix elements on number and arrangement of particles in aggregate.
2. Materials and Methods
For calculation of the light scattering matrix we use the physical optics approximation method [
30]. This method is the most applicable for this problem because of capability of calculation of particle parameter size
x > 10 and precise results in the backscattering direction [
31]. Also, it was used for solving problems related with remote sensing of atmospheric ice crystals [
32,
33]. In this method particle consist of facets with multiple vertices. The method based on the Beam-splitting algorithm [
34] that reminds the Ray-tracing algorithm [
35] but it works with plane-parallel optical beams. In this algorithm the particle, which scattered light, consists of facets. These facets consist of vertices with three-dimensional coordinates. The algorithm splits light, which incident on facets, into beams. These beams propagate in the particle and could be dividing into refracted and reflected beams multiple times before they left the particle and scattered by their cross-section frame.
The physical optics method calculates scattering field in near zone within the geometrical optics approximation and in far zone within both the geometrical and the physical optics approximation. But calculation of diffraction for each scattered beam is very expensive operation, especially for the case of random oriented particles in a cloud. Most of all the calculation time of the physical optics method increases with the number of facets in the particle. That is why first-order we calculated the light scattering matrix for aggregates within the geometrical optics approximation.
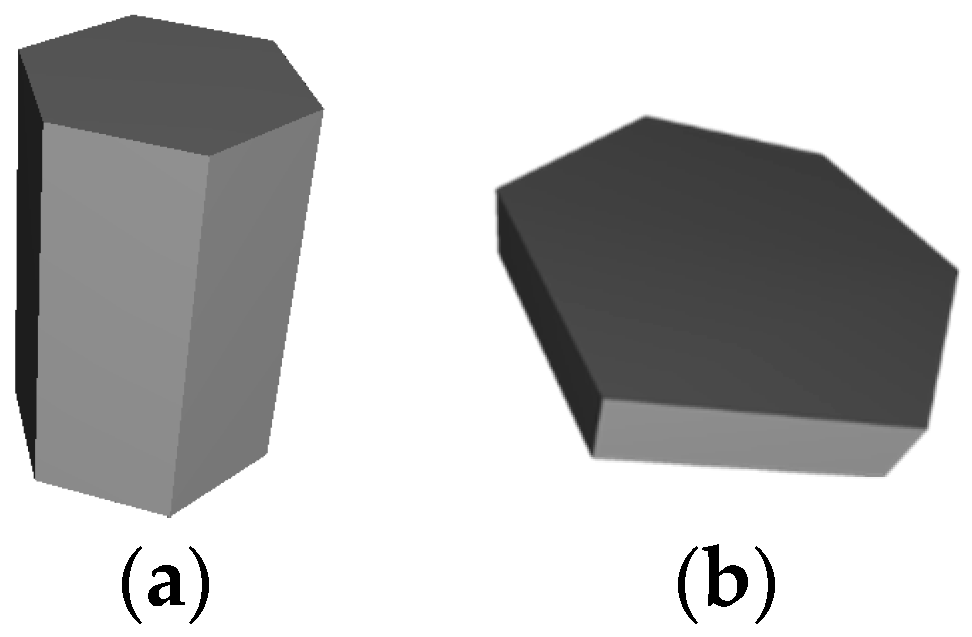
By aggregate we mean the object consisting of several particles, which are attached to each other at one or several points. Positions of these particles are fixed, but when spatial orientation of aggregate is changed all particles change their position simultaneously. In this work we use regular shapes of crystals for cirrus clouds as the basic particles for aggregates: hexagonal column; hexagonal plate [
36] (see
Figure 1).
Figure 1.
Geometrical shapes of the particles for aggregates: (a) hexagonal column; (b) hexagonal plate.
Figure 1.
Geometrical shapes of the particles for aggregates: (a) hexagonal column; (b) hexagonal plate.
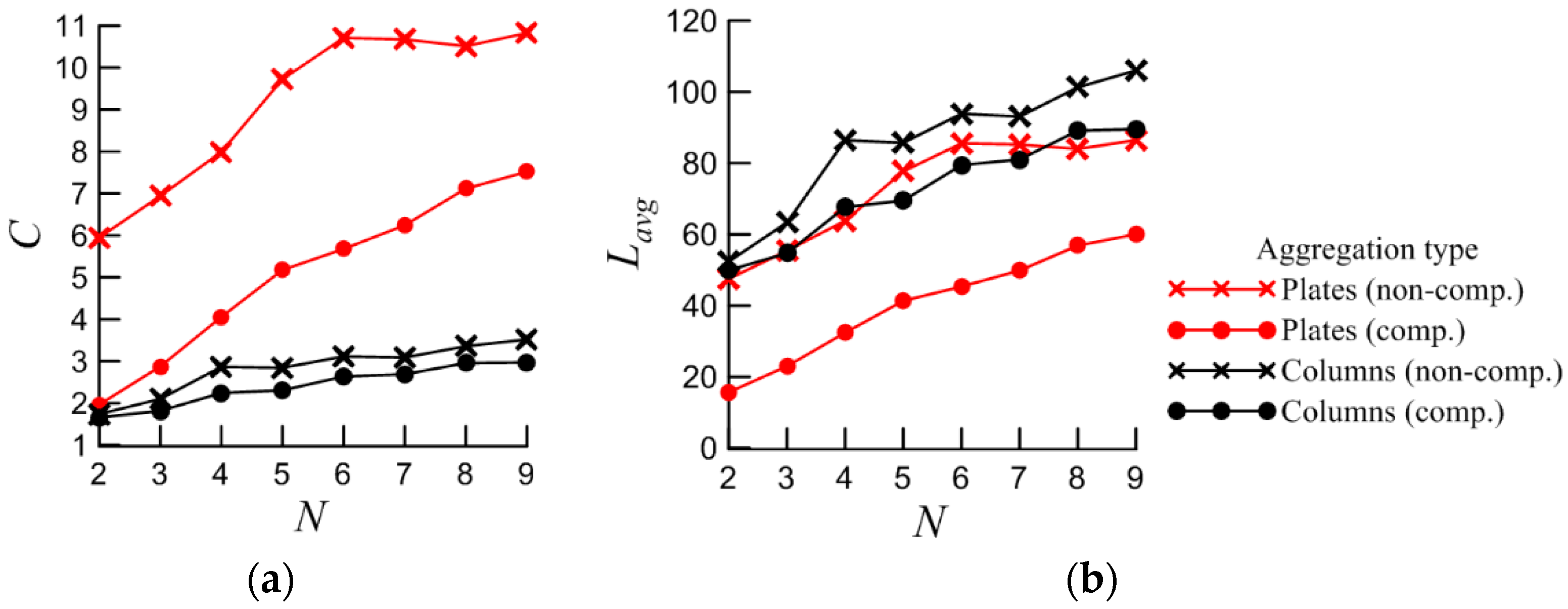
Based on the assumption that compactly packed aggregates change the scattering light direction, two types of particle arrangement in aggregates were chosen: compact and non-compact. To determine the difference between these arrangements, we add the compacity index (
C):
where
Rmin is the radius of the inscribed sphere of the single particle;
Lavg is the average distance between the center of each particle and the center of the aggregate, defined as follows:
where
Li is the distance between the geometrical aggregate’s center and the center of a single particle
i;
N is the number of particles in the aggregate. Coordinates of the center of aggregate and single particle are calculated by sum of the coordinates of all vertices of the aggregate and single particle respectively and dividing it by the number of vertices. Based on equation (1), the most compact aggregate will have
C = 1.
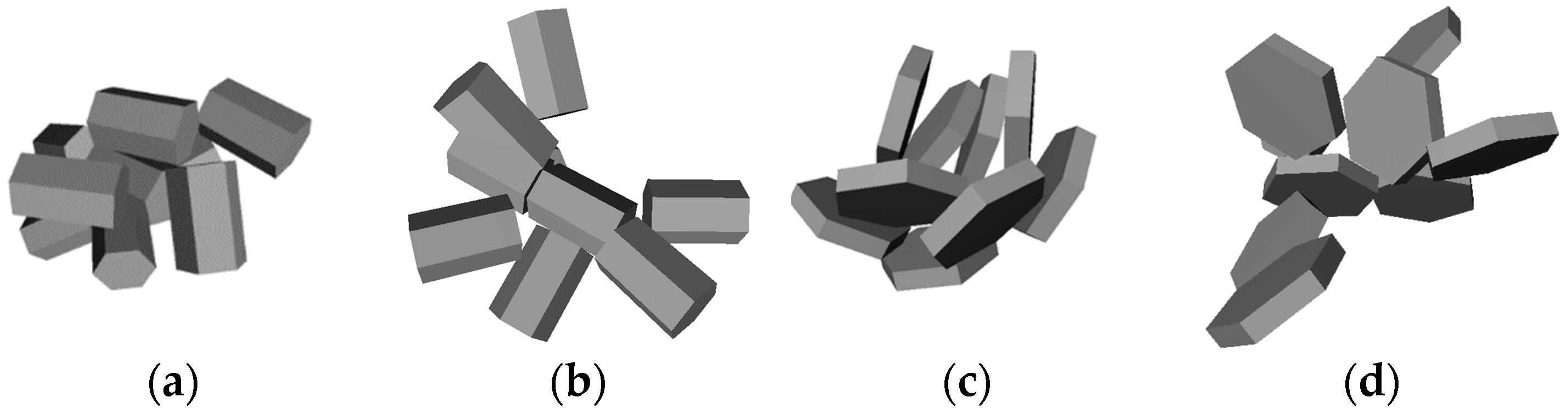
In this work aggregates are created according to the following principle: 9 particles with the same shape, size and coordinates are generated in the center of the coordinate system. It means that they are located inside each other in this stage. Then each particle (except the first one) is rotated by a random angle and moved away from the center in a random direction until the particles were not intersecting each other. The final aggregate consists of 9 particles, which are attached to each other. This procedure was done 100 times for two shapes (see
Figure 1) and 100 aggregates with different arrangement were made. Then the most compact and the most non-compact aggregates were chosen according to equation (1). Finally, we made sets of aggregates with
N from 2 to 9 by removing particles from chosen aggregates one by one. Models of aggregates of 9 particles for each type are shown in
Figure 2. The following dimensions of basic particles were used: for column height 100 µm, base diameter 69.6 µm; plates height 15.97 µm, base diameter 100 µm. The particle geometry corresponds to the model in [
37]. The dependences of the
Lavg and C on
N in the aggregate are shown in the
Figure 3.
Figure 2.
Models of aggregates of 9 particles: (a) compact columns; (b) non-compact columns; (c) compact plates; (d) non-compact plates.
Figure 2.
Models of aggregates of 9 particles: (a) compact columns; (b) non-compact columns; (c) compact plates; (d) non-compact plates.
Figure 3.
(a) Dependency of С on N; (b) Dependency of Lavg on N.
Figure 3.
(a) Dependency of С on N; (b) Dependency of Lavg on N.
3. Calculation results within the geometrical optics approximation
For created aggregates light scattering matrices were calculated for all scattering angles within the geometrical optics approximation at the wavelength 0.532 µm, with the refractive index of particles 1.3116 (ice water) [
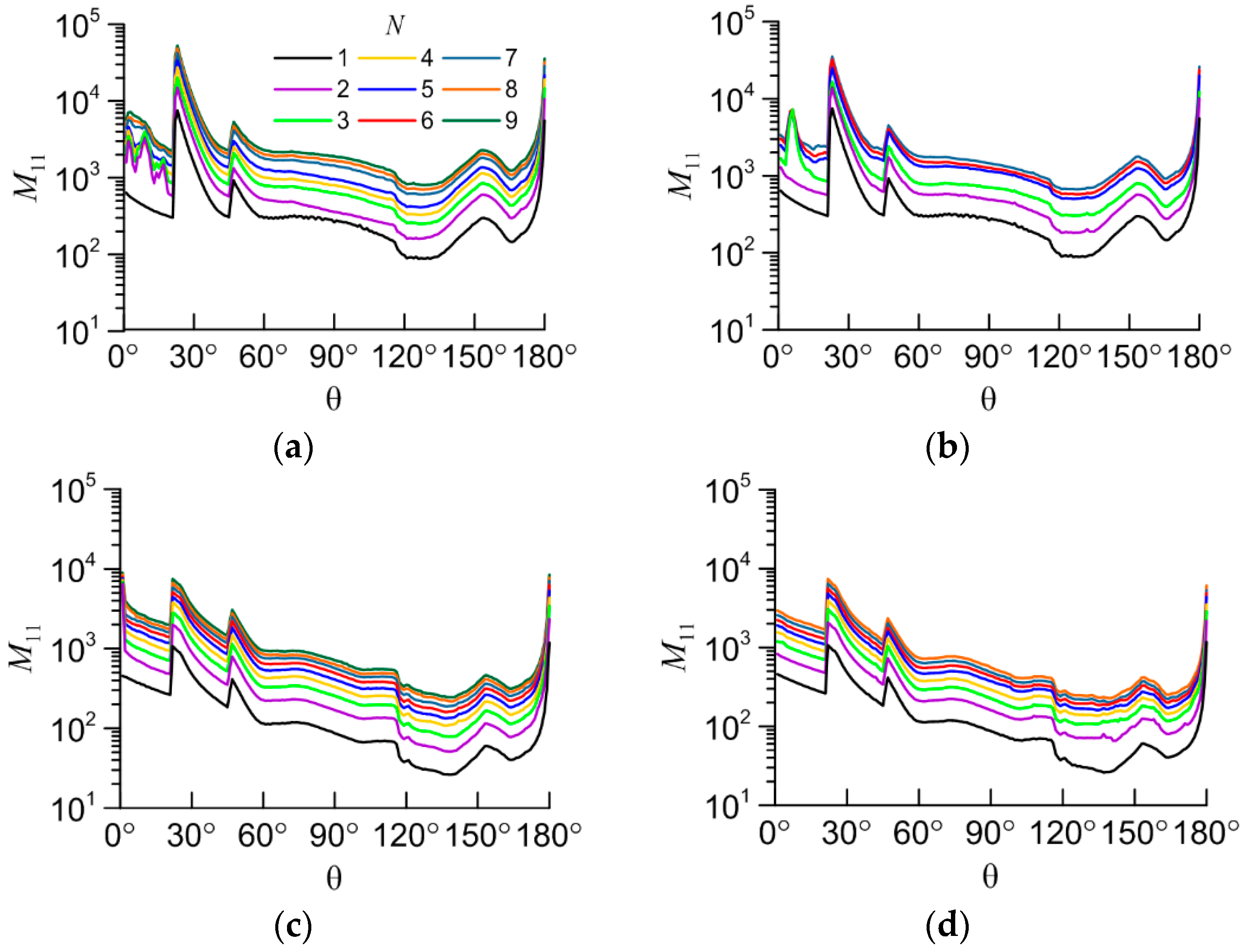
38]. Since aggregates in a cloud assumed to be randomly oriented the calculation was carried out for 1 million orientations for each aggregate. As an example, the
M11 and
M22 elements of the light scattering matrix are shown in
Figure 4 and
Figure 5. The value of
M11 for the scattering angle of 0° is removed from the plots because it is too high to display. The element
M22 is normalized over
M11:
m22=
M22/
M11.
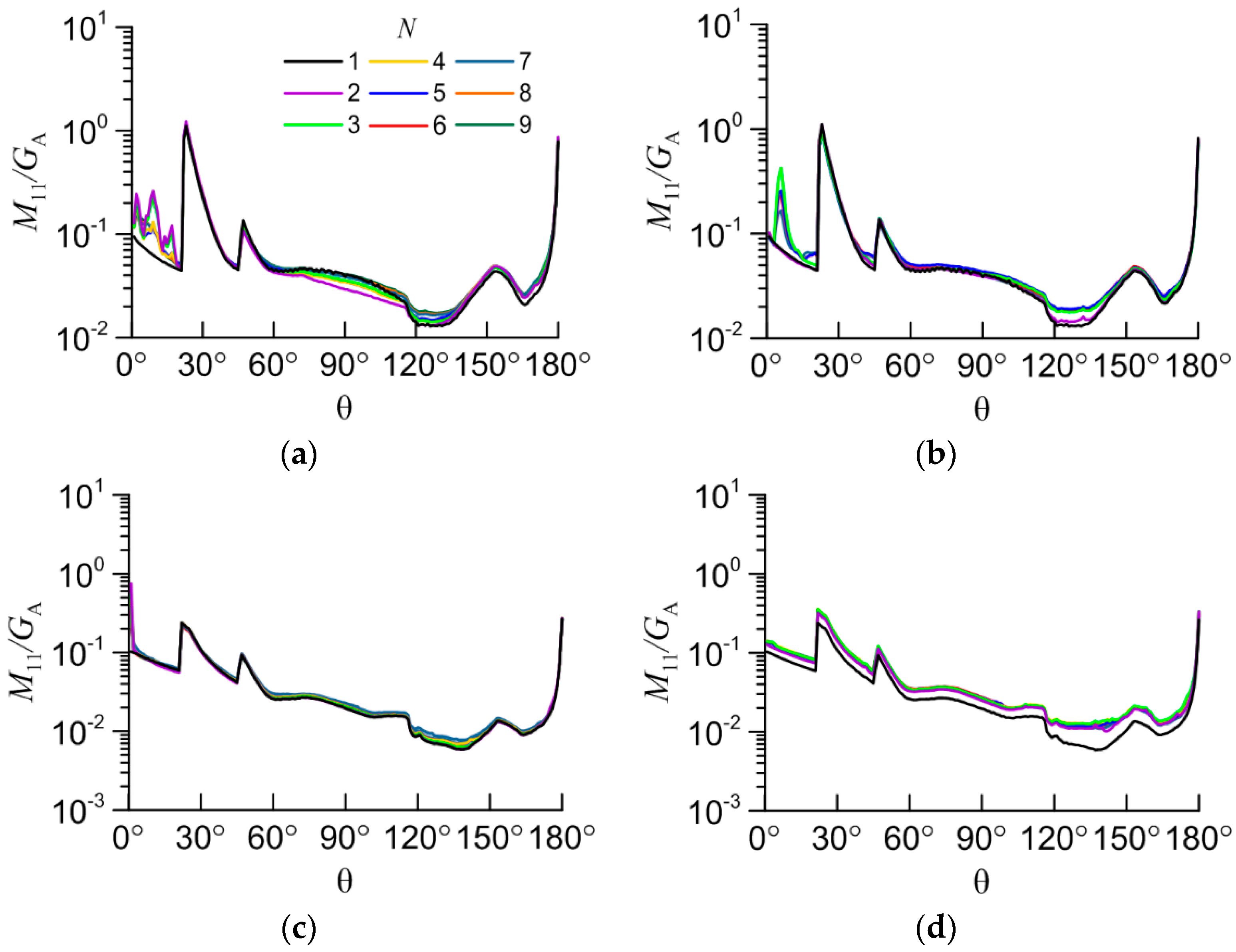
Figure 4.
The M11 element vs scattering angle (θ) for the following aggregates: (a) non-compact columns; (b) compact columns; (c) non-compact plates; (d) compact plates.
Figure 4.
The M11 element vs scattering angle (θ) for the following aggregates: (a) non-compact columns; (b) compact columns; (c) non-compact plates; (d) compact plates.
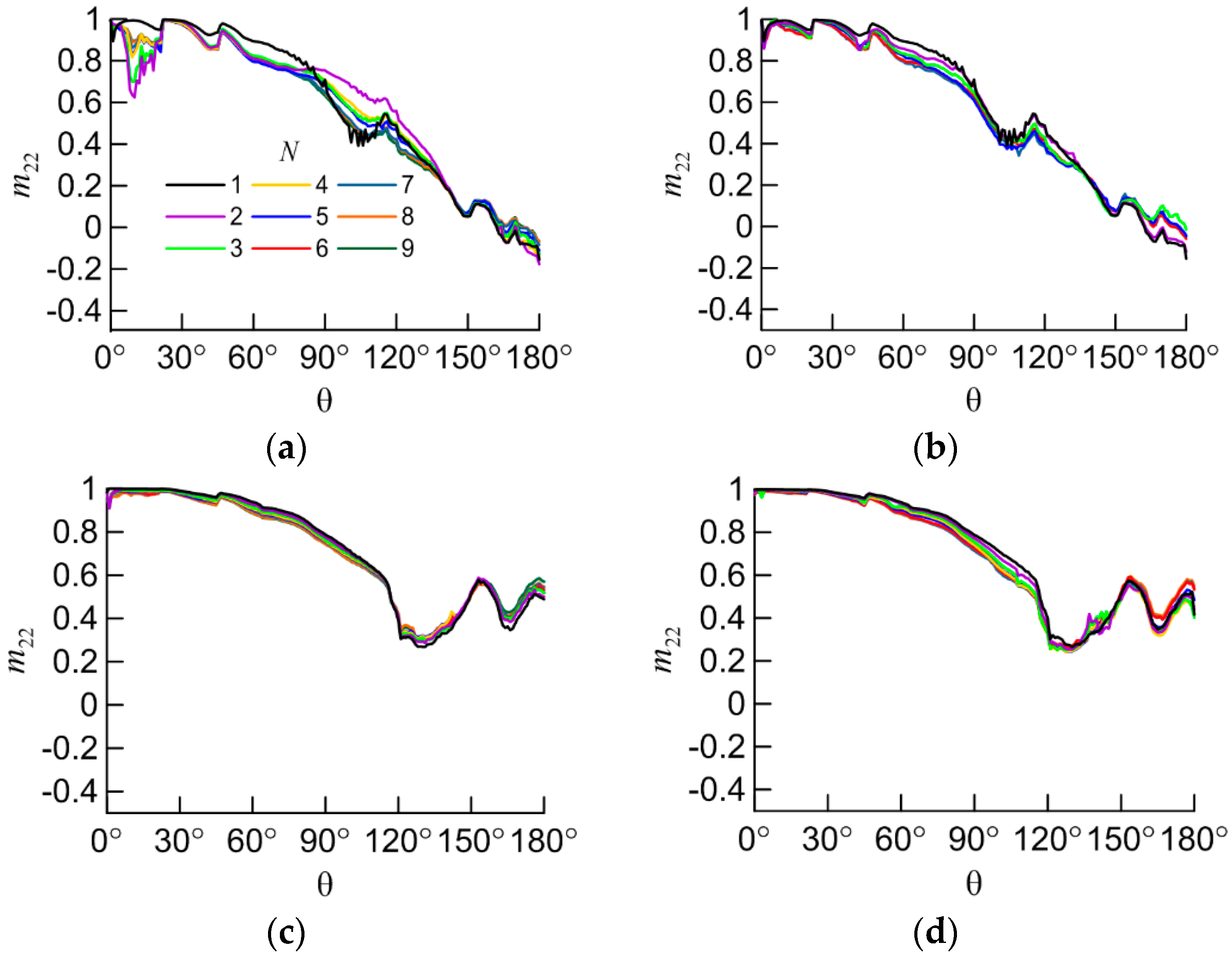
Figure 5.
The m22 element vs scattering angle (θ) for the following aggregates: (a) non-compact columns; (b) compact columns; (c) non-compact plates; (d) compact plates.
Figure 5.
The m22 element vs scattering angle (θ) for the following aggregates: (a) non-compact columns; (b) compact columns; (c) non-compact plates; (d) compact plates.
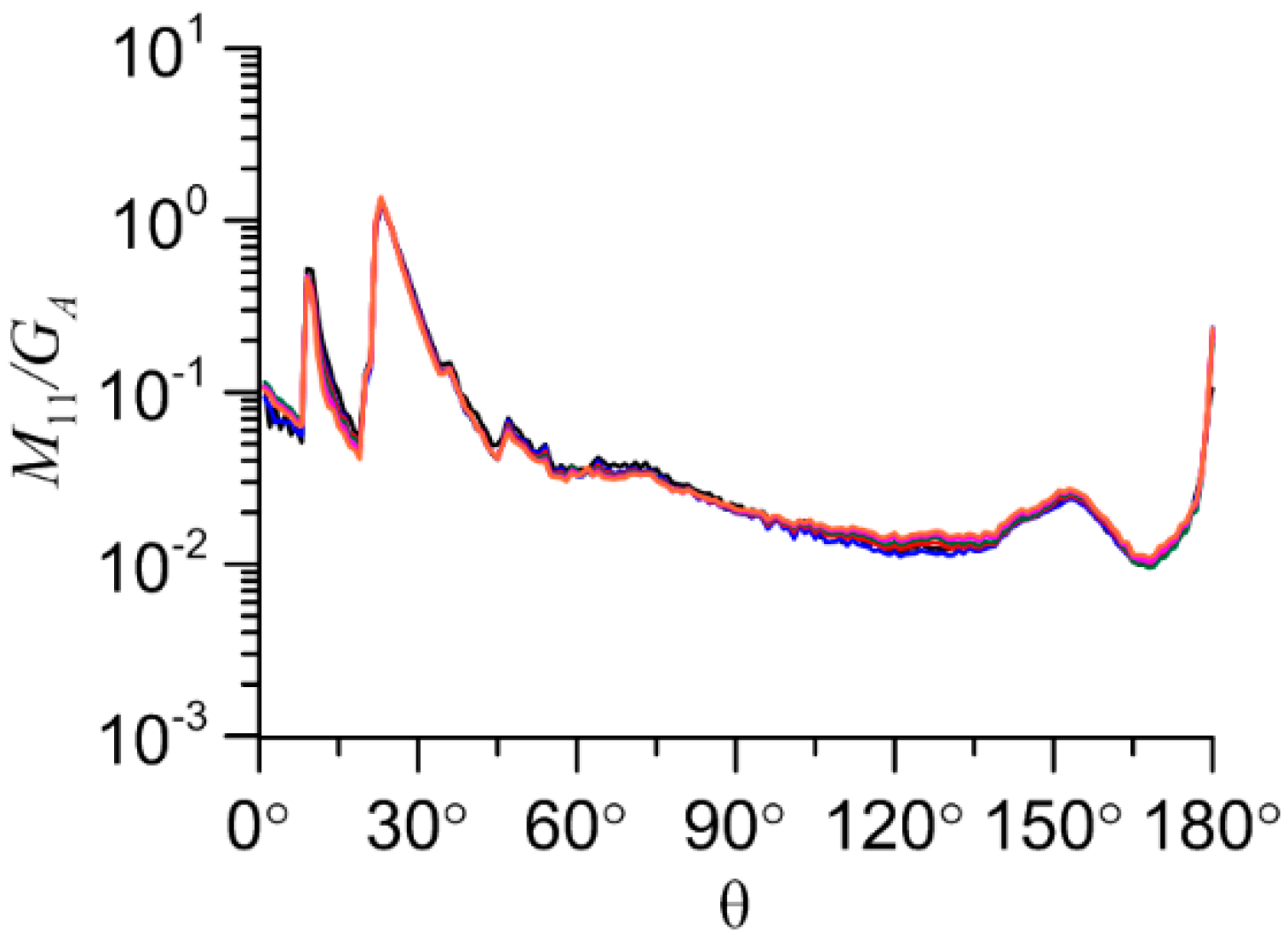
The main interest is the study of the dependency of light scattering matrix elements on the number of particles in the aggregate (N). It is better to start the study with the element M11, which defines the intensity of light in the scattering angle (θ) for unpolarized incident light. Variability of the other elements is not critical.
Because of the fact that the scattering efficiency is equal to 2 within the physical optics approximation, the most informative parameter is the M11 divided by the average geometric shadow area (GA). This area can be calculated using geometry of aggregate without solving of the light scattering problem. The result shows that the M11/GA very slightly changes with number of particles in the aggregate, except the case of aggregate of compact plates.
Figure 6.
M11/GA for the following aggregates: (a) non-compact columns; (b) compact columns; (c) non-compact plates; (d) compact plates.
Figure 6.
M11/GA for the following aggregates: (a) non-compact columns; (b) compact columns; (c) non-compact plates; (d) compact plates.
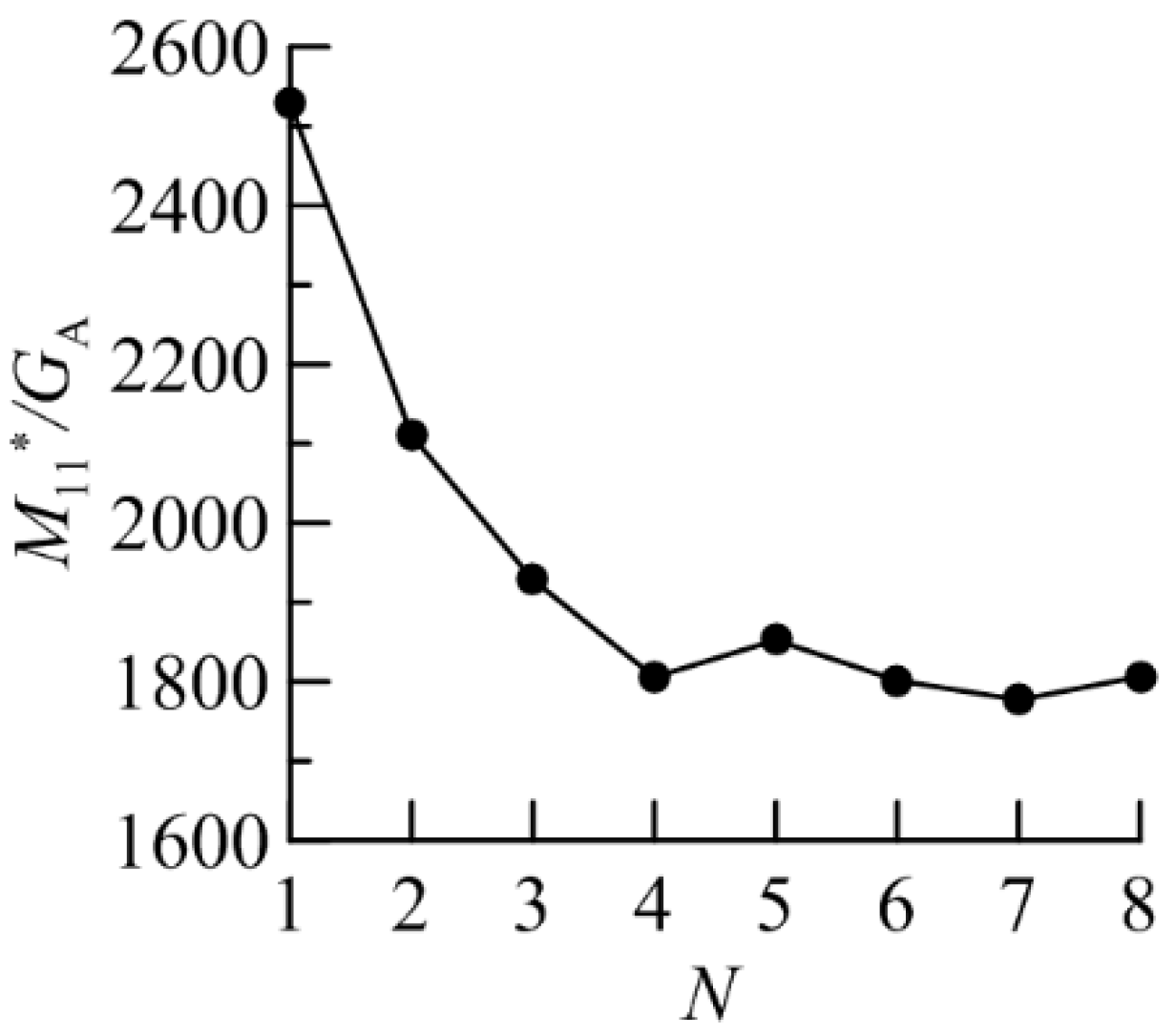
Let us examine the case of compact aggregate of plates (see
Figure 6(d)). For convenience we separately plotted
M11/
GA for forward scattering direction for these aggregates vs
N (
M11*/
GA in
Error! Reference source not found.). In this case the peak of intensity in forward scattering direction is re-scattered by another plate appearing right behind the first one with increasing of number of particles. That peak is created by the forward transmission of light through the large plane-parallel facets of a plate particle. While in case of non-compact aggregate of plates, the particles do not overlap each other, so the light goes freely in the forward scattering direction (see
Figure 8).
Figure 7.
M11*/GA for compact aggregate of plates vs N.
Figure 7.
M11*/GA for compact aggregate of plates vs N.
Figure 8.
Comparison of the compact (a) and non-compact (b) aggregates of three plates.
Figure 8.
Comparison of the compact (a) and non-compact (b) aggregates of three plates.
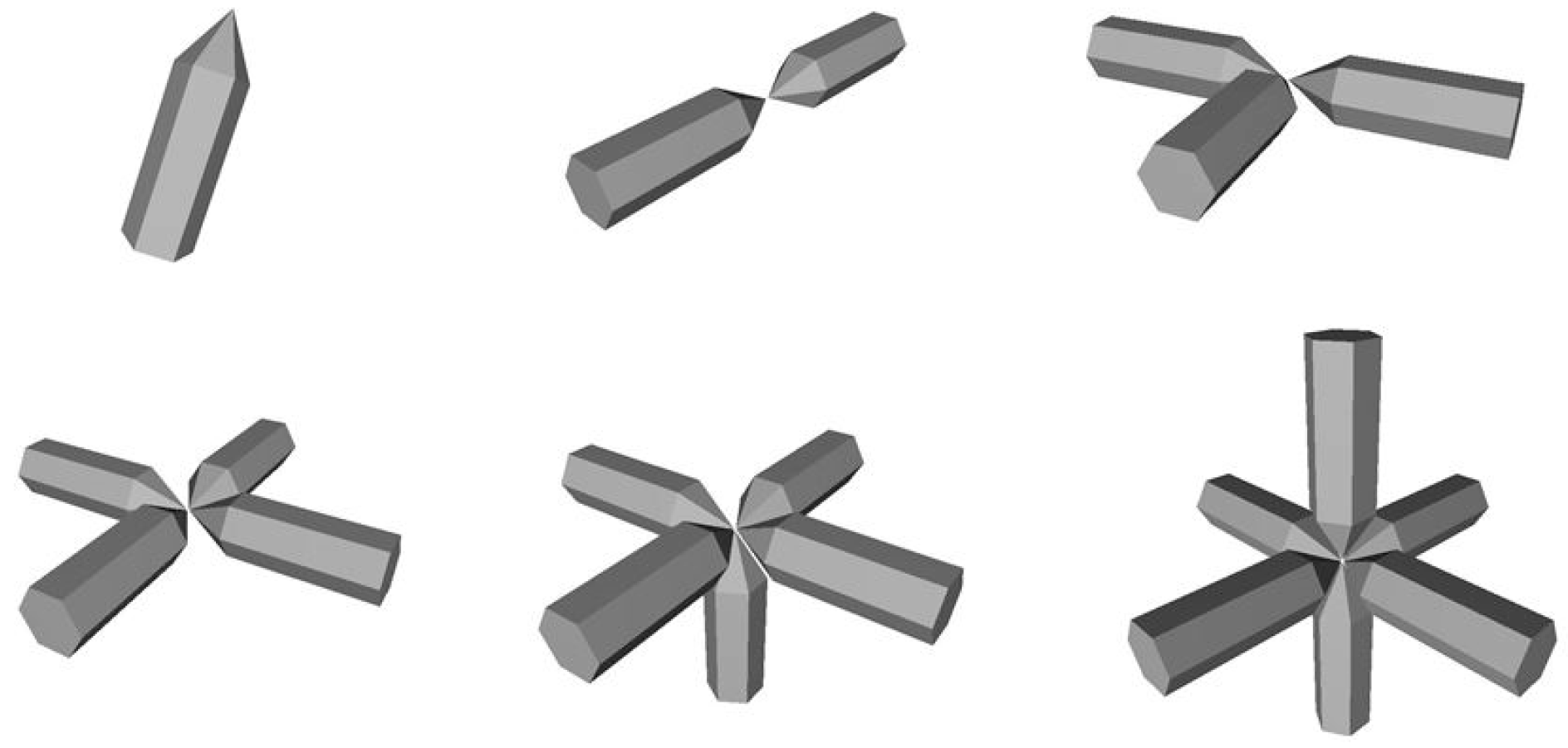
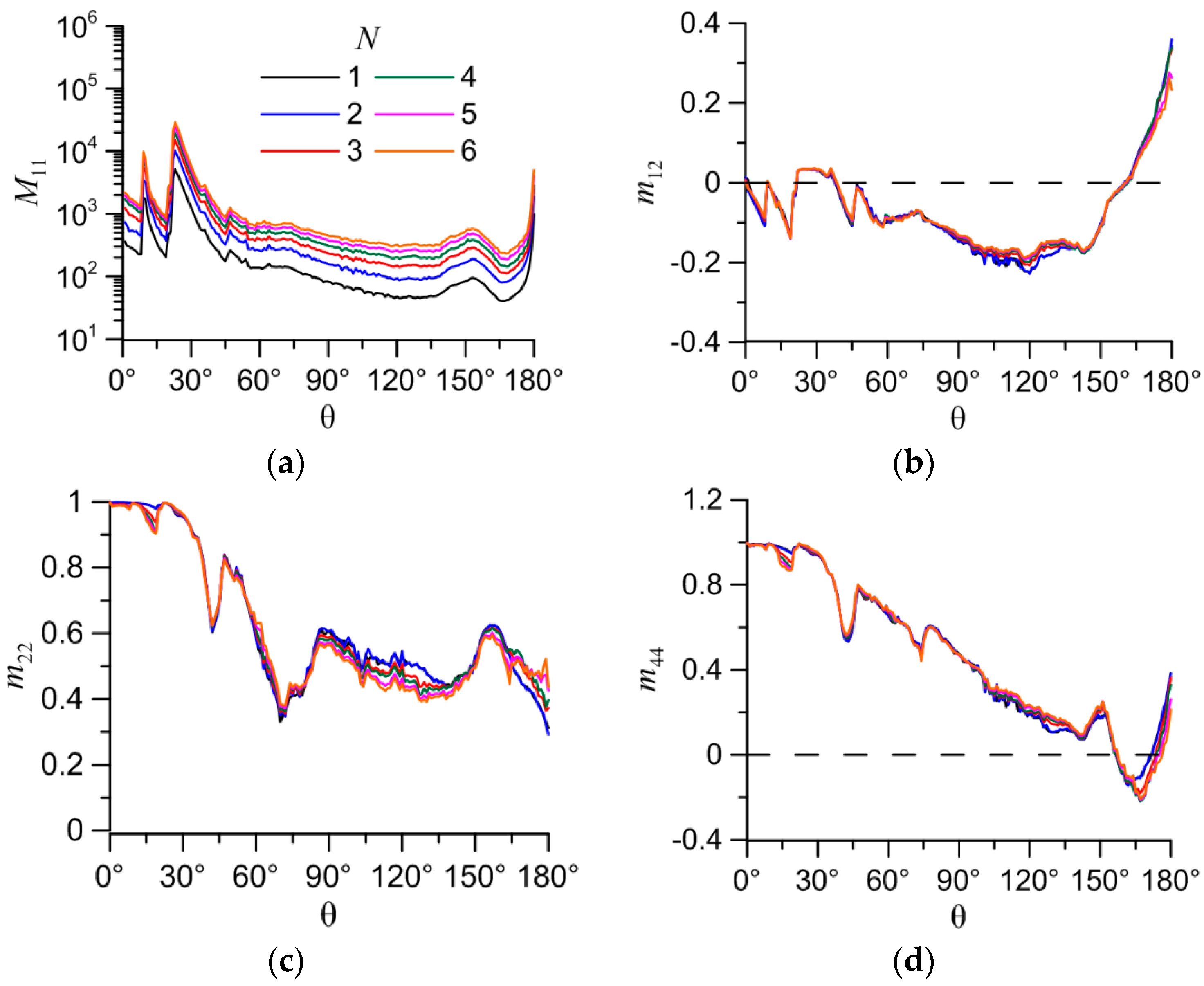
One of the typical non-compact aggregate particles in cirrus clouds is a bullet-rosette. We calculated light scattering matrices for bullet-rosette aggregates with number of bullets from 2 to 6 (
Figure 9). Unlike previous aggregates the arrangement of particles in bullet-rosette remains orthogonal. Calculation parameters were the same as previous. Sizes of every bullet in aggregates: height of hexagonal part is 100 µm; base diameter is 42.035 µm; pike angle is 19.698°. Dependences of elements of the light backscattering matrix on scattering angle (θ) are presented in
Figure 10 and
M11/
GA in
Figure 11. The normalized elements
m12,
m22 and
m44 are also shown in
Figure 11. The results show that the
M11/
GA and normalized elements
m12,
m22 and
m44 almost do not change with number of particles in the bullet-rosette. It means that the optical properties of bullet-rosette can be evaluate from the optical properties of one bullet.
Figure 9.
Models of bullet and bullet-rosette aggregates.
Figure 9.
Models of bullet and bullet-rosette aggregates.
Figure 10.
Dependences of elements of the light backscattering matrix on scattering angle (θ): (a) М11; (b) m12; (c) m22; (d) m44.
Figure 10.
Dependences of elements of the light backscattering matrix on scattering angle (θ): (a) М11; (b) m12; (c) m22; (d) m44.
Figure 11.
M11/
GA for bullet-rosette aggregates (colors are the same as in
Figure 10).
Figure 11.
M11/
GA for bullet-rosette aggregates (colors are the same as in
Figure 10).
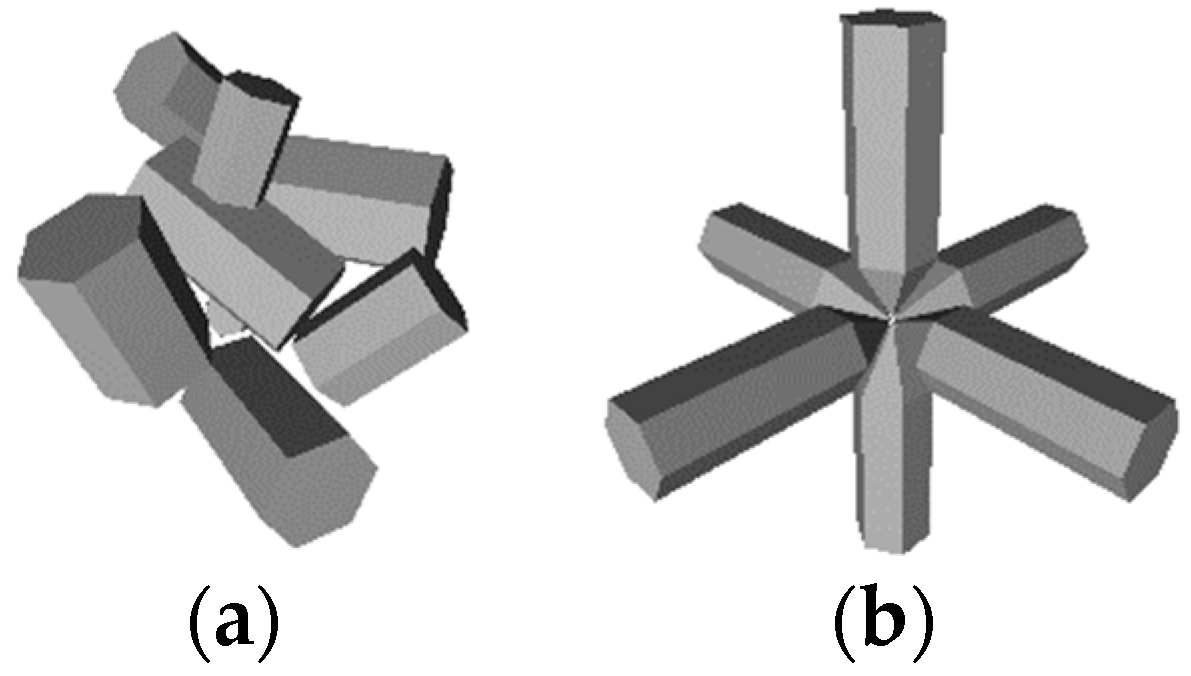
4. Calculation results within the physical optics approximation
For the lidar application only the physical optics solution is of practical interest, because the geometrical optics cannot resolve the backscattering peak of intensity of hexagonal particles. But the physical optics solution is much more demanding on computing resources, so we examine only two aggregates of ice crystals: bullet-rosette and an aggregate of 8 hexagonal columns with different size [
39]. Geometry for these particles is shown in
Figure 12.
Figure 12.
Models of aggregates: (a) aggregate of 8 columns; (b) bullet-rosette.
Figure 12.
Models of aggregates: (a) aggregate of 8 columns; (b) bullet-rosette.
For the aggregate of 8 columns, the width
D and length
L for each hexagonal column are dimensionless quantities; the center of the column in the particle system is denoted by three coordinates (
x0,
y0,
z0). Then they are scaled to obtain a proper dimension for an aggregate in calculation. The orientation of the single hexagonal column is specified by three Euler angles
α 0,
β 0, and
γ 0, where
α 0 defines rotation of the column about the vertical direction;
β 0 is the angle between the vertical direction and the crystal main axis; and
γ 0 describes the column rotation about the main axis. The main axis of the hexagonal column is assumed to pass through the centers of the hexagonal facets. Table 1 lists the values of initial geometric parameters for an aggregate composed of 8 hexagonal columns. Note that these characteristics are slightly different from the characteristics presented in the paper by P. Yang [
39] in order to avoid self-intersections. For convenience we define the aggregate size through its maximal size
Dmax.
Table 1.
Geometric parameters of aggregate of 8 columns.
Table 1.
Geometric parameters of aggregate of 8 columns.
| No. |
D, [μm] |
L, [μm] |
γ 0
|
β 0
|
α 0
|
x0
|
y0
|
z0
|
| 1 |
92 |
158 |
23 |
50 |
-54 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
| 2 |
80 |
124 |
16 |
81 |
156 |
15.808 |
107.189 |
-60.108 |
| 3 |
56 |
78 |
5 |
57 |
94 |
-26.691 |
73.005 |
49 |
| 4 |
96 |
126 |
13 |
76 |
130 |
-88 |
-39.19 |
-11.643 |
| 5 |
106 |
144 |
11 |
29 |
-21 |
106.532 |
33.08 |
27.801 |
| 6 |
38 |
54 |
8 |
62 |
-164 |
35.923 |
-51.5 |
-37.533 |
| 7 |
68 |
102 |
29 |
41 |
60 |
40.11 |
-57.227 |
112.5 |
| 8 |
86 |
138 |
19 |
23 |
-122 |
-9.7524 |
-132.57 |
57.131 |
For calculation within the physical optics approximation the bullet-rosette consists of six bullets with the same size. The bullet shape is defined by the diameter D, the length of the hexagonal part l and the angle of a tip. The angle of a tip is equal to 28° for all sizes. The relationship between the length L and the width D is D = 2.31L0.63. Sizes are given in µm.
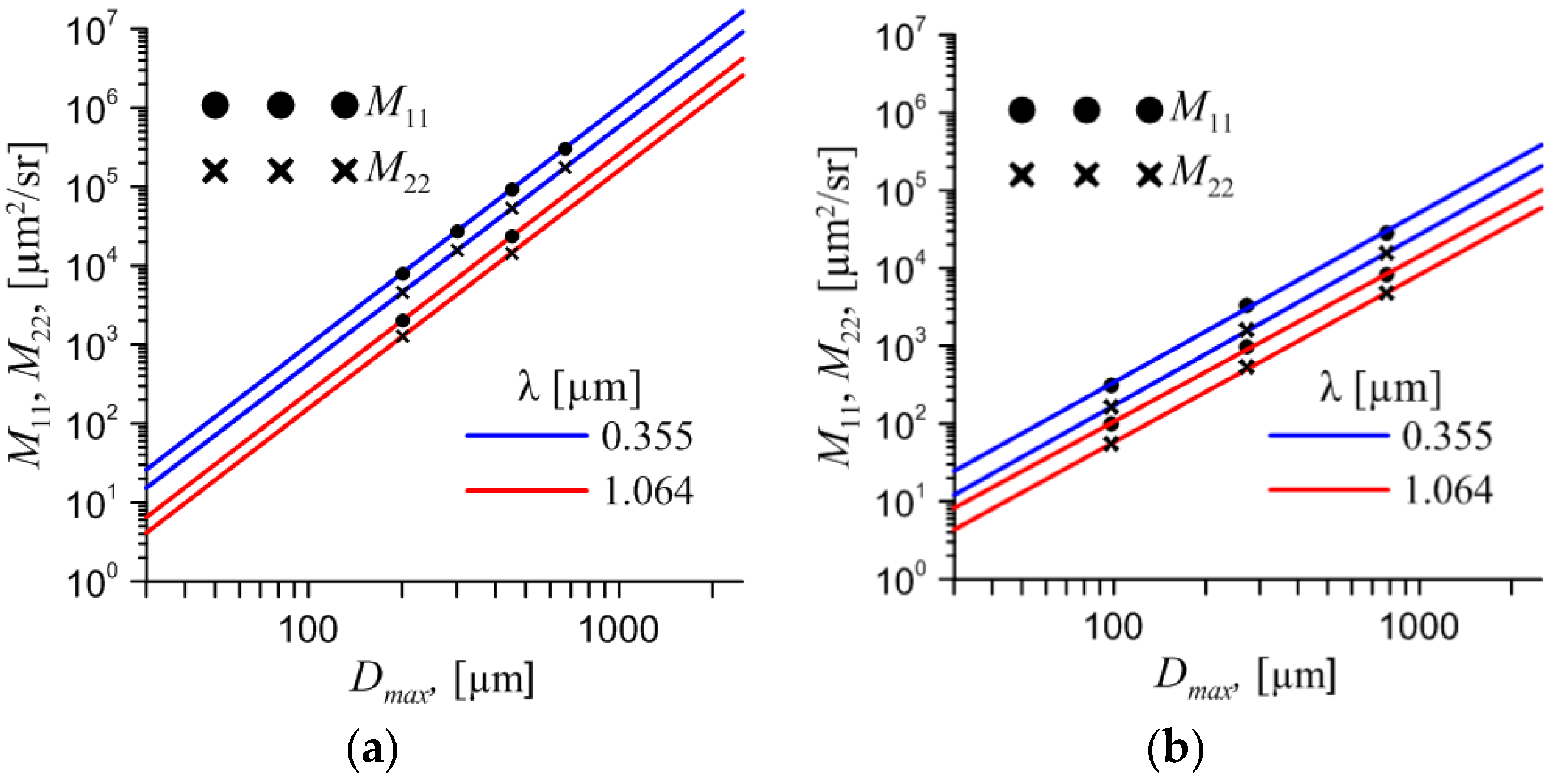
can significantly reduce the calculations time. Since one calculation for aggregate with the maximum dimension Dmax = 670 µm for the wavelengths of 0.355 µm takes about 18 days on the modern server with 2 Xeon E5-2660 v2 processors (40 threads), we precisely calculate only a few of them.
The results are presented in
Figure 13. The precise calculation for aggregate marked as dots, the solid lines correspond to light backscattering matrix of single particle, the dash lines corresponds to evaluation of light backscattering matrix of aggregate. We can see that the light scattering matrix of aggregate can be obtained from the matrix of single particle with good accuracy.
Table 2.
The power laws for the light backscattering matrices (M11).
Table 2.
The power laws for the light backscattering matrices (M11).
| Particle |
|
λ = 0.355 μm |
λ = 1.064 μm |
Aggregate of 8 columns,
|
M11
|
0.00089085∙Dmax3.0224
|
0.00022083∙Dmax3.0248
|
|
M22
|
0.00054933∙Dmax3.0081
|
0.00014407∙Dmax 3.0168
|
|
M11
|
0.0146∙Dmax2.1837
|
0.0058705∙Dmax2.1291
|
|
M22
|
0.0068022∙Dmax2.2009
|
0.0028316∙Dmax2.1554
|
Figure 13.
M11 and M22 vs Dmax at two wavelength of incident light: (a) for aggregate of 8 columns; (b) for bullet-rosette.
Figure 13.
M11 and M22 vs Dmax at two wavelength of incident light: (a) for aggregate of 8 columns; (b) for bullet-rosette.
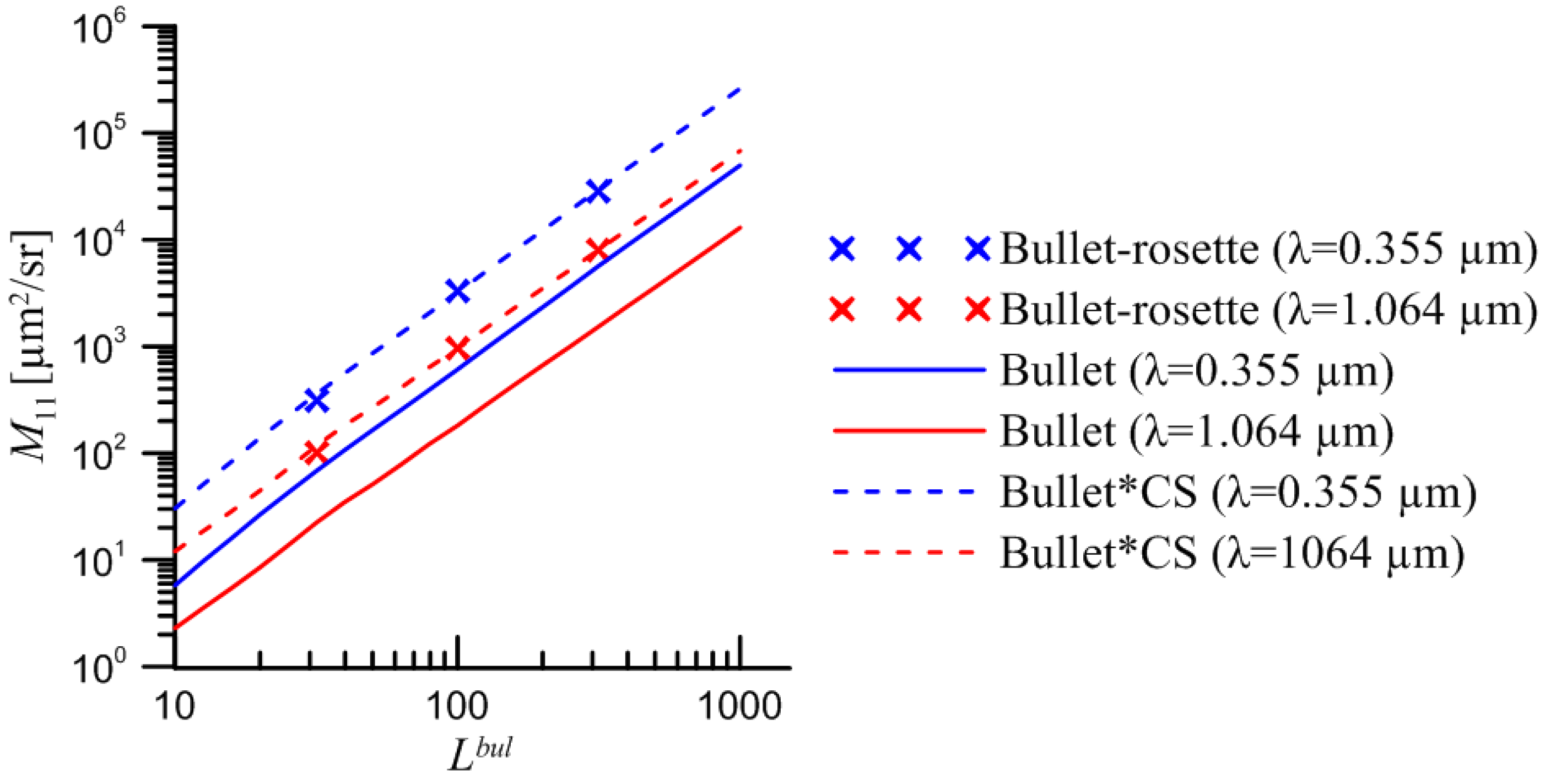
Now it is possible for us to compare
M11 for bullet-rosette (6 bullets) and for single bullet using existed data bank. Since
Dmax for aggregate and for single particle is different we use dependency of
M11 on length of single bullet (
Lbul). Then
M11 for single bullet was multiplied by the total scattering cross-section for bullet-rosette. The result is presented in
Figure 14.
Figure 14.
Dependency of M11 on Lbul for bullet-rosette and for single bullet.
Figure 14.
Dependency of M11 on Lbul for bullet-rosette and for single bullet.
5. Discussion
Light scattering matrices calculations within the geometrical optics approximation for aggregates consisting of hexagonal columns and plates with different arrangement show quasilinear dependences of the first element of the light scattering matrix (
M11) on the number of particles (
N) in the scattering angle range 20°-180° (
Figure 6). The scattering matrix can be obtained by multiplying the scattering efficiency of single particle by geometrical cross-section of an aggregate. As far as the physical optics solution is obtained from the geometrical optics solution, it also should be slightly changed with increasing
N. However, this effect doesn’t work with compactly packed plate aggregates because of specific geometry. It is very important conclusion that allows us to extend the light scattering database of a single particle to the case of aggregates of particles.
Otherwise M11 for column aggregates shows unpredictable distribution at the angles 0°-20°. This fact can be explained by decreasing of energy at the angle of 0° (forward scattering direction intensity peak) and redistribution of it to different directions. This energy peak is caused by light that fall orthogonal to surface of facets and propagates through the particle without refraction. But it can be refracted in case of aggregate of two or more particles when light that goes out one particle is redirected by falling on another particle. In the case of plate aggregates this effect is insignificant because of similar spatial orientation of plate particles in aggregates.
It is important to note that the calculation was carried out for two cases of individual arrangement of particles in the aggregate, and the results cannot predict the exact values of the elements of the light scattering matrix for different aggregates. For example, the distribution of M11 in the angular range of 0°-20° for a column aggregate with a different arrangement may be different. However, the main dependencies are consistent with the initial assumptions. Further studies should consider more examples of aggregates to obtain satisfactory statistics. It is also necessary to calculate the backscattering matrices in the physical optics approximation with the absorption coefficient.
The M11 for bullet-rosette shows more predictable dependency on the number of particles. It can be obtained by multiplying of M11 for single bullet of the same size by the total scattering cross-section for bullet-rosette both within the geometrical and the physical optics approximation.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.T. and A.K.; methodology, D.T., N.K. and A.K.; software, D.T.; validation, N.K. and V.S.; formal analysis, V.S.; investigation, D.T.; resources, V.S.; data curation, V.S.; writing—original draft preparation, D.T.; writing—review and editing, N.K.; visualization, D.T.; supervision, A.K.; project administration, A.K.; funding acquisition, N.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Russian Science Foundation, grant number 21-77-00083, https://rscf.ru/project/21-77-00083/.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the computing time support provided by the IOA SB RAS supercomputer "Felix-C".
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Liou, K.N. Influence of cirrus clouds on the weather and climate process: a global perspective. Mon. Weather Rev. 1986, 114, 1167–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, G.L.; Tsay, S.C.; Stackhouse Jr, P.W.; Flatau, P.J. The relevance of the microphysical and radiative properties of cirrus clouds to climate and climatic feedback. J. Atmos. Sci. 1990, 47, 1742–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takano, Y.; Liou, K.N. Solar radiative transfer in cirrus clouds. Part I. Single scattering and optical properties of hexagonal ice crystals. J. Atmos. Sci. Papers 1989, 46, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassen, K.; Benson, S. A midlatitude cirrus cloud climatology from the Facility for Atmospheric Remote Sensing: II. Microphysical properties derived from lidar depolarization. J. Atmos. Sci. Papers 2001, 58, 2103–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prigarin, S.M. Monte Carlo simulation of the effects caused by multiple scattering of ground-based and spaceborne lidar pulses in clouds. Atmos. Ocean. Opt. 2017, 32, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samoilova, S.V. Simultaneous reconstruction of the complex refractive index and the particle size distribution function from lidar measurements: testing the developed algorithms. Atmos. Ocean. Opt. 2019, 32(6), 628–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, E.; Mace, G.G. Cloud properties and radiative effects of the Asian summer monsoon derived from A-Train data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119(15), 9492–9508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokhanenko, G.P.; Balin, Y.S.; Klemasheva, M.G.; Nasonov, S.V.; Novoselov, M.M.; Penner, I.E.; Samoilova, S.V. Scanning polarization lidar LOSA-M3: opportunity for research of crystalline particle orientation in the ice clouds. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2020, 13, 1113–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marichev, V.N. Combined method for optical sensing of the lower and middle atmosphere. Atmos. Ocean. Opt. 2016, 29(4), 348–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russkova, T.V.; Zhuravleva, T.B. Optimization of sequential code for simulation of solar radiative transfer in a vertically heterogeneous environment. Atmos. Ocean. Opt. 2017, 30(2), 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Singh, N.; Anshumali; Solanki, R. Evaluation and utilization of MODIS and CALIPSO aerosol retrievals over a complex terrain in Himalaya. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 206, 139–155. [CrossRef]
- Pauly, R.M.; Yorks, J.E.; Hlavka, D.L.; McGill, M.J.; Amiridis, V.; Palm, S.P.; Rodier, S.D.; Vaughan, M.A.; Selmer, P.A.; Kupchock, A.W.; Baars, H.; Gialitaki, A. Cloud-Aerosol Transport System (CATS) 1064 nm calibration validation. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2019, 12(11), 6241–6258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, P.; Stegmann, P.; Tang, G.; Hioki, S.; Ding, J. Improving scattering, absorption, polarization properties of snow, graupel, and ice aggregate particles from solar to microwave wavelengths in support of the CRTM. JCSDA quarterly 2018, 59, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khademi, F.; Bayat, A. Classification of aerosol types using AERONET version 3 data over kuwait city. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 265, 118716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heymsfield, A.J.; Bansemer, A.; Field, P.R. Observations and parameterization of particle size distributions in deep tropical cirrus and stratiform precipitating clouds: Results from in-situ observations in TRMM field campaigns. J. Atmos. Sci. 2002, 59, 3457–3491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichardt, J.; Wandinger, U.; Klein, V.; Mattis, I.; Hilber, B.; Begbie, R. RAMSES: German Meteorological Service autonomous Raman lidar for water vapor, temperature, aerosol, and cloud measurements. Appl. Opt. 2012, 51, 8111–8131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aerosol Robotic Network (AERONET) Homepage. Available online: https://aeronet.gsfc.nasa.gov (accessed on 11 January 2023).
- Marichev, V.N. Combined method for optical sensing of the lower and middle atmosphere. Atmos. Ocean. Opt. 2016, 29, 348–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samoilova, S.V. Simultaneous reconstruction of the complex refractive index and the particle size distribution function from lidar measurements: testing the developed algorithms. Atmos. Ocean. Opt. 2019, 32, 628–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grynko, Y.; Shkuratov, Y.; Förstner, J. Light scattering by irregular particles much larger than the wavelength with wavelength-scale surface roughness. Opt. Lett. 2016, 41(15), 3491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubko, E.; Videen, G.; Zubko, N.; Shkuratov, Y. Reflectance of micron-sized dust particles retrieved with the Umov law. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transfer. 2017, 190, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubko, E.; Shmirko, K.; Pavlov, A.; Sun, W.; Schuster, G.L.; Hu, Y.; Stamnes, S.; Omar, A.; Baize, R.R.; McCormick, M.P.; Loughman, R.; Arnold, J.A.; Videen, G. Active remote sensing of atmospheric dust using relationships between their depolarization ratios and reflectivity. Opt. Lett. 2021, 46(10), 2352–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purcell, E.M.; Pennypacker, C.R. Scattering and absorption of light by nonspherical dielectric grains. Astrophys. J. 1973, 186, 705–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurkin, M.A.; Moskalensky, A.E. Open-source implementation of the discrete-dipole approximation for a scatterer in an absorbing host medium. J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 2021, 12167. [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Yang, P.; Kattawar, G.W.; Zhang, X. Physical-geometric optics method for large size faceted particles. Opt. Express. 2017, 25(20), 24044–24060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, P.; Ding, J.; Panetta, R.L.; Liou, K-N.; Kattawar, G.; Mishchenko, M.I. On the Convergence of Numerical Computations for Both Exact and Approximate Solutions for Electromagnetic Scattering by Nonspherical Dielectric Particles (Invited Review). Progress In Electromagnetics Research, 2019, 164, 27–61. [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yang, P.; Muinonen, K. Dust-aerosol optical modeling with Gaussian spheres: combined invariant-imbedding T-matrix and geometric-optics approach. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transfer. 2015, 161, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajikawa, M.; Heymsfield, A.J. Aggregation of ice crystals in cirrus. J. Atmos. Sci. 1989, 46(20), 3108–3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Um, J.; McFarquhar, G.M.; Hong, Y.P.; Lee, S.-S.; Jung, C.H.; Lawson, R.P.; Mo, Q. Dimensions and aspect ratios of natural ice crystals. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 3933–3956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borovoi, A.; Konoshonkin, A.; Kustova, N. The physical-optics approximation and its application to light backscattering by hexagonal ice crystals. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transfer. 2014, 146, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borovoi, A.; Konoshonkin, A.; Kustova, N. Backscatter ratios for arbitrary oriented hexagonal ice crystals of cirrus clouds. Opt. Lett. 2014, 39, 5788–5791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Shishko, V.; Kustova, N.; Konoshonkin, A.; Timofeev, D.; Xie, C.; Liu, D.; Borovoi, A. Radar-lidar ratio for ice crystals of cirrus clouds. Opt. Express 2021, 29, 4464–4474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kustova, N.; Konoshonkin, A.; Shishko, V.; Timofeev, D.; Tkachev, I.; Wang, Z.; Borovoi, A. Depolarization Ratio for Randomly Oriented Ice Crystals of Cirrus Clouds. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konoshonkin A.V., Kustova N.V., Borovoi A.G. Beam Splitting Algorithm for the Problem of Light Scattering by Atmospheric Ice Crystals. Part 1. Theoretical Foundations of the Algorithm // Atmos. Ocean. Opt. 2015. V. 28. P. 441-447.
- Macke, A.; Mueller, J.; Raschke, E. Single scattering properties of atmospheric ice crystal. J. Atmos. Sci. 1996, 53(19), 2813–2825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Stegmann, P.; Tang, G.; Hioki, S.; Ding, J. Improving scattering, absorption, polarization properties of snow, graupel, and ice aggregate particles from solar to microwave wavelengths in support of the CRTM. JCSDA quarterly 2018, 59, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, D.L.; Arnott, W.P. A model predicting the evolution of ice particle size spectra and radiative properties of cirrus clouds. Part II. Radiation. J. Atmos. Sci. 1994, 51, 817–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, S.G. Optical constants of ice from the ultraviolet to the microwave. Appl. Opt. 1984, 23, 1206–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, P.; Bi, L.; Baum, B.A.; Liou, K.-N.; Kattawar, G.W.; Mishchenko, M.I.; Cole, B. Spectrally consistent scattering, absorption, and polarization properties of atmospheric ice crystals at wavelengths from 0.2 to 100 μm. J. Atmos. Sci. 2013, 70, 330–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konoshonkin, A.; Borovoi, A.; Kustova, N.; Reichardt, J. Power laws for backscattering by ice crystals of cirrus clouds. Opt. Express. 2017, 25, 22341–22346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).